Genetics Metro NY/NJ Pediatric Board Review Course
|
|
|
- Eugenia Hudson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /4/2018 Genetics Metro NY/NJ Pediatric Board Review Course Joy M. Samanich, M.D. Robert W. Marion, M.D. Albert Einstein Col of Med/ Children s Hosp at Montefiore Question 1: In the NICU, you ve just examined a newborn with hypotonia and dysmorphic features that included epicanthal folds, upward slanting of the palpebral fissures, flat nasal bridge with anteverted nares and midface hypoplasia. Among the following, the medical complication that is MOST likely to present in the newborn period in this infant is: 1. atlantoaxial instability 2. hypothyroidism 3. leukemia 4. obstructive bowel disease 5. seizures 40% 27% 20% 7% 7% Question 2: You tell the infant s parents of your concern that their baby has Down syndrome. After the initial shock, the mother asks about her risk of having another child with a chromosomal abnormality. The statement that you are MOST likely to include in your discussion is that her risk: A. can be estimated by determination of maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein in all future pregnancies B. cannot be estimated until her infant's chromosome complement has been determined C. is increased for Down syndrome, but not for any other chromosomal abnormality D. is no greater than that of other women her age E. is not increased until she reaches the age of 35 1
2 Karyotype Trisomy 21 (95%; RR 1% for ANY TRISOMY) Unbalanced Roberstonisan Translocation (3%) Mosaicism (2%) De novo (2/3) Inherited from balanced parent (1/3) Maternal (RR 10-15%) Paternal (RR 2-5%) 21:21 translocation (RR 100%) Question 3: As long as you re already in the nursery, you re asked to see 3 infants born with cleft lip and/or palate. The first has a left CL+P; exam is otherwise normal. You tell his parents that this is apparently an isolated birth defect. During counseling about their risk for having another similarly affected child, the statement that you are MOST likely to include is that A. because the defect is isolated, their risk is no greater than that of any other couple B. Isolated cleft lip and palate is a multifactorial trait that has a 4% risk of recurrence C. the recurrence risk can be estimated only after a chromosome analysis has been obtained D. the risk is increased for future females, but not males E. the risk would be increased only if one of the parents had cleft lip and palate Question 4 The next baby you see in the nursery, a boy, has bilateral CL+P. Further exam reveals scalp defect in the parietooccipital region, microphthalmia, cryptorchidism, a cardiac murmur and polydactyly. Of the following, the MOST likely underlying condition is: A. holoprosencephaly sequence B. retinoic acid embryopathy C. trisomy 13 D. trisomy 18 E. valproate embryopathy 2
3 /4/2018 Question 5: The next baby you visit in the nursery has a CP and retrognathia, but no other anomalies. Of the following, the MOST serious complication that may occur in the first 72 hours of this child's life is: A. acute otitis media requiring antibiotic treatment B. congestive heart failure C. difficulties with breastfeeding D. upper airway obstruction with oxygen desaturation E. worsening airway obstruction when placed in the prone position Question 6: As long as you re already in the nursery, the resident asks you to see a newborn who has some unusual features. Born by C/S because of breech presentation, the baby has a deformed cranium, torticollis, facial asymmetry, a dislocated right hip, and bilateral clubfeet. Findings on the remainder of the physical examination are normal. Of the following, the MOST likely cause of this infant's abnormalities is A. a chromosomal abnormality B. a malformation syndrome C. an underlying CNS defect D. exposure to a teratogen in utero E. intrauterine compression Question 7: 0% 0% 0% You re in Spina Bifida Clinic. Your first patient is an infant recently D/C d from the NICU after having her myelomeningocele closed and a VP shunt placed. She has typical problems of an infant with an L2 lesion: hydrocephalus, dislocated hips, club feet and paraplegia. Her parents are concerned about recurrence in future pregnancies. Of the following, the statement you are MOST likely to make is that their RR 1. depends on the family's ethnic background 2. depends on the location of the defect along the neural axis 3. is increased only if the defect is part of a genetic syndrome 4. is the same as that for any other couple 5. will be reduced if the mother takes periconceptional folate supplementation 10 0% 0% 3
