Original Article. * Received for Publication: August 20, 2007 * Revision Received: September 12, 2007 * Revision Accepted: September 15, 2007
|
|
|
- Kelley Boyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article SHORT TERM OUTCOME OF TREATMENT OF FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN BY TWO METHODS: TRACTION PLUS CASTING, VERSUS INTRAMEDULLARY PIN FIXATION A COMPARATIVE STUDY Seyed Abdolhossein Mehdinasab 1, Seyed Ali Marashi Nejad 2, Nasser Sarrafan 3 ABSTRACT Objective: There is no consensus on treatment of closed femoral shaft fractures in children 6-12 years old.the aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the short term results of pediatric femoral shaft fractures at above ages with two different methods of treatment: skeletal traction followed by a hip spica cast and surgical treatment by intramedullary pin fixation and to determine which of these methods results in earlier union of fracture and independent ambulation of the patients. Methodology: This study was performed prospectively at two hospitals during a period of 32 months from 2003 through Sixty six children with closed fractures of the femoral shaft were treated and followed at least through the time of fracture healing, spica cast removal and onset of unprotected walking in two separate groups: (A) skeletal traction by technique followed by spica cast (n=30), (B) open reduction and internal fixation with intramedullary pin and cast (n=36). The length of hospital stay, casting period, union of fractures, time to start walking and the rate of complications was evaluated and compared using Chi-Squar test. Results: Mean age of all patients was 7.4 years old. Average follow-up was 6 months. Healing of the fractures was observed in all cases of both groups between 8 and 12 weeks. The length of immobilization was longer in traction versus surgery group. Average treatment duration from admission to hospital till independent walking was 75.3 days for the traction and 61.2 days for surgery group. Limb shortening and malrotation were more in traction versus intramedullary pin patients. Conclusion: Both methods of traction plus spica casting and intramedullary pinning can be used to treat femoral shaft fractures in 6-11 years old children. Intramedullary pin due to its less hospital stay, earlier walking and less complication rates can be used as the first choice in treatment of this fracture at school aged children. KEYWORDS: Femoral shaft fracture, Skeletal traction, Spica cast, Intramedullary pin. Pak J Med Sci January - March 2008 Vol. 24 No Dr. Seyed Abdolhossein Mehdinasab, 2. Dr. Seyed Ali Marashi Nejad, Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, Mehr Hospital, Kianpars, Ahwaz Iran. 3. Dr. Nasser Sarrafan, 1 & 3: Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, Dept. of Orthopedics, Imam Khomeini Hospital, Azadegan Avenue, Ahwaz Iran. Correspondence Dr. Seyed Abdolhossein Mehdinasab, hmehdinasab@yahoo.com * Received for Publication: August 20, 2007 * Revision Received: September 12, 2007 * Revision Accepted: September 15, 2007 INTRODUCTION Femoral fractures consist 1.6% of all children fractures. Their prevalence in boys is 2.6:1 fold of girls, can be seen at any age and among the long bone fractures, is responsible for the longest hospital stay, immobilization in cast, and absence from school and daily activities. 1-3 Femur is the longest bone of the body and main weight bearing and movement tolerating bone, thus, complications of this fracture can be catastrophic for the child and the family. In Pak J Med Sci 2008 Vol. 24 No
2 Seyed Abdolhossein Mehdinasab et al. younger ages and before school, child abuse or falling down is the main cause of this fracture. 4 In older children, the fractures is mainly due to sport events, on foot care contacts, or driving accident. As the age increases and bones are stiffened, fracture causing force must be more severe. 5,6 Until now, a variety of treatment methods have been used, but none of them is the standard method. In the past, almost all of these fractures have been treated conservatively by traction and spica cast and now this method also is being used for younger children only. 7 During recent years, there has been a considerable increase in closed or open reduction and internal fixation using intramedullary pin or rod to treat femoral shaft fractures in children. This can be related to technical advancements specially development of elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN), or patients intention of short stay in hospital. 8 The preferred method of treatment for femoral shaft fracture in children younger than six years age is usually by closed reduction and primary spica cast. For children more than 11 years age it is by surgery, but there is no agreement on definite method of treatment between ages 6-12 years and both nonoperative and surgery with internal fixation can be used The current study was performed to evaluate the short term results of management of pediatric femoral shaft fractures and it attempted to compare these two different methods of traction & cast and intramedullary pin fixation, regarding the time till union and unprotected ambulation by comparing the results. METHODOLOGY This study was conducted as a prospective and controlled clinical trial during 32 months (May 2003-Feb 2006) at two hospitals (Imam Khomeini and Razi), and all children with closed femoral shaft fracture between the age group of 6-11 years were enrolled in the study. Fracture characteristics for inclusion in the study were, oblique, spiral and transverse closed femoral shaft