Fusion-segment of high-grade Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: 2-year follow-up
|
|
|
- Lynne York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 730 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, x. li, l. xu, q. kong ORIGINAL STUDY Fusion-segment of high-grade Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: 2-year follow-up Xiaolong Li, Lian Xu, Qingquan Kong Department of Orthopedics, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China The clinical efficacy of reduction and fusion surgery and the suitable range of fusion-segment were evaluated in 12 pediatric patients treated for high-grade spondylolisthesis. Pre/post-operative clinical and radiological assessments were analyzed. A transient L5 nerve root paralysis was observed in one patient with L5 spondylolisthesis. No degenerative spondylolisthesis or adjacent segmental instability occurred above the fusion segments. In conclusion, we suggest that, in case of spondylolisthesis without severe structural scoliosis deformity or only associated with lumbosacral deformity, the posterior ligament complex should be protected in case of adjacent segmental instability and spondylolisthesis. If the spondylolisthesis is complicated with severe structural scoliosis deformity (Cobb 70 ), in principle, the treatment should be performed according to the characteristics of the two diseases respectively. Although satisfactory clinical outcome has been reported after in situ fusion (11,14,19), this procedure was also probably associated with higher rates of pseudarthrosis, subsequent slip progression and necessitates extended fusion to a higher normal disc level in terms of stability (1,5). In order to reduce the postoperative complications, other investigators recommended reduction and fusion (20-21). Reduction of the spondylolisthesis could enhance fusion rate. Moreover, reduction and fusion could also restore the segmental lordosis, improve lumbosacral alignment and therefore improve the sagittal profile of the spine (8-9,15). Keywords : high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis ; reduction and fusion ; posterior approach ; fusion-segment. INTRODUCTION Among pediatric patients, surgical intervention is generally indicated for severe spondylolisthesis. The primary goals of surgical treatment are neurological decompression and stability reconstruction. The investigators have recommended fusion in situ or deformity reduction and fusion (10-11,24). n Xiaolong Li n Lian Xu n Qingquan Kong Department of Orthopedics, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China Correspondence : Qingquan Kong. Department of Orthopaedics, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, No. 37 Guoxue Lane, Wainan Street, Wuhou District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China, kqqspine@163.com 2016, Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. No benefits or funds were received in support of this study. The Acta authors Orthopædica report Belgica, no conflict Vol. of 82 interests li-.indd /01/17 10:37
2 fusion-segment of high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis 731 However, adjacent segment disease (ASD) and slip progression occurred after reduction and fusion for some pediatric patients with severe lumbar spondylolisthesis. As previously reported, the fusion-segment could be regarded as one of the most important risk factors (16-18). Most authors believed that mono-segmental fusion could reduce the incidence of ASD more effectively compared with multi-segmental fusion. Therefore, it s very important to find the most appropriate extension of fusion for patients with high-grade spondylolisthesis, in order to reduce the incidence of such complications. Based on the study mentioned above, we summarized our experience in pediatric patients with highgrade lumbar spondylolisthesis by reduction and fusion through posterior approach. METHODS Inclusion and exclusion criteria Inclusion criteria are: (1) Meyerding grade III; (2) the surgical procedures include posterior pedicle screws fixation, lamina/facet and disc resection and decompression, slip reduction, intervertebral and posterolateral lumbar fusion; (3) a minimum of 2-years follow-up; (4) preoperative, postoperative and follow-up imaging data including wholespine standing anteroposterior (AP) and lateral radiographs, lumbar dynamic radiographs and 3D CT reconstruction of surgical fixation and fusion segments. Exclusion criteria were: (1) age 18 years old; (2) patients with high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis treated with in situ fusion by posterior approach. There were 2 males and 10 females with an average age of 11.3 years old (range, 7-15). The course of the disease was between 5 months and 6.3 years, with an average of 2.4 years. The clinical manifestations included low back pain, aggravated when standing and after walking, combined with pain in bilateral lower limbs in 8 cases and unilateral pain in 4 cases; intermittent claudication in 9 cases. Preoperative examination showed weakened plantar flexion strength in 3 cases, weakened dorsal extensor strength in 5 cases and symptoms of cauda equina damage in one case. Frankel grade showed D grade in 8 cases and E grade in 4 cases. Preoperative mean VAS of low back pain and leg pain was 6.58 (± 1.00) and 7.17 (± 1.12) respectively. The mean ODI was (± 10.00) %. Clinical classifications were: (1) according to the level of spondylolisthesis: 10 patients at L5, 2 patients at both L4 and L5 while only L5 was classified as severe spondylolisthesis; (2) according to Meyerding classification: 7 cases of grade III, and 5 cases of grade IV; (3) according to Marchetti-Bartolozzi classification: all cases were developmental spondylolisthesis, among which 9 cases were classified as high-dysplastic type, while 3 cases were classified as low-dysplastic type; (4) according to Spinal Deformity Study Group (SDSG) classification: 7 cases of type 4, 4 cases of type 5, 1 case of type 6. Preoperative radiographic assessments were: mean vertebral slip percentage (SP) measured by Taillard s method was (± 12.38) %; mean SDSG lumbosacral angle (L5S1 angle of kyphosis) was (± 6.04) ; pelvic incidence (PI) of all patients were greater than 60, with an average of (± 3.97). 