Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures
|
|
|
- Christopher Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:62-68 doi: /cios Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures Jong-Keon Oh, MD, Jin-Ho Hwang, MD*, Dipit Sahu, MD, Seung-Hyub Jun, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University School of Medicine, *Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Background: A second staged operation using temporary bridging external fixation (TBEF) has been widely used in patients with periarticular complex fracture, yet few papers have been published on the related complications. The purpose of this study was to report the complication rate and pitfalls directly related to TBEF through a retrospective study and to suggest some solutions. Methods: Fifty-nine cases that were treated by using TBEF were studied among 195 periarticular complex fractures. We retrospectively collected the clinical and radiological data and then the study data was evaluated for 1) cases with unsatisfactory restoration of length, 2) cases with deep infection caused by half pins invading the zone of definitive fixation, and 3) neurovascular injuries related to half pins. Results: Complications were observed in 7/59 cases (11%). Problems related to the achievement of length were observed in one case of distal tibia fracture and 2 cases of distal femur fracture. Half pin related infection was observed in 2 cases of distal femur fracture. Neurovascular injury (medial calcaneal nerve injury in a distal tibia fracture) was observed in 2 cases. Among 7 complications, four were related to using TBEF in distal femur fracture. This is because the abundant leg muscles have strong deforming force and infection might be increased due to frequent irritation by the half pins. Conclusions: TBEF is a simple procedure with several advantages. However, complications might be observed if certain principles are not followed. It is thought that many complications due to TBEF can be reduced if the half pins are not inserted in the zone of injury, restoration of length is fully achieved and the neurovascular characteristics are carefully considered. In particular, much more caution is needed in the distal femur, which has abundant muscles surrounding it. Keywords: Periarticular fractures, Bridging external fixator, Complication There are various treatments for periarticular complex fracture and these range from minimally invasive external fixation with percutaneous pinning to invasive methods Received December 28, 2009; Accepted April 1, 2010 Correspondence to: Jin-Ho Hwang, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 250 Seongsan-no (134 Sinchon-dong), Seodaemun-gu, Seoul , Korea Tel: , Fax: osjinho@naver.com using open reduction and internal fixation. However, the most widely used treatment is presently a staged operation of open reduction and internal fixation with plating after settling down the soft tissues using a temporary bridging external fixator (TBEF). A TBEF is the basis of a staged operation, and easy, fast and simple procedure with many advantages. TBEF provides relative stability to fractured areas while the soft tissues around the fractured area heal before performing formal open reduction and internal fixation. Such relative stability provides patients with mobility and thus this is considered as portable traction. 1,2) The mobility given to Copyright 2011 by The Korean Orthopaedic Association This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery pissn X eissn
2 63 patients reduces the movement of the fractured areas and it subsequently reduces the pain and the following inflammatory reactions of neighboring tissues, and so it quickly helps soft tissue to heal. The nursing care also becomes easier. Early mobilization can reduce the cardiopulmonary complication in patients with periarticular complex fracture. With these advantages, the staged operation using TBEF has been widely used and its excellent results have been reported, but there are few studies on the complication rate or pitfalls of using TBEF. We performed a retrospective study on the patients with periarticular complex fracture (distal femur, proximal tibia, distal tibia) and who were treated with TBEF to determine the complication rate and the commonly related problems and also to suggest some solutions for these pitfalls. METHODS This study is not intended to report the results of staged operations, but rather, to discuss the problems observed during the definitive fixation after soft tissue healing around the fractured areas with the use of a TBEF, and the complications and problems that developed between the time of surgery and the first postoperative outpatient visit. The study was conducted on 59 cases for which definitive plating was performed with a TBEF as the initial treatment, among the 195 fractures (distal femur, 58 cases; proximal tibia, 85 cases; distal tibia, 52 cases) that were treated between January of 2003 and June of According to the Orthopaedic Trauma Association (OTA) classification, distal femur fracture included 5 cases of C1, 4 cases of C2, and 9 cases of C3; distal tibia fracture included 2 cases of C1, 3 cases of C2, and 6 cases of C3. Proximal tibia