Infected Nonunion of Radius and Ulna Strategy of Approach
|
|
|
- Marjorie Horton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Editorial Case Study Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2012 Oct-Dec;2(4):26-31 Infected Nonunion of Radius and Ulna Strategy of Approach Abstract 1 1 Mangal Parihar, Divya Ahuja What to Learn from this Article? Clinical Decision Making (CDM), Planning and Managing cases of Infected Non union of Radius & Ulna? Technical Tips and Pearls of Surgical management in such cases. How to prevent such case? Introduction: Infected nonunion of radius and ulna are rare but difficult problems to deal. We report a case of successfully managed infected non-unonion of forearm bones and the reasoning behind strategy of approach to the case. Case Report: 42 year old female presented with history of closed forearm fracture three months back for which she was operated with open reduction and internal fixation using dynamic compression plate. There was pain and fever post-surgery and discharge and wound gape. This was treated with resuturing of the wound and oral antibiotics. She continued to have pain fever and discharge and consulted another surgeon who removed first the radius plate and then the ulna plate sequentially with stabilisation by external fixation. She presented to us at three months post injury with infected nonunion of radius and ulna with loosening of fixators, sequestrum on radiograph and wristdrop. A staged treatment was planned for her. As first stage debridement, antibiotic Calcium Sulphate cement bead insertion and intramedullary flexible nail fixation. She was given iv antibiotics as per culture report. At 3 months post surgery the infection had settled and pellets were resorbed. Double barrel vascularized fibula graft was used to fill the gap and fixation using long locked plates was done. At one year follow up radiographs showed good healing and clinically patient had a good elbow movements and was able to carry out her daily activities. Conclusions: Proper planning and staged management of such cases helps to achieve goals with good functional outcome. Keywords: Infected nonunion, radius, ulna, vascular fibula graft. Theoretical Background rarely encountered with very few reports in literature [1-5]. Infected nonunions are complications that are rare but have These are seen especially after treatment of neglected cases tremendous impact both on the patient and on the or cases with history of smoking, alcoholism or other co- surgeon's skills. Infected nonunions of forearm bones are morbidities [5]. Management options include staged 26 1 Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Mumbai. India Address of Correspondence Dr. Mangal Parihar Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Swastik Park, Chembur, Mumbai mangalparihar@gmail.com Dr. Mangal Parihar MS Ortho Copyright 2012 by Journal of Orthpaedic Case Reports Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports pissn Available on Author s Photo Gallery Dr. Divya Ahuja DNB Ortho This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
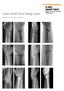
2 Figure 1: Immediate Postoperative radiograph showing radius ulna fractures stablised by DCP plate. Figure 2: Radial plate removed and Fixator applied at 3 weeks post primary surgery. Note the short fixator length well within the DCP plate length. Also long fixator pins traversing the interosseous space debridements and internal fixation after control of infection or single staged debridement and external fixator [5]. Although cases are reported individually, and as part of larger series, a definite guideline is difficult to establish. A recent case series of 15 such cases reported a protocol of aggressive debridement, early definitive fixation within 7-14 days with good results [5]. All cases of infected nonunion have unique and different presentation and require a customized approach. This case study recounts our strategy to treat one such case. Case Introduction Forty two year old house wife had a fall and sustained a closed radius ulna fracture. Open reduction and internal fixation was done at a different surgical center. She developed infection for which repeated debridement and implant removal was done. Bones were stabilized with external fixator however the infection was still not controlled. She came to us with infected non unions of both bones of forearm and external fixator in place. Case History Patient complained of fall and sustained a closed fracture on February She went to a surgical center close to her house and was operated on the same day with open Figure 3: Ulnar plate removed and fixator application. Again note the small length of fixator and long fixator pins. Figure 4: Intermediate radiograph showing worsening of pin sites with Radius sequestrating reduction and internal fixation using dynamic