This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section:
|
|
|
- Amanda McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical structural organisation of cells, tissues, organs and systems. 5.2 RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS In animals, the exchange of gases between the internal and external environments of the organism is facilitated by the structure of the exchange surface/s including spiracles, gills, alveoli and skin. 5.3 DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS In animals, the acquisition and processing of nutrients is facilitated by the structures of the digestive system; animals may have a gastrovascular cavity with one opening or a specialised alimentary canal with two opening; specialisation of alimentary canals is related to diet, for example, herbivores and carnivores. 5.4 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS In animals, the transport of materials within the internal environment for exchange with cells is facilitated by the structure of open and closed circulatory systems according to the different metabolic requirements of organisms and differing environments. 5.5 TRANSPORT IN VASCULAR PLANTS In vascular plants, gases are exchanged via stomata and the plant surface and does not involve the plant transport system. In vascular plants, transport of water and mineral nutrients from the roots occurs via xylem involving root pressure, capillary action transpiration (adhesion and cohesion of water molecules); transport of the products of photosynthesis and some mineral nutrients occurs by translocation in the phloem. Terrestrial Australian plants are adapted to minimize water loss in an arid environment. 61
2 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Terminology These are some of the terms from this section which you should know. Write the meaning of each term in the space provided. cell organ system (iv) tissue (v) vascular tissue Review Questions 1. Place the followings terms in order of their size and complexity: organ, system, cell, tissue. 2. What is meant by: cell differentiation? cell specialization? 3. Why is tissue which lines the windpipe different to that which lines the small intestine? 62
3 What are their respective functions? 4. The table below refers to higher animals. Complete the blank spaces. circulatory digestive (iv) (v) ORGAN SYSTEM MAIN ORGANS FUNCTION/S heart, arteries, veins, arterioles, venules, capillaries lungs, nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles cardiac, smooth and striated muscle protects soft tissue, anchors muscle, site for blood cell synthesis, stores fat, supports body (vi) excretory (vii) lymph vessels, lymph nodes 63
4 5. Name the system that is represented in each of the following diagrams: (iv) 64
5 (v) (vi) 6. From the diagram below, name the tissues mark A-D and describe in the table how their cells are specialized to carry out particular functions. A TISSUE NAME CELL SPECIALIZATION A B B C D C D 65
6 5.2 RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS Terminology These are some of the terms from this section which you should know. Write the meaning of each term in the space provided. alveolus gas exchange oxygenated (iv) respiratory system (v) spiracle (vi) tracheal system Review Questions 1. Two main gases are exchanged by animals lungs and gills. Name these two gases. 2. Which organisms exchange these gases using the following structures: moist skin tracheal system lungs (iv) gills 66
7 3. Why must the gills of a fish have a greater surface area than the lungs of a similarly sized mammal? Why does oxygen diffuse from the water into the plasma in the gills of a fish? Compare the gas exchange surfaces of insects and birds. (iv) Why do respiratory surfaces need to remain moist? (v) How do fish keep oxygenated water moving over their gills? 4. How are each of the following adapted to maximise their respiratory surface areas? mammals 67
8 amphibians fish 5. A microscopic protozoan has a large surface area to volume ratio. How does this assist the organism in obtaining oxygen and excreting carbon dioxide? What problem with gaseous exchange would this organism have if it were to continue to grow to the size of a human? 5.3 DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Terminology These are some of the terms from this section which you should know. Write the meaning of each term in the space provided. alimentary canal carnivore cnidaria 68
9 (iv) detrivore (v) herbivore (vi) insectivore (vii) omnivore (viii) parasite (ix) rectum (x) ruminant Review Questions 1. What is digestion? Why is digestion necessary? 2. Name the two animal phyla that have a gastrovascular cavity. Draw a simple sketch of either phyla s gastrovascular cavity in the space below. 69
10 How does this differ from the alimentary canal of higher animals? 3. Animals can be classified according to what they eat. Which animal group would consume the most protein? Explain. Which animal group would consume the most carbohydrates? Explain. 4. All animals need the six types of nutrients: water, carbohydrates, fats, protein, minerals and vitamins. The proportion of each type of nutrient in the diet varies according to the species to which the animal belongs. Complete the following with the appropriate food types. Animals that eat only plant matter obtain most of their energy from: Animals that eat only meat obtain most of their energy from: 5. Because different animals consume different foods, their digestive tracts need to be specialized. Why is the carnivore s digestive tract comparatively shorter and less complex than a herbivore s? What special role does the microflora in an herbivores gut play in their digestive process? Name two examples of ruminant herbivores and two examples of non ruminant herbivores. 70
