ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS. From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada
|
|
|
- Karen Vivien Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY D. J. OGILVIE-HARRIS, ALAIN DEMAZIERE From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada We compared two freatments for tears of the rotator cuff of 1 to 4 cm in size. One group of 22 patients had an arthroscopic subacromial decompression and rotator-cuff debridement; the other comparable group of 23 patients had open repair and acromioplasty. Review was at 2 to 5 years postoperatively. Both groups had similar pain relief and range of active forward flexion, with significant improvement from the preoperative condition. The open repair group scored better for function, strength and overall score, but patient satisfaction was similar in the two groups. We recommend the use of arthroscopic subacromial decompression and debridement for low-demand patients who require mainly pain relief and range of movement. Open repair is necessary ifstrength and functional recovery are the prime objectives. JBoneJoint Surg[Br] 1993; 75-B: Received 29 June 1992; Acceptedafter revision 9 November 1992 There is controversy about the management of rotatorcuff tears of 1 to 4 cm in size : some authors advocate repair of all or most of these tears, but others treat them conservatively or by an acromioplasty. This study compares a standard open repair with the simpler procedure of arthroscopic debridement. PATIENTS AND METHODS Study design. Our aim was to carry out a cohort study in which 25 patients had an arthroscopic debridement and 25 had an open rotator-cuff repair. The preoperative diagnosis of a rotator-cuff tear was based on the history, physical examination and failure to respond to conservative treatment of at least six months rehabilitation. Before surgery, patients were allocated alternately to D. J. Ogilvie-Harris, FRCS C, Chief of Orthopaedics and Smith & Nephew Richards Professor A. Demazi#{232}re, Research Fellow Room Fraser Fell Pavilion, Toronto Western Hospital, 399 Bathurst Street, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, MST 2S8. Correspondence should be sent to Professor D. J. Ogilvie-Harris British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery X/93/3527 $2.00 either the arthroscopic group or the open repair group. After confirmation of the diagnosis and appropriate size of the tear by arthroscopy, the operation which had been selected was performed. In this way 50 consecutive patients were assigned to either the arthroscopic group or the open repair group on a cohort basis. It took approximately three years to enrol the 50 patients, and follow-up therefore ranged from two to five years. All patients were reviewed and examined preoperatively and postoperatively using the UCLA shoulder score for evaluation (Ellman 1987). We recorded age and size of tear as independent variables and pre- and postoperative pain, function, range of active forward flexion, and strength of forward flexion, as dependent variables. Patient satisfaction and the grading of overall score were also recorded. Statistical analysis between variables pre- and postoperatively was carried out using the Wilcoxon ranksum test. The results in the open and the arthroscopic groups were compared by the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. Arthroscopic debridement. A 5.5 mm full radius resecter was used to remove loose fragments of rotator cuff, hypertrophic synovium and other debris both from within the shoulder and from the subacromial space. The arthroscope was inserted via a posterolateral portal approximately 2 cm below the posterolateral corner of the acromion and the acromioniser (a cylindrical burr) and resecter through a posterior portal (Figs 1, 2). We used a gas-operated pressure pump and added 1 : adrenaline to the irrigation saline. The thickened bursa beneath the acromion was resected completely, and bone was removed from beneath it to leave a smooth surface (Ellman 1987 ; Esch et al 1988 ; Aitchek et al 1990 ; Gartsman 1990), taking sufficient anteroinferiorly to detach the coracoacromial ligament (Fig. 3) and to leave the deltoid visible at the anterolateral edge of the acromion. Less bone, however, was resected than is usual for impingement syndrome. The shoulder was then moved through a range of movement to ensure that there was no impingement. Ope n repair. Open repair was performed through a lateral deltoid splitting approach (Fig. 4) using a 5 cm incision 416 THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
2 ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS 417 Arthroscopic debridement. Figure 1 - The patient on the operating table, in a lateral position with the trunk elevated 450W Figure 2 - The posterior arthroscopic portal is in line with the long axis of the acromion and at about the mid-point of the glenohumeral joint ; it is used for the initial arthroscopy and subsequently for the resecter and acromioniser (a cylindrical burr). The second portal is 2 cm below the posterolateral corner of the acromion. Figure 3 - Bone is resected from the undersurface of the acromion thereby removing its anterior inferior portion and detaching the coracoacromial ligament so that the deltoid can be seen. Open repair. Figure 4 - The deltoid-splitting incision for repair of a torn supraspinatus tendon is made at the mid-point of the origin of the deltoid for 4 to S cm. Deltoid is not detached. Figure 5 - Repair of the supraspinatus tendon. The edges of the tear are freshened, then repaired with interrupted nonabsorbable sutures (a). The repair is reinforced and held to the bone by interrupted nonabsorbable sutures with screwthread anchors (b). from the mid-lateral edge of the acromion to expose the rotator-cuff tear. Anterior acromioplasty was performed and the coracoacromial ligament was resected. The rotator-cuff tear was then repaired end-to-end or side-toside, the primary repair being reinforced by small anchor sutures placed in the bone at the insertion of the supraspinatus tendon (Fig. 5). Table I. Age range of4s patients treated for rotator-cuff tears Age(yr) 30to39 40to49 50to59 60to69 >69 Arthroscopic debridement Open repair Table III. Pain scores (UCLA) of 45 patients treated for rotator-cuff Postoperative management. After arthroscopic debridement patients were mobilised rapidly, starting active movements through the full range on the day after operation. Physiotherapy continued for six weeks to three months to strengthen the shoulder and maximise the range of movement. After an open repair, patients were given a sling for Table II. Size of tear in 45 patients treated for rotator-cuff tears Size (cm) I Arthroscopic debridement Open repair tears Table IV. Function scores (UCLA) of 45 patients treated for rotatorcuff tears I Total Preoperative Arthroscopic debridement I Open repair Total Preoperative S 9 17 II 3 45 Arthroscopic debridement I Openrepair VOL. 75-B, No. 3, MAY 1993
