Serum Alkaline Phosphatase, A Prospective Biomarker For Assessment of Progress of Fracture Healing
|
|
|
- Leonard Jefferson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: , p-issn: Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. I (Dec. 2017), PP Serum Alkaline Phosphatase, A Prospective Biomarker For Assessment of Progress of Fracture Healing *Dr. Anand Prakash 1,Dr. Nutan verma 2,Dr. M.P.Goyal 3, Dr. Narendra joshi 4,Dr. Mukesh Saini 5 1 Senior Resident,Department of orthopedics,churu Medical college 2 Senior Resident,Department of orthopedics,sn Medical college(department of Obs & Gynae.) Jodhpur, 3 Professor,Department of orthopedicssms MC, 4 Sr.Professor,Department of orthopedicssms MC, 5 Senior Resident,Department of orthopedicssms Medical college, Corresponding author: Dr Nutan Verma Abstract Introduction: Bone-specific alkaline phosphatase is a specific marker of osteoblasts and gives a good measure of bone forming activity. 1 bone metabolic units (BMU )are also activated in fracture healing and can be demonstrated quantitatively by estimation of bone turnover markers (BTMs). Serum alkaline phosphatase is a specific marker of osteoblasts and gives a good measure of bone forming activity. Aims :to evaluate the changes in serum alkaline phosphatase levels during healing of isolated femur shaft fractures treated with close reduction and interlocking nail Material And methods: descriptive, prospective and follow up study was conducted in the department of Orthopaedics, SMS Medical College & Attached Hospitals, Jaipur.64 healthy adults of age 18 to 45years with isolated closed fracture femur were included. The patients with any systemic condition, disease, and/or drug intake affecting bone turnover in any manner were excluded from the study. The fractures were closed reduced and internally fixed using an interlocking nail. Allthe patients were followed up every for 9 s after injury to look for clinico-radiological signs of fracture union. Biochemical monitoring was done The marker ALP was measured using in vitro qualitative measurement by p-npp method in biochemistry lab. Results: The outcome of the current study is that the serum alkaline phosphastase is suggested as non-invasive aids for monitoring fracture healing. It may help in the monitoring of fracture healing, complementing the clinico-radiological evaluation. The detection of volume of callus formed across the fracture site in combination with clinical signs of union remain the gold standard for assessing fracture healing. But early detection of a slow healing or a non-healing fracture is not possible using these methods only. Conclusion: sustained efforts need to be continued in our endeavour to find a bone turnover marker as a diagnostic or prognostic tool for monitoring bone healing. Keywords : Date of Submission: Date of acceptance: I. Introduction Bone-specific alkaline phosphatase is a specific marker of osteoblasts and gives a good measure of bone forming activity. 1 The femur fracture appears to be a good model for studying fracture healing in clinical setting because of its frequency of presentation, the levels of bone-turnover markers produced and the incidence of delayed union. 1 The ability to detect the elaboration of specific molecular markers of cellular activity may complement the clinic-radiological methods by enhancing the accuracy of assessment of fracture healing and may also allow the early detection of fractures at risk of delayed or non-union. 1 Assessment of fracture healing is a subjective process without a readily available gold standard. Clinically and radiologically, fracture healing is defined as being delayed if the healing process has not beencompleted within 6 s 18 The development of a nonunion is a common complication following long-bone fracture. Its incidence ranges up to 46%, 18,20 24 depending on injury location, bone loss, soft tissue injury. 28 Till date, no clinical or scientific assessment can reliably predict successful fracture healing. The diagnosis of a nonunion is typically made by attentive clinicalexamination. 30 Radiographic scoring has been helpful, but not perfect, in predicting fracturehealing. 34 However, computerized tomography with reconstructed views still seems to be the most useful non-operatordependent method for the evaluation of delayed or failed long bone union. 35 DOI: / Page
2 . The measurement of bone turnover markers (BTMs) in serum quantitatively assesses the rate of bone remodelling and thus could be a valid tool for monitoring changes of bone formation. The markers can represent bone formation, matrix breakdown, and enzymatic activity of bone cells 39. Alkaline phosphatase is a marker elevated in all mineralizing tissues.. 40 High ALP levels and an increased rate of matrix production are found in cartilage prior to matrix calcification. 42,43 the bone isoenzyme of ALP (BALP) is considered a more specific maker of bone formation. The ideal marker would have no short- term biological variability (i.e., stable over at least several days or weeks). The assay would be simple and automatable. The assay should have a high sensitivity as well as specificity. An individual s rate of remodeling may vary over time. 2 The day-to-day variation is ~10% for formation markers and 20% for resorption markers.. Bone resorption markers respond faster than formation markers to changes in bone remodeling because of shorter time of resorption than formation. 