Intra-capsular femoral neck fractures are treated with a
|
|
|
- Roxanne Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Clinical Medicine & Research Volume 6, Number 1: Marshfield Clinic clinmedres.org The Neglected Femoral Neck Fracture in Young Adults: Review of a Challenging Problem Amit Roshan, MRCS and Shatrughna Ram, MCh (Orth), FRCS A neglected femoral neck fracture is one where there has been a delay of more than 30 days to seek medical help from the time of the original injury. Among the spectrum of femoral neck fractures, the neglected fracture in a young adult (age <60 years) is one of the most challenging to treat if femoral head salvage is attempted.the main complication is avascular necrosis (AVN) of the femoral head with most reported incidences being <15% (range 0% to 67%), which is similar to the complication rate with non-neglected femoral neck fractures. This review consolidates our current knowledge about the problem, discusses the various treatment options and compares the published long-term results. There are no clear guidelines for management of neglected femoral neck fractures, although multiple methods have been used with varying success. Bone grafting or internal fixation in isolation does not provide a satisfactory outcome. Osteotomy has given better outcomes (AVN 6% to 17%, non-union 0% to 15%), but mechanical changes at the femoral neck may lead to a persistent painful hip. Bone grafting with internal fixation has emerged as a reliable method with good long-term functional outcomes. Keywords: Femoral neck; Neglected fracture; Young Intra-capsular femoral neck fractures are treated with a matter of urgency in young adults (age <60) in an attempt to preserve the precarious blood supply of the femoral head. Some authors have presented such patients as a vascular emergency with operative intervention advised within 6 to 8 hours. 1 While this time-capped figure is somewhat arbitrary, it emphasizes the importance of trying to preserve the femoral head in a young active patient. Multiple reports identify a subset of these patients who have delayed presentation for medical treatment. 2-5 While there is no defined lag period for such a fracture to be called neglected, Myers et al 6 introduced the term to indicate a delay of 30 days or more from the injury to seek medical help. We will use this definition for the purpose of this review. Most early reports, before 1980, have been from developed countries and consisted of unrecognized fractures or those initially managed with a wait and watch policy, and in the Reprint Requests: Amit Roshan, MRCS, Department of Plastic Surgery, Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester M23 9LT, UK, Tel/Fax: , amit.roshan@mac.com true sense of the term, the latter were not neglected Over the last 20 years, the distribution of published reports of this problem has shifted to developing countries, where the time before medical treatment sought may be several months because of poverty, ignorance, lack of facilities or faith in traditional bonesetters. 2-5 The incidence of this injury is unknown, but the burden of disease is likely to be decreasing with improving healthcare facilities in developing countries. Published literature is sporadic and from ill-defined population groups. This is compounded by differing presentations to qualified medical treatment centers and under-reporting. Among the causes for this injury, high-energy injuries from road traffic accidents and falls from heights are most common. 13 The financial burden to society is also considerable with patients tending to be economically active and the treatment lengthy and costly. With appropriate treatment, early return to function can be achieved. 14 Received: January 29, st Revision: July 23, nd Revision: October 15, 2007 Accepted: October 24, 2007 doi: /cmr
2 Table 1. Neglected femoral neck fracture in young adults a comparison of the literature. Good functional Study Total Age Neglect Method AVN Non- outcome (percentage; <60 union method) Internal fixation alone *Lifeso & Undisplaced Open reduction internal 33% 33% 33% subjective Young 4 fixation alone (3 cases) Internal fixation + osteotomy McMurray Osteotomy - - Zinghi et a NA 34 Osteotomy (Pauwells or Putti) 6% 0 *Lifeso & Displaced valgus osteotomy (6 cases) 17% 0 50% subjective Young 4 Kalra & Valgus intertrochanteric osteotomy 10% 15% 75% Askin & Byran Anand 16 Internal fixation + osteotomy + bone graft Stewart & Osteotomy + internal fixation? 45% 35% subjective Wells 7 12 NA 12 Osteotomy + internal fixation + bone 42% 0 graft Huang Closed reduction + osteotomy (3 cases) 25% 0 81% Askin & Byran Closed reduction + cortical bone graft (5 cases) Closed reduction + osteotomy + bone graft (8 cases) Non vascularized bone graft Henderson ?72 Closed reduction/open reduction % bone graft (22 tibial, 55 fibular) Inclan ?47 Closed reduction + Smith-Peterson nail?? 82% subjective + bone graft Patrick Closed reduction + Smith-Peterson nail 33% 17%? + bone graft fibula Bonfiglio & 77 NA NA Closed reduction + pins + Phemister?? 80% subjective Voke 11 Dooley Open reduction/closed reduction + 50% 0 & Hooper internal fixation + bone graft + 75% 0 osteotomy (2 cases) Closed reduction internal fixation + bone graft (4 cases) Snyder et al Open reduction internal fixation Nagi et al Open reduction internal fixation + 12% 0 75% Ratliff Slater et al Closed reduction + screws + free fibular % subjective graft Mishra Open reduction internal fixation +? 7% fairly satisfactory function Nagi et al Open reduction internal fixation + 12% 5% 70% subjective Sandhu et al closed reduction internal fixation + 6.5% 12% 3 open reduction + bone muscle pedicle graft 7 abdominal osteotomy + dynamic hip screw Roshan & Open reduction internal fixation + 0 9% 90% Harris hip score Ram 14 Vascularized bone graft Meyers et al Open reduction internal fixation +? 40% muscle pedicle graft Baksi Internal fixation + muscle pedicle bone 67% 11% 82% subjective graft Hou et al Open reduction internal fixation % subjective pedicle iliac bone graft Leung & Open reduction internal fixation + 0 0? Shen 33 pedicle iliac bone graft Hip arthroplasty *Lifeso & Age >40 total hip replacement % subjective Young 4 (19 cases) * Same report. AVN, avascular necrosis; NA, not available: age distribution did not specify proportion of patients <60 years. 34 Neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults CM&R 2008 : 1 (May)
