Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) : treatment options and proposal of a follow-up regime
|
|
|
- Kellie Phelps
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 474 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, o. hauschild et al ORIGINAL STUDY Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) : treatment options and proposal of a follow-up regime Oliver Hauschild, Martin Lüdemann, Monika Engelhardt, Daniel Baumhoer, Tobias Baumann, Tania Elger, Norbert P. Südkamp, Georg W. Herget From the Department of Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery, University Medical Centre, Freiburg, Germany The aim of this study was to describe treatment options and develop a follow-up regime for the aneurysmal bone cyst, a neoplastic bone lesion with a noticeable recurrence rate. Reports of 28 patients and a mean follow-up of 42.2 months treated multidisciplinary were analysed. Data were complemented by a literature review including 790 patients. Patient age was from seven to 57 years, in line with the literature (1-69 years). Lesions most frequently affect long bones, spine and pelvis ; pain is the most common symptom. Treatment modalities vary, recurrences occurred in 26.1% in our series, rates ranged from 0-60% in the literature, with the vast majority within 2 years. With regard to the findings we propose, irrespective of treatment, a follow-up regime including clinical survey and imaging, best with MRI, at 3 months, 6 months and at half-yearly intervals within the first two and yearly within the third to fifth year. Keywords : aneurysmal bone cyst ; symptom ; treatment ; recurrence ; follow-up. INTRODUCTION The aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) is an osteolytic, hyperaemic-hemorrhagic lesion of bone which may arise de novo (primary ABC), or secondarily complicating numerous tumors and tumor-like lesions of bone (secondary ABC), such as giant cell tumor, chondroblastoma, fibrous dysplasia, solitary bone cyst or osteoblastoma (8,13,18,23). n Priv.-Doz. Dr. Oliver Hauschild 1, 2. n Dr. Martin Lüdemann 3. n Prof. Dr. Monika Engelhardt 4. n Prof. Dr. Daniel Baumhoer 5. n Priv.-Doz. Dr. Tobias Baumann 6. n Tania Elger 1. n Prof. Dr. med. Norbert P. Südkamp 1. n Priv. Doz. Dr. Georg W. Herget 1, 2. 1 Department of Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery, University Medical Centre, Hugstetterstr. 55, Freiburg i. Br., Germany. 2 Comprehensive Cancer Centre Freiburg CCCF, University Medical Centre, Hugstetterstr. 55, Freiburg i. Br., Germany. 3 Department of Orthopaedics, König-Ludwig-Haus, University Medical Centre, Brettreichstraße 11, Würzburg. 4 Department of Hematology and Oncology, University Medical Centre Freiburg, Hugstetterstr. 55, Freiburg, Germany. 5 Bone Tumor Reference Centre, Institute of Pathology, University Medical Centre, Schönbeinstrasse 40, 4031 Basle, Switzerland. 6 Department of Radiology und Nuclear Medicine, University Medical Centre, Petersgraben 4, 4031 Basle, Switzerland. Correspondence : Georg W. Herget, Department of Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery/Comprehensive Cancer Centre Freiburg (CCCF) University Medical Centre Freiburg Hugstetterstr Freiburg i. Br., Germany. georg.herget@uniklinik-freiburg.de 2016, Acta Orthopædica Belgica. No benefits or funds were received in support of this study. The Acta authors Orthopædica report Belgica, no conflict Vol. of 82 interests hauschild-.indd 474 5/10/16 14:06
2 aneurysmal bone cyst 475 Initially regarded as a hyperplastic lesion reactive to an unknown local process of uncertain aetiology (20), the primary ABC is now widely accepted as a neoplasm owing to recent findings of recurrent chromosomal rearrangements involving the USP6 gene (20). Malignant transformation usually to an osteosarcoma is an unlikely event, but a few cases have been reported (14,22). The lesion affects all age groups, but is most common during the first two decades of life (8,13, 18,23) and the estimated annual incidence is 0.14 per 10 5 individuals (16). It comprises approximately 1 % of all bone tumors who underwent biopsy (8, 16). ABC most frequently affects the eccentric metaphyses of long tubular bones, the posterior elements of the vertebral bodies (11,18), the pelvis, short tubular bones and less frequently the clavicula, scapula and the tarsal bones (1,10). Imaging of choice is the MRI, the CT is useful is cases of compromised stability (11,13). Despite different treatment options like excision, curettage with or without bone grafting, e.g., the clinical course of ABCs is sometimes unpredictable and local recurrences often occur (4,5,10,13), while spontaneous regression following incomplete removal is unusual and only incidental (18). Although the reported recurrence rates of ABC imply a potential necessity for routine follow-up, no standardized patient management following primary treatment has been proposed thus far. The aim of this study was to propose a clinical and radiological follow-up regime based on a review of cases treated at our institutions amended by an extensive review of the available literature with complementary consideration of different treatment options including interventional radiological procedures. MATERIAL AND METHODS Twenty-eight cases of primary ABC at different sites were treated and followed up from 2000 to 2013 at two institutions. Secondary and solid ABCs were excluded. Patients were managed by a multidisciplinary team and all included in this retrospective analysis (Table I). The medical records and radiographs were reviewed including demographic data (sex, age at presentation), clinical data (presenting symptom, localisation), radiological data and treatment. Recurrence was defined as a re-appearance of a lesion or a progress of a residual lesion. For lesions that recurred, the date of recurrence(s) and the type of subsequent treatment were noted. No ethical approval and no special informed consent for participation was required, as evaluated by the ethics committees of the participating hospitals and in accordance with German law, since all data collected are part of daily clinical practice. Research carried out was in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. Additionally, a review of the literature was conducted for selected articles with papers dealing mainly with a surgical approach to ABC, including treatment procedure, clinical data and recurrence(s) published from January 1980 to December This review based on the search terms aneurysmal bone cyst and recurrence was performed using a full-text electronic journal database (PubMed). The search sets were restricted to humans. Patient population RESULTS Our patient population comprised 16 male and 12 female patients. The average age at diagnosis was 20.6 years (range, 7-59 years). All cases were classified as a primary ABC. They were located in the long tubular bones (16 ), in the pelvis (4 ), in spine/sacrum (5 ), in the talus (2) and in the metatarsal bone (1 ). A slow and gradual onset of pain was found in 18 patients with additionally swelling in two of them. Four patients suffered from pathologic fractures with a sudden onset of pain, in four patients the ABCs were detected by chance, and for four patients the clinical symptoms were not available. The primary treatment of 22 patients was curettage, with additionally autologous bone grafting in 13 of them, additional instillation of a glycocorticosteroid now abandoned in three of them and cement augmentation in one of them. Embolization was used for curative purposes in one case. Followup with watch&wait after biopsy was done in five patients, who declined (further) surgical therapies. All patients returned regularly for clinical and radiographic follow-up evaluation (mean 42.2 months ; range : months. Overall, six local recurrences (26.1%) were recorded and all hauschild-.indd 475 5/10/16 14:06
