Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
|
|
|
- Russell Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin staining (HE) of spleen tissue sections. (d and e) Immunostaining of CD45R (B220; green), a marker of B lymphocytes, with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 2 mm (a); 500 μm (b, c); 100 μm (d, e).
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Distribution of PRV-positive cells throughout the central nervous system (CNS) that are directly or indirectly connected to the spleen, i.e., a neural-splenic circuit. (a and b) Post-ganglionic adrenergic sympathetic nerves innervate the spleen. PACT clearing of spleen (a) and staining with antityrosine hydroxylase (TH) antibody (b, red). TH + fibers broadly innervate the spleen, which allows PRV to be transported retrogradely into sympathetic chain ganglia and then into the CNS. Scale bar, 2 mm. (c) Schema of retrograde and transsynaptic labeling of neural-
3 splenic circuit by PRV. (d) Distribution summary of PRV-GFP positive cells in the CNS, hours after PRV injection into the spleen (modified from 8 ). Time points when PRV-GFP + cells first appeared are indicated as black to white colors in each CNS region. (e x) Representative images of PRV-GFP + cells in different CNS regions and time points after PRV152 injection into the spleen. Mice were perfused at 48 (day 2, n = 2 mice), 72 (day 3, n = 2 mice), 96 (day 4, n = 2 mice), 108 (day 4.5, n = 1 mouse), 120 (day 5, n = 2 mice), 144 (day 6, n = 3 mice), and 168 hr (day 7, n = 2 mice) after injection. To verify that PRV labeling from the spleen occurs via the splenic nerve and is not the result of spurious labeling due to blood-borne virus, the splenic nerve was cut before PRV injection then analyzed at 120 hr (n = 2 mice). Thoracic cord (T4 8), e (72 hr), f (96 hr), g (120 hr); dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (10N), h (108 hr), i (120 hr), j (120 hr, splenic nerve cut); Reticular formation, k (120 hr), l (144 hr), m (120 hr, splenic nerve cut); paraventricular nucleus (PVN), n (120 hr), o (144 hr), p (120 hr, splenic nerve cut); PsTh, q (120 hr), r (144 hr); zona incerta (ZI), s (120 hr), t (144 hr); locus coeruleus (LC), u (144 hr); periaqueductal gray (PAG), v (144 hr); basolateral amygdaloid nucleus (BLP), w (144 hr); bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BST), x (144 hr). Coronal sections. Scale bar, 200 μm.
4 Supplementary Figure 3 PRV + spinal sympathetic neurons innervating the spleen in control and SCI mice. (a i) Horizontal sections of spinal cord in control (a c), T9 SCI (d f), and T3 SCI mice (g i), 96 hrs after PRV injection into the spleen. Stained with anti-gfp antibody (green). T2 4 (a, d, g), T9 11 (b, e, h), and L5 S1 level (c, f, i). Arrowheads, lesion sites (e and g). Rostral is left. Scale bar, 200 m. Images are representative of 4 (T9 11) and 5 (T2 4 and L5 S1) independent experiments. (j m) Distribution of PRV + cells in dorso-ventral axis of thoracic cord after T3 SCI. (j) Schematic figure of transverse section of thoracic cord. Dotted lines represent approximate dorsoventral positions of images shown in k, l, m, and Fig. 1c, f. (k m) Horizontal images of PRV- GFP + cells distributed in dorsoventral axis. Rostral is left. Scale bar, 100 m. (n q) Representative images of Vglut2-GFP + (green) / PRV + (RFP, red) neurons in the sacral spinal cord after T3 SCI. Right panels (o q) are higher magnification of the neurons indicated by arrows in (n) ± 2.86% of PRV + were Vglut2-GFP + neurons at the sacral level (n = 2 mice). Scale bars, 100 μm (n), 50 μm (o q).
