Radiography in the Initial Diagnosis of Primary Bone Tumors
|
|
|
- Joshua Smith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Residents Section Structured Review Costelloe and Madewell Radiography of Primary Bone Tumors Residents Section Structured Review Colleen M. Costelloe 1 John E. Madewell Costelloe CM, Madewell JE Keywords: bone tumors, diagnosis, imaging, radiography DOI: /AJR Received December 30, 2011; accepted after revision June 17, Both authors: Department of Diagnostic Radiology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, Unit 1273, 1515 Holcombe Blvd, Houston, TX Address correspondence to C. M. Costelloe (ccostelloe@di.mdacc.tmc.edu). AJR 2013; 200: X/13/ American Roentgen Ray Society Radiography in the Initial Diagnosis of Primary Bone Tumors R adiography is the optimal initial imaging modality for evaluating undiagnosed primary bone tumors. The advantage of radiographic technique is to collapse the density of all points in the imaging plane into a 2D image. The resulting unique anatomic information allows the efficient evaluation of characteristics that reflect the biologic activity or growth rate of primary bone tumors, such as lesion margins, periosteal reaction, cortical expansion, thinning, and destruction. Educational Objectives 1. To understand how the radiographic characteristics of the margins of primary bone tumors reflect the biologic activity/growth rate of the lesions 2. To learn the radiographic principles of bone tumor margin classification 3. To identify the secondary role of cortical expansion and periosteal reaction in the characterization of primary bone tumors 4. To correlate the radiographic appearance of mineralized matrix with histologic type 5. To understand the advantages and limitations of radiography in the initial evaluation of primary bone tumors Imaging Technique Radiographs are recommended as the initial imaging modality for the evaluation of bone pain [1, 2], and standard radiographic techniques are typically adequate for tumor imaging. The long bones should be imaged with frontal and lateral views, whereas joint imaging benefits from the addition of oblique views. Rib imaging should also include oblique views. Radiography is limited in areas that are susceptible to large amounts of anatomic overlap and complex bony structures, such as the posterior iliac bones, acetabula, and the spine. CT with multiplanar reformations can be considered in those areas, and MRI is appropriate for determining the local extent of disease. Imaging Features Imaging plays a key role in establishing the initial diagnosis of bone tumors and subsequently affects initial management. Undiag- nosed lesions are best divided into biologically aggressive or nonaggressive categories. Biopsy is indicated if the lesion is aggressive. Otherwise, watchful waiting with follow-up imaging can be pursued. Aggressive features are detected on radiographs by evaluation of imaging characteristics, such as the appearance of the margin, cortical expansion, and periosteal reaction. Clinical examination findings, such as pain, are also contributory. Margins After assessment of features such as patient age, the identity of the affected bone, and the location of the tumor in the bone, the tumor itself must be closely scrutinized. The imaging characteristic that is most reflective of the aggressive (typically malignant) or nonaggressive (typically benign) nature of primary bone tumors is the appearance of the margin, which is an indicator of the growth rate of the lesion [3, 4]. A radiographic classification of bone tumor margins has been developed [5] that identifies three main types (Fig. 1). The least-aggressive margins (type I) correspond to tumors that are round or ovoid in shape (geographic). Geographic margins have been divided into three subcategories. Type IA margins are the least aggressive, exhibiting a narrow zone of transition from the tumor to the normal surrounding bone and a sclerotic rim (e.g., fibrous cortical defect, fibrous dysplasia, nonossifying fibroma/ fibroxanthoma (Fig. 2). Lesions with type IB margins have no sclerotic rim, while remaining well defined with a narrow zone of transition. These margins indicate indeterminate biologic potential and may be seen with benign AJR:200, January
2 Costelloe and Madewell Fig. 1 Drawings show margin classification system of primary bone tumors. Type I margins are round or oval and typically correspond to less-aggressive (benign) or less-advanced malignancies than moth-eaten (type II) or permeative (type III) fields of osteolysis. Margin classification system provides general guidelines for determining aggressive from nonaggressive lesions. Information such as patient age, bone affected, and location of tumor in bone are also critical for assessing identity of primary bone tumors. or malignant lesions (e.g., giant cell tumor Fig. 3), aneurysmal bone cyst, aggressive osteoblastoma, and low-grade chondrosarcoma). Type IC margins are ill defined and indistinct, with Fig. 3 Giant cell tumor of bone of proximal tibial epiphysis in 28-year-old woman. Radiograph shows round/oval lesion is geographic (type I) with narrow zone of transition (arrowheads) but no sclerotic rim (type IB). Lack of sclerotic rim indicates that lesion is of indeterminate biologic potential and could be benign or malignant. Lesions with IB margins can be subtle in appearance on radiographs. Biopsy indicated giant cell tumor of bone, which is locally aggressive benign lesion. a wide zone of transition, corresponding to aggressive bone tumors. Most tumors with type IC margins are malignant, such as small/early chondrosarcomas or osteosarcomas (Fig. 4). Fig. 4 Osteosarcoma of proximal tibial metadiaphysis in 15-year-old boy. Radiograph shows lesion is round/oval and therefore geographic but wide zone of transition is present between ill-defined periphery of lesion and normal bone. This type IC margin is typical of aggressive bone tumors. Cortical thinning is seen laterally with deceptively mild periosteal reaction (arrowheads). Osteoid produced by osteosarcomas is microscopically apparent and may or may not be appreciable on imaging studies. Incidental osteochondroma of fibular head is partially visualized (asterisk). Fig. 2 Fibroxanthoma (nonossifying fibroma) of distal tibial metadiaphysis in 23-year-old man. Radiograph shows shape of lesion is well-defined oval (geographic) indicating that margin is type I. Narrow zone of transition (arrowheads) between tumor and normal bone indicates least aggressive margin (IA). Slowly expansile nature of tumor has resulted in mild bowing of adjacent distal fibula. Fig. 5 Primary Burkett lymphoma of distal femur in 23-year-old woman. Radiograph shows numerous lytic foci of varying size are seen throughout distal femoral diaphysis (brackets). They are not round or oval in distribution and are illustrative of type II (moth-eaten margin). More severe osteolysis is seen in lateral femoral condyle and distal epiphysis, showing fine or fuzzy osteolysis of type III (permeative) margin (arrowheads). Fracture is present at level of lateral metaphyseal region. 4 AJR:200, January 2013
