Management of lower limb open fractures: An unresolved challenge
|
|
|
- Sheena Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Management of lower limb open fractures: An unresolved challenge Abeysekera WYM, Pinto MN, Suran M, Mohan BMP Accident and Orthopaedic Service, National Hospital, Colombo, Sri Lanka. Correspondence: Dr. W Y M Abeysekera yohan.abeysekera@yahoo.com Introduction Management of lower limb open fractures is one of the major orthopaedic challenges still subjected to many arguments. Infection is the most devastating complication of all open fractures, which needs special attention. Failure of such attention may lead to a significant morbidity causing delayed union, non-union, multiple additional surgeries or even amputation (1). Many decades back Gustilo and Anderson in their landmark study expressed clearly the increased risk of infection with the increase in severity of the fracture. It was 2% in type I fractures, 2% to 15% in type II fractures, and 5% to 50% in type III fractures (2). In a recent study similar results emerged as risk of infection 1.4%, 3.6% and 22.7% for type I, II and III fractures, respectively (3). Factors leading to infections include incomplete excision of poorly vascularised tissue, inadequate haemostasis and haematoma evacuation, insufficient drainage of wound discharges, devascularization of primarily viable tissue, large metallic fixation devices implanted under poorly vascularised tissue, wound closure under tension and failure to recognize compartment syndrome (4). Many of these factors can be avoided by following a standard management procedure in handling open fractures. In the standards set by BPRAS/BOA (The British Association of Plastic Reconstructive and Aesthetic surgeons and The British Orthopedic Association) in the management of lower limb open fractures early administration of appropriate antibiotics, thorough surgical debridement, proper skeletal stabilization and early soft tissue cover have been considered as the main steps (5). Galle Medical Journal, Vol 20: No. 2, October 2015 Except in a tertiary care setup with adequate orthopedic staff and facilities the initial wound handling of an open fracture is done by General surgical teams. As the first debridement is the most important prognostic factor of open fractures the knowledge on proper handling of lower limb open fracture is an equally important topic for General surgery as well. Emergency Management Advanced Trauma Life Support Protocol would be the guide for initial management of lower limb open fractures. Resuscitation and stabilization of the patient should be done following a rapid accurate assessment of the condition of the patient. If there is evolving or already established limb threatening condition (e.g. vascular injury) immediate steps should be taken to correct it or transfer the patient to a better facility. It is appropriate inform the receiving hospital beforehand. In the emergency department the open fracture should be handled only for the removal of gross contaminants, photography and radiography related to injury. Except for saline soaked dressing nothing should be used to cover the wound (5). Limb splintage is the ideal method for immobilization of the limb. Antibiotic and anti-tetanus prophylaxis can be started at the same time. Antibiotic prophylaxis In the absence of prophylactic antibiotics the risk of infection would be nearly 20% in open fractures (6). Thus many studies have recognized the value of early prophylactic antibiotics including a recent 33
2 Cochrane group study which declared a reduction of infection rate from 13% to 5% in a comparison of prophylactic antibiotics vs placebos in the management of open fractures (7). The BAPRAS/BOA recommendations have stressed the value of early administration of antibiotics and the importance of administration them within the first 3 hours (5). This 3 hour rule emerged as a result of a study which recognized the 3% increase in the risk of infection when the administration of prophylactic antibiotics delayed beyond 3 hours (8). Many authors have reported a higher prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus in surgical site infections in open fractures (9,10,11), and some of them detected a significantly high rate of MRSA (11). In order to cover Gram positive infections, the most widely used drug of choice is the first generation cephalosporin. Some authors including recently published East guidelines (12) have suggested an additional Gram negative cover for severe open fractures (4,6,13,14). Based on evidence, British recommend Intravenous first generation cephalosporin or Co-Amoxiclav as the first line antibiotic for lower limb open fracture management. Further they suggest gentamicin single dose prior to wound debridement to cover the Gram negative organisms, combined with a single dose of vancomycin or teicoplanin at the time of skeletal stabilization or definitive soft tissue cover. In an allergy to penicillin is reported, clindamycin would be the drug of choice (5). In another evidence-based protocol clindamycin was used as the drug of choice in cases with grossly contaminated wounds eg: farmyard/sewage, (1) but some have considered metranidazole in agricultural infections (4). Due to inadequate evidence, none of the studies have recommended fluroquinolones (e.g. ciprofloxacin) for the management of open fractures (3). Some authors feel that antibiotic cover needs to be altered based on the type of contamination e.g. additional anaerobic cover in a strong soil contamination or a cover for the possible nosocomial infections during treatment in a hospital setup especially Gustillo type III open fractures (14). Mauffrey et al. suggested that even though prophylactic antibiotics are commenced in the emergency room based on the external appearance and radiological findings, the real assessment of the injury would be possible only during the first debridement, therefore the final antibiotic prophylaxis protocol should not be based on the initial open wound size but rather should be chronologically based, following an algorithm with a prophylaxis tailored to the surgical management of the open wound, the fracture, the associated bone, and vascular and muscle injury (1). Controversy still remains about the duration of antibiotics. In a recent RCT comparing prophylaxis with IV cephalosporin for 24 hours vs. 5 days showed that there is no added benefit of prolonged prophylaxis for more than 24 hours, (15) but many authors suggest antibiotics for 3-5 days. (4,5,6,14,16) Based on the current evidence British recommendations describe the continuation of antibiotic prophylaxis for hours for type I fractures and 72 hours or until the definitive soft tissue closure or whichever is shorter for type II and III fractures (5). Surgical debridement The rule of mandatory wound debridement within six hours derived as a result of studies in preantibiotic era which showed infection threshold of 5 10 organisms per gram of tissue reached in at an average of 5.17h (17). Subsequent clinical studies also have supported the importance of early debridement including Gustillo and Anderson (2,17,18). Some studies, however, have shown poor outcome resulted due to the initial surgical debridement performed in an unnecessary urgency by inexperienced non-orthopedic surgical teams under sub-optimal surgical environments (1,3). Thorough debridement by an experienced surgeon appears to be better than an inadequate performance in suboptimal conditions within 6 hours (19). Thus the initial debridement should be performed by senior plastic and orthopedic surgeons working together on scheduled trauma operating lists within normal working hours and within 24hours of the injury unless there is gross contamination eg: marine, agricultural or sewage contamination, compartment syndrome, vascular injury and multiple injuries (5). 34 Galle Medical Journal, Vol 20: No. 2, October 2015