compression plates (Fig 1). On the second day after surgery, she developed a high fever. Blood counts were asked and a WBC count of was noted. The antibiotic was changed and presumably, a higher antibiotic was administered. This settled the fever, however wound gape was noted and there was discharge from the radial wound. This was secondarily sutured on the 5th day and she was sent home. However, the patient continued to be 'ill' and had pain and swelling in the operated limb, and decided to take a second opinion. The second surgeon debrided the radial wound, removed the radial plate and applied an external fixator on the radius (Fig. 2). The ulnar incision was not opened and ulnar plate was retained. She was administered oral antibiotics. She continued to be troubled by discharge from the radial incision and after 3 weeks the ulnar incision began discharging seropurulent fluid. The ulnar wound was debrided and plate was removed. An external fixator was applied to ulna in addition to the radial fixator (Fig. 3). Patient continued to have discharge from the wound and radiographic picture worsened (Fig. 4). Patient was advised to get a CT- bone scan done. At this point the patient presented to us with discharging wounds and pain Figure 5: Clinical Appearance and pin sites at presentation. Note the 'wrist drop' Figure 6: Radiograph at presentation showing infected nonunion of radius and ulna and possible sequestration os large radius and ulna fragments 27
3 Figure 7: Central diaphysis of the Radius and Ulna sequestrated Figure 8: Bone gap stabiised by TENS nail. Stimulan Pellets for local Antibiotic Delivery Wound closure with external fixators in situ. Case Assessment The general condition of the patient was fair, she had been having fever on and off with pain and discharge from both the radial and ulnar wounds (Fig. 5). Wounds were dressed daily and oral medication [antibiotics and anti- inflammatory] were being administered. Surgical scars over radius and ulna showed sinuses with granulation tissue [as seen in Fig. 5] and had discharge on pressing the edges. There was no wide gape and no fulminant signs of infection. There was loosening and discharge from the radius pin tracts. Sequential radiographs were available with first radiograph showing fixation of the radius and ulna done using DCP plates. The second radiograph with radius plate removed by the second surgeon and external fixator applied. The third radiograph showed removal of ulna plate and application of external fixation. Radiograph at presentation showed that the middle of the radius had sequestered out, with similar changes in ulna (Fig. 6). Case Conceptualization & Management Options Problems of the Case: On presentation the patient had already undergone four surgeries [primary surgery, wound gape resuturing, radial plate removal and ulna plate removal]. Since these surgeries were not done at our center we were not sure about the extent of debridement. The reason for continued infection may be inadequate debridement or a resistant organism. Culture done at the previous center had grown Kleibsiella Pneumoniae and appropriate antibiotics were administered so possibly the debridement was an issue. Problems to the patient: The patient was really anxious. She was an earning member of her family and since last three months she had been incapacitated. Her expectations were not met and she was very unsure of the future. We explained her the positive and negative aspects of the current situation and the further treatment plan. She was difficult to convince and seemed to have lost a lot of faith. Problems to surgeon: We were looking at a case with active infection, secondary to inadequate debridement with radiological sequestrum in both radius and ulna. In current scenario there were three goals to achieve; clearance of b 28 Figure 9 : Healing of the wound Figure 10: Biodegradable CaSo4 Pellets disappear over time 2 to three months post surgery. TENS nail held the position well
4 a b c Fig 11a: Vascularized Fibula with Pedicle converted to double barrel was used to fill the gap. Plate fixation through single incision to stablise both radius and ulna. b: Vascularized Fibula with Skin paddle and final closure infection, bony union, and facilitate maximum possible functional restoration. Plan was laid down according to our goals above 1.Clearance of infection: The radiograph showed sequestrated fragments in radius and ulna. A PET-CT was done to delineate the extent of sequestrum which showed involvement along the entire length between the pin tracts of the fixator. A large abscess was also noted. A preoperative culture was send which grew staphylococcus aureus sensitive to vancomycin. Plan was to debride the wound, remove the fixator, sequestrectomy and antibiotic cement beads insertion was made. The second issue to be considered at this time was mode of bone gap