3 418 D. J. OGILVIE-HARRIS, A. DEMAZIERE three weeks, but removed the arm from the sling several times a day to carry out a range of movement. Active assisted range-of-movement exercises were started at three weeks with active strengthening exercises after six weeks. Treatment continued for about six months, until there was maximal improvement. RESULTS Of the 50 patients entered in the study, 45 were available for review at two to five years postoperatively. Of these, 23 had had open repair and 22 arthroscopic debridement. The two groups showed no significant differences in age, size of tear, preoperative pain, function, active forward flexion and strength of forward flexion (Tables I, II and X). Follow-up varied from two to five years because of the three-year period of recruitment, but again there was no significant difference between the two groups. Table V. Active forward flexion scores (UCLA) of 45 and 14 had moderate loss (4 to 7) (Table IV). Postoperatively, no patient had severe loss of function. In the open repair group, five patients (22%) had moderate loss, while in the arthroscopic debridement group 14 (64%) had moderate loss. This difference was significant (p = 0.006) in favour of the open repair group. Active forward flexion. There was a significant improvement in the amount of active forward flexion in both groups (Table V), but no significant difference between the open repair and arthroscopic debridement groups (p = 0.16). Strength offorward fiexion. Preoperatively, most patients had grade 2 or 3 power (Table VI). Both groups showed improvement, but this was significantly greater for the open repair group (p = 0.003). Arthroscopic debridement allows improvement of power but not as much as an open repair. Patient satisfaction. Patient satisfaction was greater after Table VI. Strength of forward flexion scores (UCLA) of 45 patients treated for rotator-cuff tears Preoperative Arthroscopic debridement Openrepair patients treated for rotator-cuff tears Preoperative Arthroscopic debridement Openrepair All patients in both groups showed a significant improvement in pain, function, active forward flexion and strength of forward flexion. Pain. Preoperative pain was severe (1 to 3 on the UCLA scale) in 30 patients (66%) and moderate (4 to 6) in 15 (Table III). Postoperatively, there was a highly significant improvement in pain score (p = ). The two groups showed no significant differences with regard to pain relief (p = 0.51). Twelve patients (27%) had moderate pain (4 to 7), and 73% had minimal or no pain. Function. Preoperatively, 31 patients (68%) had significant limitation of function (1 to 3 on the UCLA score) Table VII. Patient satisfaction scores(ucla)of4s patients open repair (Table VII) but the difference was not significant (p = 0.08). Pain relief and restoration of movement were probably more important to the patient than strength or overall function. Overall score. Open repair was significantly better than arthroscopic debridement (p = 0.017; Table VIII), with a higher percentage of patients with excellent or good function. Arthroscopic debridement produced effective pain relief and restored forward flexion, but failed to restore power or function as well as the open procedure. There was no significant difference in the results in relation to the age of the patient or the size of the tears (Tables IX, X). treated for rotator-cufftears. Five represents very satisfied Arthroscopic debridement Openrepair DISCUSSION Our aim was to compare the results of arthroscopic debridement and decompression with standard open repair and acromioplasty. Our results show that equal pain relief was achieved by either procedure, and both Table VIII. Overall results (UCLA) of45 patients treated for rotator-cuff tears Excellent (34 to 35) Good (28 to 33) Fair (21 to 27) Poor (0 to 20) Total Arthroscopic debridement Openrepair THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
4 ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS 419 restored the same range of active forward flexion. The arthroscopic procedure effectively relieved some symptoms, but failed to restore as much strength and therefore function as the open repair. The residual weakness and loss of function are presumably related to the residual defect in the supraspinatus tendon. Table IX. Size of tear related to overall result (UCLA) of45 patients treated for rotator-cuff tears Size of tear (cm) Total Poor(Oto2O) I Fair(2l to27) I I Good(28to33) Excellent (34 to 35) Total Debridement of the rotator cuff alone, without decompression, does not seem to lead to acceptable results (Cofield 1983 ; Rockwood 1984 ; Ogilvie-Harris and Wiley 1986). Arthroscopic acromioplasty for impingement syndrome without full-thickness tears is effective although not necessarily better than open acromioplasty (Ellman 1987; Esch et al 1988; Altchek et al 1990; Gartsman 1990; Van Holsbeeck et al 1992). Esch et al (1988) included patients with rotator-cuff tears in their report on the results of arthroscopic acromioplasty. They found that 67% (24 of 36) of those with complete tears had a satisfactory result but that few had excellent scores. Eliman (1987) had no excellent results from arthroscopic acromioplasty for complete tears. Levy, Gardner and Lemak (1991) reported 25 patients with complete tears treated in this way : minimum followup was only one year, but 84% had satisfactory results. Their results were much worse in patients with larger tears, as in our series. Other authors have reported satisfactory results in 80% to 90% of patients after open repair of the rotator cuff (Wolfgang 1974, 1978; Cofield 1981, 1983, 1985; Packer et al 1983; Hawkins, Misamore and Hobeika 1985 ; Ellman, Hanker and Bayer 1986 ; Essman, Bell and Askew 1991). Rockwood (1984) and Rockwood and Burkhead (1988), however, described 58 patients with massive rotator-cuff tears who underwent open acromioplasty and cuff debridement without repair, of whom 95% had pain relief and 