3 Technique of Debridement and Irrigation Careful Surgical debridement and thorough irrigation are the main pillars of a successful management of an open fracture. These steps would make the management of open fractures different from just another wound debridement (Table). Removal of contaminating debri would reduce the risk acute and chronic infection of the wound. Irrigation will reduce the risk by diluting the content of organisms in the lesion based on the concept of Dilution is the solution to pollution. For the irrigation, high pressure pulse lavage is discouraged due to the evidence which suggests possibility of inoculation of dirt and bacteria to the soft tissues and bone, with micro architecture damage to the tissues. Thus low or medium pressure lavage would be the ideal (4,5,20). Ideal solution to be used in irrigation is still unclear and in many instances 0.9% saline solution is used. AO suggests it is better to use optimally balanced salt solution, such as Ringer-lactate (4). Addition of antiseptics or antibiotics to the lavage fluid has not been effective (5). The volume of lavage solution has not been addressed in BAPRAS/BOA guidelines. But some institutions still use the popular protocol of 3, 6, 9 Liters of normal saline for type I to III fractures, respectively (21). Galle Medical Journal, Vol 20: No. 2, October
4 Skeletal stabilization In open fractures it is important to achieve provisional or definitive stability of the fractured bones as early as possible. This may protect the soft tissues around the zone of injury from further damage from fractured ends of bone, while restoring the length, alignment, rotation of the limb. Limb length restoration may indirectly reduce the risk of infection by reducing the soft tissue dead space of the limb. Early skeletal stabilization may also facilitate the access to the surrounding soft tissues, thus facilitating their early recovery with an additional support for the relief of pain (22,23). Based on the evidence on the management of lower limb open fractures, it was clear that when the fracture is minimally contaminated or the fracture is uncomplicated eg: without a bone loss/multilevel fractures, if primary soft tissue cover can be achieved, definitive skeletal stability with internal fixation at the same time of initial wound debridement would be the better option. Otherwise an external fixation (eg: multiplanar/circular fixators) need to be carried out. Whenever the primary soft tissue cover is impossible the provisional stabilization with a spanning fixator can be achieved with the plan for early conversion to definitive stabilization with wound closure. Recommended time period for conversion would be 72 hours. Long leg plaster slabs or traction has been discouraged as modes of provisional stabilization (5). Wound closure In spite of inadequate RCT to decide on primary vs delayed secondary wound closure (24) many authors have emphasized the value of early closure unless there is heavy contamination as it may decrease infection rates, risk of re-operations, and the time for bony union of open tibial fractures (5,25,26) but the exact time limit for soft tissue closure is yet to be determined. Some authors have suggested immediate soft tissue cover at the time of definitive fixation of the bone e.g. Fix & Flap concept (32) Gustillo type I, II and some of the IIIA cases would be suitable for primary closure (3) but this may not be practical unless there is a dedicated well experienced microsurgical team available throughout the day. If wound is left opened in cases of heavy contamination so-called second look on the Zone of injury in 48 hours time after the initial debridement has been suggested by some authorities in order to assess the viability or further excision of soft tissues and to wash out any accumulated blood clots, tissue fluid coagulum or remaining foreign material (4). Since Microsurgery is best performed before the vessels become friable and fibrosed which usually happen after 1 week, soft tissue reconstruction should be undertaken within 7 days from the injury (5). Bhattacharyya et al, agreed with this similar time limit as he observed the increased deep infection rate of open fractures when there was a delay more than 7 days for the soft tissue reconstruction even though the wounds were managed with negative pressure foam dressings (27). Negative pressure dressings Negative pressure dressings may reduce the rate of infection by reducing tissue desiccation as well as avoiding the pooling of serous fluid. It will also increase the local blood flow thus the speed of healing (4,5,28) But the literature recommends that they should never be used as a substitute for meticulous surgical wound excision for coverage of exposed fractures with vascularised flaps (5). Local antibiotic therapy Local antibiotic delivery is commonly done for extensively contaminated wounds with an antibiotic bead-pouch construct formed with antibiotic powder and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) cement. These can be easily made in the operating room via recommended technique using form beads over 24-gauge wire with 3.6g of tobramycin mixed with 40g of PMMA cement (5,29). The beads are counted and then placed into the wound and covered with an impermeable dressing. In use with systemic antibiotics this technique have shown 9% drop in infection rate of sever open fractures (30). Conclusions In spite of many arguments regarding the precise management of lower limb open fractures, it is well 36 Galle Medical Journal, Vol 20: No. 2, October 2015
