Distal femoral reconstruction following failed total knee arthroplasty is accompanied with risk for complication and reduced joint function
|
|
|
- Suzanna Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 RESEARCH ARTICLE Distal femoral reconstruction following failed total knee arthroplasty is accompanied with risk for complication and reduced joint function Klemens Vertesich, Stephan E. Puchner, Kevin Staats, Markus Schreiner, Christian Hipfl, Bernd Kubista, Johannes Holinka and Reinhard Windhager * Open Access Abstract Background: Substantial bone loss following failed total knee arthroplasty (TKA) represents a major challenge in revision arthroplasty, that can require distal femoral reconstruction (DFR). In this study, we aimed to assess the clinical outcome and the complication frequencies of individuals who underwent DFR with modular megaprostheses. Additionally, we aimed to compare functional outcome measures after DFR in these sophisticated cases to an age-matched control group of total knee prostheses to quantify the potential loss of function. Methods: A retrospective chart review of 30 consecutive patients after DFR from 1997 to 2017 with a mean age of years (± 10.1) was performed. Complications were classified according to the Henderson classification. Knee Society Score (KSS) was calculated and range of motion (ROM) was assessed. Results: Thirteen (43.3%) patients had at least one complication requiring revision surgery. Revision-free survival was 74.8% at one year, 62.5% at three and 40.9% at 10 years post-op. Soft-tissue failure complications were found in three (10.0%) patients, aseptic loosening in four (13.3%) patients, structural failure in one (3.3%) patient and infection in eight (26.6%) patients. Of those with infection, five (16.6%) experienced ongoing prosthetic joint infection and three (10.0%) developed new infection after distal femur reconstruction. Patients with DFR achieved 69.3% of KSS pain score, 23.1% KSS function score and 76.2% of ROM compared to patients with primary TKA. Conclusions: DFR after failed TKA represents a treatment procedure with high risk for complication in this particular group. Despite the prospect of rapid postoperative mobilization, reduced functionality, range of motion and mobilization have to be considered when choosing this treatment option. Keywords: Megaprosthesis, Distal femoral reconstruction, Total knee arthroplasty, Complication, Revision Background Revision surgery is a major issue in arthroplasty. By the year 2030, the annual number of revision total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is expected to triple [1, 2]. Patients with consecutive and/or multiple failed TKA frequently present with high-grade bone loss [3, 4]. This often limits options to restore joint function or salvage limbs and requires the use of special prostheses [5, 6]. * Correspondence: reinhard.windhager@akhwien.at; reinhard.windhager@meduniwien.ac.at Department of Orthopedics and Trauma-Surgery, Medical University of Vienna, Waehringer Guertel 18-20, 1090 Vienna, Austria Modular prostheses of the distal femur were initially developed for the treatment of patients who required substantial resection of the bone due to bone or soft-tissue tumors [7]. These devices are a promising alternative that could result in restoration of joint function, rapid recovery and, in extreme cases, avoid amputation [8]. Improvement of prosthetic design and biomechanics lead to enhanced functionality, motion and mobilization [9, 10]. Further, development of fixation techniques of these devices lead to improved prosthetic survival rates and reduction of revision surgeries in the group of oncologic patients [8, 11]. The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 Page 2 of 8 Individuals that have multiple complications following revision surgery often have substantial bone loss. Those individuals with periprosthetic fractures and insufficient bone healing [4, 12 14] or complex periprosthetic joint infection with consecutive reinfection may have substantial bone damage of the distal femur [15, 16]. In such cases, conventional arthroplastic and osteosynthetic methods are not sufficient for reconstruction and resection prostheses are required to restore joint function [16]. Although these prostheses promise better outcomes (more rapid mobilization and increased joint function) [17], patients face a greater risk of complications as well as potentially reduced joint functionality [16, 18]. In this study, we assessed the complication, risk, and prostheses survival frequencies of a population that underwent distal femoral reconstruction (DFR) due to substantial bone loss. Additionally, we aimed to quantify the functionality and mobilization in these patients compared to an age-matched control group of patients, who underwent primary total knee arthroplasty. Methods This is a retrospective chart review of arthroplasty and reconstruction surgeries at the Medical University of Vienna approved by its Institutional Ethical Review Board. Thirty consecutive patients who underwent reconstruction of the distal femur after failed TKA between January 1997 and December 2017 were identified. The average age of the patients at the time of DFR was years (± 10,11). There were 28 female (93.3%) and 2 male (6.7%) patients (Table 1). All DFR-procedures were performed using the Kotz Modular Femur and Tibia Reconstruction System (KMFTR, Howmedica GmbH, Kiel, Germany) in 6 (20.0%) cases, the Howmedica Modular Reconstruction System (HMRS, Howmedica GmbH, Kiel, Germany) in 3 (10.0%) cases. The Global Modular Replacement System (GMRS, Stryker Corporation, Mahwah, NJ) was used in 21 (70.0%) patients (Figs. 1 and 2). Preoperatively radiographs in two plans as well as standing entire limb radiographs have been taken. Resection length of the femur and consecutive reconstruction was chosen to be as short as possible to provide a maximum of functionality. During the procedures, intraoperative fluoroscopy was used to control the resection length and osteotomy as well as the process of reaming for final stem implantation. Due to poor bone quality, cemented fixation of stems was used in these cases. Follow-up examinations were performed 6 weeks, 6 months and then annually after surgery, respectively. During the follow-up clinical joint assessment, functional scoring and radiographic imaging were performed. Function and pain were recorded using the Knee Society Scoring System (KSS) and range of motion (ROM) was also assessed. Complications of modular megaprostheses were classified as Type I (soft-tissue failure), Type II (aseptic loosening), Type III (structural failure including periprosthetic fracture and breaking of prosthetic parts), and Type IV (prosthetic joint infection), according to the Failure Mode Classification System [19]. Type V classification, progression of tumor, was not represented in the study population. Individuals that underwent DFR after failed TKA were matched for age (± 12 months) gender and age at surgery (± 12 months) with control subjects that underwent primary TKA at our hospital (Table 1). Functional scoring and range of motion of the control group and the distal femur reconstruction group were compared to assess the difference in outcomes and the degree of potential loss of joint function in the distal femoral reconstruction group. The mean follow-up was ± months (range, one to 240). The follow-up from the index or primary procedure was ± months and the mean time after primary TKA to DFR was ± months. Two patients died during the period of postoperative hospitalization on conditions not related to the disease (after 0.7 and 2 months). Initially, all individuals in the study population underwent TKA in an attempt to alleviate the symptoms and complications of osteoarthritis. The mean number of prior revision surgeries of the index joint was 3.17 ± 2.17 (range one to 10). The indications for DFR were periprosthetic fracture in 13 (43.3%) cases, non-union or aseptic loosening of prosthetic or osteosynthetic devices in 8 (26.7%) Table 1 Demographics of patient and control group included in this study Demographic Variable Distal Femoral Reconstruction Control (Total Knee Arthroplasty) Included N =30 N =30 Sex Female = 28 (93.3%) Female = 28 (93.3%) Male = 2 (6.7%) Male = 2 (6.7%) Age years (±10,11) 73.0 years (±11.51) p =.595 Follow-up months (±58.67) months (±47.57) p =.409