fractures. Open, pathologic, segmental, trochanteric, multiple trauma and distal epiphyseal fractures were excluded from study. Patient s gender was not involved in the study. Randomizing of patients into two groups was performed consecutively based on their order of presentation and hospitalization. Treatment method was traction in the first group and surgical in the second group. After approval of Ethics committee in our hospitals and complete explanation of treatment plan to parents, a written consent was taken from patient s parents or guardians. Treatment in the first group: In the operating room, under local anesthesia after insertion a 3 or 4 mm Steinman pin into proximal tibia, skeletal traction and leg support with sling was applied. Proper reduction status was determined by serial radiographs. Following primary callus formation and early union that was characterized by loss of pain, tenderness and motion at the fracture site, pin was removed and 1 1 /2 spica cast was applied. Control radiographs were taken at interval of 3,6,12 and 16 weeks. After complete union, cast was removed, physiotherapy was initiated and walking was allowed as soon as the patient could tolerate. Second group: In the operating room, after preparation, under general anesthesia and in lateral position, fracture site was exposed by a 4-5cm incision. Then a 4-5 mm slightly bent pin was inserted retrograde first, into proximal fragment with the hip in flexion, adduction, and internally rotated and after reduction, into distal fragment. Pin end was bent above the greater trochanter subcutaneously. Control of reduction was performed by a C- arm fluoroscopy. Then, a hip spica cast was applied. Radiographic examination was sone at 4 weeks interval. After union of fracture and removal of the cast, physiotherapy and weight bearing was started when the patient could tolerate. Pins were removed after 20 to 24 weeks (mean 22 weeks) post operatively. Three time periods were considered in evaluation of the patients: (1) duration of hospital stay (2) duration of cast immobilization, (3) period in which patients start walking. 148 Pak J Med Sci 2008 Vol. 24 No. 1
3 Treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children RESULTS Out of seventy 6-11 years old children who were admitted and treated for closed femoral shaft fractures, four patients were lost to follow up and were excluded from study, but 66 cases (51 boys and 15 girls) were available and followed - up for 6 months. The cause of fracture was motor/vehicle accident in 30 (45.4%), pedestrian vehicle collision in 19 (28.8%) and falls in 17 (25.75%). Thirty of them were in the first group treated by skeletal traction, and 36 patients in the second group were treated surgically. Out of total 66 patients, 51 were male and 15 were female with male to female ratio of 3.2/1. Mean age of all patients at the time of injury was 7.4 years. Seven point two years for the first, (range, y) and 8.1 years for second group ( y). The mean duration of hospital stays, casting, ambulation, total course of treatment and results between two groups is summarized in Table-I&II. Sound unions were achieved between 8 and 12 weeks in all fractures. Total treatment period, from admission time to independent walking was days (average 75.3 days) for first group and days (average 60.2 days) for second group. No patient had peripheral neurovascular complication. In the second group (surgery), there was one case of superficial infection which was treated by antibiotics. Six patients complained of pain and discomfort at the pin end site that resolved after extracting the pins. In four patients in the first group, mean shortening of 1cm and one patient of intramedullary pin, shortening of 1cm was observed. In that patient, fracture line was of long obliquity. None of the patients had unacceptable angles of varus or valgus. In comparison with contra lateral normal limb, excessive lateral rotation of leg (average 15 degree) was observed in three patients in the first group. In second group, patients families were more satisfied of surgical treatment and shorter hospital stay. Range of motion of the knee and hip joints were normal at final follow up in both groups of patients. DISCUSSION Treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children is dependent upon age and weight of the patient, location, character of fracture and associated injuries. 12 In children younger than 5 years of age, recommended treatment is nonsurgical with primary hip spica cast with or without a period of Russell, s skin traction. Historically, skeletal traction has been a conventional and safe method of management in older children. It doesn t cause knee stiffness, bone union occurs naturally without risks of surgery, but it may result in malunion or limb shortening, and longer hospital stay, which may not be tolerated by agitated child or parents. In different reports, skeletal traction has been known as an excellent modality. 13 On the other hand, flexible intramedullary pin or nail is a minimal invasive and safe method, which maintains normal bone alignment with high rates of union. Also it can be performed in pathologic and some open fractures. The length of hospital stay is shorter than traction method. 14,15 Uncommon complications of this technique may be the surgical risks, painful bursitis at the nail or pin end site, or avascular necrosis of femoral head For children over 12 years of age, treatment of femoral shaft fracture is usually as an adult by surgery, using intramedullary nail, external fixator or plate and screw for patients Table-I: Results of treatment duration at both groups Mean Duration of treatment (days) Skeletal traction ( n=30) Intramedullary pin ( n=36) Hospital stay duration Average period of hip spica casting Ambulation time Total treatment course Pak J Med Sci 2008 Vol. 24 No