3 Radiography of Primary Bone Tumors Fig. 6 Low-grade chondrosarcoma of proximal femur in 84-year-old woman. Low-grade sarcomas can mimic benign lesions and low-grade chondrosarcomas are among most potentially confusing bone tumors. Thickened cortex does not always equate with sclerotic rim. Unlike benign fibroxanthoma in Fig. 1, radiograph shows that entire circumference of this bone is enlarged by low-grade chondrosarcoma. Although large fibrous dysplasias can also enlarge entire circumference of bone, fibrous dysplasia will typically exhibit sclerotic rim with possible fibrous matrix mineralization. This chondrosarcoma has no sclerotic rim and exhibits cartilaginous matrix mineralization (see Figs. 11 and 12 regarding mineralized matrix). In addition to thickening of cortex (arrow), endosteal scalloping of cortex by tumor also thins areas of cortex (arrowhead). Thinning of large sections of cortex by large cartilaginous bone tumors can be indicative of malignancy. Aggressive benign lesions, such as giant cell tumors, can also show this appearance. Type II and III margins are nongeographic and consist of ill-defined fields of bone destruction. The type II margin is described as moth-eaten and is composed of numerous foci of osteolysis that vary in size and shape on a background of relatively intact cortex. The type III margin corresponds to the most highly aggressive appearance and is described as permeative. The margin types can be intermingled. Margins are the interface of the tumor with the bone and therefore are typically the most sensitive radiographic indicator of lesion behavior. The osteolysis represented by these non-geographic lucent areas is fine or fuzzy in appearance (Fig. 5). Analysis of the margins is readily performed on radiographs, which are inexpensive, easily accessible, and provide a concise assessment of lesion behavior on a limited number of images. Fig. 7 Unicameral bone cyst of proximal humeral metaphysis in 16-year-old boy. Large lesions that expand bone without adequate cortical reinforcement can result in pathologic fracture. Radiograph shows this unicameral bone cyst is slightly expansile, thins cortex, and has resulted in fracture with subsequent callous formation (arrow). Cortical Expansion Cortical expansion is most commonly seen with benign tumors that grow slowly enough to allow the cortex to remain completely or partially intact. Although not all bone tumors expand the cortex, the degree of cortical expansion, when present, is reflective of the growth rate of the lesion. With a number of notable exceptions, such as low-grade chondrosarcoma (Fig. 6) and some metastases (e.g., renal cell and thyroid carcinoma), malignancies are more likely to progress rapidly and destroy rather than expand the cortex. Lesions that produce mild cortical expansion are typically well marginated and show IA margins (e.g., fibrous cortical defect, fibrous dysplasia). Lesions that produce a larger degree of cortical expansion are more likely to predispose to pathologic fracture (e.g., nonossifying fibromas/fibroxanthomas, unicameral bone cyst; (Fig. 7). Lesions that exhibit a marked degree of cortical expansion can produce severe local bone deformity or destruction, even if benign. For example, an aneurysmal bone cyst may grow across open physes (Fig. 8), predisposing the patient to limb length discrepancy, and giant cell tumor may destroy the articular surface of bone, leading to the need for arthroplasty. Periosteal Reaction Periosteal reaction can reflect the biologic potential of tumors [6], but it is less specific than other radiographic signs. Highly aggressive tumors often result in interrupted or multilaminar periosteal reactions, and the mass effect of the tumor can produce a triangular interface with the periosteum that is termed a Codman s triangle (Fig. 9). Less-aggressive processes typically produce a unilaminar periosteal reaction, although high-grade sarcomas may produce unilaminar or no detectable periosteal reaction. Matrix and Tumor Mineralization Osteoid, chondroid, and fibrous lesions often produce characteristic mineralization of matrix, which is a substance that is located in the extracellular space between tumor cells. Matrix is found in benign and malignant tumors Fig. 8 Aneurysmal bone cyst of proximal humerus in 17-year-old girl. Radiograph shows this large expansile lesion crosses physis into humeral head and also thin cortex, resulting in pathologic fracture (arrow). These features produced bowing deformity of bone. Physeal involvement can predispose to limb length discrepancy. AJR:200, January
4 Costelloe and Madewell Fig. 9 Osteosarcoma of distal femoral metadiaphysis in 14-year-old boy. Radiograph shows multilaminar onionskin periosteal reaction anteriorly (white arrow). Interrupted periosteal reaction and Codman s triangle (black arrow) are seen posteriorly and proximally, and hair-on-end or sunburst periosteal reaction (arrowheads) is seen posteriorly and distally. Although multilaminar periosteal reactions are commonly seen with Ewing sarcoma, each type of reaction can be seen in each type of tumor. Cortical and trabecular margins of this aggressive tumor are permeative (type III). Fig. 12 Fibrous dysplasia of tibia in 30-year-old woman. Lesion shows spectrum of opacities. Radiograph shows mineralized fibrous matrix is dense and mature proximally (arrow), whereas it has ground-glass appearance distally (arrowheads). Fig. 10 Dedifferentiated parosteal osteosarcoma of posterior metaphysis of distal femur in 33-year-old man. Radiograph shows proximal aspect of lesion is dedifferentiated and shows fluffy or cloudlike osteoid matrix (arrowhead) within soft-tissue mass. Distal aspect of lesion is more typical of parosteal osteosarcoma and shows dense ivory osteoid (arrow). A Fig. 11 This chondrosarcoma of calcaneus in 26-year-old male originated from sessile osteochondroma (not readily identified on radiograph). Radiograph shows arcs and rings of mineralized chondroid matrix (arrowhead) throughout lesion. Mineralized matrix is stippled posteriorly at periphery of lesion (arrow). Fig. 13 Fibrous cortical defect of proximal tibial metaphysis with fibrous dysplasia in distal diaphysis of 15-year-old girl. A, Radiograph shows small fibrous cortical defect is markedly eccentric because it is located in lateral cortex (arrowheads). Nonaggressive lesion shows sclerotic rim (IA margin). Fibrous dysplasia in distal diaphysis is centered in medullary cavity and expands entire circumference of bone. In some respects, this lesion resembles low-grade chondrosarcoma in Figure 6. Nevertheless, it shows ground-glass fibrous matrix and sclerotic distal rim (arrow). B, Radiograph obtained 3 years later shows fibrous cortical defect (arrowheads) has matured and become dense. Because of risk of pathologic fracture caused by cortical thinning, fibrous dysplasia was curetted and packed with dense bone graft, which has incorporated into surgical defect (arrow). B 6 AJR:200, January 2013
