Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan: Epidemiological Retrospective Study in Miyagi Prefecture during 15 Years
|
|
|
- Karin Knight
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 006, Epidemiological 10, Study on Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan 199 Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan: Epidemiological Retrospective Study in Miyagi Prefecture during 15 Years TOSHIMI AIZAWA, TETSURO SATO, 1 YASUHISA TANAKA, HIROSHI OZAWA, TAKESHI HOSHIKAWA, YUSHIN ISHII, NAOKI MOROZUMI, KENTARO ISHIBASHI, 3 FUMIO KASAMA, 4 HIRONORI HYODO, 1 EIICHI MURAKAMI, 5 TAKESHI NISHIHIRA 6 and SHOICHI KOKUBUN Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sendai Orthopedic Hospital, Sendai, Japan Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Nishitaga National Hospital, Sendai, Japan 3 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sendai Medical Center, Sendai, Japan 4 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tohoku Rosai Hospital, Sendai, Japan 5 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sendai Social Insurance Hospital, Sendai, Japan, and 6 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, JR Sendai Hospital, Sendai, Japan AIZAWA, T., SATO T., TANAKA, Y., OZAWA, H., HOSHIKAWA, T., ISHII, Y., MOROZUMI, N., ISHIBASHI, K., KASAMA F., HYODO, H., MURAKAMI, E., NISHIHIRA T. and KOKUBUN, S. Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan: Epidemiological Retrospective Study in Miyagi Prefecture during 15 Years. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 10 (3), Thoracic myelopathy is defined as spinal cord compression in the thoracic region, leading to sensory and motor dysfunctions in the trunk and lower extremities, and can be caused by various degenerative processes of the spine. Thoracic myelopathy is rare, and there are many unsolved problems including its epidemiological and clinical features. We have established a registration system of spinal surgeries, which covered almost all surgeries in Miyagi Prefecture, and enrolled the data of 65 patients with thoracic myelopathy from 1988 to 00. The annual rate of surgery gradually increased and averaged 0.9 per 100,000 inhabitants, which was less than 1/10 of that for cervical myelopathy. About 0 patients with thoracic myelopathy are operated on in Miyagi Prefecture each year. It frequently develops in middle-aged males. About half of the cases were caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum, followed by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament, intervertebral disc herniation and posterior spur. Patients usually noticed numbness or pain in the legs and the preoperative duration was long, averaging years. Its symptomatic similarities to lumbar disorders might cause difficulty in making a correct diagnosis. Since thoracic myelopathy can markedly restrict the activities of daily life, even general physicians should recognize this entity. thoracic myelopathy; epidemiological study; ossification of the ligamentum flavum; ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament 006 Tohoku University Medical Press Received July 7, 006; revision accepted for publication August 30, 006. Correspondence: Toshimi Aizawa, M.D., Ph.D., 1-1, Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai , Japan. toshi-7@ra.so-net.ne.jp 199
2 00 T. Aizawa et al. Thoracic myelopathy is defined as spinal cord compression in the thoracic region, leading to sensory and motor dysfunctions in the trunk and lower extremities and urinary disturbance, and can be caused by various degenerative processes of the spine such as intervertebral disc herniation (HE), ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) and the ligamentum flavum (OLF), and posterior spur (SP) (Smith and Godersky 1987; Yonenobu et al. 1987; Otani et al. 1988; Mitra et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a; Fong and Wong 004). The posterior longitudinal ligament connects the posterior aspects of the vertebral body while the ligamentum flavum is located in the interlaminar space. OPLL, HE and SP can compress the spinal cord from the anterior and OLF from the posterior. Unlike cervical myelopathy, the symptomatology of thoracic myelopathy is not well recognized by orthopedists or even by spine surgeons or neurosurgeons. It has often been overlooked or misdiagnosed as lumbar spinal disorders as the symptoms involve mainly the lower extremities (Mitra et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a). The number of the patients with thoracic myelopathy is much smaller than that of those with cervical or lumbar disorders (Mitra et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a). Most previous studies reviewed fewer than 100 patients, usually 30 patients or less (Yonenobu et al. 1987; Shiokawa et al. 001; Hamouda et al. 003). Thus, few epidemiological studies have assessed the true incidence of thoracic myelopathy necessitating surgery compared with cervical or lumbar disorders. In addition, the clinical features of thoracic myelopathy including the prevalence, age distribution, initial symptoms and the rate of corresponding spinal factors remain unclear. Since 1988, all spine surgeries at the orthopedic departments in Miyagi Prefecture, a province in northeastern Japan with a population of about.3 million, have been enrolled in the registration system of the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University School of Medicine (Kokubun et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a). Historically in Japan, patients with compressive myelopathy have been usually treated by orthopedic surgeons rather than by neurosurgeons. Therefore, the data from this registration system should be reliable and, based on these data, we have reported several epidemiological studies (Kokubun et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a; Tanaka et al. 003). Sato et al. (1997a), reported the epidemiological data on 81 patients with thoracic myelopathy based on this registration system for the 7 years between 1988 and To our knowledge, no other epidemiological studies on it have been reported from Japan or other countries. As the registry continued, more than 50 patients were surgically treated for thoracic myelopathy during the 15 years to 00. Using these data, the purpose of this study was to define the epidemiological and clinical features of thoracic myelopathy in the Japanese. This paper focuses on the epidemiological findings of this myelopathy in Miyagi Prefecture and not on the surgical outcomes nor on an analysis of the factors affecting the postoperative improvement. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Tohoku University School of Medicine. Between 1988 and 00, 15,714 surgical operations at 30 hospitals in Miyagi Prefecture were enrolled by the registration system of the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University School of Medicine (Kokubun et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a). Two hundreds and sixty five patients with thoracic myelopathy required surgical intervention among the 14,458 patients in total who were the residents of this prefecture and underwent spinal surgeries within the prefecture. These 65 patients were the subjects of this study. Ten patients required to 3 revisions, secondary posterior fusion, dura mater repair, addition decompression, and therefore, totally 78 surgical operations were performed, which accounted for % of all the spinal surgeries. Neurological deficits attributed to thoracic myelopathy mostly included lower-extremity hyperreflexia, plank paraparesis, and/or sphincter dysfunction. Neurodiagnostic studies confirming this disorder included abnormal myelograms, computed tomograms (CT) and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies. The diagnoses and subsequent surgical operations were performed by highly experienced spinal surgeons at 15 of the 30 hospitals in Miyagi prefecture. Cases of thoracic
3 Epidemiological Study on Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan 01 myelopathy caused by spinal cord tumor, primary or metastatic bone tumor, infection, spinal cord herniation (Aizawa et al. 001), and fracture or fracture dislocation, were excluded from the current study. The number of operations in each year was counted and the annual rate per 100,000 inhabitants in Miyagi Prefecture was calculated using the annual population of this prefecture. Variables contributing to the clinical features of thoracic myelopathy were assessed for the 65 patients: the gender and age, the initial symptoms, the preoperative duration from the onset of the initial symptoms, the compressive factors for the spinal cord and the locations in relation to the intervertebral disc levels, and the types of surgical procedures. In addition, operative findings on ossification of the dura mater that could not be dissected from OLF, which is closely related to the difficulty of the surgery, were investigated in the OLF patients. The preoperative disease period was divided into four: shorter than 6 months, from 6 months to 1 year, from 1 to years, and years or longer. RESULTS The annual rate of surgery for thoracic myelopathy in Miyagi Prefecture gradually increased and the average rate per 100,000 inhabitants for 5-year periods was 0.5 between 1988 and 199, 0.8 between 1993 and 1997 and 0.9 between 1998 and 00 (Fig. 1). The last rate was thus almost double that of the earliest period. Of the 65 patients undergoing thoracic decompressions, males significantly outnumbered females (. ratio), and were younger on average than their female counterparts (Table 1). The highest prevalence was for male patients in their sixties, followed by those in their fifties and seventies. On the other hand, the prevalence was almost similar for female patients in their fifties, sixties and seventies and they together accounted for about 80% of all patients (Fig. ). OLF, OPLL, HE, and SP were most consistently contributing spinal factors to thoracic myelopathy, with half showing OLF, followed by OPLL, HE, and OLF with OPLL and SP (Fig. 3). Three patients had a combination of two of OLF, HE or SP. The remaining 13 patients had rare factors such as kyphoscoliosis (Sato et al. 1997b), spondylolisthesis, or spinal canal stenosis in association with achondroplasia. The most common initial symptoms included numbness and tingling or pain in the lower extremities, followed by spastic gait and/or weakness. A handful (5%) of patients complained of back pain. A few patients noted atrophy/cramping of the lower extremities first. The preoperative duration from the onset of the initial symptoms averaged years and about half of the patients showed symptoms longer than 1 year while one third were less than 6 months. HE patients showed the shortest preoperative durations while those of the SP patients were relatively long. The mean age at surgery of the SP and HE patients Fig. 1. Yearly changes in the surgical rate for patients with thoracic myelopathy in Miyagi Prefecture from 1988 to 00.
4 0 T. Aizawa et al. TABLE 1. Summary of the patients with thoracic myelopathy. Male: Female Mean age at surgery Male (n = 18) Female (n = 83) OLF (n = 139) OPLL (n = 33) OLF + OPLL (n = 5) HE (n = 30) SP (n = ) Initial symptoms (n = 178) Tingling, numbness or pain in legs Gait disturbance Back pain Others Averaged preoperative duration of symptoms 6 month 6 months < 1yr 1 yr < yrs yrs Unknown or not decidable OLF (n = 139) OPLL (n = 33) OLF + OPLL (n = 5) HE (n = 30) SP (n = ) 18: 83 * 59 yrs (range; 9-84) 63 yrs (range; 3-85) 64 yrs (range; 38-85) 58 yrs (range; 39-84) 58 yrs (range; 36-73) 56 yrs (range; 38-79) 49 yrs (range; 9-7) 56% (n = 100) 35% (n = 6) 5% (n = 9) 4% (n = 7) yrs (range; 1 month-18 yrs) 49 patients 34 patients 9 patients 43 patients 110 patients 1.8 yrs (range; 1 month-11 yrs).1 yrs (range; 1 month-17 yrs).4 yrs (range; month-14 yrs) 1.0 yrs (range; 1 month-6 yrs) 3.0 yrs (range; month-18yrs) OLF, ossification of the ligamentum flavum; OPLL, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament; HE, intervertebral disc herniation; SP, posterior spur. Statistically significant differences can be detected only in the male/ female ratio. * p < Fig.. Age distribution of the patients with thoracic myelopathy in Miyagi Prefecture. Among males, the patients in their sixties show the highest prevalence, and among females, those in the fifties, sixties and seventies show almost equal prevalences.