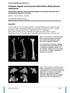
3 Materials and Methods We performed a Medline search with the keywords neglected fracture, femoral neck and young to identify published reports of this problem. We identified 22 reports in the English language that clearly identified neglected femoral neck fractures, as defined by Myers et al, 6 in patients under the age of 60. A tabulation of the reports is summarized in table 1. Some papers had an age distribution extending beyond 60 and did not distinguish between these fractures on the basis of age. 10,15,16 These reports have been included, but the exact numbers of patients under 60 have been omitted from the table. We discuss the various treatment options based on the identified papers and the reported success rates. Pathophysiology The blood supply to the femoral head has been traditionally described from three sources: 17 (1) an extracapsular arterial ring located at the base of the femoral neck, (2) ascending cervical branches of the arterial ring on the surface of the femoral neck, and (3) arteries of the ligamentum teres. Wertheimer et al 18 studied the arterial supply of the femoral head in an angiographic and histologic study and concluded there was anastomosis between different arterial sources in 62% of the cases. However, even with these arterial rings, blood supply can easily be compromised, with intracapsular and intraosseous pressures exceeding diastolic blood pressure following injury. 19,20 Most femoral neck fractures, being intracapsular, have the additional problem of synovial fluid interfering with the healing process. 21,22 As there is no periosteal layer, all healing is endosteal. Angiogenesis inhibiting factors in synovial fluid also can inhibit fracture repair. These factors, along with the precarious blood supply to the femoral head, make healing unpredictable and non-unions fairly frequent. A meta-analysis of 106 reports of displaced femoral neck fractures treated early (i.e., non-neglected) gave figures of nonunion between 23% and 37% (95% confidence interval [CI]), and a cumulative avascular necrosis (AVN) rate of 11% to 19% (95% CI). 23 Some individual reports, however, claim a nonunion rate as low as 4%, with many around 15%. The AVN rate in this meta-analysis is likely to be underestimated, as segmental collapse does not occur universally. With early anatomical reduction and stable internal fixation, the incidence of non-union should be acceptably low, as blood supply improves with some vascular continuity being established. Stromqvist et al 24 used scintigraphy and pathologic analysis to assess vascularity of femoral heads at re-operation following failure of internal fixation and concluded that there was a genuine increase in vascularity later in the course of avascular heads, with the apical part of the femoral head sustaining maximum insult and being the slowest to revascularize. This would indicate that vascularity does improve with time, although the extent of this is unknown. So why is AVN not universal to neglected fractures of the femoral neck? Soto-Hall et al 25 suggested osteonecrosis was rare when treatment for femoral neck fracture was delayed. They postulated that patients inevitably assumed the position of greatest joint capacity (i.e., the hip being flexed, abducted and externally rotated), which in turn relieved intra-articular tamponade and lessened the possibility of osteonecrosis. Reported incidence of AVN following neglected femoral neck fractures ranges between 0% to 67% (table 1) with most reports being <15%. The relationship between osteonecrosis and non-union is not fully understood. Early histological studies indicated that vascular insult to the femoral head might have a role to play in the healing. 22,26 However, osteonecrosis is not necessary for the development of nonunion, as non-union may develop with a radiologically normal femoral head. Presentation A majority of these patients are young males in the age group 30 to 40 years with a unilateral hip injury. 13,14 Most (up to 65%) manage to walk with support but have painful restricted range of movements. The bed-bound patients (17.5%) usually seek help earlier than the mobile patients. The remaining patients (17.5%) can walk without aids and have reasonable functional capacity, even managing to squat and sit crosslegged. 13,14 The remarkable amount of function that young adults often have with this injury is worth emphasizing. A relevant clinical history, including the original injury mechanism and subsequent treatment, is important. Metabolic history and other medical history may have a bearing on outcome, as may smoking. Duration of symptoms rarely has been an important factor in management. Physical examination may reveal painful range of movement as an indicator of non-union, as can a painful limp. Limb length and rotational deformity assessment are important considerations. Diagnosis Uniplanar radiography remains the cornerstone of diagnosis. 5,14 Figure 1 and Figure 2 (panel A) illustrate typical features in a neglected femoral neck fracture. Apart from the appearances of a femoral neck fracture, usually Garden III or IV, there are usually signs of neglect including femoral neck resorption, femoral head osteoporosis and signs of AVN. 27,28 On occasion, it may be difficult to assess the femoral neck, in which case computed tomography scans are effective to assess the fracture geometry. The need for this in neglected fractures is rarely necessary, as they are usually obvious. Sandhu et al 13 have proposed a radiological classification for this injury based on the following variables: (1) fracture site irregular or smooth, (2) size of proximal fragment >2.5 cm or < 2.5 cm, (3) gap between fragments (<1 cm, 1 cm 2.5 cm or CM&R 2008 : 1 (May) Roshan and Ram 35