5 Supplementary Figure 4 Time-dependent increase in number of VGLUT2 + pre-synaptic contacts on SPNs after T3 SCI. (a) Schematic illustrating intrasplenic injections of PRV and intraperitoneal injections of FG to distinguish SPNs (FG + /PRV + ) from interneurons (FG /PRV + ) in spinal cord-splenic circuit. (b g) Representative confocal images of FG + (blue) / PRV + (green) SPNs and VGLUT2 + puncta (red) in control (b, c) and at 10 (d, e) and 28 days post-injury (f, g). Images are representative of 2, 4, and 5 independent experiments for control, 7 10 days and 28 days. SPNs in (b), (d) and (f) (arrowheads) are reconstructed into 3D images using Imaris software are isolated in (c), (e) and (g), respectively. Scale bar, 40 μm. (h) Quantification of the density of VGLUT2 + synaptic puncta on FG + /PRV + SPNs at day 7 10 and day 28, the time points before and after onset of immune suppression in T3 SCI mice 3. Dotted line indicates the density of VGLUT2 + synaptic puncta quantified from naïve/uninjured mice (n = 2 mice, 44 total neurons) and is provided as a reference for post-injury changes in puncta density. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m (day 7, n = 3 mice; day 10, n = 1 mouse; day 28, n = 5 mice). Student s t test, p = , *p < 0.05.
6 Supplementary Figure 5 Activating visceral-sympathetic reflexes via CRD induces c-fos expression in Vglut2 + excitatory spinal interneurons. (a and b) CRD induced c-fos expression (red) in the thoracic cord of T3 SCI mice. T6 8 level, horizontal sections. T3 SCI without (a) and with CRD (b) at day 28. (c) Quantitative analyses of c-fos + cells at T4 9 level of control or T3 SCI mice with or without CRD. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m (T3 SCI with CRD, n = 5 mice, other groups, n = 3 mice). One way ANOVA followed by Tukey test, p = < , < , (left to right), **p < (d f) c-fos expression (red) in GFP + cells (green) in Vglut2-Cre; cc-gfp mice with T3 SCI and CRD at day 28 (arrows). Scale bars, 200 μm (a, b); 50 μm (d f). (g) Quantification of Vglut2-GFP + and Chat-GFP + population in c-fos-expressing cells with T3 SCI and CRD at day 28 (n = 3 mice). Images are representative of 3 (a, d f) and 5 (b) independent experiments.
7 Supplementary Figure 6 Introduction of hm4di in spinal interneurons by AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry. (a) Design of hm4di-mcherry-expressing AAV, using FLEX switch strategy to induce Cre-mediated transgene inversion and expression in the thoracic spinal cord. (b) hm4di-mcherry expression in Vglut2-Cre mice. T6 8 level at day 28 after T3 SCI. (c e) hm4di-mcherry (red) is expressed in GFP + neurons in Vglut2-Cre; cc-gfp mice (arrows). (f) hm4di-mcherry expression in Chat-Cre mice. T6 8 level at day 28 after T3 SCI. (g i) hm4di-mcherry (red) is expressed in GFP + neurons in Chat-Cre; cc-gfp mice (arrows). Note that most hm4di-mcherry + cells are located in the intermediate and medial zone. Few exist in the lateral zone where SPNs predominate. Images are representative of 2 independent experiments. Scale bars, 500 μm (b, f); 50 μm (c e, g i). (j) Percentage of hm4di-mcherry + /GFP + cells in total hm4di-mcherry + cells in Vglut2-Cre; cc-gfp and Chat-Cre; cc-gfp mice. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m (n = 4 horizontal sections from 2 mice). (k) A representative image of brain stem region (reticular formation) in Vglut2-Cre mice at day 28 after T3 SCI, injected with AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry at thoracic level at P14. No hm4di-mcherry was visible in any sections indicating that the AAV vector does not get retrogradely transported into the brain stem. Thus, no descending modulation by brainstem circuitry can contribute to hm4di-mediated inhibition of spinal circuitry. The image is representative of 2 independent experiments. Scale bar, 200 μm.
8 Supplementary Figure 7 Chemogenetic silencing of spinal autonomic circuitry reduces c-fos expression elicited by CRD, a potent visceral-sympathetic reflex stimulus. (a f) c-fos expression in horizontal thoracic spinal cord sections of AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry-injected T3 SCI Vglut2-Cre mice injected with vehicle (a c) or CNO and with CRD (d f). Scale bar, 50 μm. Images are representative of 3 independent experiments. (g, h) Quantification of density of c-fos + cells and percentage of cfos + / hm4di-mcherry + cells. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m (n = 3 mice). Student s t test; p = (g), (h); *p < 0.05.