5 Epidemiological Study on Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan 03 Fig. 3. Spinal factors compressing the spinal cord leading to thoracic myelopathy. OLF, ossification of the ligamentum flavum; OPLL, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament; HE, intervertebral disc herniation; SP, posterior spur. was lower than that of those with the other compressive spinal factors (Table 1). The decompression levels for the four major factors, OLF, OPLL, HE and SP, considered to be responsible for the thoracic myelopathy are shown in Fig. 4. The patients having a combination of two of those factors were excluded as it was uncertain which factor was responsible for the myelopathy. The surgical levels for OLF were between T10/11 and T11/1 in 65%, for OPLL they were between T1/ and T6/7 in 84%, for HE at T7/8 or lower in 90%, and for SP between T10/11 and T1/L1 in 64%. The surgical procedures for the four major compressing factors are summarized in Table. Laminectomy was most frequently performed for OLF followed by fenestration, partial resection of the lamina with the spinous process and upper part of the lamina kept intact. Before 1993, laminectomy was performed in 4 of 7 patients and hemilaminectomy in the others. Thereafter, OLF at a single level without fusion in the middle of the spinal canal was usually removed by fenestration and laminectomy, and fenestration was performed with equal frequency (Sato et al. 1998). Ossified dura mater that could not be dissected Fig. 4. Distribution of the four major compressive factors in the spinal cord in relation to the intervertebral disc level. OLF is most common in the lower thoracic spine while OPLL is frequently distributed in the upper to middle thoracic. Intervertebral disc herniation is mainly detected in the middle and lower thoracic spine and posterior spur in the lower thoracic spine.
6 04 T. Aizawa et al. TABLE. Surgical procedures for the common compressing spinal factors in thoracic myelopathy. OLF Laminectomy Fenestration Laminectomy + fenestration Hemilaminectomy Others 139 patients OPLL Laminectomy Anterior decompression through posterior approach Otsuka Anterior decompression & spinal fusion Anterior decompression through a diagonal anterior and posterior approach Others 33 patients 4 3 OLF + OPLL Laminectomy Laminoplasty + laminectomy Fenestration Anterior decompression through posterior approach Otsuka Disc herniation Anterior decompression & spinal fusion Hemilaminectomy Transverso-arthro-pediculectomy Others Posterior spur Anterior decompression & spinal fusion Laminectomy Others 5 patients patients patients OLF, ossification of the ligamentum flavum; OPLL, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament; HE, intervertebral disc herniation; SP, posterior spur. from the OLF was observed in 1 (9%) of 139 patients who had OLF alone (Fig. 5). Thick or beak-like OPLL combined with or without OLF (Fig. 6) usually compressed the spinal cord very severely and laminectomy alone could not achieve sufficient decompression. In such cases, anterior decompression through a diagonal anterior and posterior approach was done for two patients before 1994 (Kokubun et al. 1991), and anterior decompression through posterior approach described by Otsuka et al. (1983) was adopted for four patients after HE was treated by anterior decompression and spinal fusion (ASF) through an extrapleural or thoracotomy approach before 1996 and mainly by discectomy through a transverso-arthro-pediculectomy approach from the posterior afterwards (Sato 003).
7 Epidemiological Study on Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan 05 Fig. 5. Preoperative CT-myelogram of OLF with ossified dura mater at T10/11. OLF protrudes right-ventrally and the contrast medium between the spinal cord and OLF can not be detected (arrowhead). A B Fig. 6. Preoperative CT of a patient with OPLL. A: Sagittal plane. Continuous OPLL can be found in the upper thoracic spine including beak-like regions (arrows). B: Axial plane. Thick OPLL occupies the spinal canal at T3 level (arrowhead).