2 cases had combined scoliosis deformity. All 12 cases were followed up for 24 to 48 months with an average of 35 (± 8) months. Surgical technique (1) Nerve root decompression: the efferent and descending nerve roots, with vertebral facet as the center, were decompressed bilaterally; (2) Intervertebral loosening: after bilateral resection of facet joints and intervertebral disc tissue of target segment, a Cobb detacher or an osteotome with proper width was inserted into the intervertebral space to pry and loosen the intervertebral space, using the posterosuperior angle of the lower vertebral as a fulcrum; (3) Slip reduction: the slipped vertebrae was reduced and fixed with two-dimensional Schanz screws, using a cantilever pulling technique. In principle, the spondylolisthesis should be reduced within Meyerding grade II. A sufficient loosening of the intervertebral space was indicated before slip reduction. For spondylolisthesis of high-dysplastic type, it is necessary to resect the superior margin li-.indd /01/17 10:37
3 732 x. li, l. xu, q. kong of the dome-shaped S1 vertebral body in order to reduce not only the slip but also kyphosis; (4) Bone graft fusion: This method was a combined application of intervertebral and posterolateral fusion. To avoid the L5 nerve root palsy, spinal shortening is recommended for this procedure. The spinal fusion range was comprehensively determined according to the concept of unstable zone (9) and characteristics of spinal deformity. In this group, 3 cases underwent bi-segmental fixation at L4-S1, and 9 cases underwent mono-segmental fixation at L5-S1. After fixation, intervertebral and posterolateral fusion were performed on the corresponding segments. Intraoperative screws implantation was performed using two-dimensional navigation in 3 cases, while others were performed with manual implantation. Postoperative outcome evaluation The operation time, blood loss and postoperative complications were recorded. The nerve function of patients was evaluated by using the Frankel grading system. The visual analogue scale (VAS) for leg pain and back pain was used. Preoperative and postoperative lower limb function and daily activity state was assessed by Oswestry Disability Index (ODI). Radiological assessments included a whole-spine standing lateral radiograph, a 3D CT reconstruction, PI and lumbosacral angle (LSA). In plain radiographs, the degree of anterior displacement was evaluated by Meyerding s method (7) and Taillard s method (22). Statistical analysis Results were analyzed by ANOVA and Student s t-test, with significance at P< 0.05, using SPSS software (version 17.0, IBM Inc., Chicago). RESULTS The operation time was mins with an average of 181 ± 26 mins. The blood loss was ml with an average of 391 ± 77 ml. The success rate of screws implantation was 100%. One patient developed cerebrospinal fluid leakage. The dura mater was closed by a fine continuous suture, and drainage was continued for 5 days with satisfactory results. 2 patients developed urinary tract infection and were treated with antibiotics until the body temperature and white blood cells level had been normal for 3 days. No postoperative superficial or deep wound infection was observed. A transient L5 nerve root paralysis was observed in one patient with L5 spondylolisthesis (Meyerding grade III, highdysplastic, SDSG type 6). But the symptoms resolved spontaneously at 4 weeks after postoperation (Figure 1). The nerve function of each-case was classified as Frankel grade E at 12 months follow up. The average VAS scores of leg pain and low back pain in all cases were 1.08 (± 0.67) and 1.33 (± 0.89). The average ODI was (± 5.21) %. In addition, the VAS score and ODI of low back pain at 12 months follow up were significantly lower compared with that at 4 weeks after operation, and the difference was statistically significant (Table I.). The average PI was (± 5.46). The average percentage of vertebral slip measured by Taillard method was (± 7.58) %. The average LSA was (± 2.88). All the parameters above were statistically different compared with the preoperative parameters (P < 0.05). Visible growth of mature bone bridge was found and no broken screw or rod was observed in the 3D CT of 11 cases at 12 months follow up. During the follow-up period, no patient had degenerative spondylolisthesis or adjacent segmental instability above the fusion segments. One patient had scoliosis deformity and was completely corrected at 12 months follow up (Figure 2). 11 patients (91.7 %) showed favorable results. DISCUSSION As previously reported (7,13), high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis (Meyerding grade III) often come forth with different degrees of spinal deformity. The deformity mainly included a lumbosacral angle with kyphosis deformity (SDSG type 5) and spinal sagittal imbalance (SDSG type 6). The former was mainly due to the change of lumbosacral muscle force along with the continuous progression of lumbar spondylolisthesis, while the latter was also known as idiopathic scoliosis. li-.indd /01/17 10:37
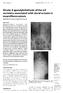
4 fusion-segment of high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis 733 Fig. 1. A 8 year-old girl with L5 spondylolisthesis (Meyerding III, high-dysplastic, SDSG 6) underwent the reduction of L5, spinal canal decompression and L5-S1 fixation and fusion by posterior approach. Preoperative AP/lateral X-ray (1a); Preoperative CT 3D reconstruction (1b) and MRI (1c) showed high-grade spondylolisthesis ; X-ray (1d) and CT 3D reconstruction (1e) at 12M FU showed good reduction and correction. Most investigators believed that it was very important to correct LSA for patients with sagittal plane deformity or loss of balance for high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis (1,10,16). The sagittal plane deformity and loss of balance would then be spontaneously corrected after the correction of LSA. For pediatric patients with high-grade (SDSG type 5, 6) lumbar spondylolisthesis, to correct LSA deems important (4,6). In recent years, many researchers have investigated adjacent segmental instability and spondylolisthesis on pediatric patients with high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis. These