Dilip D Tanna, Sangeet Gawhale, Kaustubh Shinde, Viral Gondalia, 3 4. Hayoung Park, Ashok Shyam
|
|
|
- Conrad Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Trauma International 2017 Jan- April;3(1) :27-31 Intramedullary Fibula with Rigid Osteosynthesis in Revision of Neglected and Multiple times Operated Non Union of Long Bones Abstract Dilip D Tanna, Sangeet Gawhale, Kaustubh Shinde, Viral Gondalia, 3 4 Hayoung Park, Ashok Shyam Background: Plates with Intramedullary Fibula as Strut graft(ifsg) in Non- union of long bone fractures provides most stable construct overall as fibula acts as second implant, screws have better anchorage and very high pull out strength due to penetration of four cortices and osteogenic property of the fibula is most helpful. The aim of this paper is to re-focus the importance of non-vascularised intramedullary fibula as a second internal biologic stable splint along with rigid osteosynthesis for the treatment of difficult and neglected non -union of long bones. Methods and Material: 15 cases (13 :2,males: females) of revision surgery for the neglected and multiply operated non-union of the long bones were treated with the debridement, decortication and shingling of the fracture site with addition of the trimmed fibula (as intramedullary strut). Liberal cancellous bone graft was added subperiosteally with stable and rigid internal osteosynthesis by using LCP. DASH Score was used for upper limb and VAS for lower limb for assessment. Results: Union was achieved in all patients in 12 months (range 9-12 months). Preoperative DASH score averaged 40.86(range ). DASH score at the last follow-up averaged points (range ).difference was significant. (p=0.0001) Conclusions: Intra medullary fibula almost works mimicking double plate and adds in the stability as it works as second plate. Its osteogenic property helps in the healing, not only at the fracture site but proximal and distal to it. This prevents slow union at the ends of bone which are usually avascular because of the lysis. Screws have a better hold around osteoporotic bones due to four cortices hold in presence of fibula. Strong bony union can be successfully achieved in almost all cases with rigid compression at the fracture site & additional extensive cancellous bone grafting. Key-words: Intra- medullary Fibula,revision non union, rigid osteosynthesis Introduction Non -union, of multiple times operated long bone fractures, poses the extreme challenge to the orthopaedic surgeons. Surgical treatment of proximal humeral non unions and malunions are technically challenging. Osteosynthesis with bone grafting for the treatment of nonunions is indicated in young, active patients with adequate bone stock in the proximal fragment and preservation of the glenohumeral articular surfaces[2] Vascularised bone grafting requires surgical experience and equipment not readily available in every hospital. The technique is demanding of time and resources, and vascular thrombosis may compromise the result [5] Iliac crest cancellous bone graft has no mechanical strength to withstand stresses prior to solid union of the fracture site and also is associated with quite significant graft harvest site morbidity. The fibula transmits one eighth of body weight and can be as useful as vascularised or non-vascularised graft in reconstruction of bony defects. Compression plating with autogenous grafting is accepted as the gold standard method so has yielded satisfac tory results, with 92 to 100% healing rates Operative treatment can be very successful when the techniques of plate-and-screw fixation are modified to address osteopenia and relative or absolute loss of bone. Healing of the fracture substantially improves function and the degree of independence[6] Subjects and Methods: 15 patients of multiply operated non union of long bones (13 humerus, 1 femur and one distal tibia non union) 1 Saifee Hospital Medical research center, Mumbai, India. 2 BY L Nair medical college & hospital, Mumbai 3 Researcher Department of Orthopaedics Joint Arthritis & research Laboratory Himchan Hospital Seoul,South Korea 4 Indian Orthopaedic Research Group, Thane & Sancheti Institute of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation, Pune, India. Address of Correspondence Dr D D Tanna 3A new queens road back bay view, mama parmanand marg. Mumbai ddtanna@me.com Dr. Dileep Tanna Dr. Sangeet Gawhale Dr. Viral H Gondalia Dr. Ashok Shyam Copyright: the author(s), publisher and licensee Indian Orthopaedic Research Group Available on doi: /trauma X ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 27 Trauma International Volume 3 Issue 1 Jan-June 2017 Page 27-31