fracture, according to Shazker s type, included 9 cases of type IV and 21 cases of type VI. The patients included 46 males and 13 females, and the average age was 48 years. The involved mechanism of injury was mostly high-energy injuries, with 35 cases of motor vehicle accidents, 16 cases of falls and 8 cases of industrial accidents. A total of 19 cases were open fractures, among which there were 2 cases of type I, 6 cases of type II, 4 cases of type IIIa and 5 cases of type IIIb. Two out of 19 cases were type IIIc fractures and both were proximal tibia Schazker type VI. Two cases of type IIIc were excluded due to the difficulties of determining the relationship between a half pin and infection. Among these 19 cases of open fracture, 9 cases were transferred from local private hospitals to our hospital after performing TBEF (3 distal femur fractures with 1 C2 and 2 C3, 4 proximal tibia fractures with 2 IV and 2 V and 2 distal tibia fractures with 1 C2 and 1 C3). Surgical Technique The technique of TBEF and staged treatment was applied in the cases with severe trauma to the soft tissue around the fractured area (severe swelling, ecchymosis or blistering). In cases of open fractures, debridement was performed separately from the TBEF procedure if possible. Soft tissue debridement and irrigation were performed and then a bead pouch was made. Half pins were inserted, using the safe corridor technique, through the region with less neurovascular risk. 3) Half pin insertion was performed in a percutaneous fashion with the use of soft tissue sleeves, and pre-drilling was done to avoid thermal necrosis and soft tissue damage to the underlying bone. Half pins were inserted away from the intended site of prospective plating when converting to open reduction and internal fixation. When the patient was hemodynamically unstable, only damage control surgery was performed, and TBEF was applied by focusing on maintaining the length of the limb and fractured areas. When the patient was stable, efforts were made to provide 3-dimensional alignment of fractured areas if possible. Reduction was performed by using ligamentotaxis only, and no other procedures were performed on the fractured areas. All half pins were inserted with avoiding zones of fracture and soft tissue injury, and the prospective site of definitive surgery if possible. The time period between TBEF and plating should be not more than 2 weeks, but there were cases with a time period of more than 2 weeks after TBEF such as for patients transferred from other hospitals, or wherever pin site infection was suspected, then the pin site debridement was performed later along with administration of antibiotics for 1 week, and then the surgery was performed. The TBEF was kept in place until all the soft tissue envelopes stabilized, which usually took 7 to 10 days. When skin winkles and no pitting edema were observed, this was considered as an indication for converting to the definitive surgery. The TBEF was removed before the surgery depending on the alignment of the fractured area, and if the alignment was satisfactory, then the site was disinfected with 95% isopropyl alcohol, iodine prep scrub and iodine spray, and the reduction was maintained or TBEF was used as a reduction device in the surgical field. Knee Spanning Frames Knee spanning frames were applied for complex, unstable
3 64 distal femur and proximal tibia fractures. Half pins were inserted by considering the future intended location of plates in the definitive surgery. Two half pins were inserted in the anterior femur and 2 half pins were inserted in the anteromedial tibia. Various types of external fixator devices were used, and most of which were modular type external fixators. The advantages of this device include convenient 3-dimensional reduction that can be obtained by only using bars, which were connected to the half pins inserted to each fractured area. In such cases, double-stacked anterior bars were used to increase the stability of the fractured areas. Particularly in the case of the distal femur, it is better to maintain the alignment during the TBEF procedure because of the bulky muscles in the fractured area and the characteristic displacement after injury. When a patient was hemodynamically stable, correcting the length, external rotation and flexion deformity were attempted several times under fluoroscopic guidance. It is thought that maintenance of length is a very important factor. However, if the vascularity of a limb in question was suspicious, then overdistraction could be dangerous. Therefore, the circulation was always checked after distraction. Ankle Spanning Frames These frames were used in cases of pilon fractures with severely compromised soft tissues. Lateral fibular plating was not performed in the same surgery along with TBEF. In most cases, a modular external fixator was used. Two half pins were inserted in the proximal tibia and for the distal part, 1 half pin was inserted in the lateral calcaneus and the other one was inserted in the 1st metatarsal base. Bars and medial calcaneus pin were applied in good order to increase the frame stability. If possible, a medial pin was inserted last because of possible damage to the medial calcaneal branch. 