Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Measured Regional Body Composition Least Significant Change: Effect of Region of Interest and Gender in Athletes
|
|
|
- Oswin Johns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Clinical Densitometry: Assessment of Skeletal Health, vol. -, no. -, 1e8, 2013 Ó Copyright 2013 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry /-:1e8/$ Original Article Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Measured Regional Body Composition Least Significant Change: Effect of Region of Interest and Gender in Athletes Bjoern Buehring, 1 Diane Krueger, 1 Jessie Libber, 1 Bryan Heiderscheit, 2,3 Jennifer Sanfilippo, 3 Brian Johnson, 4 Irina Haller, 4 and Neil Binkley*,1 1 Osteoporosis Clinical Research Program, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA; 2 Orthopedics and Rehabilitation, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA; 3 Intercollegiate Athletics, University of Wisconsin- Madison, Madison, WI, USA; and 4 Essentia Institute of Rural Health, Duluth, MN, USA Abstract Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is widely used to evaluate body composition in athletes. Knowledge of measurement precision is essential for monitoring body composition changes over time. This study begins characterizing DXA body composition precision in 60 (30 males and 30 females) Division 1 athletes focusing on gender, regional, and tissue type differences. Two total body scans with repositioning between were performed on the same day. Least significant change (LSC) for the root-mean-square deviation (LSC RMSD ) and the percent coefficient of variation (LSC %CV ) for total, lean, and fat mass was calculated for 6 regions of interest. The effect of gender, region, tissue type, and mass on the standard deviation (SD) and percent coefficient of variation (%CV) between the 2 scans was evaluated using repeated measures regression analysis. Statistically significant effects of gender, region, tissue type, and mass on SD and %CV were noted. To generalize, a nonlinear positive relationship between LSC RMSD and mass and a nonlinear negative relationship between LSC %CV and mass were observed. In conclusion, DXA body composition LSC varies among genders, regions, tissues, and mass. As such, when evaluating serial body composition in athletes, especially if assessing regional change, knowledge of precision in individuals of similar body size and gender to the population of interest is needed. Key Words: Body composition; DXA; precision; sports performance. Introduction Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is increasingly being used to measure body composition in various settings (1), including obesity/bariatric surgery (2,3), lipodystrophy assessment in individuals with HIV (4e7), sarcopenia (8e11), and athletic training/performance (12e16). This methodology is rapid, relatively inexpensive, and uses only a small amount of ionizing radiation. Importantly, it allows regional composition measurements, which have primarily received interest for assessing fat distribution (i.e., android/ Received 01/15/13; Accepted 02/20/13. *Address correspondence to: Neil Binkley, MD, Osteoporosis Research Program, University of Wisconsin, 2870 University Avenue, Suite 100, Madison, WI nbinkley@wisc.edu gynoid fat) (17) and appendicular lean mass as part of sarcopenia definition (8,9,11). However, the ability to evaluate regional lean mass carries substantial potential for assessing athletes to evaluate training regimens and also rehabilitation after sports injuries. This ability to evaluate not only total fat and lean mass but also mass in specific regions such as the extremities is a distinct advantage of DXA compared with other measures of body composition, such as bioelectrical impedance or hydrodensitometry (18,19). In general, a high lean mass-to-fat mass ratio is beneficial for most athletes because high body fat mass leads to less efficient energy utilization (20). However, too little fat mass might negatively impact health as seen in women with female athlete triad (disordered eating, amenorrhea, and low bone mineral density) (21). Despite the potential advantages noted 1
2 2 Buehring et al. previously, only a limited number of studies have used DXA body composition in athletes. Some reports find a high correlation between DXA and other measures of body composition (12,21e24). However, other studies comparing athletes with controls observe differences in body composition, for example, among different Cricketing skill groups and Rugby player positions (14,16). Importantly, serial DXA scans may be used to assess body composition changes over time to monitor training regimens or during the course of a season (13). One can speculate that such serial DXA body composition evaluation in athletes might be most beneficial as it can provide information about not only conditioning status, training regimens, or rehabilitation process but also negative developments that might impact the athletes health, such as excessive loss of fat or lean mass. In serial measurements, however, it is necessary to appreciate and account for method variability to determine if an intervention has altered fat and/or lean mass over time. The International Society for Clinical Densitometry (ISCD) recommends performance of a precision assessment to determine what constitutes a change in the measured parameters with 95% confidence interval (25e27). Importantly, such a precision assessment should be performed using patients representative of the clinic s patient population (26). Because diverse populations with markedly differing body composition may be evaluated depending on the clinical circumstance, it is necessary to understand if variations in body composition, body size, and fat/lean distribution affect reproducibility of these measurements. One obvious example of differences is gender, with males typically being larger with different fat/lean distribution compared with females (28,29). Moreover, although the reproducibility of total body bone, fat, and lean mass has been reported and appears to be excellent in adults with and without disease (6,30e32), there is, to our knowledge, only limited information available regarding the reproducibility of these measurements in athletes (12). Furthermore, only very limited data exist regarding the reproducibility of regional measurements in this population. As elite athletes are very specialized and have widely differing body compositions, we hypothesized that the size and body composition of Division 1 college athletes might be variable enough to warrant separate precision assessments. The goal of this study was to do an initial evaluation of total and regional body composition in Division 1 athletes with focus on gender, tissue, and regional differences. Methods Participants As recommended by the ISCD, precision assessments consisting of 2 total body DXA scans were performed in 60 student athletes (30 females and 30 males) from the University of Wisconsin selected based on the ability to fit within the densitometer scan field. Mean ( standard deviation [SD]) age was 20.6 (1.3) yr (range, 18.3e23.4 yr) and 19.9 (1.3) yr (range, 18.1e22.7 yr) for men and women, respectively. These athletes participated in various sports including hockey (17 women and 16 men), basketball (5 women and 4 men), golf (8 women), and wrestling (10 men). This study was determined to be exempt by the University of Wisconsin-Madison Institutional Review Board. All participants provided written consent before undergoing DXA assessment. DXA Acquisition, Analysis, and Precision Assessment A GE Healthcare (Madison, WI) Lunar idxa densitometer was used for all examinations. ISCD-certified technologists performed all scan acquisition and analyses in routine clinical manner following research facility standard operating procedures. All scans were acquired using encore software versions 