3 476 o. hauschild et al Table I. Data on 28 patients with primary aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) No Age [y] Sex Site Year of treatment / R Symptoms Biopsy Treatment Follow- up [m] 1 15 F Metatarsale 2010 P Yes C + A F Tibia (p) 2006 P Yes C + A F T. ischiadicum P + PF Yes W&W M Os ilium 2006 ng Yes C + S (R) 2009 (R) ng ng C + A C + A 5 20 F Acetabulum 2006 P Yes C + A M Os ilium IF No W&W F Femur (d) 2012 P Yes C + PMMA M Humerus (p) 2006 P + PF (5 ) No W&W M Tibia (p) 2008 P + Sw Yes C + A F Tibia (p) 2011 IF Yes C + A F Tibia (s) 2011 P + PF Yes C M Femur (p) (R) M Fibula (p) (R) 14 7 M Spine (L1) (R) ng Yes C + S C + A P Yes C C P Yes C + A C + A F Spine (L3) 2012 P Yes C + A M Humerus (d) 2005 P + PF (3 ) Yes C (R) C + S 17 8 M Sacrum 2006 ng Yes C + S F Humerus (d) 2004 ng Yes C M Femur (d) 2008 IF Yes C + A M Humerus (p) (R) P + Sw Yes E E M Talus 2011 P Yes C + A M Talus 2010 P Yes C +A (R) C + PMMA M Fibula (p) 2012 P No W&W M Femur (d) 2013 P Yes C + A M Spine (L5) 2013 P No W&W F Sacrum 2011 P Yes C + A F Tibia (p) 2011 P Yes C+A F Ulna (p) 2011 IF No C 10 Time till R* [m] y = years; F = female; M = male; m = month(s); R = Recurrence; p = proximal; d = distal; s = shaft; T = tuber; P = pain; Sw = Swelling; IF = Incidental finding; ng = not given; PF = pathologic fracture; C = curettage; A = autograft; S = steorid(s); E = Embolization. L = lumbar vetrebra; PMMA = polymethylmethacrylat. W&W = Watch and Wait. * In case of recurrences after revision surgery; the time to recurrence following initial treatment is mentioned (right column). hauschild-.indd 476 5/10/16 14:06
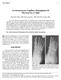
4 aneurysmal bone cyst 477 a b c d e f g Fig. 1 (a-c). Typical MR appearance of aneurysmal bone cyst. (a) T2-weighted axial turbo spin echo sequence shows an expansile cystic mass in the left acetabular region with distinct fluid-fluid levels ( ). (b) T1-weighted axial turbo spin echo sequence confirms high protein levels within cystic fluid compatible with hemorrhagic changes. (c) Coronal STIR image shows craniocaudal extension of the multiseptated lesion to the hip joint and pelvic cavity with slight displacement of the bladder (*). (d-g) Treatment and follow-up of an eccentric, diaphyseal aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) of the right tibia. (d) Small ABC with typical fluid-fluid-level ( ) on axial T2- weighted (top) and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (bottom) MR images. (e) Intraoperative fluoroscopy image after curettage of the lesion. (f) MR follow-up 3 months after treatment shows only slight enhancement of granulation tissue and confirms complete removal of the ABC. (g) 12 months after treatment, however, a de novo cystic lesion (*) with contrast enhancement can be appreciated at the endosteal margin of the resection site, indicative of recurrent ABC. of them followed incomplete curettage (mean : 20.3 months (primary recurrence) ; range : 6-31 months). The clinical data are summarized in Table I. Radiologic hallmarks In imaging ABCs were expansive and usually eccentrically growing lytic lesions with usually defined margins, marked cortical thinning and no evidence of a solid tumor in the cross sectional imaging. They consisted of blood filled cavernous spaces with internal septation(s) with a high signal intensity on T2 (Fig. 1). After treatment they progressively ossified. Literature review Within , we performed a detailed literature analysis via Pubmed of relevant publications, including description of clinical data, surgical approach and recurrence rate, which resulted in hauschild-.indd 477 5/10/16 14:06
5 478 o. hauschild et al 11 papers comprising a total of 790 patients diagnosed with ABC at various sites. These papers are summarized in Table IIa (clinical data) and IIb (treatment and recurrence with (19) missing in IIa in reason of absence of clinical data). Patient age ranged from 1-69 years with most of the patients being diagnosed within the first two decades of life. Localisations mainly comprised the long tubular bones, the spine and the pelvis. Less frequently the short tubular bones, clavicula, scapula, talus and the calcaneus were affected. Clinically, pain was the dominant symptom with an occurrence up to 99%, followed by swelling, pathologic fracture and functional impairment or combination of these. Few ABCs were discovered as an incidental finding. The duration of symptoms was mainly in between 3-6 months, some suffered from pain or swelling < 3 months or up to 24 months. When present a sudden onset of pain was attributable to a pathologic fracture. Documented treatment was curettage with or without bone grafting (or polymethylmetacrylat, PMMA) in 65.6%, curettage and embolization in 0.25%, en-bloc resection and intralesional curettage in 16.2%, curettage and radiotherapy in 7.7%, radiotherapy in 2.5%, embolization/steroid injection in 2.4% and Amputation in 0.75% patients. Recurrence rates after curettage varied widely (between 11.8%-59%). The summarized overall recurrences documented in the literature were in patients treated with curettage 17.6%, after curettage and embolization 50%, after en-bloc resection/ intralesional curettage 5.4%, after curettage and radiotherapy 6.6%, 5 after embolization/steroid injection 26.5% and after amputation 0%. Overall, in the literature documented recurrence occurred between 1-48 months, with the vast majority within the first 2 years. Only few occurred within the third and fourth year after intervention. DISCUSSION plasm owing to recent findings of recurrent chromosomal rearrangements involving the USP6 gene (Fig. 2 b, c) in approximately 70% of cases with restriction to primary ABCs (20). ABCs occur in all age groups, but is most common during the first two decades of life (8,13,18,22). Although they can involve any bone of the skeleton, they most frequently affect the long bones, the spine and the pelvis (1,10,11,18,26). In imaging ABC is an expansive and eccentrically growing lytic lesion consisting of blood filled cavernous spaces, which progressively ossifies in the reparative phase (2,19). The optimal treatment method selected for an ABC is still being debated (5), reflected by the variety of treatment strategies applied in studies published on ABC. Different factors influence the practical treatment decision, mainly anatomical site, size of the lesion, and imminence or presence of pathologic fracture (3,5). Due to the potentially high destructive capability of the cyst, treatment should be prompt and adequate. As opposed to intralesional resection techniques wide en-bloc resection has been reported to yield excellent results in terms of local control which approximates 100%, but it may be associated with considerable morbidity and higher complication rates (5,10,28). Moreover, wide resection may not always be feasible or unfavourable with regard to the proximity of joints and neurovascular structures, particularly in pelvic, sacrum or vertebra (5,10). With regard to the benign nature of the lesion and the existence of less invasive treatment alternatives we propose that wide resection should be restricted to sites in which little functional impairment is to be expected (e.g. fibular shaft) or in cases in which all other treatment options have failed accepting a higher failure rate concerning recurrence(s). Curettage with bone grafting e.g. is an accepted less invasive surgical treatment strategy. In our study, the recurrence rate after curettage (without any additionally use of radiotherapy and/or embolization, respectively) was 26.1% and in the range of recurrence rates reported by other authors (12%-59%) (Table IIb). One potential factor for recurrence may be attributed to procedures performed using a small bone window with subsequent incomplete removal of the cysts (7). Application of high-speed burs has The ABC is a cystic lesion of bone composed of blood-filled spaces separated by connective tissue septae containing fibroblasts, mononuclear cells, osteoclast-type giant cells and reactive woven bone (Fig. 2a) (12,14). It is now widely accepted as a neohauschild-.indd 478 5/10/16 14:06