2 Figure 1: 52 years old male, who was operated 4 times within last 10 years & presented to us with this latest x rays showing atrophic gap non union of the proximal humerus were included in a study. All were treated by open reduction of the fracture, debridement and excision of the fibrosis, shingling of the bone both proximally and distal to fracture site and osteosynthesis with strut non vascularised fibular graft and Locking Compression Plate with few locking screws and rest of all are cortical screws to make it rigid and stable construct with extensive cancelleous bone grafting 360⁰ surrounding the fracture site. All patients were assessed at final follow up using D.A.S.H score for upper limb and Visual analogue score for lower limb. All patients were followed up for 4 to 36 (average mean months is 20 months) except two patient, who are under study with last two-two and half months. Out of 15 patients,13 were male and 2 were female. Out of 15, 13 patients had humerus non union,two had femoral mid shaft non union and remaining one had lower third distal tibia non union. Out of the 13 humerus cases 4 had proximal humerus, 7 had mid shaft to lower third humerus(m3-l3rd) non union & two patient has non union of segmental shaft humerus fracture. a Figure 2: Humeral Medullary canal is prepared using reamers to achieve uniform medullary cavity All were closed fractures except one open fracture and all had eventual atrophic non-union upon presentation. The patients had mild pain, tenderness and abnormal mobility at the non-union site (except distal tibia and middle femur), and limitation of activities of daily living. All patients had stiff ness of shoulder and elbow to varying degrees. The patients with femoral non unions have constant pain at the fracture site and difficulty while bearing weight. distal tibia non union patient had not started bearing weight as he was on fixator for three months following the Gun shot injury operated in other country. Surgical technique: 52 years old male, who was operated 4 times within last 10 years, presented to us with this latest x rays showing atrophic gap non union of the proximal humerus (Fig 1 A,1B) Fracture site was exposed using previous scar in all cases as to avoid cosmetic ugly scar. The fibrous non-union and any devitalised bone b a b c Figure 3: Splitting the Fibula graft using an oscillating saw d e Figure 4: Method of insertion of Intramedullary fibula into Non United Bone Proximally & Distally :Distraction at fracture site to accommodate the graft (a) and C arm picture of the same (b). Method of compression at the fracture site with fibula in situ ( c). with C arm confirmation of compression (d). plate fixation Proximally & distally with fibular Intramedullary graft plus massive cancelleous autografts (e). 28 Trauma International Volume 3 Issue 1 Jan-June 2017 Page 27-31
3 a b c d Figure 5: Two month follow up radiograph shows good alignment and union (a-b) with good clinical function (c-d) were thoroughly excised and the medullary canal opened via sharp thinner humerus awl and mm drill bits. Preparation of the medullary canal: The humeral medullary canal was prepared to accept the bone graft. Fibrous and pseu doarthrosis tissue were removed completely and the medullary cavity reconstituted both proximally and distally by curettage, drill or the use of serial hand reamers (6mm-9mm). Dilate humerus medullary cavity mainly to measure the cavity Uniformly expanded medullary cavity by the reamers was prepared to put in the graft.(fig 2a,2b) Preparation of fibular graft: The mid-shaft of the fibula was then harvested under tourniquet control with care taken to identify and protect the superficial peroneal nerve. The fibular shaft of excess length was harvested so that it could be trimmed as neces sary. The fibula graft was trimmed so as to enable it to telescope snugly into the fragments across the fracture site. Size of fibula graft will be one smaller than Last reamer used. If the thickness did not permit its use, it was conversely bevelled at one of the ends leaving behind proximal wider part in hollow cavity of proximal humerus and remaining part in the distal shaft. Generally in humerus,it necessary to split fibula in the center, with oscillating saw or reciprocating saw or large bone cutter instruments to reduce the size (Fig 3) 5. Insertion of the fibular graft: The fibular autograft was pushed into one of the fracture fragments and the exact length of graft that needed trimming was assessed. Once the final shaping of the graft was done, the fracture was reduced with the intramedullary fibular graft spanning the fracture site. Confirm it is