11.0e13.31; version 13.4 was used for analysis. One technologist analyzed all scans using the software autoanalysis feature followed by manual correction of analysis markers when necessary. Precision assessment was performed in routine clinical manner following ISCD recommendations (26); specifically, each athlete was scanned twice by the same technologist with repositioning between scans. Both scans were conducted at the same scanning session. DXA Regional Analysis Total body and regional analyses were performed in routine clinical manner. Six standard regions of interest (ROI) were used for this analysis (Fig. 1). These regions were defined as follows: Total body ROI consisting of the entire body including the head; trunk ROI defined at the upper boundary by the mandible line including the chest, abdomen, and pelvic triangle; the arm ROIs (right and left) were defined by a line bisecting the shoulder joint of the right and left arm; and the leg ROIs (right and left) were defined by a line bisecting the hip joint aligned with the iliac crest and pubis. Statistical Analyses The gender differences in age and body mass index (BMI) were evaluated using Student s t-test. The mean mass, variance and SD between the measurements, and percent coefficient of variation (%CV) were calculated for each subject based on the 2 scans, resulting in 18 observations of each parameter (mean, variance, SD, and %CV) that corresponds to the region (total, trunk, left arm, right arm, left leg, and right leg) and tissue type (total, fat, and lean) combinations. The mean square error (MSE) and least significant change (LSC) with 95% confidence interval based on both the MSE (least significant change for the root-mean-square deviation [LSC RMSD ]) and %CV (least significant change for the percent coefficient of variation [LSC %CV ]) were calculated for each region and tissue type for males and females using the ISCD precision calculator available online ( org/visitors/resources/calc.cfm). The LSC values are a multiple of either the RMSD or root-mean-square %CV; hence, inferences based on the SD or %CV are applicable to the LSC
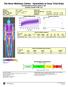
3 Effect of ROI in DXA Body Composition Precision 3 Table 1 Demographics and Body Composition in Athletes by Gender Male Female Characteristics Mean SD Mean SD Fig. 1. Total body regions of interest (ROIs). This figure depicts the total body DXA ROIs reported in this analysis. The total body region includes the entire body. The trunk region includes the pelvic triangle to the inferior mandible (noted by dark gray). The arm ROI includes the area bisected at the shoulder joint (noted in medium gray). The leg region is bisected at the hip and excludes the pelvic triangle (noted in light gray). values. Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to evaluate gender differences in variance for total, fat, and lean mass for each region and tissue type. The graphical evaluation of the relationship between mean mass for each region/tissue combination with corresponding mean LSC RMSD and mean LSC %CV was assessed in JMP (version 10.0; SAS Institute, Cary, NC) using a best-fit model. Repeated measures models with unstructured covariance matrices and Kenward-Roger approximation (33) were used to assess the effect of gender, region, tissue type, and mass on the SD and %CV. All analyzes were done with SAS v9.3 (Cary, NC). Results Body Composition The body composition results are given in Table 1. Males were larger than females ( p! 0.01). Specifically, for men, Age, yr Height, cm * 5.3 Weight, kg * 6.3 BMI, kg/m * 2.3 Total body ROI (g) Total mass 85,200 12,560 65, Lean mass 68, , Fat mass 13, , Trunk ROI (g) Total mass 40, , Lean mass 32, , Fat mass Right arm ROI (g) Total mass Lean mass Fat mass Left arm ROI (g) Total mass Lean mass Fat mass Right leg ROI (g) Total mass 14, , Lean mass 11, Fat mass Left leg ROI (g) Total mass 14, , Lean mass 11, Fat mass Note: Lean mass was higher in men ( p! 0.001), and fat mass was higher ( p! 0.05) in women at all sites. Abbr: BMI, body mass index; ROI, region of interest SD, standard deviation. *p! 0.01 using t-test for between-genders comparison. the mean (SD) BMI was 25.6 (3.0) kg/m 2 (range, 21.3e35.7 kg/m 2 ), and for women, it was 23.3 (2.3) kg/ m 2 (range, 17.7e29.4 kg/m 2 ). The mean total mass for men was 85.2 kg (range, 62.7e123.7 kg), and for women, it was 65.5 kg (range, 52.0e77.1). There was little overlap in total mass between the men and women, in that the heaviest 24 individuals were male. Absolute and percent lean mass measurements were higher in men than in women ( p! 0.001) at all ROIs. Fat mass measurements were higher in women ( p! 0.05) at all ROIs. Precision The LSC RMSD and LSC %CV values varied between the different regions, tissues, and genders (Table 2). The Wilcoxon rank-sum tests indicated that variance is smaller for females
4 4 Buehring et al. Table 2 Precision and LSC by ROI and Gender Precision LSC (95% confidence) Gender Male Female Male Female Site RMS SD %CV MSE RMS SD %CV MSE LSC RMSD LSC %CV LSC RMSD LSC %CV Total body ROI Total mass Lean mass , ,938* Fat mass , ,000* Trunk ROI Total mass , , Lean mass , ,978* Fat mass , , Right arm ROI Total mass Lean mass Fat mass Left arm ROI Total mass Lean mass Fat mass Right leg ROI Total mass , , Lean mass , , Fat mass Left leg ROI Total mass , , Lean mass , , Fat mass Note: ROI masses, RMS SD, and LSC RMSD values in grams. Abbr: %CV, percent coefficient of variation; LSC, least significant change; LSC %CV, least significant change for the root-mean-square percent coefficient of variation; LSC RMSD, least significant change for the root-mean-square deviation; MSE, mean square error; RMS SD, rootmean-square error standard deviation; ROI, region of interest. *p! 0.05 using Wilcoxon rank-sum test to compare variances between genders. than that for males in the fat and lean tissues of the total body ( p! 0.01) and in the lean tissue of the trunk ( p ). The graphical evaluation of the relationships between mean ROI/tissue mass and LSC RMSD and between mean ROI/tissue mass and LSC %CV showed that LSC RMSD increases (R ) and %CV decreases (R ) in a nonlinear fashion as the amount of regional mass increases (Fig. 2). Due to nonlinearity of the relationships between the mass and measures of precision, the dependent variables (SD and %CV) were transformed using natural logarithm for estimating the effects of gender, region, and tissue type on SD and %CV in repeated measures regression analyses (Table 3). Subsequently, the estimated effects of the explanatory variables were obtained using reversed transformation of the model parameters. As noted in Table 3, the SD and %CV for female athletes were 81% and 97% compared with males, respectively, with the effect being statistically significant ( p ) for SD. Variability also differed based on ROI. Specifically, variability based on SD for the left arm ROI, right arm ROI, and right leg ROI was less than that for the total body ROI (41%, 45%, and 95%, respectively) and greater than that for the total body ROI in left leg ROI and trunk ROI (110% and 161%). The effect of ROI was statistically significant ( p! 0.001) for both arms and the trunk. Similar analysis for variability based on %CV revealed that % CV for all regions was greater ( p! 0.001) compared with that for the total body: 343% (trunk), 519% (right leg ROI), 606% (left leg ROI), 717% (left arm ROI), and 791% (right arm ROI). Additionally, variability of fat and lean mass measurements differed from that of total mass. Specifically, the SD for fat tissue was 70% of that for total ( p! 0.001), and the SD for lean tissue was 117% of that for total ( p ). However, in similar analysis for %CV, both lean and fat tissue %CV values
