World Journal of Science and Research
|
|
|
- Donald Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN: Available online at World Journal of Science and Research Harman Publications. All rights reserved Research Article Botany SCREENING OF BIOACTIVE COMPOUNDS BY GC-MS, ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND IN SILICO STUDIES IN Cynodon dactylon L. Pers LEAVES T. Balasundari and M. Boominathan* PG and Research Department Of Botany, Kunthavai Naacchiyaar Govt.Arts College For Women (Autonomous) Thanjavur , Tamilnadu ABSTRACT In the present study was to investigate the phytochemical screening, histochemical, Fluorescence and antibacterial activity of Cynodon dactylon leaves extract. The phytochemical screening Cynodon dactylon leaves showed that the presence of saponins, flavonoids, polyphenol, Triterpenoids Steroids, anthroquinone terpenoids and tannin, glycosides whereas Alkaloids, carbohydrate, protein,and phlopatannins were absent in aqueous extract. The methanol extract of Cynodon dactylon leaves showed that the presence of, saponins, flavonoids, polyphenol, Triterpenoids terpenoids, Alkaloids, carbohydrate, protein, tannin and glycosides whereas phlopatannins was absent. In the present study twenty compounds were identified from extract of Cynodon dactylon leaves by Gas Chromatogram- Mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis. The prevailing compounds were Octadecanoic acid, 9-Octadecenoic acid, 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, 9,12-Octadecadienoyl chloride, 2- Hexadecen-1-Ol and Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester. The methanolic extract shows antibacterial activity against Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) bacteria. The methanolic extract shows antifungal activity against Candida albicans, Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus niger. In silico docking analysis of phytol and oleic acid, angiotensin converting Enzyme (ACE) further proved their anticancer and antidiabetic activity. Citation: T. Balasundari and M. Boominathan. (2018). Screening of bioactive compounds by gc-ms, antimicrobial activity and in silico studies in cynodon dactylon L. Pers leaves, World Journal of Science and Research. 3(1): Article Info: Received on 15 h Feb 2018 Accepted on 15 th Marcch 2018 Online March 2018 Keywords: Cynodon dactylon Phytochemical, antifungal activity In silico docking, *Corresponding author Dr. M. Boominathan 1, Assistant Professor PG and Research Department Of Botany, Kunthavai Naacchiyaar Govt.Arts College For Women (Autonomous) Thanjavur , Tamilnadu 7
2 INTRODUCTION Plants are widely used as a potent source for isolation of several drugs and formulations in treatment of many diseases. There arises a need to screen medicinal plants for bioactive compounds as a basis for further pharmacological studies (Hassan et al, 2007). Medicinal plants form the backbone of traditional medicine in the last few decades with intense pharmacological studies. They are regarded as potential sources of new compounds of therapeutic value and as sources of lead compounds in drug development. Plants are rich sources of secondary metabolites with interesting biological activities. In general, these secondary metabolites are an important source with a variety of structural arrangements and properties (De Fatima et al, 2006). Natural products from microbial sources have been the primary source of antibiotics, but with the increasing recognition of herbal medicine as an alternative form of health care, the screening of medicinal plants for active compounds has become very significant (Koduru et al, 2006). The drug-resistant bacteria pathogens have further complicated the treatment of infectious diseases. In recent years, drug resistance to human pathogenic bacteria has been commonly reported from all over the world. However, the situation is alarming in developing as well as developed countries due to indiscriminate use of antibiotics. In the present scenario of emergence of multiple drug resistance to human pathogenic organisms, this has necessitated a search for new antimicrobial substances from natural sources including plants. Plant and plant products play a wide range of antimicrobial properties. Keeping in view, the present study to investigate the phytochemical and antibacterial properties of Cynodon dactylon. MATERIALS AND METHODS Collection of plant materials The leaves of Cynodon dactylon were collected in December 2017 from, Thanjavur district, Tamil Nadu, India. The Cynodon dactylon leaves were washed several times with distilled water to remove the traces of impurities from the leaves. Leaves was spread out in a plain paper and shade dried at room temperature for about 10 days and makes a fine powder using grinder mixture. The powder materials were used for further studies. Preparation of plant extract: 2 gram of the powder of C. dactylon leaves were transferred in to different conical flask (250ml). The conical flask containing 50ml of different solution (methanol and water). The conical flask containing C. dactylon leaves were shake well for 30 minutes by free hand. After 24 hrs, the extracts were filtered using whatman filter paper No.1 and filtrate used for further analysis. Phytochemical screening Chemical tests were carried out on the extract using standard procedures to identify the constituents as described by Sofowara (1993), Trease and Evans (1989) and Harborne (1973 and 1984). GC-MS Analysis GC-MS analysis was carried out on Shimadzu 2010 plus comprising a AOC-20i auto sampler and gas chromatograph interfaced to a mass spectrometer instrument employing the following conditions: column RTX 5Ms (Column diameter is mm, column length is 30 m, column thickness 0.50 µm), operating in electron impact mode at 70 ev; Helium gas (99.99 %) was used as carrier gas at a constant flow of 1.73 ml /min and an injection volume of 5 µi was employed (split ratio of 10:1), injector temperature 270 ºC; ion source temperature 200 ºC. The oven temperature was programmed from 40 ºC (isothermal for 2 min), with an increase of 8 ºC/min, to 150 ºC, then 8 ºC/min to 250 ºC, ending with a 20 min isothermal at 280 ºC. Mass spectra were taken at 70 ev; a scan interval of 0.5 seconds and fragments from 40 to 450 Da. Total GC running time is min. The relative percentage amount of each component was calculated by comparing its average peak area to the total areas. Software adopted to handle mass spectra and chromatograms was a TurboMass Ver (Srinivasan and Ramarao, 2013). Interpretation on GC-MS was conducted using the database of National Institute Standard and Technology (NIST) having more than 62,000 patterns. The spectrum of the unknown component was compared with the spectrum of the known components stored in the NIST library. The name, molecular weight and structure of the components of the test materials were ascertained (Dukes, 2013). Determination of antimicrobial activity Antibiogram was done by disc diffusion method (NCCLS, 1993; Awoyinka et al., 2007) using plant extracts. Petri plates were prepared by pouring 30 ml of NA /PDA medium for bacteria/fungi. The test organism was inoculated on solidified agar plate with the help of micropipette and spread and allowed to dry for 10 mints. The surfaces of media were inoculated with bacteria/fungi from a broth culture. A sterile cotton swab is dipped into a standardized bacterial/ fungi test suspension and used to evenly inoculate the 8
3 entire surface of the Nutrient agar/pda plate. Briefly, inoculums containing specie of bacteria were spread on Nutrient agar plates for bacteria and fungus strains were spread on potato dextrose agar for. Using sterile forceps, the sterile filter papers (6 mm diameter) containing the crude extracts (50μl) were laid down on the surface of inoculated agar plate. The plates were incubated at 37 C for 24 h for the bacteria and at room temperature (30±1) for hr. for yeasts strains. Each sample was tested in triplicate. The antimicrobial potential of test compounds was determined on the basis of mean diameter of zone of inhibition around the disc in millimeters. The zones of inhibition of the tested microorganisms by the samples were measured using a millimeter scale. In Silico Docking Studies Protein and ligand structures were obtained from the protein data bank (PDB) database and Pubchem. Automated docking along with a graphical user interface, Auto Dock tools was utilized to generate grids, calculate dock score and evaluate the conformers of activators bound in the active site of protein as targets. A Lamarckian genetic algorithm method, implemented in the program Auto Dock 4.1, was employed. This software used for the estimation of energy during the interaction and identify the best flexible ligand pose with minimum energy. The scoring function is based on the inter-amolecular interaction of ligand and protein during docking. As per genetic algorithm all the torsions were allowed to rotate during docking. The grid map was centred at particular residues of the protein and was generated with Auto Grid. The Lamarckian genetic algorithm and the pseudo-solis and Wets methods were applied for minimization, using default parameters (Ghose AK, Crippen, 1987; Binkowski et al., 2007; Vidya et al., 2012; Shruthi et al., 2012). Complex structures were modeled using modeling software s Pymol (1.1 version, Delano Scientific LLC, San Carlos, CA, USA), Chimera ( version UCSF Resources for biocomputing visualization and informatics, NIH, CA, USA) and Pose view (Trot and Olson, 2010) installed on a desktop equipped with Pentium (R) Dual-E6600 at 3.05 GHz 3.06 GHz processor (2 GB RAM Core CPU) running the Ubuntu (LINUX) and Windows XP SP3 operating system. COX-2 enzyme protein structure The 3 dimensional structure of the COX-2 enzyme was taken from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) database ( The RCSB PDB (Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformati cs, Protein Data Bank) is a repository for the 3D structural data of large biological macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. It provides simple and advanced searches based on annotations related to sequence, structure and function The PDB ID is 6COX which is a complex of COX-2 enzyme with selective inhibitor SC-558 (Amaravani et al., 2012). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In the present study was carried out the phytochemical analysis on the Cynodon dactylon leaves revealed the presence of medicinally active constituents. The phytochemical characters of the Cynodon dactylon leaves investigated and summarized in Table-1 and plate 2 and 3. The phytochemical screening Cynodon dactylon leaves showed that the presence of saponins, flavonoids, polyphenol, Triterpenoids Steroids, anthroquinonesm terpenoids and tannin, glycosides whereas Alkaloids, carbohydrate, protein and phlobatannins was absent in aqueous extract. The phytochemical screening Cynodon dactylon leaves showed that the presence of, saponins, flavonoids, polyphenol, Triterpenoids terpenoids, Alkaloids, carbohydrate, protein, tannin and glycosides whereas phlobatannins was absent in methanol extract. Phytochemicals are plant derived chemicals which are beneficial to human health and disease prevention. The term is generally used to refer to those chemicals that may have biological significance, for example antioxidants, but are not established as essential nutrients which when in excess could be detrimental. Scientists estimate that there are thousands of known phytochemicals having the potential to affect diseases such as cancer, stroke and metabolic syndrome and those caused by microorganisms (Anderson et al., 2004). Hassain et al. (2011) screened phytochemical constituents from methanol leaf extract of Bombax malabaricum. Various organic 11 solvent extracts of Pedalium murex were subjected to preliminary phytochemical screenings by Thamizh mozhi et al. (2011). Selected 53 traditionally used medicinal plants from western region of India for their qualitative phytochemical screenings, total phenol and flavonoids contents. Pascaline et al. (2011) screened phytochemical constituents of some medicinal plants used by the Nandis of South Nandi District, Kenya. 9
4 Table.1: Qualitative Phytochemical analysis of Cynodon dactylon leaves extract S.No Phytochemicals Aqueous Extract Methanol Extract 1 Tannin Phlobatannins Saponnin Flavonoids Steroids Terpenoids Triterpenoids Alkaloids Carbohydrate Protein Anthroquinone Polyphenol Glycoside Absence, + presence and ++ high concentration GCMS Analysis In the present study twenty chemical constituents have been identified from extract of Cynodon dactylon leaves by Gas Chromatogram- Mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis. The prevailing compounds were Octadecanoic acid, 9-Octadecenoic acid, 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, 9,12-Octadecadienoyl chloride, 2- Hexadecen-1-Ol and Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester. The presence of various bioactive compounds justifies the use of the whole plant for various ailments by traditional practitioners. However isolation of individual phytochemical constituents and subjecting it to biological activity will definitely give fruitful results. (Fig 1, Table 2 and 3). Fig 1: Chromatogram obtained from the GC-MS with the Cynodon dactylon leaves extract 10
5 Table 2: Components identified in ethanolic extract of Cynodon dactylon leaves (GC- MS study) Table 3: Biological Activity of phyto-components identified in the ethanolic extracts of the Cynodon dactylon leaves by GC-MS S.No. Name of the compound Biological activity** 1. Octadecanoic acid Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, nemaicide, pesticde, Anti-androgenic flavor, hemalytic, 5- Alpha reductase inhibitor 2. 9-Octadecenoic acid Antihypertensive, Increase HDL and decrease LDL Cholesterol 3. 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid Antimicrobial activity 4. 9,12-Octadecadienoyl chloride Antimicrobial activity 5. Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester Anti oxidant, hypocholesterolemic, nematicide, pesticide, lubricant, anti androgenic, flavour, hemolytic-5-α reductase inhibitor. **Source: Dr.Duke's phytochemical and ethnobotanical databases [Online database. Karpagasundari and Kulothungan, (2014) screened the bioactive components of Physalisminima leaves have been evaluated using GC-MS. GC-MS analysis of extract of Physalisminima leaves revealed the existence of heneicosanoic acid (25.22), bicyclo [4.1.0] hepta-2, 11
6 4-dien (27.41) octadecanoic acid (CAS), stearic acid (31.19) and octadeca-9, 12-dienoic acid (32.02). Similarly the work was done by GC-MS analysis of bioactive components of Hugonia mystax L. (Linaceae). Thirteen compounds were identified. 1,2-benzene dicarboxylic acid, diisooctyl ester (48.75 %) was found to be major component followed by n- hexadecanoic acid (13.52 %), phytol (9.25 %), squalene (6.41 %), vitamin E (4.09 %), dianhydromannitol (3.56 %), 9,12 octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z) (3.20%) and 3,7,11,15 tetramethyl -2- hexadecen -1-ol (2.85 %). Anti-bacterial activity of Cynodon dactylon leaves extract Nowadays there exist more than 250 types of infections caused by bacteria. Among these microorganisms, we find the Bacillus subtilis Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus that are known to be one of the main elements of human physiological flora. Methanolic extract of Cynodon dactylon were screened against bacteria. The antibacterial activity was determined by measuring the diameter of zone of inhibition recorded. The ethanolic extract shows significant activity against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus (plate 4). The results of the Cynodon dactylon extract was correlated with the standard drug and show that the methanolic extract shows good activity against all bacterial strains. Anti-fungal activity of Cynodon dactylon leaves extract Fungi are ubiquitous in the environment, and infection due to fungal pathogens has become more common. The aim of this work was to evaluate in vitro the potential antifungal activity of medicinal Cynodon dactylon leaves extract against Candida albicans, Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus niger. The methanolic extract of Cynodon dactylon were screened against fungi. The antifungal activity was determined by measuring the diameter of zone of inhibition recorded. The ethanolic extract shows significant activity against Candida albicans, Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus niger (plate 4). The results of the Cynodon dactylon extract was correlated with the standard drug and show that the methanolic extract shows good activity against all fungal strains. Table 4: Antimicrobial activities of Cynodon dactylon leaves Bacteria Microorganisms 50μl 100µl 150µl Standard Escherichia coli (mm) 13.50± ± ± ±0.99 Staphylococcus aureus (mm) 11.50± ± ± ±0.77 Bacillus subtilis (mm) 6.75± ± ± ±0.63 Fungus Candida albicans (mm) 10.25± ± ± ±0.70 Aspergillus flavus (mm) 8.25± ± ± ±0.71 Aspergillus niger (mm) 14.75± ± ± ±0.52 Values were expressed as Mean ± SD. Bacterial standard - Chloramphenicol Fungal standard - Fluconazole Plate 4: Anti-bacterial activity of Cynodon dactylon leaves extract Escherichia coli Staylococcus aureus Bacillus subtilis 12