stabilization after excision of sequestrum. Patient was averse to external fixator and we considered internal fixation as our primary option. All options of internal and external fixator were made available during surgery. We had personally planned for internal fixation using a flexible nail with added stabilization with external fixator (if required). Fig 11c: Immediate post-operative radiograph 2. Achieving union: After infection has settled achieving union was the next step. There are two main options here bone transport or bone graft. Bone transport in radius ulna is technically difficult and very less work is available on this. Bone transport can have following disadvantages (a) in forearm fixation of radius will lead to transfixation of the muscles. The patient already has a wrist drop which is due to muscle fibrosis and transfixation and bone transport will worsen it (b) bone transport will lead to movement of origin of the muscles leading to clawing and other complications (c) application of fixator can functionally limit the patient for long time in cases with long gaps [as in this case]. Vascular or non vascular bone grafting can be used successfully and we had experience in using vascularized fibula graft for tibial gap nonunion and thus this modality was chosen by us. In this case the soft tissues is scarred and are less vascular, addition of new vascular graft will be more favorable in attaining successful graft incorporation. a b 29 Figure 12a: Excellent Function, except for pronation beyond midprone at one year follow up Fig 12b: Radiograph showing good healing at one year follow up
5 30 Parihar M, Ahuja D stabilization well, and radiographs showed gradual disappearance of the pellets (as expected) (Fig. 10). We had discussed with the patient, and suggested that a vascular fibula was a good option for her to shorten the recovery and maintain function (in contrast to bone transport, which would have been the other option). With help of plastic surgeons a double barreled vascular fibula was harvested and grafted in the gap of both radius and ulna (Fig. 11). Fixation was done using a long titanium plates that covered the bones almost completely (Fig. 11 b,c). For about 6 weeks she was protected in a slab, with intermittent mobilization out of the slab, and gradual weaning off of the external support after that. Rehabilitation protocol was aimed at restoring maximal elbow and wrist movements at first stage and prono- supination at second stage. Follow up: At 1 year after that surgery, she is back to an active life, happy, fairly good function from a medical standpoint, but "able to do everything that she needs to do" and the radiographs show a solid union at all the four sites, without any additional procedures being required (Fig 12 a,b ). [Watch for the patients smile at follow up, such untold outcome measures are one that are most relevant in clinical practice] Implications of the case How to prevent such cases? Theater asepsis is a must and continuous review of the sterilization process in your operation theaters is most essential. Cases of infected nonunion in forearm are rare due to good vasculature, however even if one case is infected it is 100% disaster for that case. Be vigilant about the asepsis during surgery and of course handling the soft tissue, achieving stable fixations are other basic principles that need to be kept in mind. How should the patient have been treated? Stage 1: Post-operative fever and discharge There is no role for antibiotics only and no role for wait and watch. Do not wait for infection to settle, take it head on. Also if there are two incisions in the same limb as in this case and one incision is showing signs of infection the others incision should also be considered to be infected and treated like wise. If the wound is showing all signs of infection it has to be opened up and debrided and washed. I personally use dilute betadine solution for lavage and use about 3 to 4 liters of this solution [6]. The decision on implant removal has to be taken intraoperatively after debridement and wash. Early in the course of infection the implant can be retained if the soft Treatment Given In May 2011, debridement, cement bead insertion and intramedullary flexible nailing were done. The debridement and excision of all dead bone was done till bleeding bone was found. How to stabilize a large defect was a decision to be finalized intraoperatively, however both intramedullary, extramedullary and external fixation options were kept ready. Once the necrotic bone, granulation etc was removed (Fig. 7), we decided to use Titanium elastic nails (TENS nail), along with external support by a plaster slab. We wished to use a Vacuum assisted Closure (VAC) in the postoperative period and a fixator would have made it difficult to apply the VAC (although VAC was not used, it is a point to be considered