patients underwent reduction and fusion, and the occurrence rate was 5-43% (2,24). Most investigators believed that multiple factors contributed to this postop- erative complication, while the effects of fusionsegment and secondary injury of spinal posterior ligament complex were two important factors. The concept of the lumbosacral unstable zone was proposed by Lamartina to explain an adjacent L4 segmental instability after spinal fusion on L5-S1 segments in pediatric patients with high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis (9-10). He also proposed that all the vertebras located in the unstable zone should be fixed and fused, except for cases with complete reduction, LSA correction, pelvic inversion correction and sagittal spinal alignment recovery. In fact, the main idea of this concept was to fix the upper vertebra with proper PI angle. If the PI were greater than 60, the incidence of adjacent segmental instability or even slipping would be sig- li-.indd /01/17 10:37
5 734 x. li, l. xu, q. kong Table I. Radiographic and clinical improvement after surgical correction (Mean ±SD) PI( ) SP(%) LSA ( ) VAS ODI(%) Preop ± ± ± ± ± ±8.76 4W Postop ±5.50* 13.92±4.23* -6.63±2.08* 3.75±1.22* 1.25±0.75* 22.12±5.76* LBP 12M FU 53.67±5.48* 14.67±4.52* -6.61±1.29* 1.33±0.89*# 1.08±0.67* 13.84±4.59*# Statistic F= F= F= F= F= F= P=0.000 P=0.000 P=0.000 P=0.000 P=0.000 P=0.000 W: week(s); M: month(s); FU: follow-up; SP, slip percentage; LSA, Lumbosacral angle; ODI, oswestry disability index; VAS, visual analog scale. LBP, low back pain; LP, leg pain. *Versus preop. P < 0.05; # 12M FU versus 4 W postop. P < 0.05 LP Fig. 2. A 12 year-old girl with L5 spondylolisthesis (Meyerding Ⅳ, high-dysplastic, SDSG 5) and scoliosis underwent reduction of L5, L5-S1 spinal canal decompression and L4-S1 fixation by posterior approach. Preoperative AP/lateral X-ray (2a); Preoperative CT 3D reconstruction (2b) showed spondylolisthesis (Meyerding Ⅳ ) and scoliosis; AP/lateral X-ray (2d) at 6M FU, showed spondylolisthesis was reduced to Meyerding 0 but scoliosis had no correction; X-ray (2e) and CT 3D reconstruction (2c) at 12M FU showed good reduction and correction, as well as solid bony fusion. nificantly increased. Holdsworth first introduced the notion of posterior ligament complex (PLC), the second factor responsible of postoperative adjacent instability (12). PLC is the main component of the posterior column, which includes supraspinal ligament, interspinal ligament, ligament flavum and bilateral facet joint capsule. The results of Panjabi et al showed that the supraspinal ligament, interspinal ligament and ligament flavum play important roles in maintaining the stability of spinal flexion, and the li-.indd /01/17 10:37
6 fusion-segment of high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis 735 PLC was defined as endogenous ligament stabilizing system (19). Asano et al also demonstrated that the supraspinal ligament and interspinal ligament showed significant effect on the tension load and strength coefficients, and played an important role in maintaining the stability of PLC (3). However, for patients with high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis, fusion surgery may cause various degrees of direct or indirect damages on PLC, which affects the stability of the whole spine and accelerates the adjacent segments degeneration and even leads to adjacent segmental instability or slipping. Therefore, no matter which technique is used in the vertebral fusion treatment with high-grade lumbar spondylolisthesis, PLC must be protected carefully to minimize the damage during the surgery. In our series, PI in all patients was greater than 60. Among them, two cases associated scoliosis deformity (one classified as nonstructural scoliosis, and the other as structural scoliosis) with a double segmental slippage (L4-5). Three cases underwent bisegmental fixation and fusion at L4-S1, and 9 cases underwent single segmental fixation and fusion at L5-S1. At final follow-up, the clinical efficacy was very great. And at 12 months follow up, visible growth of mature bone bridge was found and no broken screw or rod was observed in 3D CT of 11 cases. During the follow-up period, no patient had degenerative spondylolisthesis or adjacent segmental instability above the fusion segments. Although above-mentioned treatments showed a satisfactory clinical efficacy in the follow-up of 2-year, some limitations appear: a) limited number of cases, b) absence of control group, c) no blind revision. CONCLUSION In conclusion, we suggest that, in case of spondylolisthesis without severe structural scoliosis deformity or only associated with lumbosacral deformity, the posterior ligament complex should be protected in case of adjacent segmental instability and spondylolisthesis. If the spondylolisthesis is complicated with severe structural scoliosis deformity (Cobb 70 ), in principle, the treatment should be performed according to the characteristics of the two diseases respectively. REFERENCES 1. Agabegi SS, Fischgrund JS. Contemporary management of isthmic spondylolisthesis: pediatric and adult. The Spine Journal 2010 ; 10(6) : Akamaru T, Kawahara N, Yoon ST, et al. Adjacent segment motion after a simulated lumbar fusion in different sagittal alignments: a biomechanical analysis. Spine 2003 ; 28(14) : Asano S, Kaneda K, Umehara S, et al. The Mechanical Properties of the Human L4-5 Functional Spinal Unit During Cyclic Loading: The Structural Effects of the Posterior Elements. Spine 1992 ; 17(11) : Boxall D, Bradford DS, Winter RB, et al. Management of severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 1979 ; 61(4) : Bradford DS, Gotfried Y. Staged salvage reconstruction of grade-iv and V spondylolisthesis. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 1987 ; 69(2) : Crostelli M, Mazza O. AIS and spondylolisthesis. European Spine Journal 2013 ; 22(2) : Hresko MT, Labelle H, Roussouly P, et al. Classification of high-grade spondylolistheses based on pelvic version and spine balance: possible rationale for reduction. Spine 2007 ; 32(20) : Labelle H, Roussouly P, Chopin D, et al. Spino-pelvic alignment after surgical correction for developmental spondylolisthesis. European Spine Journal 2008 ; 17(9) : Lamartina C. A square to indicate the unstable zone in severe spondylolisthesis. European Spine Journal 2001 ; 10(5) : Lamartina C, Zavatsky JM, Petruzzi M, et al. Novel concepts in the evaluation and treatment of high-dysplastic spondylolisthesis. European Spine Journal 2009 ; 18(1) : Lamberg T, Remes V, Helenius I, et al. Uninstrumented in situ fusion for high-grade childhood and adolescent isthmic spondylolisthesis: long-term outcome. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 2007 ; 89(3) : Lee H-M, Kim H-S, Kim D-J, et al. Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting posterior ligament complex injury in thoracolumbar spinal fractures. Spine 2000 ; 25(16) : Mac-Thiong J-M, Labelle H. A proposal for a surgical classification of pediatric lumbosacral spondylolisthesis based on current literature. European Spine Journal 2006 ; 15(10) : Martiniani M, Lamartina C, Specchia N. In situ fusion or reduction in high-grade high dysplastic developmental spondylolisthesis (HDSS). European Spine Journal 2012 ; 21(1) : Min K, Liebscher T, Rothenfluh D. Sacral dome resection and single-stage posterior reduction in the treatment of high-grade high dysplastic spondylolisthesis in adolescents li-.indd /01/17 10:37
7 736 x. li, l. xu, q. kong and young adults. European Spine Journal 2012 ; 21(6) : Miyakoshi N, Abe E, Shimada Y, et al. Outcome of onelevel posterior lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis and postoperative intervertebral disc degeneration adjacent to the fusion. Spine 2000 ; 25(14) : Okuda Sy, Iwasaki M, Miyauchi A, et al. Risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration after PLIF. Spine 2004 ; 29(14) : Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, et al. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine 2004 ; 29(17) : Poussa M, Remes V, Lamberg T, et al. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis in adolescence with reduction or fusion in situ: long-term clinical, radiologic, and functional outcome. Spine 2006 ; 31(5) : Ruf M, Koch H, Melcher RP, et al. Anatomic reduction and monosegmental fusion in high-grade developmental spondylolisthesis. Spine 2006 ; 31(3) : Shufflebarger HL, Geck MJ. High-grade isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis: monosegmental surgical treatment. Spine 2005 ; 30(6S) : S42-S Taillard W. Spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 1954 ; 24(2) : Transfeldt EE, Mehbod AA. Evidence-based medicine analysis of isthmic spondylolisthesis treatment including reduction versus fusion in situ for high-grade slips. Spine 2007 ; 32(19) : S126-S Zencica P, Chaloupka R, Hladíková J, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbosacral fusion in spondylolisthesis: a retrospective radiological and clinical analysis. Acta chirurgiae orthopaedicae et traumatologiae Cechoslovaca 2010 ; 77(2) : li-.indd /01/17 10:37
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Spondylolysis. Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down.
 Spondylolysis Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down. Thomas J Kishen Spine Surgeon Sparsh Hospital for Advanced Surgeries Bangalore Spondylolysis Defect in the
Spondylolysis Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down. Thomas J Kishen Spine Surgeon Sparsh Hospital for Advanced Surgeries Bangalore Spondylolysis Defect in the
Coflex TM for Lumbar Stenosis with
 Coflex TM for Lumbar Stenosis with Segmental Instability : 1 yr outcomes Eun-Sang Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical Professor Dept of Neurosurgery Samsung Medical Center Seoul, Korea Surgery for Spinal Stenosis
Coflex TM for Lumbar Stenosis with Segmental Instability : 1 yr outcomes Eun-Sang Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical Professor Dept of Neurosurgery Samsung Medical Center Seoul, Korea Surgery for Spinal Stenosis
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients
 Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan. Hong Hui Hospital, Xi an Jiaotong University College. of Medicine, Xi an, Shaanxi , China
 Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China The difference of occurring superior adjacent segment pathology after lumbar posterolateral fusion by using two different pedicle screw insertion techniques
Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China The difference of occurring superior adjacent segment pathology after lumbar posterolateral fusion by using two different pedicle screw insertion techniques
The clinical features and surgical treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis: A review of 112 patientsos4_
 Orthopaedic Surgery (2009), Volume 1, No. 3, 176 183 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The clinical features and surgical treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis: A review of 112 patientsos4_030 176..183 Wei Liu MD,
Orthopaedic Surgery (2009), Volume 1, No. 3, 176 183 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The clinical features and surgical treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis: A review of 112 patientsos4_030 176..183 Wei Liu MD,
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Spinologics.com. Scoliosis Surgery Simulation
 Scoliosis Surgery Simulation Finite Element (FE) Models Finite element model: mathematical method widely used in traditional engineering fields (aeronautics, car industry, civil engineering). Principle:
Scoliosis Surgery Simulation Finite Element (FE) Models Finite element model: mathematical method widely used in traditional engineering fields (aeronautics, car industry, civil engineering). Principle:
L5-S1 Spondylolysis/listhesis in children & adolescents: When is surgery indicated? Hubert Labelle, MD
 L5-S1 Spondylolysis/listhesis in children & adolescents: When is surgery indicated? Hubert Labelle, MD Wiltse, Newman and Macnab Classification Clin Orthop 1976;117:23-29 Type I: Congenital spondylolisthesis
L5-S1 Spondylolysis/listhesis in children & adolescents: When is surgery indicated? Hubert Labelle, MD Wiltse, Newman and Macnab Classification Clin Orthop 1976;117:23-29 Type I: Congenital spondylolisthesis
Reduction of High-grade Spondylolisthesis Using a Transvertebral Surgical Approach in a Child. A Case Report and Review of the Literature.