5 Effect of ROI in DXA Body Composition Precision 5 was 124% of that for total mass ( p ). The natural log of SD increases by 0.22 for every unit increase in the log of the mean mass ( p! 0.001), and when converted to the natural scale, the SD is the mean mass raised to the 0.22 power. This suggests that although the SD increases as the mean mass increases, the rate of increase is greater for smaller masses. Conversely, the log of %CV decreases by 0.78 for every unit increase in the log of the mean mass ( p! 0.001). Converted to the natural scale, the estimated %CV is the mean mass raised to the 0.78 power. This suggests that although the %CV decreases as the mean mass increases, the rate of decrease is greater for the smaller values of the mass. Fig. 2. Relationship of LSC RMSD and %CV with mass. Graphically, there is a strong positive nonlinear relationship (r ) between LSC RMSD and mass and a strong negative nonlinear relationship (r ) between %CV and mass. %CV, percent coefficient of variation; LSC RMSD, least significant change for the root-mean-square deviation. were greater ( p! 0.01) compared with %CV for total tissue: 162% for lean and 332% for fat tissue. To account for different tissue composition and variability in mass between regions, the same models were used with log mean mass instead of region as an explanatory variable (Table 4). The effect of gender was statistically significant in both models ( p ) with both SD and %CV for females being 80% of that for males. Variability of lean mass Discussion In male and female Division 1 athletes, a group of lean and fit individuals, precision of DXA body composition is excellent for total body and lean mass in all regions assessed in this study. As a clinical generalization, measurement variability was greater in men and differed between lean, fat, and total mass. Moreover, variability generally increases as mass increases, in that measurement sites with larger mass also had higher LSC RMSD and lower LSC %CV values in a nonlinear relationship. Studies evaluating DXA body composition precision are currently quite limited. DXA body composition precision has been reported in nonobese adults (34), young individuals (not athletes) (17), obese populations (31), individuals from the Diabetes Heart Study (30), and individuals with HIV Table 3 Effect of Gender, ROI, and Tissue Type on SD and %CV SD %CV Effects Multiplying factor (95% CI) p Value Multiplying factor (95% CI) p Value Gender Female 0.81 (0.67e0.97) (0.80e1.17) Male a Reference d Reference d ROI Right arm 0.45 (0.34e0.60)! (5.94e10.53)!0.001 Left arm 0.41 (0.31e0.53)! (5.51e9.33)!0.001 Right leg 0.95 (0.71e1.28) (3.90e6.90)!0.001 Left leg 1.10 (0.85e1.43) (4.69e7.85)!0.001 Trunk 1.61 (1.35e1.92)! (2.86e4.11)!0.001 Total a Reference d Reference d Tissue type Fat mass 0.70 (0.60e0.80)! (2.72e4.04)!0.001 Lean mass 1.17 (1.03e1.34) (1.42e1.84)!0.001 Total mass a Reference d Reference d Note: The multiplying factor and the corresponding 95% CI were estimated from the repeated measures regression models on transformed values (natural logarithm) with SD or % CV as dependent variables and gender, ROI, and tissue type as explanatory variables. Abbr: CI, confidence interval; %CV, percent coefficient of variation; ROI, region of interest; SD, standard deviation. a Reference category.
6 6 Buehring et al. Table 4 Effect of Gender, Tissue Type, and Mean Mass on SD and %CV SD %CV Effects Multiplying factor (95% CI) p Value Multiplying factor (95% CI) p Value Gender Female 0.80 (0.66e0.97) (0.66e0.97) Male a Reference d Reference d Tissue mass Fat mass 1.07 (0.87e1.33) (0.87e1.33) Lean mass 1.24 (1.08e1.43) (1.08e1.43) Total mass a Reference d Reference d Mean mass b!0.001 c!0.001 Note: The multiplying factor and the corresponding 95% CI were estimated from the repeated measures regression models on transformed values (natural logarithm) with SD or %CV as dependent variables and gender, tissue type, and mean mass as explanatory variables. Abbr: CI, confidence interval; %CV, percent coefficient of variation; SD, standard deviation. a Reference category. b Mean mass raised to the power (95% CI) of 0.22 (0.13e0.30). c Mean mass raised to the power (95% CI) of 0.78 ( 0.87 to 0.70). (6). As expected, in these reports, the %CV varied among the population studied, the type of densitometer used, between fat and lean mass, and region studied. Percent CV values were generally below 4% (6,17,30,31,34), similar to that observed for most of the ROIs in this study. Consistent with our findings, most prior studies report %CV values to be higher for fat mass compared with those for lean and total mass. In obese individuals, regional values were also comparable with those found in our athletes, whereas other studies reported lower %CV studies for fat mass (31). Studies that examined separate regions also noted that precision was poorer when smaller regions have been evaluated, such as a single extremity compared with larger region like the total body (6,31,34). Although DXA body composition has been compared with other methods to assess body composition in athletes (21e24), only limited data exist on the reproducibility of serial measurements in athletic populations (12,24,35,36). One study (12) reported the %CV for fat mass to be 2.9%, but no data for regions or lean mass were reported. A more recent study that included 31 athletes reported whole-body lean and fat mass %CV values of 1.1% and 3.7%, respectively (37). Additionally, a recent report of physically active young adults found the short-term %CV to be lowest for total mass (0.1%) with total lean and fat mass values of w0.5% and w1.5% (36). These authors appropriately emphasize the potential impact of exercise sessions on body composition; however, such effects do not impact the data reported here, given that these scans were performed at the same session. However, fluid and food intake and loss should be considered when monitoring body composition change over time in athletic populations (36). To this end, it has been suggested that athletic subjects be fasting and rested before DXA measurement (35). Further study of training and food effects on body composition measurement, ideally leading to standardization of measurement approaches, is needed. DXA body composition assessment promises to be a valuable tool for athletesdit is rapid, relatively uncomplicated, and has very low radiation exposure. Various sports performanceerelated indications could be proposed including comparing body composition among different sports, different positions within team sports, or screening promising young athletes for lean, fat, and bone mass. However, in our opinion, most appealing might be the use of DXA body composition for serial measurement to monitor body composition changes over time to monitor training programs and/or injury and subsequent rehabilitation. To be able to assess whether a measured body composition change is larger than the variability of the assessment itself, a precision analysis must be performed. This can be easily performed using a relatively small number of individuals with LSC RMSD and LSC %CV being determined using the existing calculators available online (25e27). Limitations of this study include the small sample size of 60 participants, use of only a single manufacturer s densitometer, and study of only young Division 1 athletes from a limited number of sports. As such, generalization to one particular sport or another densitometer is limited. In addition, whether similar results are obtained in nonathletic populations remains to be determined. Importantly, whether the observed differences in LSC RMSD and LSC %CV are solely related to ROI mass, or whether other factors also play a role cannot be determined from this work because of the relatively small number and heterogeneous sample of these athletes. Additional studies are necessary to further define whether there is a gender and/or tissue type effect on precision or whether the differences observed in this study are simply because of larger body size of the males in this cohort.