90% had increased strength and motion. There was no deterioration with time and they considered that the pain relief and functional improvement demonstrated successful decompression of the associated impingement. Arthroscopic acromioplasty without a cuff repair has been shown to give quicker recovery and greater patient satisfaction than open acromioplasty but no improvement in long-term results (Van Hoisbeeck et al 1992). Table X. Summary of outcome results and their statistical significance in 45 patients treated for rotator-cuff tears using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (p values) REFERENCES In our series, the arthroscopic procedure produced considerably less perioperative morbidity than the open repair, and most of the patients had the procedure as outpatients, being admitted only when there was a concomitant medical problem. Patients with an open repair stayed in hospital for three to four days, mainly for pain relief, and took considerably longer to regain the range of movement and strength. Thus, although the overall results are better after open repair, the cost is considerably more in terms of hospitalisation and rehabilitation. Age 0.77 Size of tear 0.43 Preoperative arthroscoplc versus open Postoperative arthroscopic versus open Postoperative versus preoperative Pain < Function < Forward flexion < Strength < Satisfaction 0.08 Finalscore Conclusions. On the basis of our results, we consider that arthroscopic debridement is ideal for patients with limited demands whose main complaints are pain and loss of range of movement : the procedure is quicker, cheaper and involves less rehabilitation. For a patient, however, who needs good function and strength, arthroscopic debridement and acromioplasty are not sufficient, and we advise open repair and acromioplasty. The proper selection of patients is therefore important in the optimum treatment of patients with rotator-cuff tears of from 1 to 4 cm. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. Altchek DW, Warren RF, Wlckiewicz TL, et al. Arthroscopic acromioplasty : technique and results. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1990; 72- A:l Cofield RH. Tears of rotator cuff. AAOS Instr Course Lect 1981 ; 30: Cofleld RH. Arthroscopy of the shoulder. Mayo Clin Proc 1983; 58: Cofield RH. Rotator cuff disease of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1985; 67-A : Ellman H. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression : analysis of 1-3 year results. Arthroscopy 1987 ; 3: Ellman H, Hanker G, Bayer M. Repair of the rotator cuff: end result study of factors influencing reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1986; 68-A:! VOL. 75B, No. 3, MAY 1993
5 420 D. J. OGILVIE-HARRIS, A. DEMAZIERE Each JC, Ozerk.is LR, Helgager JA, et al. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression : results according to the degree of rotator cuff tear. Arthroscopy 1988; 4: Essman JA, Bell RH, Askew M. Full-thickness rotator-cuff tear: an analysis of results. Clin Orthop 1991 ; 26: Gartsman GM. Arthroscopic acromioplasty for lesions of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1990; 72-A : Hawkins RJ, Misamore GW, Hobeika PE. Surgery for full-thickness rotator-cuiftears. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1985 ; 67-A : Levy HJ, Gardner RD, Lemak U. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression in the treatment of full-thickness rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy 1991 ; 7:8-13. Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Wiley AM. Arthroscopic surgery.of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1986: 68-B : Packer NP, Calved PT, Bayley JIL, Kessel L. Operative treatment of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1983 ; 65- B : Rockwood CA Jr. Shoulder function following decompression and irrepairable cufflesions. Orthop Trans 1984, 8:92. Rockwood CA, Burkhead WZ. Management of patients with massive rotator cuffdefects by acromioplasty and rotator cuff debridement. Orthop Trans 1988; 12: Van Hoisbeeck E, DeRycke J, Declercq G, et al. Subacromial impingement. Arthroscopv 1992 ; 8: Wolfgang GL. Surgical repair of tears of the rotator cuffof the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1974; 56-A : Wolfgang GL. Rupture of the musculotendinous cuff of the shoulder. ClinOrthop 1978; 134: THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
Arthroscopic Decompression in Stage II Subacromial Impingement Five to Twelve Years Follow up
 Abstract Arthroscopic Decompression in Stage II Subacromial Impingement Five to Twelve Years Follow up Chong-Hyuk Choi, M.D. and Ogilvie-Harris DJ, M.D.* Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Youngdong Severance
Abstract Arthroscopic Decompression in Stage II Subacromial Impingement Five to Twelve Years Follow up Chong-Hyuk Choi, M.D. and Ogilvie-Harris DJ, M.D.* Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Youngdong Severance
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
The Results of Rotator Cuff Disease Treated by Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression
 Abstract The Results of Rotator Cuff Disease Treated by Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression Jae-Hwa Kim, M.D., Seung-Kwan Han, M.D., and Duck-Yun Cho, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National
Abstract The Results of Rotator Cuff Disease Treated by Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression Jae-Hwa Kim, M.D., Seung-Kwan Han, M.D., and Duck-Yun Cho, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National
Degenerative joint disease of the shoulder, while
 Arthroscopic Debridement of the Shoulder for Osteoarthritis David M. Weinstein, M.D., John S. Bucchieri, M.D., Roger G. Pollock, M.D., Evan L. Flatow, M.D., and Louis U. Bigliani, M.D. Summary: Twenty-five
Arthroscopic Debridement of the Shoulder for Osteoarthritis David M. Weinstein, M.D., John S. Bucchieri, M.D., Roger G. Pollock, M.D., Evan L. Flatow, M.D., and Louis U. Bigliani, M.D. Summary: Twenty-five
Long-Term Functional Outcome of Repair of Large and Massive Chronic Tears of the Rotator Cuff
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Long-Term Functional Outcome of Repair of Large and Massive Chronic Tears
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Long-Term Functional Outcome of Repair of Large and Massive Chronic Tears
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears. Rafael M. Williams, MD