2 So the aim of the study was to evaluate the changes in serum alkaline phosphatase levels during healing of isolated femur shaft fractures treated with close reduction and interlocking nail II. Materials And Methods Adescriptive, prospective and follow up studywas conducted in the department of Orthopaedics, SMS Medical College & Attached Hospitals, Jaipur (Rajasthan)from Januaryto December A sample size of 64 patients year,of isolated simple, fresh (< 7 days), traumatic,closed fracture of shaft of femur, treated close reduction and interlocking nail femur in young adults was studied.isolated simple closed fracture of shaft of femur bone managed as close reduction and interlocking nail femur.traumatic fracturefresh (< 7 days) fracture, with Patient giving informed consent for study. Associated head injury or polytrauma case, Alcoholism,Drug abuse, Pathological fracture,metabolic bone diseases,peripheralneuropath,inflammatoryarthritis,diabetes mellitus uncontrolled, Malignancy,Patients on medications including (steroids, anticoagulants, bisphosphonates,antiepileptics, calcium, fluorides and immunosuppressive drugs),chronic liver disease,chronic renal failure Pregnant or lactating female were excluded. The routine investigations including haemogram, blood glucose level, liver and kidney function tests were done to exclude any factor effecting fracture healing, relevant radiographs with other preoperative investigations were obtained. The case record form was filled and an informed consent was taken. All the patient were treated as internally fixed using interlocking nail with 2 distal and 2 proximal locking bolts. Early range of motion exercises were started at knee and hip joint on the first post-operative day and patient was mobilized with help of crutches. Sample size calculated as 80% study power and error 0.05, assuming standard deviation of 40 in the mean serum alkaline phosphatase level found in a pilot study conducted on 5 patients. For Biomarker Examination2 ml. of peripheral blood will be collected in EDTA coated vials under standard aseptic technique.quantitative determination of serum ALP (Alkalinephosphatase) activity (at ph 10.4, temp c was donespectrophotomatrically(405mm)usinan p-nitrophenyl phosphate as a substrate and other reagent provided by LABKIT, according to LABKIT manual.reference range of normal adult is between IU/L at 37 C.Follow up will be done on the day of admission, 14 th day, 21 st day, 1, 42 nd day, 2, 3 day counted from day of trauma and last sample was collected when serum alkaline phophataselevelreturned to in its normal rangethe patients were followed up clinically for the signs of fracture union that is pain and tenderness at the fracture site at week then every till 9 s.the fracture union was defined as the time when three of the four cortices showed bridging callus across the fracture site. An antero-posterior and a lateral radiographs weretaken to assess the fracture healing. The radiographs were taken at 0 wks(at the time of presentation),on the day of surgery then 4 wks, 8 wks, 12 wks, 16 wks, 20 wks, 24 wks, 28 wks, 32 wks and 36wks.The presence or absence of callus and the number of cortices bridged by callus were observed in each radiograph and documented in case record sheet.non-union is defined as the cessation of all reparative processes of healing without bonny union. A fracture that at minimum of 9 s post occurrence and is not completely healed which is the case of group B 2 and has not shown radiographic progression for three s is labelled as nonunion of diaphyseal fracture of femur bone.quantitative determination of serum ALP (Alkalinephosphatase) activity (at ph 10.4, temp c will be done spectrophotomatrically (405 mm) using an p-nitrophenyl phosphate as a substrate and other reagent provided by LABKIT, according to LABKIT manual.reference range of normal adult is between IU/L at 37 C.This regent kit is intended for in vitro quantitative determination of Alkaline Phosphatase activity in serum/plasma. III. Sample Required Unhaemolysed Serum, heparinized plasma/ EDTA plasmain Children 3-15 years IU/l and 18 yearsadults IU/l was the reference range. Statistical Analysis: was performed with the SPSS,Trial version 20 for Windows statistical software package (SPSS inc., Chicago, il, USA) and PRIMER. The Categorical data were presented as numbers (percent) DOI: / Page
3 and were compared among groups using Chi square test. Groups were compared for demographic data were presented as mean and standard deviationand were comparedusing by student t-test and ANOVA for more than two groups Test applying to find out the most significant groups among all the groups. The serum level of alkaline phosphatase were compared at different follow up of post injury from baseline by using Wilcoxon sign test and paired t-test (for paired analysis) Probability P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant IV. Observations And Results All thesixty four patients were followed up for 9 s with no lost to follow up, whose age ranged from years (28.17 ± years). The maximum proportion (46.88%) was observed in18-26 years of age groups.according to mean age,the mean age of group A was 28.02±7.07 and in group B 1 was 26.50±5.03 and in group B 2 mean age was 34.20±8.38.(P=0.09N) Out of 64 patients, 51 patients were male and 13 patients were female, The M:F ratio was 3.92:1. In group-a females were 17.78% and male were 82.22%, in Group B 1, females were 21.43% and male were 78.57% and group B 2 female were 20% and male were 80%,;P = 0.952In the study, the most common mode of injury was road traffic accident (92.19%), other modes were Slip &Fall(3.13%) and fall from height (4.69%).In Group B % and in Group A 95.56% were from RTA. No significant difference were observed according to mechanism of injury among the groups. The maximum proportion (75%) was observed in Middle 1/3 followed by (20.31%) in Lower 1/3 and least (4.69%)were in upper 1/3.Transverse pattern were more in all the groups followed by oblique than spiral type. No case were observed of spiral type in group B 2.The common side were right in 59.38%.Overall right side cases were more in group-a and Group B 2, while in Group B 1 both side cases were equal in numbers. Upto at 8 weeks following injury pain and tenderness was present at fracture site in all of the cases. At 4, 5,6,7 s post injury tenderness at fracture site were 45 (70.31%),25 (29.69%)19 (29.69%) 11 (17.19%) casesand 8 th and 9 th s post injury tenderness at fracture site was present in only 5(7.81%) patients. We evaluated the level of ALP in the above 3 groups