7 Effect of ROI in DXA Body Composition Precision 7 In conclusion, in this group of Division 1 athletes, fat and lean mass SD and %CV and the corresponding LSC RMSD and LSC %CV values differed by gender, ROI, tissue type, and mass. Based on analyses of the SD, males have greater variability than females and lean mass has greater variability than fat and total mass, perhaps because of their larger body size. Descriptively, a strong nonlinear positive relationship between LSC RMSD and mass and a negative relationship between LSC %CV and mass were observed. Thus, to over simplify, variability increases as mass increases and the rate of increase is greater for smaller masses. When using serial total body DXA to evaluate regional fat and lean mass changes in athletes, determination of the LSC values for the body ROIs is essential. Moreover, performance of precision assessment in individuals similar in body size and composition is necessary. References 1. Albanese CV, Diessel E, Genant HK Clinical applications of body composition measurements using DXA. J Clin Densitom 6:75e Zalesin KC, Franklin BA, Lillystone MA, et al Differential loss of fat and lean mass in the morbidly obese after bariatric surgery. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 8(1):15e Levitt DG, Beckman LM, Mager JR, et al Comparison of DXA and water measurements of body fat following gastric bypass surgery and a physiological model of body water, fat, and muscle composition. J Appl Physiol 109(3):786e Carr A, Emery S, Law M, et al An objective case definition of lipodystrophy in HIV-infected adults: a case-control study. Lancet 361(9359):726e Bonnet E, Delpierre C, Sommet A, et al Total body composition by DXA of 241 HIV-negative men and 162 HIV-infected men: proposal of reference values for defining lipodystrophy. J Clin Densitom 8(3):287e Cavalcanti RB, Cheung AM, Raboud J, Walmsley S Reproducibility of DXA estimations of body fat in HIV lipodystrophy: implications for clinical research. J Clin Densitom 8(3): 293e Freitas P, Santos AC, Carvalho D, et al Fat mass ratio: an objective tool to define lipodystrophy in HIV-infected patients under antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Densitom 13(2):197e Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, et al Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 39(4):412e Lang T, Cauley JA, Tylavsky F, et al Computed tomographic measurements of thigh muscle cross-sectional area and attenuation coefficient predict hip fracture: the health, aging, and body composition study. J Bone Miner Res 25(3):513e Muscaritoli M, Anker SD, Argiles J, et al Consensus definition of sarcopenia, cachexia and pre-cachexia: joint document elaborated by Special Interest Groups (SIG) cachexia-anorexia in chronic wasting diseases and nutrition in geriatrics. Clin Nutr 29(2):154e Di Monaco M, Vallero F, Di Monaco R, Tappero R Prevalence of sarcopenia and its association with osteoporosis in 313 older women following a hip fracture. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 52(1):71e Santos DA, Silva AM, Matias CN, et al Accuracy of DXA in estimating body composition changes in elite athletes using a four compartment model as the reference method. Nutr Metab 7: Harley JA, Hind K, O Hara JP Three-compartment body composition changes in elite rugby league players during a super league season, measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Strength Conditioning Res/Natl Strength Cond Assoc 25(4): 1024e Micklesfield LK, Gray J, Taliep MS Bone mineral density and body composition of South African cricketers. J Bone Miner Metab 30:232e Friesen KJ, Rozenek R, Clippinger K, et al Bone mineral density and body composition of collegiate modern dancers. J Dance Med Sci 15(1):31e Bell W, Evans WD, Cobner DM, Eston RG Regional placement of bone mineral mass, fat mass, and lean soft tissue mass in young adult rugby union players. Ergonomics 48(11e14):1462e Hind K, Oldroyd B, Truscott JG In vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa densitometer for the measurement of total body composition and fat distribution in adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 65(1):140e Ellis KJ Human body composition: in vivo methods. Physiol Rev 80(2):649e Lee SY, Gallagher D Assessment methods in human body composition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 11:566e Duthie GM, Pyne DB, Hopkins WG, Livingstone S, Hooper SL Anthropometry profiles of elite rugby players: quantifying changes in lean mass. Br J Sports Med 40(3): 202e Fornetti WC, Pivarnik JM, Foley JM, Fiechtner JJ Reliability and validity of body composition measures in female athletes. J Appl Physiol 87(3):1114e Stewart AD, Hannan WJ Prediction of fat and fat-free mass in male athletes using dual X-ray absorptiometry as the reference method. J Sports Sci 18(4):263e Bell W, Cobner DM, Evans WD Prediction and validation of fat-free mass in the lower limbs of young adult male Rugby Union players using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry as the criterion measure. Ergonomics 43(10):1708e van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Hartgens F, Vollaard NB, et al Body composition changes in bodybuilders: a method comparison. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(3):490e Shepherd JA, Lu Y, Wilson K, et al Cross-calibration and minimum precisions standards for dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry: the 2005 ISCD Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 9: 31e Baim S, Binkley N, Bilezikian JP, et al Official Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and executive summary of the 2007 ISCD Position Development Conference. J Clin Densitom 11:75e Simonelli C, Adler RA, Blake GM, et al Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry technical issues: the 2007 ISCD Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 11:109e Li C, Ford ES, Zhao G, et al Estimates of body composition with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in adults. Am J Clin Nutr 90(6):1457e Kelly TL, Wilson KE, Heymsfield SB Dual energy X-Ray absorptiometry body composition reference values from NHANES. PloS One 4(9):e Hsu FC, Lenchik L, Nicklas BJ, et al Heritability of body composition measured by DXA in the diabetes heart study. Obes Res 13(2):312e Cordero-MacIntyre ZR, Peters W, Libanati CR, et al Reproducibility of DXA in obese women. J Clin Densitom 5(1): 35e44.