6 aneurysmal bone cyst 479 Author (alphabetically) No. Table IIa. Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) clinical data based on literature review Age at diagnosis (y) Biesecker et al (3) Dec : Dec : Dec : Dec : 3 5. Dec : 1 Boriani et al (4) mean : 17.3 Localisation Clinical Symptoms Duration of symptoms P Sw P + SW PF FI BC (m) LTB : 39 Clavicula : 3 STB : 4 Pelvis : 8 Spine : 4 Others : 8 Cottalorda et al (7) LTB : 18 Clavicula : 2 Pelvis : 1 Calcaneus : 1 Gibbs et al (9) mean : 14.5 Hay et al (11) Dec : Dec : Dec : 9 4. Dec : 3 5. Dec : 2 6. Dec : 2 7. Dec : 3 De Kleuver et al (12) mean : 16 Mankin et al (17) mean : 13 Papagelopoulos et al (21) 35 (40 in total incl. 5 rec) Peak in 2 Dec (54.3%) Ruiter et al (24) mean : 18.8 Szendroi et al (25) 48 (52 in total) Vergel de Dios et al (27) 55% 9% 24% 8% < 3 : 33 p 3-12 : 29 p > 12 : 4 p Spine : ND : 4 D : n.g. LTB : 30 Clavicula : 1 Scapula : 2 STB : 3 Pelvis : 4 Spine : 79 CS : 3 TS : 11 LS : 14 Sacrum : 3 LTB : 87 Clavicula : 10 Scapula : 3 Spine : 8 Pelvis : 15 Rip : 2 Foot : Sacrum 12 Os pubis : 7 Os ischium + Acetablum : 17 Os ilium : mean : Dec : mean Dec : Dec : Dec : 30 5 Dec : 7 LTB : 51 Spine + sacrum : 17 STB : 15 Flat bone : 22 LTB : 33 Scapula : 2 Spine : 4 Hand : 2 Foot : 4 LTB and spine : 80% Flat bones : 50% in pelvis Foot : mainly in STB and tarsals (20 p with multiple loc.) mean n.g. P; S and Sw in most cases 14% < 1 30% < 3 mean : S : 19 D : 14 ND : 21 3 n.g Pain : + limp : 20 + ROM : 16 + ND 8/12 usually P + Sw n.g < 3 : 56 p 3-6 : 16 p 6-24 : 15 p n.g. : 18 p 7 mean : ABC = Aneurysmal bone cyst; No. = number of patients; p = patients; y = year(s); m = month(s); P = Pain; S = Stiffness; Sw = Swelling; PF = Pathologic fracture; FI = functional impairment; BC = by chance; ND = neurological deficit; D = deformity; LTB = long tubular bones; STB = short tubular bone; CS = cervical Spine; TS = thoracic spine; LS = lumbar spine; n.g. = not given. hauschild-.indd 479 5/10/16 14:06
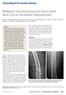
7 480 o. hauschild et al a b c Fig. 2 (a-c). (a) ABC of the talus showing fibrous septa composed of fibroblast-like mononuclear cells and intermingled multinucleated giant cells. (b) Solid ABC of the proximal femur demonstrating sheets of mononuclear and multinucleated giant cells with varying cellularity. Besides hemorrhage there is marked reactive new bone formation (black arrows). (c) USP6 break-apart FISH shows USP6 rearrangement in the mononuclear cell component (white arrows). been reported to decrease recurrence rates (28). With regard to these studies the authors today favour burring of the bone after curettage through a bone window large enough to visualize the entire cyst whenever possible. In addition, a variety of non-surgical methods have been proposed for treatment : percutaneous sclerotherapy, embolization, steroid injection, ethibloc injection, and radiotherapy. These methods may be of particular merit for sites in which surgical therapy is impossible or hazardous (e.g. pelvic, sacral or vertebral ABCs). Selective arterial embolization (SAE) can be used as an adjunct to surgical treatment to reduce blood-loss during surgery or as stand-alone treatment (23). In most cases repeated sessions are required to achieve complete regression without any surgical treatment (23). Besides, there are occasional cases in which no arterial feeding vessels suitable for SAE can be identified (23). And, although successful treatment with embolization alone has been reported for the pelvis and long bones, its role as the sole mode of therapy in the spine appears to be more limited (11,23). Regardless of the number of embolization, 67% of the total patients were considered as cured after a follow-up period longer than 2 years (23). All cases of recurrence were within 1 year after the first embolization (23), in another study beyond 2 years of embolization (4). Percutaneous sclerotherapy may also be a valuable treatment alternative (5). And, administration of polidocanol was found to be a safe and simple procedure with an excellent cure rate and will be especially valuable in ABCs of the pelvis and sacrum (5). Like SAE, several sessions are usually required to achieve complete re-calcification of the cyst (5). Radiation therapy (20-40 Gy) should not be used because of the risk for post irradiation sarcoma ; rarely it has very limited indications and may remain as an adjuvant therapy for patients with inoperable lesions, aggressive recurrent disease, and medical conditions that place them at a high surgical risk (10,29). More recently, denosumab was identified as a potential new and innovative treatment option for ABCs (15). However, much longer follow-up and clinical studies are warranted to establish the value of the drug in the treatment of ABCs (15). With regard to follow-up recommendations, it is important to state that 90% of the recurrences occur within 6 to 12 months after initial treatment and rarely after 4 years. With respect to these findings shorter follow-up intervals within the first two years and longer intervals up to the fifth year seem to be reasonable. We therefore propose a routine followup regime ideally with MRI and clinical survey performed at 3 (baseline), 6, 12, 18 and 24 months followed by yearly exams in the third to fifth year after hauschild-.indd 480 5/10/16 14:06
8 aneurysmal bone cyst 481 Author (alphabetically) Table IIb. Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC)-treatment and recurrence based on literature data No. of patients Curettage (+/- bone grafting vs. PMMA) En bloc resection / intralesional excision Treatment and Recurrence(s) [n(treated)/n(recurrence) (%)] Curettage and Radiotherapy Radiotherapy Steroidinjection/ Embolisation / percutaneous sclerotherapy Amputation Recurrence(s) In total Time interval (1. recurrence(s) Biesecker et al (3) / 26 (59%) Boriani et al (4) 41 5 / 1 (20%) Clough et al (6) / 8 (53.3) Cottalorda et al (7) / 2 (16.6%) Gibbs et al (9) / 4 (11.8%) Hay et al (11) / 7 (25%) Kleuver de et al (12) / 3 (12%) 8 / 0 (0%) 4 / 1 (25%) 7 (Cry) / 1 (14.3%) 13 / 0 (0%) 11 / 0 (0%) 3 / 0 (0%) 4 / 1 (Emb) (25%) 1 / 0 (0%) 28 / 66 (42.4%) Recurrences within 4 y after intervention 2 / 41 (5%) 1-12 m 3 / 0 (0%) 2 / 0 (0%) 8/ 21 (38.1%) 0-2 y 3 / 0 (0%) 2 / 2 (Ster) (100%) 4 / 1 (persc) (25%) 5 / 21 (23.8%) 3-16 m (one patient with multiple rec. with latest 59 m after first intervention) 6 / 0 (0%) 4/ 40 (10%) 2-24 m 8 / 0 (0%) 34 / 2 (5.8%) 9 / 1 (11.1%) 10 / 79 (12.7%) 2 / 2 (100%) (subtotal L) 1 / 0 (0%) 1 / 0 (0%) 1 (Emb) / 0 (0%) 1-12 m (mean 4 m) 6 / 31 (19.6%) 1-21 m Mankin et al (17) Papagelopoulos et al (21) C + Emb: 1 / / 29 (22.3%) 35 (40 in total including 5 rec) 21 / 5 (23.8%) Ruiter et al (24) / 28 (51.6%) C + Emb: 1 / 0 Szendroi et al (25) Vergel de Dios et al (27) 48 (52 primary ABC in total) 153 own patients (238 in total) 26 / 7 (26.9%) 124 / 27 (21.8 %) 20 / 1 (5%) 30 / 150 (20%) 1.2 +/- 0.7 y (range; y) 14 / 0 (0%) 5 / 35 (14.3%) up to 18 m (L) / 4 (26.6%) 1 / 0 (0%) 2 / 0 (0%) 1 (Emb) / 0 (0%) 4 / 0 (0%) 32 / 105 (30.5%) 22 / 0 (0%) 7/ 48 (14.6%) mean: 14 m 16 / 0 (0%) 12 / 2 (16.6%) 1 / 0 (0%) 1 / 0 (0%) 29 / 153 (19%) 26 (90%) in between 2 y; 3 later No = number; C = Curettage; Cry = cryosurgery; RT = Radiotherapy; persc = percutaneous sclerotherapy; rec = recurrences; p = primary; s = secondary; Emb = Embolization; L = laminectomy; m = month(s); y = year(s). hauschild-.indd 481 5/10/16 14:06