11 (iv) Describe the difference in digestive processes between ruminant and nonruminant herbivores. (v) Which is the most efficient? Explain. (vi) What is similar in their digestive process? 6. Study the generalized diagrams below then answer the questions that follow: a) b) c) Oesophagus Stomach Mouth Small Large intestine intestine Rectum C carnivore and omnivore non ruminant herbivore ruminant herbivore What is the main structural difference between the ruminant and the non ruminant alimentary canals? Explain. The carnivore and omnivore alimentary canals are similar. How do they differ structurally from the herbivores? Explain. 71
12 7. What are the chemical building blocks of the following organic compounds? carbohydrates lipids proteins 8. Label the four tooth types shown. What type of digestion do the teeth carry out? _ How is physical digestion different to chemical digestion? (iv) d c b a What is the function of physical (or mechanical) digestion? a b c d 72
13 (v) Explain why the human dental formula is written as (vi) The dental formula of a sheep is Describe the teeth in the sheep s upper and lower jaw. (vii) The sheep has a tough pad where its upper incisors would be expected. Explain how this may help it eat grass. (viii) How are the sheep s molars and premolars adapted for its diet? (ix) The dental formula of a domestic cat is Describe the teeth in the cat s upper and lower jaw. (x) What are carnassial teeth and what is their function? 73
14 9. Label the diagram of the alimentary canal and its associated organs. i ii iii iv v vi vii viii ix x xi xii xiii xiv xv xvi xvii 10. Name the part/s of the alimentary canal that is/are involved in: Secretion of enzymes (iv) Absorption of nutrients Peristalsis Defecation 11. Explain the role of the circulatory system in absorbing and transporting nutrients. vii viii vi iii iv v i ii xvii xvi xv xiv xiii xii xi x ix 74
15 Explain the role of lymphatic system in absorbing and transporting nutrients 12. The diagram below shows a single villus. Label the parts shown. Where are villi found in the digestive system? a c Why are the villi so small and so numerous? b a b c 75
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013
 ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
5 th Year Biology Revision Guide Summer 2010
 Topic Chapter You need to know... Unit 1 The Scientific 1 Definition and examples of the areas of study incorporated in biology. Method Process of the scientific method. The Characteristics of life Principals
Topic Chapter You need to know... Unit 1 The Scientific 1 Definition and examples of the areas of study incorporated in biology. Method Process of the scientific method. The Characteristics of life Principals
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
Science 8. Unit 2. Body Systems
 Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad , A.P.
 THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2) Nutrition in Human Beings. 3) transportation in human being 4) Excretion in human being
 1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY
 S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p.
 NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK CLASS X SUBJECT : ENGLISH
 HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK CLASS X SUBJECT : ENGLISH Make a Scrap Book for the ISA Project Voice to Voiceless. The activity will be based on the Study on the following countries - India, Spain, China, Japan and
HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK CLASS X SUBJECT : ENGLISH Make a Scrap Book for the ISA Project Voice to Voiceless. The activity will be based on the Study on the following countries - India, Spain, China, Japan and
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion. Regents Biology
 38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I
 Name: Period: Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I Assignments: Description Page(s) Due Date 1 Biology 4 th & 5 th Six Weeks MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY Feb 9 10 11 12 13 Review for Test Test - Classification
Name: Period: Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I Assignments: Description Page(s) Due Date 1 Biology 4 th & 5 th Six Weeks MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY Feb 9 10 11 12 13 Review for Test Test - Classification
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs
 Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
1b. Credit: State the chemical elements present in carbohydrates, proteins and fats. See table below
 1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER
 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 A.M. MONDAY, 3 June 2013 1 1 2 hours Question For s use Maximum Mark 1. 8 Mark Awarded 2. 13 3. 13 4. 12 5. 5 1072
Surname Other Names Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 A.M. MONDAY, 3 June 2013 1 1 2 hours Question For s use Maximum Mark 1. 8 Mark Awarded 2. 13 3. 13 4. 12 5. 5 1072
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Nutrition in Heterotrophs
 Nutrition in Heterotrophs Required Nutrients Water Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Makes up ~90% of some animals Makes up a major portion of many body parts Humans require at least
Nutrition in Heterotrophs Required Nutrients Water Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Makes up ~90% of some animals Makes up a major portion of many body parts Humans require at least