4 Seyed Abdolhossein Mehdinasab et al. Table-II: Complications of femoral shaft fracture in two patient groups. Complication Traction and Intramedullary pin+ P.value casting n=30 Casting N=36 Infection = (2.7%) Shortening 4 = (13%) 1 = (2.7%) Malrotation 3= (10%) Pin end irritation = (11%) between 6-12 years of age, both surgical and non-surgical methods can be used. Ligier et al, have used elastic intramedullary nail (ESIN) with kirshner-wires or pins, which was performed retrograde or antegrade.this technique provides a combination of stable and elastic immobilization. Rotational stability is achieved by the curved or bent wires which provides 3-point fixation. Normal tension of surrounding muscles helps this stability and elasticity of the pins help callus formation by allowing fine micro motion at the fracture site. 19,20 In our study we used the principle of ESIP with a single curved wire. Reeve et al, in a comparative study, treated 41 patients with femoral fracture by traction and casting and 49 cases by IMN surgery. Age of patients was between 4 and 12 years old. In their study, complications of traction and casting were more than the operated group. 13 In another similar study conducted by Kirby et al; on 25 children femoral shaft fracture, which were evaluated in two separate groups of traction plus cast and IMN, shortening of >2.5cm and malunion were reported in traction and casting group. 21 In studies performed by Arenson, Singer and Herndon, the complication of malunion in traction and cast was more frequent than surgical treatment. 22,23 Flynn et al, while reporting successful results of intramedullary nailing, concluded that most femoral fractures in children can be treated by traction and casting. 24 In our study the total period of treatment until onset of unprotected weight bearing for traction and cast and intramedullary pin fixation was 75.3 days, and 61.2 days respectively. We noted more complications in the traction versus intramedullary pin patients. Malrotation and limb shortening were more in traction group, with the P. value of < 0.05 and these differences were statistically significant. Although the main disadvantage of intramedullary pin was the pin end irritation, and need of the second operation to remove the pin. Both methods resulted in excellent union of fractures. Overgrowth is a common problem after femoral shaft fractures in children. Its correction is related to the child s age, and up to 2cm of overriding at the fracture site can be acceptable in younger child. The 1cm shortening in 5 patients of this short term study would be expected to resolve as the child grows and remodeling of the bone. To detect this phenomenon, another study with a follow up of two years or longer will be needed. 25 CONCLUSIONS Closed pediatric femoral shaft fractures within the ages of 6-11 years can be treated successfully by any methods of skeletal traction or intramedullary pin. However, because of shorter immobilization period and earlier ambulation, we recommend internal fixation with IM pin as the first choice to treat this fracture in school aged children REFERENCES 1. Fry K, Hoffer M, Brink J. Femoral shaft fractures in brain- injured children. J Trauma 1976;16: Hedlund R, Lindgren U. The incidence of femoral shaft fractures in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop 1986;6: Hinton RY, Lincoln A. Crockett MM. Fractures of the femoral shaft in children. Incidence, mechanism, and sociodemographic risk factors. J Bone J Surg Am 1999;81: Blakemore LC, Loder RT, Hensinger RN. Role of intentional abuse in children 1 to 5 years old with isolated femoral shaft fractures. J Pedial Orthop 1996;16: Pak J Med Sci 2008 Vol. 24 No. 1
5 Treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children 5. Daly KE, Calvert PT. Accidental femoral fracture in infants. Injury 1991;22: Loder RT. pediatric polytrauma orthopaedic care and hospital course. J Orthop Trauma.1987;1: Ferguson J, Nicol RO. Early spical treatment of pediatric femoral shaft fractures. J Pediatr Orthop 2000;20: Barry M, Paterson JM. Flexible intramedullary Nails for fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg 2004;86-B.7: Aronson DD, Singer RM, Higgins RF. Skeletal traction for fractures of the femoral for fractures of the femoral shaft in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1987;69: Cameron CD, Meek RN, Blachut PA. Intramedullary nailing of the femoral shaft: A prospective, randomized study. J Orthop Trauma 1992;6: Hughes BF, Sponseller PD, Thompson JD. Pediatric femur fracture: effect of spica cast treatment on family and community. J Pediatr Orthop 1995;15: James RK, James HB. Femoral shaft fractures in: Rockwood and Wilkins. Fractures in children. 