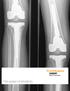
3 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 Page 3 of 8 Fig. 2 a Anteroposterior radiograph of a 72-year old female patient with arthrodesis and antibiotic bone cement spacer due to prosthetic joint infection after TKA; b Postoperative radiograph after DFR with a modular distal femoral GMRS Fig. 1 a, b Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of an 81-year old female patient with severe periprosthetic fracture of the distal femur after trauma; c, d Anteroposterior and lateral radiograph of the same patient 4 months after consecutive reconstruction of the distal femur cases, and periprosthetic joint infection in 9 (30.0%) cases. In these cases, patients were treated with two-stage revision and appropriate antibiotic therapy. DFR was performed if infection could be ruled out in preoperative and perioperative tests. Statistics Descriptive statistics were used to describe frequencies, means and ranges of complications as well as odds ratio and relative risks in infectious patients. Revision- and complication-free survival was detected using Kaplan- Meier estimating method. Comparative analyses of functional outcome were performed by using the independent t-test for continuous variables or Mann Whitney U Test for non-parametric variables, prior to being tested for normality by Kolmogorov Smirnov test. Further, comparison of the functional scores was assessed using ANOVA within the DFR group. Additionally, regression analyses were performed to assess the correlation between the length of femoral reconstruction and outcome measurements. Statistical significance was identified as a p-value of less than Statistics were performed using SPSS v24.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Results After DFR, additional revision surgery was performed on 13 (43.3%) patients after a mean period of months (range 2 weeks to 138 months). Nine (30.0%) patients had to undergo multiple revisions. Overall, revision-free survival estimation was 74.8% at 1 year, 62.5% at three and 40.9% at 10 years, respectively (Fig. 3). Type I complications were observed in three (10.0%) patients. These patients had recurrent patella dislocation and insufficiency or rupture of the extensor mechanism, and therefore underwent revision surgery (Fig. 4). Four (13.3%) patients presented with Type II complications, three of which had aseptic loosening of the femoral stem and one had loosening of the tibial component. Revision surgery was sufficient in all four of these cases (Fig. 4). One (3.3%) patient suffered from a Type III complication and underwent revision surgery due to fracture of the hinge mechanism of the prosthesis (Fig. 4). Eight (26.6%) patients suffered from Type IV complication, five of which had recurrent infection and
4 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 Page 4 of 8 Fig. 3 Kaplan-Meier estimation of survival of the entire distal femoral reconstruction group providing the overall survival underwent DFR after eradication of periprosthetic joint infection of the primary prosthesis. The remaining three patients developed Type IV complication without prior infection. Based on these findings, the odds ratio was (CI , p =.078). The relative risk for revision due to reinfection was 3.33 (CI , p =.056) if an individual previously had periprosthetic joint infection. Revision surgery and eradication of infection was sufficient in three individuals, who did not suffer from infection of the primary implant. One patient was treated with distal femoral reconstruction. Four patients had to undergo transfemoral amputation due to Fig. 4 Survival using the Kaplan-Meier method separated by type of complication, Type I Soft-tissue failure, Type II Aseptic loosening, Type III Structural failure
5 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 Page 5 of 8 disease progression and additional complications. All individuals had infection of the initial joint reconstruction. The estimated revision-free survival for patients without a prior infection was 89.5% after 10 years compared to 40.0% after 10 years for patients with a previous infection, respectively (Fig. 5). The mean post-operative KSS pain and function scores for the DFR group were ± (range 0 95) and ± (range 0 55), respectively. The mean range of motion was 82 ±16.57 (range ). Statistical analyses showed no significance in the functional outcome (ANOVA p > 0.05) (Table 2). Compared to the control group (KSS pain ± 3.78, KSS function ± 7.25, ROM 108 ±11.27), mean values after distal femur reconstruction were significantly lower (p < 0.01). After distal femoral reconstruction, individuals achieved 69.3% of KSS pain score (p < 0.001) and 23.1% KSS function score (p < 0.001). Patients with DFR achieved 76.2% of ROM compared to primary TKA (p < 0.001) (Fig. 6). The mean length of femoral reconstruction was cm (± 6.73). Regression analysis showed no significant correlation between the occurrence of any complications and the length of femoral reconstruction (p = 0.463). Further, regression analyses comparing the length of femoral reconstruction to KSS pain and functional scores indicated slightly inferior results for patients with increased reconstruction length yet results did not show a statistical significance (ANOVA reconstruction length and KSS pain: p = 0.184; ANOVA reconstruction length and KSS function p = 297) (Fig. 7). Discussion High-grade failure following TKA represents a defiant condition of which both orthopedic surgeons and patients need to be aware. Once instability is present due to fundamental loss of bone substance, treatment options are limited [16, 20]. DFR constitutes a promising method to provide mobility, joint function and limb salvage [4]. Despite to auspicious results, literature describes distal femoral reconstruction to be associated with a distinct risk of complications and revision surgery [21]. We, therefore, aimed to assess the survival and complication frequencies after DFR in patients suffering from failed TKA. We also assessed the joint function of these patients and their function relative to a matched patient group after primary TKA. The overall estimated survival rates of our study cohort were slightly lower, when compared to previously published studies, which observed survival rates of 80 to 40% after 10 years [9, 10, 12, 22 25]. Consistent in current literature is, however, the focus on the poor revision-free survival after DFR in non-oncological patients [22, 24]. A major issue in retrospective analyses is the limited comparability of data. There is a lack of consistency in defining revision and complication types in comparable studies, as many studies do not explicitly state which classification scheme has been used. Therefore, we decided to use a standardized classification for failure of modular megaprostheses provided by Henderson et al. to ensure the comparability of our findings [19]. Fig. 5 Survival estimation with Kaplan-Meier method for individuals after DFR with prior periprosthetic infection after knee prosthesis and without prior periprosthetic infection