5 clear that early administration of appropriate antibiotics, planned surgical debridement, proper skeletal stabilization and early soft tissue cover will determine the outcome in any set up. It is mandatory to develop one's own multidisciplinary management protocol for the institution, based on current evidence, in order to achieve a favorable outcome in the management of lower limb open fractures. Such protocol and the knowledge on proper initial handling of an open fracture will be equally important for General surgeons as well as for Orthopedic surgeons since initial management of open fractures are left in the hands of both these groups. References 1. Mauffrey C, Bailey JR, Bowles RJ, Price C, Hasson D, Hak DJ, Stahel PF. Acute management of open fractures: proposal of a new multidisciplinary algorithm. Orthopedics, 2012; 35(10): Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1976; 58(4): rd 3. Cross WW 3, Swiontkowski MF. Treatment principles in the management of open fractures. Indian J Orthop, 2008; 42(4): Hessmann M, Nork S, Sommer C, Twaddle B. Principles of management of open fractures. [Internet] [cited 15 January 2015]. Available from: org/wps/portal/surgery?showpage=diagnosis&bone=tibia &segment =Distal. 5. Nanchahal J, Nayagam S, Khan U, Moran C, Barrett S, Sanderson F, Pallister I. (2009) Standards for the management of open fractures of the lower limb. A Short Guide. BOA/BAPRAS. ISBN: Patzakis MJ, Wilkins J, Moore TM. Considerations in reducing the infection rate in open tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1983; 178: Gosselin RA, Roberts I, Gillespie WJ. Antibiotics for preventing infection in open limb fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2004; 1: CD Patzakis MJ, Bains RS, Lee J. Prospective, randomized, double blind study comparing single agent antibiotic therapy, ciprofloxacin, to combination antibiotic therapy in open fracture wounds. J Orthop Trauma, 2000; 14: Bergman BR. Antibiotic prophylaxis in open and closed fractures: a controlled clinical trial. Acta Orthop Scand, 1982; 53(1): Braun R, Enzler MA, Rittmann WW. A double blind clinical trial of prophylactic cloxacillin in open fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 1987; 1(1): Carsenti-Etesse H, Doyon F, Desplaces N, et al. Epidemiology of bacterial infection during management of open leg fractures. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 1999; 18(5): Hoff W, Bonadies J, Cachecho R, et al. East practice management guidelines work group: update to practice management guidelines for prophylactic antibiotic use in open fractures. J Trauma. 2011; 70(3): Patzakis MJ, Wilkins J. Factors influencing infection rate in open fracture wounds. Clin Orth Rela Res, 1989; 243: Templeman DC, Gulli B, Tsukayama DT, Gustilo RB. Update on the management of open fractures of the tibial shaft. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998; 350: Dellinger EP, Caplan ES, Weaver LD. Duration of preventive antibiotics administration for open extremity fractures. Arch Surg, 1988; 123(3): Zalavras CG, Patzakis MJ. Open fractures: Evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2003; 11: Robson MC, Duke WF, Krizek TJ. Rapid bacterial screening in the treatment of civilian wounds. J Surg Res, 1973; 14(5): Kindsfater K, Jonassen EA. Osteomyelitis in grade II and III open tibia fractures with late debridement. J Orthop Trauma,1995; 9(2): Penn-Barwell JG, Murray CK, Wenke JC. Early antibiotics and debridement independently reduce infection in an open fracture model. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2012; 94(1): Bhandari M, Thompson K, Adili A, Shaughnessy SG. High and low pressure irrigation in contaminated wounds with exposed bone. Int J Surg Investig, 2000; 2: Anglen JO. Wound irrigation in musculoskeletal injury. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2001; 9: Merritt K. Factors increasing the risk of infection in patients with open fractures. J Trauma, 1988; 28: Worlock P, Slack R, Harvey L, Mawhinney R. The prevention of infection in open fractures: An experimental study of the effect of fracture stability. Injury, 1994; 25: Galle Medical Journal, Vol 20: No. 2, October
6 24. Eliya MC, Banda GW. Primary closure versus delayed closure for non bite traumatic wounds within 24 hours post injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2011; 9: CD Gopal S, Majumder S, Batchelor AG, Knight SL, De Boer P, Smith RM. Fix and flap: The radical orthopaedic and plastic treatment of severe open fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2000; 82: Hertel R, Lambert SM, Muller S, Ballmer FT, Ganz R. On the timing of soft-tissue reconstruction for open fractures of the lower leg. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 1999; 119: Bhattacharyya T, Mehta P, Smith M, Pomahac B. Routine use of wound vacuum-assisted closure does not allow coverage delay for open tibia fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2008; 121(4): Ubbink DT, Westerbos SJ, Nelson EA, Vermeulen H. A systematic review of topical negative pressure therapy for acute and chronic wounds. Br J Surg, 2008; 95(6): Zalavras CG, Patzakis MJ, Holtom P. Local antibiotic therapy in the treatment of open fractures and osteomyelitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2004; 427: Ostermann PA, Seligson D, Henry SL. Local antibiotic therapy for severe open fractures. A review of 1085 consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1995; 77: Galle Medical Journal, Vol 20: No. 2, October 2015
Acute Management of Open Fractures: Proposal of a New Multidisciplinary Algorithm
 Section Editors: David J. Hak, MD, MBA & Philip F. Stahel, MD Acute Management of Open Fractures: Proposal of a New Multidisciplinary Algorithm Cyril Mauffrey, MD, FRCS; James R. Bailey, MD; Richard J.
Section Editors: David J. Hak, MD, MBA & Philip F. Stahel, MD Acute Management of Open Fractures: Proposal of a New Multidisciplinary Algorithm Cyril Mauffrey, MD, FRCS; James R. Bailey, MD; Richard J.
Dave Laverty MD Orthopedic Trauma Surgeon
 Austin Trauma & Critical Care Conference Open Fracture Update 2018 Dave Laverty MD Orthopedic Trauma Surgeon Take Home Points We are stuck in the 90 s Time to antibiotics matters most Gram negative bacteria
Austin Trauma & Critical Care Conference Open Fracture Update 2018 Dave Laverty MD Orthopedic Trauma Surgeon Take Home Points We are stuck in the 90 s Time to antibiotics matters most Gram negative bacteria
EAST PRACTICE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES WORK GROUP: UPDATE TO PRACTICE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTIC USE IN OPEN FRACTURES
 EAST PRACTICE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES WORK GROUP: UPDATE TO PRACTICE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTIC USE IN OPEN FRACTURES William S. Hoff, MD, FACS 1, John A. Bonadies, MD, FACS 2, Riad
EAST PRACTICE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES WORK GROUP: UPDATE TO PRACTICE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTIC USE IN OPEN FRACTURES William S. Hoff, MD, FACS 1, John A. Bonadies, MD, FACS 2, Riad
Open Fractures. Ria Dindial. Photo courtesy pic2fly.com
 Open Fractures Ria Dindial Photo courtesy pic2fly.com CLINICAL PEARL TYPE WOUND DESCRIPTION OTHER CRITERIA I < 1cm (puncture wounds) - II 1-10 cm - IIIA >10 cm, coverage available Segmental fractures,
Open Fractures Ria Dindial Photo courtesy pic2fly.com CLINICAL PEARL TYPE WOUND DESCRIPTION OTHER CRITERIA I < 1cm (puncture wounds) - II 1-10 cm - IIIA >10 cm, coverage available Segmental fractures,
The Debate: Should open fractures have their wound primarily closed?