movable in the humerus medullary cavity on both sides of fracture easily. Plate fixation: Reconfirm graft moving in canal push it up all the way proximally(fig 4 - a,b) Reduce fracture, distract slightly hold fibula end and slowly push it distally(fig 4c Compress fracture maximally and add cancellous graft after shingling (Fig 4 c & 4 d) How to achieve compression at the fracture with intramedullary graft: It is safer to do compression by Muller s device as it is applied at the end of the bone and maximum compression can be achieved by this device. If one chooses to compress by D C P holes. Fix screw on one side of fracture, and for opposite side D C P hole should be used which is not going thru the fibula, as if fibula is fixed it will not allow compression. So under C arm see the end of fibula and go beyond it to put other D C P screw and compress. Generally one hole compression is not enough in this non union set up, so it will have to be repeated also on 2nd hole. so it is suggested to use Muller s device or a webers device to do compression of the fracture. a b c d e f Figure 6: Case 2 - Pre op image of the atrophic gap non union of the humeral shaft AP and Lateral views (a,b). Intra op image showing wide gap & atrophic bony ends ( c). Harvested Autograft(Intramedullary fibula) (d). Intra operative pictures with LCP & fibula in situ (e). Final Radiograph of the patient (f). Additional BMP protein was used in this patient 29 Trauma International Volume 3 Issue 1 Jan-June 2017 Page 27-31
4 Preoperative DASH score averaged 40.86(range ). DASH score at the last follow-up averaged points (range ).(p=0.0001)[Table 1] V.A.S (visual analogue scale) in one patient was improved from 6-7 to 2 at the last follow up.[table 1] There was an average loss of abduction and flexion of the shoulder.. Range of motion of adjacent joint (knee in lower limb and elbow in upper limb) was restricted in all patients because of history of multiple surgeries and immobilization periods, but was within the functional limit in all except two patients. There was no change in shoulder rotations following surgery on the contrary three patient had pain free rotation of shoulder who had atrophic proximal humerus non union. One patient with preoperative fixed flexion deformity of elbow to varying degrees had persistence of a similar deformity at the last follow-up. Table 1: Table showing preoperative and post operative DASH Scores in all patients A LCP was used with quadricortical screw fixation till fibula is extending. Each screw hole was drilled and tapped through four cortices, two in the fractured bone and two in the intact fib ula and 4. 5 mm cortical screws were inserted. End of the bone screws were from parent bone and few locking screws were used for osteoporosis. Shoulder and elbow exercises were started a day after the opera tion. Lifting of weights using the operated limb was deferred for a period of three to four months or until osteo-integration of the fibular ends or fracture healing. After hospital discharge, patients were observed on a monthly basis until healing of the fracture. All pa tients were examined both clinically and radiologically. Fracture union was considered radiographically if callus formation was seen in three of four cortices on AP and lateral views. Clinical union was considered when the fracture site was painless. Data collected retrospectively included grip strength, range of motion, radiographic parameters, and functional outcomes as measured by the DASH (Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand) questionnaire. Results Patients were followed-up for an average of years (range 1-2 years). Union was achieved in all patients in 12 months (range9-12 months ) and patients were very satisfied with the treatment Figure 5 shows long term follow up of case 1 and figure 6 shows the results in case 2. There were no perioperative complications such as wound infection, radial nerve palsy, hematoma formation. Post op two patient had discomfort over the fibular graft harvest site, and one has ASIS graft site morbidity in the form of pain mainly. One patient has persistent fracture line visible on fresh x ray at the shaft of humerus at one year follow up, but still fracture seems to be clinically united as patient has painless arm movement. Discussion Non -union of the long bone, after repeated surgery with multiple failed attempts poses challenging reoperation. Healing is challenge & unpredicted with any kind of surgery and may have sub-optimal result. We have done 15 cases of previously operated multiple times with failed union As we have used massive mixed cortico-cancelleous auto graft in