Plain radiographs remain the primary skeletal imaging
|
|
|
- Mitchell Griffith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S84 Measuring Acetabular Component Position on Lateral Radiographs Ischio-Lateral Method Nicholas Pulos, B.A., John V. Tiberi III, M.D., and Thomas P. Schmalzried, M.D. Abstract The standard method for the evaluation of arthritis and postoperative assessment of arthroplasty treatment is observation and measurement from plain films, using the film edge for orientation. A more recent employment of an anatomical landmark, the ischial tuberosity, has come into use as orientation for evaluation and is called the ischiolateral method. In this study, the use of this method was evaluated as a first report to the literature on acetabular component measurement using a skeletal reference with lateral radiographs. Postoperative radiographs of 52 hips, with at least three true lateral radiographs taken at different time periods, were analyzed. Component position was measured with the historical method (using the film edge for orientation) and with the new method using the ischio-lateral method. The mean standard deviation (SD) for the historical approach was 3.7 and for the ischio-lateral method, 2.2 (p < 0.001). With the historical method, 19 (36.5%) hips had a SD greater than ± 4, compared to six hips (11.5%) with the ischio-lateral method. By using a skeletal reference, the ischio-lateral method provides a more consistent measurement of acetabular component position. The high intra-class correlation coefficients for both intra- and inter-observer reliability indicate that the angle measured with this simple method, which employs no Nicholas Pulos, B.A., is from the Pennsylvania University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; John V. Tiberi III, M.D., is from the Harbar-UCLA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California at Torrance; and Thomas P. Schmalzried, M.D. is from the Harbar-UCLA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California at Torrance, and the Joint Replacement Institute at St. Vincent Medical Center, Los Angeles, California. Correspondence: Nicholas Pulos, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, 2 Silverstein, 3400 Spruce Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104; nicholas.pulos@uphs.upenn.edu. further technology, increased time, or cost, is consistent and reproducible for multiple observers. Plain radiographs remain the primary skeletal imaging modality for arthritis and postoperative assessment of total joint arthroplasty. For the acetabular component, the abduction angle, or lateral opening angle, is commonly measured on an anterior-posterior (AP) projection of the angle between the inter-teardrop line (a skeletal reference on the image) and the line tangential to the opening of the acetabular component. 1 With the recognition of femoral-acetabular impingement (FAI), 2 there has been increased interest in the lateral projection radiograph. 3,4 A true lateral projection has been used in hip arthroplasty to assess the anterior (or posterior) opening angle of the acetabulum, which is a surrogate for anteversion. 5-8 This projection can be used to assess component position in the axial plane and the potential for anterior or posterior FAI, which can influence range of motion and stability Both the lateral opening angle and version of the acetabular component have been related to multiple clinical outcome measures. 12,13 Several lateral projection radiographs of the hip have been described The Johnson lateral is obtained with the patient supine and both hips extended. A 25 dorsal oblique X-ray beam is aimed at the groin and also angled approximately 25 cephalad, so that the X-ray beam is roughly perpendicular to the long axis of the femoral neck (to better visualize the femoral neck). 15 The Danelius-Miller 16 modification of the Lorenz view 14 describes a lateral projection where the patient is supine and the contralateral hip is flexed. The X-ray beam is parallel to the table and effectively shoots through the groin without dorsal angulation (Fig. 1). Such a view has been referred to as a cross-table or a shoot-through lateral view that displays the hip and pelvis at 90 from the AP radiograph (Fig. 2). Pulos N, Tiberi JV III, Schmalzried TP. Measuring acetabular component position on lateral radiographs: ischio-lateral method. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2011;69(Suppl 1):S84-9.