5 th ed.2002; Reeves RB, Ballard RI, Haghes JI. Internal fixation versus traction and casting of adolescent femoral shaft fractures. J Pediutr Orthop 1990;10: Carey TP, Galpin RD. Flexible intramedullary nail fixation of pediatric femoral fractures. Clin Orthop Rel Res 1996;332: Vransky P, Burdelat D, Burdelat D, AI Faour A. Flexible stable intramedullary pinning technique, in the treatment of pediatric fractures. J Pediatr Orthop 2000;20: Orler R, Hersche O, Helft DL. Avascular femur head necrosis as severe complication of after femoral intramedullary nailing in children and adolescents. Unfallchirurg 1998;101: Heinrich SD, Drvavic DM, Darvk. The operative stabilization of pediatric diaphyseal femur fractures with flexible intramedullary nails. J Orthop Trauma 1994;14: Maza K, Khairuni A, Pennecot GF. Closed flexible intramedullary nailing of the femoral shaft fractures in children. J Rediat Orthop 1997;6: Ligier JN, Metaizeau JP, Prevot J. Closed flexible intramedullary nailing in pediatric traumatology. Chir Pediatr 1983;24: Greisberg J, Bliss MJ, Eberson CP. Social and economic benefits of flexible intramedullary Nails in the treatment of pediatric femoral shaft fractures. Orthop 2002;25: Kirby RM, Winquist RA, Hansen ST. Femoral shaft fractures in Adolescents. A comparison between traction plus cast treatment and closed intramedullary nailing. J Rediatr Orthop 1981;1: Aronson J, Tursky RN. External fixation of femur fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1987;69: Herndon WA, Mohnken RF, Yugve DA. Management of femoral shaft fractures in the adolescents. Pediatric Orthop 1989;9: Flynn JM, Hersko T, Reynolds RAK. Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures. A multicenter study of early results with analysis of complications. Pediatr Orthop 2001;21: Shapiro F. Fractures of the femoral shaft in children: The overgrowth phenomenon. Acta Orthop Scan 1981;52: Pak J Med Sci 2008 Vol. 24 No
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace
 18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures
 대한정형외과학회지 : 제 43 권제 1 호 2008 J Korean Orthop Assoc 2008; 43: 30-35 Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures Do-Young Kim, M.D., Sung-Ryong
대한정형외과학회지 : 제 43 권제 1 호 2008 J Korean Orthop Assoc 2008; 43: 30-35 Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures Do-Young Kim, M.D., Sung-Ryong
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture Management By Titanium Elastic Nailing; A Prospective Study Of 112 Patients
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 19 Number 3 Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture Management By Titanium Elastic Nailing; A Prospective Study Of 112 P Singh, R Kumar Citation P Singh,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 19 Number 3 Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture Management By Titanium Elastic Nailing; A Prospective Study Of 112 P Singh, R Kumar Citation P Singh,
Original Research Article Treatment of Paediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture with Titanium Elastic Nails Dr. Neeraj Mahajan 1, Dr.
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(3E):981-985 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(3E):981-985 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Complications Cast Treatment Psychosocial effect on children Economoic effects on their families [Hughes 1995] ORIF with Plate Ex Fix Antegrade Nail L
![Complications Cast Treatment Psychosocial effect on children Economoic effects on their families [Hughes 1995] ORIF with Plate Ex Fix Antegrade Nail L Complications Cast Treatment Psychosocial effect on children Economoic effects on their families [Hughes 1995] ORIF with Plate Ex Fix Antegrade Nail L](/thumbs/78/78093115.jpg) Introduction Cast or Traction + cast Nicol [2000] ORIF Kregor [ 93], Ward [92] Ex Fix Aronson [ 92], Tolo [93] Antegrade Nail Beaty [94], Buford [98], Galpin [ 94], Herndon [ 89] Flexible IM Pinning [00],
Introduction Cast or Traction + cast Nicol [2000] ORIF Kregor [ 93], Ward [92] Ex Fix Aronson [ 92], Tolo [93] Antegrade Nail Beaty [94], Buford [98], Galpin [ 94], Herndon [ 89] Flexible IM Pinning [00],
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
UNCORRECTED PROOF. Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution. V.S. Pai a, *, P. David Gwynne-Jones a, Jean Claude Theis b
 Injury Extra (2004) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext 2 3 Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 V.S. Pai a,
Injury Extra (2004) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext 2 3 Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 V.S. Pai a,
Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution
 Injury Extra (2005) 36, 185 189 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution V.S. Pai a, *, P. David Gwynne-Jones a, Jean Claude Theis b a Dunedin Hospital,
Injury Extra (2005) 36, 185 189 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution V.S. Pai a, *, P. David Gwynne-Jones a, Jean Claude Theis b a Dunedin Hospital,
Mohammad Fakoor 1, Shahnam Mousavi 1, Hazhir Javherizadeh 2
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2011, 83, 9, 477 481 10.2478/v10035-011-0074-9 O R I G I N A L P A P E R S Different types of femoral shaft fracture; different types of treatment: their effects on postoperative
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2011, 83, 9, 477 481 10.2478/v10035-011-0074-9 O R I G I N A L P A P E R S Different types of femoral shaft fracture; different types of treatment: their effects on postoperative
Introduction. Mohammad Ruhullah 1*, Sanjay Shah 1, Hare Ram Singh 1, Dipak Shrestha 2. Bagmati, Nepal. Abstract
 This article has been published in whole in Maced J Med Sci. 2013 Dec 15; 6(4):350-355. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013 Dec 15; 1(1):12-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2013.003
This article has been published in whole in Maced J Med Sci. 2013 Dec 15; 6(4):350-355. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013 Dec 15; 1(1):12-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2013.003
Closed diaphyseal fractures of femur in children treated by hip spica: early result of a clinical study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Ansari MAQ et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):22-26 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175113