7 Plate 4: Anti-fungal activity of Cynodon dactylon leaves extract Candida albicans Aspergillus flavus Aspergillus niger Siva Sakthi et al. (2011) evaluated the antibacterial potentiality of ethanol and ethyl acetate solvent extracts of mature leaves of Datura metel against nine pathogenic bacterial isolates viz., Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Shigella flexneri, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Vibrio cholerae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The turbidity of the bacterial inoculums was compared with 0.5 Mc Farland standards and the antibacterial potential of Datura metel ethanol extract was tested by using Agar well diffusion method. The ethanol extract of Datura metel (100 mg/ml) showed maximum zone of inhibition (26 mm) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Staphylococcus aureus showed less zone of inhibition (8 mm). The ethyl acetate extract of Datura metel (100 mg/ml) showed maximum zone of inhibition (19 mm) against Escherichia coli. There was no zone of inhibition against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gupta et al. (2010) investigated antibacterial activity of five ethanolic and aqueous plant extracts against S. aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis and their results showed that the ethanolic extracts of four plants (Achyranthes aspera, Cynodon dactylon, Lantana camara and Tagetes patula) were effective against all tested microorganisms with MIC s ranged from 25 to 125 mg/ml. In silico studies Inflammation is the response of an organism to invasion by a foreign body such as bacteria, parasites and viruses. Studies on inflammation have become one major focus of global scientific research. Cyclooxygenases (COX) are the key enzymes in the synthesis of prostaglandins, the main mediators of inflammation, pain, and increased body temperature (hyperpyrexia). The body produces two main isoforms of COX proteins, that is, cyclooxygenases1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenases-2 (COX-2). The COX-1 is responsible for formation of important biological mediators such as prostanoids, including prostaglandins, prostacyclin, and thromboxane, and involved in pain causing, blood clotting, and protecting the stomach (Watson et al., 2000), whereas COX-2 is involved in the pain by inflammation and plays a major role in prostaglandin biosynthesis in inflammatory cells and central nervous system (Chhajed et al., 2010). COX-2 inhibition is desirable for antiinflammatory responses as it is expressed during inflammation by proinflammatory molecules, This COX-2 is believed to be the target enzyme for the anti-inflammatory activity of anti-inflammatory drugs. As selective COX-2 inhibitors are preferred drugs and since natural products have been proven to be the richest source of medicinal entities with chemical diversity, this would be better option in search of lead in drug discovery (Rosen et al., 2009). Identification and screening of bioactive molecules and their binding sites in the protein are challenging for drug development. Therefore, we planned to find out the binding ability of Octadecanoic acid with COX 2 using computational biology tools. The docked ligand molecules were selected based on docking energy and good interaction with the active site residues and the results are shown in Table 5 and 6. Hydrogen bond was indicated by dashed lines in green between atoms involved and rest of the interactions were hydrophobic. The activation energy ( Kcal/mol) was found with Octadecanoic acid (Figure 3 and 4). From the in silico docking results, it is quite evident that plant-derived compounds have the great 13
8 potential against anti-inflammatory activity of inflammatory mediator protein COX 2. In silico molecular docking in one of the most powerful techniques to discover novel ligand for proteins of known structure and thus play key role in structure based drug. Investigators often use docking computer programs to find the binding affinity for molecules that fit a binding site on the protein. Hence in this present work we have carried out in silico molecules docking to analyze the Table 5: Cyclooxygenase-2 Enzyme binding site binding properties of the mediator called COX-2 with 3 different compounds reported from Cynodon dactylon leaves. The wet analysis carried out by us showed very good result with regard to antiinflammatory property of this plant extract. So the present study may act as supportive evidence that substantiate property of this plant extract., Octadecanoic acid has potential inhibiting ability was identified from this Cynodon dactylon leaves with COX-2. S. No. Ligands Amino acids in the binding pocket 1. Octadecanoic acid Arg 208, Glu276 Table 6. Docking results of Octadecanoic acid compounds against Cyclooxygenase-2 Enzyme Sl.No. 1. Ligands Octadecanoic acid Moleccular formula Molecular Weight [g/mol] Hydrogen donor Hydrogen acceptor C 18 H 36 O Docking Energy Level (kcal/mol) Fig 3 Electrostatic surface of COX- 2 alongside of the amino acids motif with Octadecanoic acid CONCLUSION Overall, it can be concluded from the present study that Cynodon dactylon leaves contains rich source of phytochemicals. This study is the first scientific report that provides convincing phytochemicals and antibacterial activity evidence for the relevance of Cynodon dactylon leaves thus providing scientific validity to its traditional consumption by the local populace of south India. Cynodon dactylon leaves extract had a good potential for therapeutic use against infectious diseases caused by bacterial and fungal pathogens. REFERENCES Awoyinka OA, Balogun IO and Ogunnow AA. (2007) Phtochemical screening and in vitro bioactivity of Cnidoscolus aconitifolius (Euphorbiaceae). J. Med. Plant Res, 1: Anderson G.D., Phytochemical. Dynamic Chiropractic, In K.T. Chung, I. Weichang and M.G. Johnson. Are tannins a double edge sword in biology and health? Trends in Food Science Technology, 4, 2004,
9 Chhajed, M. Tamm, M.A. Malouf and A.R. Glanville (2002) Lung Transplantation: Management and Complications Chest Dis Allied Sci ; 44 : Gupta, R.N., Kartik, V., Manoj, P., Singh, P.S., Alka, G., Antibacterial activities of ethanolic extracts of plants used in flok medicine. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 1 (2), Hassan Abbas M and Mohsenzadegan M. (2007) The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 7(4): Karpagasundari C and Kulothungan S. (2014) Analysisof bioactive compounds in Physalisminima leave using GC MS, HPLC, UV-VIS and FTIR techniques. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 3(4): Koduru S, Grierson DS, Afolayan AJ (2006). Antimicrobial activity of Solanum aculeastrum.pharm. Biol. 44: NCCLS. (1993) National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobial disc susceptibility tests. PA: NCCLS Publications 25. Pascaline J, Mutai Charles, Catherine Lukhoba and Ouma George. (2011) Phyto chemical constituents of some medicinal plants used by the Nandis of South Nandi District, Kenya. J. Animal and plant Sci, 9: Rosen, L.D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2011). How do today s students task switch while studying? Lessons for technological dis- tractions and metacognitive strategies for learn-ing. Unpublished manuscript. Siva Sakthi, Angulo, E., Costa-Batllori, P., Shiva, (2011) Gram-positive resistance: Challenges for the development of new antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 39, 1 6. Sofowara A (1993). Medicinal plants and Traditional medicine in Africa. Spectrum Books Ltd, Ibadan, Nigeria. p Thenmozhi S and Rajan S. (2015) GC-MS analysis of bioactive compounds in Psidium guajava leaves. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 3(5): Trease GE and Evans WC. (1989) Phenols and Phenolic glycosides. In:Textbook of Pharmacognosy. (12th ed.). Balliese, Tindall and Co Publishers, London pp Source of support: Nil; Conflict of interest: None declared 15
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
Higher plants produced hundreds to thousands of diverse chemical compounds with different biological activities (Hamburger and Hostettmann, 1991).
 4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
ANTIMICROBIAL AND PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF TRAGIA INVOLUCRATA L. USING UV-VIS AND FTIR
 ANTIMICROBIAL AND PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF TRAGIA INVOLUCRATA L. USING UV-VIS AND FTIR Sahaya Sathish S, Vijayakanth P, Palani R, Thamizharasi T and Vimala A Department of Botany, St. Joseph s College
ANTIMICROBIAL AND PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF TRAGIA INVOLUCRATA L. USING UV-VIS AND FTIR Sahaya Sathish S, Vijayakanth P, Palani R, Thamizharasi T and Vimala A Department of Botany, St. Joseph s College
Antimicrobial activity of natural dyes obtained from Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.) Wight & Arn barks
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 98 (2018) 221-227 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Antimicrobial activity of natural dyes obtained from Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.) Wight & Arn barks
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 98 (2018) 221-227 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Antimicrobial activity of natural dyes obtained from Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.) Wight & Arn barks
A STUDY ON ANTIOXIDANT, PROXIMATE ANALYSIS, ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF CISSUS QUADRANGULARIS BY GC-MS
 : 2230-2236 ISSN: 2277 4998 A STUDY ON ANTIOXIDANT, PROXIMATE ANALYSIS, ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF CISSUS QUADRANGULARIS BY GC-MS MANIKANDAN VG * AND MUHAMMAD ILYAS MH PG & Research
: 2230-2236 ISSN: 2277 4998 A STUDY ON ANTIOXIDANT, PROXIMATE ANALYSIS, ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF CISSUS QUADRANGULARIS BY GC-MS MANIKANDAN VG * AND MUHAMMAD ILYAS MH PG & Research
In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa carandas leaf extracts
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS
 CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
Chandan Prasad.et.al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application ISSN : , Vol. 7, Issue 9, ( Part -6) September 2017, pp.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Antibacterial properties of Unripened Fruits of Trapa natans, Annona squamosa, Ficus carica and Anthocephalus cadamba against Pathogenic Gram Positive and Negative Bacteria.