in decision making). TENS nails can provide surprisingly good rotational fixation and can maintain the gap in forearms. Technical tips are to use a 'single pass method' which means to avoid repeated insertion and multiple tract formation which makes the implant loose later. If the curved end is anchored to the subchondral bone, good stability can be achieved. This gives rotational stability and also resistance against collapse. We filled in the empty space with 20 Gms of Stimulan (Calcium sulphate) loaded with 2 Gms vancomycin and 3 million units Colistin (based on the earlier culture reports) (Fig 8). Multiple tissue samples were taken, from multiple areas in the wound, for culture (which would guide the post operative IV antibiotics). The deep culture grew paesudomonas aerugenosa sensitive to colistin and Carbapenams. Since colistin was already put into cement, IV Imepenum was given for 3weeks. Postoperatively, the forearm quite clearly 'calmed down' with decrease pain, redness, swelling and discharge (Fig 9 a). Regular dressings showed consistent improvements, and blood parameters improved gradually (Fig 9 b). Deep culture grew Pseudomonas aerugenosa, which was sensitive only to Carbapenams and Colistin. Since Colistin was already added to the cement pellets, antibiotic depot IV Imipenam was given for 3 weeks. Use of IV antibiotics can be regulated based on a combination of clinical appearance and response, and blood parameters - notably CRP. Based on these, we stopped IV antibiotics after 3 weeks, despite the CRP not being normal, but it was showing a clear downward trend and the patient was comfortable. No further antibiotics were administered to her after this. Intermittent period and second surgery: Over the next few months, a regular watch was kept on her, clinically as well as by radiographs. The TENS nails did their job of
6 tissues look healthy after debridement. If there is lot of granulation tissue which is covering the plates [underside or screw holes] the plate needs to be removed. Stage 2: With radius plate removed and fixator applied and continued infection At this stage there were two errors made, first debridement of only one incision and unstable external fixation. As mentioned above, unless obvious the second incision has to be taken as infected and at least warrants opening and lavage. Secondly the fixator length chosen was short. The fixators should have at least extended beyond the screw holes and should be of more stable construct [like a delta frame]. Instability combined with inadequate debridement would have led to continued infection. One of the other mistakes that one can see is the incision size. The debridement incision was not extending beyond the original incision. The debridements should always be through extended incision on both sides and thorough exploration. For a successful debridement the 'Enough' rule can be followed with enough time, enough incision, enough exposure for thorough and complete debridement. For debridements always err towards excess. With infection in mind local antibiotic pellets are to be considered with very low threshold. One of the issues with antibiotic cement (PMMA) beads is that they require second surgery for removal. For this reason we use calcium sulphate pellets. These are self-absorbing and do not require a second surgery. The other advantage of calcium sulphatepellets over PMMA beads is the ability to use any antibiotic according to culture instead of only thermostable antibiotic for beads. We always use the antibiotic pellets in all our cases of debridement for infected bony injuries. We recommend antibiotic beads as there is a limit to soft tissue excision and residual infected material can flare the infection and also these pellets fill up the dead space, not allowing for large collections post-surgery. This particular patient really underlines the importance of recognition of the destructiveness of infection, need for experience to deal with it aggressively, the requirement of the surgeon to deal with the surgery, the pharmacology and the psychology of infection and need to use the best knowledge, techniques, and tools/implants available to achieve an optimal result. Recommendations to Surgeons and Students 1. Stage the surgeries: Plan and stage your surgeries in such Conflict of Interest: Nil Source of Support: None cases. Go for stage wise goals and keep the patient informed 2. Assess your infrastructure: Primarily the OT complex, need for specialized care like vascularized bone graft and plastic surgeons. If need be do not hesitate to refer the patient 3. If war cannot be won at one time, look to win the battles individually. Eradicate the infection first which is one battle won and then plan for reconstruction and later plan for functional improvement. Stage your treatment 4. Send for Opinions: one of the most important points is to seek as many opinions possible on such cases. Approach seniors and discuss cases. 