 Reduction of High-grade Spondylolisthesis Using a Transvertebral Surgical Approach in a Child. A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Kadir KOT L Tamer TUNÇKAYA Turgay B LGE Department of Neurosurgery,
Reduction of High-grade Spondylolisthesis Using a Transvertebral Surgical Approach in a Child. A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Kadir KOT L Tamer TUNÇKAYA Turgay B LGE Department of Neurosurgery,
5/27/2016. Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation. Disclosures. LLIF Approach
 Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation Joseph M. Zavatsky, M.D. Spine & Scoliosis Specialists Tampa, FL Disclosures Consultant - Zimmer / Biomet, DePuy Synthes Spine,
Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation Joseph M. Zavatsky, M.D. Spine & Scoliosis Specialists Tampa, FL Disclosures Consultant - Zimmer / Biomet, DePuy Synthes Spine,
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012
 Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus intertransverse fusion in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2006;14(1):21-6 Posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus intertransverse fusion in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis DN Inamdar, M Alagappan, L Shyam, S Devadoss,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2006;14(1):21-6 Posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus intertransverse fusion in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis DN Inamdar, M Alagappan, L Shyam, S Devadoss,
ASJ. Radiologic and Clinical Courses of Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis (10 25 ) after a Short-Segment Fusion. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 570 Kyu Yeol Clinical Lee et al. Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.4.570 Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 Radiologic and Clinical Courses of
Asian Spine Journal 570 Kyu Yeol Clinical Lee et al. Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.4.570 Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 Radiologic and Clinical Courses of
/ 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66
 1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
Lumbar Facet Joint Replacement
 Rome Spine 2011 THE SPINE TODAY International Congress Rome 6-7th December 2011 Lumbar Facet Joint Replacement Prof. Dr. Karin Büttner-Janz Past President International Society for the Advancement of Spine
Rome Spine 2011 THE SPINE TODAY International Congress Rome 6-7th December 2011 Lumbar Facet Joint Replacement Prof. Dr. Karin Büttner-Janz Past President International Society for the Advancement of Spine
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions:
 Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions: Radiating leg pain Greater leg / buttock pain than back pain Severe pain sets in when walking as
Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions: Radiating leg pain Greater leg / buttock pain than back pain Severe pain sets in when walking as
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
The effect of body mass index on lumbar lordosis on the Mizuho OSI Jackson spinal table
 35 35 40 The effect of body mass index on lumbar lordosis on the Mizuho OSI Jackson spinal table Authors Justin Bundy, Tommy Hernandez, Haitao Zhou, Norman Chutkan Institution Orthopaedic Department, Medical
35 35 40 The effect of body mass index on lumbar lordosis on the Mizuho OSI Jackson spinal table Authors Justin Bundy, Tommy Hernandez, Haitao Zhou, Norman Chutkan Institution Orthopaedic Department, Medical
Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments
 Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments Scoliosis Spinal Deformity 3-dimensional deformity affecting all 3 planes Can be difficult to visualize with 2-dimensional radiographs Kyphosis Deformity affecting
Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments Scoliosis Spinal Deformity 3-dimensional deformity affecting all 3 planes Can be difficult to visualize with 2-dimensional radiographs Kyphosis Deformity affecting
Free Paper Session IX Spine II
 Free Paper Session IX Spine II 9. Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for L5-S Introduction: A minimally invasive modified anterior lumbar interbody fusion technique for the lumbosacral junction is described
Free Paper Session IX Spine II 9. Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for L5-S Introduction: A minimally invasive modified anterior lumbar interbody fusion technique for the lumbosacral junction is described
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: lumbar_spine_fusion_surgery 9/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Low back pain
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: lumbar_spine_fusion_surgery 9/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Low back pain
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
QF-78. S. Tanaka 1, T.Yokoyama 1, K.Takeuchi 1, K.Wada 2, T. Tanaka 2, S.Abrakawa 2, G.Kumagai 2, T.Asari 2, A.Ono 2, Y.