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options
 Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options The following article provides in depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article "Rotator Cuff
Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options The following article provides in depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article "Rotator Cuff
Assessment of functional outcome of mini-open rotator cuff repair: a hospital based prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180681 Assessment of functional outcome of
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180681 Assessment of functional outcome of
Rotator cuff strength following open subscapularis tendon repair
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 173179 ORIGAL STUDY Rotator cuff strength following open subscapularis tendon repair Roger P. VAN RIET, Sean T. O LEARY, Alexander HOOP, Simon N. BELL From the Melbourne Shoulder
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 173179 ORIGAL STUDY Rotator cuff strength following open subscapularis tendon repair Roger P. VAN RIET, Sean T. O LEARY, Alexander HOOP, Simon N. BELL From the Melbourne Shoulder
In 1911, Codman 1 first described the open surgical
 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: 4- to 10-Year Results Eugene M. Wolf, M.D., William T. Pennington, M.D., and Vivek Agrawal, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of this article is to report the 4- to 10-year results
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: 4- to 10-Year Results Eugene M. Wolf, M.D., William T. Pennington, M.D., and Vivek Agrawal, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of this article is to report the 4- to 10-year results
Clinical determinants of a durable rotator cuff repair
 13 Surgical Technique and Functional Results of Irreparable Cuff Tears Reconstructed with the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon Osman Guven MD Murat Bezer MD Zeynep Guven MD Kemal Gokkus MD and Cihangir Tetik
13 Surgical Technique and Functional Results of Irreparable Cuff Tears Reconstructed with the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon Osman Guven MD Murat Bezer MD Zeynep Guven MD Kemal Gokkus MD and Cihangir Tetik
Cost-benefit comparison: holmium laser versus electrocautery in arthroscopic acromioplasty Murphy M A, Maze N M, Boyd J L, Quick D C, Buss D D
 Cost-benefit comparison: holmium laser versus electrocautery in arthroscopic acromioplasty Murphy M A, Maze N M, Boyd J L, Quick D C, Buss D D Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Cost-benefit comparison: holmium laser versus electrocautery in arthroscopic acromioplasty Murphy M A, Maze N M, Boyd J L, Quick D C, Buss D D Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective randomized comparison study
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Acromioplasty. Surgical Indications and Considerations
 1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Arthroscopic Versus Mini-Open Rotator Cuff Repair: A Comparison of Clinical Outcome
 Arthroscopic Versus Mini-Open Rotator Cuff Repair: A Comparison of Clinical Outcome Andreas M. Sauerbrey, M.D., Charles L. Getz, M.D., Marco Piancastelli, M.D., Joseph P. Iannotti, M.D., Ph.D., Matthew
Arthroscopic Versus Mini-Open Rotator Cuff Repair: A Comparison of Clinical Outcome Andreas M. Sauerbrey, M.D., Charles L. Getz, M.D., Marco Piancastelli, M.D., Joseph P. Iannotti, M.D., Ph.D., Matthew
St. George s Shoulder Unit Patient Information
 St. George s Shoulder Unit Patient Information SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY & ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Mr. T.D.Tennent FRCS(Orth), Mr Y.O.Pearse FRCS(Orth) This information booklet has been produced to help you obtain
St. George s Shoulder Unit Patient Information SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY & ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Mr. T.D.Tennent FRCS(Orth), Mr Y.O.Pearse FRCS(Orth) This information booklet has been produced to help you obtain
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
Review Article The Role of Acromioplasty for Management of Rotator Cuff Problems: Where Is the Evidence?
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 467571, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467571 Review Article The Role of Acromioplasty for Management of Rotator Cuff Problems:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 467571, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467571 Review Article The Role of Acromioplasty for Management of Rotator Cuff Problems:
Shoulder Surgery. Gregory M. Behm, MD Ravalli Orthopedics & Sports Medicine
 Shoulder Surgery The purpose of this handout is to help you understand the way I perform shoulder surgeries and to help you plan for the recovery. Below are some general items that apply to most surgeries
Shoulder Surgery The purpose of this handout is to help you understand the way I perform shoulder surgeries and to help you plan for the recovery. Below are some general items that apply to most surgeries
Disorders of the Rotator Cuff and Acromio-clavicular Joint
 Disorders of the Rotator Cuff and Acromio-clavicular Joint The rotator cuff is a sheath of muscles which surrounds the shoulder joint, it helps to stabilise the shoulder and powers the wide range of movements
Disorders of the Rotator Cuff and Acromio-clavicular Joint The rotator cuff is a sheath of muscles which surrounds the shoulder joint, it helps to stabilise the shoulder and powers the wide range of movements
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression
 Arthroscopic subacromial decompression Richard J. Hawkins, MD, FRCS, a Kevin D. Plancher, MD, MS, b Stephen R. Saddemi, MD, c Leigh Scott Brezenoff, MD, d and John T. Moor, MD, e Vail, Colo, Stamford,
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression Richard J. Hawkins, MD, FRCS, a Kevin D. Plancher, MD, MS, b Stephen R. Saddemi, MD, c Leigh Scott Brezenoff, MD, d and John T. Moor, MD, e Vail, Colo, Stamford,
The Upper Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
Operative skills have advanced sufficiently so that. Arthroscopic Treatment of Multidirectional Glenohumeral Instability: 2- to 5-Year Follow-up
 Arthroscopic Treatment of Multidirectional Glenohumeral Instability: 2- to 5-Year Follow-up Gary M. Gartsman, M.D., Toni S. Roddey, Ph.D., P.T., O.C.S., and Steven M. Hammerman, M.D. Purpose: We present