5. Use such cases to audit your techniques of debridement. For example, after debridement the wound should start settling by the end of one week, it should reduce in redness, discharge and swelling. If there is no change for 4 to 5 weeks that means the debridement has failed and you should review your debridement process and introspect on what was inadequate 6. Use local antibiotic delivery: have a low threshold to use beads. Calcium sulphate is most advantageous without problem of conventional beads 7. Believe the worse radiograph, follow the enough rule and err towards excess in such cases. Acknowledgment Authors will like to acknowledge Dr Sameer Kumta for performing the double barrel fibula graft in this case and also for providing the related photographs References 1. Hurst LC, Mirz MA, Spellman W.) Vascular fibular graft for infected loss of the ulna: case report. J Hand Surg 1982; 7: Meals RA. The use of flexor carpi ulnaris muscle flap in the treatment of an infected nonunion of the proximal ulna: a case report. Clin Orthop 1989; 240: Malki A, Wong-Chung J, Hariharan V. Centralization of ulna for infected nonunion of the radius with extensive bone loss. A modified Hey-Groves procedure. Injury 2000;31: Dell PC, Sheppard JE. Vascularized bone grafts in the treatment of infected forearm nonunions. J Hand Surg 1984; 9: Prasarn ML, Ouellette EA, Miller DR. Infected nonunions of diaphyseal fractures of the forearm. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2010 Jul;130(7): Brown NM, Cipriano CA, Moric M, Della Valle CJ. Dilute betadine lavage prior to closure for preventing acute deep periprosthetic joint infection. Paper #128. Presented at the 2011 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Feb San Diego. How to Cite this Article: Parihar M, Ahuja D. Infected Nonunion of Radius and Ulna Strategy of approach. J ournal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2012 Oct- Dec;2(4):
Power to Transform Outcomes
 CASE STUDIES CASE STUDY Courtesy of Dr Parihar Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Mumbai, India Clinical particulars 42-year-old female
CASE STUDIES CASE STUDY Courtesy of Dr Parihar Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Mumbai, India Clinical particulars 42-year-old female
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How
 Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures Journal Reviewer Journal of Bone
Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures Journal Reviewer Journal of Bone
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus
 The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12, No2, April, 1999 = Abstract = Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures Eui-Hwan Ahn, MD, In-Whan Chung, MD, Jeong-Hwan Oh, MD, Seong-Tae
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12, No2, April, 1999 = Abstract = Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures Eui-Hwan Ahn, MD, In-Whan Chung, MD, Jeong-Hwan Oh, MD, Seong-Tae
Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are
 The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are inserted in a multiplanar and multi-directional fashion
The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are inserted in a multiplanar and multi-directional fashion
Management of infected custom mega prosthesis by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery
 Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial Head with Both-Bone Forearm Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
A prospective study of functional outcome of primary intra-medullary nailing in type 3A and 3B open tibial diaphyseal fractures
 2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
Complex Limb Injury. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
A Patient s Guide to Adult Radial Head (Elbow) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Radial Head (Elbow) Fractures 2321 Coronado Idaho Falls, ID 83404 Phone: 208-227-1100 jpond@summitortho.net 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Adult Radial Head (Elbow) Fractures 2321 Coronado Idaho Falls, ID 83404 Phone: 208-227-1100 jpond@summitortho.net 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
ISPUB.COM. Z Ali, L Khurshid, S Vakil, A Anjum, S Dhar OBJECTIVE METHOD PATIENTS
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 22 Number 1 Prevalence Of Pin Tract Infection And Role Of Combined Saline And Povidone Iodine With Combined Spirit (Isopropyl Alcohol 70% V/V)
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 22 Number 1 Prevalence Of Pin Tract Infection And Role Of Combined Saline And Povidone Iodine With Combined Spirit (Isopropyl Alcohol 70% V/V)
Case Presentation: Comminuted Fractures of the Proximal Ulna 11/28/2017. Disclosures. Surgical Strategy. Implant Choice. Melvin P.