4 Figure 1. The typical features in a neglected femoral neck fracture. This view is with the hip in internal rotation and shows the femoral neck resorption clearly, with no avascular necrosis of the femoral head. >2.5 cm), and (4) signs of AVN. This classification involves a magnetic resonance imaging scan for determination. It has not been validated and does not alter management. Scintigraphy may have a role in early postoperative evaluation of AVN before plain radiographic features are identified. Bone scans performed within 2 weeks of operation following 306 non-neglected hip fractures have been shown to determine the healing course with an accuracy of 91% (into categories of uneventful healing, hardware failure, non-union and AVN). 29 Broeng et al 30 demonstrated that decreased uptake noted on a bone scan 1 to 3 weeks postoperatively and 2 months postoperatively was indicative of eventual loss of reduction or segmental collapse in 50% of patients, whereas normal or increased uptake at those time periods correlated with uncomplicated healing in 90%. Treatment Options There have been many studies regarding the management of neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults. All aim at preserving the femoral head with hip hemiarthroplasty being reserved as a salvage or secondary procedure. The treatment options tried have predominantly used internal fixation in conjunction with either osteotomy or bone grafting (vascularized or non-vascularized), with hip arthroplasty being a salvage procedure. Figure 2. (A) A preoperative radiograph showing typical features of a neglected left femoral neck fracture with neck resorption, osteopenia and avascular necrosis in a 33-yearold man. (B) An early postoperative radiograph shows the femoral neck with two cannulated screws and insertion. (C) A long-term follow up radiograph taken 4.5 years postoperatively shows good bony union. Harris hip score at this stage was 84. Figure 3 illustrates the various treatment options in this setting. Table 1 summarizes the various studies done in this field and their comparative outcomes. 36 Neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults CM&R 2008 : 1 (May)
5 Figure 3. The treatment options available in the neglected femoral neck fracture of a young adult. The indicative studies mentioned are compared with others in table 1. Internal Fixation Alone Internal fixation alone is seldom performed in the neglected femoral neck fracture. Lifeso and Younge 4 used this method in 3 of their 28 young patients with neglected femoral neck fractures, in those with undisplaced fractures, with one patient developing AVN and another non-union. Although it is the simplest of procedures, it does not address either the altered mechanics of shortening, or the biology of neglect and bone healing. Internal Fixation and Osteotomy ± Bone Grafting Osteotomy has been used to alter biomechanics at the fracture site to promote healing, both with or without internal fixation, and in some cases with the addition of bone grafting to help stimulate bone healing. The two main types of osteotomy used have been the medial displacement osteotomies, such as that employed by McMurray, 15 and the angulation osteotomy such as employed in studies by Kalra and Anand. 16 The valgus angulation osteotomy is usually of the subtrochanteric or intertrochanteric type, and is more efficient than the displacement osteotomy in converting the shearing forces at the fracture site into compression forces, thereby improving union chances. In addition, the angulation osteotomy can correct rotational and limb length discrepancies at the same time. However, osteotomy has two important problems. First, shortening, limp and a decreased range of movement are common, probably because of increased pressures on the femoral head leading to degenerative disease or osteonecrosis. 15,31 Secondly, there are potential risks of nonunion at the osteotomy site, although this has not been common in the literature. 4,8 The results of the osteotomy when used have resulted in rates of AVN ranging between 6% and 42% and a non-union rate between 0% and 45% (table 1). It is difficult to compare the functional outcome of these studies, as the criteria used are subjective and variable (modified Askin and Byran, 3,16 subjective evaluation 4,7 or no long-term functional followup 15,31 ). Where measured by differing criteria, a good functional outcome has been recorded in 35% to 80% of the subject population. Internal Fixation and Bone Grafting Bone grafting has been the most widely used method to address the problem of the neglected femoral neck fractures, and both vascularized and non-vascularized bone grafts have been used with often excellent results. Henderson 8 had employed non-vascularized bone grafting alone in 72 patients with a non-union rate of 28%, but this procedure has been largely abandoned in favor of combination procedures with internal fixation at the same time. Various types of bone grafts have been used to address this problem. Vascularized grafts include muscle pedicle or vascular pedicle grafts while non-vascularized grafts include Phemister-type cortical tibial grafts and free fibular strut grafts. Meyers et al 6 and Baksi 32 have employed vascularized grafts using muscle pedicle grafts in separate studies involving patients with a delay of more than 3 months. Unfortunately, the blood supply with this construct is unreliable, and there was a high incidence of non-union. In contrast, vascularized pedicle grafts using either the iliac crest or the fibula have shown excellent results with union rates of 91% to 100% in small series. 2,33 However, this technique is highly technical and requires microsurgical facilities and experience. CM&R 2008 : 1 (May) Roshan and Ram 37