2 S85 Figure 1 Positioning for radiographs as outlined by DaneliusMiller.16 The patient s right hip is to be imaged with the contralateral hip flexed.18 Figure 2 Danelius-Miller16 lateral radiograph of a female patient with osteoarthritis. F, femur; L, lesser trochanter; G, greater trochanter; N, neck of the femur; H, head of the femur; A, acetabulum; IT, ischial tuberosity. The hip to be imaged is internally rotated 15 to 20 for visualization of the femoral neck and the trochanters. The Danelius-Miller16 lateral view is sometimes referred to as a Johnson s shoot-through for apparent reasons. True lateral radiographs, such as the Danelius-Miller,16 are useful tools in the evaluation of acetabular component position. However, since such lateral radiographs are taken with a beam angle at 25 cephalad, they project a socket opening that is slightly different than the radiographic (planar) anteversion described by Murray. 19 Yao and colleagues20 termed version measured from such lateral radiographs as axiolateral version. Woo and Morrey measured acetabular component version on a lateral-projection radiograph as the angle formed by the intersection of a tangential line to the opening of the acetabulum and a line drawn perpendicular to the horizontal plane (the film edge) of the radiograph (Fig. 3).6 Arai and coworkers8 used a similar method for measuring version but utilized a metal chain to impose a gravity line instead of the perpendicular line used by Woo and Morrey.6 They noted that while anteversion measured using AP radiographs was correlated with what was measured using cross-table lateral radiographs, the differences between these two measuring techniques decreased as patient flexibility increased. Pelvic tilt (rotation in the flexion-extension plane) affects acetabular projection on radiographs, which decreases the comparability of the gravity line or a line perpendicular to the horizontal as a reference.8 Using a cross-table lateral view of the hip, Pollard and associates7 measured the version of the acetabular component as the angle formed by a line drawn tangential to the face of the acetabular component and the horizontal plane. Using this method, they calculated a mean anteversion of 72.7 (SD ± 12.3 ). Arai and colleagues8 measured 97 other total hip arthroplasties and reported a mean anteversion of 21 (S.D. ± 6.5 ) for the complement of the angle measured by Pollard and coworkers.7 For these reasons, Tannest and associates21 concluded that anteversion measurements on non-standardized radiographs without anatomic referencing is highly inaccurate. In their evaluation of acetabular anteversion on revised, cemented polyethylene cups, Hultmark and colleagues22 measured anteversion as the angle between the anterior cortex of the ischial ramus and the cup. However, no analysis has been done to evaluate whether or not a skeletal landmark can be used to increase the consistency of acetabular measurements on lateral radiographs. In the current study, we utilized a method of measuring acetabular component position on the Danelius-Miller16 lateral radiograph, applying the ischial tuberosity as an anatomic reference point and comparing the measurement variability of this method to the horizontal film edge reference method of Woo and Morrey.6 Additionally, we Figure 3 Danelius-Miller16 lateral radiograph showing the external reference used by Woo and Morrey,6 which is a line perpendicular to the horizontal film edge. A line perpendicular to the long axis of the ischial tuberosity is also drawn, demonstrating the ischiolateral skeletal reference. The measured difference between these references in this example is 16.
3 S86 assessed the inter- and intra-observer variability of this new method. Materials and Methods Fifty-two hips in 51 patients, who were implanted with the same cobalt chromium alloy hip resurfacing prosthesis with a cementless acetabular component (Articular Surface Replacement/ASR TM ; DePuy, Leeds, UK), had at least three postoperative Danelius-Miller 16 lateral radiographs taken at different times (roughly 6 weeks, 6 months, and 1-year postoperative). Thirty-four hips had a fourth exam at approximately 2-years postoperatively. There were 31 males and 20 females. The mean age of the patients at surgery was 51 years (range, 30 to 69 years) and the average body mass index was 25.7 (range, 17.7 to 34.1). The diagnosis was osteoarthritis in 43 of the patients, osteonecrosis in three of the patients, posttraumatic arthritis in three of the patients, and hip dysplasia in two of the patients. Acetabular component position was measured on each Danelius-Miller 16 lateral radiograph, using the Woo and Morrey 6 method: the angle between a line tangent to the opening of the acetabular component and a line drawn perpendicular to the horizontal plane (Fig. 3). For each hip, the mean lateral position angle and the standard deviation (SD) were calculated for the lateral radiographs taken at the different times. To measure lateral component position using the ischial tuberosity as a reference, we measured the angle between a line tangential to the opening of the acetabular component and a line perpendicular to the ischial tuberosity. For this method, we drew a line parallel to the pitch of the ischial tuberosity when viewed on the Danelius-Miller 16 lateral radiograph. A line perpendicular to this skeletal reference was used in the angle measurement (Fig. 3). The mean lateral component position angle and the SD were calculated for the series of radiographs of each hip (Fig. 4). Figure 4 Lateral radiographic series of the same hip following hip resurfacing. Note the differences in projection for the four time periods. Using the Woo and Morrey 6 method, the mean lateral component position is 22.5, with a SD of ± 9.4. Using the long axis of the ischial tuberosity as a reference, the mean lateral component position is 39, with a SD of only ± 1.4.