of patients based on absence of presence of tenderness. The levels of ALP were found to be higher in the group with presence of tenderness In radiological assessmentbridging callus in 3 or more cortices across the fracture site was visible in 56 patients at 8 weeks post injury, it was discernable in 61 patients at 12 weeks post injury, whereas it was seen in all patients at 4 s. At 12 weeks 3(4.68%) patients had bridging callus seen in 3 or more cortices whereas 61(95.3%) patients had bridging callus in <3 cortices. At 16 week 21 (37.5%) patients had bridging callus seen in 3 or more cortices whereas 43(67.18%) patients had bridging callus in <3 cortices. At 24 weeks 45 (70.31%) patients had bridging callus seen in 3 or more cortices whereas 19(29.68%) patients had bridging callus in <3 cortices. At 9 s 59(92.18%) patients had bridging callus seen in 3 or more cortices whereas 5(7.81%) patients had bridging callus in <3 cortices. So these 5 patients labeled as non union and 14 patient who developedbridging callus in 3 or more cortices between 24 to 36 weeks labeled as delayed union. The maximum proportion 45 (70.31%) was observed in group A(union) followed by 14 (21.88%) ingroup B1 (delayed union)and least5(7.81 %)were in group B 2 (non union)the bony healing occurred at 4.56 ±0.76s (range 3 to 6s) in group A and at 7.29±0.47 s (range 7 to 8 s) in group B 1 and this was statistically significant. (P<0.001S) In group B 2 all five cases were from non-union in the follow up duration of healing. There was no change at baseline in ALP level but mean ALP was significantly more in group A as compareed to group B 2 upto seven s. But at 8 th and 9 th s no significant difference was observed In the group A with delayed union, the levels of ALP hadincreased from the baseline and reached themaximum level at 21 st day then decreased graduallyand similar pattern also followed by group B 1 but levels of ALP were loweredthan group A. But through the follow up period no significant rise was observed in group B 2. The mean difference was significantly more in group A as compared to group B 1 but no significant rise was observed in 7 and 8 s of follow up between A and B 1 and no significant rise was observed in Group B 2. The mean value of serum ALP in group A at baseline was IU/L and rose significantly (P<0.0001S) to a mean value of IU/L at 14 th day. The level reached maximum IU/L at 21st day which is significantly increased from baseline (p=0.001) when compared to that of time of injury. In Group A mean serum ALP were found to be significantly elevated even till 04 s. At 5 the level of serum ALP had a mean value of which was not significant from the baseline. Significantly higher mean was observed in most of follow up period in group B 1 except in 7 and 8 of follow up from the baseline. In group B1The changes in mean serum ALP level in group B 2 were never significant and remained within normal limits throughout followup, so in our study total 64 patients were enrolled and studied which were allocated in group A (N=45), group B 1 (N=19) and group B 2 (N=5), depending on the progression, duration and type of bone healing. The average age of group A was years and Group B 1 was years and in group B 2 mean age was years. The difference between the mean age of these group was not significant. The bonny healing occurred at 4.56 (range 3 to 6 s) in group A and 7.29 (range 7 to 8 s) in group B 1 and this was statistically significant. In group B 2 all 5 cases were from non-union till the follow up duration of healing. DOI: / Page
4 V. Discussion In this study, adults of age group years have included as the level of serum alkaline phosphatase varies with age. Majority of patients were males. In an injurydatabase 131 it was seen that 70% of injury death and over half of non fatal injuries occur among males with the largest male-to-female ratio (over four-fold) seen among adolescents and young adults.female sex appeared to be a further risk factor for delayed healing in one of the studies. 31 In the present study 92% of the injuries were attributable to road traffic accidents. Adolescent and young adults are particularly at a high risk of injury due to RTA. 132 Their rates of death, hospitalization, and emergency department visits are approximately twice the rate for all ages combined.we considered road traffic accidents and fall from height are as high energy injuries when compared to household injuries which were considered as low energy injuries. In our study 96% of the injuries were high energy injuries while 4% were sustained by low energy trauma. In this study for successful union in the femur the following criteria must be observed,the absence of pain and tenderness at the site of fracture and visible bridging callus across the fracture on plain radiography. In the clinical follow up during the study all the 59 patients demonstrated clinical signs of fracture union within the study period of 36 weeks. 5 patient demonstrated tenderness at the fracture site at 36 weeks. Thus 59 fractures clinically within the 36 weeks period and 5 fractures not healed clinically within 36 week of period. Hence these 5 fracture labeled as non union. VI. Radioloical Outcome In our study,atthree s number of radiological union was 03 while number of clinical union (no tenderness at fracture side) was 09. In same manner at 4 and 5 number of patients having clinical union are higher than number of radiological union. It shows that radiological healing lags behind clinical assessment of fracture healing. VII. Biochemical Assessment Alkaline phosphatase is a marker of bone formation and the significantly raised levels of serum alkaline phosphatase at 14 th, 21 st and 28 th day 3 after fracture signify the increased osteoblastic activity occurring at the fracture site. There was no statistically significant difference in the levels of the marker with patient characteristics such as age, sex, and injury factors like the mode and severity of injury, level and pattern of the fracture and presence