6 Free ing has been widely studied as a method to introduce both structural support and a graft framework in a neglected femoral neck fracture. 5,13,14,34,35 The results with this procedure have given non-union rates between 0% to 17% and AVN rates of 0% to 33%. This is our preferred method, and 28 patients in our own case series had an average Harris hip score of 87.1 at a mean follow-up of over 6 years. 14 Figure 2 demonstrates the progression of a neglected femoral neck fracture treated through this method. The free fibular graft has the advantages of being technically simple with minimal donor site morbidity, providing additional rotational stability because of the trifin shape of the graft itself, and the medullary canal of the graft allowing a guide pin insertion for ease of introduction. Hip Arthroplasty Hip replacement arthroplasty has been reserved as a secondary salvage procedure. In the setting of neglected femoral neck fractures in the young adult, only one study has reported hip arthroplasty in 19 cases. 4 This study classified outcome as good or poor soon after the initial operation based on non-standardized criteria (i.e., not requiring further surgery, ambulatory in the community, discharged home, healed within 3 months, minimal pain.) Discussion The neglected femoral neck fracture in young adults is among the most difficult to treat in the spectrum of femoral neck fractures. Dickson s epithet of the unsolved fracture is especially applicable. Attempts at head salvage in the young are important. Bone grafting or internal fixation in isolation has not provided predictable satisfactory outcomes. Osteotomy has been used with better outcomes in this group of patients (AVN 6% to 17%, non-union rates 0% to 15%), but the functional results are modest because of the frequency of a persistent painful limp due to the mechanical changes at the femoral neck. 4,15,16 Bone grafting has emerged as a reliable method to treat these fractures with good functional outcomes in the long-term. Our preference is for a free with two cannulated screws, and early mobilization (AVN 0% to 6.5%, non-union 9% to 12%). 13,14 In his 1953 Presidential address to the American Orthopaedic Association, Dickson made a plea to avoid a defeatist attitude in sacrificing the femoral head in favor of advancing replacement technology. This plea is still as relevant over 50 years down the line. 36 References 1. Swiontkowski MF, Winquist RA, Hansen ST Jr. Fractures of the femoral neck in patients between the ages of twelve and forty-nine years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1984;66: Hou SM, Hang YS, Liu TK. Ununited femoral neck fractures by open reduction and vascularized iliac bone graft. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;(294): Huang CH. Treatment of neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1986;(206): Lifeso R, Younge D. The neglected hip fracture. J Orthop Trauma 1990;4: Nagi ON, Dhillon MS, Goni VG. Open reduction, internal fixation and fibular autografting for neglected fracture of the femoral neck. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998;80: Meyers MH, Harvey JP Jr, Moore TM. Treatment of displaced subcapital and transcervical fractures of the femoral neck by muscle-pedicle-bone graft and internal fixation. A preliminary report on one hundred and fifty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1973;55: Stewart MJ, Wells RE. Osteotomy and osteotomy combined with bone-grafting for non-union following fracture of the femoral neck. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1956;38-A: Henderson MS. Ununited fractures of the neck of the femur treated by aid of the bone graft. J Bone Joint Surg 1940;22: Inclan A. Late complications in fractures of the neck of the femur treated by nailing, bone graft or both. J Internat Coll Surg 1946;9: Patrick J. Intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck treated with a combined Smith-Peterson nail and. J Bone Joint Surg 1949;31: Bonfiglio M, Voke EM. Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head and non-union of the femoral neck: effect of treatment by drilling and bone graft (Phemister technique). J Bone Joint Surg 1968;50A: Dooley BJ, Hooper J. Fibular bone grafting for non union of fracture of the neck of the femur. Aust N Z J Surg 1982;52: Sandhu HS, Sandhu PS, Kapoor A. Neglected fractured neck of the femur: a predictive classification and treatment by osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005;(431): Roshan A, Ram S. Early return to function in young adults with neglected femoral neck fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006;447: McMurray TP. Ununited fractures of the neck of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg 1936;18: Kalra M, Anand S. Valgus intertrochanteric osteotomy for neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults. Int Orthop 2001;25: Crock HV. An atlas of the arterial supply of the head and neck of the femur in man. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1980;(152): Wertheimer LG, Lopes Sde L. Arterial supply of the femoral head. A combined angiographic and histological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1971;53: Crawfurd EJ, Emery RJ, Hansell DM, Phelan M, Andrews BG. Capsular distension and intracapsular pressure in subcapital fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1988;70: Harper WM, Barnes MR, Gregg PJ. Femoral head blood flow in femoral neck fractures. An analysis using intra-osseous pressure measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1991;73: Kregor PJ. The effect of femoral neck fractures on femoral head blood flow. Orthopedics 1996;19: Banks HH. The healing of intra-articular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1965;40: Lu-Yao GL, Keller RB, Littenberg B, Wennberg JE. Outcomes after displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis of one hundred and six published reports. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1994;76: Stromqvist B, Hansson LI, Palmer J, Thorngren KG. Femoral head vitality at reoperation for femoral neck fracture complications. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1984;103: Neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults CM&R 2008 : 1 (May)