Arthroscopic Treatment of Multidirectional Glenohumeral Instability: 2- to 5-Year Follow-up Gary M. Gartsman, M.D., Toni S. Roddey, Ph.D., P.T., O.C.S., and Steven M. Hammerman, M.D. Purpose: We present
ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR
 ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR Indications (Who Needs Surgery, When, electricity is used to cauterize small capillaries. Electricity or Why, and Goals) a motorized shaver is used to remove the bursa and
ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR Indications (Who Needs Surgery, When, electricity is used to cauterize small capillaries. Electricity or Why, and Goals) a motorized shaver is used to remove the bursa and
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
Rotator Cuff Repair TRENDS OF REPAIRS. Evolution of Arthroscopic Repair. Shoulder Girdle. Rotator Cuff Repair 8/29/2013
 Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
 www.simonmoyes.com+ www.shoulder-arthroscopy.co.uk Impingement)and)Rotator)Cuff) Tears) Presented+by+Mr+Simon+Moyes+ Shoulder)Experience) RNOH)shoulder)unit) Visi7ng)fellow)Royal)North)Shore,)Sydney) RNOH)shoulder)fellow)
www.simonmoyes.com+ www.shoulder-arthroscopy.co.uk Impingement)and)Rotator)Cuff) Tears) Presented+by+Mr+Simon+Moyes+ Shoulder)Experience) RNOH)shoulder)unit) Visi7ng)fellow)Royal)North)Shore,)Sydney) RNOH)shoulder)fellow)
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Shoulder Arthroscopy Curriculum
 ARTHRO Mentor 1 Description All those with an interest in the shoulder should develop a basic level of proficiency and should be able to perform a thorough diagnostic exam, looking from both the anterior
ARTHRO Mentor 1 Description All those with an interest in the shoulder should develop a basic level of proficiency and should be able to perform a thorough diagnostic exam, looking from both the anterior
Acute Tears of the Rotator Cuff
 Acute Tears of the Rotator Cuff The Timing of Surgical Repair RICK W. BASSETT, M.D., AND ROBERT H. COFIELD, M.D. Thirty-seven patients had surgical repair within three months after significant ruptures
Acute Tears of the Rotator Cuff The Timing of Surgical Repair RICK W. BASSETT, M.D., AND ROBERT H. COFIELD, M.D. Thirty-seven patients had surgical repair within three months after significant ruptures
Rotator Cuff Tear. Multimedia Health Education USA. Holly Edmonds RN,Clnc 1006 Triple Crown Drive Indian Trial,NC28079
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Shoulder Acromioplasty. All decisions about Acromioplasty must be made in conjunction with your surgeon
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Shoulder Acromioplasty. All decisions about Acromioplasty must be made in conjunction with your surgeon
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of
 Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment
 SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement
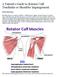 A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement Introduction Shoulder pain is a common condition whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. Shoulder pain and injuries
A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement Introduction Shoulder pain is a common condition whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. Shoulder pain and injuries
06/Μαρ/2013 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF. ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES
 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears
 Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals Alper Deveci and Metin Dogan 7 7.1 Bony Landmarks Before starting shoulder arthroscopy, the patient must be positioned and draping applied. Then the bony landmarks are identified
Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals Alper Deveci and Metin Dogan 7 7.1 Bony Landmarks Before starting shoulder arthroscopy, the patient must be positioned and draping applied. Then the bony landmarks are identified
Rotator cuff injuries are commonly attributed to repetitive
 [ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
[ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
ArthroS CASE DESCRIPTIONS SHOULDER MODULE
 ArthroS CASE DESCRIPTIONS SHOULDER MODULE Last update: November 2013 VIRTAMED ARTHROS TM SHOULDER BASIC SKILLS CASES (1/2) Guided Diagnostics I: Glenohumeral Healthy right shoulder Guided inspection of
ArthroS CASE DESCRIPTIONS SHOULDER MODULE Last update: November 2013 VIRTAMED ARTHROS TM SHOULDER BASIC SKILLS CASES (1/2) Guided Diagnostics I: Glenohumeral Healthy right shoulder Guided inspection of
Latissimus dorsi transfer for primary treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2002) 2:139 145 Springer-Verlag 2002 ORIGINAL F. Postacchini S. Gumina P. De Santis R. Di Virgilio Latissimus dorsi transfer for primary treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2002) 2:139 145 Springer-Verlag 2002 ORIGINAL F. Postacchini S. Gumina P. De Santis R. Di Virgilio Latissimus dorsi transfer for primary treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears
BIOKNOTLESSRC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR SUTURE ANCHOR SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Surgical Technique for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair. Raymond Thal, M.D.
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR BIOKNOTLESSRC SUTURE ANCHOR Surgical Technique for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Raymond Thal, M.D. Town Center Orthopaedic Associates Reston, Virginia Surgical
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR BIOKNOTLESSRC SUTURE ANCHOR Surgical Technique for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Raymond Thal, M.D. Town Center Orthopaedic Associates Reston, Virginia Surgical
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of
 Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
 SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices
 Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices Aimee S. Klapach Orthopedic Surgeon; Knee, Shoulder, & Sports Medicine Sports & Orthopaedic Specialists, part of Allina Health Minnesota Department of Labor and
Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices Aimee S. Klapach Orthopedic Surgeon; Knee, Shoulder, & Sports Medicine Sports & Orthopaedic Specialists, part of Allina Health Minnesota Department of Labor and
Acromioplasty, Mumford, Biceps What s the Indication with Rotator Cuff Tears?