9 482 o. hauschild et al 1. Adler CP. Aneurysmal bone cyst. In : Adler CP (ed). Bone diseases, 3rd ed. Springer, Berlin, 2006, pp Alvas F, James SL, Davies AM, Saiffudin A. The role of MR imaging in the diagnostic characterisation of appendicular bone tumours and tumourlike conditions. Eur Radiol 2007 ; 17 : Biesecker JL, Marcove RC, Huvos AG, Miké V. Aneurysmal bone cysts. A clinicopathologic study of 66 cases. Cancer 1970 ; 26 : Boriani S, De Iure F, Campanacci L et al. (2001) Aneurysmal bone cyst of the mobile spine : report on 41 cases. Spine 2001 ; 26 : Brosjö O, Pechon P, Hesla A Tsagozis P, Bauer H. Sclerotherapy with polidocanol for treatment of aneurysmal bone cysts. Acta Orthop 2013 ; 84 : Clough JR, Price CH. Aneurysmal bone cyst : pathogenesis and long term results of treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1973 ; 97 : Cottalorda J, Kohler R, Chotel F. Recurrence of aneurysmal bone cysts in young children : a multicenter study. J Pediatr Orthop 2005 ; B-14 : Dahlin DC, McLeod RA. Aneurysmal bone cyst and other nonneoplastic conditions. Skeletal Radiol 1982 ; 8 : Gibbs CP Jr, Hefele MC, Peabody TD et al. Aneurysmal bone cyst of the extremities. Factors related to local recurrence after curettage with a high-speed burr. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1999 ; 81 : Harrop JS, Schmidt MH, Boriani S, Shaffrey CI. Aggressive benign primary spine neoplasms : osteoinitial treatment. Using this regime, all cases of recurrence reported in the literature would have been detected irrespective of the presence of symptoms. As individual data are not reported for any of these series the exact interval from recurrence to diagnosis assuming the proposed regime had been applied cannot be stated. For our series, however, the application of such a follow-up regime would have detected all cases of recurrence within 6 months or less. Although not specifically addressed in this study the authors advocate a life-long followup in cases treated with radiotherapy acknowledging the risk for post irradiation sarcoma. Appreciation of the strengths and weaknesses of the present study is warranted. First of all one has to acknowledge that ABC is a rare entity. Excluding solid and secondary ABCs further decreased the number of available patients but added to the histologic homogeneity of this series, thus 28 patients were available for this analysis. In this respect, all but four patients who declined to undergo biopsy had histopathological confirmed primary ABC. The meticulous assessment of the available cases with an average follow-up of more than 42 months, amended by a thorough analysis of previously published cases (790 cases) is another strength of the present study. By this means we were able to show the feasibility of the proposed follow-up regimen with regard to timely detection of local recurrence. Nevertheless, the authors emphasize that the proposed follow-up regimen is based on retrospective analyses and further validation utilizing prospectively collected data is warranted. CONCLUSION Knowledge of the ABC entity, now widely accepted as a neoplastic lesion, is important, since this lesion is characterized by a high recurrence rate. Despite different treatment options, the risk for recurrence is particularly high within the first 12 months following initial treatment, diminishes over time and is extremely rare after the fourth posttreatment year. With regard to these findings, we recommend that patients with ABC should be continuously followed-up clinically and radiologically until the fifth year following initial treatment and life-long in cases treated with radiotherapy. List of abbreviations ABC : Aneurysmal Bone Cyst ; CT : Computed tomography ; MRI : Magnetic resonance imaging ; PMMA : Polymethylmethacrylat ; SAE : Selective arterial embolization. Conflict of interest The authors state that there are no financial and personal relationships with other people or organisations that inappropriately influence (bias) the work. Compliance with Ethical Standards The use of clinical data was requested and approved by local ethical committee although exams were performed according clinical indications. And, all procedures performed in study were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. Informed consent All patients gave written inform consent according to the university hospital standard. REFERENCES hauschild-.indd 482 5/10/16 14:06
10 aneurysmal bone cyst 483 blastoma, aneurysmal bone cyst, and giant cell tumor. Spine 2009 ; 34(22 Suppl) : Hay MC, Paterson D, Taylor TK. Aneurysmal bone cysts of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1978 ; 60-B : Kleuver M de, van der Heul RO, Veraart BE. Aneurysmal bone cyst of the spine : 31 cases and the importance of the surgical approach. J Pediatr Orthop B 1998 ; 7 : Kransdorf MJ, Sweet DE. Aneurysmal bone cyst : concept, controversy, clinical presentation, and imaging. Am J Roentgenol 1995 ; 164 : Kyriakos M, Hardy D. Malignant transformation of aneurysmal bone cyst, with an analysis of the literature. Cancer 1991 ; 68 : Lange T, Stehling C, Fröhlich B et al. Denosumab : a potential new and innovative treatment option for aneurysmal bone cysts. Eur Spine J 2013 ; 22 : Leithner A, Windhager R, Lang S et al. Aneurysmal bone cyst. A population based epidemiologic study and literature review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999 ; 363 : Mankin HJ, Hornicek FJ, Ortiz-Cruz E, Villafuerte J, Gebhardt MC. Aneurysmal bone cyst : a review of 150 patients. J Clin Oncol 2005 ; 23 : Nielsen GP, Fletcher JA, Oliveira AM. Aneurysmal bone cyst. In : In Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F (eds) : WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. IARC Press, Lyon, 2013, pp O Donnell P, Saifuddin A. The prevalence and diagnostic significance of fluid-fluid levels in focal lesions of bone. Skeletal Radiol 2004 ; 33 : Oliveira AM, Chou MM. USP6-induced neoplasms : the biologic spectrum of aneurysmal bone cyst and nodular fasciitis. Hum Pathol 2014 ; 45 : Papagelopoulos PJ, Choudhury SN, Frassica FJ et al. Treatment of aneurysmal bone cysts of the pelvis and sacrum. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2001 ; 83-A : Rosenberg AE, Nielsen GP, Fletcher JA. Tumours of undefined neoplastic nature. In : Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Mertens F (eds). Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. IARC Press, Lyon, 2002, pp Rossi G, Rimondi E, Bartalena T et al. Selective arterial embolization of 36 aneurysmal bone cysts of the skeleton with N-2-butyl cyanoacrylate. Skeletal Radiol 2010 ; 39 : Ruiter DJ, van Rijssel TG, van der Velde EA. Aneurysmal bone cysts : a clinicopathological study of 105 cases. Cancer 1977 ; 39 : Szendröi M, Cser I, Kónya A, Rényi-Vámos A. Aneurysmal bone cyst. A review of 52 primary and 16 secondary cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1992 ; 111 : Tillman BP, Dahlin DC, Lipscomb PR, Stewart JR. Aneurysmal bone cyst : an analysis of ninety-five cases. Mayo Clin Proc 1968 ; 43 : Vergel De Dios AM, Bond JR, Shives TC, McLeod RA, Unni KK. Aneurysmal bone cyst. A clinicopathologic study of 238 cases. Cancer 1992 ; 69 : Varshney MK, Rastogi S, Khan SA, Trikha V. Is sclerotherapy better than intralesional excision for treating aneurysmal bone cysts? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010 ; 468 : Wiklund TA, Blomqvist CP, Räty J et al. Postirradiation sarcoma. Analysis of a nationwide cancer registry material. Cancer 1991 ; 68 : hauschild-.indd 483 5/10/16 14:06
Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage
 Accepted February 13th, 2004 Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage Ludwig Schwering¹, Markus Uhl² and Georg W. Herget( )¹ ¹ Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Accepted February 13th, 2004 Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage Ludwig Schwering¹, Markus Uhl² and Georg W. Herget( )¹ ¹ Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
Aneurysmal bone cysts (ABCs) are rare, destructive,
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Review of 56 Patients Kerem BazarNr, MD,* Ahmet Pizkin,Þ Berk Güc$lü,þ Yusuf YNldNz,* and Yener SağlNk* Background: Aneurysmal bone cysts (ABCs) are benign lesions that are usually treated