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Antibacterial properties of Unripened Fruits of Trapa natans, Annona squamosa, Ficus carica and Anthocephalus cadamba against Pathogenic Gram Positive and Negative Bacteria.
6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Infectious diseases are one of man s oldest enemies. They continue to be a serious burden around the world, in developing and industrialised countries alike. It is said that every
6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Infectious diseases are one of man s oldest enemies. They continue to be a serious burden around the world, in developing and industrialised countries alike. It is said that every
Octa Journal of Biosciences
 Octa Journal of Biosciences ISSN 2321 3663 International peer-reviewed journal June 2014 Octa. J. Biosci. Vol. 2(1):59-63 Octa Journal of Biosciences journal homepage: www.sciencebeingjournal.com Antimicrobial
Octa Journal of Biosciences ISSN 2321 3663 International peer-reviewed journal June 2014 Octa. J. Biosci. Vol. 2(1):59-63 Octa Journal of Biosciences journal homepage: www.sciencebeingjournal.com Antimicrobial
Antimicrobial Potential of Whole Plant and Callus Extract of Aristolochia bracteolata Lam
 Human Journals Research Article October 2016 Vol.:7, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by A. Lavanya et al. Antimicrobial Potential of Whole Plant and Callus Extract of Aristolochia bracteolata Lam Keywords:
Human Journals Research Article October 2016 Vol.:7, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by A. Lavanya et al. Antimicrobial Potential of Whole Plant and Callus Extract of Aristolochia bracteolata Lam Keywords:
Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula
 , ISSN 2249 4340 Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 175-179, September 2011 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula M. Golam MOSTAFA, Mahdia RAHMAN, M. Manjurul KARIM* Department of Microbiology,
, ISSN 2249 4340 Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 175-179, September 2011 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula M. Golam MOSTAFA, Mahdia RAHMAN, M. Manjurul KARIM* Department of Microbiology,
International Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine 1:1 (2011) 1 7
 International Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine 1:1 (2011) 1 7 Journal homepage: http://www.interscience.org.uk/index.php/ijahm Preliminary phyto chemical screening and anti microbial activities
International Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine 1:1 (2011) 1 7 Journal homepage: http://www.interscience.org.uk/index.php/ijahm Preliminary phyto chemical screening and anti microbial activities
Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes R. Prasanna PRIST University, Tamilnadu
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes R. Prasanna PRIST University, Tamilnadu
Antimicrobial Activity of Black Fruit Variant of Solanum nigrum L.
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 2706-2713 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.303
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 2706-2713 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.303
Screening of Antimicrobials of some Medicinal Plants by TLC Bioautography
 Screening of Antimicrobials of some Medicinal Plants by TLC Bioautography Middha Himanshu 1* and Parihar Pradeep 2 1Department of Microbiology, DTM College of Biosciences, Bikaner, Rajasthan 2 Lovely Professional
Screening of Antimicrobials of some Medicinal Plants by TLC Bioautography Middha Himanshu 1* and Parihar Pradeep 2 1Department of Microbiology, DTM College of Biosciences, Bikaner, Rajasthan 2 Lovely Professional
DETERMINATION OF BIOACTIVE COMPOUNDS IN EVOLVULUS ALSINOIDES LEAF EXTRACT USING GC-MS TECHNIQUE
 Original Research Article DOI - 10.26479/2016.0203.03 DETERMINATION OF BIOACTIVE COMPOUNDS IN EVOLVULUS ALSINOIDES LEAF EXTRACT USING GC-MS TECHNIQUE T. K. Sujayil, T. S. Dhanaraj* PG and Research Department
Original Research Article DOI - 10.26479/2016.0203.03 DETERMINATION OF BIOACTIVE COMPOUNDS IN EVOLVULUS ALSINOIDES LEAF EXTRACT USING GC-MS TECHNIQUE T. K. Sujayil, T. S. Dhanaraj* PG and Research Department
Available online through
 Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITIES OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACTS OF PLANTS USED IN FOLK MEDICINE Gupta Raj Narayan 1*, Viswas Kartik 1, Pathak Manoj 1, Parihar Surendra
Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITIES OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACTS OF PLANTS USED IN FOLK MEDICINE Gupta Raj Narayan 1*, Viswas Kartik 1, Pathak Manoj 1, Parihar Surendra
TABLE - 1. Physicochemical analysis and extractive values of (Percentage) leaf powder of Aegle marmelos Var. I and Var. III
 TABLE - 1 Physicochemical analysis and extractive values of (Percentage) leaf powder of Aegle marmelos Var. I and Var. III Sl.No Parameters Variant-I (%) 1 Organoleptic characteristics a. Appearance b.
TABLE - 1 Physicochemical analysis and extractive values of (Percentage) leaf powder of Aegle marmelos Var. I and Var. III Sl.No Parameters Variant-I (%) 1 Organoleptic characteristics a. Appearance b.
A Study on Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic and Antimicrobial Activity of the Leaves of Solanum Trilobatum
 RESEARCH ARTICLE A Study on Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic and Antimicrobial Activity of the Leaves of Solanum Trilobatum Fabiola 1, Dr. V. Judia Harriet Sumathy 2 PG & Research Department of
RESEARCH ARTICLE A Study on Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic and Antimicrobial Activity of the Leaves of Solanum Trilobatum Fabiola 1, Dr. V. Judia Harriet Sumathy 2 PG & Research Department of
In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.)
 INDIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL & BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH (IJPBR). Vol. 1 (1), March., 13 In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.) G.Ramakrishnaiah * 1, T. Hariprasad
INDIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL & BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH (IJPBR). Vol. 1 (1), March., 13 In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.) G.Ramakrishnaiah * 1, T. Hariprasad
World Journal of Science and Research
 ISSN: 2455 2208 Available online at http://www.harmanpublications.com World Journal of Science and Research Harman Publications. All rights reserved Research Article Chemistry PHYTOCHEMICAL AND ANTIMICROBIAL
ISSN: 2455 2208 Available online at http://www.harmanpublications.com World Journal of Science and Research Harman Publications. All rights reserved Research Article Chemistry PHYTOCHEMICAL AND ANTIMICROBIAL
Avvaiyar govntment College for women, Karaial U.T of Puducherry. India.
 ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECT OF MEDICINAL PLANT PEDALIUM MUREX AGAINST DIFFERENT MICROORGANISMS Anandanayaki S 1 Uma C 2* 1 Department of Plant science, 2 Department of Chemistry, Avvaiyar govntment College for
ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECT OF MEDICINAL PLANT PEDALIUM MUREX AGAINST DIFFERENT MICROORGANISMS Anandanayaki S 1 Uma C 2* 1 Department of Plant science, 2 Department of Chemistry, Avvaiyar govntment College for
Research Article. Study on antibacterial activity of some medicinally important plants
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 205, 7():2520-252 Research Article ISSN : 0975-78 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Study on antibacterial activity of some medicinally
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 205, 7():2520-252 Research Article ISSN : 0975-78 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Study on antibacterial activity of some medicinally
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009) Newsletter Maridass and Raju. Investigation of Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Activity of Huberzia Species
 Investigation of Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Activity of Huberzia Species M. Maridass and G. Raju Department of Advanced Zoology and Biotechnology PioneerKumaraswamy College, Nagercoil-629003, Tamil
Investigation of Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Activity of Huberzia Species M. Maridass and G. Raju Department of Advanced Zoology and Biotechnology PioneerKumaraswamy College, Nagercoil-629003, Tamil
The textile material is goods carrier of various types
 AJHS Asian Journal of Home Science Volume 9 Issue 1 June, 2014 308-312 e ISSN-0976-8351 Open Access - www.researchjournal.co.in A Case Study Extraction and application of antimicrobial agents using neem
AJHS Asian Journal of Home Science Volume 9 Issue 1 June, 2014 308-312 e ISSN-0976-8351 Open Access - www.researchjournal.co.in A Case Study Extraction and application of antimicrobial agents using neem
Phytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activities of Carissa carandas L.
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 1 Phytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activities of Carissa carandas L. Aye Aye Naing Abstract The plant Carissa carandas L. locally known as Khan-pin,
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 1 Phytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activities of Carissa carandas L. Aye Aye Naing Abstract The plant Carissa carandas L. locally known as Khan-pin,
Antifungal activity of methanolic and ethanolic leaf extracts of medicinal plants
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT PROTECTION VOLUME 9 ISSUE 2 OCTOBER, 216 474-478 e ISSN-976-68 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in IJPP RESEARCH PAPER DOI : 1.74/HAS/IJPP/9.2/474-478 Antifungal activity
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT PROTECTION VOLUME 9 ISSUE 2 OCTOBER, 216 474-478 e ISSN-976-68 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in IJPP RESEARCH PAPER DOI : 1.74/HAS/IJPP/9.2/474-478 Antifungal activity
Life Science Archives (LSA)
 Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Life Science Archives (LSA) ISSN: 2454-1354 Volume 2; Issue - 2; Year 2016; Page: 514-518 Research Article ROLE OF Piper nigrum L. IN THE HEALTH CARE
Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Life Science Archives (LSA) ISSN: 2454-1354 Volume 2; Issue - 2; Year 2016; Page: 514-518 Research Article ROLE OF Piper nigrum L. IN THE HEALTH CARE
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS
 wjpls, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 10, 177181 Research Article ISSN 245429 Karim et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.3 GCMS ANALYSIS AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF SUDANESE CUCUMIS MELO VAR. FLEXUOUSAS
wjpls, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 10, 177181 Research Article ISSN 245429 Karim et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.3 GCMS ANALYSIS AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF SUDANESE CUCUMIS MELO VAR. FLEXUOUSAS
IN VITRO ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF VARIOUS EXTRACTS OF MIRABILIS JALAPA LEAVES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 559-564 IN VITRO ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF VARIOUS EXTRACTS OF MIRABILIS JALAPA LEAVES R. MEERA *, P. DEVI a, P. MUTHUMANI, B. KAMESWARI b and B. ESWARAPRIYA c Department
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 559-564 IN VITRO ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF VARIOUS EXTRACTS OF MIRABILIS JALAPA LEAVES R. MEERA *, P. DEVI a, P. MUTHUMANI, B. KAMESWARI b and B. ESWARAPRIYA c Department
Phytochemical screening and antibacterial properties of Garcinia kola
 2013; 2(3): 34-38 Online at: www.phytopharmajournal.com Research Article ISSN 2230-480X JPHYTO 2013; 2(3): 34-38 2013, All rights reserved Phytochemical screening and antibacterial properties of Garcinia
2013; 2(3): 34-38 Online at: www.phytopharmajournal.com Research Article ISSN 2230-480X JPHYTO 2013; 2(3): 34-38 2013, All rights reserved Phytochemical screening and antibacterial properties of Garcinia
Available online at
 Available online at www.ijpab.com ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (1): 203-206 (2015) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE Research Article Antifungal Activity of the Plant Extracts
Available online at www.ijpab.com ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (1): 203-206 (2015) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE Research Article Antifungal Activity of the Plant Extracts
Research Article. Antibacterial activity of Sivanar Vembu (Indigofera aspalathoides) against some human pathogenic bacteria
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(3):937-941 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Antibacterial activity of Sivanar Vembu (Indigofera
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(3):937-941 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Antibacterial activity of Sivanar Vembu (Indigofera
ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF LEAF AND SEED EXTRACTS OF DELONIX REGIA AND ACHYRANTHUS ASPERA AGAINST SELECTED BACTERIAL STRAINS
 Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2013 Dhanalakshmi D and Manimegalai K, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2013 2013 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY
Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2013 Dhanalakshmi D and Manimegalai K, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2013 2013 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY
Evaluation of Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Leaf and Seed Extracts of Croton Tiglium Plant against Skin Disease Causing Microbes
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2015, PP 139-144 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Evaluation of Antibacterial
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2015, PP 139-144 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Evaluation of Antibacterial
Preliminary Phytochemical Screening Analysis and Therapeutic Potential of Tecoma stans (L.)
 International Journal of Applied Chemistry. ISSN 0973-1792 Volume 13, Number 1 (2017) pp. 129-134 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Preliminary Phytochemical Screening Analysis and
International Journal of Applied Chemistry. ISSN 0973-1792 Volume 13, Number 1 (2017) pp. 129-134 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Preliminary Phytochemical Screening Analysis and
Antibacterial Activity of Francoeuria crispa, Pulicaria undulata, Ziziphus spina-christi and Cucurbita pepo Against Seven Standard Pathogenic Bacteria
 Ethnobotanical Leaflets : 733. 09. Antibacterial Activity of,, Ziziphus spinachristi and Against Seven Standard Pathogenic Bacteria Hatil Hashim ElKamali 1* and Sana AlTayeb Mahjoub 2 1 Department of Botany,
Ethnobotanical Leaflets : 733. 09. Antibacterial Activity of,, Ziziphus spinachristi and Against Seven Standard Pathogenic Bacteria Hatil Hashim ElKamali 1* and Sana AlTayeb Mahjoub 2 1 Department of Botany,
ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT.
 International Journal of Advanced Research and Review www.ijarr.in ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT. Dr.Mayuri Thanwar 1, Dr.Dhananjay Dwivedi 2 1. Scientific Officer,
International Journal of Advanced Research and Review www.ijarr.in ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT. Dr.Mayuri Thanwar 1, Dr.Dhananjay Dwivedi 2 1. Scientific Officer,
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF NON EDIBLE SEEDS AGAINST IMPORTANT PATHOGENIC MICROORGANISMS PROJECT REFERENCE NO.: 38S _B_MSC_010
 ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF NON EDIBLE SEEDS AGAINST IMPORTANT PATHOGENIC MICROORGANISMS PROJECT REFERENCE NO.: 38S _B_MSC_010 COLLGE BRANCH GUIDE STUDENTS : UNIVERSITY OF MYSORE, MYSORE : DEPARTMENT OF
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF NON EDIBLE SEEDS AGAINST IMPORTANT PATHOGENIC MICROORGANISMS PROJECT REFERENCE NO.: 38S _B_MSC_010 COLLGE BRANCH GUIDE STUDENTS : UNIVERSITY OF MYSORE, MYSORE : DEPARTMENT OF
Puducherry. Antimicrobial activity, Crude drug extraction, Zone of Inhibition, Culture Media, RVSPHF567.