7 25. Soto-Hall R, Johnson LH, Johnson RA. Variations in the intra-articular pressure of the hip joint in injury and disease. A probable factor in avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1964;46: Banks HH. Factors influencing the result in femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg 1962;44A: Martel W, Sitterley BH. Roentgenologic manifestations of osteonecrosis. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1969;106: Nordkild P, Sonne-Holm S. Necrosis of the femoral head following fracture of the femoral neck. Injury 1986;17: Stromqvist B, Kelly I, Lidgren L. Treatment of hip fractures in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1988;(228): Thorngren KG, Ceder L, Svensson K. Predicting results of rehabilitation after hip fracture. A ten-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;(287): Zinghi GF, Specchia L, Ruggieri N, Galli G. The role of osteotomy in the treatment of pseudarthrosis of the neck of the femur in younger patients. Ital J Orthop Traumatol 1985;11: Baksi DP. Internal fixation of ununited femoral neck fractures combined with muscle-pedicle bone grafting. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1986;68: Leung PC, Shen WY. Fracture of the femoral neck in younger adults. A new method of treatment for delayed and nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;(295): Nagi ON, Dhillon MS, Gill SS. Fibular osteosynthesis for delayed type II and type III femoral neck fractures in children. J Orthop Trauma 1992;6: Mishra D. Femoral neck fracture open reduction Asnis screw fixation and ing. Ind J Orthop 1998;32: Dickson JA. The unsolved fracture: A protest against defeatism. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1953;35: Snyder SJ, Sherman OH, Hattendorf K. Nine-year functional nonunion of a femoral neck stress fracture: treatment with internal fixation and. A case report. Orthopedics 1986;9: Slater RN, Gore R, Slater GJ. Free fibular bone grafting for femoral neck fractures: precise graft placement using a cannulated screw technique. J R Coll Surg Edinb 1993;38: Author Affiliations Amit Roshan, MRCS Department of Plastic Surgery Wythenshawe Hospital Manchester, M23 9LT United Kingdom Shatrughna Ram, MCh (Orth), FRCS Advanced Orthopaedic Centre Patna, India CM&R 2008 : 1 (May) Roshan and Ram 39
HIP. Z. Dewei, Y. Xiaobing. Patients and Methods We evaluated 34 patients aged < 50 years with a displaced fracture of the femoral neck who
 Z. Dewei, Y. Xiaobing From Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian, China HIP A retrospective analysis of the use of cannulated compression screws and a vascularised iliac bone graft in the treatment
Z. Dewei, Y. Xiaobing From Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian, China HIP A retrospective analysis of the use of cannulated compression screws and a vascularised iliac bone graft in the treatment
A Convenient Way to do Valgus Osteotomy for Neglected Fracture Neck of Femur
 A Convenient Way to do Valgus Osteotomy for Neglected Fracture Neck of Femur Bansal P, 1 Singhal V, 2 Lal H, 2 Mittal D, 2 Arya RK 2 Department of Orthopaedics 1 E.S.I Hospital, Manesar, Haryana 2 Dr.
A Convenient Way to do Valgus Osteotomy for Neglected Fracture Neck of Femur Bansal P, 1 Singhal V, 2 Lal H, 2 Mittal D, 2 Arya RK 2 Department of Orthopaedics 1 E.S.I Hospital, Manesar, Haryana 2 Dr.
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of 20 Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
Fixation with cancellous screws and fibular strut grafts for neglected femoral neck fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2014;22(2):181-5 Fixation with cancellous screws and fibular strut grafts for neglected femoral neck fractures Chandra Prakash Pal, 1 Binod Kumar, 2 Karuna Shankar Dinkar,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2014;22(2):181-5 Fixation with cancellous screws and fibular strut grafts for neglected femoral neck fractures Chandra Prakash Pal, 1 Binod Kumar, 2 Karuna Shankar Dinkar,
Abdul Qayyum Khan Æ Mohammad Shahnawaz Khan Æ Mohammed Khalid Anwar Sherwani Æ Rahul Agarwal
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2009) 10:71 78 DOI 10.1007/s10195-009-0049-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of valgus osteotomy and fixation with dynamic hip screw and 120 double angle barrel plate in the management of
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2009) 10:71 78 DOI 10.1007/s10195-009-0049-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of valgus osteotomy and fixation with dynamic hip screw and 120 double angle barrel plate in the management of
Outcome of Cloverleaf Locking Plate Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Adults
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1203.010 Outcome of Cloverleaf Locking Plate Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Adults Ismail HD, Ph.D, Phedy*, MD, Oktavian Irawadi Purba*, MD, Bambang Gunawan,
http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1203.010 Outcome of Cloverleaf Locking Plate Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Adults Ismail HD, Ph.D, Phedy*, MD, Oktavian Irawadi Purba*, MD, Bambang Gunawan,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.29 Clinical Study of Osteosynthesis in Fracture
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.29 Clinical Study of Osteosynthesis in Fracture
CC Wu, WJ Chen Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 129 136 inimally displaced intra-capsular femoral neck fractures in the elderly comparison of multiple threaded pins and sliding compression screws surgical
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 129 136 inimally displaced intra-capsular femoral neck fractures in the elderly comparison of multiple threaded pins and sliding compression screws surgical
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP. Dr Károly Fekete
 DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures
 Acta Orthop Scand 55, 423-429, 1984 Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures Compression screw compared with nail plate fixation In a prospective, randomized study of femoral neck fracture operations,
