Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Moody
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee BY MARK B. COVENTRY, M.D.", ROCHESTER, MINNESOTA From the Section of Orthopedic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester Attempts to treat degenerative arthritis of the knee by surgical means have been limited. Patellectomy or patelloplasty may be done in the presence of symptomatic patellofemoral arthritis; and joint dkbridement, including removal of loose bodies, large osteophytes, and damaged menisci, is occasionally used. Arthrodesis and arthroplasty are seldom carried out. Most patients with degenerative arthritis of the knee bear more of their weight on one tibial condyle than on the other. The male knee normally tends toward a varus position, the female toward a valgus position. As the articular cartilage degenerates over the tibial condyle that bears the most weight, the natural varus or valgus deviation increases and a vicious circle is set up in which increasing deformity creates increasing degenerative change. The uninvolved condyle and joint space usually appear normal. If weight-bearing and other stresses could be increased on this more normal area and decreased on the involved portion, it would seem that pain might be relieved and the useful life-span of the knee joint considerably prolonged. In 1961, Jackson and Waugh described a ball-and-socket type of osteotomy of the tibia just below the tibial tubercle (and osteotomy of the fibula at itsmiddle third) to correct the deformity created by osteo-arthritis. They reported on ten patients and stated that all had been relieved of their pain. In 1962, Wardle reported on tibial osteotomy for degenerative arthritis of the knee and stated that this type of operation had been done in Liverpool since the time of Sir Robert Jones. Wardle's osteotomy was transverse and about four inches distal to the tibial tubercle. The fibula was osteotomized at about the same level. Wardle stated that all but three of seventeen patients remained free of pain and had 90 degrees or more of flexion following osteotomy. Macintosh used an endoprosthesis to replace and shim the more degenerated of the two tibial condyles, correcting the deformity in this way. In a preliminary report he stated that eight of thirteen patients achieved good results, two fair results, and three poor results. Stimu!ated by the relief of hip pain observed after intertrochanteric osteotomy which altered weight-bearing surfaces and corrected deformity and further encouraged by the report of Gari6py's1 lateral approach to the upper part of the tibia for the correction of flexion deformity in rheumatoid arthritis, I attempted to produce a somewhat different type of osteotomy proximal to the tibial tubercle. This modification is designed to fulfill six criteria. The osteotomy should (1) fully correct and, in fact, slightly reverse the varus or valgus deformity, (2) be near the site of the deformity, (3) involve bone that will heal rapidly-the bone should be primarily cancellous, (4) allow early motion of the knee and early bearing of weight, (5) provide convenience for exploration of the knee at the time of osteotomy, if such is indicated, and (6) present no undue technical d8iculties or potential hazards. In * 200 First Street, S.W., Rochester, Minnesota THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
2 OSTEOTOMY OF THE TIBIA FOR DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS 985 addition to these advantages, an osteotomy proximal to the tibial tubercle allows the pulling force of the quadriceps mechanism to impact the site of the osteotomy. Indications If there are marked generalized degenerative changes with advanced patellofemoral arthritis and hypertrophic spurring, the indications become less clear. In a few such instances, joint dhbridement and patellectomy have been done as a first stage and an osteotomy as a second stage, or both osteotomy and dhbridement have been carried out in the same operative session. The indications, therefore, are not absolute, and more time must pass before it can be determined which patient is best suited for osteotomy. The ideal situation at the present time appears to be a patient with disabling pain and roentgenographic changes showing narrowing of the joint with resultant valgus or varus deformity but minimum degenerative change in other respects, such as loose bodies, excessive spurring, and patellofemoral arthritis. The patient should be muscular and sufficiently motivated to effect a good rehabilitation. Bilateral involvement is no contra-indication. Operative Technique and