8 8 Buehring et al. 32. Toombs RJ, Ducher G, Shepherd JA, De Souza MJ The impact of recent technological advances on the trueness and precision of DXA to assess body composition. Obesity 20:30e Kenward MG, Roger JH Small sample inference for fixed effects from restricted maximum likelihood. Biometrics 53: 983e Rothney MP, martin FP, Xia Y, et al Precision of GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of total and regional body composition in nonobese adults. J Clin Densitom 15:399e Nana A, Slater GJ, Hopkins WG, Burke LM Effects of exercise sessions on DXA measurements of body composition in active people. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45:178e Nana A, Slater GJ, Hopkins WG, Burke LM Effects of daily activities on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry measurements of body composition in active people. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44:180e Santos DA, Gobbo LA, Matias CN, et al Body composition in taller individuals using DXA: a validation study for athletic and non-athletic populations. J Sports Sci 31:405e413.
Effect of hand positioning on idxa precision error for total and regional bone and body
 Effect of hand positioning on idxa precision error for total and regional bone and body composition parameters. Abstract Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are performed
Effect of hand positioning on idxa precision error for total and regional bone and body composition parameters. Abstract Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are performed
In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in
 1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements.
 Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 1 A.Shallcross, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter,
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 1 A.Shallcross, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter,
Effect of Precision Error on T-scores and the Diagnostic Classification of Bone Status
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is rapidly
 Effects of Exercise Sessions on DXA Measurements of Body Composition in Active People ALISA NANA 1,2, GARY J. SLATER 3, WILL G. HOPKINS 4, and LOUISE M. BURKE 1 1 AIS Sports Nutrition, Australian Institute
Effects of Exercise Sessions on DXA Measurements of Body Composition in Active People ALISA NANA 1,2, GARY J. SLATER 3, WILL G. HOPKINS 4, and LOUISE M. BURKE 1 1 AIS Sports Nutrition, Australian Institute
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult
 2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
Fat Mass. Baseline. (lbs) (lbs) Composition Trend: Total. Aug 17. Apr 17. May 17. Jun 17. Jul 17. Measured Date
 Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes
 Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Body Composition Reference Values from NHANES
 Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Body Composition Reference Values from NHANES Thomas L. Kelly 1 *, Kevin E. Wilson 1, Steven B. Heymsfield 2 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford, Massachusetts, United States of America,
Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Body Composition Reference Values from NHANES Thomas L. Kelly 1 *, Kevin E. Wilson 1, Steven B. Heymsfield 2 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford, Massachusetts, United States of America,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment
 Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation study
 (2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
(2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals
 DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Surveys
 J Bone Metab 2016;23:243-247 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.243 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the
J Bone Metab 2016;23:243-247 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.243 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Prevalence of Sarcopenia Adjusted Body Mass Index in the Korean Woman Based on the
TigerPrints. Clemson University. Nadia Marie Ghassan Najm Clemson University
 Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 8-2015 Mathematical Properties that Influence Least Significant Change of Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density Measured by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 8-2015 Mathematical Properties that Influence Least Significant Change of Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density Measured by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence
 Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Medical Policy. MP Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
Quality Control of DXA System and Precision Test of Radio-technologists
 J Bone Metab 2014;21:2-7 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2014.21.1.2 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Review Article Quality Control of DXA System and Precision Test of Radio-technologists Ho-Sung Kim 1,
J Bone Metab 2014;21:2-7 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2014.21.1.2 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Review Article Quality Control of DXA System and Precision Test of Radio-technologists Ho-Sung Kim 1,
Understanding Body Composition
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section
 9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi
 DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
Is Sarcopenia a Potential Risk Factor for Distal Radius Fracture? Analysis Using Propensity Score Matching
 J Bone Metab 2018;25:99-106 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2018.25.2.99 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Is Sarcopenia a Potential Risk Factor for Distal Radius Fracture? Analysis Using Propensity
J Bone Metab 2018;25:99-106 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2018.25.2.99 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Is Sarcopenia a Potential Risk Factor for Distal Radius Fracture? Analysis Using Propensity
DXA Best Practices. What is the problem? 9/29/2017. BMD Predicts Fracture Risk. Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry: DXA
 BMD Predicts Fracture Risk Ten Year Fracture Probability (%) 50 40 30 20 10 Age 80 70 60 50 E. Michael Lewiecki, MD Director, New Mexico Clinical Research & Osteoporosis Center Director, Bone TeleHealth
BMD Predicts Fracture Risk Ten Year Fracture Probability (%) 50 40 30 20 10 Age 80 70 60 50 E. Michael Lewiecki, MD Director, New Mexico Clinical Research & Osteoporosis Center Director, Bone TeleHealth
Detecting meaningful body composition changes in athletes
 Detecting meaningful body composition changes in athletes using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry Steffi L Colyer 1, Simon P Roberts 1, Jonathan B Robinson 2, Dylan Thompson 1, Keith A Stokes 1, James L
Detecting meaningful body composition changes in athletes using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry Steffi L Colyer 1, Simon P Roberts 1, Jonathan B Robinson 2, Dylan Thompson 1, Keith A Stokes 1, James L
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2014 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2014 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density in Japanese Adults
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution
 A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
Sarcopenia Assessment
 Sarcopenia Assessment using DXA Technology from GE Healthcare Healthy Aging It s Vital gehealthcare.com What is sarcopenia? Sarcopenia muscle loss with aging Sarcopenia is a disease associated with the
Sarcopenia Assessment using DXA Technology from GE Healthcare Healthy Aging It s Vital gehealthcare.com What is sarcopenia? Sarcopenia muscle loss with aging Sarcopenia is a disease associated with the
2013 ISCD Combined Official Positions
 2013 ISCD Combined Oicial Positions Oicial Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry The International Society for Clinical Densitometry (ISCD) is a not-for-profit multidisciplinary
2013 ISCD Combined Oicial Positions Oicial Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry The International Society for Clinical Densitometry (ISCD) is a not-for-profit multidisciplinary
Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures
 BODY COMPOSITION Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures Body composition = component of health-related fitness & = component of metabolic fitness Unlike other health-related fitness Not
BODY COMPOSITION Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures Body composition = component of health-related fitness & = component of metabolic fitness Unlike other health-related fitness Not
MP Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 09/19/2018 Section: Radiology Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With Densitometry 9.01.502
Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 09/19/2018 Section: Radiology Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With Densitometry 9.01.502
Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions
 bs_bs_banner Special Article Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions Christopher PF Marinangeli and Amira N Kassis
bs_bs_banner Special Article Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions Christopher PF Marinangeli and Amira N Kassis
Purpose. Methods and Materials
 Prevalence of pitfalls in previous dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans according to technical manuals and International Society for Clinical Densitometry. Poster No.: P-0046 Congress: ESSR 2014
Prevalence of pitfalls in previous dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans according to technical manuals and International Society for Clinical Densitometry. Poster No.: P-0046 Congress: ESSR 2014
Techniques for Undertaking Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Whole-Body Scans to Estimate Body Composition in Tall and/or Broad Subjects
 International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 2012, 22, 313-322 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.ijsnem-journal.com ORIGINAL RESEARCH Techniques for Undertaking Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 2012, 22, 313-322 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.ijsnem-journal.com ORIGINAL RESEARCH Techniques for Undertaking Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302)
 PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
Evaluation and Validation of BODPOD Body Scan Method as Compared to DEXA, Effect of Calcium and Caloric Intake in Female Collegiate Track Athletes
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program 5-2010 Evaluation and Validation of BODPOD Body Scan Method as Compared to DEXA, Effect of Calcium and Caloric Intake
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program 5-2010 Evaluation and Validation of BODPOD Body Scan Method as Compared to DEXA, Effect of Calcium and Caloric Intake
Body Composition Assessment Scholars
 Body Composition Assessment Scholars PURE HEALTH REGISTERED DIETICIANS Kathy Snoeck Henkemans & Bronwen Stokes Suite 5, Doringkloof Medical Centre, Doringkloof Mall, Botha Avenue, Centurion What can screening
Body Composition Assessment Scholars PURE HEALTH REGISTERED DIETICIANS Kathy Snoeck Henkemans & Bronwen Stokes Suite 5, Doringkloof Medical Centre, Doringkloof Mall, Botha Avenue, Centurion What can screening
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT
 DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES. Abstract. Introduction. Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, UDC :572.
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
What Is Body Composition?
 Chapter Six What Is Body Composition? Body composition is the body s relative amounts of fat mass and fat-free mass Body fat includes two categories: Essential fat is crucial for normal body functioning
Chapter Six What Is Body Composition? Body composition is the body s relative amounts of fat mass and fat-free mass Body fat includes two categories: Essential fat is crucial for normal body functioning
TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION www.sportsurgeryclinic.com WHY CHOOSE DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION? DEXA, short for Dual Energy
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION www.sportsurgeryclinic.com WHY CHOOSE DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION? DEXA, short for Dual Energy
RELIABILITY OF DUAL-ENERGY X-RAY
 RELIABILITY OF DUAL-ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY IN ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION IN ELITE ATHLETES Alisa Nana BND (Hons) A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
RELIABILITY OF DUAL-ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY IN ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION IN ELITE ATHLETES Alisa Nana BND (Hons) A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity
 8 BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity Gerrit van den Berg, Manon van Eijsden, Tanja G.M. Vrijkotte, Reinoud J.B.J. Gemke Pediatric Obesity 2013; 8(3): e37-40 102 Chapter 8
8 BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity Gerrit van den Berg, Manon van Eijsden, Tanja G.M. Vrijkotte, Reinoud J.B.J. Gemke Pediatric Obesity 2013; 8(3): e37-40 102 Chapter 8
Understanding Body Composition
 Understanding Body Composition Chapter 7 Body Composition n Body composition is the ratio between fat and fat-free mass n Fat-free mass includes all tissues exclusive of fat (muscle, bone, organs, fluids)
Understanding Body Composition Chapter 7 Body Composition n Body composition is the ratio between fat and fat-free mass n Fat-free mass includes all tissues exclusive of fat (muscle, bone, organs, fluids)
Sports Performance 15. Section 3.2: Body Composition
 Sports Performance 15 Section 3.2: Body Composition The relative percentage of muscle, fat, bone and other tissue in the body Our primary concern in this unit is body fatness and how it pertains to athletic
Sports Performance 15 Section 3.2: Body Composition The relative percentage of muscle, fat, bone and other tissue in the body Our primary concern in this unit is body fatness and how it pertains to athletic
Clinical Nutrition in the 21st Century Malnutrition, sarcopenia and cachexia
 Clinical Nutrition in the 21st Century Malnutrition, sarcopenia and cachexia Stéphane M. Schneider, MD, PhD, FEBGH Professor of Nutrition and ESPEN ECPC Chair In proto-indo-european, Latin and Greek Under
Clinical Nutrition in the 21st Century Malnutrition, sarcopenia and cachexia Stéphane M. Schneider, MD, PhD, FEBGH Professor of Nutrition and ESPEN ECPC Chair In proto-indo-european, Latin and Greek Under
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT
 C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
Insights into relationships between body mass, composition and bone: findings in elite
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry Insights into relationships between body mass, composition and bone: findings in elite rugby players Hind K a, Gannon L a, Brightmore A a, Beck B b. a Carnegie Research
Journal of Clinical Densitometry Insights into relationships between body mass, composition and bone: findings in elite rugby players Hind K a, Gannon L a, Brightmore A a, Beck B b. a Carnegie Research
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at:
 Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT IN WOMEN USING SKINFOLD THICKNESS EQUATIONS, BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS AND UNDERWATER WEIGHING
 STUDIES IN PHYSICAL CULTURE AND TOURISM Vol. 17, No. 3, 2010 EFTEKHAR MOHAMMADI, SAEID SHAKERIAN Faculty of Physical Education & Sports Science, Shahid Chamran University, Iran COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION
STUDIES IN PHYSICAL CULTURE AND TOURISM Vol. 17, No. 3, 2010 EFTEKHAR MOHAMMADI, SAEID SHAKERIAN Faculty of Physical Education & Sports Science, Shahid Chamran University, Iran COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION
Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA
 Strong Bone Asia 2013 Osteoporosis in ASEAN Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA Chris Schultz Scientist-in-Charge (Bone Densitometry) Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide,
Strong Bone Asia 2013 Osteoporosis in ASEAN Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA Chris Schultz Scientist-in-Charge (Bone Densitometry) Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide,
Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment
 Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment gehealthcare.com Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment More than 40% of women with normal or osteopenic BMD had a moderate or severe vertebral deformation seen with DVA. Patrick
Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment gehealthcare.com Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment More than 40% of women with normal or osteopenic BMD had a moderate or severe vertebral deformation seen with DVA. Patrick
New Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Machines (idxa) and Vertebral Fracture Assessment
 Case 1 New Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Machines (idxa) and Vertebral Fracture Assessment (VFA) History and Examination Your wealthy friend who is a banker brings his 62-year-old mother to your office
Case 1 New Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Machines (idxa) and Vertebral Fracture Assessment (VFA) History and Examination Your wealthy friend who is a banker brings his 62-year-old mother to your office
BODY COMPOSITION (Why your weight isn't a good indication of health.)