 38 1 06 James F Kellam, Moderator Peter J O Brien and Michael J Bosse, Discussants The Debate: Should open fractures have their wound primarily closed? Introduction It has been the tradition and accepted
38 1 06 James F Kellam, Moderator Peter J O Brien and Michael J Bosse, Discussants The Debate: Should open fractures have their wound primarily closed? Introduction It has been the tradition and accepted
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Open Fractures of the Tibial Diaphysis
 Open Fractures of the Tibial Diaphysis Daniel N. Segina, MD Robert V. Cantu, MD David Templeman, MD Created March 2004 Updated May 2010 Incidence Open fractures of the tibia are more common than in any
Open Fractures of the Tibial Diaphysis Daniel N. Segina, MD Robert V. Cantu, MD David Templeman, MD Created March 2004 Updated May 2010 Incidence Open fractures of the tibia are more common than in any
A prospective study of functional outcome of primary intra-medullary nailing in type 3A and 3B open tibial diaphyseal fractures
 2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL
 Research article USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL G.C. Mwangi, MBChB, COSECSA Resident Orthopaedics, A.I.C. Kijabe Hospital, P.O.
Research article USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL G.C. Mwangi, MBChB, COSECSA Resident Orthopaedics, A.I.C. Kijabe Hospital, P.O.
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department
 Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
Research Article. Abstract
 Research Article Management of Open Tibial Shaft Fractures: Does the Timing of Surgery Affect Outcomes? Oscar A. Duyos, MD David Beaton-Comulada, MD Ariel Davila-Parrilla, MD Jose Carlos Perez-Lopez, MD
Research Article Management of Open Tibial Shaft Fractures: Does the Timing of Surgery Affect Outcomes? Oscar A. Duyos, MD David Beaton-Comulada, MD Ariel Davila-Parrilla, MD Jose Carlos Perez-Lopez, MD
Management of open lower limb injuries in South West England and Wales
 LOWER LIMB Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2015; 97: 35 39 doi 10.1308/003588414X14055925058472 Management of open lower limb injuries in South West England and Wales J Yarrow, S Rahman, N Marsden, I Pallister, S
LOWER LIMB Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2015; 97: 35 39 doi 10.1308/003588414X14055925058472 Management of open lower limb injuries in South West England and Wales J Yarrow, S Rahman, N Marsden, I Pallister, S
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
Early Management of Open Tibial Fractures in Benin - City -Result of a Structured Treatment Protocol
 JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-33-39 Early Management of Open Tibial Fractures in Benin - City -Result of a Structured Treatment Protocol Umebese Philip
JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-33-39 Early Management of Open Tibial Fractures in Benin - City -Result of a Structured Treatment Protocol Umebese Philip
We performed a retrospective review of the case
 Fix and flap: the radical orthopaedic and plastic treatment of severe open fractures of the tibia S. Gopal, S. Majumder, A. G. B. Batchelor, S. L. Knight, P. De Boer, R. M. Smith From St James s University
Fix and flap: the radical orthopaedic and plastic treatment of severe open fractures of the tibia S. Gopal, S. Majumder, A. G. B. Batchelor, S. L. Knight, P. De Boer, R. M. Smith From St James s University
Original Research Article. Ayub Ali 1 *, Mizanur Rahman 2, Sajedur Reza Faruquee 3, Tazul Islam 4, Zamil Zaidur Rahim 5, Abdullah Yusuf 6
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Ali A et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Sep;3(5):898-903 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20173931
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Ali A et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Sep;3(5):898-903 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20173931
Spartan Medical Research Journal
 Spartan Medical Research Journal Research at Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine Volume 3 Number 2 Fall, 2018 Pages 1-14 Title: Implementation of an Antibiotic Therapy Protocol for
Spartan Medical Research Journal Research at Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine Volume 3 Number 2 Fall, 2018 Pages 1-14 Title: Implementation of an Antibiotic Therapy Protocol for
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY. Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS
 CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
The principles and practice of open fracture care, 2018
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 2-21-2018 The principles and practice of open fracture care, 2018 Amna Diwan University
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 2-21-2018 The principles and practice of open fracture care, 2018 Amna Diwan University
Short Report. Determinants of management outcome in open tibia fractures in ile-ife. I.C.Ikem, L.M.Oginni and J.D Ogunlusi.
 Nigerian journal of surgical research Vol 8 No 1 2, 2006: 81-83 Short Report Determinants of management outcome in open tibia fractures in ile-ife I.C.Ikem, L.M.Oginni and J.D Ogunlusi. Department of Orthopaedic
Nigerian journal of surgical research Vol 8 No 1 2, 2006: 81-83 Short Report Determinants of management outcome in open tibia fractures in ile-ife I.C.Ikem, L.M.Oginni and J.D Ogunlusi. Department of Orthopaedic
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Open Fractures: Evaluation and Management
 Open Fractures: Evaluation and Management Charalampos G. Zalavras, MD, and Michael J. Patzakis, MD Abstract Open fractures are complex injuries that involve both the bone and surrounding soft tissues.
Open Fractures: Evaluation and Management Charalampos G. Zalavras, MD, and Michael J. Patzakis, MD Abstract Open fractures are complex injuries that involve both the bone and surrounding soft tissues.