almost all cases circumferentially at the non-union site the reason why it unites in each cases is not definite what worked out of these procedure is not predictable, like shingling & solid compression at the fracture site+cancelleous autograft Vs IMSF autograft. Before we conclude, that fracture is united, we need evidence of circumferential callus formation, and osteo-integration, which takes long time, to be observed. Though patient is using arm almost normally, probably due to good long bony rigid fixation, and hence clinical signs of union are not convincing. This is observed most often in such multiple times operated cases only after 12 months and so we feel, 12 months minimum time should be considered for union. The main weakness of our study is 1. Very few number of cases(only 15 cases)-so difficult to judge trend of results 2. What exactly helped union, out of everything we did is unclear The main strength of our study: Our procedure can not only salvage the function less atrophic non united bone ----it can even have profound effect on the overall compliance of the patient, reduce repeated morbidity from the lengthy and costly treatment like ilizarov, which has frustrated outcome and at the same time gives pain free extremity function up to its fully maximum ability. We did not seen any complication like post op infection, radial nerve palsy, implant cut through, not even fracture of the fibula graft in any case. Two patient had fibula graft site pain, which subsided within 6 months and another female patient had ASIS graft site pain mainly which also settled within a year. The reason for low complications in all cases may be we were lucky. Osteoporosis, either as a result of disuse or due to generalised metabolic causes, compounds the choice of surgical treatment in these patients. It significantly reduces the pull out strength of the screws thus increasing the chance of implant failure. Humeral nonunion in osteoporotic bone presents a reconstructive challenge for the treating orthopaedic 30 Trauma International Volume 3 Issue 1 Jan-June 2017 Page 27-31
5 surgeon [3,4]. In case of non-union, mechanical stability at the fracture site and biologic re vitalization are keys for the management. A non-union of a diaphyseal fracture of the humerus can present a major functional problem even in the elderly population. Advances in operative exposures combined with newer techniques of achieving stable internal fixation even in the presence of pathologic bone have enabled the surgeon to successfully treat even the most complex non unions [7] Approximately 10% of all long-bone fractures occur in the humerus. Although primary treatment usually is successful, humeral nonunion can lead to marked morbidity and functional limitation. Complications include joint contractures of the shoulder and elbow, especially with periarticular pseudarthrosis. Marked osteopenia or bone loss, or both, often occur after fracture and after failure to achieve union. Retained implants often break, impeding fixation and requiring removal. Soft-tissue deficits and incisions from the original injury or prior surgeries also may complicate reconstruction, as can intra-articular fractures and associated nerve palsies. Successful surgical management of humeral nonunion requires stable internal fixation that allows early joint motion and uses autogenous bone graft to promote healing [8,9] DCP with cancellous bone graft is a reliable and an effective treatment for revision of aseptic nonunion of humeral shaft fracture after surgical treatment [10,11] We have used LCP in all 15 cases. References 1. Volgas DA, Stannard JP, Alonso JE. Nonunions of the humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res Feb;(419): Cheung EV, Sperling JW. Management of proximal humeral nonunions and malunions. Orthop Clin North Am Oct;39(4): Ansell RH, Scales JT. A study of some factors which affect the strength of screws and their insertions and holding power in bone. J Biomechanics 1968;1: Schatzker J, Sanderson R, Murnaghan JP. The holding power of orthopaedic screws in vivo. Clin Orthop 1975;108: Jupiter JB. Complex non-union of the humeral diaphysis: treatment with a medial approach, an anterior plate, and a vascularized fibular graft. J Bone Joint Surg Am Jun;72(5): Ring D, Perey BH, Jupiter JB. The functional outcome of operative treatment of ununited fractures of the humeral diaphysis in older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999; 81: Jupiter JB, Von Deck M. Ununited humeral diaphyses. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 1998; 7: Pugh DMW, McKee MD. Advances in the management of humeral non-union. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2003; 1: There are four main indications reported in the literature for use of LCP in fractures:1)osteoporotic bone, 2) comminution, 3) intra-articular fracture, and4) short segment periarticular fracture [12,13] Locked plates and conventional plates rely on completely different mechanical principles to provide fracture fixation and in so doing they provide different biological environments for healing. Locked plates may increasingly be indicated for indirect fracture reduction, diaphyseal/metaphyseal fractures in osteoporotic bone, bridging severely comminuted fractures, and the plating of fractures where anatomical constraints prevent plating on the tension side of the bone. Conventional plates may continue to be the fixation method of choice for periarticular fractures which demand perfect anatomical reduction and to certain types of nonunions which require increased stability for union.[14] Conclusion Non-vascularised intramedullary fibula(along with debridement, decortication & shingling ) as a second internal biologic stable splint along with rigid osteosynthesis can achieve excellent Union for treatment of revision of difficult & neglected non -union of long bones. 9. Weber BG. Minimax fracture fixation. AO Masters Series. Stuttgart: Thieme Medical Publishers, Lin CL, Fang CK, Chiu FY, Chen CM, Chen TH. Revision with dynamic compression plate and cancellous bone graft for aseptic nonunion after surgical treatment of humeral shaft fracture. J Trauma Dec;67(6): Hierholzer C, Sama D, Toro JB, Peterson M, Helfet DL. Plate fixation of ununited humeral shaft fractures: effect of type of bone graft on healing. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006; 88A: 1442-drv7 12. SmithWR, Ziran BH,Anglen JO, et al. Locking plates: tips and tricks. J Bone Joint SurgAm 2007;89(10): PMID: Wagner M. General principles for the clinical use of the LCP. Injury 2003;34 Suppl 2:B Egol KA, Kubiak EN, Fulkerson E, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ. Biomechanics of locked plates and screws. J Orthop Trauma Sep;18(8): Conflict of Interest: NIL Source of Support: NIL How to Cite this Article Tanna DD, Gawhale S, Shinde K, Gondalia V, Park H, Shyam AK. Intramedullary Fibula with Rigid Osteosynthesis in Revision of Neglected and multiple times Operated Non Union of Long Bones. Trauma International Jan - June 2017;3(1): Trauma International Volume 3 Issue 1 Jan-June 2017 Page 27-31
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus
 The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
Surgical Management of aseptic Femoral Shaft Non-union after Intramedullary Fixation
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (7), Page 4946-4950 Surgical Management of aseptic Femoral Shaft Non-union after Intramedullary Fixation Eissa Ragheb Refaie 1, Ahmed Abd El
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (7), Page 4946-4950 Surgical Management of aseptic Femoral Shaft Non-union after Intramedullary Fixation Eissa Ragheb Refaie 1, Ahmed Abd El
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article To Study the Functional Outcome of Locking Compression Plate in Metaphyseal Fractures Saraf
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article To Study the Functional Outcome of Locking Compression Plate in Metaphyseal Fractures Saraf
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture
 Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
97% UNION. Humeral Nonunions: Issues and Strategies? Disclosure. Humeral Shaft Fractures 5/3/2016. Cory Collinge, MD
 Humeral Nonunions: Issues and Strategies? Cory Collinge, MD Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN 15 minutes Disclosure Consultant Biomet Smith and Nephew Royalties Biomet Smith & Nephew Advanced Orthopedic
Humeral Nonunions: Issues and Strategies? Cory Collinge, MD Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN 15 minutes Disclosure Consultant Biomet Smith and Nephew Royalties Biomet Smith & Nephew Advanced Orthopedic
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
ICUC Paper. Variable Angle Locked Screw (VAL): from concept to application. A. Fernández Dell'Oca, P. Regazzoni, S.M. Perren.
 Variable Angle Locked Screw (VAL): from concept to application A. Fernández Dell'Oca, P. Regazzoni, S.M. Perren September 2017 Problem: Locked plate-screw constructs, a technology that improves biology
Variable Angle Locked Screw (VAL): from concept to application A. Fernández Dell'Oca, P. Regazzoni, S.M. Perren September 2017 Problem: Locked plate-screw constructs, a technology that improves biology
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons.
 Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
 LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
Of approximately 2 million long bone fractures
 Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Neurologic Damage. The most common neurologic injury following intramedullary tibial nailing is injury to the peroneal nerve.
 COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts
 Original Article 268 Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts Lin-Hsiu Weng, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: In this study,
Original Article 268 Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts Lin-Hsiu Weng, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: In this study,
Comparative Study between Locking Compression Plate vs. Supracondylar Nail for Supracondylar Femur Fractures
 Orthop. Res. Rev. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20936/orr/160103 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study between Locking Compression Plate vs. Supracondylar Nail for Supracondylar Femur Fractures Abhijeet Shroff
Orthop. Res. Rev. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20936/orr/160103 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study between Locking Compression Plate vs. Supracondylar Nail for Supracondylar Femur Fractures Abhijeet Shroff
LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate.
 Technique Guide LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction
Technique Guide LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed?
 Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed? Dr. Emil Schemitsch, MD, FRCS(C) Richard Ivey Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Western University Chief of Surgery London Health Sciences
Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed? Dr. Emil Schemitsch, MD, FRCS(C) Richard Ivey Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Western University Chief of Surgery London Health Sciences
Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Humerus shaft - Reduction & Fixation - Compression plate - AO Surgery Reference. Compression plating
 Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia
 Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
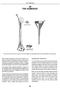 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0155-z ORIGINAL A. Megaro S. Marchesi U.E. Pazzaglia Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases Received: 5 September
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0155-z ORIGINAL A. Megaro S. Marchesi U.E. Pazzaglia Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases Received: 5 September
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS
 TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments.
 CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series
 Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual
 Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for Proximal and Distal Fractures of The Tibia: A Biological Approach
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1603.006 Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for Proximal and Distal Fractures of The Tibia: A Biological Approach Gupta P, MS Orth, Tiwari A, MS Orth, Thora A,
http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1603.006 Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for Proximal and Distal Fractures of The Tibia: A Biological Approach Gupta P, MS Orth, Tiwari A, MS Orth, Thora A,
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus
Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal Fixation in Tibial Plateau Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2015), PP 50-54 www.iosrjournals.org Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2015), PP 50-54 www.iosrjournals.org Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Management of Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5
 Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function
 Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function Fracture specific plating solutions for the most common tibia and fibula fractures Frequency of fracture occurrences* 66% 61% 36% 36% 28% 14% 20%
Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function Fracture specific plating solutions for the most common tibia and fibula fractures Frequency of fracture occurrences* 66% 61% 36% 36% 28% 14% 20%
E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct
 Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Technique Guide. LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
LCP Distal Humerus Plates
 The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Bone transport for the management of severely comminuted fractures without bone loss
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2016) 11:19 24 DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0241-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone transport for the management of severely comminuted fractures without bone loss Mootaz F. Thakeb 1 Mahmoud A.
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2016) 11:19 24 DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0241-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone transport for the management of severely comminuted fractures without bone loss Mootaz F. Thakeb 1 Mahmoud A.
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
GAMMA LOCKING NAIL INSTRUMENTS OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE
 GAMMA LOCKING NAIL INSTRUMENTS OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE FEATURES AND BENEFITS The One Shot Device is a new component of the Gamma Locking Nail instrumentation system determining the correct position of the
GAMMA LOCKING NAIL INSTRUMENTS OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE FEATURES AND BENEFITS The One Shot Device is a new component of the Gamma Locking Nail instrumentation system determining the correct position of the
Calcium Phosphate Cement
 Calcium Phosphate Cement Fast-Setting Bone Graft and AutoGraft Extender. * Ossilix is a high performance next generation calcium phosphate cement indicated for filling bony defects in cancellous bone.
Calcium Phosphate Cement Fast-Setting Bone Graft and AutoGraft Extender. * Ossilix is a high performance next generation calcium phosphate cement indicated for filling bony defects in cancellous bone.