 BODY COMPOSITION (Why your weight isn't a good indication of health.) Body Composition is the technical term used to describe the different components that, when taken together, make up a person's body
BODY COMPOSITION (Why your weight isn't a good indication of health.) Body Composition is the technical term used to describe the different components that, when taken together, make up a person's body
Lunar idxa. The intelligent DXA. gehealthcare.com
 Lunar idxa The intelligent DXA gehealthcare.com The best of DXA technology for bone and metabolic health assessment With a state-of-the-art design, Lunar idxa offers research-grade image resolution and
Lunar idxa The intelligent DXA gehealthcare.com The best of DXA technology for bone and metabolic health assessment With a state-of-the-art design, Lunar idxa offers research-grade image resolution and
Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ
 Body composition assessment issues in athletes 1 Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Body composition assessment issues in athletes 1 Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment
 Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment Ingvar Bosaeus Clinical Nutrition Unit Sahlgrenska University Hospital NSKE Oslo 2012-01-18 Outline What is body composition? What is nutritional assessment?
Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment Ingvar Bosaeus Clinical Nutrition Unit Sahlgrenska University Hospital NSKE Oslo 2012-01-18 Outline What is body composition? What is nutritional assessment?
Section II: Emerging Uses of Bone Densitometry
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry: Assessment & Management of Musculoskeletal Health, vol. 17, no. 1, 78e83, 2014 Ó Copyright 2014 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/17:78e83/$36.00
Journal of Clinical Densitometry: Assessment & Management of Musculoskeletal Health, vol. 17, no. 1, 78e83, 2014 Ó Copyright 2014 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/17:78e83/$36.00
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.28 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 12:2012 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date reviewed
MP 6.01.28 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 12:2012 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date reviewed
DXA Body Composition Scan + Visceral Fat Analysis
 DXA Body Composition Scan + Visceral Fat Analysis Charles B. Christian, Jr. M.D. Medical Director Inside Outside Wellness Center & Medical Spa 4499 Medical Drive #225 San Antonio, Texas 78229 210.616.0836
DXA Body Composition Scan + Visceral Fat Analysis Charles B. Christian, Jr. M.D. Medical Director Inside Outside Wellness Center & Medical Spa 4499 Medical Drive #225 San Antonio, Texas 78229 210.616.0836
The official position of the International Society for Clinical
 Improving Clinical Decisions for Women at Risk of Osteoporosis: Dual-Femur Bone Mineral Density Testing Raymond E. Cole, DO, CCD Context: In bone mineral density (BMD) testing, unilateral hip analysis
Improving Clinical Decisions for Women at Risk of Osteoporosis: Dual-Femur Bone Mineral Density Testing Raymond E. Cole, DO, CCD Context: In bone mineral density (BMD) testing, unilateral hip analysis
Diagnosis of Vertebral Fractures by Vertebral Fracture Assessment
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 9, no. 1, 66 71, 2006 Ó Copyright 2006 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/06/9:66 71/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2005.11.002 Original
Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 9, no. 1, 66 71, 2006 Ó Copyright 2006 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/06/9:66 71/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2005.11.002 Original
BODY COMPOSITION COMPARISON: BIOELECTRIC IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS WITH DXA IN ADULT ATHLETES
 BODY COMPOSITION COMPARISON: BIOELECTRIC IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS WITH DXA IN ADULT ATHLETES A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
BODY COMPOSITION COMPARISON: BIOELECTRIC IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS WITH DXA IN ADULT ATHLETES A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Body Composition. Sport Books Publisher 1
 Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul; 2
 J Bone Metab 2017;24:235-240 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.4.235 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Comparison of Bone Mineral Density and Appendicular Lean Body Mass between Osteoporotic
J Bone Metab 2017;24:235-240 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.4.235 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Comparison of Bone Mineral Density and Appendicular Lean Body Mass between Osteoporotic
Studiedag Geriatrie, Leuven Bewegen als geneesmiddel. Sarcopenie
 Studiedag Geriatrie, Leuven 29-05-2018 Bewegen als geneesmiddel Sarcopenie Evelien Gielen MD PhD Dienst Geriatrie & Centrum voor Metabole Botziekten, UZ Leuven Overview Introduction Muscle ageing Evolving
Studiedag Geriatrie, Leuven 29-05-2018 Bewegen als geneesmiddel Sarcopenie Evelien Gielen MD PhD Dienst Geriatrie & Centrum voor Metabole Botziekten, UZ Leuven Overview Introduction Muscle ageing Evolving
Prevalence of Osteoporosis p. 262 Consequences of Osteoporosis p. 263 Risk Factors for Osteoporosis p. 264 Attainment of Peak Bone Density p.