5 Radiography of Primary Bone Tumors such as plasmacytomas or unresectable giant cell tumors of bone. The rim may become so solidly mineralized that it can be confused with a IA margin. The margin classification system discussed in this article applies only to untreated primary bone tumors (Fig. 14). identify histologic type. Although MRI and CT provide superior soft-tissue assessment and are free from structural overlap, the unique information afforded by radiography is optimal for the efficient formation of an initial differential diagnosis of primary bone tumors. Fig. 14 Osteosarcoma of proximal tibial metaphysis in 31-year-old woman after chemotherapy. Radiograph shows periphery of lesion has mineralized after therapy and could be confused with type IA margin (arrowheads). Nevertheless, focal areas of moth-eaten osteolysis remain visible centrally (arrow). Review of medical history is essential for proper interpretation of primary bone tumors. and therefore does not closely correlate to malignant potential but may be useful in identifying the histologic type of the tumor [7]. Each type of matrix mineralization shows a spectrum of radiographic appearances. Osteoid matrix may be fluffy and cloudlike or ivory and dense (Fig. 10). Cartilaginous matrix may produce arcs and rings that form around globular cartilage lobules, or it may be stippled in appearance (Fig. 11). Fibrous lesions may show a slightly increased radiographic density, moderate ground-glass appearance, or dense mature mineralization that can be uniform or heterogeneous (Fig. 12). The gradual increase in mineralization with time is termed maturation and can be seen in tumors such as fibrous dysplasia, nonossifying fibroma, fibrous cortical defect (Fig. 13), osteoid osteoma, and bone island [8]. Maturation is an indolent process and should not be confused with the rapid posttherapeutic response of aggressive lesions that have responded well to systemic or radiation therapy. Posttherapeutic mineralization may be most evident peripherally in lesions Advantages and Pitfalls of Radiography Advantages Radiography and CT are the two major imaging modalities used for evaluating mineralized structures. The main advantages of radiography over CT include affordability, accessibility, and a concise method by which to assess the lesion on a limited number of images. It can be argued that cross-sectional imaging, even with reformations, cannot reproduce the perceived quality of depth that results from collapsing a 3D structure onto a 2D image. The margin classification system described in this article is designed primarily for use with radiography. Pitfalls Deficits of radiography include anatomic overlap that can obscure abnormalities and a limited capacity to evaluate soft tissue. Although mass effect may be detected on radiographs, they are limited for determining the degree of extraosseous tumor volume, relationship of extraosseous tumor to surrounding structures, and extent of disease in the intact marrow cavity. MRI is the modality of choice for simultaneously evaluating these relationships [9 11]. Other considerations include lower sensitivity for the detection of mineralized matrix when compared with CT or for the detection of undisplaced fracture when compared with CT or MRI. Conclusion Radiography is the single most helpful imaging modality when establishing the initial differential diagnosis of primary bone tumors. Evaluation of the margins is the greatest contributing factor to radiographic assessment of the biologic potential of the lesions. Other features, such as cortical expansion and periosteal reaction, provide additional clues as to whether immediate biopsy is indicated. Identification of mineralized matrix may help to noninvasively References 1. Berquist TH, Dalinka MK, Alazraki N, et al. Bone tumors: American College of Radiology ACR appropriateness criteria. Radiology 2000; 215(suppl): Costelloe CM, Rohren EM, Madewell JE, et al. Imaging bone metastases in breast cancer: techniques and recommendations for diagnosis. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: Lodwick GS, Wilson AJ, Farrell C, Virtama P, Dittrich F. Determining growth rates of focal lesions of bone from radiographs. Radiology 1980; 134: Oudenhoven LF, Dhondt E, Kahn S, et al. Accuracy of radiography in grading and tissue-specific diagnosis: a study of 200 consecutive bone tumors of the hand. Skeletal Radiol 2006; 35: Madewell JE, Ragsdale BD, Sweet DE. Radiologic Part I. Internal margins. Radiol Clin North Am 1981; 19: Ragsdale BD, Madewell JE, Sweet DE. Radiologic Part II. Periosteal reactions. Radiol Clin North Am 1981; 19: Sweet DE, Madewell JE, Ragsdale BD. Radiologic Part III. Matrix patterns. Radiol Clin North Am 1981; 19: Yanagawa T, Watanabe H, Shinozaki T, Ahmed AR, Shirakura K, Takagishi K. The natural history of disappearing bone tumours and tumourlike conditions. Clin Radiol 2001; 56: Aisen AM, Martel W, Braunstein EM, McMillin KI, Phillips WA, Kling TF. MRI and CT evaluation of primary bone and soft-tissue tumors. AJR 1986; 146: Tehranzadeh J, Mnaymneh W, Ghavam C, Morillo G, Murphy BJ. Comparison of CT and MR imaging in musculoskeletal neoplasms. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1989; 13: Zimmer WD, Berquist TH, McLeod RA, et al. Bone tumors: magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography. Radiology 1985; 155: AJR:200, January
Bone Tumors Clues and Cues
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp!
 APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp! DANIEL P. EVANS, DPM, FACFAOM Professor, Department of Podiatric Medicine and Radiology Dr. Wm. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine Conflict of
APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp! DANIEL P. EVANS, DPM, FACFAOM Professor, Department of Podiatric Medicine and Radiology Dr. Wm. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine Conflict of
Typical skeletal location and differential diagnosis of bone tumors.
 Typical skeletal location and differential diagnosis of bone tumors. Poster No.: C-2418 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barros, L. A. Ferreira, Y. Costa, P. J. V. Coelho, F. Caseiro
Typical skeletal location and differential diagnosis of bone tumors. Poster No.: C-2418 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barros, L. A. Ferreira, Y. Costa, P. J. V. Coelho, F. Caseiro
A Modified Lodwick-Madewell Grading System for the Evaluation of Lytic Bone Lesions
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Caracciolo et al. Evaluation of Lytic one Lesions Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Jamie T. Caracciolo 1 H. Thomas Temple 2 G. Douglas Letson 3 Mark J.
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Caracciolo et al. Evaluation of Lytic one Lesions Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Jamie T. Caracciolo 1 H. Thomas Temple 2 G. Douglas Letson 3 Mark J.