4 S87 To test the reproducibility and reliability of the ischiolateral method, a subsample of 50 lateral radiographs was randomly selected to be read by two observers, who repeated the measurements on two separate occasions. Intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated for both intra- and inter-observer reliability. 23 The null hypothesis was that the difference between the SDs for each hip would be zero as a result of measurement error and pelvic tilt. Our alternative hypothesis was that measuring acetabular component position with the ischial tuberosity as a reference would yield a smaller SD. Statistical analysis was performed using the statistical package in Microsoft Excel. A paired two sample means t-test with a hypothesized mean difference of zero was used. Our paired variables were the SD of each hip using the Woo and Morrey 6 method and the SD of each hip using the ischio-lateral method. The test reported p-values using an alpha level of 0.05 as statistical significance. Results A total of 190 radiographs were analyzed. The mean of the SDs calculated for each patient using the Woo and Morrey 6 method was 3.7. The mean of the SDs for the ischio-lateral method was 2.2. This difference was statistically significant at p < Using the Woo and Morrey 6 method, 19 (36.5%) hips had a SD greater than 4, compared to 6 (11.5%) using the ischio-lateral method (p < 0.001). The number of measured angles that were greater than 4 from the mean was 24 (12.6%) using the Woo and Morrey 6 method and seven (3.8%) using the ischio-lateral method (p = 0.002). Figure 5 is a bar graph of the distribution of the range of angles measured for each series of radiographs. The measurements from the two methods are strongly correlated (p < 0.001). The angles are increasing together, with the ischio-lateral method angle being 5 to 25 larger than the angle measured using the Woo and Morrey 6 method (Fig. 6). In seven (3.7%) films, the angle could not be measured with the ischio-lateral method; in five (2.6%) of these, the ischial tuberosity was outside the image, and in the remaining two (0.5%), there was insufficient contrast for the ischial tuberosity to be clearly seen. For the ischio-lateral measurement method, the ICC was for intra-observer reliability and for inter-observer reliability. Discussion The preferred method for evaluating acetabular component position on a lateral radiograph is the one least affected by variations in pelvic position and radiographic technique. The mean SD of acetabular component position measured using the historical method of Woo and Morrey 6 was ± 3.7, for a mean anteversion of Pollard and coworkers 7 found a similar mean SD of ± 4, for a mean anteversion of 17.3, when measuring acetabular component position on serial radiographs of the same hip using the same method. Using a skeletal landmark, Massin and associates 1 found Figure 5 Bar graph comparing the range of the angles calculated for each hip by method. Only 23.5% of hip series had a measurement range of less than 4 using the Woo and Morrey 6 method, while 66.7% of hip series had a measurement range of less than 4 with the ischio-lateral method. Figure 6 Component position on the lateral radiograph: the method of Woo and Morrey 6 versus the ischio-lateral method. The best-fit line has a correlation coefficient of r 2 = 0.50.
5 S88 a SD of ± 4.4 when measuring the lateral opening angle on serial radiographs of the same hip. The ischio-lateral method of measuring acetabular component position of lateral radiographs had a mean SD of ± 2.2, for a mean lateral component position of The lateral component position angle measured by the ischio-lateral method is larger than the surgical anteversion observed in the operating room because surgical anteversion is measured as the angle between the frontal plane of the patient and the perpendicular to the face of the acetabular component (with no consideration of the ischium). 19,24 Using an intra-class correlation coefficient in their study of hip resurfacing to show the reliability of radiologic measurements between observers, Hing and colleagues 25 used an ICC > 0.6 to represent substantial agreement and an ICC > 0.9 to represent excellent agreement, where ICC = 1.0 represents perfect agreement. Using these cut-offs, the intra-observer reliability of the ischio-lateral method was excellent, and the interobserver reliability was substantial. Thus, the ischiolateral method is a reliable way of measuring component position on lateral radiographs. Clinically, this method is analogous to what has commonly been done on AP radiographs for the measurement of the acetabular component opening or abduction angle by Massin and coworkers. 1 An internal pelvic landmark, such as the inter-teardrop line, is used as a reference. Similarly, using the ischial tuberosity as a pelvic reference decreases variability of the lateral acetabular component position measurement due to differences in pelvic tilt, which can vary temporally with changes in patient flexibility and position on the X-ray table. 