 Dedication Preface Acknowledgments Continuing Education An Introduction to Conventions in Densitometry p. 1 Densitometry as a Quantitative Measurement Technique p. 2 Accuracy and Precision p. 2 The Skeleton
Dedication Preface Acknowledgments Continuing Education An Introduction to Conventions in Densitometry p. 1 Densitometry as a Quantitative Measurement Technique p. 2 Accuracy and Precision p. 2 The Skeleton
The Impact of Recent Technological Advances on the Trueness and Precision of DXA to Assess Body Composition
 nature publishing group The Impact of Recent Technological Advances on the Trueness and Precision of DXA to Assess Body Composition Rebecca J. Toombs 1, Gaele Ducher 1, John A. Shepherd 2 and Mary Jane
nature publishing group The Impact of Recent Technological Advances on the Trueness and Precision of DXA to Assess Body Composition Rebecca J. Toombs 1, Gaele Ducher 1, John A. Shepherd 2 and Mary Jane
Article Title: Errors in Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Estimation of Body Composition Induced by Hypohydration
 Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. This article appears here in its accepted, peerreviewed form; it has
Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. This article appears here in its accepted, peerreviewed form; it has
Sarcopenia una definicion en evolucion. Hélène Payette, PhD Centre de recherche sur le vieillissement
 Sarcopenia una definicion en evolucion Hélène Payette, PhD Centre de recherche sur le vieillissement X Curso ALMA Cancun, Mexico, Julio 2011 NIA conference Epidemiologic and Methodologic Problems in Determining
Sarcopenia una definicion en evolucion Hélène Payette, PhD Centre de recherche sur le vieillissement X Curso ALMA Cancun, Mexico, Julio 2011 NIA conference Epidemiologic and Methodologic Problems in Determining
Journal of Biomedical Graphics and Computing, 2014, Vol. 4, No. 2
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Short-term precision error in dual energy x-ray absorptiometry, bone mineral density and trabecular bone score measurements; and effects of obesity on precision error Susan J Hopkins,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Short-term precision error in dual energy x-ray absorptiometry, bone mineral density and trabecular bone score measurements; and effects of obesity on precision error Susan J Hopkins,
Orthopaedic Related Conditions Literature Review
 Orthopaedic Related Conditions Literature Review Louis Cheung Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology The Chinese University of Hong Kong From: mydesultoryblog.com General Facts of Skeletal Muscles 40
Orthopaedic Related Conditions Literature Review Louis Cheung Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology The Chinese University of Hong Kong From: mydesultoryblog.com General Facts of Skeletal Muscles 40
MILK. Nutritious by nature. The science behind the health and nutritional impact of milk and dairy foods
 MILK Nutritious by nature The science behind the health and nutritional impact of milk and dairy foods Muscle mass maintenance in older people There is evidence to suggest a potential role for milk and
MILK Nutritious by nature The science behind the health and nutritional impact of milk and dairy foods Muscle mass maintenance in older people There is evidence to suggest a potential role for milk and
Total and Regional BMD Comparison of Collegiate Male and Female Athletes
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2016 Total and Regional BMD Comparison of Collegiate Male and Female Athletes
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2016 Total and Regional BMD Comparison of Collegiate Male and Female Athletes
Measurement Uncertainty in Spine Bone Mineral Density by Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
 J Bone Metab 2017;24:105-109 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.105 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Measurement Uncertainty in Spine Bone Mineral Density by Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
J Bone Metab 2017;24:105-109 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.105 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Measurement Uncertainty in Spine Bone Mineral Density by Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Body Types & Weight These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education Body Types & Weight These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Sarcopenia in older people
 Sarcopenia in older people Timothy Kwok/Ruth Chan Department of Medicine and Therapeutics / Centre for Nutritional Studies Outline What is sarcopenia? How common is sarcopenia? Risk factors of sarcopenia
Sarcopenia in older people Timothy Kwok/Ruth Chan Department of Medicine and Therapeutics / Centre for Nutritional Studies Outline What is sarcopenia? How common is sarcopenia? Risk factors of sarcopenia
Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems?
 Osteoporos Int (2010) 21:1227 1236 DOI 10.1007/s00198-009-1062-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems? B. Fan & Y. Lu
Osteoporos Int (2010) 21:1227 1236 DOI 10.1007/s00198-009-1062-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems? B. Fan & Y. Lu
Adult BMI Calculator
 For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
Healthy aging. It s vital.
 GE Healthcare Healthy aging. It s vital. encore 17 The leading edge of DXA applications This trio of new encore 17 functions will take your clinical assessment capability to the next level. We are pleased
GE Healthcare Healthy aging. It s vital. encore 17 The leading edge of DXA applications This trio of new encore 17 functions will take your clinical assessment capability to the next level. We are pleased
Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients
 OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
Nutrition to prevent and treat sarcopenia in older people
 1 Nutrition to prevent and treat sarcopenia in older people Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Madrid, Spain Roma, 17 dicembre 2014 + The objective of Gerontology is not to increase
1 Nutrition to prevent and treat sarcopenia in older people Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Madrid, Spain Roma, 17 dicembre 2014 + The objective of Gerontology is not to increase
Does Body Mass Index Adequately Capture the Relation of Body Composition and Body Size to Health Outcomes?
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A A BRIEF ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Does
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A A BRIEF ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Does
Lunar Prodigy Advance
 GE Medical Systems Lunar Prodigy Advance Direct-Digital Densitometry imagination at work Your practice needs to move fast, yet you want peace of mind. A partnership is a journey - expertise, support and
GE Medical Systems Lunar Prodigy Advance Direct-Digital Densitometry imagination at work Your practice needs to move fast, yet you want peace of mind. A partnership is a journey - expertise, support and
Interpretation Guide. What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd. Mobile Body Composition Analysis
 Interpretation Guide Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd Mobile Body Composition Analysis Interpreting your results Total Body Water (TBW) TBW is all the
Interpretation Guide Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd Mobile Body Composition Analysis Interpreting your results Total Body Water (TBW) TBW is all the
ESPEN Congress Prague 2007
 ESPEN Congress Prague 2007 Nutrition implication of obesity and Type II Diabetes Nutrition support in obese patient Claude Pichard Nutrition Support in Obese Patients Prague, 2007 C. Pichard, MD, PhD,
ESPEN Congress Prague 2007 Nutrition implication of obesity and Type II Diabetes Nutrition support in obese patient Claude Pichard Nutrition Support in Obese Patients Prague, 2007 C. Pichard, MD, PhD,
Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timisoara, Romania b
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2015; 10(3): 204-209 ORIGINAL PAPERS Reliability of Measuring Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Thickness Using Ultrasound in Non-Athletic
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2015; 10(3): 204-209 ORIGINAL PAPERS Reliability of Measuring Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Thickness Using Ultrasound in Non-Athletic
Prodigy. from GE Healthcare. Most trusted, reliable and best-selling DXA system with one of the largest installed base in the world. gehealthcare.
 Prodigy from GE Healthcare Most trusted, reliable and best-selling DXA system with one of the largest installed base in the world gehealthcare.com Prodigy High performance, efficient and reliable DXA system
Prodigy from GE Healthcare Most trusted, reliable and best-selling DXA system with one of the largest installed base in the world gehealthcare.com Prodigy High performance, efficient and reliable DXA system
Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative. International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011
 Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011 Slide 1-3 Topics to be covered: What is vertebral fracture assessment? How does VFA compare to standard
Annotations Part III Vertebral Fracture Initiative International Osteoporosis Foundation March 2011 Slide 1-3 Topics to be covered: What is vertebral fracture assessment? How does VFA compare to standard
Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration of Pencil-Beam and Fan-Beam Dual- Energy X-Ray Absorptiometers*
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
