Low-grade surface tumours of bone may
|
|
|
- Derrick Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hemicortical allograft reconstruction after resection of low-grade malignant bone tumours R. L. M. Deijkers, R. M. Bloem, P. C. W. Hogendoorn J. J. Verlaan, H. M. Kroon, A. H. M. Taminiau From Leiden University Medical Centre, Leiden, The Netherlands Low-grade surface tumours of bone may theoretically be treated by hemicortical resection, retaining part of the circumference of the cortex. An inlay allograft may be used to reconstruct the defect. Since 1988 we have performed 22 hemicortical procedures in selected patients with low-grade parosteal osteosarcoma (6), peripheral chondrosarcoma (6) and adamantinoma (10). Restricted medullary involvement was not a contraindication for this procedure. There was no evidence of local recurrence or distant metastasis at a mean follow-up of 64 months (27 to 135). Wide resection margins were obtained in 19 patients. All allografts incorporated completely and there were no fractures or infections. Fractures of the remaining hemicortex occurred in six patients and were managed successfully by casts or by osteosynthesis. The functional results were excellent or good in all except one patient. Hemicortical procedures for selected cases of low-grade surface tumours give excellent oncological and functional outcomes. There was complete remodelling and fewer complications when compared with larger intercalary procedures. The surgery is technically demanding but gives good clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2002;84-B: Received 28 November 2001; Accepted after revision 2 April 2002 Advances in MRI 1-3 and histological and molecular pathology 4,5 have dramatically improved the diagnosis R. L. M. Deijkers, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Reinier de Graaf Gasthuis, Reinier de Graafweg, 3, 2625 AD Delft, The Netherlands. R. M. Bloem, MD, PhD, Orthopaedic Surgeon J. J. Verlaan, MD, Orthopaedic Registrar A. H. M. Taminiau, MD, PhD, Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery P. C. W. Hogendoorn, MD, PhD, Professor of Pathology Department of Pathology H. M. Kroon, MD, PhD, Radiologist Department of Radiology Leiden University Medical Centre, Albinusdreef 2, 2300 RC Leiden, The Netherlands. Correspondence should be sent to Dr R. L. M. Deijkers British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery X/02/ $2.00 and staging of bone tumours. The sensitivity of MRI to determine the extent of a tumour makes wide resection possible without unnecessary removal of normal bone. The indications for such 'limited' wide resection have not been determined. Wide en-bloc resection while retaining part of the cortical circumference should be possible for low-grade surface tumours of bone. We believe that this so-called hemicylindrical or hemicortical resection may be used in selected cases of low-grade parosteal osteosarcoma, peripheral chondrosarcoma and adamantinoma. In contrast to previous reports, 6-8 we believe that medullary involvement does not always necessitate resection of an intercalary segment in order to achieve a wide surgical margin. Recently, hemicortical resection for parosteal osteosarcoma has been described. 9 We now add our experience of hemicortical resection for peripheral chondrosarcoma and adamantinoma. It should be possible to tailor an inlay allograft precisely to reconstruct a hemicortical defect. Because of the limited soft-tissue dissection and the large contact area with the patient's own bone an excellent environment for the allograft is provided. Due to this, more complete remodelling and fewer graft complications, as compared with larger intercalary allograft reconstruction, may occur. We describe our medium-term clinical results with such hemicortical procedures for selected cases of low-grade malignant bone tumours and have analysed the oncological and allograft outcome to determine the efficacy and safety of this technique. Patients and Methods Between 1989 and 1999, 22 patients with low-grade malignant surface bone tumours had a reconstruction using an inlay allograft after en-bloc resection (Table I). The mean follow-up period was 64 months (27 to 135). There were 12 men and ten women with a median age at the time of surgery of 22 years (16 to 60), with six lowgrade parosteal osteosarcomas, six low-grade peripheral chondrosarcomas, and ten adamantinomas. All the parosteal osteosarcomas were located in the distal femur and all adamantinomas in the tibia. The peripheral chondrosarcomas, which arise within an osteochondroma, 4 VOL. 84-B, NO. 7, SEPTEMBER
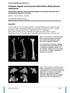
2 1010 R. L. M. DEIJKERS, R. M. BLOEM, P. C. W. HOGENDOORN, J. J. VERLAAN, H. M. KROON, A. H. M. TAMINIAU Fig. 1b Fig. 1a Fig. 1c Fig. 1d Case 6. A 46-year-old man with a parosteal osteosarcoma of the femur. Figure 1a Preoperative radiograph. Figure 1b Preoperative axial T1-weighted MR scan showing predominantly low signal intensity from the parosteal osteosarcoma arising from the anterior cortex of the femur (arrowheads). About 40% of the circumferential cortex is involved. There is relatively ill-defined delineation from the surrounding soft tissue (the final histological examination showed microscopic invasion into the soft tissues) and no indication of medullary involvement. Figure 1c initial postoperative radiograph showing reconstruction with a fitted inlay allograft and plate fixation. Figure 1d Radiograph showing complete union at 16 months. were located in the proximal humerus (2), the proximal femur (2) and the distal femur (2). Local preoperative staging of the tumour was done using plain radiography and MRI with T1- and T2-weighted sequences and contrast-enhanced series with gadolinium. 1-3 Distant metastases were sought using plain radiography and CT of the lungs, and bone scintigraphy. The nature of the tumour was established by histological examination of a biopsy and definitive staging by examination of the resected specimen. All resected specimens were sliced on a diamond-band saw (Exact Apparatebau, Norderstedt, Germany), in planes corresponding to the MR images and sections were made for tumour typing and assessment of surgical margins. All tumours were low grade (stage I). 10 Since the three selected types of tumour originated from different compartments, different criteria for extracompartmental involvement (stage IB) were used. 10 For parosteal osteosarcoma and peripheral chondrosarcoma, spread from the parosteal compartment was recognised by invasion of the medullary canal or penetration of soft-tissue structures. For adamantinoma, cortical destruction with subperiosteal bulging in the soft tissues and medullary invasion were indicative of extracompartmental involvement. The sites of resection and osteotomy were determined on the basis of preoperative MRI (Figs 1 to 3). Frozen sections were analysed if there was a close or questionable surgical margin as assessed at operation. Additional bone was resected in one patient because residual tumour tissue was seen in the medulla, and confirmed on frozen sections (case 9). The mean length of resected bone was 10.9 cm (6 to 26). The extent of the circumferential resection varied between 50% and 80%. In two patients (cases 13 and 18) the resection included the inner part of the opposing cortex, because of extensive intramedullary involvement (Fig. 3). The defects were reconstructed