9 Supplementary Figure 8 Representative flow cytometry scatter plots of splenocytes derived from control and SCI mice with or without chemogenetic manipulation of autonomic circuitry. (a, c, e, g, i) Gating strategies using FSC-A vs SSC-A, FSC-H vs FSC-W and SSC-H vs SSC-W plots (to remove doublets). (b, d, f, h, j) Dot plots of B220, CD4, and CD8-labeled lymphocytes from WT control (b), WT + T3 SCI (d), WT + AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry + T3 SCI + CNO (f), Vglut2-Cre + AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry + T3 SCI + CNO (h), and Chat-Cre + AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry group (j). Mean percentage of B220 +, CD4 + or CD8 + cells generated by gating for each cell population was multiplied by total number of splenocytes to generate graphs in Fig. 3e g.
10 Supplementary Figure 9 Proposed model by which activation of a sympathetic anti-inflammatory reflex (SAR) causes immune suppression after highlevel SCI. (a) Normally, there is tonic brainstem control over sympathetic preganglionic neurons (SPNs). This tonic regulation is essential for normal neural-immune communication and maintenance of homeostasis. (b) After high-level T3 SCI (red dotted lines), supraspinal control over SPNs is lost allowing normally innocuous stimuli below the level of injury to elicit exaggerated and potentially life-threatening autonomic reflexes (gray dotted lines). New data show that profound plasticity develops within spinal autonomic circuitry below the level of SCI. Notably, new connections form between SPNs and spinal excitatory interneurons throughout and beyond the thoracic spinal cord (Supplementary Fig. 3i and n q). This rewired circuit is the neural substrate underlying SAR-mediated suppression of immune function.
11 Supplementary Table 1. Temporal distribution of PRV-infected neurons Area 48 hr 72 hr 96 hr 108 hr 120 hr 144 hr 168 hr (n = 2) (n = 2) (n = 2) (n = 1) (n = 2) (n = 3) (n = 2) Spinal cord T1 3 (n.e.) (n.e.) ~ ± (n.e.) (n.e.) (n.e.) T4 9 ± ~ (d) + (d) T10 12 (n.e.) (n.e.) ~ ± (n.e.) (n.e.) Brain dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (10N) (d) ++ (d) reticular formation ± ~ + ++ locus coeruleus (LC) ~ ± ++ subcoeruleus nucleus (SubC) ~ ± ++ periaqueductal gray (PAG) + parasubthalamic nucleus (PsTh) ± ~ + ++ zona incerta (ZI) ± ~ + ++ dorsomedial hypothalamus (DM) + paraventricular nucleus (PVN) (n.e.) ± ~ + ++ basolateral amygdaloid nucleus (BLP) ++ bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BST) ++ dead, not detected; ±, a few positive cells; +, moderate number of positive cells; ++: numerous positive cells; (d), neurons start degenerating; (n.e.), not examined; dead, mice were dead Supplementary Table 1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Neural Control of Lower Urinary Tract Function. William C. de Groat University of Pittsburgh Medical School
 Neural Control of Lower Urinary Tract Function William C. de Groat University of Pittsburgh Medical School Disclosures Current funding: NIH Grants, DK093424, DK-091253, DK-094905, DK-090006. Other financial
Neural Control of Lower Urinary Tract Function William C. de Groat University of Pittsburgh Medical School Disclosures Current funding: NIH Grants, DK093424, DK-091253, DK-094905, DK-090006. Other financial
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Visualization of AT1a-positive cells using AT1a lacz/+ mouse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Visualization of AT1a-positive cells using AT1a lacz/+ mouse. (a f) Immunohistochemical detection of β-gal in the mouse brain. Coronal sections at the respective anteroposterior
Supplementary Figure 1 Visualization of AT1a-positive cells using AT1a lacz/+ mouse. (a f) Immunohistochemical detection of β-gal in the mouse brain. Coronal sections at the respective anteroposterior
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Supplemental Information. A Labeled-Line Neural Circuit. for Pheromone-Mediated Sexual Behaviors in Mice
 Neuron, Volume Supplemental Information A Labeled-Line Neural Circuit for Pheromone-Mediated Sexual Behaviors in Mice Kentaro K. Ishii, Takuya Osakada, Hiromi Mori, Nobuhiko Miyasaka, Yoshihiro Yoshihara,
Neuron, Volume Supplemental Information A Labeled-Line Neural Circuit for Pheromone-Mediated Sexual Behaviors in Mice Kentaro K. Ishii, Takuya Osakada, Hiromi Mori, Nobuhiko Miyasaka, Yoshihiro Yoshihara,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Hypothalamus. To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine secretions NTA Ch 14, pgs Key Figs: 14-3; 14-4,
 Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit. Supplementary Information. Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M.
 Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit Supplementary Information Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M. Jessell Supplementary Results Characterizing the origin of primary
Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit Supplementary Information Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M. Jessell Supplementary Results Characterizing the origin of primary
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system
 General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0595 TITLE: Enhancing Propriospinal Relays to Improve Functional Recovery after SCI PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Smith CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University of the Commonwealth
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0595 TITLE: Enhancing Propriospinal Relays to Improve Functional Recovery after SCI PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Smith CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University of the Commonwealth
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6
 Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9
 Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
The Nervous System. Autonomic Division. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles (n = 5). (C) Plasma norepinephrine
 Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon Limbic System II. David P. Wolfer MD
 ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon 05.05.2014 Limbic System II David P. Wolfer MD Institute of Anatomy, University of Zurich Institute for Human Movement Sciences and Sport, ETH Zurich http://www.dpwolfer.ch
ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon 05.05.2014 Limbic System II David P. Wolfer MD Institute of Anatomy, University of Zurich Institute for Human Movement Sciences and Sport, ETH Zurich http://www.dpwolfer.ch
The Nervous System: The
 C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of GlyT2::eGFP fibers in the mouse thalamus at three different coronal levels. Note the innervation centered in the rostral (CL, PC) and caudal (PF) nuclear groups of
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of GlyT2::eGFP fibers in the mouse thalamus at three different coronal levels. Note the innervation centered in the rostral (CL, PC) and caudal (PF) nuclear groups of
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu
 Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY
 Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Neuropsychiatry Block
 Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH).
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Central catecholamine pathways in stress reactions
 Central catecholamine pathways in stress reactions Palkovits Miklós Semmelweis University, Budapest 2016 Selye János (1907-1982) In 1936, when this definition was formulated, we knew of only three objective
Central catecholamine pathways in stress reactions Palkovits Miklós Semmelweis University, Budapest 2016 Selye János (1907-1982) In 1936, when this definition was formulated, we knew of only three objective
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S
 The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus
 Lu Chen LSA room 201 Phone: (510) 643-8163 Email: luchen@berkeley.edu Office hours: M,W,F, 10-11 am 1 Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 2 Hypothalamus Brain stem
Lu Chen LSA room 201 Phone: (510) 643-8163 Email: luchen@berkeley.edu Office hours: M,W,F, 10-11 am 1 Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 2 Hypothalamus Brain stem
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Transduction of adipocytes after intra-ewat administration of AAV vectors. A: Immunostaining against GFP (green) in sections of ewat two weeks after the intra-ewat administration
Supplementary Figure 1. Transduction of adipocytes after intra-ewat administration of AAV vectors. A: Immunostaining against GFP (green) in sections of ewat two weeks after the intra-ewat administration
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
!! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
University of Groningen. Neuronal control of micturition Kuipers, Rutger
 University of Groningen Neuronal control of micturition Kuipers, Rutger IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
University of Groningen Neuronal control of micturition Kuipers, Rutger IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions
 16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
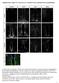 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Reflexes. Handout on The Basic Reflex Arc and Stretch and Tendon Reflexes. -55 mv -70 mv EPSP. By Noel Ways
 Reflexes Handout on The Basic Reflex Arc and Stretch and Tendon Reflexes By Noel Ways Basic Reflex Arch 2. : s are always unipolar and will conduct and impulse to a control center. In this case the control
Reflexes Handout on The Basic Reflex Arc and Stretch and Tendon Reflexes By Noel Ways Basic Reflex Arch 2. : s are always unipolar and will conduct and impulse to a control center. In this case the control
Supplementary Materials for. c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration
 Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
The Nervous System PART D. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
4/8/2015. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS. Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
Arcuate neuropeptide Y inhibits sympathetic nerve activity via multiple neuropathways
 Arcuate neuropeptide Y inhibits sympathetic nerve activity via multiple neuropathways Zhigang Shi,, Christopher J. Madden, Virginia L. Brooks J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2868-2880. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci92008.
Arcuate neuropeptide Y inhibits sympathetic nerve activity via multiple neuropathways Zhigang Shi,, Christopher J. Madden, Virginia L. Brooks J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2868-2880. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci92008.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
4/9/2019. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Chapter 49: Nervous Systems
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Name Period Chapter 49: Nervous Systems Concept 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells 1.
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Name Period Chapter 49: Nervous Systems Concept 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells 1.
Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were
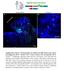 Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