6 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 Page 6 of 8 Table 2 Knee Society Score (KSS) and range of motion (ROM) of patients after distal femoral reconstruction separated by complication. There was no significant difference when comparing each complication type with the no complications group KSS pain KSS function ROM Mean (SD) p Mean (SD) p Mean (SD) p No complication (N = 17) (22.34) (20.39) 85 (17.50) Complication (N = 13) (21.98) (17.97) (14.80).616 Type I (N = 3) (7.94) (7.64) (12.58).562 Type II (N = 4) (10.79) (19.31) (8.16).110 Type III (N = 1) ( ) ( ) ( ).196 Type IV (N = 8) (26.33) (17.88) (17.6).805 (SD Standard deviation) The reliability of DFR represents a problem that is apparent in this study. Initially, these special prostheses were developed for patients who required substantial bone resection due to malignant diseases [8]. Compared to complication rates described in these populations, complication rates in our study population were observed to be higher [7, 11, 26]. Soft tissue and vascularity damage potentially caused by prior procedures may not be present in patients requiring DFR as primary procedure. Furthermore, bone biology in the comparably younger group of tumor patients may provide a superior environment for osseointegration, as current research describes the issue of general age-related loss of bone as a limitation for osseointegration [27 29]. The problem of advanced age and the accompanied change in bone formation may be reasons for the high rates of aseptic loosening in older individuals. Prosthetic joint infection is a major problem with severe impact on prosthetic survival. The use of megaprostheses is associated with an increased risk for infection [6]. Generally large metal surfaces provide an environment for potential colonization of microorganisms [30 32]. Prior failed two-stage revision is also a potential risk factor for reinfection [33]. Our findings indicate that the frequency of prosthetic joint infection is higher in the group, which developed infection of the primary device and had DFR after eradication of infection. Further, the estimated survival rates describe different trends for the two separated infection groups. A poor survival of 40% in the group of individuals who had infection of the primary prostheses was assessed. Additionally, these patients had two re-revisions after DFR and required total femoral reconstruction in one case and amputation in four cases. In contrast, the infection free survival for individuals without prior infection of the artificial knee joint was 89.5% after 10 years. Generally, the management of periprosthetic joint infection is constantly evolving. Research revealed that surgical intervention with debridement and targeted antibiotic treatment is crucial for the success of intervention [34, 35]. Current recommendations for treatment suggest the two-stage exchange as algorithm of Fig. 6 Functional results of the distal femoral reconstruction group (DFR) in comparison with the results of the control group. DFR group had significantly lower KSS scores and ROM than the control group (p < 0.001)
7 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 Page 7 of 8 Fig. 7 Regression analyses indicate a correlation between resection length and KSS outcome measurements but statistical significance was not shown choice [36], which was utilized in the study population. Concluding on these findings, sufficient treatment of periprosthetic joint infection after DFR can be achieved in those individuals who had no infection of the primary prostheses. The risk for re-revision is elevated and the revision-free outcome after DFR is inferior for individuals who suffered already from an infected primary implant. Decision making should take prior infection into account, due to the high risk for following infections and complications and the limited treatment options and poor results after multiple reinfections [33]. Limb salvage and preservation of joint function and the prospect for rapid mobilization are the major advantages of distal femoral reconstruction for patients that have previously undergone total knee arthroplasty. This may be especially true for older patients or those with reduced physical conditions who may be mobilized sooner when the limb is preserved [17, 37]. Joint functionality after DFR in individuals with multiple revisions is expected to be at an acceptable level [9, 10, 15, 23]. Our results confirm these findings. Furthermore, the complication type did not significantly affect joint function (evaluated by KSS score) or the range of motion (Table 2). However, when comparing the DFR group with matched controls, functional results were significantly inferior in the DFR group. In most cases, mobilization was possible with crutches or with a walking frame, which is expressed as reaching just 23% of KSS functional score in the distal femoral reconstruction group. This study has several shortcomings. Due to the retrospective character and the long observational period of two decades, surgical methods, prosthetic material and especially recommendations in the treatment of periprosthetic infection have changed over the study period. Additionally, comorbidities, that might influence the outcome of these individuals were not included due to inconsistent records. The vast majority of individuals included in the DFR group had their index procedure at external institutions and were transferred to our institution for further treatment and care. Due to that, records of joint function prior to the index procedure were not consistently accessible and not included in the analysis. Furthermore, due to the small study population, extrapolation of our results is limited. However, our sample size is similar to other studies on this particular topic [9, 10, 15, 18]. Conclusion Our findings show that distal femoral reconstruction after severely failed total knee arthroplasty is a procedure with high risk for complication especially when individuals have suffered from prosthetic joint infection of the primary implant. Despite the potential positive outcomes promised by this treatment, it is imperative that the possibility of serious complications (reduced functionality, decreased range of motion and limited mobilization) are considered during the decision-making process in such cases. Abbreviations DFR: Distal femoral reconstruction; KSS: Knee Society Score; ROM: Range of motion; TKA: Total knee arthroplasty Acknowledgements Not applicable. Funding There has been no specific funding for the implementation of this study. Availability of data and materials The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors contributions KV, SP, KS, MS, CH, BK, JH and RW made substantial contributions to conception and study design. KV, SP, KS and MS made substantial contributions in acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. RW, BK and JH have been involved in revising the manuscript critically for important