 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Unstable elbow dislocations: a case report of a new surgical technique
 SICOT J 2016, 2, 15 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2016010 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Unstable elbow dislocations: a case report of
SICOT J 2016, 2, 15 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2016010 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Unstable elbow dislocations: a case report of
Infected forearm nonunion treated by bone transport after debridement
 Liu et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:273 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Infected forearm nonunion treated by bone transport after debridement Tang Liu 1, Zhenyang Liu 2,3, Lin Ling 1* and Xiangsheng
Liu et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:273 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Infected forearm nonunion treated by bone transport after debridement Tang Liu 1, Zhenyang Liu 2,3, Lin Ling 1* and Xiangsheng
Forearm Fracture Solutions. Product Overview
 Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre
 Original article : Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre Chandra Prakash Singh Associate Professor, Department
Original article : Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre Chandra Prakash Singh Associate Professor, Department
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna with Distraction Osteogenesis: Three Cases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware. Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA
 Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Treatment of Distal Radius Bone Defects with Injectable Calcium Sulphate Cement
 Treatment of Distal Radius Bone Defects with Injectable Calcium Sulphate Cement Deng Lei, Ma Zhanzhong, Yang Huaikuo, Xue Lei and Yang Gongbo Orthopaedic Department, Beijing XiYuan Hospital, China Academy
Treatment of Distal Radius Bone Defects with Injectable Calcium Sulphate Cement Deng Lei, Ma Zhanzhong, Yang Huaikuo, Xue Lei and Yang Gongbo Orthopaedic Department, Beijing XiYuan Hospital, China Academy
Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture. 70 yo female 7/22/2013
 Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture Philip J. Kregor, MD 70 yo female Mild hypertension, Type II Diabetes Fell from 20 feet while at a party when the porch collapsed Mild head injury, Rib fractures Had been
Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture Philip J. Kregor, MD 70 yo female Mild hypertension, Type II Diabetes Fell from 20 feet while at a party when the porch collapsed Mild head injury, Rib fractures Had been
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series
 Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Fractures (Broken Bones)
 Fractures (Broken Bones) A fracture is a broken bone. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces). Types of Fractures Bones
Fractures (Broken Bones) A fracture is a broken bone. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces). Types of Fractures Bones
Case Report Surgical Treatment of Posttraumatic Radioulnar Synostosis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5956304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5956304 Case Report Surgical Treatment of Posttraumatic Radioulnar Synostosis S. Pfanner, P. Bigazzi,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5956304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5956304 Case Report Surgical Treatment of Posttraumatic Radioulnar Synostosis S. Pfanner, P. Bigazzi,
Management of fractures of both bones of forearm with dynamic compression plate with screw fixation
 of both bones of forearm Original Research Article ISSN: 2394-0026 (P) Management of fractures of both bones of forearm with dynamic compression plate with screw fixation Meeravali SK 1*, Dasaraiah CV
of both bones of forearm Original Research Article ISSN: 2394-0026 (P) Management of fractures of both bones of forearm with dynamic compression plate with screw fixation Meeravali SK 1*, Dasaraiah CV
A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of Both Bone Leg In Patients Attending Assam Medical College Hospital, Dibrugarh. Partha Pratim Das 5
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL
 Research article USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL G.C. Mwangi, MBChB, COSECSA Resident Orthopaedics, A.I.C. Kijabe Hospital, P.O.
Research article USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL G.C. Mwangi, MBChB, COSECSA Resident Orthopaedics, A.I.C. Kijabe Hospital, P.O.