Non-Anatomical Surgical Solutions for Difficult Non-Unions: Case Series
 KOWSAR Non-Anatomical Surgical Solutions for Difficult Non-Unions: Case Series Galal Zaki Said 1, *, Osama Ahmed Farouk 1, Hatem Galal Said 1, Mohamed Mostafa Mohamed El-Sharkawi 1 1 Department of Orthopedic
KOWSAR Non-Anatomical Surgical Solutions for Difficult Non-Unions: Case Series Galal Zaki Said 1, *, Osama Ahmed Farouk 1, Hatem Galal Said 1, Mohamed Mostafa Mohamed El-Sharkawi 1 1 Department of Orthopedic
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Locked Plating: Clinical Indications
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
LCP Distal Tibia Plate
 Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
CiSE. PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Humerus through an Anterolateral Approach. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Surgical Technique. Targeter Systems Overview
 Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Bipolar Radial Head System
 Bipolar Radial Head System Katalyst Surgical Technique DESCRIPTION The Katalyst Telescoping Bipolar Radial Head implant restores the support and bearing surface of the radial head in the face of fracture,
Bipolar Radial Head System Katalyst Surgical Technique DESCRIPTION The Katalyst Telescoping Bipolar Radial Head implant restores the support and bearing surface of the radial head in the face of fracture,
AO / Synthes Proximal Posterior Medial Tibia Plate. Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis
 Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis Articular Fractures Osteosynthesis Characteristics of the LCP system LCP 3.5 system LCP 4.5 system Many different traditional plates (small, large) Lag screws Rafting
Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis Articular Fractures Osteosynthesis Characteristics of the LCP system LCP 3.5 system LCP 4.5 system Many different traditional plates (small, large) Lag screws Rafting
Infected forearm nonunion treated by bone transport after debridement
 Liu et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:273 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Infected forearm nonunion treated by bone transport after debridement Tang Liu 1, Zhenyang Liu 2,3, Lin Ling 1* and Xiangsheng
Liu et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:273 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Infected forearm nonunion treated by bone transport after debridement Tang Liu 1, Zhenyang Liu 2,3, Lin Ling 1* and Xiangsheng
Lengthening & Deformity correction with. Fixator Assisted Nailing
 Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. INTER TROCHANTERIC # NECK FEMUR FIXATION WITH TFN 250 CASES. Prasad Vijaykumar Joshi, Chandrashekar Yadav.
 INTER TROCHANTERIC # NECK FEMUR FIXATION WITH TFN 250 CASES. Prasad Vijaykumar Joshi, Chandrashekar Yadav. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, Joshi Hospital Pvt. Ltd. Phaltan, Maharashtra.
INTER TROCHANTERIC # NECK FEMUR FIXATION WITH TFN 250 CASES. Prasad Vijaykumar Joshi, Chandrashekar Yadav. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, Joshi Hospital Pvt. Ltd. Phaltan, Maharashtra.
Surgical Technique. Distal Humerus Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA. Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System
 Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System Installing the PANTERA is a 4-Step Process: The following technique is designed to optimize the surgical exercise. Step
Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System Installing the PANTERA is a 4-Step Process: The following technique is designed to optimize the surgical exercise. Step
Technique Guide. LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
TheUseofaFreeFibularStrutasa Biological Intramedullary Nail for the Treatment of Complex Nonunion of Long Bones
 TheUseofaFreeFibularStrutasa Biological Intramedullary Nail for the Treatment of Complex Nonunion of Long Bones Surender Singh Yadav, MS(Ortho), FAMS, DLitt Investigation performed at Mirpur Institute
TheUseofaFreeFibularStrutasa Biological Intramedullary Nail for the Treatment of Complex Nonunion of Long Bones Surender Singh Yadav, MS(Ortho), FAMS, DLitt Investigation performed at Mirpur Institute
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Technique Guide. PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 08 Page August 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.08 Study of Functional and Radiological Outcome
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.08 Study of Functional and Radiological Outcome
A study of MIPO by locking compression plate fixation in the management of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Venkateswarlu K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Mar;3(3):675-679 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20150328
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Venkateswarlu K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Mar;3(3):675-679 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20150328