8 Vertesich et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:47 Page 8 of 8 intellectual content. All authors have given their final approval of the version to be published. All authors agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Ethics approval and consent to participate The implementation of this study, with the protocol number 2019/2016, was approved by the institutional ethics committee of the Medical University of Vienna. Due to the retrospective character of the study a consent to participated was not required according to the decision of the ethics committee. Consent for publication Not applicable. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Received: 19 November 2018 Accepted: 22 January 2019 References 1. Patel A, Pavlou G, Mujica-Mota RE, Toms AD. The epidemiology of revision total knee and hip arthroplasty in England and Wales: a comparative analysis with projections for the United States. A study using the National Joint Registry dataset. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(8): Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4): Harrison RJ Jr, Thacker MM, Pitcher JD, Temple HT, Scully SP. Distal femur replacement is useful in complex total knee arthroplasty revisions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;446: Windhager R, Schreiner M, Staats K, Apprich S. Megaprostheses in the treatment of periprosthetic fractures of the knee joint: indication, technique, results and review of literature. Int Orthop. 2016;40(5): Nelson CL, Gioe TJ, Cheng EY, Thompson RC Jr. Implant selection in revision total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(Suppl 1):S Pour AE, Parvizi J, Slenker N, Purtill JJ, Sharkey PF. Rotating hinged total knee replacement: use with caution. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(8): Choong PFM, Sim FH, Pritchard DJ, Rock MG, Chao EYS. Megaprostheses after resection of distal femoral tumors: a rotating hinge design in 30 patients followed for 2-7 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2009;67(4): Kotz R, Dominkus M, Zettl T, Ritschl P, Windhager R, Gadner H, Zielinski C, Salzer-Kuntschik M. Advances in bone tumour treatment in 30 years with respect to survival and limb salvage. A single institution experience. Int Orthop. 2002;26(4): Springer BD, Sim FH, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG. The modular segmental kinematic rotating hinge for nonneoplastic limb salvage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;421: Springer BD, Hanssen AD, Sim FH, Lewallen DG. The kinematic rotating hinge prosthesis for complex knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 392: Mittermayer F, Windhager R, Dominkus M, Krepler P, Schwameis E, Sluga M, Kotz R, Strasser G. Revision of the Kotz type of tumour endoprosthesis for the lower limb. J Bone Jt Surg British Vol. 2002;84(3): Appleton P, Moran M, Houshian S, Robinson CM. Distal femoral fractures treated by hinged total knee replacement in elderly patients. J Bone Jt Surg British Vol. 2006;88(8): Backstein D, Safir O, Gross A. Periprosthetic fractures of the knee. J Arthroplast. 2007;22(4 Suppl 1): Cannon SR. The use of megaprosthesis in the treatment of periprosthetic knee fractures. Int Orthop. 2015;39(10): Holl S, Schlomberg A, Gosheger G, Dieckmann R, Streitbuerger A, Schulz D, Hardes J. Distal femur and proximal tibia replacement with megaprosthesis in revision knee arthroplasty: a limb-saving procedure. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12): Shen C, Lichstein PM, Austin MS, Sharkey PF, Parvizi J. Revision knee arthroplasty for bone loss: choosing the right degree of constraint. J Arthroplast. 2014;29(1): Bernthal NM, Greenberg M, Heberer K, Eckardt JJ, Fowler EG. What are the functional outcomes of endoprosthestic reconstructions after tumor resection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(3): Haidukewych GJ, Springer BD, Jacofsky DJ, Berry DJ. Total knee arthroplasty for salvage of failed internal fixation or nonunion of the distal femur. J Arthroplast. 2005;20(3): Henderson ER, Groundland JS, Pala E, Dennis JA, Wooten R, Cheong D, Windhager R, Kotz RI, Mercuri M, Funovics PT, et al. Failure mode classification for tumor endoprostheses: retrospective review of five institutions and a literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(5): Pradhan NR, Bale L, Kay P, Porter ML. Salvage revision total knee replacement using the Endo-model rotating hinge prosthesis. Knee. 2004; 11(6): Toepfer A, Harrasser N, Petzschner I, Pohlig F, Lenze U, Gerdesmeyer L, Pforringer D, Toepfer M, Beirer M, Cronlein M, et al. Short- to long-term follow-up of total femoral replacement in non-oncologic patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1): Berend KR, Lombardi AV Jr. Distal femoral replacement in nontumor cases with severe bone loss and instability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(2): Molenaers B, Arnout N, Bellemans J. Complex total knee arthroplasty using resection prostheses at mid-term follow-up. Knee. 2012;19(5): Utting MR, Newman JH. Customised hinged knee replacements as a salvage procedure for failed total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2004;11(6): McLean AL, Patton JT, Moran M. Femoral replacement for salvage of periprosthetic fracture around a total hip replacement. Injury. 2012;43(7): Pala E, Trovarelli G, Angelini A, Ruggieri P. Distal femur reconstruction with modular tumour prostheses: a single institution analysis of implant survival comparing fixed versus rotating hinge knee prostheses. Int Orthop. 2016; 40(10): Khosla S. Pathogenesis of age-related bone loss in humans. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013;68(10): Seeman E. Age- and menopause-related bone loss compromise cortical and trabecular microstructure. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013;68(10): Piarulli G, Rossi A, Zatti G. Osseointegration in the elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2013;25(Suppl 1):S Gristina AG. Biomaterial-centered infection: microbial adhesion versus tissue integration. Science (New York, NY). 1987;237(4822): Arciola CR, Campoccia D, Speziale P, Montanaro L, Costerton JW. Biofilm formation in Staphylococcus implant infections. A review of molecular mechanisms and implications for biofilm-resistant materials. Biomaterials. 2012;33(26): Puchner SE, Doring K, Staats K, Bohler C, Lass R, Hirschl AM, Presterl E, Windhager R, Holinka J. Sonication culture improves microbiological diagnosis of modular megaprostheses. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(7): Epub 2016 Sep Staats K, Boehler C, Frenzel S, Puchner SE, Holinka J, Windhager R. Failed two-stage exchange: factors leading to unachievable Endoprosthetic reconstruction after multiple revision surgeries. J Arthroplast. 2018;33(1): Zimmerli W, Ochsner PE. Management of infection associated with prosthetic joints. Infection. 2003;31(2): Zimmerli W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implantassociated infection. J Intern Med. 2014;276(2): Parvizi J, Adeli B, Zmistowski B, Restrepo C, Greenwald AS. Management of periprosthetic joint infection: the current knowledge: AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(14):e Lopresti M, Daolio PA, Rancati JM, Ligabue N, Andreolli A, Panella L. Rehabilitation of a patient receiving a large-resection hip prosthesis because of a Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor. Clin Pract. 2015;5(4):814.