8 For example, using the Woo and Morrey 6 method, the lateral component position measured on one patient s lateral radiographs was 27.0, 37.0, and 36.0, at 6 weeks, 6 months, and 1-year follow-up, respectively. Using the ischio-lateral method on the same set of films, lateral component position was measured as 53.0, 53.0, and 55.0 the ischio-lateral method providing a more consistent measurement by decreasing the number of outlier angles (Fig. 5). A limitation of our method is that the ischium must be visible on the lateral radiograph. For the films used in this series, the ischium was not a usable landmark on seven films (3.7%). The radiographs analyzed had been taken prior to the initiation of this study, and the technicians had not been given any special instructions regarding visualization of the ischium. Discussion with the technician regarding the importance of including the ischium on this view should reduce the number of unusable films. We recognize that computed tomography (CT) scanning can be used to determine acetabular anteversion. However, the goal of this study was to investigate a simple method using plain radiographs that improved on the current measurement standard and that required neither special equipment nor additional time or cost to the patient or payer. Conclusion Similar to what is commonly done with the inter-teardrop line on AP films, the long axis of the ischial tuberosity can be used as a skeletal landmark on a true lateral radiograph. The ischio-lateral method of measuring component position on a lateral radiograph significantly improved measurement consistency by reducing variation due to pelvic tilt. The high intra-class correlation coefficients for both intra- and inter-observer reliability indicated that the angle measured with this method is consistent and reproducible for multiple observers. Disclosure Statement None of the authors have a financial or proprietary interest in the subject matter or materials discussed, including, but not limited to, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, honoraria, and paid expert testimony. References 1. Massin P, Schmidt L, Engh CA. Evaluation of cementless acetabular component migration: an experimental study. J Arthroplasty. 1989;4: Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, et al. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;417: TL, Schenker ML, Brigs KK, Philippon MJ. Relationship between offset angle alpha and hip chondral injury in femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy. 2008;24: Meyer DC, Beck M, Ellis T, et al. Comparison of six radiographic projections to assess femoral head/neck asphericity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;445: Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, et al. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60: Woo RY, Morrey BF. Dislocations after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64: Pollard JA, Daum WJ, Uchida T. Can simple radiographs be predictive of total hip dislocation? J Arthroplasty. 1995;10: Arai N, Nakamura S, Matsushita T. Difference between 2 measurement methods of version angles of the acetabular component. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22: D Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82: D Lima DD, Chen PC, Colwell CW. Optimizing acetabular component positioning to minimize impingement and reduce contact stress. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83: Amstutz HC, LeDuff MJ, Campbell PA, Dorey FJ. The effects of technique changes on aseptic loosening of the femoral component in hip resurfacing. Results of 600 conserve plus with a 3 to 9 year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22: Langton DJ, Jameson SS, Joyce TC, et al. The effect of component size and orientation on the concentrations of metal ions after resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint
6 S89 Surg Br. 2008;90: Schmalzried TP. The importance of proper acetabular component position and the challenges to achieving it. Oper Tech Orthop. 2009;19: Lorenz. Die rontgenographische darstellung des subskapularen raumes und des schnkelhalses im querschnitt. Fortschr Röentgenstr ;25: [German] 15. Johnson CR. A new method for roentgenographic examination of the upper end of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1932;14: Danelius G, Miller LF. Lateral view of the hip. Am J Roentgen. 1936;35: Laage H, Barnett JC, Brady JM, et al. Horizontal roentgenography of the hip in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953;35: Ballinger PW. Merrill s Atlas of Radiographic Positions and Radiologic Procedures. Vol 1. (6th ed). St. Louis: Mosby, 1986, pp Murray DW. The definition and measurement of acetabular orientation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75: Yao L, Yao J, Gold RH. Measurement of acetabular version on the axiolateral radiograph. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;316: Tannast M, Langlotz U, Siebenrock KA, et al. Anatomic referencing of cup orientation in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;436: Hultmark P, Hostner J, Herberts P, Karrholm J. Radiographic evaluation of Charnley cups used in first-time revision: repeated observations for 7-15 years. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18: Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979;86: McKee GK. Development of total prosthetic replacement of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970;72: Hing CB, Back DL, Bailey M, et al. The results of primary Birmingham hip resurfacings at a mean of five years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:431-8.
Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide Toacetabular Component Anteversion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Reliability and validity of measuring version of the acetabular component
 HIP Reliability and validity of measuring version of the acetabular component J-H. Nho, Y-K. Lee, H. J. Kim, Y-C. Ha, Y-S. Suh, K-H. Koo From Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Gyeonggido, Korea
HIP Reliability and validity of measuring version of the acetabular component J-H. Nho, Y-K. Lee, H. J. Kim, Y-C. Ha, Y-S. Suh, K-H. Koo From Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Gyeonggido, Korea
Are Portable Imaging Intraoperative Radiographs Helpful for Assessing Adequate Acetabular Cup Positioning in Total Hip Arthroplasty?
