Chapter 13! Chapter 13 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
|
|
|
- Eunice Robertson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system! 2! Grouping of Neural Tissues (1 of 3)! White matter! Myelinated (and unmyelinated) neuron processes! Schwann cells in PNS! Oligodendrocytes in CNS! Gray matter! Nerve cell bodies and dendrites! Unmyelinated axons! Neuroglia (e.g. astrocytes)! Nerve! Bundle of nerve fibers (axons) outside the CNS! Has associated CT layers! 3! 1!
2 Grouping of Neural Tissue (2 of 3)! Ganglion! Collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS! E.g. Dorsal root ganglion! Nucleus! Collection of nerve cell bodies with a common function found inside the CNS! In brain or spinal cord! Unmyelinated! E.g. Basal nuclei! 4! Grouping of Neural Tissue (3 of 3)! Columns are major regions of cord! E.g., posterior columns! Tracts are bundles of axons with common:! Structural characteristics (e.g. axon diameter, myelinated or not)! Function/direction! E.g., spinothalamic tract! Ascending tracts (in cord) = sensory! Descending tracts (in cord) = motor! Horns! Major areas of gray matter in spinal cord! 5! SECTION 13-2! The spinal cord is surrounded by three meninges and conveys sensory and motor information! 6! 2!
3 Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Figure 13-2! 7! Spinal Cord Functions/Anatomy! Spinal cord functions:! Convey sensory information to brain! Convey motor information to PNS! Reflexively integrate sensory and motor info! Gross anatomical features:! Length! Extends from medulla to L1 L2 in adults! 16 to 18 in. long! About 0.5 in. diameter! 8! Spinal Cord Gross Anatomy (1 of 2)! Enlargements:! Regions where cord is thicker! Cervical enlargement! Fibers to and from arms! Lumbar enlargement! Fibers to and from legs! Conus medullaris! Tapered end of the cord! About L1 or L2! E E E 9! 3!
4 Spinal Cord Gross Anatomy (2 of 2)! Filum terminale! Fibrous extension of pia mater! Forms part of coccygeal ligament! Coccygeal ligament! Dura mater + filum terminale (pia)! Attaches conus medullaris to coccyx! Cauda equina ( horse s tail )! Nerves arising from lower portion of cord! Descend in spinal canal! Exit spinal canal as spinal nerves! 10! Conus Medullaris, Filum Terminale! 1st lumbar! Vertebra! Gray s anatomy! Subarachnoid! space! Conus medullaris! Dura mater! Filum terminale -! Intradural portion! 2nd sacral vertebra! 1st coccygeal! vertebra! Filum terminal -! extradural portion! (coccygeal ligament)! 11! Spinal Tap, Spinal Nerves! Spinal tap! Deliver anesthetics, sample CSF fluid or pressure, etc.! Done between L3 and L4 or L4 and L5! (Cord not present here)! Spinal nerves contain two roots! Spinal nerves are mixed nerves! Ventral root - motor! Dorsal root - sensory! Dorsal root ganglion! Sensory cell bodies (unipolar neurons)! 12! 4!
5 Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Figure 13-2b! sensory! mixed! motor! 13! The Spinal Meninges Figure 13-3a! 14! Spinal Meninges and Associated Structures! Continuous with cranial meninges at F. magnum! Functions:! Provide support, stability, shock absorption!!! Epidural space:! Between dura mater and walls of vertebral canal! Contains areolar CT, blood vessels! Cushions cord! 15! 5!
6 Dura Mater! Dura mater = tough mother! Not firmly attached to bone (as in cranium)! Dense irregular CT! Inner lining of simple squamous EPI! Tubular portion runs from F. Magnum to S2! Fuses to form coccygeal ligament (with filum terminale) that extends to coccyx! Fuses with CT coverings of spinal nerves! Subdural space! Probably not present in life! 16! Arachnoid Membrane! Arachnoid = spider-like = refers to trabeculae! Avascular! Simple squamous EPI + CT trabeculae! Collagen + elastin fibers form trabeculae! EPI adheres to dura across subdural space! Extends with dura to end of intradural portion of filum terminale, so roots of nerves making up the cauda equina are in subarachnoid space! Subarachnoid space! Contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)! 17! Pia Mater! Pia mater = soft or delicate mother! Adheres to surface of brain and cord! Delicate collagen and elastin fibers! Highly vascular! Runs to coccyx as filum terminale (with dura, forms coccygeal ligament)! Denticulate (dentate) ligaments (Fig. 13-5)! Formed from pia mater! Extend through arachnoid to attach to dura! Suspend cord within subarachnoid space! 18! 6!