using fresh, deep-frozen inlay allografts. They were retrieved and preserved according to the guidelines of the American Association of Tissue Banks and the European Association of Musculoskeletal Transplantion, and were stored at -80 C. 11 The grafts were not irradiated. Each graft was meticulously cut to fit the defect precisely, and was secured by lag screws, cerclage wires or a neutralisation plate (Figs 1c and 2c). In one patient no osteosynthesis was needed since the allograft was pressfitted into the defect. We preferred the minimal use of fixation material to avoid interference with radiological and MR evaluation of potential local recurrences. Allogenic and autogenous cancellous bone was placed and impacted in the medullary cavity beneath the allograft. Postoperatively, the limb was immobilised in a cast or brace until radiological union was demonstrated. Partial weight-bearing was started when there appeared to be at least 50% union of the transverse and longitudinal osteotomies. Plain radiographs of the primary site and of the chest were taken every three to four months for the first two years and at least yearly thereafter to evaluate potential local recurrence and distant metastases. Radiological features of the allograft and the percentage of allograft- THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
3 HEMICORTICAL ALLOGRAFT RECONSTRUCTION AFTER RESECTION OF LOW-GRADE MALIGNANT BONE TUMOURS 1011 Fig. 2b Fig. 2a Fig. 2c Fig. 2d Case 5. A 17-year-old girl with an adamantinoma of the tibia. Figure 2a Preoperative lateral radiograph. Figure 2b Preoperative axial T1-weighted MR scan showing intermediate signal intensity from the centre of the tumour (large arrow), low signal intensity from the sclerotic ridge (small arrow) and medullary involvement (arrowhead). Figure 2c Postoperative radiograph showing reconstruction with a fitted inlay allograft and fixation with screws. Figure 2d Radiograph at 84 months showing incorporation and hypertrophy of the remaining hemicortex. Table I. Details of the 22 patients undergoing hemicortical resection and inlay allograft reconstruction Age Length Surgical Graft Follow-up Reconstruction MSTS Case (yrs) Gender Tumour* Stage Site (cm) margin fixation (mths) complication score 1 31 F CS IA Humerus 12 m-st Screws 135 No M POS IA Femur dist 14 w Screws 117 No F AD IA Tibia 9 w No osteosynthesis 115 No F AD IB Tibia 7 w Screw 84 Sympathetic dystrophy of legs and arms after 2 years 5 17 F AD IA Tibia 15 w Screws 84 No M POS IB Femur 11 m-st Plate 75 No M POS IB Femur dist 13 m-st Screws 72 Peroperative fracture host bone ( screws) Fixation failure at 1 mth ( plate) Fixation failure at 17 mth ( new plate) F AD IB Tibia 8 w Screws 69 Fracture host bone at 1 mth 29 ( conservative) 9 16 F CS IB Humerus 7 m-b Screws 65 No M CS IA Femur prox 11 w Cerclage 64 Fracture host bone at first day ( plate and screws) F POS IB Femur dist 7 w Plate 64 No M CS IA Femur dist 14 m-st Plate 56 No F AD IB Tibia 10 m-b Screws 51 Peroperative fissure host bone ( initially conservative, at 5 mth plate) M AD IA Tibia 14 w Plate 48 Peroperative fracture host bone ( plate) F AD IA Tibia 6 w Screw 46 No F AD IA Tibia 12 w Screws 45 No F AD IA Tibia 20 w Screws 43 No M AD IA Tibia 14 m-b Screws 43 No M POS IB Femur dist 9 m-st Screws 33 Fracture host bone at 13 days ( plate) M CS IA Femur prox 10 w Plate 33 No M CS IB Femur dist 7 m-st Screws 31 No F POS IA Femur dist 9 m-st Plate 27 No 24 *POS, parosteal osteosarcoma; CS, chondrosarcoma; AD, adamantinoma according to MSTS w, wide; m-st, marginal in soft tissue; m-b, marginal in bone VOL. 84-B, NO. 7, SEPTEMBER 2002
4 1012 R. L. M. DEIJKERS, R. M. BLOEM, P. C. W. HOGENDOORN, J. J. VERLAAN, H. M. KROON, A. H. M. TAMINIAU Fig. 3a Fig. 3b Fig. 3c Fig. 3d Case 13. A 17-year-old girl with an adamantinoma involving 80% of the circumferential cortex. Figure 3a Preoperative axial T1-weighted MR image of the tibia showing the tumour arising from the anterior cortex (arrow) with intermediate signal intensity in the centre and low signal intensity from the surrounding sclerotic border. Figure 3b MR scan distal to the centre of the tumour, showing extensive horseshoe-shaped medullary involvement (arrowheads) extending close to the dorsal cortex of the tibia. Resection of more than 80% of the circumferential cortex was needed to obtain wide margins. Figure 3c Postoperative radiograph showing reconstruction with a fitted inlay allograft and fixation by a lag screw. Distally, where less than 20% of the cortical circumference remained, a fracture occurred (arrow). Figure 3d Radiograph at 51 months after plate fixation of the distal fracture showing incorporation of the allograft beneath the plate. There is hypertrophy of the remaining hemicortex at the site of the fracture. to-host union were estimated according to the criteria of the International Symposium on Limb Salvage. 12 Functional analysis of all patients was assessed at final follow-up using the revised 30-point functional evaluation system of the Musculoskeletal Tumor Society (MSTS). 13 This system assigns numerical values (0 to 5) for each of six categories of pain, function, emotional acceptance in both the upper and lower limb, support, walking and gait in the lower limb or hand positioning, dexterity and lifting ability in the upper limb. Results The resection margins were judged to be wide in 12 specimens and marginal in ten (Table I). Marginal resections, through apparently tumour-free but reactive tissue, occurred in four of six chondrosarcomas (3 in soft tissue and 1 in bone), four of six parosteal osteosarcomas (all in soft tissue) and two of ten adamantinomas (both in bone). Marginal resections in soft tissue occurred in order to preserve neurovascular structures. In one patient (case 4) the peroneal nerve had to be sacrificed. Marginal bone resection was made twice at the transverse osteotomies (cases 13 and 18) and once at the longitudinal osteotomy (case 9). Inadequate bone resection at the longitudinal osteotomy (case 9) was detected during surgery and was treated by additional resection and application of phenol and alcohol to extend the margin further. Marginal bone resection at the transverse osteotomy (cases 13 and 18) was diagnosed after surgery, and no additional resection was undertaken. No adjuvant therapy was given after marginal resection in soft tissue or bone. At the final follow-up, at a mean of 64 months (27 to 135), there was no local recurrence or metastasis. After the reconstruction there were no wound complications or infections. There was complete incorporation of all grafts and no allograft fractures occurred. There was fracture of the remaining hemicortex in three patients during the operation and in three others shortly afterwards (Table I). They occurred mainly at a sharp corner of the resection, close to a transverse osteotomy, but not through a screw hole. In one patient (case 7), the fracture progressed between the THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