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3022478872* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core May/June 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3022478872* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core May/June 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Multicellular Organisms Homework
 Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM III
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM III Chapter 41 1. Distinguish between herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. 2. Describe the following feeding mechanisms and give examples of animals that use each:
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM III Chapter 41 1. Distinguish between herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. 2. Describe the following feeding mechanisms and give examples of animals that use each:
My Question Paper. Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 22
 My Question Paper Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 22 1. The diagrams below show sections through the duodenum and ileum at the same magnification (a) Name the structure labelled
My Question Paper Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 22 1. The diagrams below show sections through the duodenum and ileum at the same magnification (a) Name the structure labelled
SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL
 Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
LIFE PROCESSES
 LIFE PROCESSES Usually we differentiate living organisms from non-living by observing the movements in them. These movements can be: Locomotion movements In animals, e.g. running, chewing cud, etc. Growth
LIFE PROCESSES Usually we differentiate living organisms from non-living by observing the movements in them. These movements can be: Locomotion movements In animals, e.g. running, chewing cud, etc. Growth
WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus
 )ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
)ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
Cambridge O Level Biology Syllabus code 5090 All candidates enter for three papers Papers 1 and 2 and Paper 6. PAPER 1 Multiple Choice
 1 Dawood Public School Syllabus for 2010 2011 Class IX Subject Biology Books: Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology(3 ed),singapore; Federal Publication Mackean.D, GCE O Level Biology, Oxford University
1 Dawood Public School Syllabus for 2010 2011 Class IX Subject Biology Books: Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology(3 ed),singapore; Federal Publication Mackean.D, GCE O Level Biology, Oxford University
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Biology 1030 Winter 2009
 Meeting Tissue Needs Chapter 41 (844 866) Chapter 42 (867 891) Winter 2009 Lectures 10-13 Cellular Work Cellular work Source of energy Cellular currency Cellular respiration Reactants Products Trafficking
Meeting Tissue Needs Chapter 41 (844 866) Chapter 42 (867 891) Winter 2009 Lectures 10-13 Cellular Work Cellular work Source of energy Cellular currency Cellular respiration Reactants Products Trafficking
Meeting Tissue Needs
 Meeting Tissue Needs Chapter 41 (41.1 4) Chapter 42 (42.1,5 7) Winter 2009 Lectures 10-13 Cellular Work Cellular work Source of energy Cellular currency Cellular respiration Reactants Products 1 Trafficking
Meeting Tissue Needs Chapter 41 (41.1 4) Chapter 42 (42.1,5 7) Winter 2009 Lectures 10-13 Cellular Work Cellular work Source of energy Cellular currency Cellular respiration Reactants Products 1 Trafficking
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Digestive Systems. Design of Digestive Systems. Functions: detect, acquire, store, digest, absorb
 blood-brain barrier brain fat cells cells of muscles, organs, & tissues lymph(fats, immune cells) blood alimentary canal lungs interstitial fluid kidney bladder fetus placenta barrier 1 Digestive Systems
blood-brain barrier brain fat cells cells of muscles, organs, & tissues lymph(fats, immune cells) blood alimentary canal lungs interstitial fluid kidney bladder fetus placenta barrier 1 Digestive Systems
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Downloaded from
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? The heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins & capillaries).
 Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Year 13 Extended Diploma in Health & Social Care. Summer Independent Learning Task 2018
 Year 13 Extended Diploma in Health & Social Care Summer Independent Learning Task 2018 Unit 5 Anatomy and Physiology for Health and Social Care When we have a group of similar cells working together this
Year 13 Extended Diploma in Health & Social Care Summer Independent Learning Task 2018 Unit 5 Anatomy and Physiology for Health and Social Care When we have a group of similar cells working together this
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Name: Class: Date: Question #1. Question #2. What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels.
 9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
o Nutrition in human beings 33
 KEY CONCEPTS & GIST OF THE LESSON Life processes The processes that are necessary for an organism to stay alive. Eg. Nutrition, respiration, etc. Criteria of life- (i) Growth (ii) Movement Nutrition- The
KEY CONCEPTS & GIST OF THE LESSON Life processes The processes that are necessary for an organism to stay alive. Eg. Nutrition, respiration, etc. Criteria of life- (i) Growth (ii) Movement Nutrition- The
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1
 INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
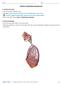 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Secondary 3 Final Exam Review
 Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs
 INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