4 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% /4/2018 Question 8: In genetics clinic, you re seeing a 5 y.o. girl who has multiple café au lait spots and axillary freckling. Slitlamp ophthalmic exam reveals the presence of Lisch nodules, confirming the diagnosis of neurofibromatosis. Of the following, the MOST appropriate statement about the potential for the development of tumors in this child is that: 1. acoustic neuromas are common and annual screening with MRI is indicated 2. all patients with neurofibromatosis eventually develop plexiform neurofibromas 3. annual urinary catecholamine screening for the presence of pheochromocytoma is indicated 4. cutaneous neurofibromas usually do not appear until preadolescence 5. the overall lifetime risk for the development of a malignancy is 50% 10 Question 9: The next patient in clinic is the mother of a 13-mo-old boy recently diagnosed with factor VIII deficiency hemophilia. The woman is in the 1st trimester of her 2nd pregnancy, and is interested in knowing if prenatal diagnosis is available. Of the following, the statement about prenatal diagnosis that you are MOST likely to include in your discussion is that: A. factors VIII and IX deficiency hemophilia can be dx d prenatally in over 95% of families B. factors VIII and IX deficiency hemophilia can be dx d prenatally only in 20% of families C. neither type of hemophilia can be dx d prenatally D. only factor IX deficiency hemophilia can be dx d prenatally E. only factor VIII def. hemophilia can be dx d prenatally It s lunch time in Clinic. Time for some quickies: Question 10: Of the following, the findings that are MOST suggestive of the dx of Prader-Willi syndrome are: 1. gigantism and visceromegaly 2. hyperactivity and ataxic movements 3. hypocalcemia and a congenital heart defect 4. MR and macroorchidism 5. obesity and small hands and feet 10 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
5 PWS results from deficiency of the gene product of the SNRPN gene. SNRPN (15q11) is only expressed in the chromosome 15 inherited from the father. Thus, PWS results when a copy of paternal chromosome 15 is missing. This can be caused by: Deletion of pat 15q11.2 (seen in 60-70%): Use FISH to diagnose Maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15 (yielding two copies of maternal chromosome 15 and no copies of paternal chromosome 15) (seen in 20%) Another quickie: Question 11: All of the following are associated with Williams syndrome EXCEPT A. Cocktail party personality B. Hypercalcemia C. Supravalvular aortic stenosis D. Short philtrum E. Mental retardation A third quickie: Question 12: Noonan syndrome is characterized by each of the following EXCEPT A. Autosomal recessive inheritance B. Short stature C. Pulmonic stenosis D. Webbed neck E. Low set ears 5
6 Question 12: The answer is A Noonan syndrome is caused by a mutation in the PTPN11 gene on chromosome 12. Occurs in 1 in 10,000 births Features include all those listed in question except for AR inheritance 50% also have Factor 11 deficiency causing prolonged PTT. Yet another: Question 13: A child is born with esophageal atresia. Other associated abnormalities might include all of the following EXCEPT A. Cardiac defect such as VSD B. Absence of the left radius C. Renal malformations D. Hemivertebra E. Cataracts Last quick one: Question 14: Which of the following is typical of Ehlers Danlos syndrome? A. Osteoporosis B. Hypotrichosis C. Large head and short extremities D. Joint laxity E. Progressive neurologic and ophthalmologic problems 6
7 Question 14: The answer is D Osteoporosis is seen in osteogenesis imperfecta. Hypotrichosis occurs in anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Large head and short extremities describes achondroplasia. Ehlers Danlos is a disorder of collagen that leads to: Joint laxity Spontaneous joint dislocation Hyperelastic skin Poor scar formation ( cigarette paper scars) Easy bruisability Okay, really last quick one: Question 15: For which of the following disorders would you use PCR testing for trinucleotide repeats to make the diagnosis? A. Crouzon syndrome B. Fragile X syndrome C. Cri-du-chat syndrome D. MELAS syndrome E. Down syndrome OKAY, LUNCH IS OVER TIME TO GO TO METABOLIC CLINIC: 7
8 Question 16: 1 st Patient in Metabolic Clinic: The parents of a 2 y.o. boy with Tay-Sachs disease (TSD) (hexosaminidase A deficiency) ask you about the availability of prenatal testing during their next pregnancy. Of the following, the MOST appropriate statement to include in your counseling is that: A. prenatal dx should be considered only after testing each parent to determine carrier status B. testing can be performed on chorionic villus cells obtained as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy C. testing is possible only if the parents' mutations in the hexosaminidase gene are known D. the results of prenatal diagnostic testing for TSD are considered investigational E. their risk of having another similarly affected child is no greater than that of any other couple Question 17: Next Pt. in Metab Clinic: You re seeing a 3 y.o. with Hunter syndrome (MPS-II) for F/U. His parents tell you the boy s newborn brother has just been dx d with this same disorder, and they ve heard that bone marrow transplantation can cure the baby of his condition. Of the following, the statement you are MOST likely to include in a discussion of transplantation for Hunter