Postoperative Program The osteotomy is done through the upper part of the tibia in the general region of the previous epiphyseal line, just proximal to the tibial tubercle (Fig. 1-A). While niy colleagues and I have made our osteotomy a horizontal one, some obliquity, as emphasized by Garihpy 2, may be desirable to prevent fracture of the proximal fragment through the region of the tibial spines. (Such fracture occurred on a few occasions but did not seemingly alter the result.) Exposure of the medial tibial condyle for varus osteotomy to correct genu valgum presents no problem. Lateral exposure to perform valgus osteotomy for genu varum is done according to Garihpy's description. The knee should always be flexed to at least 45 degrees to allow the popliteal and peroneal structures to be relaxed and to fall back. Either a transverse or a longitudinal incision is made over the fibular head and laieral knee-joint line. The upper portion of the fibula is exposed by subperiosteal dissection and removal of the fibular collateral ligament and biceps femoris tendon with the other soft tissues; this allows these structures to retract posteriorly. The peroneal nerve may be isolated and retracted, but this need not be done once experience with the technique has been gained. Enough of the fibula should be removed (the amount ranges from the entire fibular head to the proximal tip) to expose the lateral aspect of the tibia. The proximal end of the tibia is exposed subperiosteally both anteriorly and posteriorly to at least the mid-line. A Kirschner guide wire may be inserted, and roentgenograms may be made to determine the location and depth of the proposed osteotomy. A lateral wedge is removed with an osteotome; the posterior structures of the knee should be protected during the process. Although the osteotomy is carried to the opposite cortex, it should not be carried completely through it. After the wedge is removed, valgus force is exerted and the medial cortex breaks in a greenstick manner, and the osteotomized edges come together. Rotation is completely controlled if the opposite cortex is treated in this manner. The cortical edges can be held securely with one or two staples (Fig. 1-B). The anterior tibial artery is distal to the fibular head; the popliteal vessels are posterior and are protected by a retractor. If more anterior than medial or lateral wedging is needed, as in a flexion contracture, an anterior incision can be used to effect the osteotomy. In this case, the patellar tendon is retracted both medially and laterally for exposure of the anterior aspect of the tibia proximal to the tibial tubercle. The knee joint may be exposed through the osteotomy incision or a separate VOL. 474, NO. 5, JULY 1965
3 986 M. B. COVENTRY FIG.1-A FIG.1-B Fig. 1-A: Anteroposterior roentgenogram of the knee of a man, sixty-seven years old. The site of osteotomy is generally marked on the roentgenogram before the osteotomy is begun. Fig. 1-B: Anteroposterior roentgenogram made six weeks after valgus osteotomy. )lore two THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
4 OSTEOTOMY OF THE TIBIA FOR DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS TABLE I UPPER TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY FOR DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS (September 1960 to September 1964) 987 Knees Patients Total 22 Male 17 Female 5 Age (years) Knees involved Right 16 Left 14 Osteotomy Valgus (varus deformity) 24 Varus (valgus deformity) 6 Results Satisfactory Unsatisfactory 4 3 Unknown (patient died of unrelated cause) 1 1 Less than one year follow-up 7 6 incision may be employed at the time of the osteotomy. After the osteoton~y has been completed, the common insertion of the biceps femoris tendon and the fibular collateral ligament is sutured either to the remaining portion of the fibular head or anteriorly to the iliotibial band near its insertion, and the wound is sutured. The limb is placed in a large compressive bulky dressing of the Robert Jones type, with a posterior plaster slab. This seems to be important in order to prevent pressure on the vessels or nerves that might result from a cast. The day after surgery, the patient is allowed out of bed, on crutches with the foot touching. Some weight-bearing is Figs. 3-A and 3-B: Old osteochondritis dissecans with degenerative arthritis. Fig. 3-A: Before operation, the patient was unable to work because of pain. Fig. 3-B: One year later. The patient had returned to work four months after operation and remained at full active farm labor without pain since that time. This patient was followed for four years.