5 HEMICORTICAL ALLOGRAFT RECONSTRUCTION AFTER RESECTION OF LOW-GRADE MALIGNANT BONE TUMOURS 1013 femoral condyles into the knee. Treatment of the fractures varied. One undisplaced postoperative fracture (case 8) was successfully treated in a cast and another undisplaced fracture (case 13) was initially treated in a cast, but it proved to be unstable and internal fixation was eventually necessary (Figs 3c and 3d). The four displaced fractures were treated by immediate internal fixation. The internal fixation of a supraand intercondylar fracture of the femur (case 7) was inadequate, and further fixation was necessary followed by prolonged immobilisation resulting in a restricted range of movement of the knee (flexion 25 ). None of the other fractures affected the final functional outcome. The exact time of incorporation was difficult to define. Complete incorporation was assumed when the osteotomy line disappeared (Fig. 1d). 12 All grafts incorporated at a mean of 15 months (6 to 30) after adequate internal fixation. If the initial gap between the graft and host was 1 mm or less, complete incorporation occurred within 12 months. Sufficient union to allow partial weight-bearing occurred at a mean of seven months (3 to 12). Radiological examination showed marked hypertrophy of the remaining hemicortex in seven cases. The hemicortex showed increased density or thickening (Figs 2d and 3d). No relation to the site of the graft, localisation or the time of the graft incorporation could be found. There was no massive resorption or progressive deterioration of allografts. Minor subcortical resorption of the graft was seen in two patients, most pronounced in one in whom there was no spongiosa impacted beneath it (case 1). Good or excellent functional results with MSTS scores above 20 were found in all except one patient (case 7, Table I). The maximal score of 30 was seen in six patients. All except one (case 7) returned to their preoperative level of activity; only four (cases 3, 7, 17, 21) had recreational restriction because of modest pain or insecurity. In one patient (case 4) no reliable score was obtained because of the development of reflex sympathetic dystrophy affecting both legs and arms which began two years after surgery. This patient, however, had no pain at the site of the reconstructed proximal tibia, with good knee function and rapid and complete ingrowth of the graft. Discussion Our results of 22 hemicortical precedures for low-grade malignant bone tumours showed good oncological and functional outcomes. There was no evidence of local recurrence or distant metastases in any of the patients. No allograft complications occurred and all incorporated completely. Fracture of the remaining hemicortex occurred in six patients and these were managed successfully by a cast or osteosynthesis. The functional results were excellent or good for all except one patient, and compare favourably with those of larger intercalary procedures. 6,8,14 A hemicortical resection is potentially possible for lowgrade tumours arising from the parosteal or cortical compartment such as parosteal osteosarcoma, peripheral chondrosarcoma and adamantinoma. We defined peripheral chondrosarcoma as a tumour arising within the cartilaginous cap of an osteochondroma. 4 All these tumours are usually well differentiated with slow growth and are unlikely to metastasise. Medullary involvement may occur, but we considered its mere presence not to be a contraindication for a hemicortical resection. Our decision to carry out a hemicortical resection depended on the possibility of obtaining a wide medullary surgical margin. This seems possible for many patients with parosteal osteosarcoma or peripheral chondrosarcoma because invasion usually involves less than 25% of the medullary canal. 4,7 Adamantinomas, however, are less reliable. An osteofibrous dysplasia-like adamantinoma is usually confined to the cortex, but the classic type of adamantinoma may show extensive medullary involvement. 15 In two cases, in order to obtain wide resection of an adamantinoma we needed to resect 80% of the medullary canal, including the inner part of the opposing cortex. It is also important preoperatively to identify dedifferentiated high-grade areas and satellite or skip lesions which must be differentiated from the conventional low-grade parosteal tumour. The former is not suitable for hemicortical resection and may need adjuvant chemotherapy. Satellite or skip lesions occur frequently in adamantinoma. MRI is essential for the detection of such dedifferentation and satellite lesions. 3 Contrast-enhanced MRI with gadolinium has been a part of our preoperative evaluation, enabling us to distinguish between oedema and tumour. 2,3 With this protocol, wide resection margins can be determined accurately. Initial resection with an adequate margin remains the most critical factor in determining a good prognosis. 7,14,16 In 22 hemicortical resections we achieved wide margins in 12 and marginal margins through tumour-free but reactive tissue in ten. The marginal resections occurred most often (7 of 10) in the soft tissues in order to preserve adherent neurovascular structures. Other investigators encountered the same difficulty in obtaining a wide resection margin in the area of neurovascular structures. 6,7,9 Marginal bone resection occurred twice at the transverse osteotomy and only once at the longitudinal medullary osteotomy. Only the latter is typical for a hemicortical resection. It is often difficult to distinguish normal cortical bone from tumour while undertaking the longitudinal osteotomy. Nevertheless, hemicortical resections with wide bone margins can be obtained even when medullary involvement or satellite lesions are present. We found no local recurrences or metastases after a mean follow-up of 5.3 years (2.2 to 11.2). This seems low compared with other findings. In large clinical studies rates of recurrence of 18% to 20% for parosteal sarcomas, 6,7 15% for all types of low-grade chondrosarcoma, 16 and 18% to 32% for adamantinoma have been found. 14,15 Comparison with these results, however, is not valid because the studies included a variety of tumour grades, surgical margins and VOL. 84-B, NO. 7, SEPTEMBER 2002
6 1014 R. L. M. DEIJKERS, R. M. BLOEM, P. C. W. HOGENDOORN, J. J. VERLAAN, H. M. KROON, A. H. M. TAMINIAU follow-up times. The time to recurrence may be eight years for parosteal osteosarcomas 7 and 21 years for adamantinomas. 15 Our satisfactory oncological outcomes so far may be due to selection of relatively small-to-moderately sized, lowgrade stage-i lesions. The principal advantage of a hemicortical over an intercalary procedure is that less normal bone is resected. The resultant defect provides an excellent environment for reconstruction with an inlay allograft. The limited dissection of soft tissue, the good vascularity of the remaining hemicortex and the large contact area between allograft and host bone may reduce infection and facilitate union and remodelling. Our results with inlay reconstructions compare favourably with those of large studies using intercalary allograft reconstruction 8,14 which recorded a rate of infection of 12%, of fracture of the allograft of 18% and of nonunion of 30%. The time of incorporation of the graft is always difficult to assess and varied widely in our group between five and 30 months. Stable fixation and close contact between the allograft and host bone will facilitate incorporation. 17,18 We found incorporation to be faster when the initial gap between the allograft and host was less than 1 mm. Because of the irregular shape of the resection specimen, it was sometimes difficult to cut the allograft exactly to the same shape. Other reasons for the large variation in the time of incorporation may be the location (diaphysis or metaphysis) 17,18 and the immunological response to the allograft. 