Bone tumors. RMG: jan
 Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
Imaging Findings Of Bone Tumors: A Pictorial Review
 Imaging Findings Of Bone Tumors: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-2511 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Limeme, N. Benzina, A. BelKhiria, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, N. Mallat, H.
Imaging Findings Of Bone Tumors: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-2511 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Limeme, N. Benzina, A. BelKhiria, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, N. Mallat, H.
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
General Approach to Lytic Bone Lesions D. Lee Bennett, MD, MA, Georges Y. El Khoury, MD Appl Radiol. 2004;33(5)
 General Approach to Lytic Bone Lesions D. Lee Bennett, MD, MA, Georges Y. El Khoury, MD Appl Radiol. 2004;33(5) www.medscape.com Abstract and Introduction Abstract When interpreting musculoskeletal radiographs,
General Approach to Lytic Bone Lesions D. Lee Bennett, MD, MA, Georges Y. El Khoury, MD Appl Radiol. 2004;33(5) www.medscape.com Abstract and Introduction Abstract When interpreting musculoskeletal radiographs,
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
VALORACIÒN RADIOLÓGICA DE LA LESIÒN ÒSEA SOLITARIA IMAGENOLOGIA MEDICA UNIVERSIDAD HISPANOAMERICANA
 VALORACIÒN RADIOLÓGICA DE LA LESIÒN ÒSEA SOLITARIA IMAGENOLOGIA MEDICA UNIVERSIDAD HISPANOAMERICANA TUMORES ÓSEOS SE PRESENTAN POR RANGOS DE EDAD, PRINCIPALMENTE: MENORES DE 20 AÑOS 20 A 40 AÑOS MAYORES
VALORACIÒN RADIOLÓGICA DE LA LESIÒN ÒSEA SOLITARIA IMAGENOLOGIA MEDICA UNIVERSIDAD HISPANOAMERICANA TUMORES ÓSEOS SE PRESENTAN POR RANGOS DE EDAD, PRINCIPALMENTE: MENORES DE 20 AÑOS 20 A 40 AÑOS MAYORES
Malignant bone tumors. Incidence Myeloma 45% Osteosarcoma 24% Chondrosarcoma 12% Lyphoma 8% Ewing s Sarcoma 7%
 Malignant bone tumors Incidence Myeloma 45% Osteosarcoma 24% Chondrosarcoma 12% Lyphoma 8% Ewing s Sarcoma 7% Commonest primary bone sarcoma is osteosarcoma X ray Questions to ask 1. Solitary or Multiple
Malignant bone tumors Incidence Myeloma 45% Osteosarcoma 24% Chondrosarcoma 12% Lyphoma 8% Ewing s Sarcoma 7% Commonest primary bone sarcoma is osteosarcoma X ray Questions to ask 1. Solitary or Multiple
Fluid-fluid levels in bone tumors: A pictorial review
 Fluid-fluid levels in bone tumors: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-578 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: L. Figueroa Nasra, C. Martín Hervás, M. Tapia-Viñé,
Fluid-fluid levels in bone tumors: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-578 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: L. Figueroa Nasra, C. Martín Hervás, M. Tapia-Viñé,
Radiologic approach to pediatric lytic bone lesions
 Radiologic approach to pediatric lytic bone lesions Poster No.: C-1177 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. L. LERMA GALLARDO, I. de la Pedraja, A. Lancharro 1 1 1 2 1 1 Zapata, J.
Radiologic approach to pediatric lytic bone lesions Poster No.: C-1177 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. L. LERMA GALLARDO, I. de la Pedraja, A. Lancharro 1 1 1 2 1 1 Zapata, J.
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Bubbly Lesions of Bone
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month w79 08.18.09 Eisenberg Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Ronald L. Eisenberg 1 Eisenberg RL Keywords: bubbly lesions, fegnomashic, skeletal
Residents Section Pattern of the Month w79 08.18.09 Eisenberg Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Ronald L. Eisenberg 1 Eisenberg RL Keywords: bubbly lesions, fegnomashic, skeletal
Malignant Bone Tumors - Part I: a brief revision of diagnostic aspects with conventional radiology
 Malignant Bone Tumors - Part I: a brief revision of diagnostic aspects with conventional radiology Poster No.: C-2473 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Candelaria, L. B. Barbosa,
Malignant Bone Tumors - Part I: a brief revision of diagnostic aspects with conventional radiology Poster No.: C-2473 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Candelaria, L. B. Barbosa,
Skeletal Radiology. Solitary (unicameral) bone cyst. The fallen fragment sign revisited
 Skeletal Radiol (1989) 18:261-265 Skeletal Radiology Solitary (unicameral) bone cyst The fallen fragment sign revisited S. Struhl, M.D., C. Edelson, M.D., H. Pritzker, M.D., L.P. Seimon, M.D., and H.D.
Skeletal Radiol (1989) 18:261-265 Skeletal Radiology Solitary (unicameral) bone cyst The fallen fragment sign revisited S. Struhl, M.D., C. Edelson, M.D., H. Pritzker, M.D., L.P. Seimon, M.D., and H.D.
GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
MRI and CT Evaluation of Primary Bone and Soft- Tissue Tumors
 749 Alex M. Aisen1 William Martel1 Ethan M. Braunstein1 Kim I. McMillin1 William A. Phillips2 Thomas F. KIing2 Received June 10, 1985; accepted after revision December 23, 1985. Presented at the annu meeting
749 Alex M. Aisen1 William Martel1 Ethan M. Braunstein1 Kim I. McMillin1 William A. Phillips2 Thomas F. KIing2 Received June 10, 1985; accepted after revision December 23, 1985. Presented at the annu meeting
Review Course «Musculoskeletal Oncology» October 6, 2011 UNIKLINIK BALGRIST. Imaging of Bone and Soft Tissue. Tumors
 Imaging of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors Approach from a radiologist s point of view Florian Buck Radiology Radio- Radio- Oncologist Oncologist Orthopedist Orthopedist Patient Management Oncologist Oncologist
Imaging of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors Approach from a radiologist s point of view Florian Buck Radiology Radio- Radio- Oncologist Oncologist Orthopedist Orthopedist Patient Management Oncologist Oncologist
Disclosures. Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone. Outline. The osteoclast. Giant cell rich tumors 5/21/11
 Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Primary bone tumors according to the WHO classification: a review of 13 years with illustrative examples
 Primary bone tumors according to the WHO classification: a review of 13 years with illustrative examples Poster No.: C-1741 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Silva, M. A. Ramírez
Primary bone tumors according to the WHO classification: a review of 13 years with illustrative examples Poster No.: C-1741 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Silva, M. A. Ramírez
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Incidental bone tumors are asymptomatic lesions that are. Incidental Bone Lesions. When to Refer to the Tumor Specialist
 Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases 2012;70(4):235-40 235 Incidental Bone Lesions When to Refer to the Tumor Specialist LT Suezie Kim, M.D., M.C., U.S.N., Catherine N. Laible, M.D., Leon D.
Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases 2012;70(4):235-40 235 Incidental Bone Lesions When to Refer to the Tumor Specialist LT Suezie Kim, M.D., M.C., U.S.N., Catherine N. Laible, M.D., Leon D.
Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older
 Dr Brajesh Nandan Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older patients. Cancers of the breast, prostate,
Dr Brajesh Nandan Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older patients. Cancers of the breast, prostate,
Key points in the evaluation of focal bone lesions: from plain film to multidetector CT
 Key points in the evaluation of focal bone lesions: from plain film to multidetector CT Poster No.: C-2060 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Rubio Marco, M. Arraiza Sarasa, H. Gómez
Key points in the evaluation of focal bone lesions: from plain film to multidetector CT Poster No.: C-2060 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Rubio Marco, M. Arraiza Sarasa, H. Gómez
Unusual location of bone sarcoma in children
 Unusual location of bone sarcoma in children Poster No.: C-1517 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. JERBI, A. Khalfalli, G. Abid, O. Bradai, N. chouchane, H. HAMZA; Mahdia/TN Keywords:
Unusual location of bone sarcoma in children Poster No.: C-1517 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. JERBI, A. Khalfalli, G. Abid, O. Bradai, N. chouchane, H. HAMZA; Mahdia/TN Keywords:
FEGNOMASHIC: from x-ray to MRI
 FEGNOMASHIC: from x-ray to MRI Poster No.: C-2441 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Fouassier, A. L. C. Duarte, C. Ruivo, J. Velez ; Évora/PT, 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 Coimbra/PT, PT Keywords:
FEGNOMASHIC: from x-ray to MRI Poster No.: C-2441 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Fouassier, A. L. C. Duarte, C. Ruivo, J. Velez ; Évora/PT, 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 Coimbra/PT, PT Keywords:
Bone Tumours - a synopsis. Dr Zena Slim SpR in Histopathology QAH 2009
 Bone Tumours - a synopsis Dr Zena Slim SpR in Histopathology QAH 2009 Aims General approach to diagnosis Common entities.and not so common ones. Mini quiz Challenge of bone tumour diagnosis Bone tumours
Bone Tumours - a synopsis Dr Zena Slim SpR in Histopathology QAH 2009 Aims General approach to diagnosis Common entities.and not so common ones. Mini quiz Challenge of bone tumour diagnosis Bone tumours
Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions
 Chapter 2 Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions Introduction There are many lesions that are associated with reactive new bone formation; this chapter predominantly covers those in which deposition of osteoid/bone
Chapter 2 Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions Introduction There are many lesions that are associated with reactive new bone formation; this chapter predominantly covers those in which deposition of osteoid/bone
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors. James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon
 Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
Downloaded from by on 11/21/17 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.196.1 on 11/21/17 from IP address 46.3.196.1. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved T he scapula is a small bone in which many neoplasms can
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.196.1 on 11/21/17 from IP address 46.3.196.1. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved T he scapula is a small bone in which many neoplasms can
Recognizing Cartilaginous Tumors: Spectrum of Imaging Characteristics with Radiologic-Pathologic correlation.
 Recognizing Cartilaginous Tumors: Spectrum of Imaging Characteristics with Radiologic-Pathologic correlation. Poster No.: C-1451 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Barcina García,
Recognizing Cartilaginous Tumors: Spectrum of Imaging Characteristics with Radiologic-Pathologic correlation. Poster No.: C-1451 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Barcina García,
Fluid fluid levels in bone tumors and tumoral lesions - Pictorial essay
 Review Fluid fluid levels in bone tumors and tumoral lesions - Pictorial essay Subbarao Kakarla 1,* 1 KIMS Foundation and Research Centre, Minister Road, Secunderabad - 500003, Telangana, India Abstract
Review Fluid fluid levels in bone tumors and tumoral lesions - Pictorial essay Subbarao Kakarla 1,* 1 KIMS Foundation and Research Centre, Minister Road, Secunderabad - 500003, Telangana, India Abstract
Department of Radiology, University of Szeged. Imaging of the skeleton
 Imaging of the skeleton Methods of examination: plain x-ray (radiography, densitometry) x-ray with contrast material (fistulography, angiography) ultrasound (b-mode, Doppler, color, duplex) computed tomography
Imaging of the skeleton Methods of examination: plain x-ray (radiography, densitometry) x-ray with contrast material (fistulography, angiography) ultrasound (b-mode, Doppler, color, duplex) computed tomography
Aprimary bone tumor is a
 Radiographic and Scintigraphic Evaluation of Bone Tumors and Diseases Young Lu, BA Camilo Villalobos, MD Rodolfo Zamora, MD Marisa C. Cornejo, BA James C. Wittig, MD Investigation performed at Hackensack
Radiographic and Scintigraphic Evaluation of Bone Tumors and Diseases Young Lu, BA Camilo Villalobos, MD Rodolfo Zamora, MD Marisa C. Cornejo, BA James C. Wittig, MD Investigation performed at Hackensack
A comprehensive review of osseous Ewing sarcoma: clinical data, skeletal location and imaging features.
