JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline
|
|
|
- Shana Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 1 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN An International Electronic Journal Volume 6 Number 4 November 2003 Body Composition ACCURACY OF ESTIMATING INTRA-ABDOMINAL FAT IN OBESE WOMEN STEPHEN D. BALL, PAMELA D. SWAN Exercise and Wellness Research Laboratory, Department of Exercise and Wellness, Arizona State University ABSTRACT ACCURACY OF ESTIMATING INTRA-ABDOMINAL FAT IN OBESE WOMEN. Stephen D. Ball, Pamela D. Swan. JEPonline. 2003;6(4):1-7. Intra-abdominal fatness (IAF) has been linked to a cluster of risk factors for cardiovascular disease. An accurate assessment of IAF is therefore critical for clinicians when assessing disease risk. The aim of this investigation was to examine the accuracy of a previously developed equation by Treuth, Hunter, and Kekes-Szabo (1) using dual-energy absorptiometry (DXA) combined with anthropometry for predicting IAF in obese women. Thirty-five peri- and post-menopausal obese women (age: 47.0 yr±7.0; BMI: 32.2±6.3 kg/m 2 ; and percent fat: 43.5±6.7 %) underwent a single-slice computed tomography (CT) scan at the level of L4-L5. In addition, a total body DXA scan and anthropometric measures including waist circumference and supine sagittal diameter measures at the level of the umbilicus, were also made. DXA-IAF was predicted using the equation: (SD) (A) (W) (DXA). (SD=anthropometric sagittal diameter, cm; A=age, yrs; W=waist circ., cm; DXA=DXA trunk fat, %). DXA-IAF was significantly correlated with CT-IAF (r=0.628, P<0.001, SEE=53.0 cm 2 ). However, DXA-IAF values (172.2±46.9 cm 2 ) significantly overestimated CT-IAF (114.0±67.1 cm 2 ) in this population. The results from the current study indicate that the Treuth et al. equation was not able to adequately estimate IAF in obese women. Although this equation was originally generated on a wide selection of women, a limited number of the original cohort were obese. In summary, this equation may be more generalizable for normal weight women than for obese women. Key Words: Dual -Energy X-ray Absorptiometry, Computed Tomography, Intraabdominal Fat INTRODUCTION Intra-abdominal fat (IAF), or more commonly called visceral fat, is the fat tissue that accumulates beneath the muscle wall that surrounds organs and other structures within the abdominal cavity. Research has consistently shown that an increased distribution of fat in and around the abdomen is associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease (2) and diabetes (3). Abdominal fat has been linked to a cluster of risk factors for
2 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 2 cardiovascular disease called Syndrome X (4) or the Metabolic Syndrome (5), which includes hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance, hypertension, and hyperinsulinemia (5, 6). However, it appears that increased IAF, a component of total abdominal fat, may be even more predictive of these complications than abdominal fat itself (7). Computed tomography (CT) is an imaging technique capable of directly measuring abdominal tissue and IAF with a very high degree of accuracy (8). However, this procedure is expensive and requires skilled technicians. CT scans also expose subjects to ionizing radiation. In clinical practice abdominal adiposity has been estimated using indirect anthropometric methods such as the waist to hip ratio (WHR) or waist circumference. These are inexpensive and quick procedures that give estimates of fat distribution. Although some researchers feel that anthropometric estimates are an acceptable measure of intraabdominal fat (9) and therefore disease risk, others have suggested that this technique is only moderately related to the amount of abdominal visceral adipose tissue (10-13). For example, the percent of variance explained (R 2 ) in IAF by the WHR has been reported to be <0.58 (14). These estimates are also subject to variability between technicians and do not accurately assess changes in visceral fat mass (15). Researchers have thus begun to evaluate other techniques that are easy, accessible and more accurate estimates of IAF. A safer (less radiation compared to CT) and less expensive method to assess IAF may be with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA). DXA has typically been used to assess bone mineral density but has also been found to be a valuable tool in assessing body composition (16) and regional body composition (1, 17, 18). In 1993, Svendsen et al. (18) developed two regression equations that used DXA data along with several anthropometric measurements in order to predict IAF (R 2 =0.63 and 0.71, respectively) in postmenopausal women. Treuth et al. (1), in an attempt to validate the Svendsen et al. equations, developed a new generalizable equation for estimating IAF from DXA in women of varying ages and body composition. The resulting equation was more highly correlated with IAF (R 2 = 0.81) than the Svendsen equation. Utilizing CT as the criterion method, this new model used % trunk fat from DXA in conjunction with anthropometric data (sagittal diameter, waist circumference), and age in order to predict the amount of IAF fat {y= (sagittal diameter, cm) (age, y) (waist, cm) (trunk fat %)}. Although Treuth et al. (1) reported that some obese women were used in developing their equation (% fat ), the mean body mass index BMI (kg/m 2 ) for the 151 women in the estimation sample was relatively low (23.8?4.7) compared to the average range of BMI ( ) reported for middle-aged women (19). It is not clear if this equation would be generalizable to women with relatively greater body fat amounts. The purpose of this study was to examine the accuracy of the Treuth, Hunter, and Kekes-Szabo (1) equation to predict IAAT in obese women. METHODS Subjects Thirty five obese women (total % fat >30% from DXA) with a mean age of 47.4?7.0 years (range 35-65) living in a large metropolitan area in the southwestern United States volunteered to participate in the study. All subjects were informed of the procedures and risks of the study and signed a written informed consent in accordance with the policies and procedures of the University Human Subjects Institutional Review Board. Anthropometry Body weight was measured to the nearest 0.1 kg and height to the nearest 0.5 cm. Duplicate circumferences were taken to the nearest 0.1 cm with a Gulick tension retractable tape. Waist circumference was measured as the narrowest part of the torso between the ribs and the iliac crest. Abdominal circumference was measured as the extension of the abdomen at the level of the umbilicus (20). In several subjects (N=7) it was impossible to identify the waist circumference, therefore the abdominal circumference was used as an alternative. Sagittal diameter was measured as the maximum diameter of the abdomen in the sagittal plane. All sagittal diameter measurements were taken in the supine position with the knees bent using sliding calipers at the point directly above the umbilicus (21). The average of the duplicate measures was used in the statistical analysis.