19,20 The hemicortical reconstruction is vulnerable until the graft becomes incorporated. No fractures of the allograft occurred, but in six patients there was fracture of the remaining host hemicortex. All fractures occurred when plate fixation was not (yet) present. The remaining hemicortex is specially vulnerable when a large hemicortical segment is resected and stress rising corners are present. 21 Although these fractures can successfully be managed by a cast or internal fixation and in general do not affect the outcome, initial plate fixation should be considered when the residual cortex is judged to be fragile. The good clinical results with high MSTS scores seem the logical result of the limited resection, complete incorporation of the allograft and no serious complications. All except one patient had an MSTS score above 20; six patients had a maximal score of 30. In summary, hemicortical procedures for the treatment of low-grade surface tumours are safe and effective. Wide resection bone margins can be achieved, even when the medulla is involved and satellite or skip lesions are present. Precise preoperative planning using MRI is essential to define the margins of resection. Although the hemicortical resection is technically demanding, gratifying clinical results make it clearly worthwhile for selected patients. We thank Dr H. M. Hazelbag of the Department of Pathology, Leiden University Medical Centre for the helpful discussion and critical reading of the manuscript. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. References 1. Bloem JL, Taminiau AH, Eulderink F, Hermans J, Pauwels EK. Radiologic staging of primary bone sarcoma: MR imaging, scintigraphy, angiography, and CT correlated with pathologic examination. Radiology 1988;169: Van der Woude HJ, Bloem JL, Verstraete KL, et al. Osteoscarcoma and Ewing s sarcoma after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: value of dynamic MR imaging in detecting viable tumor before surgery. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995;165: Van der Woude HJ, Bloem JL, Pope TL Jr. Magnetic resonance imaging of the musculoskeletal system: Part 9. Primary tumors. Clin Orthop 1998;347: Bovee JV, Cleton-Jansen AM, Kuipers-Dijkshoorn NJ, et al. Loss of heterozygosity and DNA ploidy point to a diverging genetic mechanism in the origin of peripheral and central chondrosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1999;26: Graadt van Roggen JF, Bovee JV, Van der Woude HJ, Hogendoorn PC. An update of diagnostic strategies using molecular genetic and magnetic resonance imaging techniques for musculoskeletal tumours. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2000;12: Kavanagh TG, Cannon SR, Pringle J, Stoker DJ, Kemp HBS. Parosteal osteosarcoma: treatment by wide resection and prosthetic replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1990;72-B: Okada K, Frassica FJ, Sim FH, et al. Parosteal osteosarcoma: a clinicopathological study. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1994;76-A: Ortiz-Cruz E, Gebhardt MC, Jennings LC, Springfield DS, Mankin HJ. The results of transplantation of intercalary allografts after resection of tumors: a long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1997;79-A: Lewis VO, Gebhardt MC, Springfield DS. Parosteal osteosarcoma of the posterior aspect of the distal part of the femur: oncological and functional results following a new resection technique. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2000;82-A: Enneking WF. The staging system for benign and malignant tumors of the musculoskeletal system. In: Enneking WF, ed. Clinical musculoskeletal pathology. Gainesville, Florida: University Presses of Florida, 1990: Deijkers RL, Bloem RM, Petit PLC, et al. Contamination of bone allografts: analysis of incidence and predisposing factors. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1997;79-B: Glasser D, Langlais F. The ISOLS radiological implants evaluation system. In: Langlais F, Tomeno B, eds. Limb salvage: major reconstructions in oncologic and nontumoral conditions. 5th International Symposium on Limb Salvage (ISOLS). Berlin, etc: Springer-Verlag; 1991: Enneking WF, Dunham W, Gebhardt MC, Malawar M, Pritchard DJ. A system for the functional evaluation of reconstructive procedures after surgical treatment of tumors of the musculoskeletal system. Clin Orthop 1993;286: Qureshi AA, Shott S, Mallin BA, Gitelis S. Current trends in the management of adamantinoma of long bones: an international study. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2000;82-A: Hazelbag HM, Taminiau AH, Fleuren GJ, Hogendoorn PC. Adamantinoma of the long bones: a clinicopathological study of thirty-two patients with emphasis on histological subtype, precursor lesion, and biological behavior. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1994;76-A: Lee FY, Mankin HJ, Fondren G, et al. Chondrosarcoma of bone: an assessment of outcome. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1999;81-A: Vander Griend RA. The effect of internal fixation on the healing of large allografts. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1994;76-A: San Julian Aranguren M, Leyes M, Mora G, Canadell J. Consolidation of massive bone allografts in limb-preserving operations for bone tumours. Int Orthop 1995;19: Stevenson S, Li XQ, Martin B. The fate of cancellous and cortical bone after transplantation of fresh and frozen tissue-antigen-matched and mismatched osteochondral allografts in dogs. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1991;73-A: Deijkers RL, Bouma GJ, van der Meer-Prins EM, et al. Human bone allografts can induce T cells with high affinity for donor antigens. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1999;81-B: Clark CR, Morgan C, Sonstegard DA, Matthews LS. The effect of biopsy-hole shape and size on bone strength. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1977;59-A: THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing Tumor Resections
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 426, pp. 97 102 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 426, pp. 97 102 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing
Evaluation of surgical treatment results in parosteal osteosarcoma
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 24, No. 1, May, 2010. pp. 11-16. Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 1:31 IRDT on Wednesday September 19th 2018 Evaluation of surgical
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 24, No. 1, May, 2010. pp. 11-16. Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 1:31 IRDT on Wednesday September 19th 2018 Evaluation of surgical
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized
 Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized autologous bone graft in leg reconstruction for patients with osteosarcoma Names of authors Masataka Noguchi, Hiroo Mizobuchi,
Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized autologous bone graft in leg reconstruction for patients with osteosarcoma Names of authors Masataka Noguchi, Hiroo Mizobuchi,
BONE TRANSPLANTATION IN LIMB SAVING SURGERIES: THE PHILIPPINE EXPERIENCE
 BONE TRANSPLANTATION IN LIMB SAVING SURGERIES: THE PHILIPPINE EXPERIENCE EDWARD HM WANG, MD UP-Musculoskeletal Tumor Unit and Tissue & Bone Bank Dept. of Orthopedics University of the Philippines-Philippine