Functional Outcome Study of Mega-Endoprosthetic Reconstruction in Limbs With Bone Tumour Surgery
 192 Original Article Functional Outcome Study of Mega-Endoprosthetic Reconstruction in Limbs With Bone Tumour Surgery Peh Khee Tan, 1 MBBS, MRCS (Edin), MMed (Orthop), Mann Hong Tan, 1 MBBS, FRCS (Edin
192 Original Article Functional Outcome Study of Mega-Endoprosthetic Reconstruction in Limbs With Bone Tumour Surgery Peh Khee Tan, 1 MBBS, MRCS (Edin), MMed (Orthop), Mann Hong Tan, 1 MBBS, FRCS (Edin
Distal femoral replacement with the MML system: a single center experience with an average follow-up of 86 months
 Toepfer et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:206 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1570-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Distal femoral replacement with the MML system: a single center experience with an average follow-up
Toepfer et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:206 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1570-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Distal femoral replacement with the MML system: a single center experience with an average follow-up
Clinical Study Distal Femur Allograft Prosthetic Composite Reconstruction for Short Proximal Femur Segments following Tumor Resection
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 397456, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/397456 Clinical Study Distal Femur Allograft Prosthetic Composite Reconstruction for Short Proximal Femur
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 397456, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/397456 Clinical Study Distal Femur Allograft Prosthetic Composite Reconstruction for Short Proximal Femur
Case Report StructuralFailureofaModernKneeTumorMegaendoprosthesis
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 2429459, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2429459 Case Report StructuralFailureofaModernKneeTumorMegaendoprosthesis Katrin Koch, 1 Dieter
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 2429459, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2429459 Case Report StructuralFailureofaModernKneeTumorMegaendoprosthesis Katrin Koch, 1 Dieter
Survival of Modern Knee Megaprosthesis USA/Canada
 Survival of Modern Knee Megaprosthesis USA/Canada Arthroplasty Disaster Conference Miami September 2016 Anna A. Kulidjian MD, MSc, FRCSC Chief, MSK Oncology & Joint Reconstruction UC San Diego Health Moores
Survival of Modern Knee Megaprosthesis USA/Canada Arthroplasty Disaster Conference Miami September 2016 Anna A. Kulidjian MD, MSc, FRCSC Chief, MSK Oncology & Joint Reconstruction UC San Diego Health Moores
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Periprosthetic joint infection: are patients with multiple prosthetic joints at risk?
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Rothman Institute Rothman Institute 6-1-2012 Periprosthetic joint infection: are patients with multiple prosthetic joints at risk? S Mehdi Jafari The
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Rothman Institute Rothman Institute 6-1-2012 Periprosthetic joint infection: are patients with multiple prosthetic joints at risk? S Mehdi Jafari The
Mid-term results of rotating hinge knee prostheses
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 61-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Mid-term results of rotating hinge knee prostheses Ashok RAJGOpAl, Attique VASDEV, Asit S. CHIDGUpKAR, Vivek DAHIyA, Vipin C. TyAGI From the Medanta Bone
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 61-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Mid-term results of rotating hinge knee prostheses Ashok RAJGOpAl, Attique VASDEV, Asit S. CHIDGUpKAR, Vivek DAHIyA, Vipin C. TyAGI From the Medanta Bone
Outcome of revision total knee arthroplasty with bone allograft in 30 cases
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 427-434 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of revision total knee arthroplasty with bone allograft in 30 cases Katrina F. Franke, Iulian Nusem, Gaugin Gamboa, David A.F. Morgan From Queensland
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 427-434 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of revision total knee arthroplasty with bone allograft in 30 cases Katrina F. Franke, Iulian Nusem, Gaugin Gamboa, David A.F. Morgan From Queensland
Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Metaphyseal Sleeves at Short-term Follow-up
 Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Metaphyseal Sleeves at Short-term Follow-up Ronald Huang, MD; Gustavo Barrazueta, BS; Alvin Ong, MD; Fabio Orozco, MD; Mehdi Jafari, MD; Catelyn Coyle, BS; Matthew
Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Metaphyseal Sleeves at Short-term Follow-up Ronald Huang, MD; Gustavo Barrazueta, BS; Alvin Ong, MD; Fabio Orozco, MD; Mehdi Jafari, MD; Catelyn Coyle, BS; Matthew
Zimmer Segmental System
 Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page 1599-1603 Elsherbiny Ali Elsherbiny *, Ismail Ahmed Yaseen *, and Hisham Mohamed Safwat * Department of Orthopedic surgery, Faculty
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (7), Page 1599-1603 Elsherbiny Ali Elsherbiny *, Ismail Ahmed Yaseen *, and Hisham Mohamed Safwat * Department of Orthopedic surgery, Faculty
Custom Total Femur Spacer and Second-Stage Total Femur Arthroplasty as a Novel Approach to Infection and Periprosthetic Fracture
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 5 2008 Case Report Custom Total Femur Spacer and Second-Stage Total Femur Arthroplasty as a Novel Approach to Infection and Periprosthetic Fracture Seth L. Sherman,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 5 2008 Case Report Custom Total Femur Spacer and Second-Stage Total Femur Arthroplasty as a Novel Approach to Infection and Periprosthetic Fracture Seth L. Sherman,
Medium- to Long-term Results of Strut Allografts Treating Periprosthetic Bone Defects
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.23 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Medium- to Long-term Results of Strut Allografts Treating Periprosthetic Bone Defects Jun Sung Park,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.23 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Medium- to Long-term Results of Strut Allografts Treating Periprosthetic Bone Defects Jun Sung Park,
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Rotating Hinge Knee versus Constrained Condylar Knee in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty : A meta-analysis
 Rotating Hinge Knee versus Constrained Condylar Knee in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty : A meta-analysis Jung-Ro Yoon M.D 1., In-Wook Seo M.D 1., Young-Soo Shin M.D 2. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Rotating Hinge Knee versus Constrained Condylar Knee in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty : A meta-analysis Jung-Ro Yoon M.D 1., In-Wook Seo M.D 1., Young-Soo Shin M.D 2. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
European Journal of Medical Research. Open Access RESEARCH
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-018-0302-4 European Journal of Medical Research RESEARCH Is total femoral replacement for non oncologic and oncologic indications a safe procedure in limb preservation surgery?
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-018-0302-4 European Journal of Medical Research RESEARCH Is total femoral replacement for non oncologic and oncologic indications a safe procedure in limb preservation surgery?