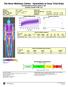
3 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 3 Computed tomography Abdominal adipose tissue was assessed by computed tomography (CT) (Picker PQ 6000, Picker International, Cleveland, Ohio) at the level of the fourth to fifth lumbar vertebra (L4-L5). The scan was performed at 125 kv with an 8 mm slice thickness. An initial scan was taken from a lateral view to establish the bony landmarks on a radiograph of the skeleton as a reference to establish the position of the scan to the nearest mm. Each woman was examined in a supine position with her arms stretched above her head. Visceral and total fat were calculated with a fat tissue-highlighting technique using an attenuation range of -190 to -30 Hounsfield units (HU). Each area was delineated with a computerized pen and then expressed as cross sectional area of tissue (cm 2 ). Visceral adipose tissue was distinguished by drawing a line within the inner portion of the muscle wall surrounding the abdominal cavity. Total fat area was determined by demarcating the whole abdominal scan with the electronic pen. Then visceral area was subtracted from the total fat area to calculate abdominal subcutaneous tissue. A single investigator performed all CT measures. Test-retest reliability for repeated CT scan analyses of 10 subjects yielded a correlation coefficient of Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) (model DPX-IQ 5705; Lunar Radiation Corporation, Madison, WI) was used to assess percent body fat and regional tissue composition analysis. The 20 minute scan (pencil beam) was used on all women. The Lunar DPX-IQ computer using software version 4.6b calculated total trunk % fat. Total trunk % fat was designated as all the trunk area (not arms, legs or head) below the neck and to the diagonal leg cuts. Statistical Analyses Statistical analyses were performed using commercial computer software (SPSS v. 9 for Windows). Descriptive statistics were calculated for subject characteristics. Mean differences in IAAT between the CT measured values and the predicted values were determined with a paired t- test. Linear regression and Pearson Product-Moment correlations defined the relationship between the prediction equation (y= (sagittal diameter, cm) (age, y) (waist, cm) (trunk fat %) and CT measured IAAT. An alpha level of 0.05 was used to indicate statistical significance. RESULTS The descriptive characteristics of body composition for this study compared to those reported from Treuth et al. (1) are shown in Table 1. Subjects ranged from % fat. There was a significant difference (P<0.001) in measured (114.0?67.1) versus predicted (172.2?46.9) IAAT values. The correlation coefficients of IAAT by CT with anthropometry and DXA are shown in Table 2. IAAT was significantly correlated with weight, body mass index, sagittal diameter, waist circumference, and umbilicus circumference. The Bland and Altman (22) plot of residual scores illustrates the overestimation of IAAT by the prediction equation for each subject (Figure 1). DISCUSSION Other research has demonstrated that the combination of DXA with simple anthropometric measures can be used to estimate the amount of IAAT in women (1, 23). However, only a limited number of studies have examined the accuracy of this technique in obese women. Although more work is necessary, it appears that the equations of Treuth et al. (1) do not sufficiently estimate IAAT in obese women (R 2 =0.39). The possible areas of discrepancy arise from inconsistencies in anthropometric measurements and also the assumptions and limitations in DXA technology.
4 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 4 Table 1. Body composition comparison data. Current Study (N = 35) Treuth et al., 1995 (N = 151) Mean?SD Range Mean?SD Range Age (yrs) 47? Weight (kg) 85.6?16.9 ( ) 63.5?13.3 ( ) Height (m) 1.63?0.07 ( ) 1.63?0.06 ( ) BMI (kg/m 2 ) 32.2?6.31 ( ) 23.8?4.7 ( ) Sagittal diameter (cm) 30.5?4.4 ( ) 20.9?4.2 ( ) Waist circ. (cm) 99.4?16.3 ( ) 73.4?10.6 ( ) Umbilicus circ. (cm) ?11.17 ( ) 79.9?14.4 ( ) Total body fat (%) ?6.7 ( ) 32.3?9.0 ( ) Total trunk fat (%) ?5.1 ( ) 29.9?10.3 ( ) IAAT (cm 2 ) 114.0?67.1 ( ) 72.3?55.0 ( ) SAAT (cm 2 ) 429.9?147.3 ( ) 207.2?122.0 ( ) Mean?SD. Range in parentheses. IAAT=Intra-abdominal adipose tissue measured by CT; SAAT=subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue measured by CT; 1 =measured by DXA. One potential source of error is from the measurement of the anthropometric values used in the equation. For example, in some large women with primarily upper body fat distribution, the narrow location of the waist circumference was difficult to distinguish on the torso. In these instances (n=7), we recorded the umbilicus circumference that is easy to identify and a reliable measurement, but is located inferior to the waist and is typically a larger value. This inconsistency in measurement may limit the validity of the waist measurement in obese women. It is worth noting that substitution of the waist circumference by the umbilicus circumference for all subjects reduced the R 2 from 0.39 to IAAT (cm 2 ) Predicted vs Measured IAAT % Body Fat Figure 1. Values are the difference between predicted (Treuth et al. equation) IAAT and measured (CT) IAAT for each subject. Positive values represent an overestimation by the prediction equation. Another anthropometric source of inaccuracy may be the inconsistency in the measurement of the sagittal diameter. There are no standard procedures in measuring sagittal diameter and it was not clear in the original equation if this measurement was taken with the knees bent or straight. In this study we measured the sagittal diameter in the supine position with the knees bent. Any difference in body position may have influenced the measurement value as somewhat smaller sagittal diameter values will be obtained with the legs straight. It is noteworthy that the correlation between IAAT with DXA trunk % fat was not statistically significant. Although some studies have found substantially higher correlations ( ) between IAAT and DXA trunk % fat (1), others have not reported significant correlations (10). Ferland et al. (10) found that total adipose tissue from CT at the abdominal level was not significantly correlated with total body fat mass in obese women. It seems reasonable to assume that if there is not a consistent relationship between DXA measured values of trunk