BONE TRANSPLANTATION IN LIMB SAVING SURGERIES: THE PHILIPPINE EXPERIENCE EDWARD HM WANG, MD UP-Musculoskeletal Tumor Unit and Tissue & Bone Bank Dept. of Orthopedics University of the Philippines-Philippine
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Fractures of allografts used in limb preserving operations
 Fractures of s used in limb preserving operations M. San-Julian, J. Cañadell Department of Orthopaedics, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain Reprint requests to: M. San-Julian Departamento de Cirugía
Fractures of s used in limb preserving operations M. San-Julian, J. Cañadell Department of Orthopaedics, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain Reprint requests to: M. San-Julian Departamento de Cirugía
Chondrosarcoma with a late local relapse
 Chondrosarcoma with a late local relapse J. Shinoda, T. Ozaki, T. Oka, T. Kunisada, H. Inoue Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Okayama University Medical School, Okayama, 700-8558, Japan Correspondence:
Chondrosarcoma with a late local relapse J. Shinoda, T. Ozaki, T. Oka, T. Kunisada, H. Inoue Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Okayama University Medical School, Okayama, 700-8558, Japan Correspondence:
Laura M. Fayad, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University
 Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
Giant Cell Tumour of the Distal Radius: Wide Resection and Reconstruction by Non-vascularised Proximal Fibular Autograft
 900 Original Article Giant Cell Tumour of the Distal Radius: Wide Resection and Reconstruction by Non-vascularised Proximal Fibular Autograft Ayman Abdelaziz Bassiony, 1 MD Abstract Introduction: Giant
900 Original Article Giant Cell Tumour of the Distal Radius: Wide Resection and Reconstruction by Non-vascularised Proximal Fibular Autograft Ayman Abdelaziz Bassiony, 1 MD Abstract Introduction: Giant
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service
 North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
Preoperative MR Imaging Assessment of Osteosarcoma: A Radiological - Surgical Correlation
 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 9-16 9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Preoperative MR Imaging Assessment of Osteosarcoma: A Radiological - Surgical Correlation HUNG-TA HONDAR WU 1 CHENG- YEN CHANG 1 JEFF LIN 2 TAIN-HSIUNG CHEN
Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 9-16 9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Preoperative MR Imaging Assessment of Osteosarcoma: A Radiological - Surgical Correlation HUNG-TA HONDAR WU 1 CHENG- YEN CHANG 1 JEFF LIN 2 TAIN-HSIUNG CHEN
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Result of extracorporeal irradiation and re-implantation for malignant bone tumors: A review of 30 patients
 bs_bs_banner Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012 doi: 10.1111/ajco.12036 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Result of extracorporeal irradiation and re-implantation for malignant bone tumors: A review of 30 patients
bs_bs_banner Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012 doi: 10.1111/ajco.12036 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Result of extracorporeal irradiation and re-implantation for malignant bone tumors: A review of 30 patients
Objectives. Limb salvage surgery. Age distribution bone cancer. Age distribution soft tissue sarcomas
 LifeSource October, 2011 Disclosure Information Putting humpty dumpty back together again is easier with tissue allografts! Limb Salvage Surgery for Bone Tumors Edward Cheng, MD October 6, 2011 Disclosure
LifeSource October, 2011 Disclosure Information Putting humpty dumpty back together again is easier with tissue allografts! Limb Salvage Surgery for Bone Tumors Edward Cheng, MD October 6, 2011 Disclosure
ARMS. Reconstruction of Large Femur and Tibia Defect with Free Vascularized Fibula Graft and Locking Plate INTRODUCTION.
 Original Article ARMS Archieves of Reconstructive Microsurgery pissn 2383-5257 eissn 2288-6184 Arch Reconstr Microsurg 2015;24(2):68-74 http://dx.doi.org/10.15596/arms.2015.24.2.68 Reconstruction of Large
Original Article ARMS Archieves of Reconstructive Microsurgery pissn 2383-5257 eissn 2288-6184 Arch Reconstr Microsurg 2015;24(2):68-74 http://dx.doi.org/10.15596/arms.2015.24.2.68 Reconstruction of Large
Biological Reconstruction after Excision of Juxta-articular Osteosarcoma around the Knee: A New Classification System
 Biological Reconstruction after Excision of Juxta-articular Osteosarcoma around the Knee: A New Classification System HIROYUKI TSUCHIYA 1, MOHAMED E. ABDEL-WANIS 2 and KATSURO TOMITA 1 1 Department of
Biological Reconstruction after Excision of Juxta-articular Osteosarcoma around the Knee: A New Classification System HIROYUKI TSUCHIYA 1, MOHAMED E. ABDEL-WANIS 2 and KATSURO TOMITA 1 1 Department of
Methods Used for Reconstruction in Aggressive Bone Tumours: An Early Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Methods Used for Reconstruction in Aggressive Bone Tumours: An Early Experience K L Pan, FRCS*, S STing, FRCS**, A W K Mohamad, MS (Orth)*, W GLee, FRCS**, C C Wong, FRCS**, A H Rasit,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Methods Used for Reconstruction in Aggressive Bone Tumours: An Early Experience K L Pan, FRCS*, S STing, FRCS**, A W K Mohamad, MS (Orth)*, W GLee, FRCS**, C C Wong, FRCS**, A H Rasit,
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
Malignant bone tumors. Incidence Myeloma 45% Osteosarcoma 24% Chondrosarcoma 12% Lyphoma 8% Ewing s Sarcoma 7%
 Malignant bone tumors Incidence Myeloma 45% Osteosarcoma 24% Chondrosarcoma 12% Lyphoma 8% Ewing s Sarcoma 7% Commonest primary bone sarcoma is osteosarcoma X ray Questions to ask 1. Solitary or Multiple
Malignant bone tumors Incidence Myeloma 45% Osteosarcoma 24% Chondrosarcoma 12% Lyphoma 8% Ewing s Sarcoma 7% Commonest primary bone sarcoma is osteosarcoma X ray Questions to ask 1. Solitary or Multiple
Effective local and systemic therapy is necessary for the cure of Ewing tumor Most chemotherapy regimens are a combination of cyclophosphamide,
 Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Clinical Study Primary Malignant Tumours of Bone Following Previous Malignancy
 Sarcoma Volume 2008, Article ID 418697, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2008/418697 Clinical Study Primary Malignant Tumours of Bone Following Previous Malignancy J. T. Patton, S. M. M. Sommerville, and R. J. Grimer
Sarcoma Volume 2008, Article ID 418697, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2008/418697 Clinical Study Primary Malignant Tumours of Bone Following Previous Malignancy J. T. Patton, S. M. M. Sommerville, and R. J. Grimer
Functional Outcome Study of Mega-Endoprosthetic Reconstruction in Limbs With Bone Tumour Surgery
 192 Original Article Functional Outcome Study of Mega-Endoprosthetic Reconstruction in Limbs With Bone Tumour Surgery Peh Khee Tan, 1 MBBS, MRCS (Edin), MMed (Orthop), Mann Hong Tan, 1 MBBS, FRCS (Edin
192 Original Article Functional Outcome Study of Mega-Endoprosthetic Reconstruction in Limbs With Bone Tumour Surgery Peh Khee Tan, 1 MBBS, MRCS (Edin), MMed (Orthop), Mann Hong Tan, 1 MBBS, FRCS (Edin
History. 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation
 History 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation Imaging Photo Album Patient also had a smaller lesion 1 cm proximal to this lesion, not seen radiographically.