5 988 M. B. COVENTRY beneficial because of its compressing effect at the site of the osteotomy. After the wound has healed, a cylinder cast is applied with the knee in zero degree of extension (straight). The cast is worn until there is early union at the osteotomy site, four to six weeks after operation. Exercises are then begun, with gradual return to full activity. The varus (or valgus) deformity should then have been corrected (Figs. 2-A and 2-B). Results Results were classified satisfactory or unsatisfactory after a minimum follow-up of one year. To the present time, all patients who had a satisfactory result at the end of one year continued to do well for as long as four years. In a satisfactory result, most of the preoperative pain was relieved, at least 90 degrees of flexion and full active extension was possible, and the knee was stable and free of any catching or intermittent swelling (Figs. 3-A and 3-B and 4-A through 4-D). In an unsatisfactory result one or more of these criteria were not met. Thirty knees of twenty-two patients with degenerative arthritis were operated on in a four-year period (Table I).There was a predominance of men and of valgus osteotomies for vanxs deformity. Eighteen knees of twelve patients had satisfactory results, and four knees of three patients had unsatisfactory results. One patient (one knee) died of unrelated cause before adequate follow-up could be made. Seven knees of six patients had been operated on too recently to be evaluated (less than one year). Twenty-three knees of sixteen patients were operated on more than one year ago. All were evaluated except one knee of a patient who died of unrelated cause. The majority were examined at the clinic and roentgenograms were made. A few were questioned by letter and roentgenograms made in the patient's home community were sent to us for study. Roentgenograms made postoperatively showed transference of weight-bearing to the opposite (uninvolved) tibia1 condyle, with usually a widening of joint space at the previously narrowed femoral-tibia1 junction. Exact comparison of nzotion before and after osteotomy was not possible in all cases, but 90 degrees of motion was usually present before surgery and had to be obtained postoperatively for the procedure to be considered as satisfactory. The unsatisfactory results could not be traced to any one factor and did not occur in any of the patients with the complications listed. One patient, a nurse, sixty-two years old, was obese and had long-standing, diffuse, degenerative arthritis of the knees, with resulting valgus deformity. Varus osteotomies straightened her knees; she obtained 90 degrees of flexion. But, at the time of writing, she continued to complain of pain and weakness in both knees and walked with a cane. She had not returned to her occupation despite attempts at muscle strengthening exercises, intra-articular steroid injections, and attempted weight reduction. Probably, her arthritis was too generalized throughout her knees, including the medial condylar surfaces, and her muscles were not capable of rehabilitation. A second patient was a farmer, thirty-six years old, with ancient osteochondritis dissecans. Exploration of his knee at the time of valgus osteotomy revealed a generalized degenerative change that was much greater medially than laterally. Correction of the deformity was obtained and full motion resulted, but he continued to complain of pain. Arthrodesis was done eventually. The cause for his unsatisfactory result is not clear. The third patient was a farmer, fifty-five years old, who had bilateral valgus osteotomies for degenerative arthritis of the knees. He achieved a satisfactory result in one knee. The other knee had instability on its medial side which existed prior to the osteotomy done laterally. At the time of follow-up, he was working regularly in a meat-packing THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
6 OSTEOTOMY OF THE TIBIA FOR DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS 989 Figs. 4-A through 4D: Degenerative arthritis of the right knee that caused pain and limping in a farmer, seventy-two years old. Fig. 4-A: Anteroposterior roentgenogram made before operation shows narrowing of the medial part of the joint. Fig. 4-B: Lateral roentgenogram made before operation. Fig. 4-C: Anteroposterior roentgenogram made five months after operation. The patient was fully active and his pain was relieved. Fig. 4-D: Lateral roentgenogram made five months after operation. plant on his feet all day. He had no discomfort if he wore a brace on this extremity. A medial collateral ligament tightening procedure is planned if his instability and pain continue. Although this report deals chiefly with the problem of degenerative arthritis, osteotomy has been found useful in certain patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Six VOL. 47-A, NO. 5, JULY 1965
7 990 M. B. COVENTRY knees of four patients with rheumatoid arthritis were operated on. These patients were carefully selected and included those with chronic and inactive stages of the disease. Two knees had synovectomies combined with osteotomy and, in two knees, the osteotomy to correct varus deformity was also fashioned to remove the wedge more anteriorly in order to correct flexion deformity. The results in all six knees were satisfactory two to five years after operation. Complications There were no vascular problems. Two wounds healed slowly because of softtissue infection. Staples (smooth, round, stainless-stecl) loosened in two instances within a year after they were inserted. At the present time my colleagues and I use the rectangular bridged staple of Vitallium and have seen none of this type loosen. One patient who suffered a peroneal palsy has recovered motor function but not all of the sensory function. The palsy was caused by pressure from the cast and was not a result of the operation, since peroneal function was intact when the patient was returned to his room after operation. The ligamentous structures at the site of the osteotomy tightened and became secure in all instances. One patient (the farmer, fifty-five years old, with an unsatisfactory result) continued to show some ligamentous relaxation on the medial (opposite) side two years postoperatively; the relaxation was present before surgery. There was no lack of conlplete active extension power in any of the patients (and no lag or difference between active and passive extension). Summary and Conclusions Thirty knees of twenty-two patients have been operated on in the past four years (196G1964) to correct the varus or valgus deformity resulting from degenerative changes. Six knees in four other patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis had similar procedures. An upper tibial wedge osteotomy was used in the general region of