8 06 T. Aizawa et al. DISCUSSION Thoracic spinal disorders including tumors and fractures warranting surgical intervention constituted only 7% of all spinal procedures performed in the registration system of the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University School of Medicine (Tanaka et al. 003). Cases of thoracic myelopathy caused by degenerative processes of spine were even fewer, representing only % of all the spinal surgeries in this study. The annual rate of surgery was 0.9 per 100,000 inhabitants from 1998 to 00 in Miyagi Prefecture, which was less than 1/10 of that for cervical myelopathy (10.9) in the same prefecture in the same period, but nearly doubled during those 15 years (Tanaka et al. 003). This increase might be attributed to advances in neurodiagnostic imaging including CT and MRI and in the training of spinal surgeons. The present study showed that thoracic myelopathy more frequently develops in middleaged males. Previous studies also indicated that male cases were more common than female cases (Sato et al. 1997a; Shiokawa et al. 001; Hamouda et al. 003). Thoracic myelopathy patients were younger at operation than those with cervical myelopathy. The patients in the latter group were more frequently in their sixties to seventies (Tanaka et al. 003). It is unclear why thoracic myelopathy more often develops in middleaged people compared to cervical myelopathy patients. OLF and OPLL, the major causes of thoracic myelopathy, might be associated with some genetic factors (Koga et al. 1998; Yamamoto et al. 00). The thoracic spine is naturally kyphotic and the spinal cord runs anterior of the spinal canal, which suggests the cord is more easily damaged from the anterior side. Additionally, the spinal cord in the thoracic spine has a particularly vulnerable region called the watershed zone due to poor blood supply and the ratio of the cord to the canal is larger than in other parts of the spine (Stillerman and Weiss 1991). Since the cord is debilitated more easily by compressive spinal factors, thoracic myelopathy might develop earlier than in the cases of cervical myelopathy. The symptomatology of thoracic myelopathy is similar to that of lumbar disorders (Mitra et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a). It usually appears first in the lower extremities (Sato et al. 1997a). In the current study, more than one half of the patients initially noticed tingling, numbness or pain in the lower legs. Interestingly enough, 5% of the patients complained of back pain, which was in contrast to patients with cervical myelopathy who rarely presented with neck pain (Smith and Godersky 1987; Bernhardt et al. 1993; Kokubun et al. 1996; Mitra et al. 1996; Sato et al. 1997a). Thoracic myelopathy usually progresses slowly (Shiokawa et al. 001; Fong and Wong 004). In the present study, the preoperative duration from the initial onset of symptoms until surgery was also relatively long, years on average, which might result from by this slow progression and the difficulty of the diagnosis because of similarities with lumbar disorders. However, the fact that about one third of the patients showed preoperative durations of less than 6 months suggests that thoracic myelopathy sometimes progresses rapidly (Otani 1988; Shiokawa et al. 001; Fong and Wong 004). Careful observation is necessary in order to avoid deterioration of the myelopathy. OLF is the most common compressive factor contributing to thoracic myelopathy in the Japanese (Yonenobu et al. 1987; Sato et al. 1997a), and was responsible for 60% of all thoracic cord compression diseases in this series, either alone or in combination with OPLL. As for the location of the ossification of spinal ligaments, OLF and OPLL showed contrasting appearances. OLF is hardly found in the cervical spine (Kokubun et al. 1996). On the other hand, OPLL is one of the most frequent compressive factors of cervical myelopathy and was found in 0% of such patients (Kokubun et al. 1996). OPLL was found mostly in the upper to middle thoracic spine, whereas OLF was mostly in the lower thoracic in the current study as previously described (Yonenobu et al. 1987; Sato et al. 1997a). For the development of OLF, mechanical stress also plays an important role. Higher mechanical forces cause more pronounced degenerative changes of the facet joints and intervertebral discs at the
9 Epidemiological Study on Thoracic Myelopathy in Japan 07 thoracolumbar junction, which might lead to further degeneration of the ligamentum flavum at the lower thoracic spine (Payer et al. 000). Laminectomy is the standard procedure for OLF. From our experience, however, some technical modifications have been required based on the conditions of OLF, depending on whether bilateral OLFs are fused at the middle of the spinal canal (Sato et al. 1998; Sato 003). Fenestration or French-door laminectomy was performed for the non-fused OLF as longitudinal resection of the lamina and ligamentum flavum at the middle of the spinal canal is easy. Since it is difficult to cut the fused OLF at the middle, en bloc laminectomy was selected in such cases (Sato et al. 1998; Sato 003). Based on this surgical strategy, the number of surgical procedures for OLF myelopathy changed. About 10% of the OLF patients in this study had the ossification of the dura mater. The OLF needs to be removed together with the ossified dura while keeping the arachnoid intact, and subsequent dural repair is required in order to avoid cerebrospinal fluid leak (Sato 003; Fong and Wong 004). There are still many unsolved problems in the treatment of thoracic OPLL. In some patients, laminectomy alone does not sufficiently decompress the spinal cord impinged from the front by thick or beak-like OPLL in the thoracic spine since the spinal curvature is kyphotic and the spinal cord does not shift backward enough by it (Yonenobu et al. 1987). Several surgical procedures have been developed in order to ensure sufficient decompression for OPLL, and these had also been performed in this series (Ohtsuka et al. 1983; Kokubun et al. 1991). But the indications for each procedure, the range of decompression and the necessity for combined spinal fusion have not been clarified completely. Thoracic myelopathy is not common and not well recognized by orthopedists or even by spinal surgeons, particularly outside Japan (Yonenobu et al. 1987). Not only orthopaedists but also general physicians should know this entity since a delay in diagnosis and subsequent treatment might result in severe gait and urinary disturbance, which can markedly restrict the activities of daily life. In addition, spinal surgeons should better recognize the clinical features and neurodiagnostic findings of thoracic myelopathy that indicate the need