4) Blunt dissection and sleeves were used prior to half pin insertion. When a patient was hemodynamically stable, reduction was performed by ligamentotaxis under fluoroscopic guidance to preferentially obtain the lengthening of the fracture sites and to achieve ankle joint stability. This is because if the ankle joint has no stability, then soft tissue healing can be very slow. When the circulation was doubtful, overdistraction was avoided and the circulation was checked after the surgery. Evaluation The patients were evaluated clinically and radiologically for the following three possible TBEF related problems. 1. Cases with unsatisfactory achievement of length. Failure of lengthening was defined as cases in which any procedure such as the push technique was performed or a femoral distractor was used to obtain lengthening, but it did not achieve the desired length. 2. Cases with deep infection caused by half pins invading the zone of definitive fixation without considering the plating position for definitive fixation. Delayed deep infection that developed in the fracture zone without being invaded by half pins was excluded. Also, deep infection of fractured areas related to open fracture was excluded. 3. Neurovascular injuries observed after TBEF fixation. RESULTS TBEF related problems were observed in 7 out of 59 cases (11%). Among these 7 cases, failure to achieve length was observed in 3 cases, including 1 case in distal tibia fracture and 2 cases in distal femur fracture. Neurovascular injuries Table 1. Summary of the Patients with Complications No. Gender/ Age Classification Complications Location Open fracture Hospital applying TBEF Final results Comments 1 2 M/21 M/56 33 C1 33 C2 Length Length Distal tibia Distal femur No No Author s Other s Restoration Restoration Needs an additional procedure to get the proper length, which 3 F/43 33 C2 Length Distal femur No Author s Restoration makes the operation time longer. 4 M/65 33 C3 Infection Distal femur Yes (the other site) Other s Knee fusion 5 F/41 33 C2 Infection Distal femur No Author s Revision surgery 6 M/25 43 B2 Neurovascular injury Distal tibia No Author s Partial recovery 7 M/39 43 C2 Neurovascular injury Distal tibia Yes Author s Partial recovery TBEF: temporary bridging external fixation.
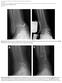
4 65 were observed in 2 out of 7 cases. Both cases were medial calcaneal nerve injury. Half pin site related deep infection was observed in 2 cases, and both were cases of distal femur. Four out of the 7 cases of complications were cases of distal femur fractures. Two of the the nine were transferred from another local private hospital. The average time for definitive plating after TBEF was 15.3 days (range, 4 to 81 days). If the cases with deep infection were excluded, then the actual time was 11.3 days. Table 1 summarizes the complications. Two cases among the cases with lengthening related problems were distal femur fractures. Achieving the lengthening in the management of distal femur fracture is easier than that for other deformities. When surgeons see just the AP image of C-arm fluoroscopy during the procedures, they make mistakes such as shortening because of flexion deformity of the distal femur. Fig. 1 showed a 45-year male patient who was transferred from a local private hospital after the application of initial TBEF for severe soft tissue compromise. Proximal half pins were involved not only in the zone of definitive surgery, but also in the zone of soft tissue injury. In addition, a distal femur articular fragment showed typical deformity such as internal rotation, flexion and shortening. Fortunately, no infection was observed in the proximal half pin site and the second surgery could be done at the 12th day after surgery without debridement of the pin site, and no specific infection was observed. Neurovascular injury was observed in 2 out of 7 cases and both were medial calcaneal nerve injuries. Fig. 2 showed a 40-year male patient who received TBEF for soft tissue swelling and blister formation after pilon fracture. The patient did complain about continuous paresthesia in the heel area. All the TBEF related deep infections on the half pins sites developed in distal femur fractures. A 60-year patient who had a tibia open fracture, including a distal femur fracture, from a traffic accident was transferred from a local hospital after 4 weeks of treatment (Fig. 3). Infection was found in the tibia, but this was controlled by performing radical debridement and muscle transfer, and proximal half pin was re-applied. after debridement. At that time of Fig. 1. (A) Radiographs showing the severe external rotation of the proximal femur (white arrow), shortening and flexion deformity of the distal femur (arrow head) and valgus deformity of the proximal tibia (star). The proximal and distal half pins were placed without considering the definitive fixation. (B) A fluoroscopy image shows obtaining lengthening with the use of the push technique during the operation. (C) Restoration of all alignments after surgery. Fig. 2. (A) Distal half pins were inserted in the medial calcaneal side and the 1st metatarsal base. (B, C) A medial calcaneal pin was inserted almost at the end of the heel.