5 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 5 % fat with IAAT, then the DXA technique may be less sensitive to subtle changes in IAAT and thus will result in invalid estimates of IAAT in obese women. Interestingly, when an analysis was run with two non-obese (% fat <30) women included in the sample, the Pearson correlation between IAAT and predicted IAAT improved slightly from to It is possible that an increased correlation might be expected simply because the range in IAAT was extended. But perhaps this increased correlation might imply that the Treuth et al. equation may be more appropriate for normal weight than obese women. The Trueth equation should be validated on a less obese group to determine the answer. Interestingly, a recent study by Bertin et al. (23) using a different DXA model (QDR 2000/W HOLOGIC) also attempted to apply the Treuth et al. equation to their sample (44 overweight women) and found results similar to ours. They found that the mean difference between the estimated and measured IAAT was significantly larger (+31?8.8 cm 2, p< 0.01) with a correlation of Thus, consistent with our findings, Bertin et al. (23) also found the Treuth et al. equation to overestimate the amount of IAAT in obese women. However, Bertin et al. (23) did find promising results for the usefulness of DXA in estimating visceral fat in obese subjects when the abdominal trunk region was analyzed with more sophisticated software at a higher precision. Using a protocol version of the DXA software, Bertin et al. (23) identified two abdominal transverse diameters on the DXA scans. Their new prediction equation [79.6 (sagittal diameter subcutaneous fat width) X (transverse internal diameter/height) 149] yielded an R 2 of 0.86 (p < ). Perhaps DXA software that divides the abdominal region into more precise sections is necessary in order to use DXA to measure visceral fat in obese women. Even though DXA is gaining momentum as the gold standard for assessing body composition, it still has limitations in accurately assessing trunk fat in obese women. For example, DXA fat analysis technology has limitations in assessing and delimiting differences between breast tissue and arm fat tissue due to the overlap of fat in the scan area. Although increases in breast tissue may increase the overall regional measurement, this trunk fat tissue is not associated with IAAT. In addition, the effect of how DXA software extrapolates pixels over bone in the trunk area may influence the estimation of trunk fat in obese subjects. Since pixels directly over bone are extrapolated from non-skeleton pixels, a proportionally greater error would occur in obese subjects because a greater tissue mass is being estimated and not measured. These factors raise questions about DXA s ability to predict the amount of IAAT in obese subjects. Others have attempted to develop prediction equations with sample sizes similar to ours (18). However, most experts agree that a minimum of subjects are necessary to develop and validate accurate prediction equations (24). Therefore with our small sample (n=35), it was not statistically possible or practical to develop an accurate regression equation specific to this group. Nevertheless, in an attempt to establish the relative importance of each of the variables tested by Treuth et al., stepwise linear regression was conducted using our data. The variables entered into our model were the same as those used by Treuth et al. Similar to the Treuth et al. equation, sagittal diameter was the first variable to enter into the equation. However, contrary to the Treuth equation, the R square change for the remaining variables (DXA trunk fat, age, waist circumference) were not significant, and therefore, none of these variables significantly added to our equation. Thus, DXA trunk fat % was not a significant predictor of IAAT for our sample. In regards to the Treuth et al. equation, it is surprising that the R square change (0.80 to 0.81) for the addition of DXA trunk fat % was significant. The results from the current study indicate that the Treuth et al. equation was not able to adequately estimate IAAT in obese women. Unfortunately, it was not statistically feasible to develop a new regression equation for obese women. However, the results from this study support the call for researchers to develop new prediction equations and/or different DXA software/hardware to estimate IAAT in high-risk populations such as obese
6 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 6 women. Although DXA technology is a safe and fairly inexpensive estimate of body composition, its limitations in accurately assessing regional adiposity may restrict its use for estimating IAAT. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Grateful acknowledgement is given to Eliot Brinton, M.D., Kristin Araki, M.S., DXA technician Cheryl Berneir, RT(R)(M), CT technician Bruce Mable, ARRT/CT, and the Carl T Hayden VA Medical Center for their contributions. Additional financial support of this research was provided by a grant from the National Heart Association. Address for Correspondence: Stephen Daniel Ball, University of Missouri, 315A Gwynn Hall, Columbia MO 65211; Phone: (573) ; FAX: (573) ; ballsd@missouri.edu REFERENCES Treuth MS., Hunter GR, Kekes-Szabo K. Estimating intraabdominal adipose tissue in women by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995; 62: Donahue RP, Abbott RD. Central obesity and coronary heart disease in men. Lancet. 1987; 2: Despres JP, Nadeau A, Tremblay A, Ferland M, Moorjani S, Lupien PJ, Theriault G, Pinault S, Bouchard C. Role of deep abdominal fat in the association between regional adipose tissue distribution and glucose tolerance in obese women. Diabetes. 1989; 38: Reaven G. M. Role of insulin resistance in human disease (syndrome X): an expanded definition. Annu Rev Med. 1993; 44: Despres JP, Lesage M, Lemieux S, Prud'Homme D. Grouping of risk factors for cardiovascular diseases in visceral obesity. Therapeutic implications. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 1995; 56: Kissebah AH., Vydelingum N, Murray R, Evans DJ, Hartz AJ, Kalkhoff RK, Adams PW. Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982; 54: Despres JP, Moorjani S, Ferland M, Tremblay A, Lupien PJ, Nadeau A, Pinault S, Theriault G, Bouchard C. Adipose tissue distribution and plasma lipoprotein levels in obese women. Importance of intra-abdominal fat. Arteriosclerosis. 1989; 9: Seidell J. C., Bakker CJ, van der Kooy K. Imaging techniques for measuring adipose-tissue distribution--a comparison between computed tomography and 1.5-T magnetic resonance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990; 51: Jakicic JM., Donnelly JE, Jawad AF, Jacobsen DJ, Gunderson SC, Pascale R. Association between blood lipids and different measures of body fat distribution: effects of BMI and age. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1993; 17: Ferland M., Despres JP, Tremblay A, Pinault S, Nadeau A, Moorjani S, Lupien PJ, Theriault G, Bouchard C. Assessment of adipose tissue distribution by computed axial tomography in obese women: association with body density and anthropometric measurements. Br J Nutr. 1989; 61: Ross R., Leger L, Morris D, de Guise J, Guardo R. Quantification of adipose tissue by MRI: relationship with anthropometric variables. J Appl Physiol. 1992; 72: Seidell JC, Oosterlee A, Thijssen MA, Burema J, Deurenberg P, Hautvast JG, Ruijs JH. Assessment of intra-abdominal and subcutaneous abdominal fat: relation between anthropometry and computed tomography. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987; 45: Sjostrom L. Kvist H. Regional body fat measurements with CT-scan and evaluation of anthropometric predictions. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1988; 723: Despres JP, Prud'homme D, Pouliot MC, Tremblay A, Bouchard C. Estimation of deep abdominal adiposetissue accumulation from simple anthropometric measurements in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991; 54: van der Kooy K., Leenen R, Seidell JC, Deurenberg P, Droop A, Bakker CJ. Waist-hip ratio is a poor predictor of changes in visceral fat. Am J Clin Nutr. 1993; 57:
7 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat Kohrt WM. Body composition by DXA: tried and true? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995; 27: Jensen MD, Kanaley JA, Reed JE, Sheedy PF. Measurement of abdominal and visceral fat with computed tomography and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995; 61: Svendsen OL, Hassager C, Bergmann I, Christiansen C. Measurement of abdominal and intra-abdominal fat in postmenopausal women by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry: comparison with computerized tomography. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1993; 17: Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Campbell SM, Johnson CL. Increasing prevalence of overweight among US adults. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1960 to Jama. 1994; 272: Lohman T, Roche AF, Martorell R. Anthropometric Standardization Manual. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, Zamboni M, Turcato E, Armellini F, Kahn HS, Zivelonghi A, Santana H, Bergamo-Andreis IA, Bosello O. Sagittal abdominal diameter as a practical predictor of visceral fat. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998; 22: Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986; 1: Bertin E, Marcus C, Ruiz JC, Eschard JP, Leutenegger M. Measurement of visceral adipose tissue by DXA combined with anthropometry in obese humans. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000; 24: Lohman TG. Skinfolds and body density and their relation to body fatness: a review. Hum Biol. 1981; 53:
Introduction. Methods
 International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 655±660 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Sagittal abdominal diameter as a practical predictor
International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 655±660 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Sagittal abdominal diameter as a practical predictor
Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density in Japanese Adults
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 11:201 207 (1999) Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth MICHAEL I. GORAN* Division of Physiology
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 11:201 207 (1999) Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth MICHAEL I. GORAN* Division of Physiology
Cut-Off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist-to-Height Ratio: Diagnostic Criteria for Obesity-Related Disorders in Korean Children and Adolescents
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.99 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(1):99-105, 2012 Cut-Off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist-to-Height Ratio: Diagnostic
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.99 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(1):99-105, 2012 Cut-Off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist-to-Height Ratio: Diagnostic
An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh.
 An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh. Md. Golam Hasnain 1 Monjura Akter 2 1. Research Investigator,
An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh. Md. Golam Hasnain 1 Monjura Akter 2 1. Research Investigator,
Comparisons of waist circumferences measured at 4 sites 1 3
 Comparisons of waist circumferences measured at 4 sites 1 3 Jack Wang, John C Thornton, Salina Bari, Bennett Williamson, Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Mary Horlick, Donald Kotler, Blandine Laferrère,
Comparisons of waist circumferences measured at 4 sites 1 3 Jack Wang, John C Thornton, Salina Bari, Bennett Williamson, Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Mary Horlick, Donald Kotler, Blandine Laferrère,
Introduction. EG Kamel 1 *, G McNeill 1, TS Han 1, FW Smith 2, A Avenell 3, L Davidson 1 and P Tothill 4
 International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 686±692 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Measurement of abdominal fat by magnetic resonance
International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 686±692 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Measurement of abdominal fat by magnetic resonance
In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in
 1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference
 Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference Poster No.: C-934 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference Poster No.: C-934 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT
 DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
The Indian subcontinent is undergoing epidemiological transition, as noncommunicable
 22 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 63 january, 2015 Original Article Correlation and Comparison of Various Anthropometric Measurements of Body Fat Distribution and Sagittal Abdominal
22 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 63 january, 2015 Original Article Correlation and Comparison of Various Anthropometric Measurements of Body Fat Distribution and Sagittal Abdominal
Abdominal diameters as indicators of visceral fat : comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and anthropometry
 ~ British Journal of Nutrition (1993), 70, 47-58 47 Abdominal diameters as indicators of visceral fat : comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and anthropometry BY KARIN VAN DER KOOY, RIANNE LEENEN,
~ British Journal of Nutrition (1993), 70, 47-58 47 Abdominal diameters as indicators of visceral fat : comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and anthropometry BY KARIN VAN DER KOOY, RIANNE LEENEN,
Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation study
 (2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
(2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
Section II: Emerging Uses of Bone Densitometry
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry: Assessment & Management of Musculoskeletal Health, vol. 17, no. 1, 78e83, 2014 Ó Copyright 2014 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/17:78e83/$36.00
Journal of Clinical Densitometry: Assessment & Management of Musculoskeletal Health, vol. 17, no. 1, 78e83, 2014 Ó Copyright 2014 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/17:78e83/$36.00
BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES. Abstract. Introduction. Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, UDC :572.