7 The Spinal Cord and Spinal Meninges! Figure 13-3b! Note orientation compared to that in Figure 13-5! 19! SECTION 13-3! Gray matter is the region of integration and command, and white matter carries information from place to place! 20! Sectional Organization of Cord Figure 13-5b! Note orientation compared to that in Figure 13-3! 21! 7!
8 Internal Anatomy of the Cord! Ventral (anterior) median fissure! (A fissure is larger than a sulcus.)! Dorsal (posterior) median sulcus! (smaller than fissure)! Gray commissures! Commissure = crossing from one side of the body to the other! Gray = gray matter! Central canal! Contains CSF! 22! Gray Matter in the Cord see Figure 13-5a! Nuclei - collections of cell bodies with a similar function! Ventral (anterior) gray horns! Somatic motor nuclei! Efferent information to skeletal muscles! Lateral gray horns! Visceral (autonomic) motor nuclei! Only in thoracic and lumbar segments! Dorsal (posterior) gray horns (see slide #63)! Sensory area! Somatic and autonomic (visceral) nuclei! 23! Sectional Organization of Cord Figure 13-5a! Note interneurons in dorsal horns! 24! 8!
9 White Matter Columns and Tracts! Columns:! Large collections of fibers conveying information to or from the brain! Have similar origin and similar destinations! Tracts:! Collections of fibers within a column! Carry same type of information in the same direction to the same destination! 25! Examples of Columns and Tracts! Posterior columns! Sensory (ascending)! Spinothalamic tracts! Sensory (ascending)! Corticospinal tracts! Motor (descending)! Voluntary movements! Vestibulospinal tracts! Motor (descending)! Automatic (involuntary) movements! Note that the name usually tells you the direction of information flow.! 26! Sensory Columns and Tracts Figure 15-4! Posterior column pathway Spinothalamic pathway Note organization and direction. Do not try to memorize locations.! 27! 9!
10 Motor Columns and Tracts Figure 15-8! Lateral corticospinal tract Note organization and direction. Do not try to memorize locations.! Anterior corticospinal tract Vestobulospinal tract 28! SECTION 13-4! Spinal nerves form plexuses that are named according to their level of emergence from the vertebral canal! 29! Spinal Nerves! Spinal nerves are mixed nerves! Contain both sensory and motor fibers! Exist in 31 pairs! Exit vertebral canal via intervertebral foramina! Named for where they exit vertebral column! Cord stops at level of L2! Nerves exiting below this level form the cauda equina! 30! 10!
11 Spinal Nerve Categories Figure 13-9! Pairs of spinal nerves:!! 8 cervical! (C1 exits between atlas and occipital bone)! 12 thoracic! 5 lumbar! 5 sacral! 1 coccygeal! 31 pairs! 31! Peripheral Nerve Anatomy Figure 13-6! Connective tissue coverings! 1. Epineurium! Surrounds entire nerve! 2. Perineurium! Delineates fascicles (bundles)! 3. Endoneurium! Surrounds individual nerve fibers! Does this terminology seem familiar?! 32! Rami (Branches) of Spinal Nerves! Ramus = branch ; plural = rami! 1. Dorsal ramus! Information to and from skin, skeletal muscles of back! Somatic and visceral, both motor and sensory!! 2. Ventral ramus! Information to and from ventrolateral body surface, body wall and limbs! Somatic and visceral, both motor and sensory! Form plexuses or thoracic (intercostal) nerves! 33! 11!
12 Nerve Roots and Rami modified from Fig. 13-3b! Dorsal! Dorsal root ganglion! Dorsal root! Dorsal ramus! Ventral ramus! Ventral root! Ventral! Denticulate ligament! Rami communicantes! Sympathetic chain ganglion! 34! Rami Communicantes (much more in Ch. 16)! 3. Rami communicantes! Communicate between ventral rami and sympathetic ganglia! Visceral sensory and visceral motor! Information to and from interoceptors, smooth muscle, visceral organs, glands! 3a. White ramus! Myelinated preganglionic fibers! 3b. Gray ramus! Unmyelinated postganglionic fibers! Gray and white rami unite at sympathetic ganglia! Form sympathetic nerves! 35! Thoracic (Intercostal) Nerves! Formed by ventral rami of T2 - T12 spinal nerves! Go directly to innervated structures.! Most axons from these segments do NOT join plexuses! Thoracic nerves 36! 12!