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Ansari MAQ et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):22-26 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175113
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Titanium elastic intramedullary nailing : closed or mini-open reduction?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 406-410 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic intramedullary nailing : closed or mini-open reduction? Bekir Yavuz Uçar, Mehmet Gem, Mehmet Bulut, Ibrahim Azboy, Abdullah Demirtaş,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 406-410 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic intramedullary nailing : closed or mini-open reduction? Bekir Yavuz Uçar, Mehmet Gem, Mehmet Bulut, Ibrahim Azboy, Abdullah Demirtaş,
PAEDIATRIC FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES MANAGED WITH TENS
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 7(1) : 119-124, 2016 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) PAEDIATRIC FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES MANAGED WITH TENS AMIT BATRA, ADITYA JAIN, MOHIT KHANNA, DHARVIN LAMBA, SURESH
Indian J.Sci.Res. 7(1) : 119-124, 2016 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) PAEDIATRIC FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES MANAGED WITH TENS AMIT BATRA, ADITYA JAIN, MOHIT KHANNA, DHARVIN LAMBA, SURESH
Reconstruction plate fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 200,, -90 ORIGINAL STUDY Reconstruction plate fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in children oustafa EL-SAYED, azen ABULSAAD, ahmoud EL- HADIDI, Wael EL-ADL, agdy EL-BATOUTY
Acta Orthop. Belg., 200,, -90 ORIGINAL STUDY Reconstruction plate fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in children oustafa EL-SAYED, azen ABULSAAD, ahmoud EL- HADIDI, Wael EL-ADL, agdy EL-BATOUTY
FIRST DESCRIBED RETROGRADE TECHNIQUE USING MEDIAL EPICONDYLE 6/5/2018. RETROGRADE vs. ANTEGRADE FEMORAL NAILING
 What do I do? ISSUES ANTEGRADE vs. RETROGRADE PIRIFORMIS vs. TROCHANTER FLAT vs. FRACTURE TABLE SWIONTKOWSKI, 1984 FIRST DESCRIBED RETROGRADE TECHNIQUE USING MEDIAL EPICONDYLE 1 RETROGRADE NAILING SANDERS
What do I do? ISSUES ANTEGRADE vs. RETROGRADE PIRIFORMIS vs. TROCHANTER FLAT vs. FRACTURE TABLE SWIONTKOWSKI, 1984 FIRST DESCRIBED RETROGRADE TECHNIQUE USING MEDIAL EPICONDYLE 1 RETROGRADE NAILING SANDERS
Management and outcome of diaphyseal femur fracture in Children: A tertiary care Experience
 Original article: Management and outcome of diaphyseal femur fracture in Children: A tertiary care Experience Ravi Kant Jain 1, Chirag Sethi 1, Pranav Mahajan 1, Ravindra Kumar 2 1Department of Orthopaedics,
Original article: Management and outcome of diaphyseal femur fracture in Children: A tertiary care Experience Ravi Kant Jain 1, Chirag Sethi 1, Pranav Mahajan 1, Ravindra Kumar 2 1Department of Orthopaedics,
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Intramedullary Nailing for Femur Fracture Management
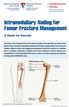 514-412-4400, ext. 23310 thechildren.com/trauma Intramedullary Nailing for Femur Fracture Management A Guide for Parents The femur is the longest bone in the body. It begins at the hip joint and ends at
514-412-4400, ext. 23310 thechildren.com/trauma Intramedullary Nailing for Femur Fracture Management A Guide for Parents The femur is the longest bone in the body. It begins at the hip joint and ends at
Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old
 1 Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City MO, USA rmschwend@cmh.edu 5 th Annual SLAOTI
1 Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City MO, USA rmschwend@cmh.edu 5 th Annual SLAOTI
M.S (orthopedics), FRAS (Germany) Chairman and chief Orthopedic consultant Surgeon, Q1 Hospital, Vizag. AP.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.1.OR3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Management of Diaphyseal Fractures of Long Bones in Children with Titanium Elastic Nails A Prospective Study of
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.1.OR3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Management of Diaphyseal Fractures of Long Bones in Children with Titanium Elastic Nails A Prospective Study of
Assessment of outcome of early versus delayed spica cast treatment of closed femoral shaft fractures in children
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 5, Issue 5-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.05.007
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 5, Issue 5-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.05.007
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture
 Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Pediatric femoral shaft fractures: treatment strategies according to age - 13 years of experience in one medical center
 Sela et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pediatric femoral shaft fractures: treatment strategies according to age - 13 years of experience in one
Sela et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pediatric femoral shaft fractures: treatment strategies according to age - 13 years of experience in one
Titanium elastic nail in femur fractures as an alternative to spica cast in preschoolers
 J Child Orthop (2012) 6:505 511 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0448-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Titanium elastic nail in femur fractures as an alternative to spica cast in preschoolers Yasser M. Assaghir Received:
J Child Orthop (2012) 6:505 511 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0448-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Titanium elastic nail in femur fractures as an alternative to spica cast in preschoolers Yasser M. Assaghir Received:
Outcome of Titanium Elastic Intramedullary Nail in the Treatment of Shaft of Femur Fracture in Children. Khan JA, 1 Singh GP, 2 Pandey A 2
 Outcome of Titanium Elastic Intramedullary Nail in the Treatment of Shaft of Femur Fracture in Children. Khan JA, 1 Singh GP, 2 Pandey A 2 ABSTRACT Background 1 Karnali Academy of Health Sciences Jumla,
Outcome of Titanium Elastic Intramedullary Nail in the Treatment of Shaft of Femur Fracture in Children. Khan JA, 1 Singh GP, 2 Pandey A 2 ABSTRACT Background 1 Karnali Academy of Health Sciences Jumla,
Comparative Study between the Elastic Nail versus Hip Spica Cast in Early Treatment of Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2016, 6, 259-267 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo ISSN Online: 2164-3016 ISSN Print: 2164-3008 Comparative Study between the Elastic Nail versus Hip Spica Cast in Early Treatment
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2016, 6, 259-267 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo ISSN Online: 2164-3016 ISSN Print: 2164-3008 Comparative Study between the Elastic Nail versus Hip Spica Cast in Early Treatment
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 104: , 2014
 529275SJS104010.1177/1457496914529275A. Salonen, T. Lahdes-Vasama, V. M. Mattila, J. Välipakka, O. PajuloScandinavian Journal of Surgery research-article2014 Original Article Scandinavian Journal of Surgery
529275SJS104010.1177/1457496914529275A. Salonen, T. Lahdes-Vasama, V. M. Mattila, J. Välipakka, O. PajuloScandinavian Journal of Surgery research-article2014 Original Article Scandinavian Journal of Surgery
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures
 TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya
 Original Article Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya O.O. Soren, MBChB (Moi), MMed (Orthopaedics) (Makerere), Consultant Orthopaedic
Original Article Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya O.O. Soren, MBChB (Moi), MMed (Orthopaedics) (Makerere), Consultant Orthopaedic
Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee): A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
spica of fracture at or below the junction of the upper and middle third of femur in children
 Original Article Chaudhary et.al. Randomized control trial comparing primary hip spica versus initial traction and hip spica of fracture at or below the junction of the upper and middle third of femur
Original Article Chaudhary et.al. Randomized control trial comparing primary hip spica versus initial traction and hip spica of fracture at or below the junction of the upper and middle third of femur
Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale
 Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale Overview 1. What is IM Nailing? 2. History 3. Design Rationale & Evolution 4. Modern IM Nails 5. The Future What is IM Nailing? Method of internal fixation in
Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale Overview 1. What is IM Nailing? 2. History 3. Design Rationale & Evolution 4. Modern IM Nails 5. The Future What is IM Nailing? Method of internal fixation in
Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures
 Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Paul Thompson, PhD Biomedical
Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Paul Thompson, PhD Biomedical
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Surgical Management Of Fractures Of The Femur Shaft In Children And Adolescents Using Flexible Nails - A Prospective Study
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 23 Number 1 Surgical Management Of Fractures Of The Femur Shaft In Children And Adolescents Using Flexible Nails - A Prospective Study V Sidhu,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 23 Number 1 Surgical Management Of Fractures Of The Femur Shaft In Children And Adolescents Using Flexible Nails - A Prospective Study V Sidhu,
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHYSEAL FEMUR FRACTURE WITH INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL AND K. NAIL
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Segmental tibial fractures treated with unreamed interlocking nail A prospective study
 2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing
 Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4
 Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails
 Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Anatomical and functional evaluation of diaphyseal femoral fractures in. children under 6 years old
 854 Acta Orthop. Belg., a. alhefzi, 2016, 82, d. alshammari, 854-860 l. bund, l. schneider, p. gicquel ORIGINAL STUDY Anatomical and functional evaluation of diaphyseal femoral fractures in children under
854 Acta Orthop. Belg., a. alhefzi, 2016, 82, d. alshammari, 854-860 l. bund, l. schneider, p. gicquel ORIGINAL STUDY Anatomical and functional evaluation of diaphyseal femoral fractures in children under
Use Of Ender's Nailing in Treatment of Pediatric Fracture Shaft Femur
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 33-40 www.iosrjournals.org Use Of Ender's Nailing in Treatment
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 33-40 www.iosrjournals.org Use Of Ender's Nailing in Treatment
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences October 2015; 2(10) ISSN: ISSN: Impact Factor (PIF): 2.