History 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation Imaging Photo Album Patient also had a smaller lesion 1 cm proximal to this lesion, not seen radiographically.
Surgical management of Grade I chondrosarcoma of the long bones
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 331-337 ORIGINAL STUDY Surgical management of Grade I chondrosarcoma of the long bones Cuneyd Gunay, Hakan Atalar, Onur Hapa, Kerem Basarir, Yusuf Yildiz, Yener Saglik From
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 331-337 ORIGINAL STUDY Surgical management of Grade I chondrosarcoma of the long bones Cuneyd Gunay, Hakan Atalar, Onur Hapa, Kerem Basarir, Yusuf Yildiz, Yener Saglik From
The early results of joint-sparing proximal tibial replacement for primary bone tumours, using extracortical plate fixation
 The early results of joint-sparing proximal tibial replacement for primary bone tumours, using extracortical plate fixation B. G. I. Spiegelberg, M. D. Sewell, W. J. S. Aston, G. W. Blunn, R. Pollock,
The early results of joint-sparing proximal tibial replacement for primary bone tumours, using extracortical plate fixation B. G. I. Spiegelberg, M. D. Sewell, W. J. S. Aston, G. W. Blunn, R. Pollock,
We have studied 560 patients with osteosarcoma of a
 Osteosarcoma of the limb AMPUTATION OR LIMB SALVAGE IN PATIENTS TREATED BY NEOADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY G. Bacci, S. Ferrari, S. Lari, M. Mercuri, D. Donati, A. Longhi, C. Forni, F. Bertoni, M. Versari, E.
Osteosarcoma of the limb AMPUTATION OR LIMB SALVAGE IN PATIENTS TREATED BY NEOADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY G. Bacci, S. Ferrari, S. Lari, M. Mercuri, D. Donati, A. Longhi, C. Forni, F. Bertoni, M. Versari, E.
The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening
 2008 62 5 333 339 The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening a* b a a a a a a b 334 62 5 5 1 16 9 0 100 11 31 131 14 2 16 9 0
2008 62 5 333 339 The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening a* b a a a a a a b 334 62 5 5 1 16 9 0 100 11 31 131 14 2 16 9 0
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Malignant fibrous histiocytoma of the distal femur after an arthroscopic anterior cruciate liagement reconstruction: A case report and a review of the literature Authors:
Author's response to reviews Title: Malignant fibrous histiocytoma of the distal femur after an arthroscopic anterior cruciate liagement reconstruction: A case report and a review of the literature Authors:
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur
 CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.140 A Case Report of Recurrent
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.140 A Case Report of Recurrent
Management of infected custom mega prosthesis by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
Chondroblastoma of bone
 Chronology Chondroblastoma of bone LONG-TERM RESULTS AND FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER INTRALESIONAL CURETTAGE R. Suneja, R. J. Grimer, M. Belthur, L. Jeys, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, A. M. Davies From The
Chronology Chondroblastoma of bone LONG-TERM RESULTS AND FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER INTRALESIONAL CURETTAGE R. Suneja, R. J. Grimer, M. Belthur, L. Jeys, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, A. M. Davies From The
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service
 North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after replacement of the proximal femur Proximal femoral replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after replacement of the proximal femur Proximal femoral replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Secondary Chondrosarcoma from an Osteochondroma of the Proximal Tibia Involving the Fibula
 Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:249-254 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.249 Secondary Chondrosarcoma from an Osteochondroma of the Proximal Tibia Involving the Fibula Hwan Seong
Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:249-254 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.249 Secondary Chondrosarcoma from an Osteochondroma of the Proximal Tibia Involving the Fibula Hwan Seong
ARTICLE. MR imaging in staging of bone tumors
 Cancer Imaging (2006) 6, 158 162 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2006.0026 CI ARTICLE MR imaging in staging of bone tumors Shigeru Ehara Department of Radiology, Iwate Medical University School of Medicine, Morioka
Cancer Imaging (2006) 6, 158 162 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2006.0026 CI ARTICLE MR imaging in staging of bone tumors Shigeru Ehara Department of Radiology, Iwate Medical University School of Medicine, Morioka
Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus
 The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Vascularised free fibular flap in bone resection and reconstruction *
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 425 430 Vascularised free fibular flap in bone resection and reconstruction * P.J. Belt*, I.C. Dickinson, D.R.B. Theile Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 425 430 Vascularised free fibular flap in bone resection and reconstruction * P.J. Belt*, I.C. Dickinson, D.R.B. Theile Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Endoprosthetic treatment of primary bone sarcomas with pathological fractures
 SA Orthopaedic Journal Winter 2016 Vol 15 No 2 Page 43 Endoprosthetic treatment of primary bone sarcomas with pathological fractures Dr Thomas L Hilton MBChB(UCT), DA(SA), DipPEC(SA), FCS(Orth), MMed(UCT)
SA Orthopaedic Journal Winter 2016 Vol 15 No 2 Page 43 Endoprosthetic treatment of primary bone sarcomas with pathological fractures Dr Thomas L Hilton MBChB(UCT), DA(SA), DipPEC(SA), FCS(Orth), MMed(UCT)
The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
Clinical Study The Use of Massive Endoprostheses for the Treatment of Bone Metastases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Sarcoma Volume 2007, Article ID 62151, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2007/62151 Clinical Study The Use of Massive Endoprostheses for the Treatment of Bone Metastases D. H. Park, P.