13 Distribution of Sensory Nerve Fibers Fig. 13-8a! Exteroceptors in skin are:! Ambient temperature! Pain! Light touch, pressure! 37! Distribution of Motor Nerve Fibers Fig. 13-8b! 38! Dermatomes Figure 13-7! Dermatome = specific region of skin innervated by a single pair of spinal nerves.!!! Clinically important for diagnoses of specific neuropathies.! 39! 13!
14 Nerve Plexuses! Plexus = network! Formed from ventral rami! T2 - T12 do not participate in plexuses! Plexuses are formed by nerve fibers from different spinal nerves. During development, small skeletal muscles innervated by different ventral rami fuse to form larger muscles with compound origins. The anatomical distinctions between the component muscles may disappear, but separate ventral rami continue to control each part of the compound muscle. p. 439! 40! Peripheral Nerves and Nerve Plexuses! Cervical plexus! Brachial plexus! Figure 13-9! Lumbar plexus! Sacral plexus! 41! Brachial Plexus 1 Figure 13-11a! 42! 14!
15 The Brachial Plexus 2 See your copy of Netter! Netter Plate ! Brachial Plexus 3 Figure 13-11b! 44! SECTION 13-5! Interneurons are organized into functional groups called neuronal pools! 45! 15!
16 ! Chapter 13 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! The Organization of Neuronal Pools! Figure 13-13! 46! SECTION 13-6! Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli! 47! Reflexes! Definition:! Unconscious, rapid, stereotyped responses to a stimulus.! Involve a reflex arc! Advantages of reflexes. Why important?! 1. Fast response! Don t have to think about it! 2. Predictable! Absence indicates damage to N.S.! 48! 16!
17 Reflex Arc 1! Spinal cord is the integrating center.! Components of a Reflex Arc:! 1. Sensory receptor! Responds to stimulus! Generates signal to be sent to integrator! 2. Sensory neuron! Cell body in dorsal root ganglion! Carries info to integrating center! Info enters via dorsal root! 49! Reflex Arc 2! 3. Integrating center = spinal cord! Usually involves interneurons! Polysynaptic reflex (most reflexes)! May not involve interneurons! Monosynaptic reflex! 4. Motor neuron! Transmits impulses to muscle or gland! 5. Effector! Muscle or gland that responds to motor neuron! Effects a change in controlled variable! 50! Events of a Reflex Arc Figure 13-14a! 51! 17!
18 Classification of Reflexes Figure 13-15! 52! Types of Spinal Reflexes! Wiring diagrams! Ipsilateral! Contralateral! Intersegmental! Reflex responses initiated by:! 1. Changes in muscle length! Stretch reflex - e.g. patellar reflex! 2. Changes in tendon tension! Golgi tendon reflex! 3. Pain! Flexor reflex, crossed extensor reflex! 53! 1. Muscle Spindle (Stretch) Reflex! Responds to changes in muscle length A.K.A. knee-jerk or patellar reflex! A monosynaptic reflex! Receptor (muscle spindle) located in muscle! Cord sends excitatory message to the muscle being stretched! Adjusts stretch of muscle! Adjust muscle tone at rest! Prevents overstretch! 54! 18!
19 The Patellar (Knee-jerk) Reflex Figure 13-17! + + = excitatory synapse! 55! Muscle Spindles 1! Intrafusal fibers! Specialized muscle cells! Surrounded by extrafusal ( normal ) muscle fibers! (Extrafusal fibers innervated by alpha motor neurons)! Innervated by both motor and sensory neurons! A. Gamma motor neurons (γ motor neurons)! Innervate ends of intrafusal fibers! Contraction adjusts sensitivity of spindle 56! Muscle Spindle Intrafusal Fibers 2! B. Sensory innervation of intrafusal fibers! Innervate center of intrafusal fibers! (no actin or myosin here)! Synapse in cord with motor neurons that innervate extrafusal fibers in the same muscle! Collaterals inform brain of degree of spindle stretch! Function to adjust muscle tone! 1. Stretch AP frequency stimulate extrafusal fibers muscle tone! 2. Compress AP frequency stimulation of extrafusal fibers muscle tone! 57! 19!
20 Intrafusal Fibers From 7 th edition! Note that gamma afferent fires! to some degree even at normal length.! 58! 2. (Golgi) Tendon Reflex! Function:! Senses changes in muscle tension (via tendon tension)! Receptor located in tendon (Golgi tendon organ)! Prevents injury to tendons! Ipsilateral reflex! Sends inhibitory message to muscle under tension! 59! Golgi Tendon Organ! 60! 20!