 J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 315-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.315 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Are Portable Imaging Intraoperative Radiographs Helpful for Assessing Adequate
J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 315-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.315 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Are Portable Imaging Intraoperative Radiographs Helpful for Assessing Adequate
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
Cup Alignment Error Model for Total Hip Arthroplasty
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 437, pp. 132 137 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Cup Alignment Error Model for Total Hip Arthroplasty Alon Wolf, PhD; Anthony M. DiGioia, III, MD; Andrew
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 437, pp. 132 137 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Cup Alignment Error Model for Total Hip Arthroplasty Alon Wolf, PhD; Anthony M. DiGioia, III, MD; Andrew
Supine and Standing AP Pelvis Radiographs in the Evaluation of Pincer Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Disclosure. Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table. History 11/3/2015
 Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table J. Masonis, M.D. OrthoCarolina Hip & Knee Center Chief Adult Hip & Knee reconstruction Carolinas Medical Center Disclosure Consultant & Design Smith & Nephew Zimmer
Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table J. Masonis, M.D. OrthoCarolina Hip & Knee Center Chief Adult Hip & Knee reconstruction Carolinas Medical Center Disclosure Consultant & Design Smith & Nephew Zimmer
HIP FOLLOW-UP. Thank you for your attention to this matter. If you have any questions, please contact us for assistance. Thomas P.
 HIP FOLLOW-UP It is important to review the status of your hip implant(s) during an office visit at six weeks, one year, two years, and every other year postoperatively thereafter for your safety even
HIP FOLLOW-UP It is important to review the status of your hip implant(s) during an office visit at six weeks, one year, two years, and every other year postoperatively thereafter for your safety even
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes
 The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
Measurement of the Acetabular Cup Anteversion on Simulated Radiographs
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 3 2009 Measurement of the Acetabular Cup Anteversion on Simulated Radiographs Chen-Kun Liaw, MD,*y 1 Rong-Sen Yang, MD, PhD,z 1 Sheng-Mou Hou, MD, PhD, MPH,z Tai-Yin
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 3 2009 Measurement of the Acetabular Cup Anteversion on Simulated Radiographs Chen-Kun Liaw, MD,*y 1 Rong-Sen Yang, MD, PhD,z 1 Sheng-Mou Hou, MD, PhD, MPH,z Tai-Yin
The role of the transverse acetabular ligament in total hip arthroplasty
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 135-140 ASPECT OF CURRENT MANAGEMENT The role of the transverse acetabular ligament in total hip arthroplasty Sameer Jain, Joseph Aderinto, Peter Bobak From Chapel Allerton
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 135-140 ASPECT OF CURRENT MANAGEMENT The role of the transverse acetabular ligament in total hip arthroplasty Sameer Jain, Joseph Aderinto, Peter Bobak From Chapel Allerton
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI
 Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 3 2000 The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty Motoi Yamaguchi, MD, PhD,* Toshihiro Akisue, MD, PhD,* Thomas W. Bauer, MD, PhD,* and Yasushi
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 3 2000 The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty Motoi Yamaguchi, MD, PhD,* Toshihiro Akisue, MD, PhD,* Thomas W. Bauer, MD, PhD,* and Yasushi
DURALOC. Acetabular Cup System. Surgical Technique
 DURALOC Acetabular Cup System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Technique Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5
DURALOC Acetabular Cup System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Technique Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Preoperative Planning. The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to:
 Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
ORIGINAL PAPER. Aleksi Reito & Timo Puolakka & Antti Paakkala & Jorma Pajamäki
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:519 525 DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1328-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Assessment of inter- and intra-observer reliability in the determination of radiographic version and inclination
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:519 525 DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1328-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Assessment of inter- and intra-observer reliability in the determination of radiographic version and inclination
Galileo Positioning System
 Galileo Positioning System Surgeon s Checklist Software Version 3.8.0.50 Anterior Workflow Anterior Workflow 1 Click the SURG S CHKLIST button from the bottom menu to launch the Surgeon s Checklist software.
Galileo Positioning System Surgeon s Checklist Software Version 3.8.0.50 Anterior Workflow Anterior Workflow 1 Click the SURG S CHKLIST button from the bottom menu to launch the Surgeon s Checklist software.
The Young Adult Hip: FAI. Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California
 The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006
 The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
Poor accuracy of freehand cup positioning during total hip arthroplasty
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2007) 127:375 379 DOI 10.1007/s00402-007-0294-y ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Poor accuracy of freehand cup positioning during total hip arthroplasty B. H. Bosker C. C. P. M. Verheyen W.
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2007) 127:375 379 DOI 10.1007/s00402-007-0294-y ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Poor accuracy of freehand cup positioning during total hip arthroplasty B. H. Bosker C. C. P. M. Verheyen W.