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes
 Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment
 Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
3/25/2010. Age-adjusted incidence rates for coronary heart disease according to body mass index and waist circumference tertiles
 Outline Relationships among Regional Adiposity, Physical Activity, and CVD Risk Factors: Preliminary Results from Two Epidemiologic Studies Molly Conroy, MD, MPH Obesity Journal Club February 18, 2010
Outline Relationships among Regional Adiposity, Physical Activity, and CVD Risk Factors: Preliminary Results from Two Epidemiologic Studies Molly Conroy, MD, MPH Obesity Journal Club February 18, 2010
Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class
 Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Regional Subcutaneous-Fat Loss Induced by Caloric Restriction in Obese Women
 Regional Subcutaneous-Fat Loss Induced by Caloric Restriction in Obese Women Jack Wang, Blandine Laferrère, John C. Thornton, Richard N. Pierson, Jr., and F. Xavier Pi-Sunyer Abstract WANG, JACK, BLANDINE
Regional Subcutaneous-Fat Loss Induced by Caloric Restriction in Obese Women Jack Wang, Blandine Laferrère, John C. Thornton, Richard N. Pierson, Jr., and F. Xavier Pi-Sunyer Abstract WANG, JACK, BLANDINE
Downloaded from ijem.sbmu.ac.ir at 20: on Sunday February 24th 2019
 ( ) ( ). :. :. - -.. -. ( ) %/ :. SPSS %/. %/. %/ :.(r= / p
( ) ( ). :. :. - -.. -. ( ) %/ :. SPSS %/. %/. %/ :.(r= / p
Influence of sex on total and regional fat loss in overweight and obese men and women
 (2009) 33, 629 634 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0307-0565/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of sex on total and regional fat loss in overweight and obese
(2009) 33, 629 634 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0307-0565/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of sex on total and regional fat loss in overweight and obese
Assessment of intra-abdominal and subcutaneous abdominal fat: relation between anthropometry and computed tomography1-3
 Original Research Communications--general Assessment of intra-abdominal and subcutaneous abdominal fat: relation between anthropometry and computed tomography1-3 Jacob C Seidell, MSc, Arie Oosterlee, MD,
Original Research Communications--general Assessment of intra-abdominal and subcutaneous abdominal fat: relation between anthropometry and computed tomography1-3 Jacob C Seidell, MSc, Arie Oosterlee, MD,
Understanding Body Composition
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
Can the LeanScreen App Accurately Assess Percent Body Fat and Waistto-Hip
 Can the LeanScreen App Accurately Assess Percent Body Fat and Waistto-Hip Ratio? EXCLUSIVE ACE SPONSORED RESEARCH BY RAY MARX, JOHN P. PORCARI, PH.D., SCOTT DOBERSTEIN, M.S., RICHARD MIKAT, PH.D., AND
Can the LeanScreen App Accurately Assess Percent Body Fat and Waistto-Hip Ratio? EXCLUSIVE ACE SPONSORED RESEARCH BY RAY MARX, JOHN P. PORCARI, PH.D., SCOTT DOBERSTEIN, M.S., RICHARD MIKAT, PH.D., AND
Comparison of Methods for Assessing Abdominal Adipose Tissue from Magnetic Resonance Images
 Comparison of Methods for Assessing Abdominal Adipose Tissue from Magnetic Resonance Images Hassan Arif,* Susan B. Racette,* Dennis T. Villareal,* John O. Holloszy,* and Edward P. Weiss* Abstract ARIF,
Comparison of Methods for Assessing Abdominal Adipose Tissue from Magnetic Resonance Images Hassan Arif,* Susan B. Racette,* Dennis T. Villareal,* John O. Holloszy,* and Edward P. Weiss* Abstract ARIF,
Visceral fat in white and African American prepubertal children13
 Original Research Communications Visceral fat in white and African American prepubertal children13 Michael I Goran, Tim R Nagy, Margarita S Treuth, Chris Trowbridge, Carl Dezenberg, Aileen McGloin, and
Original Research Communications Visceral fat in white and African American prepubertal children13 Michael I Goran, Tim R Nagy, Margarita S Treuth, Chris Trowbridge, Carl Dezenberg, Aileen McGloin, and
University of Groningen. The epidemiology of abdominal adiposity De Lucia Rolfe, Emanuella
 University of Groningen The epidemiology of abdominal adiposity De Lucia Rolfe, Emanuella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen The epidemiology of abdominal adiposity De Lucia Rolfe, Emanuella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Quantification of Visceral Fat
 nature publishing group Open articles Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Quantification of Visceral Fat Sanjiv Kaul 1, Megan P. Rothney 2, Dawn M. Peters 3, Wynn K. Wacker 4, Cynthia E. Davis 2, Michael
nature publishing group Open articles Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Quantification of Visceral Fat Sanjiv Kaul 1, Megan P. Rothney 2, Dawn M. Peters 3, Wynn K. Wacker 4, Cynthia E. Davis 2, Michael
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13
 Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL studies often report an association
 0163-769X/00/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 21(6): 697 738 Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue: Their Relation to the Metabolic Syndrome BERNARDO
0163-769X/00/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 21(6): 697 738 Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue: Their Relation to the Metabolic Syndrome BERNARDO
Procedures for taking physical measurements
 Procedures for taking physical measurements Dr Diane Cooper PhD Exercise physiology and metabolism Partner in True Fitness Coordinator & lecturer on BSc Sports Science, AIT Metabolic researcher on European
Procedures for taking physical measurements Dr Diane Cooper PhD Exercise physiology and metabolism Partner in True Fitness Coordinator & lecturer on BSc Sports Science, AIT Metabolic researcher on European
EFFECT OF TRUNCAL ADIPOSITY ON PLASMA LIPID AND LIPOPROTEIN CONCENTRATIONS
 EFFECT OF TRUNCAL ADIPOSITY ON PLASMA LIPID AND LIPOPROTEIN CONCENTRATIONS C.M. NIEDERAUER, T.L. BINKLEY, B.L. SPECKER Ethel Austin Martin Program in Human Nutrition, South Dakota State University, Brookings,
EFFECT OF TRUNCAL ADIPOSITY ON PLASMA LIPID AND LIPOPROTEIN CONCENTRATIONS C.M. NIEDERAUER, T.L. BINKLEY, B.L. SPECKER Ethel Austin Martin Program in Human Nutrition, South Dakota State University, Brookings,
ISPUB.COM. D Adeyemi, O Komolafe, A Abioye INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Biological Anthropology Volume 2 Number 2 Variations In Body Mass Indices Among Post-Pubertal Nigerian Subjects With Correlation To Cormic Indices, Mid- Arm Circumferences
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Biological Anthropology Volume 2 Number 2 Variations In Body Mass Indices Among Post-Pubertal Nigerian Subjects With Correlation To Cormic Indices, Mid- Arm Circumferences
Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue: Their Relation to the Metabolic Syndrome
 Administrator Access Store Join Endocrine Society Sign In Advanced Search 0 ITEMS Journals Books Meeting Abstracts Endocrine News Advertise Permissions ISSN (print journal): 0163-769X ISSN (online): 1945-7189
Administrator Access Store Join Endocrine Society Sign In Advanced Search 0 ITEMS Journals Books Meeting Abstracts Endocrine News Advertise Permissions ISSN (print journal): 0163-769X ISSN (online): 1945-7189
Adult BMI Calculator