21 3. Flexor Reflex a.k.a. Withdrawal Reflex! Characteristics responds to PAIN 1. Polysynaptic! 2. Ipsilateral! 3. Intersegmental! Synapses occur within multiple cord segments! Activates several muscle groups! (i.e. stimulates more than one effector)! 4. Reciprocal innervation! (i.e. flexors and extensors)! 61! Flexor Reflex a.k.a. Withdrawal Reflex 2! Mechanism:! 1. Stimulate pain-sensitive sensory neuron! 2. Message sent to cord! 3. Activate interneurons! 4. Relay to several segments! 5. Several flexors activated, extensors inhibited! 62! Flexor Reflex 3 Figure 13-14! Be able to draw this!! See study guide.! + + _ + Back to #23! + _ indicates excitatory synapse indicates inhibitory synapse 63! 21!
22 Crossed Extensor Reflex! Characteristics:! 1. Polysynaptic! 2. Contralateral! 3. Reciprocal innervation! Activates flexors on one side! Inhibits extensors on this side! Activates extensors on the other side! Inhibits flexors on this side! 4. Intersegmental! 64! Crossed Extensor Reflex 2 Figure 13-18! Mechanism:! 1. Pain! 2. Sensory info to cord! 3. Contract flexors on one side, extensors on other side! ! Flexor and Crossed Extensor Reflexes! Comparison Figures 13-19, -20 from 9 th edition! 66! 22!
23 SECTION 13-8! The brain can affect spinal cord-based reflexes! 67! Integration and Control of Spinal Reflexes! Higher centers can modify spinal reflexes! Inhibit or facilitate reflex patterns! Continuous inputs (IPSP, EPSP) to neurons! involved in reflexes! Allows a few neurons from brain to control complex motor functions! e.g. Walking, running based on spinal reflexes! Modified by higher centers! Example: decerebrate cat! 68! 23!
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Spinal Cord Protection. Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. External Anatomy of Spinal Cord. Structures Covering the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Chapter 14. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
 Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD. Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes The Nervous System Coordinates the activity of muscles, organs, senses, and actions Made
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes The Nervous System Coordinates the activity of muscles, organs, senses, and actions Made
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 12 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Spinal Cord Learning Outcomes 12.1 Describe how the spinal cord can
12 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Spinal Cord Learning Outcomes 12.1 Describe how the spinal cord can
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Chapter 12
 Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
The Nervous System: The
 C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. C1. Cervical spinal ner ves. Thor acic. T12 Spinal nerve rootlets
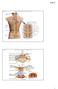 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13)
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S
 The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System. DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy
 The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
Lab Activity 13. Spinal Cord. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
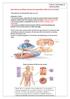 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Spinal nerves. Aygul Shafigullina. Department of Morphology and General Pathology
 Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
With other members of your lab group, discuss the following questions: - The spinal cord connects directly to which part of the brain?
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD
 THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
The Nervous System An overview
 Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Nervous System. Basic Divisions of the Nervous System C H A P T E R 12.
 C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 14 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 14 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity
 Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
4/5/2015. Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
 Peripheral Nervous System Learn and Understand: Peripheral nerves connect the edges of the body and outside world to the CNS. Most nerves carry specific types of information to/from specific locations.
Peripheral Nervous System Learn and Understand: Peripheral nerves connect the edges of the body and outside world to the CNS. Most nerves carry specific types of information to/from specific locations.
Chapter 13. The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Spinal Cord Anatomy. Key Points. What is the spine? Areas of the spine: Spinal Cord Anatomy
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Authors: SCIRE Community Team Reviewed by: Riley Louie, PT Last updated: Sept 21, 2017 This page provides an overview of the structures of the spinal cord and how the spinal cord works.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Authors: SCIRE Community Team Reviewed by: Riley Louie, PT Last updated: Sept 21, 2017 This page provides an overview of the structures of the spinal cord and how the spinal cord works.
Spinal cord. We have extension of the pia mater below L1-L2 called filum terminale
 Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
THE BACK. Dr. Ali Mohsin. Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Nervous system. The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions
 Nervous system The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions Questions Neuron The reflex arc The nervous centers Properties of the nervous centers The general principles of coordination Inhibition
Nervous system The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions Questions Neuron The reflex arc The nervous centers Properties of the nervous centers The general principles of coordination Inhibition
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint
 Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
Nervous System. Part Two
 Nervous System Part Two CNS: Spinal Cord Protected by bone, fluid, & membranes Composed of gray and white matter Serves as conduction pathway btwn brain and peripheral nerves Extends from base of brain
Nervous System Part Two CNS: Spinal Cord Protected by bone, fluid, & membranes Composed of gray and white matter Serves as conduction pathway btwn brain and peripheral nerves Extends from base of brain
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Nervous System. The Peripheral Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Reflexes Pathways
 Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