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement
 Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Computer Aided Evaluation of Total Hip Prosthesis Stability
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 2 (1998), No. 2, 141 149 Computer Aided Evaluation of Total Hip Prosthesis Stability Natasa D. Miljkovic, Goran M. Ercegan, Radovan B. Stulic, and Zoran B. Jandric
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 2 (1998), No. 2, 141 149 Computer Aided Evaluation of Total Hip Prosthesis Stability Natasa D. Miljkovic, Goran M. Ercegan, Radovan B. Stulic, and Zoran B. Jandric
Failure to correct femoral anteversion on the AP Pelvis radiograph leads to errors in prosthesis selection in total hip arthroplasty
 Australian Institute of Radiography Original research The Radiographer 2008; 55 (2):?? Failure to correct femoral anteversion on the AP Pelvis radiograph leads to errors in prosthesis selection in total
Australian Institute of Radiography Original research The Radiographer 2008; 55 (2):?? Failure to correct femoral anteversion on the AP Pelvis radiograph leads to errors in prosthesis selection in total
Functional safe zone. Safe zone
 Functional safe zone Every patient moves differently 1, and the amount of pelvic rotation through functional activities should be accounted for with total hip replacement. Pelvic tilt can change significantly
Functional safe zone Every patient moves differently 1, and the amount of pelvic rotation through functional activities should be accounted for with total hip replacement. Pelvic tilt can change significantly
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing has become a
 154 Quantifying Degree of Difficulty in Hip Resurfacing of Pistol-Grip Deformity Burton Ma, Ph.D., Stephane G. Bergeron, M.D., Heather J. Grant, M.Sc., John Rudan, M.D., and John Antoniou, M.D., Ph.D.
154 Quantifying Degree of Difficulty in Hip Resurfacing of Pistol-Grip Deformity Burton Ma, Ph.D., Stephane G. Bergeron, M.D., Heather J. Grant, M.Sc., John Rudan, M.D., and John Antoniou, M.D., Ph.D.
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
What Is Normal Femoral Head/Neck Anatomy? An Analysis of Radial CT Reconstructions in Adolescents
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
Navigation for total hip arthroplasty
 Interact Surg (2008) 3: 128 134 Springer 2008 DOI 10.1007/s11610-008-0084-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Navigation for total hip arthroplasty O. Guyen 1,V.Pibarot 1, J. Bejui-Hugues 2,SCORGroup 1 Service de chirurgie
Interact Surg (2008) 3: 128 134 Springer 2008 DOI 10.1007/s11610-008-0084-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Navigation for total hip arthroplasty O. Guyen 1,V.Pibarot 1, J. Bejui-Hugues 2,SCORGroup 1 Service de chirurgie
Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Research Article Clinical Validation of Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 171783, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/171783 Research Article Clinical Validation of Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Hip
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 171783, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/171783 Research Article Clinical Validation of Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Hip
Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs: Report of Two Cases
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur
 A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur Tadashi Tsukeoka, Yoshikazu Tsuneizumi, TaeHyun Lee. Chiba Rehabilitation Center, Chiba, Japan. Disclosures:
A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur Tadashi Tsukeoka, Yoshikazu Tsuneizumi, TaeHyun Lee. Chiba Rehabilitation Center, Chiba, Japan. Disclosures:
PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs
 Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs Moin Khan 1, Anil Ranawat 2, Dale Williams 1, Rajiv Gandhi 3, Hema Choudur
Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs Moin Khan 1, Anil Ranawat 2, Dale Williams 1, Rajiv Gandhi 3, Hema Choudur
Sciatic Nerve Injury in Total Hip Resurfacing
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 8 2010 Sciatic Nerve Injury in Total Hip Resurfacing A Biomechanical Analysis Dustin P. Gay, MD, Dana R. Desser, MD, Brent G. Parks, MSc, and Henry R. Boucher, MD
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 8 2010 Sciatic Nerve Injury in Total Hip Resurfacing A Biomechanical Analysis Dustin P. Gay, MD, Dana R. Desser, MD, Brent G. Parks, MSc, and Henry R. Boucher, MD
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
1/15/ year old male. Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA
 29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement?
 Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Disclosure. FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software. Acceptance of Hip Arthroscopy & FAI. Public. Payors. Orthopaedic Community
 2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
Are There Long-term Benefits to Cementing the Metaphyseal Stem in Hip Resurfacing?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:3197 3203 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4402-y Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Are There
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:3197 3203 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4402-y Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Are There
Why large-head metal-on-metal hip replacements are painful
 HIP Why large-head metal-on-metal hip replacements are painful THE ANATOMICAL BASIS OF PSOAS IMPINGEMENT ON THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK JUNCTION J. P. Cobb, K. Davda, A. Ahmad, S. J. Harris, M. Masjedi, A. J.
HIP Why large-head metal-on-metal hip replacements are painful THE ANATOMICAL BASIS OF PSOAS IMPINGEMENT ON THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK JUNCTION J. P. Cobb, K. Davda, A. Ahmad, S. J. Harris, M. Masjedi, A. J.