 For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution
 A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
In middle-aged adults, obesity is associated
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Association Between Regional Adipose Tissue Distribution and Both Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Glucose Tolerance in Elderly
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Association Between Regional Adipose Tissue Distribution and Both Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Glucose Tolerance in Elderly
Development of a Viable Bedside Ultrasound Protocol to Accurately Predict Appendicular Lean Tissue Mass
 Development of a Viable Bedside Ultrasound Protocol to Accurately Predict Appendicular Lean Tissue Mass by Michael Paris A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement
Development of a Viable Bedside Ultrasound Protocol to Accurately Predict Appendicular Lean Tissue Mass by Michael Paris A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at:
 Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
Measuring abdominal adiposity in 6 to 7-year-old children
 (2009) 63, 835 841 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Measuring abdominal adiposity in 6 to 7-year-old children ET Liem 1,2,
(2009) 63, 835 841 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Measuring abdominal adiposity in 6 to 7-year-old children ET Liem 1,2,
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Understanding Body Composition
 Understanding Body Composition Chapter 7 Body Composition n Body composition is the ratio between fat and fat-free mass n Fat-free mass includes all tissues exclusive of fat (muscle, bone, organs, fluids)
Understanding Body Composition Chapter 7 Body Composition n Body composition is the ratio between fat and fat-free mass n Fat-free mass includes all tissues exclusive of fat (muscle, bone, organs, fluids)
Jackson Heart Study Manuscript Proposal Form
 Jackson Heart Study Manuscript Proposal Form Submission Date: 2/15/2017 Proposal ID: P0859 I. TITLE I. Title Information A. Proposal Title: Age related variations in obesity and diabetes correlates in
Jackson Heart Study Manuscript Proposal Form Submission Date: 2/15/2017 Proposal ID: P0859 I. TITLE I. Title Information A. Proposal Title: Age related variations in obesity and diabetes correlates in
Growth of Visceral Fat, Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat, and Total Body Fat in Children
 Growth of Visceral Fat, Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat, and Total Body Fat in Children Terry T.-K. Huang,* Maria S. Johnson,* Reinaldo Figueroa-Colon, James H. Dwyer,* and Michael I. Goran* Abstract HUANG,
Growth of Visceral Fat, Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat, and Total Body Fat in Children Terry T.-K. Huang,* Maria S. Johnson,* Reinaldo Figueroa-Colon, James H. Dwyer,* and Michael I. Goran* Abstract HUANG,
Using a Phantom to Compare MR Techniques for Determining the Ratio of Intraabdominal to Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
 Lane F. Donnelly 1,2 Kendall J. O Brien 1 Bernard J. Dardzinski 1,2 Stacy A. Poe 2 Judy A. Bean 2 Scott K. Holland 1,2 Stephen R. Daniels 2 Received April 29, 2002; accepted after revision August 27, 2002.
Lane F. Donnelly 1,2 Kendall J. O Brien 1 Bernard J. Dardzinski 1,2 Stacy A. Poe 2 Judy A. Bean 2 Scott K. Holland 1,2 Stephen R. Daniels 2 Received April 29, 2002; accepted after revision August 27, 2002.
Usefulness of the metabolic syndrome criteria as predictors of insulin resistance among obese Korean women
 Public Health Nutrition: 13(2), 181 186 doi:10.1017/s1368980009991340 Usefulness of the metabolic syndrome criteria as predictors of insulin resistance among obese Korean women Kayoung Lee* Department
Public Health Nutrition: 13(2), 181 186 doi:10.1017/s1368980009991340 Usefulness of the metabolic syndrome criteria as predictors of insulin resistance among obese Korean women Kayoung Lee* Department
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Predicting abdominal adipose tissue among women with familial partial lipodystrophy
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Metabolism Clinical and Experimental 58 (2009) 828 834 www.metabolismjournal.com Predicting abdominal adipose tissue among women with familial partial lipodystrophy
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Metabolism Clinical and Experimental 58 (2009) 828 834 www.metabolismjournal.com Predicting abdominal adipose tissue among women with familial partial lipodystrophy
Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model of DXA
 ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
Neck circumference measurement as a screening tool for obesity in children
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Yashoda HT et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Mar;4(2):426-430 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Yashoda HT et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Mar;4(2):426-430 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density in Healthy Volunteers
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.289 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(2):289-293, 2012 The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.289 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(2):289-293, 2012 The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density
INFLUENCE OF OBESITY ASSESSMENTS ON CARDIOMETABOLIC RISKS IN AFRICAN AND EUROPEAN AMERICAN WOMEN
 INFLUENCE OF OBESITY ASSESSMENTS ON CARDIOMETABOLIC RISKS IN AFRICAN AND EUROPEAN AMERICAN WOMEN Objectives: African American women (AAW) have increased odds of developing cardiometabolic (CME) risks and
INFLUENCE OF OBESITY ASSESSMENTS ON CARDIOMETABOLIC RISKS IN AFRICAN AND EUROPEAN AMERICAN WOMEN Objectives: African American women (AAW) have increased odds of developing cardiometabolic (CME) risks and
Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition measurement in COPD
 Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timisoara, Romania b
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2015; 10(3): 204-209 ORIGINAL PAPERS Reliability of Measuring Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Thickness Using Ultrasound in Non-Athletic
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2015; 10(3): 204-209 ORIGINAL PAPERS Reliability of Measuring Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Thickness Using Ultrasound in Non-Athletic
Obesity is an important risk factor for diabetes mellitus, hypertension,
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:99 105 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 GENERAL RADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Compatibility of different methods for the measurement of visceral fat in different body mass index
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:99 105 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 GENERAL RADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Compatibility of different methods for the measurement of visceral fat in different body mass index
CHAPTER 9. Anthropometry and Body Composition
 CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
This is a digitised version of a dissertation submitted to the University of Bedfordshire. It is available to view only.