 A comprehensive review of osseous Ewing sarcoma: clinical data, skeletal location and imaging features. Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit R. Gil 1, P. Pereira 1,
A comprehensive review of osseous Ewing sarcoma: clinical data, skeletal location and imaging features. Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit R. Gil 1, P. Pereira 1,
ORTHOPAEDIC ONCOLOGY OITE REVIEW COURSE
 ORTHOPAEDIC ONCOLOGY OITE REVIEW COURSE Richard D. Lackman, MD FACS Director, Orthopaedic Oncology Center Cancer Institute Introduction In the evaluation of a patient with a bone tumor, there are several
ORTHOPAEDIC ONCOLOGY OITE REVIEW COURSE Richard D. Lackman, MD FACS Director, Orthopaedic Oncology Center Cancer Institute Introduction In the evaluation of a patient with a bone tumor, there are several
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
A review of Tumoral lesions of the shoulder
 A review of Tumoral lesions of the shoulder Poster No.: P-0109 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M. Milán Rodríguez, Á. E. Moreno Puertas, J. M. Giménez, 1 1 1 1 2 1 A. Rubio Fernández,
A review of Tumoral lesions of the shoulder Poster No.: P-0109 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M. Milán Rodríguez, Á. E. Moreno Puertas, J. M. Giménez, 1 1 1 1 2 1 A. Rubio Fernández,
Radiology Corner. Osteoid Osteoma
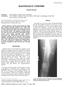 Radiology Corner Osteoid Osteoma Guarantor: COL Timothy G. Sanders, MC, USAF (Ret.) Contributors: COL Timothy G. Sanders, USAF, MC, (Ret.); CAPT John P. Lichtenberger, USAF, MC; COL Les Folio, USAF, MC,
Radiology Corner Osteoid Osteoma Guarantor: COL Timothy G. Sanders, MC, USAF (Ret.) Contributors: COL Timothy G. Sanders, USAF, MC, (Ret.); CAPT John P. Lichtenberger, USAF, MC; COL Les Folio, USAF, MC,
Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia V Monappa, R Kudva Citation V Monappa, R Kudva. Multifocal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia V Monappa, R Kudva Citation V Monappa, R Kudva. Multifocal
Department of Radiology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea 4
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.4.240 Bone Tumors with an Associated Pathologic Fracture: Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Status Using
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.4.240 Bone Tumors with an Associated Pathologic Fracture: Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Status Using
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
The term bone tumor is a broad category, encompassing benign and malignant neoplasms, reactive focal abnormalities, metabolic abnormalities, and misce
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Chealon Miller, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD. November Stress Fractures. Chealon Miller, Harvard Medical School Year IV Gillian Lieberman, MD
 November 2005 Stress Fractures Chealon Miller, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient G.F. 29 year old female runner c/o left shin pain and swelling Evaluated at OSH with MRI showing a mass Referred
November 2005 Stress Fractures Chealon Miller, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient G.F. 29 year old female runner c/o left shin pain and swelling Evaluated at OSH with MRI showing a mass Referred
Grading of Bone Tumors
 Grading of Bone Tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D. Department of Pathology College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Introduction to grading system of bone tumor used at Mayo Clinic WHO Histologic Classification
Grading of Bone Tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D. Department of Pathology College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Introduction to grading system of bone tumor used at Mayo Clinic WHO Histologic Classification
Bread and Butter Bone Pathology
 Bread and Butter Bone Pathology NICOLE D. RIDDLE, MD RUFFOLO, HOOPER, AND ASSOC. / UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH FLORIDA Goals: Fundamentals of neoplastic bone pathology Bone Producing Cartilage Producing Miscellaneous
Bread and Butter Bone Pathology NICOLE D. RIDDLE, MD RUFFOLO, HOOPER, AND ASSOC. / UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH FLORIDA Goals: Fundamentals of neoplastic bone pathology Bone Producing Cartilage Producing Miscellaneous
A peculiar location of a rare bone tumor: sternal lipoma
 A peculiar location of a rare bone tumor: sternal lipoma Poster No.: P-0033 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster Z. Akkaya, C. Uzun, S. Enon, G. Kocaman, G. Sahin; Ankara/TR
A peculiar location of a rare bone tumor: sternal lipoma Poster No.: P-0033 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster Z. Akkaya, C. Uzun, S. Enon, G. Kocaman, G. Sahin; Ankara/TR
USCAP 2014 Common problems in bone and soft tissue pathology: Cartilage tumors
 USCAP 2014 Common problems in bone and soft tissue pathology: Cartilage tumors Andrew Horvai MD PhD Clinical Professor, Pathology UCSF, San Francisco, CA Outline Common intramedullary tumors Enchondroma
USCAP 2014 Common problems in bone and soft tissue pathology: Cartilage tumors Andrew Horvai MD PhD Clinical Professor, Pathology UCSF, San Francisco, CA Outline Common intramedullary tumors Enchondroma
Bone Tumors: In 1 Simple Chart
 Bone Tumors with PowerPoint Interactivity Download this entire slideshow from When running this on your own computer you can jump from slide to slide using these buttons at bottom of each slide: Last slide
Bone Tumors with PowerPoint Interactivity Download this entire slideshow from When running this on your own computer you can jump from slide to slide using these buttons at bottom of each slide: Last slide
Bone Imaging. Scopes. Objective. Part 1 : bone tumor. Important Factors in Diagnosis of Bone tumor. Part 2 : infection and joint disease
 Scopes Bone Imaging Part 1 : bone tumor Part 2 : infection and joint disease Jitsupa Wongsripuemtet, M.D. Radiology Department Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University Objective ให น กศ กษาแพทย สามารถแปลผลภาพทางร
Scopes Bone Imaging Part 1 : bone tumor Part 2 : infection and joint disease Jitsupa Wongsripuemtet, M.D. Radiology Department Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University Objective ให น กศ กษาแพทย สามารถแปลผลภาพทางร
Case McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
 Case 14477 McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Lukasz Augsburg 1, Filip M. Vanhoenacker 1, 2, 3, Jan Gielen1 1. University Hospital Antwerp, Department of Radiology, University
Case 14477 McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Lukasz Augsburg 1, Filip M. Vanhoenacker 1, 2, 3, Jan Gielen1 1. University Hospital Antwerp, Department of Radiology, University
SMALL ROUND BLUE CELL LESION OF BONE
 DISCLOSURE SMALL ROUND BLUE CELL LESION OF BONE Dr. Alistair Jordan University of South Alabama No financial support or endorsement OBJECTIVES Describe the more common small round cell lesions of bone
DISCLOSURE SMALL ROUND BLUE CELL LESION OF BONE Dr. Alistair Jordan University of South Alabama No financial support or endorsement OBJECTIVES Describe the more common small round cell lesions of bone