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC LONG BONE FRACTURES OF LOWER LIMB BY TITANIUM ELASTIC NAILS *Dr.K.Venkataswamy, Dr.J.Venkateshwarulu, Dr.TandraVenkateshwararao, Dr.Shivanshu Mittal, Dr.J.Sreenath Rao
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC LONG BONE FRACTURES OF LOWER LIMB BY TITANIUM ELASTIC NAILS *Dr.K.Venkataswamy, Dr.J.Venkateshwarulu, Dr.TandraVenkateshwararao, Dr.Shivanshu Mittal, Dr.J.Sreenath Rao
A comparative study of locking plate by MIPO versus closed interlocking intramedullary nail in extraarticular distal tibia fractures
 2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
Journal of American Science 2017;13(11) Submuscular Plating in Spiral Unstable Pediatric Femur Fractures
 Submuscular Plating in Spiral Unstable Pediatric Femur Fractures M. Salah Abdel hafiz, MD, Ibrahim Elsebaey, MD, Ahmed Elshorbagy MBBCH Department of Orthopedic Surgery Al-Azhar Faculty of Medicine ah_shorbagy@yahoo.com
Submuscular Plating in Spiral Unstable Pediatric Femur Fractures M. Salah Abdel hafiz, MD, Ibrahim Elsebaey, MD, Ahmed Elshorbagy MBBCH Department of Orthopedic Surgery Al-Azhar Faculty of Medicine ah_shorbagy@yahoo.com
Fractures (Broken Bones)
 Fractures (Broken Bones) A fracture is a broken bone. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces). Types of Fractures Bones
Fractures (Broken Bones) A fracture is a broken bone. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces). Types of Fractures Bones
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 512-520 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures Gamal EL-ADL, Mohamed F. MOSTAFA, Mohamed A. KHALIL, Ahmed ENAN From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 512-520 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures Gamal EL-ADL, Mohamed F. MOSTAFA, Mohamed A. KHALIL, Ahmed ENAN From Mansoura
Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference?
 Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference? CK Yu, MBBS (UM), HY Wong*, MD (UKM), AS Vivek, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To*, FRCS (Edin)
Unlocked Nailing vs. Interlocking Nailing for Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fractures. Is there a Difference? CK Yu, MBBS (UM), HY Wong*, MD (UKM), AS Vivek, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To*, FRCS (Edin)
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ABSTRACT: Orthopaedic surgeons often encounter diaphyseal femur fractures, because these
 A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE SHAFT FEMUR WITH CLOSED INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL. Mahendranath Reddy D 1, Muralidhar B.M 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mahendranath Reddy D,
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE SHAFT FEMUR WITH CLOSED INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL. Mahendranath Reddy D 1, Muralidhar B.M 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mahendranath Reddy D,
Type I : At the level of lesser trochanter Type II : Less than 2.5 cm below lesser trochanter. Type III : cm below lesser trochanter
 Type II : Major fracture line along the intertrochanteric line with communition in coronal plain. Type III : Fracture at the level of lesser trochanter with variable communition and extension in subtrochanteric
Type II : Major fracture line along the intertrochanteric line with communition in coronal plain. Type III : Fracture at the level of lesser trochanter with variable communition and extension in subtrochanteric
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
KEYWORDS: Tibial fracture, Diaphyseal fracture, closed interlocking intramedullary nailing,
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: A treatment concept
 Original Article Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: A treatment concept Ramji Lal Sahu* *Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics SMS and RI, Sharda University, Greater Noida,
Original Article Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: A treatment concept Ramji Lal Sahu* *Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics SMS and RI, Sharda University, Greater Noida,
COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS
 COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS D.M. Kamau, MBChB, MMed (Ortho Surg), L.N. Gakuu, MBChB, MMed (Surg), FCS (ECSA), Professor, E.M. Gakuya,
COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS D.M. Kamau, MBChB, MMed (Ortho Surg), L.N. Gakuu, MBChB, MMed (Surg), FCS (ECSA), Professor, E.M. Gakuya,
Lengthening & Deformity correction with. Fixator Assisted Nailing
 Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent
 Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski, Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker, Lida Acuña-Huete Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Wan-Ju Li, PhD Biomedical
Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski, Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker, Lida Acuña-Huete Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Wan-Ju Li, PhD Biomedical
Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction. Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center
 OTA Specialty Day 2016 Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center 8:55 am 9:55 am Tips and Tricks: Practical Reduction Techniques
OTA Specialty Day 2016 Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center 8:55 am 9:55 am Tips and Tricks: Practical Reduction Techniques
TECHNIQUE FOR CLOSED REDUCTION OF FEMORAL SHAFT DISPLACED FRACTURE USING INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL WITH STEINMANN PIN SUPPORT: CASE STUDY
 TECHNIQUE FOR CLOSED REDUCTION OF FEMORAL SHAFT DISPLACED FRACTURE USING INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL WITH STEINMANN PIN SUPPORT: CASE STUDY Nitesh Raj Pandey 1, Sumendra raj pandey, Jue-HuaJing 1, XuXin Zhong
TECHNIQUE FOR CLOSED REDUCTION OF FEMORAL SHAFT DISPLACED FRACTURE USING INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL WITH STEINMANN PIN SUPPORT: CASE STUDY Nitesh Raj Pandey 1, Sumendra raj pandey, Jue-HuaJing 1, XuXin Zhong
Management of Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5
 Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN USE OF STAINLESS STEEL ENDERS NAILS AND TITANIUM ELASTIC NAILS FOR TREATMENT OF FRACTURES OF SHAFT FEMUR IN CHILDREN
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 12 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 09/05/14 Revised on: 26/05/14 Accepted on: 12/06/14 COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN USE OF STAINLESS STEEL ENDERS NAILS AND TITANIUM
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 12 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 09/05/14 Revised on: 26/05/14 Accepted on: 12/06/14 COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN USE OF STAINLESS STEEL ENDERS NAILS AND TITANIUM
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO :
 CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
Percutaneous pinning in displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
management of sports injuries
 Br J Sp Med 1991; 25(4) Internal fixation of closed tibial fractures for the management of sports injuries A. Abdel-Salam FRCS, K. S. Eyres* FRCS and J. Cleary FRCS Department of Orthopaedics, Huddersfield
Br J Sp Med 1991; 25(4) Internal fixation of closed tibial fractures for the management of sports injuries A. Abdel-Salam FRCS, K. S. Eyres* FRCS and J. Cleary FRCS Department of Orthopaedics, Huddersfield
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus Fractures with Tens - A Retrospective Analysis.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA
 JOT Special Case Report Series CASE REPORTS www.jorthotrauma.com JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF Orthopaedic Trauma Association Belgian Orthopaedic Trauma Association Canadian Orthopaedic
JOT Special Case Report Series CASE REPORTS www.jorthotrauma.com JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF Orthopaedic Trauma Association Belgian Orthopaedic Trauma Association Canadian Orthopaedic
Treatment of traumatic conditions of the femur using the Huckstep nail
 East and Central African Journal of Sulgey Vol. 2, No. I Treatment of traumatic conditions of the femur using the Huckstep nail T F Wisniewski MD PhD(0rth) Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Bone and
East and Central African Journal of Sulgey Vol. 2, No. I Treatment of traumatic conditions of the femur using the Huckstep nail T F Wisniewski MD PhD(0rth) Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Bone and
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons.
 Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
FRACTURE SHAFT OF FEMUR IN CHILDREN; MANAGED WITH EXTERNAL FIXATION - A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/16.3366 ORIGINAL PROF-3366 FRACTURE SHAFT OF FEMUR IN CHILDREN; MANAGED WITH EXTERNAL FIXATION - A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES fayyaz_ao@hotmail.com
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/16.3366 ORIGINAL PROF-3366 FRACTURE SHAFT OF FEMUR IN CHILDREN; MANAGED WITH EXTERNAL FIXATION - A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES fayyaz_ao@hotmail.com
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children
 PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
Functional outcome of both bone fracture forearm managed with titanium elastic intramedullary nail system in pediatric age group
 2018; 2(1): 37-41 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 37-41 Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 24-12-2017 Harish K Assistant Professor, Mandya,
2018; 2(1): 37-41 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 37-41 Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 24-12-2017 Harish K Assistant Professor, Mandya,