Surgical management of fracture both bone forearm in adult using limited contact dynamic compression plate
 2017; 3(2): 852-856 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 852-856 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2017 Accepted: 02-03-2017 Muralidhar BM Associate Professor, Department Ravi KB Assistant Professor,
2017; 3(2): 852-856 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 852-856 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2017 Accepted: 02-03-2017 Muralidhar BM Associate Professor, Department Ravi KB Assistant Professor,
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
STIMULAN POWER TO TRANSFORM OUTCOMES
 STIMULAN POWER TO TRANSFORM OUTCOMES Perfect partner for your infection management strategy In contrast to today s growing economic and performance challenges, STIMULAN has been shown to transform outcomes
STIMULAN POWER TO TRANSFORM OUTCOMES Perfect partner for your infection management strategy In contrast to today s growing economic and performance challenges, STIMULAN has been shown to transform outcomes
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient
 Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
Implant removal Bruce Twaddle
 Implant removal Bruce Twaddle How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning outcomes
Implant removal Bruce Twaddle How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning outcomes
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Angle Stable Distal Radial Plate System WINSTA-R
 Angle Stable Distal Radial Plate System WINSTA-R Priv.-Doz.Dr.med. Martin Walz Dr. med. Felix Menzinger Prof.Dr.med. Jürgen Rudigier www.marquardt-medizintechnik.de General The problem posed by metaphyseal
Angle Stable Distal Radial Plate System WINSTA-R Priv.-Doz.Dr.med. Martin Walz Dr. med. Felix Menzinger Prof.Dr.med. Jürgen Rudigier www.marquardt-medizintechnik.de General The problem posed by metaphyseal
Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics, Regional institute of medical sciences, Imphal,Manipur, india. 2
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. I January. (2017), PP 38-45 www.iosrjournals.org A Novel Technique of Management of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. I January. (2017), PP 38-45 www.iosrjournals.org A Novel Technique of Management of
D-RAD SMART PACK Plating System. A series of case studies
 D-RAD SMART PACK Plating System A series of case studies AO fracture classification: C3 Eben A. Carroll, MD Associate Professor Director Orthopaedic Trauma Service Director Orthopedic Trauma Fellowship
D-RAD SMART PACK Plating System A series of case studies AO fracture classification: C3 Eben A. Carroll, MD Associate Professor Director Orthopaedic Trauma Service Director Orthopedic Trauma Fellowship
Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia
 Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia Nazri MY a, AS Halim b a Department of Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation, Kulliyyah of Medicine, International Islamic
Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia Nazri MY a, AS Halim b a Department of Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation, Kulliyyah of Medicine, International Islamic
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures
 TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y.
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars
 Disclosures Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars I have no financial disclosures Cherrie Heinrich, MD, FACS Department of Plastic Surgery Regions Hospital Assistant Professor University
Disclosures Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars I have no financial disclosures Cherrie Heinrich, MD, FACS Department of Plastic Surgery Regions Hospital Assistant Professor University
Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur *
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
OF SURGICALLY TREATED FRACTURE FOREARM BONES WITH PLATING IN BOTH BONE VERSUS PLATING IN RADIUS AND NAILING IN ULNA
 www.ijmse.com International Journal Medical Science and Education An ficial Publication Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
www.ijmse.com International Journal Medical Science and Education An ficial Publication Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
Distal Ulnar Locking Plate
 INDEX Indications Patient Position Surgical Technique - Step 1 Approach - Step 2 Plate Contouring - Step 3 Fracture Reduction - Step 4 Distal Plate Fixation - Step 5 Confirm Proper Reconstruction - Step
INDEX Indications Patient Position Surgical Technique - Step 1 Approach - Step 2 Plate Contouring - Step 3 Fracture Reduction - Step 4 Distal Plate Fixation - Step 5 Confirm Proper Reconstruction - Step
Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set. Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1)
 Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1) The Distal Radius Plates Indications For fixation of fractures and osteotomies, including
Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1) The Distal Radius Plates Indications For fixation of fractures and osteotomies, including
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
Article ID: WMC00596 ISSN
 Article ID: WMC00596 ISSN 2046-1690 "Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Following Isolated Fracture Of Shaft Of Ulna And Its Treatment By Radical Excision And Interposition Of Tensor Fascia Lata Graft" Author(s):Dr.
Article ID: WMC00596 ISSN 2046-1690 "Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Following Isolated Fracture Of Shaft Of Ulna And Its Treatment By Radical Excision And Interposition Of Tensor Fascia Lata Graft" Author(s):Dr.
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Using Animal Models to Help Solve Clinical Problems
 Using Animal Models to Help Solve Clinical Problems -Overview -Epidemiology -Improving the Standards for Initial Wound Care -Use of dual purpose bone grafts -Developing a more relevant animal model Research
Using Animal Models to Help Solve Clinical Problems -Overview -Epidemiology -Improving the Standards for Initial Wound Care -Use of dual purpose bone grafts -Developing a more relevant animal model Research
Carpal rows injuries!
 Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
PROXIMAL TIBIAL PLATE
 SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
DISTAL RADIUS. Instructions for Use
 DISTAL RADIUS Instructions for Use CAUTION: FEDERAL LAW RESTRICTS THESE DEVICES TO SALE BY OR ON THE ORDER OF A PHYSICIAN. Table of Contents 1. INTENDED USE... 3 2. DEVICE DESCRIPTION... 3 3. METHOD OF
DISTAL RADIUS Instructions for Use CAUTION: FEDERAL LAW RESTRICTS THESE DEVICES TO SALE BY OR ON THE ORDER OF A PHYSICIAN. Table of Contents 1. INTENDED USE... 3 2. DEVICE DESCRIPTION... 3 3. METHOD OF
INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
 INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagram of the ulnar nerve supplying the muscles of forearm and hand Cubital Tunnel is a condition that refers to the ulnar nerve being compressed around the elbow.
INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagram of the ulnar nerve supplying the muscles of forearm and hand Cubital Tunnel is a condition that refers to the ulnar nerve being compressed around the elbow.
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Neurologic Damage. The most common neurologic injury following intramedullary tibial nailing is injury to the peroneal nerve.
 COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Motec. Wrist Joint Arthrodesis Metacarpal Taper and Radius Connector
 Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis Metacarpal Taper and Radius Connector Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis The Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis has been developed as a part of the Motec Wrist Prosthesis family to
Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis Metacarpal Taper and Radius Connector Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis The Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis has been developed as a part of the Motec Wrist Prosthesis family to
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Journal of Hand Surgery (British & European Volume)
 Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Journal of Hand Surgery (British & European Volume) Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: Title: Double-Barrel Free Fibula Flap for Treatment of Infected Nonunion of Both
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Journal of Hand Surgery (British & European Volume) Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: Title: Double-Barrel Free Fibula Flap for Treatment of Infected Nonunion of Both
AcUMEDr. FoREARM ROD SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr FoREARM ROD SYSTEM FoREARM ROD SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been
AcUMEDr FoREARM ROD SYSTEM FoREARM ROD SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been
Radial head fractures; ORIF radial head; radial head arthroplasty; coronoid process fracture; ligament repair Elbow Anatomy Spectrum of injuries
 Radial head fractures; ORIF radial head; radial head arthroplasty; coronoid process fracture; ligament repair This information aims to help you understand your condition and gain maximum benefit from your
Radial head fractures; ORIF radial head; radial head arthroplasty; coronoid process fracture; ligament repair This information aims to help you understand your condition and gain maximum benefit from your
Motec. Wrist Joint Arthrodesis Metacarpal Nail and Radius Connector
 Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis Metacarpal Nail and Radius Connector Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis The Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis has been developed as a part of the Motec Wrist Prosthesis family to enable
Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis Metacarpal Nail and Radius Connector Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis The Motec Wrist Joint Arthrodesis has been developed as a part of the Motec Wrist Prosthesis family to enable
FRACTURES OF THE TIBIA COMPLICATED BY SKIN LOSS
 m FRACTURES OF THE TIBIA COMPLICATED BY SKIN LOSS By STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Windsor Group of Hospitals and the Mount Vernon Centre for Plastic Surgery, Northwood, Middlesex
m FRACTURES OF THE TIBIA COMPLICATED BY SKIN LOSS By STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Windsor Group of Hospitals and the Mount Vernon Centre for Plastic Surgery, Northwood, Middlesex
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
Complications of Treatment: Nonsurgical and Surgical
 Complications of Treatment: Nonsurgical and Surgical Whenever orthopedic surgeons discuss a treatment with patients we must always consider the risks and complications of any treatment we recommend. Part
Complications of Treatment: Nonsurgical and Surgical Whenever orthopedic surgeons discuss a treatment with patients we must always consider the risks and complications of any treatment we recommend. Part