Update on the Management of Compound Lower Limb Fractures
 Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae 518 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 3: M4) 518-524 Update on the Management of Compound Lower Limb Fractures M. Griffin 1, M. Malahias
Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae 518 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 3: M4) 518-524 Update on the Management of Compound Lower Limb Fractures M. Griffin 1, M. Malahias
Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12, No2, April, 1999 = Abstract = Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures Eui-Hwan Ahn, MD, In-Whan Chung, MD, Jeong-Hwan Oh, MD, Seong-Tae
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12, No2, April, 1999 = Abstract = Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures Eui-Hwan Ahn, MD, In-Whan Chung, MD, Jeong-Hwan Oh, MD, Seong-Tae
Management of severe open tibial fractures
 Trauma Management of severe open tibial fractures THE NEED FOR COMBINED ORTHOPAEDIC AND PLASTIC SURGICAL TREATMENT IN SPECIALIST CENTRES S. B. Naique, M. Pearse, J. Nanchahal From Department of Musculoskeletal
Trauma Management of severe open tibial fractures THE NEED FOR COMBINED ORTHOPAEDIC AND PLASTIC SURGICAL TREATMENT IN SPECIALIST CENTRES S. B. Naique, M. Pearse, J. Nanchahal From Department of Musculoskeletal
Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia
 Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia Nazri MY a, AS Halim b a Department of Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation, Kulliyyah of Medicine, International Islamic
Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia Nazri MY a, AS Halim b a Department of Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation, Kulliyyah of Medicine, International Islamic
Gastrocnemius Muscle Flap Coverage of Chronically= Infected Knee Joints
 Gastrocnemius Muscle Flap Coverage of Chronically= Infected Knee Joints ABSTRACT Chronically infected open knee joints present dif cult problem. Aggressive debridement of chronically infected soft tissue
Gastrocnemius Muscle Flap Coverage of Chronically= Infected Knee Joints ABSTRACT Chronically infected open knee joints present dif cult problem. Aggressive debridement of chronically infected soft tissue
Presented at 2015 TQIP conference. Developed by a panel of experts. Evidence based with expert opinion as needed
 Presented at 2015 TQIP conference Developed by a panel of experts Evidence based with expert opinion as needed Orthopaedic Trauma Best Practice Guidelines (BPG) Goals Offer guidance on what is practical
Presented at 2015 TQIP conference Developed by a panel of experts Evidence based with expert opinion as needed Orthopaedic Trauma Best Practice Guidelines (BPG) Goals Offer guidance on what is practical
Principles of Management of Open Fractures
 Principles of Management of Open Fractures A.M. Buteera, J. Byimana Consultant Orthopedic Surgeons, King Faisal and Kanombe Military Hospitals, Kigali, Rwanda. Correspondences to: Dr Alex M Buteera, E-mail
Principles of Management of Open Fractures A.M. Buteera, J. Byimana Consultant Orthopedic Surgeons, King Faisal and Kanombe Military Hospitals, Kigali, Rwanda. Correspondences to: Dr Alex M Buteera, E-mail
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
Assessment of Frequency of Long Bone Osteomyelitis in Traumatic Patients Undergoing Orthopedic Surgery in Imam Reza (AS) Hospital-Tabriz
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 1(2016) pp. 818-825 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.501.084
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 1(2016) pp. 818-825 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.501.084
Key words: Gustilo and Anderson, antibiotics, irrigation, negative pressure therapy, amputation
 The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Open Fractures: A Systematic Review by NicoleNicolosi, DPM 1 The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal 1 (1): 1 Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Abstract:
The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Open Fractures: A Systematic Review by NicoleNicolosi, DPM 1 The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal 1 (1): 1 Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Abstract:
Using Animal Models to Help Solve Clinical Problems
 Using Animal Models to Help Solve Clinical Problems -Overview -Epidemiology -Improving the Standards for Initial Wound Care -Use of dual purpose bone grafts -Developing a more relevant animal model Research
Using Animal Models to Help Solve Clinical Problems -Overview -Epidemiology -Improving the Standards for Initial Wound Care -Use of dual purpose bone grafts -Developing a more relevant animal model Research
Fracture Classification
 Fracture Classification Lisa K. Cannada MD Updated: 05/2016 18 th & 19 th century History of Fracture History based on clinical appearance of limb alone Classification Colles Fracture Dinner Fork Deformity
Fracture Classification Lisa K. Cannada MD Updated: 05/2016 18 th & 19 th century History of Fracture History based on clinical appearance of limb alone Classification Colles Fracture Dinner Fork Deformity
EXTERNAL PIN FIXATION WITH EARLY FLAP COVERAGE FOR OPEN TIBIAL FRACTURES WITH SOFT TISSUE LOSS
 J MEDICINE 2010; 11 : 28-32 JM Vol. 11, No. 1 EXTERNAL PIN FIXATION WITH EARLY FLAP COVERAGE FOR OPEN TIBIAL FRACTURES WITH SOFT TISSUE LOSS MD.SHAMSUZZAMAN 1, MD.ANOWARUL ISLAM 2, SHAH MOHAMMAD AMANULLAH
J MEDICINE 2010; 11 : 28-32 JM Vol. 11, No. 1 EXTERNAL PIN FIXATION WITH EARLY FLAP COVERAGE FOR OPEN TIBIAL FRACTURES WITH SOFT TISSUE LOSS MD.SHAMSUZZAMAN 1, MD.ANOWARUL ISLAM 2, SHAH MOHAMMAD AMANULLAH
Wound Management for Severe Open Fractures: Use of Antibiotic Bead Pouches and Vacuum-Assisted Closure
 A Review Paper Wound Management for Severe Open Fractures: Use of Antibiotic Bead Pouches and Vacuum-Assisted Closure Mark L. Prasarn, MD, Gregory Zych, DO, and Peter A. W. Ostermann, MD, PhD Abstract
A Review Paper Wound Management for Severe Open Fractures: Use of Antibiotic Bead Pouches and Vacuum-Assisted Closure Mark L. Prasarn, MD, Gregory Zych, DO, and Peter A. W. Ostermann, MD, PhD Abstract
We carried out a randomised, controlled trial in