or absence of comminution in fracture. The rise in levels of the marker was in agreement with various previous studiesby Nyman et al 106, Leung et al 108, Bowles et al 109,Ingle et al 111,112 andherman et al 120. However the serial measurements in our study differed from that ofveitchet al 122,in our study the levels peaked between 8 and 12 weeks whereas in the study by Veitch et-al the levels peaked at 24 weeks.in our study the mean serum ALP level remained within normal limits in all included patients at the time of admission. The variation in serum ALP level followed the same pattern in Group-A and B1, reaching a maximum level at 3 rd week in both groups.serum ALP level remained elevated significantly till 4 s in Group-A and reached within normal limit when clinico-radiological union occurred. In Group B 1 mean serum ALP remained significantly elevated till 6 s. Till bony union occurred in Group A, at every interval the mean value of serum ALP of group A were significantly higher than of group B 1. The changes in mean serum ALP level in group B 2 were never significant and remained within normal limit till 9 s.depending on the clinico-radiological parameters of progression of fracture healing, all 64 patients were allocated into two groups by the end of active follow up; Group A (n=45) clinico-radiological union achieved before or by the end of six s; and Group B (n=19) clinico-radiological union not completed by the end of six s. The Group B was further subdivided into B 1 (n=14); clinico-radiological healing not completed by six s but completed by the end of nine s, and B 2 (n=05) clinico-radiological healing not achieved even by the end of nine s- Non-union. the determination of serum ALP levels during fracture healing could be an additional tool in predicting fractures at risk of healed/ non-union of simple diaphyseal fractures, adding the clinician to prefer the early appropriate intervention at appropriate period. The outcome of this study is that estimation of serum alkaline phosphatase correlates with the clinicoradiological signs of fracture healing in femur diaphyseal fracture. There is a significant rise in the level of the bone formation marker demonstrating an increased osteoblastic activity. The radiographic detection of callus also correlates with the level of serum alkaline phosphatase suggesting its role in the mineralization of the callus and consolidation of the fracture.the bone turnover markers are suggested as a non-invasive aid for monitoringfracture healing. They may help in the monitoring of fracture healing, complementing the clinicoradiological evaluation.further studies in this direction can throw more light on the complex process of bone healing and the delicate balance between bone formation and resorption. Analyses of the volume of callus that is formed across the fracture site in combination with clinical signs of union remain the gold standard for monitoring fracture healing. But early detection of a slow healing or a non healing fracture is not possible using these methods only. 2 DOI: / Page
5 Radiological features lag behind clinical assessment of fracture healing. Delayed diagnosis of a nonunion is costly from both the patient and treatment standpoints. The complex mechanisms and the mysterious pathways of a bone not healing normally need to be revealed as the secret of predicting which injured bone will not heal lies within them. Therefore, sustained efforts need to be continued in our endeavour to find bone turnover markers as diagnostic or prognostic tools for monitoring bone healing. Hence there is a need to develop an accurate, precise, reliable, reproducible, patient-doctor friendly and post-detective method to measure fracture healing objectively. Skeletal turn-over can be assessed easily and non-invasively by the measurement of turn-over markers. Thus, early knowledge of the individual progress of fracture could help to keep of delayed or non-union by enabling modification of the host biological response.in adult patients under the ideal circumstances the expected time of bone-union of an uncomplicated diaphyseal femur fracture is approximately 4 to 8 s which is the case of group-a (mean union at 4.56 s). Delayed union is considered as a fracture that requires more time for complete bone union than the usual but will unite ultimately, which is the case of group B 1 (mean union of 7.29 s).in the present study the incidence of clinicoradiological non-union at the end of 9 s was 7.8%. In our study the serial serum ALP levels were correlated with the clinico-radiological progression of bonny fracture healing in all patients. In all 64 patients we were able to credit the fate of fracture healing process by the serial estimation of serum ALP level. We observed that serum ALP level at 3 rd week was correlated with future outcome of these fractures. We may predict the future outcome of these fractures at as early as 3 rd week. Our findings were related with ALP level variation during fracture healing were corresponding with that of other studies.in our study, changes in serum ALP level in group A and B 1 paralleled the process of fracture healing as documented by clinico-radiological evidences. Though, in group A, mean ALP returned to normal reference limits by clinico-radiological fracture healing, in group B 2 these levels remained elevated till six s. Suggestive of ongoing osteoblastic activity in these patients. At six s clinico-radiology it was not evident that which patients will fall into delayed union and which one will be in non-union. Waiting 9 s to diagnose and treat a non-union is patentlyunreasonable in modern world. These dilemma raised a question that whether a clinician should wait for radiological sign to settle down for an establish diagnosis of non-union or one can predict and can intervene early by observing a biomarker, like serum ALP.We may predict the future outcome of these fractures as early as 3 rd week by observing the serum ALP level. VIII. Limitations of the study 1. The number of patients was limited in this time bound study. 