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
warwick.ac.uk/lib-publications
 A Thesis Submitted for the Degree of PhD at the University of Warwick Permanent WRAP URL: http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/102063/ Copyright and reuse: This thesis is made available online and is protected by
A Thesis Submitted for the Degree of PhD at the University of Warwick Permanent WRAP URL: http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/102063/ Copyright and reuse: This thesis is made available online and is protected by
Periosteal Osteosarcoma Arising from the Rib and Scapula: Imaging Features in Two Cases
 Case Report Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.3.370 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(3):370-375 Periosteal Osteosarcoma Arising from the Rib and Scapula:
Case Report Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.3.370 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(3):370-375 Periosteal Osteosarcoma Arising from the Rib and Scapula:
Essential Dermatopathology. Jinah Kim, MD, PhD Department of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University Medical Center
 Essential Dermatopathology Jinah Kim, MD, PhD Department of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University Medical Center OBJECTIVES Review clinical, pathologic and molecular aspects of bone and fat tumors
Essential Dermatopathology Jinah Kim, MD, PhD Department of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University Medical Center OBJECTIVES Review clinical, pathologic and molecular aspects of bone and fat tumors
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor A-G
 Bone tumor A-G Bone tumors and tumor-like lesions in alphabethic order Henk Jan van de Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor A-G Bone tumors and tumor-like lesions in alphabethic order Henk Jan van de Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone and Joint Part 2. Leslie G Dodd, MD
 Bone and Joint Part 2 Leslie G Dodd, MD Relative rates of cancer Sarcomas are relatively uncommon tumors New cancer cases 2007 All sites 1.4 million prostate 218,890 lung 213,380 breast 180,510 Soft tissue
Bone and Joint Part 2 Leslie G Dodd, MD Relative rates of cancer Sarcomas are relatively uncommon tumors New cancer cases 2007 All sites 1.4 million prostate 218,890 lung 213,380 breast 180,510 Soft tissue
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1
 Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1 Hee-Jin Park, M.D., Sung-Moon Lee, M.D., Hee-Jung Lee, M.D., Jung-Sik Kim, M.D., Hong Kim, M.D. Primary lymphoma of bone is uncommon
Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1 Hee-Jin Park, M.D., Sung-Moon Lee, M.D., Hee-Jung Lee, M.D., Jung-Sik Kim, M.D., Hong Kim, M.D. Primary lymphoma of bone is uncommon
Case Report Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Documented Progression over 4 Years from Its Origin at the Metaphysis to the Articular Surface
 Volume 2016, Article ID 9786925, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9786925 Case Report Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Documented Progression over 4 Years from Its Origin at the Metaphysis to the Articular
Volume 2016, Article ID 9786925, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9786925 Case Report Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Documented Progression over 4 Years from Its Origin at the Metaphysis to the Articular
Pictorial Essay Benign and Malignant Bone Tumors: Radiological Diagnosis and Imaging Features
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Pictorial Essay Benign and Malignant Bone Tumors: Radiological Diagnosis and Imaging Features Katharina Grünberg, M.D.; Christoph Rehnitz, M.D.; Marc-André Weber, M.D., M.Sc.
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Pictorial Essay Benign and Malignant Bone Tumors: Radiological Diagnosis and Imaging Features Katharina Grünberg, M.D.; Christoph Rehnitz, M.D.; Marc-André Weber, M.D., M.Sc.
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,700 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,700 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Common Primary Tumors of Bone
 Special Report Common Primary Tumors of Bone Primary bone tumors are a relatively rare occurrence, however, they can have serious deleterious consequences. Many possess the ability to degenerate into malignant
Special Report Common Primary Tumors of Bone Primary bone tumors are a relatively rare occurrence, however, they can have serious deleterious consequences. Many possess the ability to degenerate into malignant
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title Benign bone tumors Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7h86k14t Journal Radiologic Clinics of North America, 49(6) ISSN 0033-8389 Authors Motamedi, K Seeger,
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title Benign bone tumors Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7h86k14t Journal Radiologic Clinics of North America, 49(6) ISSN 0033-8389 Authors Motamedi, K Seeger,
Primary Tumors of Ribs
 Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Case Report Intramedullary Chondrosarcoma of Proximal Humerus
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2012, Article ID 642062, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/642062 Case Report Intramedullary Chondrosarcoma of Proximal Humerus Pratiksha Yadav, Dolly
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2012, Article ID 642062, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/642062 Case Report Intramedullary Chondrosarcoma of Proximal Humerus Pratiksha Yadav, Dolly
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
Mark D. Murphey, MD, FACR
 Fundamental Concepts of Musculoskeletal Neoplasm: CT and MRI Mark D. Murphey, MD, FACR Important Features in Evaluation of Musculoskeletal Masses Differential diagnosis Preoperative assessment and staging
Fundamental Concepts of Musculoskeletal Neoplasm: CT and MRI Mark D. Murphey, MD, FACR Important Features in Evaluation of Musculoskeletal Masses Differential diagnosis Preoperative assessment and staging
Residents Section Pattern of the Month
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Rana et al. Periosteal Reaction Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Rich S. Rana 1 Jim S. Wu Ronald L. Eisenberg Rana RS, Wu JS, Eisenberg
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Rana et al. Periosteal Reaction Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Rich S. Rana 1 Jim S. Wu Ronald L. Eisenberg Rana RS, Wu JS, Eisenberg
Giant cell tumour of the sternum-two cases
 Giant cell tumour of the sternum-two cases Nishaa.P 1, Raghuram.P 2, Navin patil 3, Jaipal B.R 4 Akkamahadevi patel 5 Assistant Professor ESIC medical college and PGIMSR 1 Professor and HOD, 2 Professor
Giant cell tumour of the sternum-two cases Nishaa.P 1, Raghuram.P 2, Navin patil 3, Jaipal B.R 4 Akkamahadevi patel 5 Assistant Professor ESIC medical college and PGIMSR 1 Professor and HOD, 2 Professor
Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
FDG PET/CT of Primary Bone Tumors