 QF-78 Patient-oriented outcomes after musclepreserving interlaminar decompression for patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis: Multi-center study to identify risk factors for poor outcomes S. Tanaka
QF-78 Patient-oriented outcomes after musclepreserving interlaminar decompression for patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis: Multi-center study to identify risk factors for poor outcomes S. Tanaka
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
A minimally invasive surgical approach reduces cranial adjacent segment degeneration in patients undergoing posterior lumbar interbody fusion
 A minimally invasive surgical approach reduces cranial adjacent segment degeneration in patients undergoing posterior lumbar interbody fusion T. Tsutsumimoto, M. Yui, S. Ikegami, M. Uehara, H. Kosaku,
A minimally invasive surgical approach reduces cranial adjacent segment degeneration in patients undergoing posterior lumbar interbody fusion T. Tsutsumimoto, M. Yui, S. Ikegami, M. Uehara, H. Kosaku,
Long lumbar instrumented fusions have been described
 SPINE Volume 37, Number 16, pp 1407 1414 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY Upper Instrumented Vertebral Fractures in Long Lumbar Fusions What Are the Associated Risk Factors? Stephen J. Lewis,
SPINE Volume 37, Number 16, pp 1407 1414 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY Upper Instrumented Vertebral Fractures in Long Lumbar Fusions What Are the Associated Risk Factors? Stephen J. Lewis,
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with Thoracolumbar Fractures
 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint
 J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know
 The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know Poster No.: C-1018 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit D. Shah 1, C. J. Burke 1, A. C. andi 2, R. Houghton
The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know Poster No.: C-1018 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit D. Shah 1, C. J. Burke 1, A. C. andi 2, R. Houghton
Idiopathic scoliosis Scoliosis Deformities I 06
 What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
5/19/2017. Interspinous Process Fixation with the Minuteman G3. What is the Minuteman G3. How Does it Work?
 Interspinous Process Fixation with the Minuteman G3 LLOYDINE J. JACOBS, MD CASTELLVI SPINE MEETING MAY 13, 2017 What is the Minuteman G3 The world s first spinous process plating system that is: Minimally
Interspinous Process Fixation with the Minuteman G3 LLOYDINE J. JACOBS, MD CASTELLVI SPINE MEETING MAY 13, 2017 What is the Minuteman G3 The world s first spinous process plating system that is: Minimally
Spina bifida occulta in high grade spondylolisthesis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2014; 18(Suppl 1): 8-14 Spina bifida occulta in high grade spondylolisthesis L. BABBI, S. TERZI, S. BANDIERA, G. BARBANTI BRODANO Department of
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2014; 18(Suppl 1): 8-14 Spina bifida occulta in high grade spondylolisthesis L. BABBI, S. TERZI, S. BANDIERA, G. BARBANTI BRODANO Department of
Microendoscope-assisted posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a technical note
 Original Study Microendoscope-assisted posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a technical note Hirohiko Inanami 1, Fumiko Saiki 1, Yasushi Oshima 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inanami Spine and Joint
Original Study Microendoscope-assisted posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a technical note Hirohiko Inanami 1, Fumiko Saiki 1, Yasushi Oshima 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inanami Spine and Joint
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
 Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
Adult Spinal Deformity: Principles of Surgical Correction
 Adult Spinal Deformity: Principles of Surgical Correction S. Samuel Bederman, MD PhD FRCSC Department of Orthopaedic Surgery California Orthopaedic Association, Indian Wells, CA April 25, 2015 2 3 4 Adult
Adult Spinal Deformity: Principles of Surgical Correction S. Samuel Bederman, MD PhD FRCSC Department of Orthopaedic Surgery California Orthopaedic Association, Indian Wells, CA April 25, 2015 2 3 4 Adult
Simultaneous anterior vertebral column resection-distraction and posterior rod contouring for restoration of sagittal balance: report of a technique
 Case Report Simultaneous anterior vertebral column resection-distraction and posterior rod contouring for restoration of sagittal balance: report of a technique Shaishav Bhagat 1, Alexander Z. E. Durst
Case Report Simultaneous anterior vertebral column resection-distraction and posterior rod contouring for restoration of sagittal balance: report of a technique Shaishav Bhagat 1, Alexander Z. E. Durst
Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach. Travios. Surgical Technique
 Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach Travios Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach Travios Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Radicular pain of the lower extremity is one of the
 J Neurosurg Spine 21:171 178, 2014 AANS, 2014 Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with total facetectomy for low-dysplastic isthmic spondylolisthesis: effects of slip reduction on surgical outcomes Clinical
J Neurosurg Spine 21:171 178, 2014 AANS, 2014 Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with total facetectomy for low-dysplastic isthmic spondylolisthesis: effects of slip reduction on surgical outcomes Clinical
PARADIGM SPINE. Brochure. coflex-f Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion
 PARADIGM SPINE Brochure coflex-f Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion coflex-f THE UNIQUE, MINIMALLY INVASIVE FUSION DEVICE The coflex-f implant is designed to deliver surgeon confidence and patient satisfaction.
PARADIGM SPINE Brochure coflex-f Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion coflex-f THE UNIQUE, MINIMALLY INVASIVE FUSION DEVICE The coflex-f implant is designed to deliver surgeon confidence and patient satisfaction.
Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion. Description
 Section: Surgery Effective Date: April 15, 2014 Subject: Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2014 Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion Description Axial lumbosacral
Section: Surgery Effective Date: April 15, 2014 Subject: Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2014 Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion Description Axial lumbosacral
PARADIGM SPINE. Interlaminar Technology. Interlaminar Implant
 PARADIGM SPINE Interlaminar Technology Interlaminar Implant SPINAL STENOSIS WITH BACK PAIN THE RATIONALE FOR STABILIZATION For the treatment of spinal stenosis, surgeons have various treatment options.
PARADIGM SPINE Interlaminar Technology Interlaminar Implant SPINAL STENOSIS WITH BACK PAIN THE RATIONALE FOR STABILIZATION For the treatment of spinal stenosis, surgeons have various treatment options.