2. The periodic longitudinal estimation of bone turnover markers for assessing fracture healing till consolidation and remodeling could not be carried out due to the fixed time period and the limited financial resources available.other Bone turnover markers have not been considered due limited financial resources available. IX. Conclusion The bone turnover markers are suggested as a non-invasive aid for monitoring fracture healing. They may help in the monitoring of fracture healing, complementing the clinico-radiological evaluation. Table No 1: Baseline Charactorstics Of The Study Population Group A(N=45) Group B1(N=14) Group B2(N=5) Total Age Group No No No No 18 To 26 21(46.67%) 8(57.14%) 1(20%) 30(46.88%) 27 To 35 17(37.78%) 6(42.86%) 2(40%) 25(39.06%) 36 To 45 7(15.56%) 0 2(40%) 9(14.06%) Sex F 8(17.78%) 3(21.43%) 1(20%) 12(18.75%) M 37(82.22%) 11(78.57%) 4(80%) 52(81.25%) Mode Of Injury Fall From Height 1(2.22%) 2(14.29%) 0 3(4.69%) RTA 43(95.56%) 11(78.57%) 5(100%) 59(92.19%) Slip & Fall 1(2.22%) 1(7.14%) 0 2(3.13%) Oblique 17(37.78%) 6(42.86%) 3(60%) 26(40.63%) Spiral 7(15.56%) 2(14.29%) 0 9(14.06%) Transverse 21(46.67%) 6(42.86%) 2(40%) 29(45.31%) Location P Value LS 0.23NS 0.95NS 0.29NS 0.842NS DOI: / Page
6 Lower 1/3 10(22.22%) 2(14.26%) 1(20%) 13(20.31%) Middle 1/3 34(75.56%) 11(78.57%) 3(60%) 48(75%) Upper 1/3 1(2.22%) 1(7.14%) 1(20%) 3(4.69%) Side Wise Left 14(31.11%) 7(50%) 2(40%) 26(35.94%) Right 31(68.89%) 7(50%) 3(60%) 38(64.06%) 0.438NS 0.009S Table No 2: Fracture charactorstics among the groups Level of fracture No. of patients(n=64) Percentage(%) Upper 1/ Middle 1/ Lower 1/ Level of fracture No. of patients % Transverse Oblique Spiral 9 15 Side Left Right Table No3: Comparison Between Radiological And Clinical Signs Of Fracture Healing Among The Groups Tenderness On day of 1 m 2 m 3 m 4 m 5 m 6 m 7 m 8 m 9 m operation Present Percentage % No. of cortices in bridging callus (10 37(4 New) New) No. of 3 < cortices in bridging callus Visible Not visible Biochemical Monitoring Table No 4: Serum Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)at different time interval DOA 14th day 21st day 1 42nd day N Mean Std. Deviation Median Minimum Maximum Figure: 1Distribution Of Cases Among The Groups According To Mean Difference In ALP From Baseline At Different Interval Of Follow Up DOI: / Page
7 Table No. 5 Serum Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) At Different Time Interval Of Injury Among The Groups Group DOA 14 th 21 st 1 42 nd day day day mont h mont h A N Mean SD B1 N Mean SD B2 N Mean P value LS Group from Baseline SD N <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 < N 0.053N NA S S S S S S S S S S S S Table 6: Distribution of cases among the group according to ALP at different interval of follow up from baseline Group B 2(N=5) Group A(N=45) Group B1(N=14) N Mean SD N Mean SD N Mean SD P Value LS <0.001S NS 14th day <0.001S <0.001S st day <0.001S <0.001S NS <0.001S <0.001S NS 42nd day <0.001S <0.001S NS <0.001S <0.001S NS <0.001S <0.001S NS <0.001S <0.001S NS NS <0.001S NS NS <0.001S NS NS NS NS NS NS *Dr. Anand Prakash. Serum Alkaline Phosphatase, A Prospective Biomarker For Assessment of Progress of Fracture Healing. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS), vol. 16, no. 12, 2017, pp DOI: / Page
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis
 Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHYSEAL FEMUR FRACTURE WITH INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL AND K. NAIL
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Segmental tibial fractures treated with unreamed interlocking nail A prospective study
 2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace
 18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre
 Original article : Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre Chandra Prakash Singh Associate Professor, Department
Original article : Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre Chandra Prakash Singh Associate Professor, Department
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of Both Bone Leg In Patients Attending Assam Medical College Hospital, Dibrugarh. Partha Pratim Das 5
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion. Norbert Wiegand
 Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion Norbert Wiegand 2/3 of traumatology: treatment of fractures We have to understand: Structure of the bone Biology of the bone Bone healing Types of Bone
Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion Norbert Wiegand 2/3 of traumatology: treatment of fractures We have to understand: Structure of the bone Biology of the bone Bone healing Types of Bone
Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics, Regional institute of medical sciences, Imphal,Manipur, india. 2
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. I January. (2017), PP 38-45 www.iosrjournals.org A Novel Technique of Management of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. I January. (2017), PP 38-45 www.iosrjournals.org A Novel Technique of Management of
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
MANAGEMENT OF BILATERAL FRACTURE FEMUR WITH IMPLANT FAILURE: A CASE REPORT
 CASE REPORT East African Orthopaedic Journal MANAGEMENT OF BILATERAL FRACTURE FEMUR WITH IMPLANT FAILURE: A CASE REPORT J.C. Mwangi, MBChB, MMed(Surg), Lecturer, and A.A. Admani, MBChB, Resident, Department
CASE REPORT East African Orthopaedic Journal MANAGEMENT OF BILATERAL FRACTURE FEMUR WITH IMPLANT FAILURE: A CASE REPORT J.C. Mwangi, MBChB, MMed(Surg), Lecturer, and A.A. Admani, MBChB, Resident, Department
Malunion in floating knee injuries An analysis in 30 patients presenting to a tertiary care facility and are surgically treated
 2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
A prospective study of functional outcome of primary intra-medullary nailing in type 3A and 3B open tibial diaphyseal fractures
 2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons.
 Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
Product: Denosumab (AMG 162) Clinical Study Report: month Primary Analysis Date: 21 November 2016 Page 1
 Date: 21 November 2016 Page 1 2. SYNOPSIS Name of Sponsor: Amgen Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA, USA Name of Finished Product: Prolia Name of Active Ingredient: denosumab Title of Study: Randomized, Double-blind,
Date: 21 November 2016 Page 1 2. SYNOPSIS Name of Sponsor: Amgen Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA, USA Name of Finished Product: Prolia Name of Active Ingredient: denosumab Title of Study: Randomized, Double-blind,
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
From Fragile to Firm. Monika Starosta MD. Advocate Medical Group
 From Fragile to Firm Monika Starosta MD Advocate Medical Group Bone Remodeling 10% remodeled each year Calcium homoeostasis Maintain Mechanical strength Replace Osteocytes Release Growth Factors Bone remodeling
From Fragile to Firm Monika Starosta MD Advocate Medical Group Bone Remodeling 10% remodeled each year Calcium homoeostasis Maintain Mechanical strength Replace Osteocytes Release Growth Factors Bone remodeling
A comparative study of locking plate by MIPO versus closed interlocking intramedullary nail in extraarticular distal tibia fractures
 2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Section 20: Fracture Mechanics and Healing 20-1
 Section 20: Fracture Mechanics and Healing 20-1 20-2 From: Al-Tayyar Basic Biomechanics Bending Axial Loading Tension Compression Torsion Bending Compression Torsion 20-3 From: Le Fracture Mechanics Figure
Section 20: Fracture Mechanics and Healing 20-1 20-2 From: Al-Tayyar Basic Biomechanics Bending Axial Loading Tension Compression Torsion Bending Compression Torsion 20-3 From: Le Fracture Mechanics Figure
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis
 Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct
 Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures
 Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Dynamization Versus Static Antegrade Intramedullary Interlocking Nail In Femoral Shaft Fractures
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dynamization Versus Static Antegrade Intramedullary Interlocking Nail In Femoral Shaft Fractures Muhammad Khalid, Imtiaz Hashmi, Sohail Rafi, Muhammad Idrees Shah ABSTRACT Objective Study
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dynamization Versus Static Antegrade Intramedullary Interlocking Nail In Femoral Shaft Fractures Muhammad Khalid, Imtiaz Hashmi, Sohail Rafi, Muhammad Idrees Shah ABSTRACT Objective Study
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Hypophosphatasia. Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX
 Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of Cystatin C With Creatinine In The Sample Of Patient Of T2 DM With Diabetic Nephropathy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2017), PP 53-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2017), PP 53-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ABSTRACT: Orthopaedic surgeons often encounter diaphyseal femur fractures, because these
 A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE SHAFT FEMUR WITH CLOSED INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL. Mahendranath Reddy D 1, Muralidhar B.M 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mahendranath Reddy D,
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE SHAFT FEMUR WITH CLOSED INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL. Mahendranath Reddy D 1, Muralidhar B.M 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mahendranath Reddy D,
Sprain or fracture? An analysis of 2000
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1986, 3, 101-106 Sprain or fracture? An analysis of 2000 ankle injuries P. SUJITKUMAR, J. M. HADFIELD* AND D. W. YATES* Accident and Emergency Department, Hope Hospital,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1986, 3, 101-106 Sprain or fracture? An analysis of 2000 ankle injuries P. SUJITKUMAR, J. M. HADFIELD* AND D. W. YATES* Accident and Emergency Department, Hope Hospital,
COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS
 COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS D.M. Kamau, MBChB, MMed (Ortho Surg), L.N. Gakuu, MBChB, MMed (Surg), FCS (ECSA), Professor, E.M. Gakuya,
COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS D.M. Kamau, MBChB, MMed (Ortho Surg), L.N. Gakuu, MBChB, MMed (Surg), FCS (ECSA), Professor, E.M. Gakuya,
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP
 Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya
 Original Article Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya O.O. Soren, MBChB (Moi), MMed (Orthopaedics) (Makerere), Consultant Orthopaedic
Original Article Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya O.O. Soren, MBChB (Moi), MMed (Orthopaedics) (Makerere), Consultant Orthopaedic
KEYWORDS: Tibial fracture, Diaphyseal fracture, closed interlocking intramedullary nailing,
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid Carcinoma: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture
 Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Type I : At the level of lesser trochanter Type II : Less than 2.5 cm below lesser trochanter. Type III : cm below lesser trochanter
 Type II : Major fracture line along the intertrochanteric line with communition in coronal plain. Type III : Fracture at the level of lesser trochanter with variable communition and extension in subtrochanteric
Type II : Major fracture line along the intertrochanteric line with communition in coronal plain. Type III : Fracture at the level of lesser trochanter with variable communition and extension in subtrochanteric
IMPORTANT MEDICAL INFORMATION Advanced Orthopaedic Solutions INTRAMEDULLARY NAILS Warnings and Precautions (SINGLE USE ONLY)
 IMPORTANT MEDICAL INFORMATION Advanced Orthopaedic Solutions INTRAMEDULLARY NAILS Warnings and Precautions (SINGLE USE ONLY) IMPORTANT NOTE Intramedullary nails provide an alternative to open reduction
IMPORTANT MEDICAL INFORMATION Advanced Orthopaedic Solutions INTRAMEDULLARY NAILS Warnings and Precautions (SINGLE USE ONLY) IMPORTANT NOTE Intramedullary nails provide an alternative to open reduction
Sponsor / Company: sanofi-aventis and Proctor & Gamble Drug substance(s): Risedronate (HMR4003)
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: sanofi-aventis and
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: sanofi-aventis and
Supracondylar Process Congenitalis Of The Femur
 Article ID: WMC00544 ISSN 2046-1690 Supracondylar Process Congenitalis Of The Femur Author(s):Dr. S S Suresh Corresponding Author: Dr. S S Suresh, Head of Department, IBRI Regional Referral Hospital, Department