 Title The Validity of Two Compartment Model Methods of Body Composition as Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Asian Indian Versus Caucasian Males Name Ben Davies This is a digitised version of a
Title The Validity of Two Compartment Model Methods of Body Composition as Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Asian Indian Versus Caucasian Males Name Ben Davies This is a digitised version of a
Familial resemblance of body composition in prepubertal girls and their biological parents 1 4
 Familial resemblance of body composition in prepubertal girls and their biological parents 1 4 Margarita S Treuth, Nancy F Butte, Kenneth J Ellis, Lisa J Martin, and Anthony G Comuzzie ABSTRACT Background:
Familial resemblance of body composition in prepubertal girls and their biological parents 1 4 Margarita S Treuth, Nancy F Butte, Kenneth J Ellis, Lisa J Martin, and Anthony G Comuzzie ABSTRACT Background:
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Body Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: BMX_D.XPT November 2007 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component: Body Measurements
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Body Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: BMX_D.XPT November 2007 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component: Body Measurements
CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2008; 52 (4) : 383 388 CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS ANURADHA R. JOSHI*, RATAN SINGH AND A. R. JOSHI Department of Physiology,
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2008; 52 (4) : 383 388 CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS ANURADHA R. JOSHI*, RATAN SINGH AND A. R. JOSHI Department of Physiology,
Computed tomography assessment of fat distribution in male and female patients with Cushing s syndrome
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2003) 149 561 567 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Computed tomography assessment of fat distribution in male and female patients with Cushing s syndrome A G Rockall, S
European Journal of Endocrinology (2003) 149 561 567 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Computed tomography assessment of fat distribution in male and female patients with Cushing s syndrome A G Rockall, S
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years-
 Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
IMPACT OF SELECTED MINOR GAMES ON PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS AND RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OBESITY; AMONG SCHOOL STUDENTS
 184 IMPACT OF SELECTED MINOR GAMES ON PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS AND RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OBESITY; AMONG SCHOOL STUDENTS INTRODUCTION PRADEEP.C.S*; AJEESH.P.T**; ARUN.C.NAIR*** *Lecturer in Physical Education,
184 IMPACT OF SELECTED MINOR GAMES ON PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS AND RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OBESITY; AMONG SCHOOL STUDENTS INTRODUCTION PRADEEP.C.S*; AJEESH.P.T**; ARUN.C.NAIR*** *Lecturer in Physical Education,
Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline (JEPonline)
 Fat Estimation Of Black Females 20 Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline (JEPonline) Volume 8 Number 4 August 2005 Managing Editor Tommy Boone, Ph.D. Editor-in-Chief Robert Robergs, Ph.D. Review Board Todd
Fat Estimation Of Black Females 20 Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline (JEPonline) Volume 8 Number 4 August 2005 Managing Editor Tommy Boone, Ph.D. Editor-in-Chief Robert Robergs, Ph.D. Review Board Todd
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
Can Thigh Girth Be Measured Accurately? A Preliminary Investigation
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999,8,43-49 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Thigh Girth Be Measured Accurately? A Preliminary Investigation Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard D.M. Nokes,
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999,8,43-49 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Thigh Girth Be Measured Accurately? A Preliminary Investigation Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard D.M. Nokes,
Body Composition. Sport Books Publisher 1
 Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Relationship Among Three Field Methods of Estimating Percent Body Fat in Young Adults
 Relationship Among Three Field Methods of Estimating Percent Body Fat in Young Adults A O AKINPELU Department of Physiotherapy, College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria CA GBIRI Department
Relationship Among Three Field Methods of Estimating Percent Body Fat in Young Adults A O AKINPELU Department of Physiotherapy, College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria CA GBIRI Department
A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital
 Original Research Article A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital M. Arivumani * Assistant Professor of General Medicine, Government
Original Research Article A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital M. Arivumani * Assistant Professor of General Medicine, Government
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease
 The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION
 CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
Blood pressure is continually changing depending on activity, temperature, diet, emotional state, posture, physical state, and medication use.
 Blood Pressure Test Blood pressure is a measurement of the force applied to the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood through the body. The pressure is determined by the force and amount of blood
Blood Pressure Test Blood pressure is a measurement of the force applied to the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood through the body. The pressure is determined by the force and amount of blood
Introduction. KR Fox 1 *, DM Peters 2, P Sharpe 3 and M Bell 3
 (2000) 24, 1653±1659 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0307±0565/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo Assessment of abdominal fat development in young adolescents using magnetic resonance imaging
(2000) 24, 1653±1659 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0307±0565/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo Assessment of abdominal fat development in young adolescents using magnetic resonance imaging
What Is Body Composition?
 Chapter Six What Is Body Composition? Body composition is the body s relative amounts of fat mass and fat-free mass Body fat includes two categories: Essential fat is crucial for normal body functioning
Chapter Six What Is Body Composition? Body composition is the body s relative amounts of fat mass and fat-free mass Body fat includes two categories: Essential fat is crucial for normal body functioning
International Journal of Pediatric Obesity
 This article was downloaded by:[goran, Michael I] [Mr Michael I Goran] On: 5 January 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 762314357] Publisher: Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England
This article was downloaded by:[goran, Michael I] [Mr Michael I Goran] On: 5 January 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 762314357] Publisher: Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England
Note that metric units are used in the calculation of BMI. The following imperial-metric conversions are required:
 Body Composition Body Composition: Assessment and Interpretation Body composition has great practical and functional significance for many of us: scientists, clinicians and the general population. It can
Body Composition Body Composition: Assessment and Interpretation Body composition has great practical and functional significance for many of us: scientists, clinicians and the general population. It can
Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age, and anthropometry
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Jean-Claude Pineau, PhD*; Jean Robert Filliard, PhDÀ; Michel Bocquet, PhD`
 Journal of Athletic Training 2009;44(2):142 147 g by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.nata.org/jat original research Ultrasound Techniques Applied to Body Fat Measurement in Male and
Journal of Athletic Training 2009;44(2):142 147 g by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.nata.org/jat original research Ultrasound Techniques Applied to Body Fat Measurement in Male and
ANTHROPOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF SOME LIMB AND BODY CIRCUMFERENCES IN MALES AND FEMALES WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 159 164) ANTHROPOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 159 164) ANTHROPOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT IN WOMEN USING SKINFOLD THICKNESS EQUATIONS, BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS AND UNDERWATER WEIGHING
 STUDIES IN PHYSICAL CULTURE AND TOURISM Vol. 17, No. 3, 2010 EFTEKHAR MOHAMMADI, SAEID SHAKERIAN Faculty of Physical Education & Sports Science, Shahid Chamran University, Iran COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION
STUDIES IN PHYSICAL CULTURE AND TOURISM Vol. 17, No. 3, 2010 EFTEKHAR MOHAMMADI, SAEID SHAKERIAN Faculty of Physical Education & Sports Science, Shahid Chamran University, Iran COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION
Neck Circumference as a Simple Screening Measure for Identifying Egyptian Overweight and Obese Adults
 Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013 Sep 15; 6(3):232-237. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/mjms.1857-5773.2013.0309 Basic Science Neck Circumference as a Simple Screening Measure for Identifying Egyptian
Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013 Sep 15; 6(3):232-237. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/mjms.1857-5773.2013.0309 Basic Science Neck Circumference as a Simple Screening Measure for Identifying Egyptian
The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 1 Number 1 The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects L Zhu, K Liu Citation L Zhu, K
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 1 Number 1 The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects L Zhu, K Liu Citation L Zhu, K
Waist-hip ratio is a poor predictor of changes in visceral fat13
 Waist-hip ratio is a poor predictor of changes in visceral fat13 Karin van der Kooy, Rianne Leenen, Jaap C Seideli, Patti Deurenberg, Anneke Droop, and Chris JG Bakker ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance imaging
Waist-hip ratio is a poor predictor of changes in visceral fat13 Karin van der Kooy, Rianne Leenen, Jaap C Seideli, Patti Deurenberg, Anneke Droop, and Chris JG Bakker ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance imaging
Effect of Physical Training on Body Composition in Moscow Adolescents
 Effect of Physical Training on Body Composition in Moscow Adolescents Elena Godina, Irena Khomyakova, Arsen Purundzhan, Anna Tretyak and Ludmila Zadorozhnaya Institute and Museum of Anthropology, Moscow
Effect of Physical Training on Body Composition in Moscow Adolescents Elena Godina, Irena Khomyakova, Arsen Purundzhan, Anna Tretyak and Ludmila Zadorozhnaya Institute and Museum of Anthropology, Moscow
Obesity has become a alarming public health problem
 Ultrasonography for the Evaluation of Visceral Fat and Cardiovascular Risk Fernando F. Ribeiro-Filho, Alessandra N. Faria, Oswaldo Kohlmann, Jr, Sérgio Ajzen, Artur B. Ribeiro, Maria Teresa Zanella, Sandra
Ultrasonography for the Evaluation of Visceral Fat and Cardiovascular Risk Fernando F. Ribeiro-Filho, Alessandra N. Faria, Oswaldo Kohlmann, Jr, Sérgio Ajzen, Artur B. Ribeiro, Maria Teresa Zanella, Sandra
Does the Rule of Nines Apply to Morbidly Obese Burn Victims? A Post- Bariatric Surgery Longitudinal Follow-up to the Original Patient Data Set
 Does the Rule of Nines Apply to Morbidly Obese Burn Victims? A Post- Bariatric Surgery Longitudinal Follow-up to the Original Patient Data Set Stephen D. WOHLGEMUTH a,b, David STEFAN c a Eastern Virginia
Does the Rule of Nines Apply to Morbidly Obese Burn Victims? A Post- Bariatric Surgery Longitudinal Follow-up to the Original Patient Data Set Stephen D. WOHLGEMUTH a,b, David STEFAN c a Eastern Virginia
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Santosh Metgud 1, Charleen D Silva * 2, Anand Heggannavar 3. Access this Article online. Quick Response code. Original Research Article
 Original Research Article EFFECT OF 30 DAYS ABDOMINALS CHALLENGE VERSUS 30 DAYS PLANKS CHALLENGE ON WAIST CIRCUMFERENCE AND ABDOMINAL SKIN FOLD MEASUREMENTS IN HEALTHY YOUNG INDIVIDUALS: RANDOMIZED CLINICAL
Original Research Article EFFECT OF 30 DAYS ABDOMINALS CHALLENGE VERSUS 30 DAYS PLANKS CHALLENGE ON WAIST CIRCUMFERENCE AND ABDOMINAL SKIN FOLD MEASUREMENTS IN HEALTHY YOUNG INDIVIDUALS: RANDOMIZED CLINICAL
Bioelectrical Impedance versus Body Mass Index for Predicting Body Composition Parameters in Sedentary Job Women
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bioelectrical Impedance versus Body Mass Index for Predicting Body Composition Parameters in Sedentary Job Women Mohammad Javad Shekari-Ardekani 1, Mohammad Afkhami-Ardekani 2*, Mehrshad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bioelectrical Impedance versus Body Mass Index for Predicting Body Composition Parameters in Sedentary Job Women Mohammad Javad Shekari-Ardekani 1, Mohammad Afkhami-Ardekani 2*, Mehrshad
Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions
 bs_bs_banner Special Article Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions Christopher PF Marinangeli and Amira N Kassis
bs_bs_banner Special Article Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions Christopher PF Marinangeli and Amira N Kassis
BODY COMPOSITION COMPARISON: BIOELECTRIC IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS WITH DXA IN ADULT ATHLETES
 BODY COMPOSITION COMPARISON: BIOELECTRIC IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS WITH DXA IN ADULT ATHLETES A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
BODY COMPOSITION COMPARISON: BIOELECTRIC IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS WITH DXA IN ADULT ATHLETES A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 6, November 2008 Diabetes Technology Society OBESITY TECHNOLOGY Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation Dana L., Ph.D., 1,2 Richard
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 6, November 2008 Diabetes Technology Society OBESITY TECHNOLOGY Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation Dana L., Ph.D., 1,2 Richard
Spinal Cord Rehab Program, Toronto Rehabilitation Institute, University Health Network, 520 Sutherland Drive, Toronto, ON, Canada M4G 3V9 2
 Journal of Obesity Volume 212, Article ID 936, 9 pages doi:1.11/212/936 Clinical Study Bioelectrical Impedance and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Assessments of Changes in Body Composition Following
Journal of Obesity Volume 212, Article ID 936, 9 pages doi:1.11/212/936 Clinical Study Bioelectrical Impedance and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Assessments of Changes in Body Composition Following