 Acromioplasty, Mumford, Biceps What s the Indication with Rotator Cuff Tears? James C. Esch MD Oceanside, CA Consultant Smith & Nephew Endoscopy Financial Disclosure You just finished a cuff repair using
Acromioplasty, Mumford, Biceps What s the Indication with Rotator Cuff Tears? James C. Esch MD Oceanside, CA Consultant Smith & Nephew Endoscopy Financial Disclosure You just finished a cuff repair using
Fluoroscopic Comparison of Kinematic Patterns in Massive Rotator Cuff Tears
 Fluoroscopic Comparison of Kinematic Patterns in Massive Rotator Cuff Tears A Suspension Bridge Model STEPHEN S. BURKHART, M.D. Twelve shoulders with known massive rotator cuff tears were imaged fluoroscopically.
Fluoroscopic Comparison of Kinematic Patterns in Massive Rotator Cuff Tears A Suspension Bridge Model STEPHEN S. BURKHART, M.D. Twelve shoulders with known massive rotator cuff tears were imaged fluoroscopically.
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
Fully Torn Rotator Cuff Repair
 Fully Torn Rotator Cuff Repair A torn rotator cuff is a common condition that can cause shoulder pain, weakness, and loss of mobility. If the tear is severe enough, surgical intervention is often necessary
Fully Torn Rotator Cuff Repair A torn rotator cuff is a common condition that can cause shoulder pain, weakness, and loss of mobility. If the tear is severe enough, surgical intervention is often necessary
Surgical treatment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular dislocation Tossy type III and V using the Hook Plate
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 4, 441-44 ORIGINAL STUDY Surgical treatment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular dislocation Tossy type and using the Hook Plate Samir EJAM, Thomas LIND, Boe FALKENBERG From
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 4, 441-44 ORIGINAL STUDY Surgical treatment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular dislocation Tossy type and using the Hook Plate Samir EJAM, Thomas LIND, Boe FALKENBERG From
Case Report Rotator Interval Lesion and Damaged Subscapularis Tendon Repair in a High School Baseball Player
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890721, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890721 Case Report Rotator Interval Lesion and Damaged Subscapularis Tendon Repair in a High School Baseball
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890721, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890721 Case Report Rotator Interval Lesion and Damaged Subscapularis Tendon Repair in a High School Baseball
Retrospective Analysis of Arthroscopic Management of Glenohumeral Degenerative Disease
 Retrospective Analysis of Arthroscopic Management of Glenohumeral Degenerative Disease Geoffrey S. Van Thiel, M.D., M.B.A., Steven Sheehan, B.S., Rachel M. Frank, B.S., Mark Slabaugh, M.D., Brian J. Cole,
Retrospective Analysis of Arthroscopic Management of Glenohumeral Degenerative Disease Geoffrey S. Van Thiel, M.D., M.B.A., Steven Sheehan, B.S., Rachel M. Frank, B.S., Mark Slabaugh, M.D., Brian J. Cole,
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair CHRISTOPHER S. AHMAD, MD; WILLIAM N. LEVINE, MD; LOUIS U. BIGLIANI, MD Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair offers less pain, quicker recovery, and less stiffness compared
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair CHRISTOPHER S. AHMAD, MD; WILLIAM N. LEVINE, MD; LOUIS U. BIGLIANI, MD Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair offers less pain, quicker recovery, and less stiffness compared
Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder
 original research ARTICLE Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder Z Oschman (MB ChB, DCH, MSc (Sports Medicine)) 1 C Janse
original research ARTICLE Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder Z Oschman (MB ChB, DCH, MSc (Sports Medicine)) 1 C Janse
Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Speaker Disclosure
 Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Eric C. McCarty, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Eric C. McCarty, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Repair of Full Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Gender, Age, and Other Factors AfSecting Outcome SECTION 11
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 367, pp. 243-255 0 1999 Lippincolt Williams & Wilkins, Inc. SECTION 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Repair of Full Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Gender, Age, and Other
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 367, pp. 243-255 0 1999 Lippincolt Williams & Wilkins, Inc. SECTION 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Repair of Full Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Gender, Age, and Other
Rotator Cuff Tear FAQs
 What is the rotator cuff? The rotator cuff is the joined-up of tendon of four of the muscles which move the shoulder, namely the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor. While most
What is the rotator cuff? The rotator cuff is the joined-up of tendon of four of the muscles which move the shoulder, namely the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor. While most
The anteromedial approach for shoulder arthroplasty: The importance of the anterior deltoid
 The anteromedial approach for shoulder arthroplasty: The importance of the anterior deltoid David R. J. Gill, MB, ChB, FRACS, a Robert H. Cofield, MD, b and Charles Rowland, MS, c Joondalup, Australia,
The anteromedial approach for shoulder arthroplasty: The importance of the anterior deltoid David R. J. Gill, MB, ChB, FRACS, a Robert H. Cofield, MD, b and Charles Rowland, MS, c Joondalup, Australia,
PATIENT EDUCATION. Why Let Shoulder Pain Hold You Back? Embrace life with a ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR
 PATIENT EDUCATION Why Let Shoulder Pain Hold You Back? Embrace life with a ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR What to Expect Open shoulder surgery often requires a short stay in the hospital, whereas arthroscopic repairs
PATIENT EDUCATION Why Let Shoulder Pain Hold You Back? Embrace life with a ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR What to Expect Open shoulder surgery often requires a short stay in the hospital, whereas arthroscopic repairs
Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes. Patrick Birmingham, MD
 Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes Patrick Birmingham, MD Outline Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Subjective Outcomes Objective Outcomes Timing Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Sauerbrey Arthroscopy 2005 Twenty-six patients
Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes Patrick Birmingham, MD Outline Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Subjective Outcomes Objective Outcomes Timing Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Sauerbrey Arthroscopy 2005 Twenty-six patients
Technical Note. The Accessory Posteromedial Portal Revisited: Utility for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Technical Note The Accessory Posteromedial Portal Revisited: Utility for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair R. Edward Glenn, Jr., M.D., L. Pearce McCarty, M.D., and Brian J. Cole, M.D., M.B.A. Abstract:
Technical Note The Accessory Posteromedial Portal Revisited: Utility for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair R. Edward Glenn, Jr., M.D., L. Pearce McCarty, M.D., and Brian J. Cole, M.D., M.B.A. Abstract:
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Part II: Rotator Cuff Repair, Day of Surgery and Postoperative Course
 Part II: Rotator Cuff Repair, Day of Surgery and Postoperative Course Benjamin W. Sears, MD 303-321-1333 western-ortho.com denvershoulder.com Day of Surgery Most patients will undergo outpatient surgery
Part II: Rotator Cuff Repair, Day of Surgery and Postoperative Course Benjamin W. Sears, MD 303-321-1333 western-ortho.com denvershoulder.com Day of Surgery Most patients will undergo outpatient surgery
Controversies and Alternative Approaches
 Solid Foundations for Successful Shoulder Surgery Advantages of the 70 lens in specific procedures are shown in Table 1. Figure 1 Arthroscopic images of a loose body in an axillary pouch as viewed from
Solid Foundations for Successful Shoulder Surgery Advantages of the 70 lens in specific procedures are shown in Table 1. Figure 1 Arthroscopic images of a loose body in an axillary pouch as viewed from
Arthroscopic Tenodesis Through Positioning Portals to Treat Proximal Lesions of the Biceps Tendon
 Cell Biochem Biophys (2014) 70:1499 1506 DOI 10.1007/s12013-014-0071-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Arthroscopic Tenodesis Through Positioning Portals to Treat Proximal Lesions of the Biceps Tendon Ji Shen Qing-feng
Cell Biochem Biophys (2014) 70:1499 1506 DOI 10.1007/s12013-014-0071-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Arthroscopic Tenodesis Through Positioning Portals to Treat Proximal Lesions of the Biceps Tendon Ji Shen Qing-feng
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Mastering the Essentials
 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Mastering the Essentials Dr. Robert Hunter Director, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center Heart of the Rockies Regional Medical Center Salida, Colorado CU Sports Medicine
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Mastering the Essentials Dr. Robert Hunter Director, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center Heart of the Rockies Regional Medical Center Salida, Colorado CU Sports Medicine
ABSTRACT. Background: Many causes can lead to shoulder pain, and subacromial impingement syndrome (SIS) is the most
 Diminutive Incision Acromioplasty Assisted with Arthroscopy in the Treatment of Chinese Patients with Subacromial Impingement Syndrome Z-Q Wen, J Pan, Z Chen, J-Y Du, P-C Gu, X-J Lin ABSTRACT Background:
Diminutive Incision Acromioplasty Assisted with Arthroscopy in the Treatment of Chinese Patients with Subacromial Impingement Syndrome Z-Q Wen, J Pan, Z Chen, J-Y Du, P-C Gu, X-J Lin ABSTRACT Background:
3712 Southwestern Blvd, Orchard Park 14127, Park Club Lane Suite 225, Williamsville 14221, Subacromial Decompression
 The Knee Center of WNY Dr. Michael A. Parentis Dr. Keith C. Stube Matthew J. Mazurczal< RPAC Jeff Rassman RPAC Breanne Finucane RPAC Allison Nixon RPAC 3712 Southwestern Blvd, Orchard Park 14127, 508-8252
The Knee Center of WNY Dr. Michael A. Parentis Dr. Keith C. Stube Matthew J. Mazurczal< RPAC Jeff Rassman RPAC Breanne Finucane RPAC Allison Nixon RPAC 3712 Southwestern Blvd, Orchard Park 14127, 508-8252
( 1 ) Ball and socket. Shoulder capsule. Rotator cuff.
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, arthro
Shoulder Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, arthro
SUB ACROMIAL DECOMPRESSION SURGERY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 SUB ACROMIAL DECOMPRESSION SURGERY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION If your shoulder has not recovered with appropriate conservative management, the next step to consider is
SUB ACROMIAL DECOMPRESSION SURGERY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION If your shoulder has not recovered with appropriate conservative management, the next step to consider is
Orthopaedics. Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Orthopaedics Shoulder Arthroscopy Shoulder Arthroscopy_PRINT.indd 1 5/10/2016 11:46:08 AM Understanding shoulder problems The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm
Orthopaedics Shoulder Arthroscopy Shoulder Arthroscopy_PRINT.indd 1 5/10/2016 11:46:08 AM Understanding shoulder problems The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs
 Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Anatomic AC Joint TightRope Fixation
 Arthroscopic Anatomic Stabilization of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation using the TightRope System Surgical Technique Anatomic AC Joint TightRope Fixation Background Disruption of the coracoclavicular
Arthroscopic Anatomic Stabilization of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation using the TightRope System Surgical Technique Anatomic AC Joint TightRope Fixation Background Disruption of the coracoclavicular
ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAM
 ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAM The Arthromentor The first commandment: "Thou shalt stop when frustrated so as to avoid breaking expensive equipment" 1. A signup sheet should be used to
ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAM The Arthromentor The first commandment: "Thou shalt stop when frustrated so as to avoid breaking expensive equipment" 1. A signup sheet should be used to
Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression Ms. Ruth Delaney Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon www.sportssurgeryclinic.com INTRODUCTION
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression Ms. Ruth Delaney Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon www.sportssurgeryclinic.com INTRODUCTION
rotator cuff injuries among patients under 50 years of age
 Original Article Evaluation of the results from arthroscopic repair on rotator cuff injuries among patients Alberto Naoki Miyazaki 1, Marcelo Fregoneze 2, Pedro Doneux Santos 3, Luciana Andrade da Silva