Article ID: WMC00544 ISSN 2046-1690 Supracondylar Process Congenitalis Of The Femur Author(s):Dr. S S Suresh Corresponding Author: Dr. S S Suresh, Head of Department, IBRI Regional Referral Hospital, Department
A Tale of Four Traumas. Understanding how bones break
 A Tale of Four Traumas Understanding how bones break Bone Break Classifications First Classification Based on whether the break is open to the environment or not. CLOSED- not an open wound. Broken but
A Tale of Four Traumas Understanding how bones break Bone Break Classifications First Classification Based on whether the break is open to the environment or not. CLOSED- not an open wound. Broken but
Index. B BMC. See Bone mineral content BMD. See Bone mineral density Bone anabolic impact, Bone mass acquisition
 A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
Functional outcome and complications in closed and grade I open tibia shaft fracture operated with intramedullary interlocking nail
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Khairnar G et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):114-119 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175658
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Khairnar G et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):114-119 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175658
Surgical management of fracture both bone forearm in adult using limited contact dynamic compression plate
 2017; 3(2): 852-856 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 852-856 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2017 Accepted: 02-03-2017 Muralidhar BM Associate Professor, Department Ravi KB Assistant Professor,
2017; 3(2): 852-856 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 852-856 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2017 Accepted: 02-03-2017 Muralidhar BM Associate Professor, Department Ravi KB Assistant Professor,
Original Contribution
 doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.11.008 Ultrasound in Med. & Biol., Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 389 395, 2004 Copyright 2004 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology Printed in the USA. All rights
doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.11.008 Ultrasound in Med. & Biol., Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 389 395, 2004 Copyright 2004 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology Printed in the USA. All rights
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with longer hospital stay and lower functional outcome after total knee arthroplasty.
 Reference number to be mentioned by correspondence : ORTHO/- Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 83, 00-00 ORIGINAL STUDY Vitamin D deficiency is associated with longer hospital stay and lower functional outcome
Reference number to be mentioned by correspondence : ORTHO/- Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 83, 00-00 ORIGINAL STUDY Vitamin D deficiency is associated with longer hospital stay and lower functional outcome
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal Fixation in Tibial Plateau Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2015), PP 50-54 www.iosrjournals.org Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2015), PP 50-54 www.iosrjournals.org Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Section: Orthopaedics. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4.3.OR2 Original Article ISSN (O):239-2822; ISSN (P):239-284 A Comparative Study of Operative Management of Internal Fixation of Closed Tibial Plateau Fracture by Plates with Screws
DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4.3.OR2 Original Article ISSN (O):239-2822; ISSN (P):239-284 A Comparative Study of Operative Management of Internal Fixation of Closed Tibial Plateau Fracture by Plates with Screws
Atypical Femoral Fractures With Long Term Bisphosphonates Use
 Atypical Femoral Fractures With Long Term Bisphosphonates Use There has been an increase in the number of atypical femoral fractures in pa4ents on long term bisphosphonate therapy (e.g Fosamax) Accordingly
Atypical Femoral Fractures With Long Term Bisphosphonates Use There has been an increase in the number of atypical femoral fractures in pa4ents on long term bisphosphonate therapy (e.g Fosamax) Accordingly
Osteomedullography: a simple tool for early detection of impending non union of diaphyseal fracture of tibia
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Vashisht A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Jan;4(1):115-119 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20160015
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Vashisht A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Jan;4(1):115-119 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20160015
Unreamed Solid Locked Nailing In The Treatment Of Compound Diaphyseal Fractures Of The Tibia.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 Unreamed Solid Locked Nailing In The Treatment Of Compound Diaphyseal Fractures Of The Tibia. R Singh, T Motten, N Kalsotra, R Gupta,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 Unreamed Solid Locked Nailing In The Treatment Of Compound Diaphyseal Fractures Of The Tibia. R Singh, T Motten, N Kalsotra, R Gupta,
Imaging Choices in Occult Hip Fracture
 Introduction Imaging Choices in Occult Hip Fracture Jesse Cannon, MD; Salvatore Silvestri, MD; Mark Munro, MD J Emerg Med. 2009;32(3):144-152 Reporter PGY 宋兆家 Supervisor VS 侯勝文 990220 High dependence on
Introduction Imaging Choices in Occult Hip Fracture Jesse Cannon, MD; Salvatore Silvestri, MD; Mark Munro, MD J Emerg Med. 2009;32(3):144-152 Reporter PGY 宋兆家 Supervisor VS 侯勝文 990220 High dependence on
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
spica of fracture at or below the junction of the upper and middle third of femur in children
 Original Article Chaudhary et.al. Randomized control trial comparing primary hip spica versus initial traction and hip spica of fracture at or below the junction of the upper and middle third of femur
Original Article Chaudhary et.al. Randomized control trial comparing primary hip spica versus initial traction and hip spica of fracture at or below the junction of the upper and middle third of femur
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
The Bone Densitometry Examination
 The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique
 PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
Bone strength is proportional to bone mass, measured with DXA. Bone turnover markers indicate the status of bone quality.