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Case Report Total femur replacement: a limb-saving strategy for patients with primary malignant femoral tumors
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5186-5192 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067064 Case Report Total femur replacement: a limb-saving strategy for patients with primary malignant femoral tumors Shengjun
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5186-5192 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067064 Case Report Total femur replacement: a limb-saving strategy for patients with primary malignant femoral tumors Shengjun
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with Paprosky III or IV Acetabular Bone Defects: A Minimum 2-year Follow Up Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 28(2): 98-103, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.2.98 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 28(2): 98-103, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.2.98 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 22/ Mar 16, 2015 Page 3785
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Complications of limb salvage surgery in childhood tumors and recommended solutions
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s11751-009-0075-y REVIEW Complications of limb salvage surgery in childhood tumors and recommended solutions H. Ozger M. Bulbul L. Eralp Received: 19 January
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s11751-009-0075-y REVIEW Complications of limb salvage surgery in childhood tumors and recommended solutions H. Ozger M. Bulbul L. Eralp Received: 19 January
10-year results following impaction bone grafting of major bone defects in 29 rotational and hinged knee revision arthroplasties
 Acta Orthopaedica 2013; 84 (4): 387 391 387 10-year results following impaction bone grafting of major bone defects in 29 rotational and hinged knee revision arthroplasties A follow-up of a previous report
Acta Orthopaedica 2013; 84 (4): 387 391 387 10-year results following impaction bone grafting of major bone defects in 29 rotational and hinged knee revision arthroplasties A follow-up of a previous report
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections
 Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Both Knee Re-revision Operations with Different Types of Endoprosthesis after Septic Complications
 DOI: 10.2478/v10163-012-0036-2 ACTA CHIRURGICA LATVIENSIS 2011 (11) CASE REPORT Both Knee Re-revision Operations with Different Types of Endoprosthesis after Septic Complications Silvestris Zebolds*/***,
DOI: 10.2478/v10163-012-0036-2 ACTA CHIRURGICA LATVIENSIS 2011 (11) CASE REPORT Both Knee Re-revision Operations with Different Types of Endoprosthesis after Septic Complications Silvestris Zebolds*/***,
Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing Tumor Resections
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 426, pp. 97 102 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 426, pp. 97 102 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing
Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur
 CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Title of the article: the epidemiology of revision knee arthroplasty at a tertiary care center in india.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. VII (May. 2016), PP 124-128 www.iosrjournals.org Title of the article: the epidemiology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. VII (May. 2016), PP 124-128 www.iosrjournals.org Title of the article: the epidemiology
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 16 LONG-TERM FAILURE MECHANISMS AND SURVIVORSHIP Long-Term Failure Mechanisms and Survivorship Presented by: Michael A. Mont, MD, Assem A. Sultan, MD, and Michael
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 16 LONG-TERM FAILURE MECHANISMS AND SURVIVORSHIP Long-Term Failure Mechanisms and Survivorship Presented by: Michael A. Mont, MD, Assem A. Sultan, MD, and Michael
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Knee Revision. Portfolio
 Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
Laura M. Fayad, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University
 Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
The power of simplicity
 The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
Periprosthetic joint infections in modular endoprostheses of the lower extremities: a retrospective observational study in 101 patients
 Zajonz et al. Patient Safety in Surgery (2016) 10:6 DOI 10.1186/s13037-016-0095-8 RESEARCH Open Access Periprosthetic joint infections in modular endoprostheses of the lower extremities: a retrospective
Zajonz et al. Patient Safety in Surgery (2016) 10:6 DOI 10.1186/s13037-016-0095-8 RESEARCH Open Access Periprosthetic joint infections in modular endoprostheses of the lower extremities: a retrospective
Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques. Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018
 Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018 I have no disclosures relevant to this talk 3 Phases of Revision 1. Exposure Key to the case!! 2. Component Removal
Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018 I have no disclosures relevant to this talk 3 Phases of Revision 1. Exposure Key to the case!! 2. Component Removal
Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
THE VALUE OF JOINT REPLACEMENT IN TREATING PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS
 THE VALUE OF JOINT REPLACEMENT IN TREATING PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS Total Joint Replacement is a valuable treatment option for many of the 27 million Americans who suffer from Osteoarthritis, a disease
THE VALUE OF JOINT REPLACEMENT IN TREATING PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS Total Joint Replacement is a valuable treatment option for many of the 27 million Americans who suffer from Osteoarthritis, a disease
Methods Used for Reconstruction in Aggressive Bone Tumours: An Early Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Methods Used for Reconstruction in Aggressive Bone Tumours: An Early Experience K L Pan, FRCS*, S STing, FRCS**, A W K Mohamad, MS (Orth)*, W GLee, FRCS**, C C Wong, FRCS**, A H Rasit,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Methods Used for Reconstruction in Aggressive Bone Tumours: An Early Experience K L Pan, FRCS*, S STing, FRCS**, A W K Mohamad, MS (Orth)*, W GLee, FRCS**, C C Wong, FRCS**, A H Rasit,
Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty: Causes and Outcomes
 178 Revision TKA: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay et al Original Article Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay, 1 MBBS, Ngai Nung Lo, 1 MMed (Surg), FRCS (Edin), FAMS, Seng
178 Revision TKA: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay et al Original Article Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty: Causes and Outcomes Kae Sian Tay, 1 MBBS, Ngai Nung Lo, 1 MMed (Surg), FRCS (Edin), FAMS, Seng
Exposure EXPOSURE. Exposure - Incision. Extend old incision proximally Expose virgin quadriceps tendon
 Exposure Aaron G Rosenberg MD Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Rush Medical College Chicago, Illinois Exposure - Incision Single incision can be used or modified Multiple longitudinal incisions favor the
Exposure Aaron G Rosenberg MD Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Rush Medical College Chicago, Illinois Exposure - Incision Single incision can be used or modified Multiple longitudinal incisions favor the
Clinical Study The Use of Massive Endoprostheses for the Treatment of Bone Metastases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Sarcoma Volume 2007, Article ID 62151, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2007/62151 Clinical Study The Use of Massive Endoprostheses for the Treatment of Bone Metastases D. H. Park, P.
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Sarcoma Volume 2007, Article ID 62151, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2007/62151 Clinical Study The Use of Massive Endoprostheses for the Treatment of Bone Metastases D. H. Park, P.
Citation for published version (APA): Meijer, M. (2015). Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty. [Groningen]: University of Groningen.
![Citation for published version (APA): Meijer, M. (2015). Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty. [Groningen]: University of Groningen. Citation for published version (APA): Meijer, M. (2015). Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty. [Groningen]: University of Groningen.](/thumbs/96/128989192.jpg) University of Groningen Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty Meijer, Marrigje IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Innovations in revision total knee arthroplasty Meijer, Marrigje IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Insert dissociation after fixed bearing PS constrained Genesis II total knee arthroplasty. A case series of nine patients
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 747-751 ORIGINAL STUDY Insert dissociation after fixed bearing PS constrained Genesis II total knee arthroplasty. A case series of nine patients Timothy Voskuijl, Thijs A.
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 747-751 ORIGINAL STUDY Insert dissociation after fixed bearing PS constrained Genesis II total knee arthroplasty. A case series of nine patients Timothy Voskuijl, Thijs A.
Management of infected TKR (total knee replacement) and results of two stage surgery
 Original Research Article Management of infected TKR (total knee replacement) and results of two stage surgery for infected TKR Mohit M. Patel 1, Kaushal R. Patel 2,*, Zulfikar M. Patel 3, Kalpesh A. Mehta
Original Research Article Management of infected TKR (total knee replacement) and results of two stage surgery for infected TKR Mohit M. Patel 1, Kaushal R. Patel 2,*, Zulfikar M. Patel 3, Kalpesh A. Mehta
Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis
 Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide The Best Thing Next to Bone Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide Key Features & Benefits Proximal Trabecular Metal
Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide The Best Thing Next to Bone Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide Key Features & Benefits Proximal Trabecular Metal
Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty in the Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Can Spacer Be a Source of Reinfection?