Case Report Unilateral Pedicle Stress Fracture in a Long-Term Hemodialysis Patient with Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 426940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/426940 Case Report Unilateral Pedicle Stress Fracture in a Long-Term Hemodialysis Patient with Isthmic
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 426940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/426940 Case Report Unilateral Pedicle Stress Fracture in a Long-Term Hemodialysis Patient with Isthmic
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture: Severe Canal Compromise but Neurologically Intact Cases
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
Spinal fusion for paediatric lumbosacral spondylolisthesis
 South African Orthopaedic Journal http://journal.saoa.org.za Horn A et al. SA Orthop J 2018;17(4) DOI 10.17159/2309-8309/2018/v17n4a5 SPINE TRAUMA Spinal fusion for paediatric lumbosacral spondylolisthesis
South African Orthopaedic Journal http://journal.saoa.org.za Horn A et al. SA Orthop J 2018;17(4) DOI 10.17159/2309-8309/2018/v17n4a5 SPINE TRAUMA Spinal fusion for paediatric lumbosacral spondylolisthesis
Surgical treatment for adult spinal deformity: Conceptual approach and surgical strategy
 REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical treatment for adult spinal deformity: Conceptual approach and surgical strategy Yukihiro Matsuyama Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hamamatsu
REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical treatment for adult spinal deformity: Conceptual approach and surgical strategy Yukihiro Matsuyama Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hamamatsu
Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up
 Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up Janek Frantzén M.D., Neurosurgeon Turku University Hospital, Finland ROME SPINE 2011 7.12.2011 1 Clinical Development
Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up Janek Frantzén M.D., Neurosurgeon Turku University Hospital, Finland ROME SPINE 2011 7.12.2011 1 Clinical Development
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study.
 ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
INTERSPINOUS STABILIZATION-FUSION IN THE UNSTABLE SPINE.
 INTERSPINOUS STABILIZATION-FUSION IN THE UNSTABLE SPINE. A PRELIMINARY REPORT F. POSTACCHINI, A. PALMESI LUMBAR VERTEBRAL INSTABILITY Still the subject of discussion Variously defined and interpreted Postacchini
INTERSPINOUS STABILIZATION-FUSION IN THE UNSTABLE SPINE. A PRELIMINARY REPORT F. POSTACCHINI, A. PALMESI LUMBAR VERTEBRAL INSTABILITY Still the subject of discussion Variously defined and interpreted Postacchini
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws
 Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Biomechanics of Interspinous Process Fixation and Lateral Modular Plate Fixation to Support Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (LLIF)
 Biomechanics of Interspinous Process Fixation and Lateral Modular Plate Fixation to Support Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (LLIF) Calusa Ambulatory Spine Conference 2016 Jason Inzana, PhD 1 ; Anup Gandhi,
Biomechanics of Interspinous Process Fixation and Lateral Modular Plate Fixation to Support Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (LLIF) Calusa Ambulatory Spine Conference 2016 Jason Inzana, PhD 1 ; Anup Gandhi,
Patient Information MIS TLIF. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine..............................................
Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine..............................................
Lumbosacral Spondyloptosis Treated By Two-Staged Fusion in Situ Operation: A Case Report
 Lumbosacral Spondyloptosis Treated By Two-Staged Fusion in Situ Operation: A Case Report Erhan EMEL 1 Fahri ÖZER 2 Feyza KARAGÖZ GÜZEY 3 brahim ALATAfi 4 Deniz GÜZEY 5 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: Various operation
Lumbosacral Spondyloptosis Treated By Two-Staged Fusion in Situ Operation: A Case Report Erhan EMEL 1 Fahri ÖZER 2 Feyza KARAGÖZ GÜZEY 3 brahim ALATAfi 4 Deniz GÜZEY 5 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: Various operation
Unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) using a single cage for treatment of low grade lytic spondylolisthesis
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 667-671 ORIGINAL STUDY Unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) using a single cage for treatment of low grade lytic spondylolisthesis Mohamed Adel EL MASRY,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 667-671 ORIGINAL STUDY Unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) using a single cage for treatment of low grade lytic spondylolisthesis Mohamed Adel EL MASRY,
Patient Information MIS TLIF. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine...4 6 MIS-TLIF
Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine...4 6 MIS-TLIF
Comparison of Sagittal Plane Realignment and Reduction with Posterior Instrumentation in Developmental Low or High Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 52, No. 6, pp. 151-169, 2006 Comparison of Sagittal Plane Realignment and Reduction with Posterior Instrumentation in Developmental Low or High Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis İ. TEOMAN
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 52, No. 6, pp. 151-169, 2006 Comparison of Sagittal Plane Realignment and Reduction with Posterior Instrumentation in Developmental Low or High Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis İ. TEOMAN
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Lorenzo Nigro 1, Marika Rullo 2, Domenico Messina 3, Daniele Diacinti 4, Roberto Delfini 1.