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Costelloe et al. FDG PET/CT of one Tumors Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Colleen M. Costelloe 1 Hubert H. Chuang 2 John E. Madewell 1 Costelloe CM, Chuang HH, Madewell JE
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Costelloe et al. FDG PET/CT of one Tumors Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Colleen M. Costelloe 1 Hubert H. Chuang 2 John E. Madewell 1 Costelloe CM, Chuang HH, Madewell JE
5/4/ OBJECTIVES. Roentgen Signs. Approach to Interpretation. Radiographic Technique. Developmental Bone Diseases
 OBJECTIVES Small Animal Orthopedic Radiography Matthew Paek, VMD, MS, DACVR Basic Approach to Interpretation Basic Technical Parameters Developmental Bone Diseases Aggressive vs. Non aggressive Bone Diseases
OBJECTIVES Small Animal Orthopedic Radiography Matthew Paek, VMD, MS, DACVR Basic Approach to Interpretation Basic Technical Parameters Developmental Bone Diseases Aggressive vs. Non aggressive Bone Diseases
Osteosarcoma Anatomic and Histologic Variants
 natomic Pathology / OSTEOSRCOM Osteosarcoma natomic and Histologic Variants Michael J. Klein, MD, and Gene P. Siegal, MD, PhD Key Words: Osteosarcoma; Malignant bone tumors; ones; Imaging DOI: 10.1309/UC6KQHLD9LV2KENN
natomic Pathology / OSTEOSRCOM Osteosarcoma natomic and Histologic Variants Michael J. Klein, MD, and Gene P. Siegal, MD, PhD Key Words: Osteosarcoma; Malignant bone tumors; ones; Imaging DOI: 10.1309/UC6KQHLD9LV2KENN
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings
 Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
CASE STUDY: PRO-DENSE Injectable Regenerative Graft Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor
 : PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
: PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
Primary periosteal lymphoma rare and unusual
 Skeletal Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00256-006-0096-2 CASE REPORT Ibrahim Fikry Abdelwahab Benjamin Hoch George Hermann Stefano Bianchi Michael J. Klein Dempsey S. Springfield Primary periosteal lymphoma rare
Skeletal Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00256-006-0096-2 CASE REPORT Ibrahim Fikry Abdelwahab Benjamin Hoch George Hermann Stefano Bianchi Michael J. Klein Dempsey S. Springfield Primary periosteal lymphoma rare
Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage
 Accepted February 13th, 2004 Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage Ludwig Schwering¹, Markus Uhl² and Georg W. Herget( )¹ ¹ Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Accepted February 13th, 2004 Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage Ludwig Schwering¹, Markus Uhl² and Georg W. Herget( )¹ ¹ Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 672. FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA PETER G. BULLOUGH, M.B., Ch.B. JON WALIFY, F.R.C.S. Nuffield Department of Orthopaedic University of Oxford, Surgery,
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 672. FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA PETER G. BULLOUGH, M.B., Ch.B. JON WALIFY, F.R.C.S. Nuffield Department of Orthopaedic University of Oxford, Surgery,
MR Imaging of the Knee: Incidental Osseous Lesions
 943 RADIOLOGIC CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA MR Imaging of the Knee: Incidental Osseous Lesions Mark J. Kransdorf, MD a,b, *,JeffreyJ.Peterson,MD c, Laura W. Bancroft, MD c Radiol Clin N Am 45 (2007) 943 954
943 RADIOLOGIC CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA MR Imaging of the Knee: Incidental Osseous Lesions Mark J. Kransdorf, MD a,b, *,JeffreyJ.Peterson,MD c, Laura W. Bancroft, MD c Radiol Clin N Am 45 (2007) 943 954
Fine Needle Aspiration of Bone Tumours
 Fine Needle Aspiration of Bone Tumours Monographs in Clinical Cytology Vol. 19 Series Editor Svante R. Orell Kent Town Fine Needle Aspiration of Bone Tumours The Clinical, Radiological, Cytological Approach
Fine Needle Aspiration of Bone Tumours Monographs in Clinical Cytology Vol. 19 Series Editor Svante R. Orell Kent Town Fine Needle Aspiration of Bone Tumours The Clinical, Radiological, Cytological Approach
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling
 Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Focal Sclerosis in a Vertebra: Differential Diagnosis of a Solitary Osteoblastic Metastasis
 July 2001 Focal Sclerosis in a Vertebra: Differential Diagnosis of a Solitary Osteoblastic Metastasis Alice L. Fisher, Harvard Medical School Year IV Review of the Normal Anatomy of a Lumbar Vertebra:
July 2001 Focal Sclerosis in a Vertebra: Differential Diagnosis of a Solitary Osteoblastic Metastasis Alice L. Fisher, Harvard Medical School Year IV Review of the Normal Anatomy of a Lumbar Vertebra:
Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia of the Bone: A Rare Variant of Fibrous Dysplasia
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.448 Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia of the Bone: A Rare Variant of Fibrous Dysplasia Raju Vaishya 1, Amit Kumar Agarwal 1, Nishint Gupta 2, Vipul Vijay 1 1. Department
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.448 Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia of the Bone: A Rare Variant of Fibrous Dysplasia Raju Vaishya 1, Amit Kumar Agarwal 1, Nishint Gupta 2, Vipul Vijay 1 1. Department
Benign Tumors of Bone
 REVIEW ARTICLE Benign Tumors of Bone Subbarao K Padmshri Prof. Dr. Kakarla Subbara, Hyderabad, India. Benign tumors of bone are common while malignant tumors are rare. Benign tumors constitute about 75%
REVIEW ARTICLE Benign Tumors of Bone Subbarao K Padmshri Prof. Dr. Kakarla Subbara, Hyderabad, India. Benign tumors of bone are common while malignant tumors are rare. Benign tumors constitute about 75%
Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014
![Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014 Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014](/thumbs/89/100531147.jpg) Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
Incidental Enchondromas of the Knee
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Michael J. Walden 1 Mark D. Murphey 1,2,3 Jorge. Vidal 1,2 Walden MJ, Murphey MD, Vidal J Keywords: appendicular musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Michael J. Walden 1 Mark D. Murphey 1,2,3 Jorge. Vidal 1,2 Walden MJ, Murphey MD, Vidal J Keywords: appendicular musculoskeletal
History. 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation
 History 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation Imaging Photo Album Patient also had a smaller lesion 1 cm proximal to this lesion, not seen radiographically.
History 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation Imaging Photo Album Patient also had a smaller lesion 1 cm proximal to this lesion, not seen radiographically.
The role of Imaging in Ewing sarcoma
 The role of Imaging in Ewing sarcoma Poster No.: P-0109 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: D. Beomonte Zobel, C. Dell'atti, M. Bartocci, V. Martinelli, N. 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 Magarelli,
The role of Imaging in Ewing sarcoma Poster No.: P-0109 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: D. Beomonte Zobel, C. Dell'atti, M. Bartocci, V. Martinelli, N. 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 Magarelli,