 ANTI-MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE DRUGS AND THE POLYHERBAL FORMULATION (RVSPHF567) BY STANDARDIZED CUP AND PLATE METHOD C.S. Kandasamy 1,2*, Suman Nath 2, P. Arulraj 1,2, V. Gopal 3, P. Muthusamy 4,
ANTI-MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE DRUGS AND THE POLYHERBAL FORMULATION (RVSPHF567) BY STANDARDIZED CUP AND PLATE METHOD C.S. Kandasamy 1,2*, Suman Nath 2, P. Arulraj 1,2, V. Gopal 3, P. Muthusamy 4,
A study on phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial activity of Hyptis suaveolens (L.) poit
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(6):438-442 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 A study on phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(6):438-442 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 A study on phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 ISSN: 09758585 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Detection of Antimicrobial Activity of Oscimum sanctum (Tulsi) & Trigonella foenum graecum (Methi) against some selected
ISSN: 09758585 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Detection of Antimicrobial Activity of Oscimum sanctum (Tulsi) & Trigonella foenum graecum (Methi) against some selected
Influence of the crude Phenolic, Alkaloid and Terpenoid compounds extracts of Cardaria draba (Lepidium draba L.) on Human Pathogenic Bacteria
 Influence of the crude Phenolic, Alkaloid and Terpenoid extracts of Cardaria draba (Lepidium draba L.) on Human Pathogenic Bacteria Nebras M. Sahi Al-Khafaji 1, Ali Hussein Al-Marzoqi 2* (Corresponding
Influence of the crude Phenolic, Alkaloid and Terpenoid extracts of Cardaria draba (Lepidium draba L.) on Human Pathogenic Bacteria Nebras M. Sahi Al-Khafaji 1, Ali Hussein Al-Marzoqi 2* (Corresponding
. Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkom University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand. Antibacterial Activity of Some Essential Oils
 Antibacterial Activity of Some Essential Oils Sophon Roengsumran*, Amorn Petsom*, Suthep Thaniyavarn**, Surachai Pompakakul*, and Suntree Khantahiran*. Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkom
Antibacterial Activity of Some Essential Oils Sophon Roengsumran*, Amorn Petsom*, Suthep Thaniyavarn**, Surachai Pompakakul*, and Suntree Khantahiran*. Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkom
Evaluation of antifungal activity of Zingiber officinale against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2016, 7(2):5-9 Evaluation of antifungal activity of Zingiber officinale against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2016, 7(2):5-9 Evaluation of antifungal activity of Zingiber officinale against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici
PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS AND IN VITRO INVESTIGATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF EICHHORNIA CRASSIPES
 PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS AND IN VITRO INVESTIGATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF EICHHORNIA CRASSIPES (MART.) SOLMS. AGAINST POULTRY PATHOGENS *Kayathri B., Kanimozhi K. and Panneerselvam A.
PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS AND IN VITRO INVESTIGATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF EICHHORNIA CRASSIPES (MART.) SOLMS. AGAINST POULTRY PATHOGENS *Kayathri B., Kanimozhi K. and Panneerselvam A.
Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial properties of leaf extract of Azima tetracantha (Lam.)
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (2):110-114 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial properties
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (2):110-114 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial properties
In vitro Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Bark and Flower Extracts of Pimenta officinalis Lindl.
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH, Vol 1 [2] December 2010: 61-68 Society of Education, India http://www.soeagra.com ISSN 0976-4585 RESEARCH PAPER In vitro Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Bark and Flower
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH, Vol 1 [2] December 2010: 61-68 Society of Education, India http://www.soeagra.com ISSN 0976-4585 RESEARCH PAPER In vitro Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Bark and Flower
PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF DIFFERENT EXTRACTS OF Saccharum officinarum Linn (Ikshu) ROOTS
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 2315 2322 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF DIFFERENT
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 2315 2322 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF DIFFERENT
Antimicrobial activity of some medicinal plants against multidrug resistant skin pathogens
 Journal of Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 5(16), pp. 3856-3860, 18 August, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jmpr ISSN 1996-0875 2011 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper
Journal of Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 5(16), pp. 3856-3860, 18 August, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jmpr ISSN 1996-0875 2011 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper
PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND IN-VITRO ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF CUCURBITA MAXIMA SEED EXTRACT
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND INVITRO ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF CUCURBITA MAXIMA
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND INVITRO ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF CUCURBITA MAXIMA
Jigna Parekh, Nehal Karathia and Sumitra Chanda*
 African Journal of Biomedical Research, Vol. 9 (); 53-5 ISSN 1119 59 Ibadan Biomedical Communications Group Full Length Research Article Evaluation of antibacterial activity and phytochemical analysis
African Journal of Biomedical Research, Vol. 9 (); 53-5 ISSN 1119 59 Ibadan Biomedical Communications Group Full Length Research Article Evaluation of antibacterial activity and phytochemical analysis
Received: ; Revised; Accepted:
 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 2(5): September-October 2012 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Life Sciences Original Article!!! Received:
International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 2(5): September-October 2012 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Life Sciences Original Article!!! Received:
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page:
 Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Antimicrobial activity of Trinpanchmool drugs
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2010, 2 (3): 183-187 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2010, 2 (3): 183-187 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Available online at Phytochemical analysis and inhibitory activity of Ornamental Plant (Bougainvillea spectabilis)
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 13, 3(2):1- ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Phytochemical analysis and inhibitory activity of Ornamental
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 13, 3(2):1- ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Phytochemical analysis and inhibitory activity of Ornamental
Chapter 4. Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata. 4.1 Introduction
 Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata C o n t e n t s 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Materials and Methods 4.2.1 Extract Preparation and Determination of PUFA
Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata C o n t e n t s 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Materials and Methods 4.2.1 Extract Preparation and Determination of PUFA
Phytochemical study and bioactivity of solvent extracts on Coriandrum sativum
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com Volume 3, Issue 5-2016 Research Article Phytochemical study and bioactivity of solvent extracts on Coriandrum
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com Volume 3, Issue 5-2016 Research Article Phytochemical study and bioactivity of solvent extracts on Coriandrum
COMPARATIVE ANTI MICROBIAL STUDY OF SHUDDHA KASISA AND KASISA BHASMA
 Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 COMPARATIVE ANTI MICROBIAL STUDY OF SHUDDHA KASISA AND KASISA BHASMA Dr. Nisha Kumari.P. R *Dr. Dinesh Nayak J **, Dr. Sathyanarayana
Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 COMPARATIVE ANTI MICROBIAL STUDY OF SHUDDHA KASISA AND KASISA BHASMA Dr. Nisha Kumari.P. R *Dr. Dinesh Nayak J **, Dr. Sathyanarayana
EVALUATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF Zingiber officinale (GINGER) RHIZOME EXTRACT
 International Journal of Allied Practice, Research and Review Website: www.ijaprr.com (ISSN 2350-1294) EVALUATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF Zingiber officinale (GINGER) RHIZOME
International Journal of Allied Practice, Research and Review Website: www.ijaprr.com (ISSN 2350-1294) EVALUATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF Zingiber officinale (GINGER) RHIZOME
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2011) ewsletter Tiwari et al. A EVALUATIO OF A TIMICROBIAL ACTIVITIES OF ROOT EXTRACT OF CALE DULA OFFICI ALIS (LI.
 A EVALUATIO OF A TIMICROBIAL ACTIVITIES OF ROOT EXTRACT OF CALE DULA OFFICI ALIS (LI.) *Prashant Tiwari 1, Ritesh Jain 1, Kuldeep Kumar 2, Rajnikant Panik 3, Pratap Kumar Sahu 4 1. School of Pharmacy,
A EVALUATIO OF A TIMICROBIAL ACTIVITIES OF ROOT EXTRACT OF CALE DULA OFFICI ALIS (LI.) *Prashant Tiwari 1, Ritesh Jain 1, Kuldeep Kumar 2, Rajnikant Panik 3, Pratap Kumar Sahu 4 1. School of Pharmacy,
There is restriction of free rotation ( freedom) across. for vicinal hydrogen & OH to take trans position.