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Review of 56 Patients Kerem BazarNr, MD,* Ahmet Pizkin,Þ Berk Güc$lü,þ Yusuf YNldNz,* and Yener SağlNk* Background: Aneurysmal bone cysts (ABCs) are benign lesions that are usually treated
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Aneurysmal bone cyst of the scapula A case report
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 684-689 CASE REPORT Aneurysmal bone cyst of the scapula A case report Panagiotis MEGAS, Zafiria G. PAPATHANASSIOU, George KASIMATIS, Dionysios J. PAPACHRISTOU From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 684-689 CASE REPORT Aneurysmal bone cyst of the scapula A case report Panagiotis MEGAS, Zafiria G. PAPATHANASSIOU, George KASIMATIS, Dionysios J. PAPACHRISTOU From the University
Disclosures. Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone. Outline. The osteoclast. Giant cell rich tumors 5/21/11
 Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Treatment of Aneurysmal Bone Cysts with Bioactive Glass in Children
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Treatment of Aneurysmal Bone Cysts with Bioactive Glass in Children Syvänen, J. 2018-03 Syvänen, J, Nietosvaara, Y, Kohonen, I, Koskimies, E, Haara, M, Korhonen, J, Pajulo, O
https://helda.helsinki.fi Treatment of Aneurysmal Bone Cysts with Bioactive Glass in Children Syvänen, J. 2018-03 Syvänen, J, Nietosvaara, Y, Kohonen, I, Koskimies, E, Haara, M, Korhonen, J, Pajulo, O
Primary Treatment of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis by Transcatheter Arterial Embolization
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, June: 449-455, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Primary Treatment of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis by Transcatheter Arterial Embolization AMR A. NASSEF,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, June: 449-455, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Primary Treatment of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis by Transcatheter Arterial Embolization AMR A. NASSEF,
Case Report Lower Limb Reconstruction with Tibia Allograft after Resection of Giant Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7980593, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7980593 Case Report Lower Limb Reconstruction with Tibia Allograft after Resection of Giant Aneurysmal
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7980593, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7980593 Case Report Lower Limb Reconstruction with Tibia Allograft after Resection of Giant Aneurysmal
Case Report Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Documented Progression over 4 Years from Its Origin at the Metaphysis to the Articular Surface
 Volume 2016, Article ID 9786925, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9786925 Case Report Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Documented Progression over 4 Years from Its Origin at the Metaphysis to the Articular
Volume 2016, Article ID 9786925, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9786925 Case Report Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Documented Progression over 4 Years from Its Origin at the Metaphysis to the Articular
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Hip Salvaging Surgery in Complicated Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of Proximal Femur
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(1):71-75 Hip Salvaging Surgery in Complicated Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of Proximal Femur T.B. Dhanasekaraprabu, Sumit Mahajan, Yash Mohan Lal, Himani Sharma 1, Rajesh Chandra
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(1):71-75 Hip Salvaging Surgery in Complicated Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of Proximal Femur T.B. Dhanasekaraprabu, Sumit Mahajan, Yash Mohan Lal, Himani Sharma 1, Rajesh Chandra
Endovascular and surgical treatment of giant pelvic tumor
 Endovascular and surgical treatment of giant pelvic tumor Mitrev Z., MD FETCS; Anguseva T., MD; Milev I., MD; Zafiroski G., PhD MD Center for Cardiosurgery, Filip the II, Skopje, Macedonia Background Giant
Endovascular and surgical treatment of giant pelvic tumor Mitrev Z., MD FETCS; Anguseva T., MD; Milev I., MD; Zafiroski G., PhD MD Center for Cardiosurgery, Filip the II, Skopje, Macedonia Background Giant
Chondrosarcoma with a late local relapse
 Chondrosarcoma with a late local relapse J. Shinoda, T. Ozaki, T. Oka, T. Kunisada, H. Inoue Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Okayama University Medical School, Okayama, 700-8558, Japan Correspondence:
Chondrosarcoma with a late local relapse J. Shinoda, T. Ozaki, T. Oka, T. Kunisada, H. Inoue Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Okayama University Medical School, Okayama, 700-8558, Japan Correspondence:
Effective local and systemic therapy is necessary for the cure of Ewing tumor Most chemotherapy regimens are a combination of cyclophosphamide,
 Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Chondroblastoma of bone
 Chronology Chondroblastoma of bone LONG-TERM RESULTS AND FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER INTRALESIONAL CURETTAGE R. Suneja, R. J. Grimer, M. Belthur, L. Jeys, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, A. M. Davies From The
Chronology Chondroblastoma of bone LONG-TERM RESULTS AND FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER INTRALESIONAL CURETTAGE R. Suneja, R. J. Grimer, M. Belthur, L. Jeys, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, A. M. Davies From The
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Spine
 Copynghi 1985 8) The Journal o[ Bone and Joint.5urger IPIOrp()ratetI Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Spine BY R. CAPANNA, M.D.*, U. ALBISINNI, M.D.*, P. PICCI, M.D.*, P. CALDERONI, M.D.*, M. CAMPANACCI, M.D.*,
Copynghi 1985 8) The Journal o[ Bone and Joint.5urger IPIOrp()ratetI Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Spine BY R. CAPANNA, M.D.*, U. ALBISINNI, M.D.*, P. PICCI, M.D.*, P. CALDERONI, M.D.*, M. CAMPANACCI, M.D.*,
SICOT Online Report E057 Accepted April 23th, in Fibula and Rib
 Metachronous, multicentric giant cell tumors in Fibula and Rib Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka
Metachronous, multicentric giant cell tumors in Fibula and Rib Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka
Surgical Management for Giant Cell Tumor of Bones
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 6, No., September: 5-5, 00 Surgical Management for Giant Cell Tumor of Bones EL SAYED ASHRAF KHALIL, M.D. FRCS; ALAA YOUNIS, M.D.; SHERIF A. AZIZ, M.D and
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 6, No., September: 5-5, 00 Surgical Management for Giant Cell Tumor of Bones EL SAYED ASHRAF KHALIL, M.D. FRCS; ALAA YOUNIS, M.D.; SHERIF A. AZIZ, M.D and
Giant cell tumour of the proximal femur
 ONCOLOGY Giant cell tumour of the proximal femur IS JOINT-SPARING MANAGEMENT EVER SUCCESSFUL? A. E. Wijsbek, B. L. Vazquez- Garcia, R. J. Grimer, S. R. Carter, A. A. Abudu, R. M. Tillman, L. Jeys From
ONCOLOGY Giant cell tumour of the proximal femur IS JOINT-SPARING MANAGEMENT EVER SUCCESSFUL? A. E. Wijsbek, B. L. Vazquez- Garcia, R. J. Grimer, S. R. Carter, A. A. Abudu, R. M. Tillman, L. Jeys From
Fluid-fluid levels in bone tumors: A pictorial review
 Fluid-fluid levels in bone tumors: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-578 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: L. Figueroa Nasra, C. Martín Hervás, M. Tapia-Viñé,
Fluid-fluid levels in bone tumors: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-578 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: L. Figueroa Nasra, C. Martín Hervás, M. Tapia-Viñé,
APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp!
 APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp! DANIEL P. EVANS, DPM, FACFAOM Professor, Department of Podiatric Medicine and Radiology Dr. Wm. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine Conflict of
APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp! DANIEL P. EVANS, DPM, FACFAOM Professor, Department of Podiatric Medicine and Radiology Dr. Wm. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine Conflict of
Clear Cell Chondrosarcoma of the Sacrum
 Clear Cell Chondrosarcoma of the Sacrum Yasunobu Iwasaki MD 1, Tetsuji Yamamoto MD (!) 2, Mitsuo Tsuji MD 1, Akira Kurihara MD 1, Masaaki Uratsuji MD 1, Norihide Sha MD 1, and Shinichi Yoshiya MD 2 1 Department
Clear Cell Chondrosarcoma of the Sacrum Yasunobu Iwasaki MD 1, Tetsuji Yamamoto MD (!) 2, Mitsuo Tsuji MD 1, Akira Kurihara MD 1, Masaaki Uratsuji MD 1, Norihide Sha MD 1, and Shinichi Yoshiya MD 2 1 Department
33 & ABSTRACT
 Surgical Treatment Of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst In AL- Najaf City: Aretrospective study on 33 patients Dr. MOHAMMAD MOHI AL-TALLAL & Dr. HAMDELLA HADI AL-BUSAISY. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, AL-SADDER
Surgical Treatment Of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst In AL- Najaf City: Aretrospective study on 33 patients Dr. MOHAMMAD MOHI AL-TALLAL & Dr. HAMDELLA HADI AL-BUSAISY. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, AL-SADDER
Laura M. Fayad, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University
 Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
Society of Pediatric Radiology, May 2013 Laura M. Fayad, MD Associate Professor of Radiology, Orthopaedic Surgery & Oncology The Johns Hopkins University Describes surgical techniques that resect and reconstruct
CASE PRESENTATION. Dr. Faseeh Shahab PGY3 Orthopaedic Resident, Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, PAKISTAN
 CASE PRESENTATION Dr. Faseeh Shahab PGY3 Orthopaedic Resident, Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, PAKISTAN CASE PRESENTATION - History Ms. SB, 30yo Afghan National Presented with 3 months history of Swelling
CASE PRESENTATION Dr. Faseeh Shahab PGY3 Orthopaedic Resident, Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, PAKISTAN CASE PRESENTATION - History Ms. SB, 30yo Afghan National Presented with 3 months history of Swelling
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report
 Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.140 A Case Report of Recurrent
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.140 A Case Report of Recurrent
Aneurysmal bone cysts (ABCs)
 Review Article Aneurysmal Bone Cyst Timothy B. Rapp, MD James P. Ward, MD Michael J. Alaia, MD From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York, NY. Dr. Rapp or an
Review Article Aneurysmal Bone Cyst Timothy B. Rapp, MD James P. Ward, MD Michael J. Alaia, MD From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York, NY. Dr. Rapp or an
Bone Tumors Clues and Cues
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
MRI Findings of Giant Cell Tumors of the Spine
 MRI of Spinal Tumors Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Jong Won Kwon 1 Hye Won Chung 1,2 Eun Yoon Cho 3 Sung Hwan Hong 4 Sang-Hee Choi 1 Young Cheol Yoon 1 Sang Kyu Yi 1 Kwon JW, Chung HW,
MRI of Spinal Tumors Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Jong Won Kwon 1 Hye Won Chung 1,2 Eun Yoon Cho 3 Sung Hwan Hong 4 Sang-Hee Choi 1 Young Cheol Yoon 1 Sang Kyu Yi 1 Kwon JW, Chung HW,
Primary Intraosseus Xanthoma Involving the Proximal Femur in a Normolipidemic Patient: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 182-186, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.182 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Primary Intraosseus Xanthoma Involving the Proximal Femur in a Normolipidemic
CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 182-186, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.182 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Primary Intraosseus Xanthoma Involving the Proximal Femur in a Normolipidemic
Primary osteosarcoma of the spine
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 457-462 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary osteosarcoma of the spine A review of 10 cases Jason B.T. Lim, Himanshu Sharma, Elaine MacDuff, Anthony T. Reece From the Western Infirmary,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 457-462 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary osteosarcoma of the spine A review of 10 cases Jason B.T. Lim, Himanshu Sharma, Elaine MacDuff, Anthony T. Reece From the Western Infirmary,
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis: A Challenge in Treatment: Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis: A Challenge in Treatment: Review of the Literature S Bajracharya, G Khanal, A Sundas, S Pandey,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis: A Challenge in Treatment: Review of the Literature S Bajracharya, G Khanal, A Sundas, S Pandey,
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF LOWER END OF FEMUR IN A SKELETALLY IMMATURE-A RARE CASE
 GIANT CELL TUMOR OF LOWER END OF FEMUR IN A SKELETALLY IMMATURE-A RARE CASE *Surojit Mondal 1, Aniket Chowdhury 2 and Goutam Bandyopadhyay 3 1 Department of Orthopaedics, B.S.Medical College, Bankura,
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF LOWER END OF FEMUR IN A SKELETALLY IMMATURE-A RARE CASE *Surojit Mondal 1, Aniket Chowdhury 2 and Goutam Bandyopadhyay 3 1 Department of Orthopaedics, B.S.Medical College, Bankura,
Clinical Study Primary Malignant Tumours of Bone Following Previous Malignancy
 Sarcoma Volume 2008, Article ID 418697, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2008/418697 Clinical Study Primary Malignant Tumours of Bone Following Previous Malignancy J. T. Patton, S. M. M. Sommerville, and R. J. Grimer
Sarcoma Volume 2008, Article ID 418697, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2008/418697 Clinical Study Primary Malignant Tumours of Bone Following Previous Malignancy J. T. Patton, S. M. M. Sommerville, and R. J. Grimer
Giant-cell tumours of the sacrum are difficult to
 The treatment of sacral giant-cell tumours by serial arterial embolisation R. D. Lackman, L. D. Khoury, A. Esmail, R. Donthineni-Rao The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA Giant-cell
The treatment of sacral giant-cell tumours by serial arterial embolisation R. D. Lackman, L. D. Khoury, A. Esmail, R. Donthineni-Rao The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA Giant-cell
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Giant cell tumor of the patella: An uncommon cause of anterior knee pain
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 3: 207-211, 2015 Giant cell tumor of the patella: An uncommon cause of anterior knee pain TATSUYA SHIBATA 1, JUN NISHIO 1, TAIKI MATSUNAGA 1, MIKIKO AOKI 2, HIROSHI IWASAKI
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 3: 207-211, 2015 Giant cell tumor of the patella: An uncommon cause of anterior knee pain TATSUYA SHIBATA 1, JUN NISHIO 1, TAIKI MATSUNAGA 1, MIKIKO AOKI 2, HIROSHI IWASAKI
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
Tumours and tumour-like lesions of the patella : A report of eight cases
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 391-396 ORIGINAL STUDY Tumours and tumour-like lesions of the patella : A report of eight cases Yener SAGLIK, Yusuf YILDIZ, Kerem BASARIR, Engin TEZEN, Derviş GÜNER From Ankara
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 391-396 ORIGINAL STUDY Tumours and tumour-like lesions of the patella : A report of eight cases Yener SAGLIK, Yusuf YILDIZ, Kerem BASARIR, Engin TEZEN, Derviş GÜNER From Ankara
Cystic Lesions of Bone
 Cystic Lesions of Bone Intraosseous Ganglion Cyst Definition. Intraosseous pseudocyst of unknown etiology that is filled with viscous mucinous material and is not associated with osteoarthritis in the
Cystic Lesions of Bone Intraosseous Ganglion Cyst Definition. Intraosseous pseudocyst of unknown etiology that is filled with viscous mucinous material and is not associated with osteoarthritis in the
Intraosseous hemangioma is an uncommon benign
 Case Report 71 An Intraosseous Capillary Hemagioma Of The Foot In A Child Kah-Wai Ngan, MD; Hui-Ling Hsu 1, MD; Shir-Hwa Ueng, MD An 8-year-old boy presented with an osteolytic lesion at the fourth metatarsal
Case Report 71 An Intraosseous Capillary Hemagioma Of The Foot In A Child Kah-Wai Ngan, MD; Hui-Ling Hsu 1, MD; Shir-Hwa Ueng, MD An 8-year-old boy presented with an osteolytic lesion at the fourth metatarsal
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of a lumbar vertebral body with secondary aneurysmal bone cyst formation: a case report Marieke N Snieders 1, Folkert J van Kemenade 2 and Barend J
Open Access Case report Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of a lumbar vertebral body with secondary aneurysmal bone cyst formation: a case report Marieke N Snieders 1, Folkert J van Kemenade 2 and Barend J
Symptoms and signs associated with benign and malignant proximal fibular tumors: a clinicopathological analysis of 52 cases
 Sun et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:92 DOI 10.1186/s12957-017-1162-z RESEARCH Open Access Symptoms and signs associated with benign and malignant proximal fibular tumors: a clinicopathological
Sun et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:92 DOI 10.1186/s12957-017-1162-z RESEARCH Open Access Symptoms and signs associated with benign and malignant proximal fibular tumors: a clinicopathological
CASE STUDY: PRO-DENSE Injectable Regenerative Graft Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor
 : PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
: PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF BONE
 GIANT CELL TUMOR OF BONE Definition. First described by Jaffe et al. 1, giant cell tumor of bone is a locally aggressive primary neoplasm of bone that is composed of proliferation of bland looking oval
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF BONE Definition. First described by Jaffe et al. 1, giant cell tumor of bone is a locally aggressive primary neoplasm of bone that is composed of proliferation of bland looking oval
GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
Skeletal Radiology. Solitary (unicameral) bone cyst. The fallen fragment sign revisited
 Skeletal Radiol (1989) 18:261-265 Skeletal Radiology Solitary (unicameral) bone cyst The fallen fragment sign revisited S. Struhl, M.D., C. Edelson, M.D., H. Pritzker, M.D., L.P. Seimon, M.D., and H.D.