Original Article Evaluation of the results from arthroscopic repair on rotator cuff injuries among patients Alberto Naoki Miyazaki 1, Marcelo Fregoneze 2, Pedro Doneux Santos 3, Luciana Andrade da Silva
Functional Outcomes after Arthroscopic Single Row Rotator Cuff Repair: A Retrospective Study of 40 Cases
 Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Abstract Functional Outcomes after Arthroscopic Single Row Rotator Cuff Repair: A Retrospective Study of 40 Cases Purpose: Purpose of the study is to report
Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Abstract Functional Outcomes after Arthroscopic Single Row Rotator Cuff Repair: A Retrospective Study of 40 Cases Purpose: Purpose of the study is to report
Telephone Arthroscopic rotator cuff debridement icd 9 P.O. Box 189 Navan, ON, K4B 1J4 Canada. Sitemap
 Telephone 613-835-9490 Arthroscopic rotator cuff debridement icd 9 P.O. Box 189 Navan, ON, K4B 1J4 Canada Sitemap 14-3-2018 ICD - 9 -CM Diagnosis Codes;. M75 Shoulder lesions. M75.0 Adhesive capsulitis
Telephone 613-835-9490 Arthroscopic rotator cuff debridement icd 9 P.O. Box 189 Navan, ON, K4B 1J4 Canada Sitemap 14-3-2018 ICD - 9 -CM Diagnosis Codes;. M75 Shoulder lesions. M75.0 Adhesive capsulitis
 The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
Selected. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 763 Selected The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Printed with permission of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. A modified version of this article, as well as other lectures presented
763 Selected The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Printed with permission of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. A modified version of this article, as well as other lectures presented
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, "arthro" (joint)
Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, "arthro" (joint)
Impingement syndrome. Clinical features. Management. Rotator cuff tear diagnosed. Go to rotator cuff tear
 Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
OBJECTIVES. Therapists Management of Shoulder Instability SHOULDER STABILITY SHOULDER STABILITY WHAT IS SHOULDER INSTABILITY? SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 Therapists Management of Shoulder Instability Brian G. Leggin, PT, DPT, OCS Lead Therapist, Penn Therapy and Fitness at Valley Forge Adjunct Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, University
Therapists Management of Shoulder Instability Brian G. Leggin, PT, DPT, OCS Lead Therapist, Penn Therapy and Fitness at Valley Forge Adjunct Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, University
Icd 10 rotator cuff repair
 Search Search pages & people Search Search Search pages & people Search Icd 10 rotator cuff repair UPDATED. February 4, 2016. Question: Patient has been seen in office during the global period after a
Search Search pages & people Search Search Search pages & people Search Icd 10 rotator cuff repair UPDATED. February 4, 2016. Question: Patient has been seen in office during the global period after a
Arthroscopic biceps tenodesis is indicated for the
 Technical Note Arthroscopic Biceps Tenodesis Anthony A. Romeo, M.D., Augustus D. Mazzocca, M.D., and Joseph C. Tauro, M.D. Abstract: Arthroscopic biceps tenodesis is indicated for the treatment of severe
Technical Note Arthroscopic Biceps Tenodesis Anthony A. Romeo, M.D., Augustus D. Mazzocca, M.D., and Joseph C. Tauro, M.D. Abstract: Arthroscopic biceps tenodesis is indicated for the treatment of severe
Work-related shoulder pain
 Work-related shoulder pain Stadler Kirsten M.B., Ch.B. (1987) (Pret), M. Med. (Orthop) (1998) (Stell.), Orthopaedic Surgeon, Room 333, Louis Leipoldt Medical Centre, Broadway Street, Bellville Cape Town
Work-related shoulder pain Stadler Kirsten M.B., Ch.B. (1987) (Pret), M. Med. (Orthop) (1998) (Stell.), Orthopaedic Surgeon, Room 333, Louis Leipoldt Medical Centre, Broadway Street, Bellville Cape Town
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Rotator Cuff Repair in Patients over 75 Years of Age: Clinical Outcome and Repair Integrity
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:420-427 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.420 Rotator Cuff Repair in Patients over 75 Years of Age: Clinical Outcome and Repair Integrity Jung
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:420-427 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.420 Rotator Cuff Repair in Patients over 75 Years of Age: Clinical Outcome and Repair Integrity Jung
Biceps Tendon Rupture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about Biceps Tendon Rupture must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about Biceps Tendon Rupture must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes
 Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
Management of arthritis of the shoulder. Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
SHOULDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION. Disclosure. Case. Learning Objectives MRI. Plan? 3/23/2017 5
 Disclosure Doc, My Shoulder Keeps me Up at Night! Evaluation and Treatment of Atraumatic Shoulder Pain Matthew F. Dilisio, MD Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, CHI Health Orthopedics Assistant Professor, Creighton
Disclosure Doc, My Shoulder Keeps me Up at Night! Evaluation and Treatment of Atraumatic Shoulder Pain Matthew F. Dilisio, MD Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, CHI Health Orthopedics Assistant Professor, Creighton
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections
 Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
S ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stiffness after arthroscopic shoulder surgery: incidence, management and classification
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 S ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stiffness after arthroscopic shoulder surgery: incidence, management and classification Puneet Monga, Holly N. Raghallaigh & Lennard Funk Upper Limb
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 S ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stiffness after arthroscopic shoulder surgery: incidence, management and classification Puneet Monga, Holly N. Raghallaigh & Lennard Funk Upper Limb
Options for the Irreparable RCT 3/9/2018. Your Patient has an Irreparable RC Tear: What Now? Asheesh Bedi, MD
 Your Patient has an Irreparable RC Tear: What Now? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery Head Team
Your Patient has an Irreparable RC Tear: What Now? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery Head Team
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