 5. SUMMARY & CONCLUSION. 5.1. Synthesis of Novel dihydro methyl Chalcones and their biological activity. The starting materials for the synthesis of various substituted dihydro 3-methyl chalcones were
5. SUMMARY & CONCLUSION. 5.1. Synthesis of Novel dihydro methyl Chalcones and their biological activity. The starting materials for the synthesis of various substituted dihydro 3-methyl chalcones were
Invitro screening of antimicrobial potentials of Cissus quadrangularis L.
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):52 ISSN : 22497412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Invitro screening of antimicrobial potentials of Cissus
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):52 ISSN : 22497412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Invitro screening of antimicrobial potentials of Cissus
Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity of Salvia officinalis L. flowers. Mona A. M. Abd-Elmageed 1 and B. A. Hussein 2
 Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity of officinalis L. flowers Mona A. M. Abd-Elmageed 1 and B. A. Hussein 2 Abstract: In this study a comparison of the Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial action of the
Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity of officinalis L. flowers Mona A. M. Abd-Elmageed 1 and B. A. Hussein 2 Abstract: In this study a comparison of the Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial action of the
CHAPTER 3 PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND ANTI-MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF THE EXTRACTS OF SELECTED MEDICINAL PLANTS
 CHAPTER 3 PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND ANTI-MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF THE EXTRACTS OF SELECTED MEDICINAL PLANTS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are of important therapeutic aid for various ailments. Naturally
CHAPTER 3 PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING AND ANTI-MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF THE EXTRACTS OF SELECTED MEDICINAL PLANTS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are of important therapeutic aid for various ailments. Naturally
Antibacterial Activity of Various Solvent Extracts of the Indian Herbal Plant Acalypha indica against Human Pathogens Causing Nosocomial Infection
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(5):1473-1478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Antibacterial Activity of Various Solvent
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(5):1473-1478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Antibacterial Activity of Various Solvent
*MIAN SHAHZADA ZIA AHMAD & ZAHEER-UD-DIN KHAN. Department of Botany, GC University, Lahore. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 BIOLOGIA (PAKISTAN) 01, 8 (1&), 17-17 PK ISSN 000-09 Antibacterial activity of crude s of different parts of Butea monosperma (Lamk.) Taub. *MIAN SHAHZADA ZIA AHMAD & ZAHEER-UD-DIN KHAN Department of Botany,
BIOLOGIA (PAKISTAN) 01, 8 (1&), 17-17 PK ISSN 000-09 Antibacterial activity of crude s of different parts of Butea monosperma (Lamk.) Taub. *MIAN SHAHZADA ZIA AHMAD & ZAHEER-UD-DIN KHAN Department of Botany,
ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 5, 2013, 989 993 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 5, 2013, 989 993 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
Supporting Information. Rec. Nat. Prod. 12:6 (2018)
 Supporting Information Rec. Nat. Prod. 12:6 (2018) 638-642 Comparisons of Chemical and Biological studies of Essential Oils of Stem, Leaves and Seeds of Zanthoxylum alatum Roxb growing wild in the State
Supporting Information Rec. Nat. Prod. 12:6 (2018) 638-642 Comparisons of Chemical and Biological studies of Essential Oils of Stem, Leaves and Seeds of Zanthoxylum alatum Roxb growing wild in the State
Jl. Perintis Kemerdekaan KM.5 Makassar 90231, South Sulawesi Indonesia.
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com ANTIMICROBIAL POTENCY OF PASSIFLORA FOETIDA LINN FROM SOUTH SULAWESI INDONESIA AGAINST BACTERIA IN VITRO Andi
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com ANTIMICROBIAL POTENCY OF PASSIFLORA FOETIDA LINN FROM SOUTH SULAWESI INDONESIA AGAINST BACTERIA IN VITRO Andi
Screening of Phytochemistry and Secondary Metabolites: A Case Study on Nyctanthes arboritis
 Research Article Screening of Phytochemistry and Secondary Metabolites: A Case Study on Nyctanthes arboritis *B. Ramachandran, M. Kamaraj, V. Subramani, J. Jerome Jeyakumar PG and Research Department of
Research Article Screening of Phytochemistry and Secondary Metabolites: A Case Study on Nyctanthes arboritis *B. Ramachandran, M. Kamaraj, V. Subramani, J. Jerome Jeyakumar PG and Research Department of
Screening of Antibacterial Activity of the Medicinal Plant Phyllanthus amarus Against Urinary Tract Infection Causing Bacterial Pathogens
 Applied Journal of Hygiene 1 (3): 19-24, 2012 ISSN 2309-8910 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajh.2012.1.3.71111 Screening of Antibacterial Activity of the Medicinal Plant Phyllanthus amarus
Applied Journal of Hygiene 1 (3): 19-24, 2012 ISSN 2309-8910 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajh.2012.1.3.71111 Screening of Antibacterial Activity of the Medicinal Plant Phyllanthus amarus
Phytochemical analysis and antifungal activity of Cauliflower stem (Brassica oleraceae var botrytis L.)
 Phytochemical analysis and antifungal activity of Cauliflower stem (Brassica oleraceae var botrytis L.) Gowri, G 1 and Manimegalai, K 2 1,2 Department of Zoology, Avinashilingam Institute for Home Science
Phytochemical analysis and antifungal activity of Cauliflower stem (Brassica oleraceae var botrytis L.) Gowri, G 1 and Manimegalai, K 2 1,2 Department of Zoology, Avinashilingam Institute for Home Science
Evaluation of antimicrobial activity and phytochemical analysis of Citrus limon
 Available online at www.jpbms.info Research article ISSN NO- 2230 7885 CODEN JPBSCT JPBMS JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES Evaluation of antimicrobial activity and phytochemical analysis
Available online at www.jpbms.info Research article ISSN NO- 2230 7885 CODEN JPBSCT JPBMS JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES Evaluation of antimicrobial activity and phytochemical analysis
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS
 wjpls, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 7, 05-10 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Oji et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.223 EVALUATION OF THE MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF IMPERATA CYLINDRICA (ATA) LEAF Oji
wjpls, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 7, 05-10 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Oji et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.223 EVALUATION OF THE MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF IMPERATA CYLINDRICA (ATA) LEAF Oji
Studies on the Antibacterial Activity of Quercus Infectoria Galls
 2011 International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics IPCBEE vol.5 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Studies on the Antibacterial Activity of Quercus Infectoria Galls T.Leela
2011 International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics IPCBEE vol.5 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Studies on the Antibacterial Activity of Quercus Infectoria Galls T.Leela
Prof. Dr. K. Aruna Lakshmi (DEAN Academic Affairs) Dept. of Microbiology GITAM University Visakhapatnam. Under the Guidance of.
 Antimicrobial Activity of Essential oils from Selected Culinary herbs of Zingiberaceae and Detection of Antimicrobial Compounds using TLC- Bioautography Under the Guidance of Prof. Dr. K. Aruna Lakshmi
Antimicrobial Activity of Essential oils from Selected Culinary herbs of Zingiberaceae and Detection of Antimicrobial Compounds using TLC- Bioautography Under the Guidance of Prof. Dr. K. Aruna Lakshmi
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Research Article Biotechnology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF ALLIUM SATIVUM (GARLIC) AND IDENTIFICATION OF ACTIVE COMPOUND BY GC-MS ANALYSIS
Research Article Biotechnology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF ALLIUM SATIVUM (GARLIC) AND IDENTIFICATION OF ACTIVE COMPOUND BY GC-MS ANALYSIS
FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F4) of B.zeylanica. FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F5) of B.zeylanica
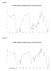 Fig. 39 FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F4) of B.zeylanica Fig. 40 FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F5) of B.zeylanica Fig. 41 FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F1) of P.persica Fig. 42 FT-IR Analysis
Fig. 39 FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F4) of B.zeylanica Fig. 40 FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F5) of B.zeylanica Fig. 41 FT-IR Analysis of column extract (F1) of P.persica Fig. 42 FT-IR Analysis
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):420-424 Screening of invitro antimicrobial activity
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):420-424 Screening of invitro antimicrobial activity
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF SERIAL EXTRACTS FROM LEAVES OF AEGLE MARMELOS (LINN.)