for surgical intervention. References Aizawa, T., Sato, T., Tanaka, Y., Kotajima, S., Sekiya, M. & Kokubun, S. (001) Idiopathic herniation of the thoracic spinal cord. Spine, 6, E488-E491. Bernhardt, M., Hynes, R.A., Blume, H.W. & White, A.A., III (1993) Current concepts review: cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am., 75, Fong, S.Y. & Wong, H.K. (004) Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ligamentum flavum ossification. Annals. Acad. Med., 33, Hamouda, K.B., Jemel, H. & Khaldi, M. (003) Thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum: a report of 18 cases. J. Neurosurg. (Spine ), 99, Koga, H., Sakou, T., Taketomi, E., Hayashi, K., Numasawa, T., Harata, S., Yone, K., Matsunaga, S., Otterud, B., Inoue, I. & Leppert, M. (1998) Genetic mapping of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 6, Kokubun, S., Kashimoto, O., Ozawa, H., Hashimoto, Y., Kikawa, T., Gomibuchi, S. & Sakurai, M. (1991) Anterior decompression in the thoracic spine through a diagonal antero-posterior approach. Tohoku Archives Orthop. Surg. Traumatol., 35, (in Japanese) Kokubun, S., Sato, S., Ishii, Y. & Tanaka, Y. (1996) Cervical myelopathy in the Japanese. Clin. Orthop., 33, Mitra, S.R., Gurjar, S.G. & Mitra, K.R. (1996) Degenerative disease of the thoracic spine in central India. Spinal Cord., 34, Otani, K., Yoshida, M., Fujii, E., Nakai, S. & Shibasaki, K. (1988) Thoracic disc herniation-surgical treatment in 3 patients-. Spine, 13, Otsuka, K., Terayama, K., Tsuchiya, T., Wada, K., Furukawa, K. & Okubo, M. (1983) A surgical procedure of the anterior decompression of the thoracic spinal cord through the posterior approach. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol., 6, (in Japanese) Payer, M., Bruder, E., Fischer, J.A. & Benini, A. (000) Thoracic myelopathy due to enlarged ossified yellow ligaments. J. Neurosurg. (Spine 1), 9, Smith, D.E. & Godersky, J.C. (1987) Thoracic spondylosis: an unusual cause of myelopathy. Neurosurgery, 0, Sato, T., Kokubun, S., Tanaka, Y. & Ishii, Y. (1997a) Thoracic myelopathy in the Japanese: epidemiological and clinical observations on the cases in Miyagi Prefecture. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 184, Sato, T., Kokubun, S., Tanaka, Y. & Aizawa, T. (1997b) Paraparesis associated with mild congenital kyphoscoliosis in an adult. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 183, Sato, T., Tanaka, Y., Aizawa, T., Koizumi, Y.& Kokubun, S. (1998) Surgical treatment for ossification of ligamentum flavum in the thoracic spine and its complications. Spine Spinal Cord, 11, (in Japanese) Sato, T. (003) Operative method for thoracic myelopathy based on each spinal pathological factor. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol., 46, (in Japanese) Shiokawa, K., Hanakita, J., Suwa, H., Saiki, M., Oda, M. &
10 08 T. Aizawa et al. Kajiwara, M. (001) Clinical analysis and prognostic study of ossified ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. J. Neurosurg. (Spine ), 94, 1-6. Stillerman, C.B. & Weiss, M.H. (1991) Management of thoracic disc disease. In: Proceeding of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. Los Angeles, California Clin. Neurosurg. vol 38, edited by W. Selman, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp Tanaka, Y., Kokubun, S., Sato, T. & Ishii, Y. (003) Changes on spine and spinal cord lesions in frequencies of their surgeries; an observation based on the registered cases for 14 years. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol., 46, (in Japanese) Yonenobu, K., Ebara, S., Fujiwara, K., Yamashita, K., Ono, K., Yamamoto, T., Harada, N., Ogino, H. & Ojima, S. (1987) Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ossification of the spinal ligament. J. Neurosurg., 66, Yamamoto, Y., Furukawa, K., Ueyama, K., Nakanishi, T., Takigawa, M. & Harata, S. (00) Possible roles of CTGF/ Hcs4 in the initiation and development of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine, 7,
Contributing factors affecting the prognosis surgical outcome for thoracic OLF
 Eur Spine J (2006) 15: 485 491 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0903-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sung Uk Kuh Young Soo Kim Yong Eun Cho Byung Ho Jin Keun Su Kim Young Sul Yoon Dong Kyu Chin Contributing factors affecting
Eur Spine J (2006) 15: 485 491 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0903-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sung Uk Kuh Young Soo Kim Yong Eun Cho Byung Ho Jin Keun Su Kim Young Sul Yoon Dong Kyu Chin Contributing factors affecting
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine
 J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy in 60 consecutive patients with cervical ossi cation of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
We performed CT myelography in 38 patients
 Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ossification of the spinal ligament
 J Neurosurg 66:11-18, 1987 Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ossification of the spinal ligament KAZUO YONENOBU, M.D., D.Ms., SOHE EBARA, M.D., KEJU FUJWARA, M.D., KAZUO YAMASH TA, M.D., KERO ONO, M.D.,
J Neurosurg 66:11-18, 1987 Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ossification of the spinal ligament KAZUO YONENOBU, M.D., D.Ms., SOHE EBARA, M.D., KEJU FUJWARA, M.D., KAZUO YAMASH TA, M.D., KERO ONO, M.D.,
Elderly-onset degenerative lumbar spondylotic myelopathy in a patient with a low-placed spinal cord successfully treated by laminotomy: a case report
 CASE REPORT Elderly-onset degenerative lumbar spondylotic myelopathy in a patient with a low-placed spinal cord successfully treated by laminotomy: a case report Ko Hashimoto 1,2, Takumi Tsubakino 1, Takeshi
CASE REPORT Elderly-onset degenerative lumbar spondylotic myelopathy in a patient with a low-placed spinal cord successfully treated by laminotomy: a case report Ko Hashimoto 1,2, Takumi Tsubakino 1, Takeshi
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Ossification of the ligamentum flavum
 REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Ossification of the ligamentum flavum Shigeru Hirabayashi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Teikyo University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan Abstract: Ossification
REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Ossification of the ligamentum flavum Shigeru Hirabayashi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Teikyo University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan Abstract: Ossification
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics
 Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Minamide A*, Yoshida M*, Yamada H*, Hashizume H*, NakagawaY*, Iwasaki H*, Tsutsui S*, Hiroyuki Oka H**.
 Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Lamina Osteotomy and Replantation With Miniplate Fixation for Thoracic Myelopathy Due to Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum
 Lamina Osteotomy and Replantation With Miniplate Fixation for Thoracic Myelopathy Due to Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum Zhi-Hong Nie, MD; Fa-Jing Liu, MD; Yong Shen, MD; Wen-Yuan Ding; Lin-Feng
Lamina Osteotomy and Replantation With Miniplate Fixation for Thoracic Myelopathy Due to Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum Zhi-Hong Nie, MD; Fa-Jing Liu, MD; Yong Shen, MD; Wen-Yuan Ding; Lin-Feng
흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 -
 대한척추외과학회지제 14 권제 1 호 Journal of Korean Spine Surg. Vol. 14, No. 1, pp 52~56, 2007 흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 - 하기용 김영훈 # 지원희 $ 가톨릭대학교의과대학강남성모병원정형외과, 성모자애병원정형외과 #, 강남성모병원영상의학과 $ Fracture of Ossification
대한척추외과학회지제 14 권제 1 호 Journal of Korean Spine Surg. Vol. 14, No. 1, pp 52~56, 2007 흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 - 하기용 김영훈 # 지원희 $ 가톨릭대학교의과대학강남성모병원정형외과, 성모자애병원정형외과 #, 강남성모병원영상의학과 $ Fracture of Ossification
Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy
 Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy Department of Spinal Surgery 1), Brain Attack Center Ota Memorial Hospital,
Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy Department of Spinal Surgery 1), Brain Attack Center Ota Memorial Hospital,
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients
 Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
ASJ. Analysis of the Prevalence and Distribution of Cervical and Thoracic Compressive Lesions of the Spinal Cord in Lumbar Degenerative Disease
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD
 CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy V Kumar,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy V Kumar,
Spinal Cord (2005) 43, & 2005 International Spinal Cord Society All rights reserved /05 $
 (2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
(2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging
 Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis
 Original Article Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis D. Agrawal, B. S. Sharma, A. Gupta, V. S. Mehta Department of
Original Article Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis D. Agrawal, B. S. Sharma, A. Gupta, V. S. Mehta Department of
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome
 Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
 Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
Appendix: Diagnostic Criteria for OPLL and Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm
 Appendix: Diagstic Criteria for OPLL and Diagsis and Treatment Algorithm Diagstic Criteria for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine (Proposed by the Committee for Development
Appendix: Diagstic Criteria for OPLL and Diagsis and Treatment Algorithm Diagstic Criteria for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine (Proposed by the Committee for Development
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
CMEARTICLE * * * Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed
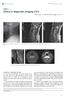 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy.
 Journal of the International Society of Head and Neck Trauma (ISHANT) Case report Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy. Dr. Reinel A. Junco Martin. Neurosurgeon. Assistant professor Miguel Enriquez
Journal of the International Society of Head and Neck Trauma (ISHANT) Case report Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy. Dr. Reinel A. Junco Martin. Neurosurgeon. Assistant professor Miguel Enriquez
Yoshifumi Kudo, 1 Tomoaki Toyone, 1 Toshiyuki Shirahata, 1 Tomoyuki Ozawa, 1 Akira Matsuoka, 1 Yoichi Jin, 2 and Katsunori Inagaki 1. 1.
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1250810, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1250810 Case Report A Case of Successful Foraminotomy for Severe Bilateral C5 Palsy following Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1250810, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1250810 Case Report A Case of Successful Foraminotomy for Severe Bilateral C5 Palsy following Posterior
POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION
 AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS
 Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF INCIDENTAL DURAL TEARS IN MICROENDOSCOPIC LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY: INCIDENCE AND OUTCOMES
 A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF INCIDENTAL DURAL TEARS IN MICROENDOSCOPIC LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY: INCIDENCE AND OUTCOMES Takahiro Tsutsumimoto, Mutsuki Yui, Masashi Uehara, Hiroki Ohba, Hiroshi Ohta, Hidemi
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF INCIDENTAL DURAL TEARS IN MICROENDOSCOPIC LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY: INCIDENCE AND OUTCOMES Takahiro Tsutsumimoto, Mutsuki Yui, Masashi Uehara, Hiroki Ohba, Hiroshi Ohta, Hidemi
Key words: Professional Med J 2018;25(8): CERVICAL LAMINOPLASTY
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4872 1. MBBS Post graduate Trainee, 2. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 3. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 4. MBBS Honorary Researcher, 5. MBBS, FCPS
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4872 1. MBBS Post graduate Trainee, 2. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 3. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 4. MBBS Honorary Researcher, 5. MBBS, FCPS
Review Article Operative Treatment of Cervical Myelopathy: Cervical Laminoplasty
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 508534, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/508534 Review Article Operative Treatment of Cervical Myelopathy: Cervical Laminoplasty Brett
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 508534, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/508534 Review Article Operative Treatment of Cervical Myelopathy: Cervical Laminoplasty Brett
Surgical Treatment for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (OPLL) at the Thoracic Spine: Usefulness of the Posterior Approach
 REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical Treatment for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (OPLL) at the Thoracic Spine: Usefulness of the Posterior Approach Shigeru Hirabayashi,
REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical Treatment for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (OPLL) at the Thoracic Spine: Usefulness of the Posterior Approach Shigeru Hirabayashi,
Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior Endplate Lesion after Recurrent Disc Herniation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
Department of Neurological Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
 online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA
 AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
Modified open-door cervical expansive laminoplasty for spondylotic myelopathy: operative technique, outcome, and predictors for gait improvement
 Modified open-door cervical expansive laminoplasty for spondylotic myelopathy: operative technique, outcome, and predictors for gait improvement Thomas T. Lee, M.D., Glen R. Manzano, B.S., and Barth A.