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
Effect of Superior Placement of the Hip Center on Abductor Muscle Strength in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 2 2009 Effect of Superior Placement of the Hip Center on Abductor Muscle Strength in Total Hip Arthroplasty Takahiko Kiyama, MD, Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD, Hiroshi
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 2 2009 Effect of Superior Placement of the Hip Center on Abductor Muscle Strength in Total Hip Arthroplasty Takahiko Kiyama, MD, Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD, Hiroshi
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
Influences of head/neck ratio and femoral antetorsion on the safe-zone of operative acetabular orientations in total hip arthroplasty
 . 206. Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2010; 13(4):206-211 Influences of head/neck ratio and femoral antetorsion on the safe-zone of operative acetabular orientations in total hip arthroplasty LI Yong-jiang
. 206. Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2010; 13(4):206-211 Influences of head/neck ratio and femoral antetorsion on the safe-zone of operative acetabular orientations in total hip arthroplasty LI Yong-jiang
Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty
 Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty Qianqian Wang, John Fisher, Sophie Williams. Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty Qianqian Wang, John Fisher, Sophie Williams. Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering,
Assessment of cup orientation in hip resurfacing: a comparison of TraumaCad and computed tomography
 Westacott et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Assessment of cup orientation in hip resurfacing: a comparison of TraumaCad and computed tomography Daniel
Westacott et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Assessment of cup orientation in hip resurfacing: a comparison of TraumaCad and computed tomography Daniel
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures
 Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Incidence of femoro-acetabular impingement in adult Indian population on the basis of specific radiological findings: A prospective study
 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. 78 Int J Res Med. 2013; 2(1);78-82 e ISSN: p ISSN: Morphological aspect of acetabulum of hip bone
 AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD
 Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Adult hip
Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Adult hip
Hip Resurfacing.
 Hip Resurfacing http://www.birminghamhipresurfacing.com/hipresurfacing/technology.cfm The end of the femur is capped somewhat like a tooth cap The hip socket receives a cupped implant to move together
Hip Resurfacing http://www.birminghamhipresurfacing.com/hipresurfacing/technology.cfm The end of the femur is capped somewhat like a tooth cap The hip socket receives a cupped implant to move together
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View
 Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Surgical Technique r5.indd 1 12/8/10 10:36 AM
 Surgical Technique The science of simplicity With more than 700,000 implantations and two and a half decades of clinical success, the Corail Total Hip System now has the most extensive experience with
Surgical Technique The science of simplicity With more than 700,000 implantations and two and a half decades of clinical success, the Corail Total Hip System now has the most extensive experience with
A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
Exam Corner. Hips and Knees. Prepared by Ahmed El-Bakoury, Asif Parkar and Mohamed Sukeik
 Exam Corner Hips and Knees Prepared by Ahmed El-Bakoury, Asif Parkar and Mohamed Sukeik 1) The anterior impingement test used for diagnosis of Femoroacetabular impingement includes: a) Passive flexion,
Exam Corner Hips and Knees Prepared by Ahmed El-Bakoury, Asif Parkar and Mohamed Sukeik 1) The anterior impingement test used for diagnosis of Femoroacetabular impingement includes: a) Passive flexion,
Partial hip resurfacing is considered investigational/not medically necessary for all other indications not listed above.
 Subject: Policy #: Current Effective Date: 11/13/2006 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 09/14/2006 Description/Scope Hip resurfacing can be categorized in two ways: as a partial (hemi) hip resurfacing
Subject: Policy #: Current Effective Date: 11/13/2006 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 09/14/2006 Description/Scope Hip resurfacing can be categorized in two ways: as a partial (hemi) hip resurfacing
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
STAIRS. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care. I have no relevant disclosures. Top 5 (or 6) Pathologies. Big 3- Questions to Ask
 I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
Bilaterally primary cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:344 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bilaterally primary cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with ankylosing spondylitis Wanchun Wang *, Guoliang
Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:344 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bilaterally primary cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with ankylosing spondylitis Wanchun Wang *, Guoliang
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH
 DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication?
 CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
F.A.I. indications. E. Sabetta. Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta
 F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
Recently, the new generation of metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing. arthroplasty is well known for preserving the proximal femoral bone stock,
 HOW TO DO RESURFACING IN HIP DYSPLASIA KOEN DE SMET Recently, the new generation of metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing arthroplasty is well known for preserving the proximal femoral bone stock, minimizing
HOW TO DO RESURFACING IN HIP DYSPLASIA KOEN DE SMET Recently, the new generation of metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing arthroplasty is well known for preserving the proximal femoral bone stock, minimizing
Complex Fractures and Hip Dislocations
 IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Leg Length Discrepancy in a Patient with Ipsilateral Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty
 texas orthopaedic journal CASE REPORT Leg Length Discrepancy in a Patient with Ipsilateral Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty Gaurav S. Sharma, BA; Ronald W. Lindsey, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
texas orthopaedic journal CASE REPORT Leg Length Discrepancy in a Patient with Ipsilateral Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty Gaurav S. Sharma, BA; Ronald W. Lindsey, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular rim during normal hip range of motion.
 RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Comparison of navigation accuracy in THA between the mini-anterior and -posterior approaches
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2009; 5: 20 25. Published online 23 December 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..226
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2009; 5: 20 25. Published online 23 December 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..226
Snapping Hip and Impingement
 Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement
 Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
Do Football Players Have a Greater Risk of Developing a Hip Impingement?
 Do Football Players Have a Greater Risk of Developing a Hip Impingement? Madeline Kay Johnson and Robert Stow, PhD Department of Kinesiology, University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire, Eau Claire, WI Acknowledgements
Do Football Players Have a Greater Risk of Developing a Hip Impingement? Madeline Kay Johnson and Robert Stow, PhD Department of Kinesiology, University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire, Eau Claire, WI Acknowledgements
Revision hip arthroplasty with S-ROM prosthesis: a study of clinical outcomes and implant stability
 J Orthopaed Traumatol () 7:1 1 DOI 1.17/s1195--15- ORIGINAL M. El-Deen S. Zahid D.T. Miller A. Nargol R. Logishetty Revision hip arthroplasty with S-ROM prosthesis: a study of clinical outcomes and implant
J Orthopaed Traumatol () 7:1 1 DOI 1.17/s1195--15- ORIGINAL M. El-Deen S. Zahid D.T. Miller A. Nargol R. Logishetty Revision hip arthroplasty with S-ROM prosthesis: a study of clinical outcomes and implant
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
CORAIL HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 CORAIL HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE SCIENCE OF SIMPLICITY With 2,000,000 stems provided for patients worldwide 1 and thirty years of clinical history, the CORAIL Total Hip System now has a very extensive
CORAIL HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE SCIENCE OF SIMPLICITY With 2,000,000 stems provided for patients worldwide 1 and thirty years of clinical history, the CORAIL Total Hip System now has a very extensive
DISLOCATION OF TOTAL HIP PROSTHESES*
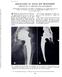 VOL. 115, No. 3 DISLOCATION OF TOTAL HIP PROSTHESES* API EARANCE ON FRONTAL ROENTGENOGRAMS By RICHARI) H. DAFFNER, M.D.,f JOHN A. GEHWEILER, M.l).,f JOHN OLSON, M.D.,f JAMES W. WILSON, PH.1)., M.l)., and
VOL. 115, No. 3 DISLOCATION OF TOTAL HIP PROSTHESES* API EARANCE ON FRONTAL ROENTGENOGRAMS By RICHARI) H. DAFFNER, M.D.,f JOHN A. GEHWEILER, M.l).,f JOHN OLSON, M.D.,f JAMES W. WILSON, PH.1)., M.l)., and
An Investigation into the Dynamic Loading of Ceramic-on-Ceramic Total Hip Replacements and its Relevance to Squeaking
 An Investigation into the Dynamic Loading of Ceramic-on-Ceramic Total Hip Replacements and its Relevance to Squeaking Jim W. Pierrepont, MEng 1, Andrew J. Shimmin, MBBS, FRACS 2, Jonathan V. Baré, MBBS,
An Investigation into the Dynamic Loading of Ceramic-on-Ceramic Total Hip Replacements and its Relevance to Squeaking Jim W. Pierrepont, MEng 1, Andrew J. Shimmin, MBBS, FRACS 2, Jonathan V. Baré, MBBS,
The Learning Curve for Adopting Hip Resurfacing Among Hip Specialists
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-009-1106-1 SYMPOSIUM: PAPERS PRESENTED AT THE HIP SOCIETY MEETINGS 2009 The Learning Curve for Adopting Hip Resurfacing Among Hip Specialists Ryan M. Nunley MD,
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-009-1106-1 SYMPOSIUM: PAPERS PRESENTED AT THE HIP SOCIETY MEETINGS 2009 The Learning Curve for Adopting Hip Resurfacing Among Hip Specialists Ryan M. Nunley MD,
Is the cup orientation different in bilateral total hip arthroplasty with right-handed surgeons using posterolateral approach?
 Song et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:123 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0789-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Is the cup orientation different in bilateral total hip arthroplasty
Song et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:123 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0789-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Is the cup orientation different in bilateral total hip arthroplasty