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 68 No. 5 pp. 687ñ692, 2011 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society NATURAL DRUGS ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF SERIAL EXTRACTS
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 68 No. 5 pp. 687ñ692, 2011 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society NATURAL DRUGS ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING OF SERIAL EXTRACTS
Antibacterial activities of extracts and their fractions of leaves of Tridax procumbens Linn
 Antibacterial activities of extracts and their fractions of leaves of Tridax procumbens Linn Dhasarathan. P 1, Hemalatha. N 2, Theriappan. P 1 and Ranjitsingh, A.J.A 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, Prathyusha
Antibacterial activities of extracts and their fractions of leaves of Tridax procumbens Linn Dhasarathan. P 1, Hemalatha. N 2, Theriappan. P 1 and Ranjitsingh, A.J.A 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, Prathyusha
GC-MS Analysis of Methanalic Leaf Extract of Nilakkumil, Gmelina asiatica
 African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 6 (5): 153-158, 2014 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2014.6.5.9120 GC-MS Analysis of Methanalic Leaf Extract of Nilakkumil,
African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 6 (5): 153-158, 2014 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2014.6.5.9120 GC-MS Analysis of Methanalic Leaf Extract of Nilakkumil,
Phytochemical screening and a comparative study of antibacterial activity of Aloe vera green rind, gel and leaf pulp extracts
 International Research Journal of Microbiology (IRJM) (ISSN: 2141-5463) Vol. 2(10) pp. 382-386, November 2011 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/irjm Copyright 2011 International Research
International Research Journal of Microbiology (IRJM) (ISSN: 2141-5463) Vol. 2(10) pp. 382-386, November 2011 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/irjm Copyright 2011 International Research
Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Disulfiram.
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.5, pp 1476-1481, Sept-Oct 2014 Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Disulfiram., Muthukumar.V Janakiraman.K
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.5, pp 1476-1481, Sept-Oct 2014 Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Disulfiram., Muthukumar.V Janakiraman.K
Alkaloidal Fraction and Antibacterial Assay of Bryophyllum Pinnatum
 International Journal of Innovative Biosciences Research 5(4):13-23, Oct.-Dec., 2017 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2017 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2467-8457 Alkaloidal Fraction and Antibacterial Assay of Bryophyllum
International Journal of Innovative Biosciences Research 5(4):13-23, Oct.-Dec., 2017 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2017 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2467-8457 Alkaloidal Fraction and Antibacterial Assay of Bryophyllum
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2010, 2(6):86-91 In vitro studies on antibacterial activity and
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2010, 2(6):86-91 In vitro studies on antibacterial activity and
Pinus glabra - As a potential source of anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis agent: Phytochemical and antimicrobial studies of its stem extracts
 Pinus glabra - As a potential source of anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis agent: Phytochemical and antimicrobial studies of its stem extracts I. O. Olanrewaju 1, J. O. Echeme 2, E. E. Adjere-Taunu 1, R.
Pinus glabra - As a potential source of anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis agent: Phytochemical and antimicrobial studies of its stem extracts I. O. Olanrewaju 1, J. O. Echeme 2, E. E. Adjere-Taunu 1, R.
Antifungal activity of some plant extracts against Clinical Pathogens
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Pelagia Research Library Advances in Applied Science Research, 2011, 2 (2): 260-264 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Antifungal activity of some plant
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Pelagia Research Library Advances in Applied Science Research, 2011, 2 (2): 260-264 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Antifungal activity of some plant
Studies on antibacterial activity of some medicinal plant against Human pathogenic Micro Organism
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2011, 1 ():8690 ISSN : 229 712 Studies on antibacterial activity of some medicinal plant against Human pathogenic
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2011, 1 ():8690 ISSN : 229 712 Studies on antibacterial activity of some medicinal plant against Human pathogenic
THE EFFECT OF ALKALOIDS AND FLAVONOIDS EXTRACTS OF VITEX DONIANA SEED ON SOME MICROORGANISMS
 THE EFFECT OF ALKALOIDS AND FLAVONOIDS EXTRACTS OF VITEX DONIANA SEED ON SOME MICROORGANISMS E.I. Okoye Department of Pure and Industrial Chemistry, Anambra State University, Uli, Nigeria ABSTRACT: This
THE EFFECT OF ALKALOIDS AND FLAVONOIDS EXTRACTS OF VITEX DONIANA SEED ON SOME MICROORGANISMS E.I. Okoye Department of Pure and Industrial Chemistry, Anambra State University, Uli, Nigeria ABSTRACT: This
Asian Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Research Journal home page:
 Research Article ISSN: 2321 0915 Asian Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Research Journal home page: www.ajpcrjournal.com PHYTOCHEMICAL ESTIMATIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF METHANOLIC AND ACETONE
Research Article ISSN: 2321 0915 Asian Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Research Journal home page: www.ajpcrjournal.com PHYTOCHEMICAL ESTIMATIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF METHANOLIC AND ACETONE
SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO. Iyyanuchamy, S.K and A. Periyanayagasamy*
 Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
Evaluation of Biological Activity (In-Vitro) of Some 2-Phenyl Oxazoline Derivatives
 Human Journals Research Article April 2016 Vol.:6, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by V.Niraimathi et al. Evaluation of Biological Activity (In-Vitro) of Some 2-Phenyl Oxazoline Derivatives Keywords: Antimicrobial
Human Journals Research Article April 2016 Vol.:6, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by V.Niraimathi et al. Evaluation of Biological Activity (In-Vitro) of Some 2-Phenyl Oxazoline Derivatives Keywords: Antimicrobial
in vitro Evaluation of Aqueous and Solvent extract of Tribulus terrestris L. leaf against Human bacteria
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.3, No.3,pp 1897-1903, July-Sept 2011 in vitro Evaluation of Aqueous and Solvent extract of Tribulus terrestris L. leaf
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.3, No.3,pp 1897-1903, July-Sept 2011 in vitro Evaluation of Aqueous and Solvent extract of Tribulus terrestris L. leaf
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYLLANTHUS MADERASPATENSIS LEAVES EXTRACT Karthikeyan. M, Jeethu Anu Mathews and A. Annamalai* Department
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYLLANTHUS MADERASPATENSIS LEAVES EXTRACT Karthikeyan. M, Jeethu Anu Mathews and A. Annamalai* Department
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES
 International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2249-6807 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 5(4): July-August 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE
International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2249-6807 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 5(4): July-August 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE
Determination of Bioactive Components of Cynodon dactylon by GC-MS Analysis. R.K. Jananie, V. Priya, K. Vijaya Lakshmi a*
 Determination of Bioactive Components of Cynodon dactylon by GC-MS Analysis R.K. Jananie, V. Priya, K. Vijaya Lakshmi a* * Department of Biochemistry, Barathi Women s College, Chennai-600108, Tamil Nadu,
Determination of Bioactive Components of Cynodon dactylon by GC-MS Analysis R.K. Jananie, V. Priya, K. Vijaya Lakshmi a* * Department of Biochemistry, Barathi Women s College, Chennai-600108, Tamil Nadu,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences EFFICACY OF CLERODENDRUM INERME L. (GARDEN QUININE) AGAINST SOME HUMAN PATHOGENIC STRAINS
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences EFFICACY OF CLERODENDRUM INERME L. (GARDEN QUININE) AGAINST SOME HUMAN PATHOGENIC STRAINS JASVINDER KAUR CHAHAL, RENU SARIN AND MANVI MALWAL Laboratory
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences EFFICACY OF CLERODENDRUM INERME L. (GARDEN QUININE) AGAINST SOME HUMAN PATHOGENIC STRAINS JASVINDER KAUR CHAHAL, RENU SARIN AND MANVI MALWAL Laboratory