 Dwuetapowa endoprotezoplastyka rewizyjna w leczeniu zakażeń okołoprotezowych. Czy spacer może stanowić źródło reinfekcji? Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty in the Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections.
Dwuetapowa endoprotezoplastyka rewizyjna w leczeniu zakażeń okołoprotezowych. Czy spacer może stanowić źródło reinfekcji? Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty in the Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections.
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Uncemented, curved, short endoprosthesis stem for distal femoral reconstruction: early follow-up outcomes
 Lu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:183 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1486-3 RESEARCH Open Access Uncemented, curved, short endoprosthesis stem for distal femoral reconstruction:
Lu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:183 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1486-3 RESEARCH Open Access Uncemented, curved, short endoprosthesis stem for distal femoral reconstruction:
Soft Tissue Releases in Valgus Knees
 Soft Tissue Releases in Valgus Knees Ke Xie, MD Steven Lyons, MD Florida Orthopaedic Institute June 17, 2016 Background Valgus deformities make up 10-15% of all primary TKA s performed Restoration of the
Soft Tissue Releases in Valgus Knees Ke Xie, MD Steven Lyons, MD Florida Orthopaedic Institute June 17, 2016 Background Valgus deformities make up 10-15% of all primary TKA s performed Restoration of the
CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS
 CASE REPORT CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS Bruno Dutra Roos 1, Milton Valdomiro Roos 2, Antero
CASE REPORT CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS Bruno Dutra Roos 1, Milton Valdomiro Roos 2, Antero
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
What Are the Risk Factors and Complications Associated With Intraoperative and Postoperative Fractures in Total Wrist Arthroplasty?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2017) 475:2694 2700 DOI 10.1007/s11999-017-5442-2 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Are
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2017) 475:2694 2700 DOI 10.1007/s11999-017-5442-2 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Are
THE PERSONALIZED KNEE
 THE PERSONALIZED KNEE REDEFINING PERSONALIZATION Total knee replacement has long ranked among the most successful procedures in modern medicine. While you can expect excellent implant survivorship with
THE PERSONALIZED KNEE REDEFINING PERSONALIZATION Total knee replacement has long ranked among the most successful procedures in modern medicine. While you can expect excellent implant survivorship with
The Orthopaedic In-Training Examination (OITE)
 168 Reconstructive Knee Surgery Literature as a Tool for the Orthopaedic In-Training Examination Siraj A. Sayeed, M.D., M. Eng., David R. Marker, B.S., Simon C. Mears, M.D., Ronald E. Delanois, M.D., and
168 Reconstructive Knee Surgery Literature as a Tool for the Orthopaedic In-Training Examination Siraj A. Sayeed, M.D., M. Eng., David R. Marker, B.S., Simon C. Mears, M.D., Ronald E. Delanois, M.D., and
Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs: Report of Two Cases
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
operative technique Kent Hip
 operative technique Kent Hip The Kent Hip Operative Technique The Kent Hip was developed by Mr Cliff Stossel, FRCS in Maidstone, Kent, UK and first implanted in 1986. It was designed to deal with problems
operative technique Kent Hip The Kent Hip Operative Technique The Kent Hip was developed by Mr Cliff Stossel, FRCS in Maidstone, Kent, UK and first implanted in 1986. It was designed to deal with problems
Gender Solutions Patello-Femoral Joint System
 Zimmer Biomet is the leading company in partial knee arthroplasty (PKA) 1 with over 40 years experience, offering a comprehensive range of anatomic and innovative solutions. Research shows that surgeons
Zimmer Biomet is the leading company in partial knee arthroplasty (PKA) 1 with over 40 years experience, offering a comprehensive range of anatomic and innovative solutions. Research shows that surgeons
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Elb-2: Does previous surgery (arthroscopic, fracture fixation, other nonarthroplasty) increase the risk of subsequent elbow PJI?
 Elbow ICM 2018 Elb-2: Does previous surgery (arthroscopic, fracture fixation, other nonarthroplasty) increase the risk of subsequent elbow PJI? RESEARCHED BY: Barco Laakso, Raul MD, Spain Antuña, Samuel
Elbow ICM 2018 Elb-2: Does previous surgery (arthroscopic, fracture fixation, other nonarthroplasty) increase the risk of subsequent elbow PJI? RESEARCHED BY: Barco Laakso, Raul MD, Spain Antuña, Samuel
Sequential soft tissue release and unconstrained TKA implants in severe varus deformity- Prospective study in 75 knees
 2017; 3(3): 15-20 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 15-20 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 04-05-2017 Accepted: 05-06-2017 Dr. Ranganatha B Thimmegowda MS, DNB, Assistant Professor, ESIC Medical College,
2017; 3(3): 15-20 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 15-20 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 04-05-2017 Accepted: 05-06-2017 Dr. Ranganatha B Thimmegowda MS, DNB, Assistant Professor, ESIC Medical College,
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury
 Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Objectives. Limb salvage surgery. Age distribution bone cancer. Age distribution soft tissue sarcomas
 LifeSource October, 2011 Disclosure Information Putting humpty dumpty back together again is easier with tissue allografts! Limb Salvage Surgery for Bone Tumors Edward Cheng, MD October 6, 2011 Disclosure
LifeSource October, 2011 Disclosure Information Putting humpty dumpty back together again is easier with tissue allografts! Limb Salvage Surgery for Bone Tumors Edward Cheng, MD October 6, 2011 Disclosure
A further enhanced classic. Wagner SL Revision Hip Stem
 A further enhanced classic Wagner SL Revision Hip Stem The original Wagner SL Revision Stem offers a time-proven solution in the treatment of revision hips. While its underlying anchorage philosophy and
A further enhanced classic Wagner SL Revision Hip Stem The original Wagner SL Revision Stem offers a time-proven solution in the treatment of revision hips. While its underlying anchorage philosophy and
Knee Replacement Complications
 Knee Replacement Complications Knee replacements have become a routine surgery in the United States. Nearly 700,000 people each year receive this life-improving surgery and are able to enjoy richer, more
Knee Replacement Complications Knee replacements have become a routine surgery in the United States. Nearly 700,000 people each year receive this life-improving surgery and are able to enjoy richer, more
Revision Arthroplasty Using a MUTARS Prosthesis in Comminuted Periprosthetic Fracture of the Distal Femur
 Technical Report Yonsei Med J 2016 Nov;57(6):1517-1522 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Revision Arthroplasty Using a MUTARS Prosthesis in Comminuted Periprosthetic Fracture of the Distal Femur Hyung-Suk
Technical Report Yonsei Med J 2016 Nov;57(6):1517-1522 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Revision Arthroplasty Using a MUTARS Prosthesis in Comminuted Periprosthetic Fracture of the Distal Femur Hyung-Suk
The choice of internal fixator for fractures around the femoral trochanter depends on area classification
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3206-1 RESEARCH Open Access The choice of internal fixator for fractures around the femoral trochanter depends on area classification Hiroaki Kijima 1,2*, Shin Yamada 1,2, Natsuo
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3206-1 RESEARCH Open Access The choice of internal fixator for fractures around the femoral trochanter depends on area classification Hiroaki Kijima 1,2*, Shin Yamada 1,2, Natsuo
Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient Instrumentation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Management of periprosthetic fractures in patients treated with a megaprosthesis for malignant bone tumours around the knee
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 558-563 CASE REPORT Management of periprosthetic fractures in patients treated with a megaprosthesis for malignant bone tumours around the knee Michael GEBHARt, Félix SHuMElInSky
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 558-563 CASE REPORT Management of periprosthetic fractures in patients treated with a megaprosthesis for malignant bone tumours around the knee Michael GEBHARt, Félix SHuMElInSky
Assessing And Quantifying Instability In Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Assessing And Quantifying Instability In Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty David F. Hamilton, PHD, Richard Burnett, FRCS (Ed), James T. Patton, FRCS (Ed), Colin R. Howie, FRCS (Ed), Hamish Simpson, DPhil.