 Vascular injuries in compound fractures of the leg with initially adequate circulation Saranatra Waikakul, Somjet Sakkarnkosol, Vichai Vanadurongwan From Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand We carried
Vascular injuries in compound fractures of the leg with initially adequate circulation Saranatra Waikakul, Somjet Sakkarnkosol, Vichai Vanadurongwan From Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand We carried
Malunion in floating knee injuries An analysis in 30 patients presenting to a tertiary care facility and are surgically treated
 2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
Bacteriological Study and its Role in the Management of Open Tibial Fracture
 Bacteriological Study and its Role in the Management of Open Tibial Fracture WI Faisham, M.Med (Ortho), S Nordin, M.S(Ortho), M Aidura M.Med(Ol"tho), Department of Orthopaedics, School ofmedical Science
Bacteriological Study and its Role in the Management of Open Tibial Fracture WI Faisham, M.Med (Ortho), S Nordin, M.S(Ortho), M Aidura M.Med(Ol"tho), Department of Orthopaedics, School ofmedical Science
Tibial osteomyelitis is a challenging problem for
 Case Report 542 Treatment of Infected Tibial Nonunion with Tobramycin- Impregnated Calcium Sulfate: Report of Two Cases Yao-Hung Tsai, MD; Tsung-Jen, Huang, MD; Hsin-Nung Shih, MD; Robert Wen-Wei Hsu,
Case Report 542 Treatment of Infected Tibial Nonunion with Tobramycin- Impregnated Calcium Sulfate: Report of Two Cases Yao-Hung Tsai, MD; Tsung-Jen, Huang, MD; Hsin-Nung Shih, MD; Robert Wen-Wei Hsu,
Open Fracture. Disclaimer. Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only. 07-Jul-14
 Open Fracture นพ. ส หธ ช งามอ โฆษ ภาคว ชา ออร โธป ด กส คณะแพทย ศาสตร จ ฬาลงกรณ มหาว ทยาล ย Disclaimer Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only 1 Scope Open fracture
Open Fracture นพ. ส หธ ช งามอ โฆษ ภาคว ชา ออร โธป ด กส คณะแพทย ศาสตร จ ฬาลงกรณ มหาว ทยาล ย Disclaimer Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only 1 Scope Open fracture
Controversies in the Management of Open Fractures
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 178 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2014, 8, (Suppl 1: M7) 178-184 Controversies in the Management of Open Fractures C.L. O Brien, M. Menon and N.M.
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 178 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2014, 8, (Suppl 1: M7) 178-184 Controversies in the Management of Open Fractures C.L. O Brien, M. Menon and N.M.
Update on the Management of Open Lower Limb Fractures
 Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 3: M13) 571-577 571 Update on the Management of Open Lower Limb Fractures M. Griffin 1, M. Malahias 2,
Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 3: M13) 571-577 571 Update on the Management of Open Lower Limb Fractures M. Griffin 1, M. Malahias 2,
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis
 Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of Both Bone Leg In Patients Attending Assam Medical College Hospital, Dibrugarh. Partha Pratim Das 5
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
Open fractures. Reto Babst MD, Prof. of Surg. Head of Trauma Surgery Clinic for Orthopedics and Trauma Luzerner Kantonsspital 6002 Luzern
 Open fractures Reto Babst MD, Prof. of Surg. Head of Trauma Surgery Clinic for Orthopedics and Trauma Luzerner Kantonsspital 6002 Luzern Outline Problem list Emercency room treatment + assessment Debridement
Open fractures Reto Babst MD, Prof. of Surg. Head of Trauma Surgery Clinic for Orthopedics and Trauma Luzerner Kantonsspital 6002 Luzern Outline Problem list Emercency room treatment + assessment Debridement
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
BOAST 4 Algorithm. 6th September 2013
 BOAST 4 Algorithm 6th September 2013 Background The British Orthopaedic Association and the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons reviewed their 1997 guidance and published
BOAST 4 Algorithm 6th September 2013 Background The British Orthopaedic Association and the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons reviewed their 1997 guidance and published
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware. Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA
 Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Current Concepts of Prophylactic Antibiotics in Trauma: A Review
 Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 3: M3) 511-517 511 Current Concepts of Prophylactic Antibiotics in Trauma: A Review Jennifer C.E. Lane,1,
Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 3: M3) 511-517 511 Current Concepts of Prophylactic Antibiotics in Trauma: A Review Jennifer C.E. Lane,1,
System of Gustilo and Anderson At the time of surgical débridement is useful in guiding treatment and predicting outcomes.
 Open Fractures Definition Breach in the overlying skin of a fracture. Epidemiology Lower limb: 3.3% Tibia more than 20 folds common than femur. [since tibia is subcutaneous] Gustillo: 25% each in I, II,
Open Fractures Definition Breach in the overlying skin of a fracture. Epidemiology Lower limb: 3.3% Tibia more than 20 folds common than femur. [since tibia is subcutaneous] Gustillo: 25% each in I, II,
Open tibial fractures in children under 13 years of age 10 years experience
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 34 (2003) 776 780 Open tibial fractures in children under 13 years of age 10 years experience B.G. Jones, R.D.D. Duncan The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Yorkhill, Glasgow
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 34 (2003) 776 780 Open tibial fractures in children under 13 years of age 10 years experience B.G. Jones, R.D.D. Duncan The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Yorkhill, Glasgow
The VERSAJET II Hydrosurgery System
 Precise Excision The VERSAJET II Hydrosurgery System The VERSAJET II Hydrosurgery System The VERSAJET II system enables a surgeon to precisely select, excise and evacuate nonviable tissue, bacteria and
Precise Excision The VERSAJET II Hydrosurgery System The VERSAJET II Hydrosurgery System The VERSAJET II system enables a surgeon to precisely select, excise and evacuate nonviable tissue, bacteria and
Management of Segmental Tibial Fractures.