the closed epiphysis. The thrust of weight-bearing and other stresses was thus lessened on the degenerated tibial condyle and transferred to the more normal condyle. The results at froin one to four years after operation have been encouraging. It is hoped that by this procedure the pain of degenerative arthritis of the knee can be relieved or reduced and the usefulness of the knee prolonged. References 1. GARI~PY, ROGER: Correction du genou flechi dam l'arthrite. In Huitikme CongrBs International de Chirurgie OrthopCdique, pp , New York, 4-9 septembre Rapports, discussions et communications particulikres publies par M. A. Bailleux, SecrCtaire gcn&al. Bruxelles, Imprimerie des Sciences, GARIBPY, ROGER: Genu Varum Treated by High Tibial Osteotomy. Paper read at the Fourth Combined Meeting of The American, British, and Canadian Orthopaedic Associations with the Orthopaedic Associations of South Africa, New Zealand, Australia, and France, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, June 18, JACKSON, J. P., and WAUGH, W. W.: Tibial Osteotomy for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 43-B : , Nov MACINTOSH, 1). L.: Hemiarthroplasty of the Knee Using a Space Occupying Prosthesis for Painful Varus and Valgus Deformities. In Proceedings of the Joint Meeting of the Orthopaedic Associations of the English-Speaking World. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 40-A: 1431, Dec WARDLE,E. N.: Osteotomy of the Tibia and Fibula. Surg., Gynec., and Obstet., 115:61-64, THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Case Study: Christopher
 Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements:
 Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System. Surgical Technique
 Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System Surgical Technique Opening Wedge Osteotomy Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy 2 Prior to the osteotomy, a diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to verify
Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System Surgical Technique Opening Wedge Osteotomy Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy 2 Prior to the osteotomy, a diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to verify
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Results of arthroscopic surgery, with or without high Tibial osteotomy, in osteoarthritis of knee
 2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis
 A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Plaster-Wedging Technique:
 Plaster-Wedging Technique: An Appropriate, Safe, Quick, & Economical Method To Stretch Soft Tissue Contractures Of The Knee H.M. Steenbeek General Information. In the field of physical rehabilitation of
Plaster-Wedging Technique: An Appropriate, Safe, Quick, & Economical Method To Stretch Soft Tissue Contractures Of The Knee H.M. Steenbeek General Information. In the field of physical rehabilitation of
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
Integra. Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella Treated with a Different Method in Each Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
Lateral tibial condyle reconstruction by pedicled vascularized fibular head graft: Long-term result
 Title Lateral tibial condyle reconstruction by pedicled vascularized fibular head graft: Long-term result Author(s) Ahmed, SK; Fung, BKK; Ip, WY; Chow, SP Citation Strategies In Trauma And Limb Reconstruction,
Title Lateral tibial condyle reconstruction by pedicled vascularized fibular head graft: Long-term result Author(s) Ahmed, SK; Fung, BKK; Ip, WY; Chow, SP Citation Strategies In Trauma And Limb Reconstruction,
Knee Disarticulation Amputation
 Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
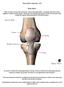 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Maquet: Maquet: Biomechanics. Maquet: /21/10. Philippe Landreau, MD
 Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing
 A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
KNEE EXAMINATION. Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective. EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine
 KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
The Knee. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Knee 7/28/2013. The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint
 The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthritis PATIENT INFORMATION. The ankle joint. What is ankle arthritis?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
The Biceps Femoris Tendon and Its
 The Biceps Femoris Tendon and Its Functional Significance BY JOHN L. MARSHALL, D.V.M., M.D.t, FAKHRY G. GIRGIS, M.D., PH.D., AND RUSSELL R. ZELKO, M.D., NEW YORK, NEW YORK From the Department of Sports
The Biceps Femoris Tendon and Its Functional Significance BY JOHN L. MARSHALL, D.V.M., M.D.t, FAKHRY G. GIRGIS, M.D., PH.D., AND RUSSELL R. ZELKO, M.D., NEW YORK, NEW YORK From the Department of Sports
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM)
 BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Lateral knee injuries
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM
 AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY
 ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES
 A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
FOLLOW-UP OF THE MACINTOSH ARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE JOINT*
 Rheum, phys. Med., 1972,11, 217 ORIGINAL PAPER FOLLOW-UP OF THE MACINTOSH ARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE JOINT* BY J. D. JESSOPt AND C. J. MOOREt SUMMARY The results of arthroplasty of the knee joint in 2 patients
Rheum, phys. Med., 1972,11, 217 ORIGINAL PAPER FOLLOW-UP OF THE MACINTOSH ARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE JOINT* BY J. D. JESSOPt AND C. J. MOOREt SUMMARY The results of arthroplasty of the knee joint in 2 patients
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures
 Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Objectives. The BIG Joint. Case 1. Boney Architecture. Presenter Disclosure Information. Common Knee Problems
 3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Massive Varus- Overview. Massive Varus- Classification. Massive Varus- Definition 07/02/14. Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR
 07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
Femoral Shaft Fracture
 Femoral Shaft Fracture The femoral shaft is well padded with muscles(an advantage in protecting the bone from all but the most powerful forces)but the disadvantage is that fractures are often severely
Femoral Shaft Fracture The femoral shaft is well padded with muscles(an advantage in protecting the bone from all but the most powerful forces)but the disadvantage is that fractures are often severely
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB.
 ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
Freedom and safety in treatment
 medi GmbH & Co. KG Medicusstraße 1 95448 Bayreuth Germany T +49 921 912-0 F +49 921 912 780 ortho@medi.de www.medi.de 97E37/09.2012 Freedom and safety in treatment An informative brochure with an individual
medi GmbH & Co. KG Medicusstraße 1 95448 Bayreuth Germany T +49 921 912-0 F +49 921 912 780 ortho@medi.de www.medi.de 97E37/09.2012 Freedom and safety in treatment An informative brochure with an individual
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field
 Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Presents ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Multimedia Health Education
 HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY. How the Normal Knee Works
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY If you have persistent pain, catching, or swelling in your knee, a procedure known as arthroscopy may help relieve these problems. Arthroscopy allows the diagnoses and treatment of knee
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY If you have persistent pain, catching, or swelling in your knee, a procedure known as arthroscopy may help relieve these problems. Arthroscopy allows the diagnoses and treatment of knee
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW?
 ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW? Christian Veillette M.D., M.Sc., FRCSC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Shoulder & Elbow Reconstructive Surgery Toronto Western Hospital @ University Health
ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW? Christian Veillette M.D., M.Sc., FRCSC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Shoulder & Elbow Reconstructive Surgery Toronto Western Hospital @ University Health
Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 415-420 Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement in rheumatoid arthritis G. P. ARDEN From the Windsor Group of Hospitals SUMMARY A computer-aided analysis
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 415-420 Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement in rheumatoid arthritis G. P. ARDEN From the Windsor Group of Hospitals SUMMARY A computer-aided analysis
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the
 The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
A lateral approach defect closure technique with deep fascia flap for valgus knee TKA
 Jiang and Fernandes Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:173 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0316-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A lateral approach defect closure technique with deep fascia flap
Jiang and Fernandes Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:173 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0316-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A lateral approach defect closure technique with deep fascia flap
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
In the name of god. Knee. By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions. Heat: Dr. Babakhani. Nov.
 In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative arthritis. Long-term clinical follow-up and current indications
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO
 Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY
 1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity
 ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
SMALL GROUP SESSION 21B February 10 th or February 12 th. Lower Extremity Examination and Ethics Case Discussion
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 21B February 10 th or February 12 th Lower Extremity Examination and Ethics Case Discussion Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
SMALL GROUP SESSION 21B February 10 th or February 12 th Lower Extremity Examination and Ethics Case Discussion Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
PATIENT INFORMATION THE DIFFERENCE IS MOVING.
 PATIENT INFORMATION THE DIFFERENCE IS MOVING. THIS BROCHURE IS WRITTEN TO HELP YOU MAKE AN INFORMED DECISION ABOUT YOUR SURGERY. Please read this entire brochure carefully. Keep this brochure. You may
PATIENT INFORMATION THE DIFFERENCE IS MOVING. THIS BROCHURE IS WRITTEN TO HELP YOU MAKE AN INFORMED DECISION ABOUT YOUR SURGERY. Please read this entire brochure carefully. Keep this brochure. You may
W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco
 Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