Modified open-door cervical expansive laminoplasty for spondylotic myelopathy: operative technique, outcome, and predictors for gait improvement Thomas T. Lee, M.D., Glen R. Manzano, B.S., and Barth A.
Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki 3), Masatsune Yamagata 1), Yoshikazu Ikeda 1), Fumitake Nakajima 1)
 Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Spine Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine
 Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Case Report Iatrogenic Spinal Cord Injury during Removal of the Inferior Articular Process in the Presence of Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 2318759, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2318759 Case Report Iatrogenic Spinal Cord Injury during Removal of the Inferior Articular Process in the
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 2318759, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2318759 Case Report Iatrogenic Spinal Cord Injury during Removal of the Inferior Articular Process in the
Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태
 KNS Main Topic Session Spine Surgery : Case-Based Lecture of Spinal Disease Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy ( CSM ) (1984,
KNS Main Topic Session Spine Surgery : Case-Based Lecture of Spinal Disease Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy ( CSM ) (1984,
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI /s
 Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy. Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86
 Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
We have reviewed the cervical spine radiographs
 THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY OF 180 PATIENTS TAKEO HARADA, SOHEI EBARA, MONZOOR M. ANWAR, ATSUKO OKAWA, ICHIRO KAJIURA, KAZUO HIROSHIMA, KEIRO ONO From Osaka Police
THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY OF 180 PATIENTS TAKEO HARADA, SOHEI EBARA, MONZOOR M. ANWAR, ATSUKO OKAWA, ICHIRO KAJIURA, KAZUO HIROSHIMA, KEIRO ONO From Osaka Police
Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
 283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical Treatment of Cervical Compressive Myelopathy
 International Journal of Neurosurgery 2018; 2(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijn doi: 10.11648/j.ijn.20180201.14 Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical
International Journal of Neurosurgery 2018; 2(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijn doi: 10.11648/j.ijn.20180201.14 Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical
Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto
 Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic resonance imaging study evidence
 See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
Junming Cao, Yongsheng Lin, Xiangbei Qi, Zhihong Wang, Yipeng Yang, Hehuan Xia, Bin Xu
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):741-746 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067327 Original Article Effect of intramedullary signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images on prognosis in patients
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):741-746 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067327 Original Article Effect of intramedullary signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images on prognosis in patients
INTRODUCTION.
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.2.112 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (2) : 112-118, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.2.112 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (2) : 112-118, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review
 Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 J Neurosurg Spine 19:431 435, 2013 AANS, 2013 Upper cervical cord compression due to a C-1 posterior arch in a patient with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and a kyphotic cervical spine
J Neurosurg Spine 19:431 435, 2013 AANS, 2013 Upper cervical cord compression due to a C-1 posterior arch in a patient with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and a kyphotic cervical spine
Retro-odontoid pseudotumors are mass lesions formed
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Microscopic Posterior Transdural Resection of Cervical Retro-Odontoid Pseudotumors Yasushi Fujiwara, MD, PhD,* Hideki Manabe,* Tadayoshi Sumida,w Nobuhiro Tanaka,z and Takahiko Hamasakiy
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Microscopic Posterior Transdural Resection of Cervical Retro-Odontoid Pseudotumors Yasushi Fujiwara, MD, PhD,* Hideki Manabe,* Tadayoshi Sumida,w Nobuhiro Tanaka,z and Takahiko Hamasakiy
Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures
 9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
Original Investigation. Byung-Wan CHOI. INTRODUCTION Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament ABSTRACT
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring with Tce-MEP for cervical laminoplasty
 Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring with Tce-MEP for cervical laminoplasty Nobuhiro Tanaka 1, 2), Kazuyoshi Nakanishi 2), Naosuke Kamei 2), Toshio Nakamae 2), Shinji Kotaka 2), Yoshinori Fujimoto 1),
Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring with Tce-MEP for cervical laminoplasty Nobuhiro Tanaka 1, 2), Kazuyoshi Nakanishi 2), Naosuke Kamei 2), Toshio Nakamae 2), Shinji Kotaka 2), Yoshinori Fujimoto 1),
Complex Spine Symposium January 12th, Balgrist University Hospital
 DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
Lift-up laminoplasty for myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine
 Original Article Lift-up laminoplasty for myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine T. Takami, K. Ohata, T. Goto, M. Nishikawa, A. Nishio, N. Tsuyuguchi,
Original Article Lift-up laminoplasty for myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine T. Takami, K. Ohata, T. Goto, M. Nishikawa, A. Nishio, N. Tsuyuguchi,
Morphological Patterns of the Anterior Median Fissure in the Cervical Spinal Cord Evaluated by Computed Tomography After Myelography
 Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. / January - March 4 57-6 Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion Ahmed
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. / January - March 4 57-6 Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion Ahmed