 72 Management of Segmental Tibial Fractures. N. S. Motsitsi Chief Specialist / Head of Department.Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery., Kalafong Hospital Pretoria.Email: silas.motsitsi@up.ac.za. Fax : (012);
72 Management of Segmental Tibial Fractures. N. S. Motsitsi Chief Specialist / Head of Department.Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery., Kalafong Hospital Pretoria.Email: silas.motsitsi@up.ac.za. Fax : (012);
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Amputations. Chapter 23
 Amputations Chapter 23 Amputations Introduction Battle casualties who sustain amputations have the most severe extremity injuries. Historically, 1 in 3 patients with a major amputation (proximal to the
Amputations Chapter 23 Amputations Introduction Battle casualties who sustain amputations have the most severe extremity injuries. Historically, 1 in 3 patients with a major amputation (proximal to the
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
Wound culture. (Sampling methods) M. Rostami MSn.ICP Rajaei Heart Center
 Wound culture (Sampling methods) M. Rostami MSn.ICP Rajaei Heart Center Infection is a major impairment in delayed and nonhealing chronic wounds. Cultures of chronic wounds are not routinely performed
Wound culture (Sampling methods) M. Rostami MSn.ICP Rajaei Heart Center Infection is a major impairment in delayed and nonhealing chronic wounds. Cultures of chronic wounds are not routinely performed
The tibial bayonet method of wound closure
 Strategies in Trauma and Limb Reconstruction (2018) 13:103 108 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-018-0304-3 CASE REPORT The tibial bayonet method of wound closure Peter O Farrell 1 Annette Christi Barnard
Strategies in Trauma and Limb Reconstruction (2018) 13:103 108 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-018-0304-3 CASE REPORT The tibial bayonet method of wound closure Peter O Farrell 1 Annette Christi Barnard
INFECTION AFTER FRACTURE FIXATION A N T E K A L S T A D, S T O L A V S H O S P I T A L, N O R W A Y
 INFECTION AFTER FRACTURE FIXATION A N T E K A L S T A D, S T O L A V S H O S P I T A L, N O R W A Y INCIDENCE 5% of all osteosynthesis 0.5 2% closed fractures 10 30% open fractures Rabih, N Engl J Med,
INFECTION AFTER FRACTURE FIXATION A N T E K A L S T A D, S T O L A V S H O S P I T A L, N O R W A Y INCIDENCE 5% of all osteosynthesis 0.5 2% closed fractures 10 30% open fractures Rabih, N Engl J Med,
Treatment of infection
 Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Orthopaedica Belgica 2018
 POSTTRAUMA WOUND MANAGEMENT PRONTOSAN. Polyhexanide + Betaine: Slows growth of bacteria, Removes the biofilm, Cleans the wound. BVOT Congress Brussels May 3th PRIMARY SOFT TISSUE LESIONS prepatellar bursitis-skin
POSTTRAUMA WOUND MANAGEMENT PRONTOSAN. Polyhexanide + Betaine: Slows growth of bacteria, Removes the biofilm, Cleans the wound. BVOT Congress Brussels May 3th PRIMARY SOFT TISSUE LESIONS prepatellar bursitis-skin
Chapter 2 Limb Damage Control Orthopedics
 Chapter 2 Limb Damage Control Orthopedics Madhusudhan Yakkanti, Cyril Mauffrey, and Craig S. Roberts 2.1 Introduction The damage control (DCO) approach to the injured limb requires the application of damage
Chapter 2 Limb Damage Control Orthopedics Madhusudhan Yakkanti, Cyril Mauffrey, and Craig S. Roberts 2.1 Introduction The damage control (DCO) approach to the injured limb requires the application of damage
Treatment of open diaphyseal fractures of long bones of the limbs. Biology and Medicine
 eissn: 09748369 Treatment of open diaphyseal fractures of long bones of the limbs Biology and Medicine Research Article Volume 7, Issue 1, Article ID: BM-065-15, 2015 Indexed by Scopus (Elsevier) www.biolmedonline.com
eissn: 09748369 Treatment of open diaphyseal fractures of long bones of the limbs Biology and Medicine Research Article Volume 7, Issue 1, Article ID: BM-065-15, 2015 Indexed by Scopus (Elsevier) www.biolmedonline.com
The Mangled Extremity: It s NOT Just a Flesh Wound. William Hakeos, MD September 22, 2017
 The Mangled Extremity: It s NOT Just a Flesh Wound William Hakeos, MD September 22, 2017 Disclosures: Financial I tried to find somebody to pay me to give this talk, but couldn t Disclosures: Intellectual
The Mangled Extremity: It s NOT Just a Flesh Wound William Hakeos, MD September 22, 2017 Disclosures: Financial I tried to find somebody to pay me to give this talk, but couldn t Disclosures: Intellectual
Interesting Case Series. Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review
 Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
34 th Annual Meeting of the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS)
 34 th Annual Meeting of the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS) 10-12 September 2015 Estoril, Portugal Free Paper: #135 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE BIOABSORBABLE ANTIBIOTIC CARRIERS IN CHRONIC
34 th Annual Meeting of the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS) 10-12 September 2015 Estoril, Portugal Free Paper: #135 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE BIOABSORBABLE ANTIBIOTIC CARRIERS IN CHRONIC
Lawnmower Injuries. Kyle Kenoyer PGY-1 Madigan Army Medical Center
 Lawnmower Injuries Kyle Kenoyer PGY-1 Madigan Army Medical Center Demographics 60000 ED visits per year 75 deaths annually 7% require hospitalization 2-5 surgeries per injury 64% require amputation $457
Lawnmower Injuries Kyle Kenoyer PGY-1 Madigan Army Medical Center Demographics 60000 ED visits per year 75 deaths annually 7% require hospitalization 2-5 surgeries per injury 64% require amputation $457
Bhaskar Raj Pant, MD Orthopedic Surgeon
 Bhaskar Raj Pant, MD Orthopedic Surgeon SIGN Program Manager Board of Director Grande International Hospital [Nyaya Health Nepal] Dhapasi, NEPAL POSSIBLE SIGN Conference 2015 Is amputation a FAILURE? Bhaskar
Bhaskar Raj Pant, MD Orthopedic Surgeon SIGN Program Manager Board of Director Grande International Hospital [Nyaya Health Nepal] Dhapasi, NEPAL POSSIBLE SIGN Conference 2015 Is amputation a FAILURE? Bhaskar
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Complex Limb Injury. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Standards for the management of OPEN FRACTURES OF THE LOWER LIMB A SHORT GUIDE. British Orthopaedic Association
 Standards for the management of OPEN FRACTURES OF THE LOWER LIMB A SHORT GUIDE British Orthopaedic Association who should read this guide? Standards for the management of open fractures of the lower limb
Standards for the management of OPEN FRACTURES OF THE LOWER LIMB A SHORT GUIDE British Orthopaedic Association who should read this guide? Standards for the management of open fractures of the lower limb
Property Latmedical, LLC.
 Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
Segmental tibial fractures treated with unreamed interlocking nail A prospective study
 2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT
 INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT An injury is damage to the body caused by external forces, which may be physical or chemical. 1) Incisions 2) Types of wounds and their closure
INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT An injury is damage to the body caused by external forces, which may be physical or chemical. 1) Incisions 2) Types of wounds and their closure
The Ortho-Plastic Approach to Soft Tissue Management in Trauma
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2014, 8, (Suppl 2: M2) 399-408 399 The Ortho-Plastic Approach to Soft Tissue Management in Trauma Daniel J. Jordan
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2014, 8, (Suppl 2: M2) 399-408 399 The Ortho-Plastic Approach to Soft Tissue Management in Trauma Daniel J. Jordan
Power to Transform Outcomes
 CASE STUDIES CASE STUDY Courtesy of Dr Parihar Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Mumbai, India Clinical particulars 42-year-old female
CASE STUDIES CASE STUDY Courtesy of Dr Parihar Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Mumbai, India Clinical particulars 42-year-old female
Chronic Wounds and Ulcers
 1 Chapter 2 Chronic Wounds and Ulcers Louis Carter Chronic wounds are likely the greatest cause of morbidity and cost to both patients and hospitals in Africa. With more surgeons and the availability of
1 Chapter 2 Chronic Wounds and Ulcers Louis Carter Chronic wounds are likely the greatest cause of morbidity and cost to both patients and hospitals in Africa. With more surgeons and the availability of
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome
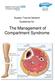 Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Injuries to the Pelvis and Extremities
 Injuries to the Pelvis and Extremities Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee General Common occur in 85% of blunt trauma
Injuries to the Pelvis and Extremities Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee General Common occur in 85% of blunt trauma
STIMULAN POWER TO TRANSFORM OUTCOMES
 STIMULAN POWER TO TRANSFORM OUTCOMES Perfect partner for your infection management strategy In contrast to today s growing economic and performance challenges, STIMULAN has been shown to transform outcomes
STIMULAN POWER TO TRANSFORM OUTCOMES Perfect partner for your infection management strategy In contrast to today s growing economic and performance challenges, STIMULAN has been shown to transform outcomes
Gustilo-Anderson Classification
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2012) 470:3270 3274 DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2376-6 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons IN BRIEF Gustilo-Anderson
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2012) 470:3270 3274 DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2376-6 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons IN BRIEF Gustilo-Anderson
Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures
 Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Management of compound fractures of shaft femur: a study of 55 cases
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Singla G et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):313-317 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164160
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Singla G et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):313-317 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164160
Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How
 Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures Journal Reviewer Journal of Bone
Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures Journal Reviewer Journal of Bone
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of Surgical Site Infection in orthopaedic implants surgery with its common bacteria and antibiotic sensitivity
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of Surgical Site Infection in orthopaedic implants surgery with its common bacteria and antibiotic sensitivity Muhammad Salman, Muhammad Ayaz Khan, Tamjeed Gul, Muhammad Bilal,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of Surgical Site Infection in orthopaedic implants surgery with its common bacteria and antibiotic sensitivity Muhammad Salman, Muhammad Ayaz Khan, Tamjeed Gul, Muhammad Bilal,
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Antibiotic Loaded Acrylic Bone Cement in Orthopaedic Trauma
 Antibiotic Loaded Acrylic Bone Cement in Orthopaedic Trauma Sumant Samuel Department of Orthopaedics (III), Christian Medical College, Vellore India 6 1. Introduction Local antibiotic delivery with antibiotic
Antibiotic Loaded Acrylic Bone Cement in Orthopaedic Trauma Sumant Samuel Department of Orthopaedics (III), Christian Medical College, Vellore India 6 1. Introduction Local antibiotic delivery with antibiotic
KEYWORDS: Tibial fracture, Diaphyseal fracture, closed interlocking intramedullary nailing,
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Multi drug resistant pseudomonas infection in open fractures post definitive fixation leading to limb loss: A report of three cases
 IJCRI 2011;2(5):1-6. Doshi et. al. 1 CASE SERIES OPEN ACCESS Multi drug resistant pseudomonas infection in open fractures post definitive fixation leading to limb loss: A report of three cases Hitendra
IJCRI 2011;2(5):1-6. Doshi et. al. 1 CASE SERIES OPEN ACCESS Multi drug resistant pseudomonas infection in open fractures post definitive fixation leading to limb loss: A report of three cases Hitendra
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
REPLANTATION OF POST-TRAUMATIC LOWER LIMB AMPUTATION
 Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Sanjitsingh R Sulhyan et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved REPLANTATION OF POST-TRAUMATIC
Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Sanjitsingh R Sulhyan et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved REPLANTATION OF POST-TRAUMATIC
DePuy CMW Heritage Bone Cements. Product Information
 DePuy CMW Heritage Bone Cements Product Information INTRODUCTION Our experience in Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) bone cements is extensive. The long clinical heritage of our DePuy CMW bone cement product
DePuy CMW Heritage Bone Cements Product Information INTRODUCTION Our experience in Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) bone cements is extensive. The long clinical heritage of our DePuy CMW bone cement product