5 66 Fig. 3. (A) The proximal half pins were invading the zone of definitive fixation (white arrow). Also, the distal half pins were invading the infected areas of the open fracture. (B) Just before converting, the displaced half pins and debridement wound are shown (arrow heads). (C) A photo showing the invasion to the zone of definitive fixation even after the surgery was performed without the findings of infection at 2 weeks after reframe and debridement. (D) The infected area at 10 days after surgery. the initial debridement, there was no infection observed at the external fixator half pin site in the distal femur. Since the half pin had been placed for more than 2 weeks, pin site debridement was performed and the location of the half pins was changed from the lateral thigh to the anterior thigh. Intravenous antibiotics were injected for one week. However, infection developed at the original half pin site after converting to plating. DISCUSSION According to several studies, staged open reduction and internal fixation with the use of TBEF in complex periarticular fracture with compromised soft tissue (distal femur, proximal tibia and distal tibia) has greatly decreased the rate of infection.5-7) Pin site infection and hardware related infection have been continuously reported, but these reports are now much less frequent than earlier. Most studies have not particularly emphasized infections that are directly related to TBEF. Sirkin et al.7) have reported a 3% infection rate in closed fracture and a 10% rate in the open fracture among 56 cases of severe pilon fracture. However, TBEF with half pin site related infection was not especially mentioned. TBEF is a simple, convenient procedure with several advantages and it has been widely used, but there have been few reports on its problems and pitfalls. We performed a retrospective study with emphasizing 3 problems that could be potentially damaging when using TBEF and we found that 7 out of 59 cases (11%) had those problems. These 3 problems are important because of the following reasons. First, there are some cases in which 1 cm of desired length could not be obtained during the definitive surgery if 2 weeks had already passed since the injury. In such cases, several procedures were tried in the surgical field to obtain lengthening and the operation time was extended, which is accompanied by an increased risk of infection. Second, the site of half pins should be carefully considered because it is directly related to infection. Third, the pain caused by neurovascular injury can worsen the results when evaluating complex periarticular fractures. Thus, it becomes difficult to evaluate if pain problems are due to a fracture itself or the increased pain from nerve damage. Especially noticeable was that four among 7 complications were observed in distal femur fractures, and no particular problem was observed in the proximal tibia. Distal femur fracture can be considered as resistant to infection due to relatively abundant muscle envelope, but this infection problem is especially observed after TBEF application. Infection related to TBEF may occur because the deforming force is strong in the fractured area due to abundant muscles and the risk for infection in the area surrounding the pins is high due to irritation that develops after inserting half pins. Also, half pin insertion in the proximal side is often more difficult because the possibility for neurovascular injury becomes greater as the proximal anterior half pins are inserted in the more proximal region. Some investigators have avoided anterior half pins because this may injure the quadriceps mechanism. These investigators often inserted lateral half pins, but more cautions for infection is needed because inserting lateral half pins can directly involve the zone of definitive surgery compared to anterior fixation. In figure 4, the proximal
6 67 Fig. 4. (A) Distal two half pins were inserted and traction was performed to restore the length (big white arrow). After that, another half pin was inserted in the proximal femur to correct the internal rotation (small white arrow). Then two proximal half pins were inserted. (B) Restoration of length during the operation. (C, D) The internal rotation after proximal external rotation during the operation. (E) A photo after surgery shows that the length and external rotation were corrected. side of the fracture showed external rotation and the distal fragment appeared shortened and flexed (Fig. 1A). One cm of shortening can be considered as insignificant, but if the patient is unstable such as the case of polytraumatized patients, a converting procedure might not be performed for a certain period of time after TBEF application. In such cases, it is very difficult to restore the length during the second surgery. Therefore, it is the best to correct several alignments at the same time if a patient is hemodynamically stable, but the ultimate goal should be the restoration of lengthening if a patient is hemodynamically unstable. In case of distal femur fracture, we first inserted 2 distal half pins in the anteromedial side of the proximal tibia to obtain good alignment and then traction was performed to restore the lengthening without muscle irritation. If half pins are inserted first in the proximal thigh, then sufficient lengthening can not be obtained because pins cause irritation to the muscle during the traction, and such continuous irritation can give rise to infection after the surgery. After that, one half pin is inserted in the proximal side and then internal rotation is performed to correct the external rotation. Finally, two half pins were inserted anteriorly in the proximal femur and then fixation was performed (Fig. 4). TBEF is a safe procedure if safe corridors are used for pin insertion and neurovascular damage is not caused on the other side of the cortex while pre-drilling before inserting the half