Assessing And Quantifying Instability In Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty David F. Hamilton, PHD, Richard Burnett, FRCS (Ed), James T. Patton, FRCS (Ed), Colin R. Howie, FRCS (Ed), Hamish Simpson, DPhil.
Sung-Hyun Lee 1, Sung-Hyun Noh 1, Keun-Churl Chun 1, Joung-Kyue Han 2 and Churl-Hong Chun 1*
 Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:69 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1981-2 CASE REPORT Open Access A case of bilateral revision total knee arthroplasty using distal femoral allograft
Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:69 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1981-2 CASE REPORT Open Access A case of bilateral revision total knee arthroplasty using distal femoral allograft
Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
Condylar constrained system in primary total knee replacement: our experience and literature review
 Original Article Page 1 of 5 Condylar constrained system in primary total knee replacement: our experience and literature review Luigi Sabatini 1, Salvatore Risitano 1, Lorenzo Rissolio 1, Andrea Bonani
Original Article Page 1 of 5 Condylar constrained system in primary total knee replacement: our experience and literature review Luigi Sabatini 1, Salvatore Risitano 1, Lorenzo Rissolio 1, Andrea Bonani
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric fractures
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric s G.Z. Said, O. Farouk
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric s G.Z. Said, O. Farouk
Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after High Tibial Osteotomy
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series
 Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
AN EVOLUTION IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SENSOR-ASSISTED TKA AN EVOLUTION IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY OrthoSensor s Sensor-Assisted TKA disposable instrument delivers evidence-based data wirelessly to an intra-operative monitor that enables surgeons
SENSOR-ASSISTED TKA AN EVOLUTION IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY OrthoSensor s Sensor-Assisted TKA disposable instrument delivers evidence-based data wirelessly to an intra-operative monitor that enables surgeons
EXACTECH SHOULDER. Design Rationale. Humeral Reconstruction Prosthesis. Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM
 EXACTECH SHOULDER Design Rationale Humeral Reconstruction Prosthesis Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM Humeral Reconstruction Prosthesis TABLE OF CONTENTS DESIGN TEAM...1 INTRODUCTION...2 DESIGN HISTORY
EXACTECH SHOULDER Design Rationale Humeral Reconstruction Prosthesis Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM Humeral Reconstruction Prosthesis TABLE OF CONTENTS DESIGN TEAM...1 INTRODUCTION...2 DESIGN HISTORY
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED NAVIGATION FOR KNEE AND HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Gold standard of a TKA. Conflicting goals? POLYETHYLENE WEAR THE SOLUTION: MOBILE BEARING KNEES. MOBILE BEARING A totally new approach (1977)
 Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: 07/26/17 Page 1 of 9
 Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Prolonged infection at the tibial bone tunnel after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
 Fukushima J. Med. Sci., Vol. 63, No. 2, 2017 [Case Report] Prolonged infection after ACL Reconstruction 121 Prolonged infection at the tibial bone tunnel after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Fukushima J. Med. Sci., Vol. 63, No. 2, 2017 [Case Report] Prolonged infection after ACL Reconstruction 121 Prolonged infection at the tibial bone tunnel after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World. Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation
 Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty Instrumentation
Simplifying the Most Clinically Proven 1 Partial Knee in the World Oxford Partial Knee with Microplasty Instrumentation 1 Microplasty Instrumentation Innovative, Accurate, Reproducible Microplasty Instrumentation
why bicompartmental? A REVOLUTIONARY ALTERNATIVE TO TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 why bicompartmental? A REVOLUTIONARY ALTERNATIVE TO TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS TKR is not always the answer Today, many patients with medial or lateral disease and patellofemoral involvement receive a Total
why bicompartmental? A REVOLUTIONARY ALTERNATIVE TO TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS TKR is not always the answer Today, many patients with medial or lateral disease and patellofemoral involvement receive a Total
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service
 North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Unusually High Rate of Early Failure of Tibial Component in ATTUNE Total Knee Arthroplasty System at Implant Cement Interface
 Original Article 435 Unusually High Rate of Early Failure of Tibial Component in ATTUNE Total Knee Arthroplasty System at Implant Cement Interface Peter M. Bonutti, MD 1 Anton Khlopas, MD 2 Morad Chughtai,
Original Article 435 Unusually High Rate of Early Failure of Tibial Component in ATTUNE Total Knee Arthroplasty System at Implant Cement Interface Peter M. Bonutti, MD 1 Anton Khlopas, MD 2 Morad Chughtai,
Use of tantalum cones in primary arthroplasty of acute proximal tibial fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, 593-598 ORIGINAL STUDY Use of tantalum cones in primary arthroplasty of acute proximal tibial fractures Harish Sivasubramanian, Sunil Gurpur Kini, Kai Yun Ang, S. S. Sathappan
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, 593-598 ORIGINAL STUDY Use of tantalum cones in primary arthroplasty of acute proximal tibial fractures Harish Sivasubramanian, Sunil Gurpur Kini, Kai Yun Ang, S. S. Sathappan