Skeletal Radiol (1989) 18:261-265 Skeletal Radiology Solitary (unicameral) bone cyst The fallen fragment sign revisited S. Struhl, M.D., C. Edelson, M.D., H. Pritzker, M.D., L.P. Seimon, M.D., and H.D.
CASE REPORT PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE.
 PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji
 Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Osteosarcoma Arising from Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Ten Years After Primary Surgery: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, Osteosarcoma 208, 157-162 Arising from Giant Cell Tumor of Bone 157 Osteosarcoma Arising from Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Ten Years After Primary Surgery: A Case Report and Review
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, Osteosarcoma 208, 157-162 Arising from Giant Cell Tumor of Bone 157 Osteosarcoma Arising from Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Ten Years After Primary Surgery: A Case Report and Review
Unusual presentation of giant cell tumor originating from a facet joint of the thoracic spine in a child: a case report and review of the literature
 Siribumrungwong et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:178 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Unusual presentation of giant cell tumor originating from a facet joint of the
Siribumrungwong et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:178 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Unusual presentation of giant cell tumor originating from a facet joint of the
An aggressive aneurysmal bone cyst of the proximal humerus and related complications in a pediatric patient
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2012) 7:51 56 DOI 10.1007/s11751-012-0132-9 CASE REPORT An aggressive aneurysmal bone cyst of the proximal humerus and related complications in a pediatric patient Melih Güven Murat
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2012) 7:51 56 DOI 10.1007/s11751-012-0132-9 CASE REPORT An aggressive aneurysmal bone cyst of the proximal humerus and related complications in a pediatric patient Melih Güven Murat
Successful Treatment of Aggressive Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis With Serial Embolization
 Successful Treatment of Aggressive Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis With Serial Embolization Giuseppe Rossi, MD; Andreas F. Mavrogenis, MD; Panayiotis J. Papagelopoulos, MD; Eugenio Rimondi, MD; Pietro
Successful Treatment of Aggressive Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Pelvis With Serial Embolization Giuseppe Rossi, MD; Andreas F. Mavrogenis, MD; Panayiotis J. Papagelopoulos, MD; Eugenio Rimondi, MD; Pietro
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Giant Cell Tumour of the Distal Radius: Wide Resection and Reconstruction by Non-vascularised Proximal Fibular Autograft
 900 Original Article Giant Cell Tumour of the Distal Radius: Wide Resection and Reconstruction by Non-vascularised Proximal Fibular Autograft Ayman Abdelaziz Bassiony, 1 MD Abstract Introduction: Giant
900 Original Article Giant Cell Tumour of the Distal Radius: Wide Resection and Reconstruction by Non-vascularised Proximal Fibular Autograft Ayman Abdelaziz Bassiony, 1 MD Abstract Introduction: Giant
History. 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation
 History 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation Imaging Photo Album Patient also had a smaller lesion 1 cm proximal to this lesion, not seen radiographically.
History 33 y/o F with hx of palpable anterior tibial mass x 2 years, only painful with palpation Imaging Photo Album Patient also had a smaller lesion 1 cm proximal to this lesion, not seen radiographically.
Functional and oncological outcomes after total claviculectomy for primary malignancy
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 170-174 ORIGINAL STUDY Functional and oncological outcomes after total claviculectomy for primary malignancy Zhaoxu Li, Zhaoming YE, Miaofeng ZHAng From the Department of
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 170-174 ORIGINAL STUDY Functional and oncological outcomes after total claviculectomy for primary malignancy Zhaoxu Li, Zhaoming YE, Miaofeng ZHAng From the Department of
Comprehensive Case Report Of A Giant Cell Tumor Involving The Proximal Phalanx Of The Left Great Toe Managed With Fibular Grafting
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 1 Number 1 Comprehensive Case Report Of A Giant Cell Tumor Involving The Proximal Phalanx Of The Left Great Toe T Dasan, K Vijay, C Satish, B Nagraj,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 1 Number 1 Comprehensive Case Report Of A Giant Cell Tumor Involving The Proximal Phalanx Of The Left Great Toe T Dasan, K Vijay, C Satish, B Nagraj,
Response of an aggressive periosteal aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) of the radius to denosumab therapy
 Pauli et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:17 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access Response of an aggressive periosteal aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) of the radius to denosumab
Pauli et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:17 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access Response of an aggressive periosteal aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) of the radius to denosumab
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma with Cystic Change of the Femur: a Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:264-268 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.264 Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma with Cystic Change of the Femur: a Case Report Jung Ah Park, Sung Gyu Moon,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:264-268 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.264 Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma with Cystic Change of the Femur: a Case Report Jung Ah Park, Sung Gyu Moon,
CME/SAM. Differential Diagnostic Value of Blue Reticulated Chondroid-Like Material in Aneurysmal Bone Cysts
 AJCP / Original Article Differential Diagnostic Value of Blue Reticulated Chondroid-Like Material in Aneurysmal Bone Cysts A Classic Histopathologic Analysis of 215 Cases Won-Jong Bahk, MD, 1 and Joseph
AJCP / Original Article Differential Diagnostic Value of Blue Reticulated Chondroid-Like Material in Aneurysmal Bone Cysts A Classic Histopathologic Analysis of 215 Cases Won-Jong Bahk, MD, 1 and Joseph
Case report. Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma. Open Access
 Case report Open Access Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma Khaled Kamoun 1,&, Tarak Sellami 1, Zied Jlailia 1, Layla Abid 2, Mourad Jenzri 1, Mouna Bouaziz 3, Omar Zouar
Case report Open Access Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma Khaled Kamoun 1,&, Tarak Sellami 1, Zied Jlailia 1, Layla Abid 2, Mourad Jenzri 1, Mouna Bouaziz 3, Omar Zouar
Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma
 49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
Chondroblastoma associated with aneurysmal cyst of the navicular bone: a case report
 Fang and Chen World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:50 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access Chondroblastoma associated with aneurysmal cyst of the navicular bone: a case report
Fang and Chen World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:50 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access Chondroblastoma associated with aneurysmal cyst of the navicular bone: a case report
Review Article Chondrosarcoma of the Mobile Spine and Sacrum
 Sarcoma Volume 2011, Article ID 274281, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/274281 Review Article Chondrosarcoma of the Mobile Spine and Sacrum Ryan M. Stuckey and Rex A. W. Marco Department of Orthopaedics, University
Sarcoma Volume 2011, Article ID 274281, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/274281 Review Article Chondrosarcoma of the Mobile Spine and Sacrum Ryan M. Stuckey and Rex A. W. Marco Department of Orthopaedics, University
Retrospective review of radiographically occult femoral and pelvic fractures detected by MRI following low-energy trauma.