pins. In 2 cases of pilon fracture, medial calcaneal nerve injury was noticed (the medial calcaneal branch was damaged). Some authors have reported that safe placements could be at the back of the half point of the line connecting the posteroinferior medial calcaneus and the inferior medial malleolus, and at the back of the one third point of the line connecting the posteroinferior medial calcaneus and the navicular tuberosity.4,8) However, they suggested that half pin insertion is safer when the pins are placed behind the heel, if possible, because of many anatomic variations. They also suggested using blunt dissection and sleeves. We used the similar technique, as seen in Fig. 2, that the half pins were inserted at the posterior area near the heel and we used blunt dissection and sleeves, but two cases of medial calcaneal nerve damage developed. To solve this problem we do lateral calcaneal pin insertion and 1st metatarsal pin insertion primarily and if this is unable to provide sufficient stability, then more bars are added; if it is not stable enough, then pins are added to the medial side for further stability. There was no TBEF related problem in the proximal tibia fractures. At the time of injury, this is a region that is
7 68 easily damaged due to open fracture, but this region seems to have less problems for TBEF application, in which proximal half pins are easily inserted in the distal femur, because it is not a fixation zone and also the pins are relatively easily inserted in the distal part to the ankle area because the anteromedial side is skin on bone. Although our results were obtained from a retrospective study and the number of total cases was small, this is the first study on the TBEF problems that most orthopedic surgeons easily fail to notice. Also, it is thought that a rate of complications over 10% can sufficiently affect the final results of complex periarticular fracture. Therefore, we feel this study on the application of TBEF will catch the attention of diligent and thoughtful surgeons. In conclusion, TBEF is a basic procedure for the staged operation technique and this technique has recently been widely used. It is considered to be a relatively easy technique, but its importance has been less emphasized than definitive plating. However, special concerns are needed because the frequency of TBEF related complications is high in cases of distal femur fracture. Thus, better results will be obtained if TBEF is performed with giving full consideration to the fixation zone, the restoration of length and the neurovascular structures. Much caution is needed when performing TBEF and particularly for distal femur fractures. CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. 1. Watson JT, Coufal C. Treatment of complex lateral plateau fractures using Ilizarov techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(353): REFERENCES options for the treatment of severe tibial pilon fractures: a study of three techniques. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(3): Watson JT, Moed BR, Karges DE, Cramer KE. Pilon fractures. Treatment protocol based on severity of soft tissue injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(375): Behrens F. General theory and principles of external fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(241): Casey D, McConnell T, Parekh S, Tornetta P 3rd. Percutaneous pin placement in the medial calcaneus: is anywhere safe? J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(1): Blauth M, Bastian L, Krettek C, Knop C, Evans S. Surgical 6. Collinge C, Sanders R, DiPasquale T. Treatment of complex tibial periarticular fractures using percutaneous techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(375): Sirkin MS, Bono CM, Reilly MC, Behrens FF. Percutaneous methods of tibial plateau fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(375): Santi MD, Botte MJ. External fixation of the calcaneus and talus: an anatomical study for safe pin insertion. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10(7):
Pilon fractures. Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota
 Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
The high energy trauma associated with comminuted. Staged Management of High-Energy Proximal Tibia Fractures
 62 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 62, Numbers 1 & 2 2004 Staged Management of High-Energy Proximal Tibia Fractures Nirmal C. Tejwani, M.D., and Pramod Achan, F.R.C.S. Abstract High-energy
62 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 62, Numbers 1 & 2 2004 Staged Management of High-Energy Proximal Tibia Fractures Nirmal C. Tejwani, M.D., and Pramod Achan, F.R.C.S. Abstract High-energy
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia.
 Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique
 Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Surgical Technique Guide
 Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction. Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center
 OTA Specialty Day 2016 Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center 8:55 am 9:55 am Tips and Tricks: Practical Reduction Techniques
OTA Specialty Day 2016 Practical Reduction Techniques: Diaphyseal Reduction Philip Wolinsky University of California at Davis Medical Center 8:55 am 9:55 am Tips and Tricks: Practical Reduction Techniques
Foot and Ankle Update
 Foot and Ankle Update 2019 Instructional Course Hiro Tanaka It s your on-call weekend Objectives We are going to apply evidence based treatment for 2 patients who are admitted under your care 1. Dislocated
Foot and Ankle Update 2019 Instructional Course Hiro Tanaka It s your on-call weekend Objectives We are going to apply evidence based treatment for 2 patients who are admitted under your care 1. Dislocated
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Original Research Article
 TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts.
 Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Skeletal Stabilization in the Severely Injured Limb: Fixation Techniques Compatible with Soft Tissue Trauma. Michael A. Miranda MD
 Skeletal Stabilization in the Severely Injured Limb: Fixation Techniques Compatible with Soft Tissue Trauma. Michael A. Miranda MD Skeletal Stabilization in the Severely Injured Limb: Fixation Techniques
Skeletal Stabilization in the Severely Injured Limb: Fixation Techniques Compatible with Soft Tissue Trauma. Michael A. Miranda MD Skeletal Stabilization in the Severely Injured Limb: Fixation Techniques
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures
 FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
Cost and Time Considerations: Are Minifragment Plates Worth It? Disclosure. More Disclosures. Are minifragment plates worth it? it depends!
 Cost and Time Considerations: Are Minifragment Plates Worth It? Andrew Choo, MD Vumedi Webinar November 15, 2016 Disclosure Paid speaker: Depuy Synthes More Disclosures Price quotes are estimates only!
Cost and Time Considerations: Are Minifragment Plates Worth It? Andrew Choo, MD Vumedi Webinar November 15, 2016 Disclosure Paid speaker: Depuy Synthes More Disclosures Price quotes are estimates only!
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique
 PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Contour Femur Plate Surgical Technique Surgical Technique Contour Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the
Locking Ankle Plating System. Surgical Technique
 Locking Ankle Plating System Surgical Technique Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that
Locking Ankle Plating System Surgical Technique Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique
 TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
Hoffmann II External Fixation System
 Hoffmann II External Fixation System Modular System for Long Bones Pelvis Introduction In 1938, Raoul Hoffmann, a surgeon from Geneva, Switzerland, designed a revolutionary External Fixation System. The
Hoffmann II External Fixation System Modular System for Long Bones Pelvis Introduction In 1938, Raoul Hoffmann, a surgeon from Geneva, Switzerland, designed a revolutionary External Fixation System. The
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Bowed Femur Plate Surgical Technique
 PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Bowed Femur Plate Surgical Technique 2957 Bow Broch_REV_B.indd 1 2/10/11 12:47 PM Surgical Technique Bowed Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the
PediLoc 3.5mm and 4.5mm Bowed Femur Plate Surgical Technique 2957 Bow Broch_REV_B.indd 1 2/10/11 12:47 PM Surgical Technique Bowed Femur Plate The technique description herein is made available to the
GREENS SURGICALS. Redefining Excellence INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR
 GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate
 Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Biomet. Vision Pin-To-Bar System. Surgical Technique. Calcaneal Reduction Frame
 Biomet Vision Pin-To-Bar System Surgical Technique Calcaneal Reduction Frame One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized care to one patient.
Biomet Vision Pin-To-Bar System Surgical Technique Calcaneal Reduction Frame One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized care to one patient.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures.
 LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
Accepted: 3 April 2009
 Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics
 MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
ISPUB.COM. Z Ali, L Khurshid, S Vakil, A Anjum, S Dhar OBJECTIVE METHOD PATIENTS
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 22 Number 1 Prevalence Of Pin Tract Infection And Role Of Combined Saline And Povidone Iodine With Combined Spirit (Isopropyl Alcohol 70% V/V)
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 22 Number 1 Prevalence Of Pin Tract Infection And Role Of Combined Saline And Povidone Iodine With Combined Spirit (Isopropyl Alcohol 70% V/V)
Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot)
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Introduction. Introduction 10/2/2009. Bryan Lapinski, MD
 Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series
 Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Diabetics. Referred for management of complex pilon fracture? 5/10/2017. Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?)
 Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
Open Access Case Report DOI: /cureus.599. Ashok K. Rathod 1, Rakesh P. Dhake 1, Aditya Pawaskar 1
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.599 Minimally Invasive Treatment of a Complex Tibial Plateau Fracture with Diaphyseal Extension in a Patient with Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.599 Minimally Invasive Treatment of a Complex Tibial Plateau Fracture with Diaphyseal Extension in a Patient with Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate
 wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Alan Cooney Northern Deanery Registrar Teaching June 2011
 Alan Cooney Northern Deanery Registrar Teaching June 2011 Introduction Anatomy Classification Surgical approaches What is the evidence? What are pilon fractures? Intra-articular # distal tibia Pilon (pestle)
Alan Cooney Northern Deanery Registrar Teaching June 2011 Introduction Anatomy Classification Surgical approaches What is the evidence? What are pilon fractures? Intra-articular # distal tibia Pilon (pestle)
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. Arthrodesis. Joint Fusion. By Dr. S. Agostini and Dr. F. Lavini
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 5 Arthrodesis Joint Fusion By Dr. S. Agostini and Dr. F. Lavini QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE ARTHRODESIS OF THE HIP Apply the ProCallus Fixator to the lateral aspect of the thigh. Insert
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 5 Arthrodesis Joint Fusion By Dr. S. Agostini and Dr. F. Lavini QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE ARTHRODESIS OF THE HIP Apply the ProCallus Fixator to the lateral aspect of the thigh. Insert
Surgical Technique. Fibula Rod System
 Surgical Technique Fibula Rod System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve patient
Surgical Technique Fibula Rod System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve patient
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.13, No.3, July, 2000
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol13, No3, July, 2000 2, 3 ) : 40-12, Tel : (02) 966-1616 Fax : (02) 968-2394 E-mail : adkajs@thrunetcom 471 8, 1 2 ) (Table 1) 1 6 14, 2 1 2 1 Ender 29
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol13, No3, July, 2000 2, 3 ) : 40-12, Tel : (02) 966-1616 Fax : (02) 968-2394 E-mail : adkajs@thrunetcom 471 8, 1 2 ) (Table 1) 1 6 14, 2 1 2 1 Ender 29
EBI FIX DYNAFIX SYSTEM VISION EXTERNAL FIXATION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Patent 6,277,119
 EBI DYNAFIX FIX SYSTEM DYNAFIX VISION EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Patent 6,277,119 1 CONTENTS Basic Principles and Biomechanical Concepts...Page 2 Introduction...Page 2 Component Review...
EBI DYNAFIX FIX SYSTEM DYNAFIX VISION EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Patent 6,277,119 1 CONTENTS Basic Principles and Biomechanical Concepts...Page 2 Introduction...Page 2 Component Review...
Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Posterior Malleolus Fractures and Iatrogenic Injuries: A Cadaveric Study
 Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Posterior Malleolus Fractures and Iatrogenic Injuries: A Cadaveric Study JOHN KARBASSI, MD, MPH ANDREW BRAZIEL, MD MICHAEL HEFFERNAN, MD ABHAY PATEL, MD UNIVERSITY OF
Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Posterior Malleolus Fractures and Iatrogenic Injuries: A Cadaveric Study JOHN KARBASSI, MD, MPH ANDREW BRAZIEL, MD MICHAEL HEFFERNAN, MD ABHAY PATEL, MD UNIVERSITY OF
Tibia plateau fractures getting worse all the time
 Session 4: the knee: part I Tibia plateau fractures getting worse all the time Christoph Sommer, Head of Trauma Surgery Session 4: the knee: part I Tibia plateau fractures getting worse all the time Christoph
Session 4: the knee: part I Tibia plateau fractures getting worse all the time Christoph Sommer, Head of Trauma Surgery Session 4: the knee: part I Tibia plateau fractures getting worse all the time Christoph
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Biomet Vision Pin-To-Bar Fixation System. Surgical Technique
 Biomet Vision Pin-To-Bar Fixation System Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Indications and Contraindications... Page 2 Basic Principles And Biomechanical Concepts...Page 3 Instruments...
Biomet Vision Pin-To-Bar Fixation System Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Indications and Contraindications... Page 2 Basic Principles And Biomechanical Concepts...Page 3 Instruments...