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Sarcoma Volume 2007, Article ID 62151, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2007/62151 Clinical Study The Use of Massive Endoprostheses for the Treatment of Bone Metastases D. H. Park, P.
Does Intraoperative Navigation Assistance Improve Bone Tumor Resection and Allograft Reconstruction Results?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-3604-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2013 MEETINGS OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-3604-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2013 MEETINGS OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Growth in the lower lim b following chem otherapy for a malignant prim ary bone tumour: a straight-line graph
 Sarcoma (1997) 1, 75± 77 O RIGINAL ARTIC LE Growth in the lower lim b following chem otherapy for a malignant prim ary bone tumour: a straight-line graph PAUL COOL, M ARK D AVIES, ROB J. GRIM ER, SIM ON
Sarcoma (1997) 1, 75± 77 O RIGINAL ARTIC LE Growth in the lower lim b following chem otherapy for a malignant prim ary bone tumour: a straight-line graph PAUL COOL, M ARK D AVIES, ROB J. GRIM ER, SIM ON
A multiplanar complex resection of a low-grade chondrosarcoma of the distal femur guided by K-wires previously inserted under CT-guide: a case report
 Zoccali et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:52 CASE REPORT Open Access A multiplanar complex resection of a low-grade chondrosarcoma of the distal femur guided by K-wires previously inserted under CT-guide: a
Zoccali et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:52 CASE REPORT Open Access A multiplanar complex resection of a low-grade chondrosarcoma of the distal femur guided by K-wires previously inserted under CT-guide: a
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Reconstruction of Massive Femur Defect with Free Vascularized Fibula Graft Following Tumor Resection
 Reconstruction of Massive Femur Defect with Free Vascularized Fibula Graft Following Tumor Resection KEIICHI MURAMATSU 1, KOICHIRO IHARA 2, KAZUTERU DOI 3, MITSUNORI SHIGETOMI 1, TAKAHIRO HASHIMOTO 1 and
Reconstruction of Massive Femur Defect with Free Vascularized Fibula Graft Following Tumor Resection KEIICHI MURAMATSU 1, KOICHIRO IHARA 2, KAZUTERU DOI 3, MITSUNORI SHIGETOMI 1, TAKAHIRO HASHIMOTO 1 and
Primary Bone Tumors: Spine Surgery Live -Video Techniques Mobile Spine
 Primary Bone Tumors: Spine Surgery Live -Video Techniques Mobile Spine Christopher Ames MD Professor of Neurosurgery and Orthopedic Surgery Director of Spine Tumor And Deformity Surgery UCSF Department
Primary Bone Tumors: Spine Surgery Live -Video Techniques Mobile Spine Christopher Ames MD Professor of Neurosurgery and Orthopedic Surgery Director of Spine Tumor And Deformity Surgery UCSF Department
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
Limb Salvage Surgery Using Whole Knee Joint Allograft Reconstruction in Osteosarcoma
 244 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2014; 49: 244-249 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.3.244 www.jkoa.org Limb Salvage Surgery Using Whole Knee Joint Allograft
244 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2014; 49: 244-249 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.3.244 www.jkoa.org Limb Salvage Surgery Using Whole Knee Joint Allograft
Functional and oncological outcomes after total claviculectomy for primary malignancy
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 170-174 ORIGINAL STUDY Functional and oncological outcomes after total claviculectomy for primary malignancy Zhaoxu Li, Zhaoming YE, Miaofeng ZHAng From the Department of
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 170-174 ORIGINAL STUDY Functional and oncological outcomes after total claviculectomy for primary malignancy Zhaoxu Li, Zhaoming YE, Miaofeng ZHAng From the Department of
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis
 Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
THE NANCY NAIL. The End Caps ADVANTAGES OF NANCY NAIL
 NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
Evaluation of Bone tumors with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and correlation with surgical and gross pathological findings.
 9-137 611 Evaluation of Bone tumors with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and correlation with surgical and gross pathological findings. S BAWEJA, R ARORA, S SINGH, A SHARMA, P NARANG, S GHUMAN, SK KAPOOR, S
9-137 611 Evaluation of Bone tumors with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and correlation with surgical and gross pathological findings. S BAWEJA, R ARORA, S SINGH, A SHARMA, P NARANG, S GHUMAN, SK KAPOOR, S
Limb Salvage Surgery for Musculoskeletal Oncology
 Editorial Limb Salvage Surgery for Musculoskeletal Oncology Wan Faisham Nu man Bin Wan Ismail Submitted: 2 May 2015 Accepted: 18 June 2015 Orthopaedic Oncology Unit, Orthopaedic Department, School of Medical
Editorial Limb Salvage Surgery for Musculoskeletal Oncology Wan Faisham Nu man Bin Wan Ismail Submitted: 2 May 2015 Accepted: 18 June 2015 Orthopaedic Oncology Unit, Orthopaedic Department, School of Medical
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct
 Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
CASE REPORT PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE.
 PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia
 Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors. James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon
 Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What?
 Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
What Is the Outcome of Allograft and Intramedullary Free Fibula (Capanna Technique) in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients With Bone Tumors?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:660 668 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4204-2 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 MUSCULOSKELETAL
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:660 668 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4204-2 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 MUSCULOSKELETAL
Lateral tibial condyle reconstruction by pedicled vascularized fibular head graft: Long-term result
 Title Lateral tibial condyle reconstruction by pedicled vascularized fibular head graft: Long-term result Author(s) Ahmed, SK; Fung, BKK; Ip, WY; Chow, SP Citation Strategies In Trauma And Limb Reconstruction,
Title Lateral tibial condyle reconstruction by pedicled vascularized fibular head graft: Long-term result Author(s) Ahmed, SK; Fung, BKK; Ip, WY; Chow, SP Citation Strategies In Trauma And Limb Reconstruction,
Clinical Study Distal Femur Allograft Prosthetic Composite Reconstruction for Short Proximal Femur Segments following Tumor Resection
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 397456, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/397456 Clinical Study Distal Femur Allograft Prosthetic Composite Reconstruction for Short Proximal Femur
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 397456, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/397456 Clinical Study Distal Femur Allograft Prosthetic Composite Reconstruction for Short Proximal Femur
Of approximately 2 million long bone fractures
 Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Effects of metaphyseal bone tumor removal with preservation of the epiphysis and knee arthroplasty
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 567-572, 2014 Effects of metaphyseal bone tumor removal with preservation of the epiphysis and knee arthroplasty PENG ZHANG 1, FEIFEI FENG 2, QIQING CAI 1, WEITAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 567-572, 2014 Effects of metaphyseal bone tumor removal with preservation of the epiphysis and knee arthroplasty PENG ZHANG 1, FEIFEI FENG 2, QIQING CAI 1, WEITAO
STAGING, BIOPSY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF TUMORS SCOTT D WEINER MD
 STAGING, BIOPSY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF TUMORS SCOTT D WEINER MD WHAT DO YOU DO WHEN THIS SHOWS UP IN YOUR OFFICE? besides panicking KEY PRINCIPLE!!! Reactive zone is the edema, neovascularity and inflammation
STAGING, BIOPSY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF TUMORS SCOTT D WEINER MD WHAT DO YOU DO WHEN THIS SHOWS UP IN YOUR OFFICE? besides panicking KEY PRINCIPLE!!! Reactive zone is the edema, neovascularity and inflammation
2. Assessment of interobserver variability and histological parameters to improve. central cartilaginous tumours.
 . Assessment of interobserver variability and histological parameters to improve central cartilaginous tumours. Daniel Eefting, Yvonne M. Schrage, Maartje J. Geirnaerdt, Saskia Le Cessie, Antonie H.M.
. Assessment of interobserver variability and histological parameters to improve central cartilaginous tumours. Daniel Eefting, Yvonne M. Schrage, Maartje J. Geirnaerdt, Saskia Le Cessie, Antonie H.M.
OSSEOUS INVASION IN ALVEOLAR SARCOMA OF SOFT TISSUES: A HEALING APPROACH AND LIMB-SALVAGING SURGERY. Summary
 Kovachev V. et. al. Osseous invasion in alveolar sarcoma of soft tissues: Case report OSSEOUS INVASION IN ALVEOLAR SARCOMA OF SOFT TISSUES: A HEALING APPROACH AND LIMB-SALVAGING SURGERY Vihar Ì. Kovachev,
Kovachev V. et. al. Osseous invasion in alveolar sarcoma of soft tissues: Case report OSSEOUS INVASION IN ALVEOLAR SARCOMA OF SOFT TISSUES: A HEALING APPROACH AND LIMB-SALVAGING SURGERY Vihar Ì. Kovachev,
Resection Arthrodesis of the Knee for Osteosarcoma: An Alternative When Mobile Joint Reconstruction Is Not Feasible
 Original Article 411 Resection Arthrodesis of the Knee for Osteosarcoma: An Alternative When Mobile Joint Reconstruction Is Not Feasible Hsin-Nung Shih, MD; Lih-Yuann Shih, MD Results: Background: Wide
Original Article 411 Resection Arthrodesis of the Knee for Osteosarcoma: An Alternative When Mobile Joint Reconstruction Is Not Feasible Hsin-Nung Shih, MD; Lih-Yuann Shih, MD Results: Background: Wide
Is double-approach surgery and tenodesis without a gastrocnemius flap better for
 Wan et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:65 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1364-z RESEARCH Open Access Is double-approach surgery and tenodesis without a gastrocnemius flap better for
Wan et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:65 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1364-z RESEARCH Open Access Is double-approach surgery and tenodesis without a gastrocnemius flap better for
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Bone Tumors Clues and Cues
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
Olecranon fracture. Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital
 Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE CANCER CHONDROSARCOMA. Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information
 RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE CANCER CHONDROSARCOMA Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information CONTENTS What is it? Who does it affect? Symptoms Types of Chondrosarcoma Cause and Risk
RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE CANCER CHONDROSARCOMA Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information CONTENTS What is it? Who does it affect? Symptoms Types of Chondrosarcoma Cause and Risk
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR
 OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR S G Chee, K S Lam, B K Tay, N Balachandran SYNOPSIS Operative treatment of 28 intercondylar fractures of femur were done from 98 to 985. The
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR S G Chee, K S Lam, B K Tay, N Balachandran SYNOPSIS Operative treatment of 28 intercondylar fractures of femur were done from 98 to 985. The
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
Aesculap Targon FN. Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures. Aesculap Orthopaedics
 Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Adamantinoma of the distal femur diagnosed 5 years after initial surgery: a case report
 Cao et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2016) 10:185 DOI 10.1186/s13256-016-0974-8 CASE REPORT Adamantinoma of the distal femur diagnosed 5 years after initial surgery: a case report Open Access Kai
Cao et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2016) 10:185 DOI 10.1186/s13256-016-0974-8 CASE REPORT Adamantinoma of the distal femur diagnosed 5 years after initial surgery: a case report Open Access Kai
CASE STUDY: PRO-DENSE Injectable Regenerative Graft Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor
 : PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
: PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Maquet: Maquet: Biomechanics. Maquet: /21/10. Philippe Landreau, MD
 Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
Original article. F. Gherlinzoni, P. Picci, G. Bacci & D. Campanacci
 Annals of Oncology 3 (Suppl. 2): S23-S27, 1992. 1992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Original article Limb sparing versus amputation in osteosarcoma Correlation between local control,
Annals of Oncology 3 (Suppl. 2): S23-S27, 1992. 1992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Original article Limb sparing versus amputation in osteosarcoma Correlation between local control,
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Looking for the limit of limb sparing in pelvic bone sarcomas Isidro Gracia Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, Barcelona
 Unidad de Cirugía Ortopédica Oncológica. Servicio COT Unidad Funcional de Tumores Mesenquimales Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau Barcelona Looking for the limit of limb sparing in pelvic bone sarcomas
Unidad de Cirugía Ortopédica Oncológica. Servicio COT Unidad Funcional de Tumores Mesenquimales Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau Barcelona Looking for the limit of limb sparing in pelvic bone sarcomas