 Retrospective review of radiographically occult femoral and pelvic fractures detected by MRI following low-energy trauma. Poster No.: P-0129 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: P. M. Yeap,
Retrospective review of radiographically occult femoral and pelvic fractures detected by MRI following low-energy trauma. Poster No.: P-0129 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: P. M. Yeap,
Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh
 Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Malignant Transformation of an Aneurysmal Bone Cyst to Fibroblastic Osteosarcoma
 Case Report & Literature Review Malignant Transformation of an neurysmal one Cyst to Fibroblastic Osteosarcoma kash P. Kansagra, MD, MS, Jennifer J. Wan, MD, Kavi K. Devulapalli, MD, ndrew E. Horvai, MD,
Case Report & Literature Review Malignant Transformation of an neurysmal one Cyst to Fibroblastic Osteosarcoma kash P. Kansagra, MD, MS, Jennifer J. Wan, MD, Kavi K. Devulapalli, MD, ndrew E. Horvai, MD,
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis
 Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Management of Campanacci type III giant cell tumor
 2017; 3(1): 836-841 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 836-841 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 16-12-2016 Brig. Muhammad Suhail Amin Head of Orthopedics Surgery Department, Combined
2017; 3(1): 836-841 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 836-841 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 16-12-2016 Brig. Muhammad Suhail Amin Head of Orthopedics Surgery Department, Combined
Typical skeletal location and differential diagnosis of bone tumors.
 Typical skeletal location and differential diagnosis of bone tumors. Poster No.: C-2418 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barros, L. A. Ferreira, Y. Costa, P. J. V. Coelho, F. Caseiro
Typical skeletal location and differential diagnosis of bone tumors. Poster No.: C-2418 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barros, L. A. Ferreira, Y. Costa, P. J. V. Coelho, F. Caseiro
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal imbalance
 Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:538 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1902-9 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal
Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:538 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1902-9 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal
A Guide to Ewing Sarcoma
 A Guide to Ewing Sarcoma Written By Physicians For Physicians WHAT IS EWING SARCOMA (ES) ES is a malignant bone tumor that can evolve from any bone in the body (and occasionally soft tissue) and mostly
A Guide to Ewing Sarcoma Written By Physicians For Physicians WHAT IS EWING SARCOMA (ES) ES is a malignant bone tumor that can evolve from any bone in the body (and occasionally soft tissue) and mostly
Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review
 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0102-7 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review F. Muratori M. Esposito F. Rosa F. Liuzza N. Magarelli B. Rossi H.M. Folath F. Pacelli G. Maccauro
DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0102-7 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review F. Muratori M. Esposito F. Rosa F. Liuzza N. Magarelli B. Rossi H.M. Folath F. Pacelli G. Maccauro
CASE REPORT TOTAL EN BLOC SPONDYLECTOMY FOR L2 CHORDOMA: A CASE REPORT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 73. 197 ~ 203, 2011 CASE REPORT TOTAL EN BLOC SPONDYLECTOMY FOR L2 CHORDOMA: A CASE REPORT NORIMITSU WAKAO 1, SHIRO IMAGAMA 1, ZENYA ITO 1, KEI ANDO 1, KENICHI HIRANO 1, RYOJI TAUCHI
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 73. 197 ~ 203, 2011 CASE REPORT TOTAL EN BLOC SPONDYLECTOMY FOR L2 CHORDOMA: A CASE REPORT NORIMITSU WAKAO 1, SHIRO IMAGAMA 1, ZENYA ITO 1, KEI ANDO 1, KENICHI HIRANO 1, RYOJI TAUCHI
Associated Terms: Osteosarcoma, Bone Cancer, Limb Salvage, Appendicular Osteosarcoma, Pathologic Fracture, Chondrosarcoma
 1 of 9 9/29/2014 8:25 PM Associated Terms: Osteosarcoma, Bone Cancer, Limb Salvage, Appendicular Osteosarcoma, Pathologic Fracture, Chondrosarcoma The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who
1 of 9 9/29/2014 8:25 PM Associated Terms: Osteosarcoma, Bone Cancer, Limb Salvage, Appendicular Osteosarcoma, Pathologic Fracture, Chondrosarcoma The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who
Intraosseous lipoma of the talus
 Intraosseous lipoma of the talus Shigeki Maruyama, M.D. 1, Tetsuji Yamamoto, M.D (!). 2, Masataka Hashimura, M.D. 1, and Nobuhiro Ohsaki, M.D. 1, Toshihiro Akisue, M.D. 2, Shinichi Yoshiya, M.D 2 1 Department
Intraosseous lipoma of the talus Shigeki Maruyama, M.D. 1, Tetsuji Yamamoto, M.D (!). 2, Masataka Hashimura, M.D. 1, and Nobuhiro Ohsaki, M.D. 1, Toshihiro Akisue, M.D. 2, Shinichi Yoshiya, M.D 2 1 Department
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report of Neoadjuvant Use Enabling Complete Surgical Resection
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase 5b is a Useful Serum Marker for Diagnosis and Recurrence Detection of Giant Cell Tumor of Bone
 392 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 392-399 Open Access Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase 5b is a Useful Serum Marker for Diagnosis and Recurrence Detection of Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Tetsuya
392 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 392-399 Open Access Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase 5b is a Useful Serum Marker for Diagnosis and Recurrence Detection of Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Tetsuya
Malignant Bone Tumours. PathoBasic, Daniel Baumhoer
 Malignant Bone Tumours PathoBasic, 20.03.18 Daniel Baumhoer FNCLCC Grading The differentiation score is defined as the extent to which a tumor resembles adult mesenchymal tissue (score 1), the extent to
Malignant Bone Tumours PathoBasic, 20.03.18 Daniel Baumhoer FNCLCC Grading The differentiation score is defined as the extent to which a tumor resembles adult mesenchymal tissue (score 1), the extent to
Clinical Study Enchondroma versus Low-Grade Chondrosarcoma in Appendicular Skeleton: Clinical and Radiological Criteria
 Oncology Volume 2012, Article ID 437958, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/437958 Clinical Study Enchondroma versus Low-Grade Chondrosarcoma in Appendicular Skeleton: Clinical and Radiological Criteria Eugenio
Oncology Volume 2012, Article ID 437958, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/437958 Clinical Study Enchondroma versus Low-Grade Chondrosarcoma in Appendicular Skeleton: Clinical and Radiological Criteria Eugenio
Evaluation of surgical treatment results in parosteal osteosarcoma
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 24, No. 1, May, 2010. pp. 11-16. Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 1:31 IRDT on Wednesday September 19th 2018 Evaluation of surgical
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 24, No. 1, May, 2010. pp. 11-16. Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 1:31 IRDT on Wednesday September 19th 2018 Evaluation of surgical
Imaging Gorham's disease (vanishing bone)
 Imaging Gorham's disease (vanishing bone) Poster No.: C-2201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: D. Vanel, P. Ruggieri, M. Alberghini; Bologna/IT Keywords: Gorham,
Imaging Gorham's disease (vanishing bone) Poster No.: C-2201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: D. Vanel, P. Ruggieri, M. Alberghini; Bologna/IT Keywords: Gorham,
The other bone sarcomas
 ONCOLOGY The other bone sarcomas PROGNOSTIC FACTORS AND OUTCOMES OF SPINDLE CELL SARCOMAS OF BONE E. E. Pakos, R. J. Grimer, D. Peake, D. Spooner, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, S. Abudu, L. Jeys From Royal
ONCOLOGY The other bone sarcomas PROGNOSTIC FACTORS AND OUTCOMES OF SPINDLE CELL SARCOMAS OF BONE E. E. Pakos, R. J. Grimer, D. Peake, D. Spooner, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, S. Abudu, L. Jeys From Royal
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION
 GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
Chondrosarcoma of 5 th metatarsal Right Foot: An Unusual Presentation and Review of Literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 8 Ver. 13 (August. 2018), PP 27-33 www.iosrjournals.org Chondrosarcoma of 5 th metatarsal Right
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 8 Ver. 13 (August. 2018), PP 27-33 www.iosrjournals.org Chondrosarcoma of 5 th metatarsal Right
FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING OSTEOSARCOMA
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