Acta Orthop Scand 55, 423-429, 1984 Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures Compression screw compared with nail plate fixation In a prospective, randomized study of femoral neck fracture operations,
Clinical Results of Internal Fixation of Subcapital Femoral Neck Fractures
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:146-152 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.146 Clinical Results of Internal Fixation of Subcapital Femoral Neck Fractures Joon Soon Kang, MD,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:146-152 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.146 Clinical Results of Internal Fixation of Subcapital Femoral Neck Fractures Joon Soon Kang, MD,
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Carlos Roberto Schwartsmann 1, Marco Aurélio Telöken 2, Leonardo Carbonera Boschin 2, Ivo Schmiedt 3, Ricardo Falavinha 4, Marcus Vinicius Crestani 5 ABSTRACT Purpose: The purpose of the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Carlos Roberto Schwartsmann 1, Marco Aurélio Telöken 2, Leonardo Carbonera Boschin 2, Ivo Schmiedt 3, Ricardo Falavinha 4, Marcus Vinicius Crestani 5 ABSTRACT Purpose: The purpose of the
The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification D Iyer Citation D Iyer. The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification. The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification D Iyer Citation D Iyer. The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification. The
Dr. Manojkumar HV, Dr. Hemanth HP, Dr. Ponnilavan Jayakanthan, Dr. Bhaskar Jyoti Pegu and Dr. Prathmesh MH
 2017; 3(3): 537-542 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 537-542 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 16-05-2017 Accepted: 17-06-2017 Dr. Manojkumar HV Professor Department of Dr. Hemanth HP Senior Resident,
2017; 3(3): 537-542 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 537-542 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 16-05-2017 Accepted: 17-06-2017 Dr. Manojkumar HV Professor Department of Dr. Hemanth HP Senior Resident,
Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: a retrospective analysis of two treatment methods
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:141 147 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0025-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: a retrospective analysis of two treatment methods Roop Singh Æ Rajesh
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:141 147 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0025-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: a retrospective analysis of two treatment methods Roop Singh Æ Rajesh
Medial circumflex artery Lateral circumflex artery
 Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
PAUWELS' OSTEOTOMY FOR FEMORAL NECK NON-UNION
 Medical Journal of the slamic Republic of ran Volume 0 Number Spring 375 May 6 PAUWELS' OSTEOTOMY FOR FEMORAL NECK NON-UNON F. ABDlNEJAD, M.D., AND MJ. EMAME, M.D. From the Department of Orthopedics, Shiraz
Medical Journal of the slamic Republic of ran Volume 0 Number Spring 375 May 6 PAUWELS' OSTEOTOMY FOR FEMORAL NECK NON-UNON F. ABDlNEJAD, M.D., AND MJ. EMAME, M.D. From the Department of Orthopedics, Shiraz
Valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy for malunited intertrochanteric fractures : Our experience in 5 cases
 Original article : Valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy for malunited intertrochanteric fractures : Our experience in 5 cases Rajendraprasad Butala *, Sunirmal Mukherjee, Prakash Samant, Ravindra Khedekar
Original article : Valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy for malunited intertrochanteric fractures : Our experience in 5 cases Rajendraprasad Butala *, Sunirmal Mukherjee, Prakash Samant, Ravindra Khedekar
76 F: Plays tennis, lives independently, told she has weak bone
 Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip
 Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric fractures
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric s G.Z. Said, O. Farouk
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric s G.Z. Said, O. Farouk
Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur *
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Fractures of Lower extremity
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Fractures of Lower extremity FRACTURES OF FEMORAL NECK Anatomy Neck-Shaft Angle: In the anteroposterior roentgenogram, it is the angle between the long axis of the femoral neck
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Fractures of Lower extremity FRACTURES OF FEMORAL NECK Anatomy Neck-Shaft Angle: In the anteroposterior roentgenogram, it is the angle between the long axis of the femoral neck
Femoral Neck Fractures- Gold standards and breaking news. Anna Ekman, MD, PhD Stockholm South hospital Sweden
 Femoral Neck Fractures- Gold standards and breaking news Anna Ekman, MD, PhD Stockholm South hospital Sweden Learning outcomes Learning Outcomes Epidemiology Preoperative planning Reduction techniques
Femoral Neck Fractures- Gold standards and breaking news Anna Ekman, MD, PhD Stockholm South hospital Sweden Learning outcomes Learning Outcomes Epidemiology Preoperative planning Reduction techniques
9/24/2015. When Can I Use a SHS? When CAN T I Use a SHS? Sliding Hip Screw. Time proven. Technically simple. Cheap. Quick
 When Can I Use a SHS? Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Trauma Research Director of Orthopaedic Trauma Jersey City Medical Center New York University / Hospital for Joint
When Can I Use a SHS? Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Trauma Research Director of Orthopaedic Trauma Jersey City Medical Center New York University / Hospital for Joint
Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts
 Original Article 268 Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts Lin-Hsiu Weng, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: In this study,
Original Article 268 Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts Lin-Hsiu Weng, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: In this study,
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do?
 Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
Hip Fractures. Anatomy. Causes. Symptoms
 Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay
 Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay Pelvis anatomy Pelvis function - axial load bearing - protection: abdominal, pelvic structures Pelvic injury mechanism Falling from
Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay Pelvis anatomy Pelvis function - axial load bearing - protection: abdominal, pelvic structures Pelvic injury mechanism Falling from
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER. undisplaced, but as a consequence of the delay in diagnosis displacement occurred SUMMARY
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Femoral Neck Fractures
 Femoral Neck Fractures Michael Monge, Harvard Medical School Agenda Epidemiology Normal anatomy of the femur Garden classifications Patients Summary 1 Epidemiology 1 250,000 yearly hip fractures in the
Femoral Neck Fractures Michael Monge, Harvard Medical School Agenda Epidemiology Normal anatomy of the femur Garden classifications Patients Summary 1 Epidemiology 1 250,000 yearly hip fractures in the
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0155-z ORIGINAL A. Megaro S. Marchesi U.E. Pazzaglia Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases Received: 5 September
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0155-z ORIGINAL A. Megaro S. Marchesi U.E. Pazzaglia Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases Received: 5 September
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 22/ Mar 16, 2015 Page 3785
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 08 Page August 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.08 Study of Functional and Radiological Outcome
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.08 Study of Functional and Radiological Outcome
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement
 Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Study on the Efficiency of Fractures Treated With Proximal Femoral Locking Compression Plate
 Original Research Article Study on the Efficiency of Fractures Treated With Proximal Femoral Locking Compression Plate Ravi G.O 1, Shaik Hussain Saheb * 2. 1 Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics,
Original Research Article Study on the Efficiency of Fractures Treated With Proximal Femoral Locking Compression Plate Ravi G.O 1, Shaik Hussain Saheb * 2. 1 Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics,
TREATMENT OF POST-TRAUMATIC AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD BY MULTIPLE DRILLING AND MUSCLE-PEDICLE BONE GRAFTING
 TREATMENT OF POST-TRAUMATIC AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD BY MULTIPLE DRILLING AND MUSCLE-PEDICLE BONE GRAFTING PRELIMINARY REPORT D. P. From the Nilratan Sircar Medical College and Hospital,
TREATMENT OF POST-TRAUMATIC AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD BY MULTIPLE DRILLING AND MUSCLE-PEDICLE BONE GRAFTING PRELIMINARY REPORT D. P. From the Nilratan Sircar Medical College and Hospital,
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME BETWEEN DYNAMIC HIP SCREW AND PROXIMAL FEMORAL NAIL IN SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PER-TROCHANTERIC FRACTURES Umesh M. Shivanna 1, Girish H. Rudrappa 2 HOW TO CITE
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME BETWEEN DYNAMIC HIP SCREW AND PROXIMAL FEMORAL NAIL IN SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PER-TROCHANTERIC FRACTURES Umesh M. Shivanna 1, Girish H. Rudrappa 2 HOW TO CITE
Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Surgical Management of aseptic Femoral Shaft Non-union after Intramedullary Fixation
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (7), Page 4946-4950 Surgical Management of aseptic Femoral Shaft Non-union after Intramedullary Fixation Eissa Ragheb Refaie 1, Ahmed Abd El
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (7), Page 4946-4950 Surgical Management of aseptic Femoral Shaft Non-union after Intramedullary Fixation Eissa Ragheb Refaie 1, Ahmed Abd El
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Introduction. Femoral neck fracture in the elderly
 Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
THE RING BUTTERFLY FRAGMENT
 THE RING BUTTERFLY FRAGMENT Pages with reference to book, From 80 To 82 Philip D`Sousa, Masood Umer, Riaz Hussain Lakdawala ( Department of Surgery (Orthopaedics), The Aga Khan University, Karachi. ) In
THE RING BUTTERFLY FRAGMENT Pages with reference to book, From 80 To 82 Philip D`Sousa, Masood Umer, Riaz Hussain Lakdawala ( Department of Surgery (Orthopaedics), The Aga Khan University, Karachi. ) In
Bone and Joint Surgery
 The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume VOLUME 59-A, No. 4 JUNE 1977 Fracture of the Neck and Intertrochanteric Region of the Femur in Children* BY S. TERRY CANALE, M.D.t, AND WILLIAM L.
The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume VOLUME 59-A, No. 4 JUNE 1977 Fracture of the Neck and Intertrochanteric Region of the Femur in Children* BY S. TERRY CANALE, M.D.t, AND WILLIAM L.
A Case Report of a Delayed Diagnosed Femoral Neck Fracture
 International Journal of Caring Sciences September-December 2017 Volume 10 Issue 3 Page 1652 Original Article A Case Report of a Delayed Diagnosed Femoral Neck Fracture Angelo V. Vasiliadis, MD, PhD Nikolaos
International Journal of Caring Sciences September-December 2017 Volume 10 Issue 3 Page 1652 Original Article A Case Report of a Delayed Diagnosed Femoral Neck Fracture Angelo V. Vasiliadis, MD, PhD Nikolaos
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
The Result of In Situ Pinning for Valgus Impacted Femoral Neck Fractures of Patients over 70 Years Old
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 26(4): 263-268, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.263 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 The Result of In Situ Pinning for Valgus Impacted Femoral Neck Fractures
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 26(4): 263-268, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.263 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 The Result of In Situ Pinning for Valgus Impacted Femoral Neck Fractures
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture
 Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures Treated with Russell-Taylor Reconstruction Intramedullary Nails
 Original Article 79 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures Treated with Russell-Taylor Reconstruction Intramedullary Nails Hsuan-Kai Kao, MD; Chi-Chuan Wu, MD; Po-Cheng Lee, MD; Chun-Yi Su, MD; Kuo-Feng
Original Article 79 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures Treated with Russell-Taylor Reconstruction Intramedullary Nails Hsuan-Kai Kao, MD; Chi-Chuan Wu, MD; Po-Cheng Lee, MD; Chun-Yi Su, MD; Kuo-Feng
Ilizarov Hip Reconstruction
 Ilizarov Hip Reconstruction Percutaneous Rx of Dysplastic & Deformed Hips! For many young people with Hip Joint problems with limb shortening, this is the ideal procedure. Dr MilindChaudhary Chief Orth.
Ilizarov Hip Reconstruction Percutaneous Rx of Dysplastic & Deformed Hips! For many young people with Hip Joint problems with limb shortening, this is the ideal procedure. Dr MilindChaudhary Chief Orth.
Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication?
 CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture
 Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures: An Atlas
 Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures: An Atlas Manninger, Jeno ISBN-13: 9783211685839 Table of Contents Foreword. 1. Importance of hip fractures. The intact femoral neck. 1.1. Introduction 1.2.
Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures: An Atlas Manninger, Jeno ISBN-13: 9783211685839 Table of Contents Foreword. 1. Importance of hip fractures. The intact femoral neck. 1.1. Introduction 1.2.
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
PIN SYSTEM HIP FRACTURE SYSTEMS
 PIN SYSTEM HIP FRACTURE SYSTEMS INDEX Introduction 2 Indications 3 Features & Benefits Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis 4 Intracapsular Femoral Neck Fracture 5 Operative Technique Slipped Capital Femoral
PIN SYSTEM HIP FRACTURE SYSTEMS INDEX Introduction 2 Indications 3 Features & Benefits Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis 4 Intracapsular Femoral Neck Fracture 5 Operative Technique Slipped Capital Femoral
Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients
 Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip
 Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip DG Nabi, MS, TS Rashid, MS, KK Ahmed, MS Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College, Srinagar, India ABSTRACT
Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip DG Nabi, MS, TS Rashid, MS, KK Ahmed, MS Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College, Srinagar, India ABSTRACT
Scaphoid Non-Union Current Treatment Options
 Scaphoid Non-Union Current Treatment Options Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, FRCSC Director Upper Extremity Center, Peripheral Nerve Center, Cleveland Combined Hand Fellowship Cleveland Clinic Outline The Basics
Scaphoid Non-Union Current Treatment Options Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, FRCSC Director Upper Extremity Center, Peripheral Nerve Center, Cleveland Combined Hand Fellowship Cleveland Clinic Outline The Basics
Comparison of the functional outcome of DHS versus cannulated cancellous screws in pauwels type II and III fracture neck femur in young adults
 2017; 3(2): 745-749 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 745-749 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 20-02-2017 Accepted: 21-03-2017 Dr. Mandeep Singh Resident, Department of Orthopaedics Gandhi Medical
2017; 3(2): 745-749 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 745-749 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 20-02-2017 Accepted: 21-03-2017 Dr. Mandeep Singh Resident, Department of Orthopaedics Gandhi Medical
Non-Anatomical Surgical Solutions for Difficult Non-Unions: Case Series
 KOWSAR Non-Anatomical Surgical Solutions for Difficult Non-Unions: Case Series Galal Zaki Said 1, *, Osama Ahmed Farouk 1, Hatem Galal Said 1, Mohamed Mostafa Mohamed El-Sharkawi 1 1 Department of Orthopedic
KOWSAR Non-Anatomical Surgical Solutions for Difficult Non-Unions: Case Series Galal Zaki Said 1, *, Osama Ahmed Farouk 1, Hatem Galal Said 1, Mohamed Mostafa Mohamed El-Sharkawi 1 1 Department of Orthopedic
A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Management of Hip Fractures
 Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
THE EFFECT OF FRACTURE DISPLACEMENT ON LATE COMPLICATIONS IN FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES
 Act& orthop. Scandinav. 41, 572-577, 1970 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery (Head: Anders G. Hulth), Malmo General Hospital, University of Lund, Malmo, Sweden. THE EFFECT OF FRACTURE DISPLACEMENT ON LATE
Act& orthop. Scandinav. 41, 572-577, 1970 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery (Head: Anders G. Hulth), Malmo General Hospital, University of Lund, Malmo, Sweden. THE EFFECT OF FRACTURE DISPLACEMENT ON LATE
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.16, No.1, January, 2003
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
Outcome of undisplaced and moderately displaced femoral neck fractures
 498 Acta Orthopaedica 2007; 78 (4): 498 504 Outcome of undisplaced and moderately displaced femoral neck fractures A prospective study of 466 patients treated by internal fixation Kristian Bjørgul 1 and
498 Acta Orthopaedica 2007; 78 (4): 498 504 Outcome of undisplaced and moderately displaced femoral neck fractures A prospective study of 466 patients treated by internal fixation Kristian Bjørgul 1 and
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
Risk factors associated with the early failure of cannulated hip screws
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 34-38 ORIGINAL STUDY Risk factors associated with the early failure of cannulated hip screws Robert W. JORdAn, nick A Smith, Edward dickenson, helen PARSOnS, Xavier GRiffin
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 34-38 ORIGINAL STUDY Risk factors associated with the early failure of cannulated hip screws Robert W. JORdAn, nick A Smith, Edward dickenson, helen PARSOnS, Xavier GRiffin
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
Hansson Pin System. Strong stable fixation, through simple precise procedure with minimal surgical trauma
 Hansson Pin System Hansson Pin System Strong stable fixation, through simple precise procedure with minimal surgical trauma The Hansson Pin system was designed by Professor Lars Ingvar Hansson at the University
Hansson Pin System Hansson Pin System Strong stable fixation, through simple precise procedure with minimal surgical trauma The Hansson Pin system was designed by Professor Lars Ingvar Hansson at the University
ORIGINAL STUDY INTRODUCTION
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 48-54 ORIGINAL STUDY Comparison of outcomes following uncemented hemiarthroplasty and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of displaced subcapital hip fractures in patients
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 48-54 ORIGINAL STUDY Comparison of outcomes following uncemented hemiarthroplasty and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of displaced subcapital hip fractures in patients
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