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs
 Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs Module Five: Movement Assessment of the Foot/Ankle (1 hour CEU Time) Skilled
Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs Module Five: Movement Assessment of the Foot/Ankle (1 hour CEU Time) Skilled
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Humerus shaft - Reduction & Fixation - Compression plate - AO Surgery Reference. Compression plating
 Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Surgical Technique. Ankle Plating System
 Surgical Technique Ankle Plating System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve
Surgical Technique Ankle Plating System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve
Fibula Rod System. Lateral Malleolus Fracture Indications:
 Fibula Rod System Fibula Rod System Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions for the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Fibula Rod System Fibula Rod System Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions for the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
pat hways Medtech innovation briefing Published: 14 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib166
 pat hways Galaxy UNYCO for temporary stabilisation of lower limb fractures Medtech innovation briefing Published: 14 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib166 Summary The technology described in this briefing
pat hways Galaxy UNYCO for temporary stabilisation of lower limb fractures Medtech innovation briefing Published: 14 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib166 Summary The technology described in this briefing
Clinical. Solutions. Synthes Solutions. Foot and Ankle.
 Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function
 Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function Fracture specific plating solutions for the most common tibia and fibula fractures Frequency of fracture occurrences* 66% 61% 36% 36% 28% 14% 20%
Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function Fracture specific plating solutions for the most common tibia and fibula fractures Frequency of fracture occurrences* 66% 61% 36% 36% 28% 14% 20%
2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP. Ankle Trauma System
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique
 TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique Choice, Simplicity, Transition TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique Choice, Simplicity, Transition TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Satisfaction analysis of Figure 8 (open heel) short leg cast
 Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
OBSOLETED. LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Surgical Technique LCP Small Fragment System This publication
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Surgical Technique LCP Small Fragment System This publication
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
Technique Guide. LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. The XCaliber Articulated Ankle Fixator. By Dr. S. Berki, Dr. V. Caiaffa, Dr. F. Lavini and Dr. M. Manca
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 18 The XCaliber Articulated Ankle Fixator By Dr. S. Berki, Dr. V. Caiaffa, Dr. F. Lavini and Dr. M. Manca GENERAL POINTS The XCaliber Articulated Ankle Fixator is made of radiolucent
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 18 The XCaliber Articulated Ankle Fixator By Dr. S. Berki, Dr. V. Caiaffa, Dr. F. Lavini and Dr. M. Manca GENERAL POINTS The XCaliber Articulated Ankle Fixator is made of radiolucent
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
 LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. Arthrodiatasis. Articulated Joint Distraction
 4 Arthrodiatasis Articulated Joint Distraction ARTHRODIATASIS OF THE HIP To prepare the assembly, remove the female component and replace it with the ProCallus articulated body for the hip. Remove cam
4 Arthrodiatasis Articulated Joint Distraction ARTHRODIATASIS OF THE HIP To prepare the assembly, remove the female component and replace it with the ProCallus articulated body for the hip. Remove cam
The pilon tibiale fracture
 The pilon tibiale fracture Thomas Beck Spitalzentrum Oberwallis OTC Trauma course september 2017 xxx I have no financial relationships with commercial entities that produce healthcare related products.
The pilon tibiale fracture Thomas Beck Spitalzentrum Oberwallis OTC Trauma course september 2017 xxx I have no financial relationships with commercial entities that produce healthcare related products.
Intelligent Orthopaedics
 Intelligent Orthopaedics Nailing Stand Instructions for Use and Guidance doc - iostorm-04-1.1 Contents Instructions for use 2 Description 3 Caution 3 Preparation 4 Pre-setting height 4 Proximal Wire Insertion
Intelligent Orthopaedics Nailing Stand Instructions for Use and Guidance doc - iostorm-04-1.1 Contents Instructions for use 2 Description 3 Caution 3 Preparation 4 Pre-setting height 4 Proximal Wire Insertion
Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame. Using rings with clamps.
 Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame. Using rings with clamps. Technique Guide Part of the External Fixation System Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame Technique Overview 1 Insert wires 2 Attach wires to
Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame. Using rings with clamps. Technique Guide Part of the External Fixation System Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame Technique Overview 1 Insert wires 2 Attach wires to
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
The Hybrid Ring Fixator Surgical Technique
 The Hybrid Ring Fixator Surgical Technique Table of contents Page Indications 4 Preoperative planning 6 Tibial plateau fracture 7 Restore articular surface and stabilize... 7 Determine wire position...
The Hybrid Ring Fixator Surgical Technique Table of contents Page Indications 4 Preoperative planning 6 Tibial plateau fracture 7 Restore articular surface and stabilize... 7 Determine wire position...