 Original Study Decompression versus decompression and fusion for degenerative lumbar stenosis: analysis of the factors influencing the outcome of back pain and disability Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto
Original Study Decompression versus decompression and fusion for degenerative lumbar stenosis: analysis of the factors influencing the outcome of back pain and disability Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto
Surgical treatment of high-dysplastic developmental spondylolisthesis in a child: A case report
 www.edoriumjournals.com case Report open ACCESS Surgical treatment of high-dysplastic developmental spondylolisthesis in a child: A case report Nalli Ramanathan Uvaraj, Aju Bosco ABSTRACT Introduction:
www.edoriumjournals.com case Report open ACCESS Surgical treatment of high-dysplastic developmental spondylolisthesis in a child: A case report Nalli Ramanathan Uvaraj, Aju Bosco ABSTRACT Introduction:
Original Article Selection of proximal fusion level for degenerative scoliosis and the entailing proximal-related late complications
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):5731-5738 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006438 Original Article Selection of proximal fusion level for degenerative scoliosis and the entailing proximal-related late
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):5731-5738 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006438 Original Article Selection of proximal fusion level for degenerative scoliosis and the entailing proximal-related late
Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity with long spinal fusion from T9/T10 to the ilium
 Original Study Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity with long spinal fusion from T9/T10 to the ilium Tatsuya Yasuda, Tomohiko Hasegawa, Yu Yamato, Sho Kobayashi, Daisuke Togawa, Shin
Original Study Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity with long spinal fusion from T9/T10 to the ilium Tatsuya Yasuda, Tomohiko Hasegawa, Yu Yamato, Sho Kobayashi, Daisuke Togawa, Shin
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft. Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD
 Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.110 Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search12/2013 Return to Medical
MP 7.01.110 Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search12/2013 Return to Medical
A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal imbalance
 Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:538 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1902-9 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal
Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:538 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1902-9 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
SKELETAL AWARENESS & DEXTERITY. Update, Misnomers & Insights for Non-Specific Low Back Pain
 SKELETAL AWARENESS & DEXTERITY Spondylolisthesis I: Update, Misnomers & Insights for Non-Specific Low Back Pain Robert Burgess BEd, PT, PhD, Huggins Hospital Newsletter# 7 January 2015 Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
SKELETAL AWARENESS & DEXTERITY Spondylolisthesis I: Update, Misnomers & Insights for Non-Specific Low Back Pain Robert Burgess BEd, PT, PhD, Huggins Hospital Newsletter# 7 January 2015 Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures
 MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
Spine Tango annual report 2012
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2943-x SPINE TANGO REPORT 2012 Spine Tango annual report 2012 M. Neukamp G. Perler T. Pigott E. Munting M. Aebi C. Röder Received: 31 July 2013 / Published online: 30 August 2013
DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2943-x SPINE TANGO REPORT 2012 Spine Tango annual report 2012 M. Neukamp G. Perler T. Pigott E. Munting M. Aebi C. Röder Received: 31 July 2013 / Published online: 30 August 2013
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4): /ISSN: /IJCEM Xiaokang Liu, Yingjie Liu, Xiaofeng Lian, Jianguang Xu
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):6097-6102 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006352 Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging on disc degeneration changes after implantation of an interspinous spacer and
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):6097-6102 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006352 Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging on disc degeneration changes after implantation of an interspinous spacer and
Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance: Surgical technique.
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 3-1-2004 Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance: Surgical technique. Keith
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 3-1-2004 Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance: Surgical technique. Keith
Technique Guide. NFlex. Semi-rigid rods for posterior lumbar stabilization.
 Technique Guide NFlex. Semi-rigid rods for posterior lumbar stabilization. Table of Contents Introduction NFlex 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 NFlex Principles 6 Surgical Technique Preoperative
Technique Guide NFlex. Semi-rigid rods for posterior lumbar stabilization. Table of Contents Introduction NFlex 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 NFlex Principles 6 Surgical Technique Preoperative
vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in
 e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
When is Degenerative Disease Really Deformity
 When is Degenerative Disease Really Deformity Cabo State of Spine Surgery Think Tank June 2017 Gurvinder S. Deol, MD Wake Orthopaedics/WakeMed Health and Hospitals Clinical Assistant Professor Department
When is Degenerative Disease Really Deformity Cabo State of Spine Surgery Think Tank June 2017 Gurvinder S. Deol, MD Wake Orthopaedics/WakeMed Health and Hospitals Clinical Assistant Professor Department
There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid Construct in the Correction of Lenke Type-1 Curves
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr Hesarikia BUMS
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Contact Fusion Cage. Surgical Technique
 Contact Fusion Cage Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction by a surgeon experienced
Contact Fusion Cage Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction by a surgeon experienced
Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis
 35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
APSS-MEDTRONIC FELLOWSHIP REPORT 2016
 APSS-EDTRONIC ELLOWSHIP REPORT 2016 Dr Aiyer Siddharth Narasimhan Host spine centre: Department of Orthopaedic surgery, National University Hospital, Singapore. Duration of fellowship: 26th October to
APSS-EDTRONIC ELLOWSHIP REPORT 2016 Dr Aiyer Siddharth Narasimhan Host spine centre: Department of Orthopaedic surgery, National University Hospital, Singapore. Duration of fellowship: 26th October to
The Most Reliable Spinal Solution
 MFG : 09.02.20 REV : 1 4CIS VANE introduces you the reliable pedicle screw The Most Reliable Spinal Solution Non-slip threaded joint Ergonomic design Wedged trapezoid thread Superior locking mechanism
MFG : 09.02.20 REV : 1 4CIS VANE introduces you the reliable pedicle screw The Most Reliable Spinal Solution Non-slip threaded joint Ergonomic design Wedged trapezoid thread Superior locking mechanism
The Spine Journal 6 (2006)
 The Spine Journal 6 (2006) 421 427 Outcomes of L1 L2 posterior lumbar interbody fusion with the Lumbar I/F cage and the variable screw placement system: reporting unexpected poor fusion results at L1 L2
The Spine Journal 6 (2006) 421 427 Outcomes of L1 L2 posterior lumbar interbody fusion with the Lumbar I/F cage and the variable screw placement system: reporting unexpected poor fusion results at L1 L2