Spine Surgery: Techniques, Complication Avoidance, and Management. 2 Volume Set
 Spine Surgery: Techniques, Complication Avoidance, and Management. 2 Volume Set Benzel, E ISBN-13: 9781437705874 Table of Contents SECTION 1 - HISTORY 1 - History 2 - History of Spine Instrumentation -
Spine Surgery: Techniques, Complication Avoidance, and Management. 2 Volume Set Benzel, E ISBN-13: 9781437705874 Table of Contents SECTION 1 - HISTORY 1 - History 2 - History of Spine Instrumentation -
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: Make the difficult diagnosis, then refer for surgery
 REVIEW CME CREDIT WILLIAM E. MCCORMICK, MD Department of Neurosurgery, The Cleveland Clinic MICHAEL P. STEINMETZ, MD Department of Neurosurgery, The Cleveland Clinic EDWARD C. BENZEL, MD Department of
REVIEW CME CREDIT WILLIAM E. MCCORMICK, MD Department of Neurosurgery, The Cleveland Clinic MICHAEL P. STEINMETZ, MD Department of Neurosurgery, The Cleveland Clinic EDWARD C. BENZEL, MD Department of
Bilateral Foot Drop Without Cauda Equinae Syndrome Due To L4-L5 Disc Prolapse: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 1 Bilateral Foot Drop Without Cauda Equinae Syndrome Due To L4-L5 Disc Prolapse: A Case Report R Ramnaryan, C Palinikumar Citation R Ramnaryan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 1 Bilateral Foot Drop Without Cauda Equinae Syndrome Due To L4-L5 Disc Prolapse: A Case Report R Ramnaryan, C Palinikumar Citation R Ramnaryan,
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
Abstract Study Design Prospective clinical study.
 812 Technical Report GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Resection of Beak-Type Thoracic Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament from a Posterior Approach under Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring
812 Technical Report GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Resection of Beak-Type Thoracic Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament from a Posterior Approach under Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring
Anterior decompression for cervical spondylosis associated with an early form of cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 Neurosurg Focus 12 (1):Article 12, 2002, Click here to return to Table of Contents Anterior decompression for cervical spondylosis associated with an early form of cervical ossification of the posterior
Neurosurg Focus 12 (1):Article 12, 2002, Click here to return to Table of Contents Anterior decompression for cervical spondylosis associated with an early form of cervical ossification of the posterior
Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty
 CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
Jing Tao Zhang 1, Lin Feng Wang 1, Yue Ju Liu 2, Jun Ming Cao 1, Jie Li 1, Shuai Wang 1 and Yong Shen 1*
 Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Recent Surgical Methods of Double-door Laminoplasty of the Cervical Spine (Kurokawa s Method)
 TECHNICAL NOTE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Recent Surgical Methods of Double-door Laminoplasty of the Cervical Spine (Kurokawa s Method) Shigeru Hirabayashi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Teikyo
TECHNICAL NOTE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Recent Surgical Methods of Double-door Laminoplasty of the Cervical Spine (Kurokawa s Method) Shigeru Hirabayashi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Teikyo
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 08
 What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
Degenerative Disease of the Spine
 Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
APSS DHAKA OPERATIVE COURSE 13 th 15 th March 2018
 13 th 15 th March 2018 Local Organizing Chairman: Kh Abdul Awal Rizvi Local Organizing Secretary: Md Shah Alam APSS President: K S Sivananthan Venue: National Institute of Traumatology & Orthopaedic Rehabilitation
13 th 15 th March 2018 Local Organizing Chairman: Kh Abdul Awal Rizvi Local Organizing Secretary: Md Shah Alam APSS President: K S Sivananthan Venue: National Institute of Traumatology & Orthopaedic Rehabilitation
Tethered cord syndrome is a disorder involving an. Spine-shortening osteotomy for patients with tethered cord syndrome caused by lipomyelomeningocele
 See the corresponding editorial in this issue, pp 19 20. J Neurosurg Spine 15:21 27, 2011 Spine-shortening osteotomy for patients with tethered cord syndrome caused by lipomyelomeningocele Clinical article
See the corresponding editorial in this issue, pp 19 20. J Neurosurg Spine 15:21 27, 2011 Spine-shortening osteotomy for patients with tethered cord syndrome caused by lipomyelomeningocele Clinical article
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Introduction SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy
 Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Cervical myelopathy is caused by spinal canal narrowing
 An Original Study Instrumented Open-Door Laminoplasty as Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in 104 Patients John R. Dimar II, MD, Kelly R. Bratcher, RN, CCRP, Dylan C. Brock, BS, Steven D. Glassman, MD,
An Original Study Instrumented Open-Door Laminoplasty as Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in 104 Patients John R. Dimar II, MD, Kelly R. Bratcher, RN, CCRP, Dylan C. Brock, BS, Steven D. Glassman, MD,
SpineFAQs. Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
 SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up
 Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Microendoscopic Decompression Surgery for Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis via the Paramedian Approach: Preliminary Results
 Original Article 87 Microendoscopic Decompression Surgery for Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis via the Paramedian Approach: Preliminary Results Kazunori omura 1 Munehito Yoshida 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic
Original Article 87 Microendoscopic Decompression Surgery for Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis via the Paramedian Approach: Preliminary Results Kazunori omura 1 Munehito Yoshida 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic
ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. An introduction to
 An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