 Bone strength is proportional to bone mass, measured with DXA Bone quality depend on bone architecture, rate of bone turnover, quality of bone matrix. Bone turnover markers indicate the status of bone
Bone strength is proportional to bone mass, measured with DXA Bone quality depend on bone architecture, rate of bone turnover, quality of bone matrix. Bone turnover markers indicate the status of bone
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Anterior Plating of Displaced Middle Third Fractures of Clavicle An Effective Alternate Method
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.8 March. (2018), PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org Anterior Plating of Displaced Middle Third
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.8 March. (2018), PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org Anterior Plating of Displaced Middle Third
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series
 Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
POWER TO RESTORE WITHOUT LEAVING A TRACE. The only remaining evidence of the trauma
 POWER TO RESTORE WITHOUT LEAVING A TRACE The only remaining evidence of the trauma Perfect partner for your trauma and non-unions Your choice of synthetic bone graft not only influences the efficiency
POWER TO RESTORE WITHOUT LEAVING A TRACE The only remaining evidence of the trauma Perfect partner for your trauma and non-unions Your choice of synthetic bone graft not only influences the efficiency
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
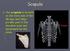 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Fri., 10/11/13 Basic Science, PAPER #55, 1:40 pm OTA 2013
 Fri., 10/11/13 Basic Science, PAPER #55, 1:40 pm OTA 2013 Is There an International Consensus as to How to Assess Fracture Healing Based on Clinical and Radiological Findings? Wojciech Glinkowski, MD,
Fri., 10/11/13 Basic Science, PAPER #55, 1:40 pm OTA 2013 Is There an International Consensus as to How to Assess Fracture Healing Based on Clinical and Radiological Findings? Wojciech Glinkowski, MD,
Hip Fractures. Anatomy. Causes. Symptoms
 Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World
 2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World September 21-24, 2016 Long Bone Osteosynthesis Failure DUONG BUNN Trauma-Orthopedique ward Preah Kossamak Preah Sihaknouk Ville Beach
2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World September 21-24, 2016 Long Bone Osteosynthesis Failure DUONG BUNN Trauma-Orthopedique ward Preah Kossamak Preah Sihaknouk Ville Beach
Bisphosphonate-related bilateral atypical femoral fractures be aware and beware
 Case Report Bisphosphonate-related bilateral atypical femoral fractures be aware and beware Ruben Depasquale, Claire Matthews, Victor N. Cassar-Pullicino Abstract Although bisphosphonates have a well established
Case Report Bisphosphonate-related bilateral atypical femoral fractures be aware and beware Ruben Depasquale, Claire Matthews, Victor N. Cassar-Pullicino Abstract Although bisphosphonates have a well established
The Role of Biplanar Distal Locking in Intramedullary Nailing of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 )33( COPYRIGHT 2019 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE The Role of Biplanar Distal Locking in Intramedullary Nailing of Tibial Shaft Fractures Kadir Bahadır Alemdaroğlu, MD; Serkan
)33( COPYRIGHT 2019 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE The Role of Biplanar Distal Locking in Intramedullary Nailing of Tibial Shaft Fractures Kadir Bahadır Alemdaroğlu, MD; Serkan
Screw Placement and Types Matter
 Screw Placement and Types Matter The Blasted Distal Femur Facture: How to Improve Outcomes Abstract ID#: 1506 Friday October 13, 2017 Kyle Jeray University of South Carolina, Greenville Pinpoint open 59
Screw Placement and Types Matter The Blasted Distal Femur Facture: How to Improve Outcomes Abstract ID#: 1506 Friday October 13, 2017 Kyle Jeray University of South Carolina, Greenville Pinpoint open 59
Tobacco and Bone Health
 Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
Clinico-radiological outcome of closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of proximal humerus fractures
 2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
Bone Densitometry. Total 30 Maximum CE 14. DXA Scanning (10) 7
 STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus Fractures with Tens - A Retrospective Analysis.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 76/ Sept. 21, 2015 Page 13162
 A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
A clinical study on role of surgical management of clavicle fractures in adults
 Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.36 Research Article A clinical study on role of surgical management of in adults Siva Sankar Murthy T 1, Syam Kumar R 2* 1 Assistant Professor, Department
Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.36 Research Article A clinical study on role of surgical management of in adults Siva Sankar Murthy T 1, Syam Kumar R 2* 1 Assistant Professor, Department
Evaluation of Serum Lactate as Predictor of Morbidity and Mortality in Sepsis and Trauma Cases
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-38, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 3 Ver. VII (May June 217), PP 1-5 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of Serum Lactate as Predictor
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-38, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 3 Ver. VII (May June 217), PP 1-5 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of Serum Lactate as Predictor
Treatment of Open Fractures of Tibia by Ilizarov Technique
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. I (December. 2016), PP 18-22 www.iosrjournals.org Treatment of Open Fractures of Tibia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. I (December. 2016), PP 18-22 www.iosrjournals.org Treatment of Open Fractures of Tibia
Atypical Femoral Fracture: 2015 Position Statement of the Korean Society for Bone and Mineral Research
 J Bone Metab 2015;22:87-91 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.3.87 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Review Article Atypical Femoral Fracture: 2015 Position Statement of the Korean Society for Bone and
J Bone Metab 2015;22:87-91 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.3.87 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Review Article Atypical Femoral Fracture: 2015 Position Statement of the Korean Society for Bone and
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS ARRT BOARD APPROVED: JANUARY 2017 IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