syndrome and other inborn errors of metabolism is that A. family members who are carriers of the disorder cannot be donors B. infections are less common than in patients who have a hematologic disorder C. it is contraindicated in disorders that include adverse neurologic symptoms D. it never has been successful in the treatment of enzyme deficiency disorders E. successful transplantation may halt disease progression for some disorders Question 17: Preferred Response: E Organ & bone marrow transplantation (BMT) may halt progression of some metabolic disorders Used more b/c better immunosuppressants & no other effective treatment strategies Each case must be considered individually Sometimes, BMT is undertaken to provide a source of enzyme that s not produced in sufficient quantities Sometimes, organ tx replaces an organ that s been damaged by the disease process 8
9 Question 18: Next Pt. in Metab Clinic: You are called down to the ED to see a previously healthy 2 y.o. boy who was brought to the ED by his mother, who reported that he has had a cold and fever for the past 2 days. He has been taking only small amounts of juice and no solid foods. When she tried to arouse him after his nap today, he was lethargic and unresponsive. Results of laboratory studies include a glucose concentration of 40 mg/dl, an ammonia level of 200 mcg/dl, and an arterial blood ph of 7.4. At this time, the MOST important study to obtain is 1. plasma acylcarnitine profile 2. plasma insulin levels 3. serum acetylsalicylic acid concentration 4. urine and stool porphyrins 5. urine organic acids 10 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Question 18: Preferred Response: A Fatty acid oxidation defects Defects in mitochondrial beta-oxidation of fatty acids (MBOFA) Autosomal recessive MCAD (medium-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency) is most common Presents by age 2 with lethargy after fasting, typically associated with a URI or AGE Hypoketotic hypoglycemia and hyperammonemia Dx by plasma acylcarnitine profile MBOFA for the production of energy is only required during periods of fasting, clinical manifestations do not become apparent unless substantial fasting has occurred. Thus, there can be great heterogeneity in clinical course. Question 18: Preferred Response: A Between episodes of illness, affected pts are normal. 1st episode may result in death and is frequently mis-dx d as Reye syndrome or SIDS Treatment includes avoidance of fasting, carnitine supplementation, and dextrose during acute episodes. Molecular diagnosis of MCAD is available > 90% point mutation in the MCAD gene 9
10 Question 18: Incorrect responses An organic acidemia should be suspected in pts presenting with hypoglycemia and hyperammonemia in the presence of metabolic acidosis. Plasma insulin levels should be obtained in a child suspected of having hyperinsulinemia, which may cause hypoglycemia but usually is not associated with hyperammonemia. Urine and stool porphyrin analysis is useful in the diagnosis of the porphyria different sx s (abdominal pain, vomiting constipation) Acetylsalicylic acid poisoning usually presents with hyperventilation and dehydration, but hyperammonemia is not typical. Question 19: Call from the ED You receive an emergent call from the ED. A baby boy, DOL#4, is lethargic, with history of irritability and poor feeding for 2 days. They are concerned about a metabolic disorder. The parent has also noted some abnormal movements, that look like the baby is fencing, or bicycling. Newborn screen results are not available, but laboratory studies reveal metabolic acidosis with anion gap, normal ammonia level, and positive urinary ketones. Which do you expect to find on your examination? A. Cataracts B. Hepatomegaly C. Maple syrup odor of the cerumen D. Eczematous skin rash E. Overriding sutures Question 20: Match each metabolic disorder with its characteristic feature A. Galactosemia B. Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) C. Phenylketonuria (PKU) D. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTC) 1. X-linked disorder 2. Musty body odor 3. Treated with lactosefree diet 4. Missing enzyme to break down branched chain amino acids 10
11 Question 20: Correct matches A. Galactosemia B. Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) C. Phenylketonuria (PKU) D. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTC) 1. X-linked disorder 2. Musty body odor 3. Treated with lactosefree diet 4. Missing enzyme to break down branched chain amino acids Question 20 summary Galactosemia: disorder of carbohydrate metabolism; GALT deficiency; AR; sx s: days to weeks of life (vomiting, jaundice, hepatomegaly, lethargy, bacterial infection, cataracts); dx: newborn screen, molecular; tx: lactose-free diet PKU: amino acid disorder, Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency; AR; sx s: poor feeding, lethargy, light eyes/skin/hair, musty odor, eczematous like rash, untreated severe ID; dx: newborn screen; tx: low Phe diet OTC: urea cycle DO; X-linked; sx s: 24 hrs-few days, vomiting, poor feeding, lethargy, sz, hepatomegaly; dx: NOT newborn screen, ammonia, UOA, PAA, genetic testing; tx: low protein diet, alternate pathway meds to get rid of nitrogen, arginine GENETICS CLINIC IS OVER. BEST OF LUCK ON THE BOARDS! 11
Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism Cases Studies Angela Sun, M.D. University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Case 1 5 day old with poor feeding Exclusively breastfeeding Decreased urine
Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism Cases Studies Angela Sun, M.D. University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Case 1 5 day old with poor feeding Exclusively breastfeeding Decreased urine
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Genetics
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) IAP UG Teaching slides
 INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
MEDICAL GENETICS CLINICAL CARE ROTATION
 Medical Genetics Clinical Care Rotation 1 MEDICAL GENETICS CLINICAL CARE ROTATION Overview: The Medical Genetics Clinical Care Rotation (MGC) is the backbone of the clinical genetics experience for the
Medical Genetics Clinical Care Rotation 1 MEDICAL GENETICS CLINICAL CARE ROTATION Overview: The Medical Genetics Clinical Care Rotation (MGC) is the backbone of the clinical genetics experience for the
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.014 02/18/2000 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 08/23/2013 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.014 02/18/2000 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 08/23/2013 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial,
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial,
Common Genetic syndromes. Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria
 Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Formal Genetics of Humans: Modes of Inheritance. Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 Formal Genetics of Humans: Modes of Inheritance Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 Autosomal dominant (AD) a: Wild type (Wt) allele A: Mutant allele aa: Normal phenotype Aa: Affected (heterozygous) AA: Affected (homozygous)
Formal Genetics of Humans: Modes of Inheritance Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 Autosomal dominant (AD) a: Wild type (Wt) allele A: Mutant allele aa: Normal phenotype Aa: Affected (heterozygous) AA: Affected (homozygous)
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Legal aspects in accidents and neglect.
 Al-Al Bayt University Princess Salma Faculty of Nursing Adult Health nursing Course Title :Child Health Nursing Course Number :1001341 Credit Hours :3 Pre requisite :1001222 Placement : Instructor:,, Course
Al-Al Bayt University Princess Salma Faculty of Nursing Adult Health nursing Course Title :Child Health Nursing Course Number :1001341 Credit Hours :3 Pre requisite :1001222 Placement : Instructor:,, Course
Ch 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics
 Ch 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics Studying Human Genetics A pedigree is a chart for tracing genes in a family. Used to determine the chances of offspring having a certain genetic disorder. Karyotype=picture
Ch 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics Studying Human Genetics A pedigree is a chart for tracing genes in a family. Used to determine the chances of offspring having a certain genetic disorder. Karyotype=picture
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF)
 CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF) NNFF International NF1 Genetic Mutation Analysis Consortium Submission Form FORM USE Name of investigator (required field): Institution (required field):
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF) NNFF International NF1 Genetic Mutation Analysis Consortium Submission Form FORM USE Name of investigator (required field): Institution (required field):
Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders
 Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Metabolic Emergencies and the Pediatrician
 Metabolic Emergencies and the Pediatrician Stephen G. Kahler, MD Professor of Pediatrics Section of Genetics and Metabolism, UAMS and ACH Hot Springs, AR March 8, 2012 INHERITED METABOLIC DISORDERS HOW
Metabolic Emergencies and the Pediatrician Stephen G. Kahler, MD Professor of Pediatrics Section of Genetics and Metabolism, UAMS and ACH Hot Springs, AR March 8, 2012 INHERITED METABOLIC DISORDERS HOW
Nutritional Management of Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Kay Davis, RD, CSP Esther Berenhaut, RD, CSP, CSR Aug 28, 2017
 Nutritional Management of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Kay Davis, RD, CSP Esther Berenhaut, RD, CSP, CSR Aug 28, 2017 OBJECTIVES Brief overview of newborn screening of metabolic disorders, inheritance patterns.
Nutritional Management of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Kay Davis, RD, CSP Esther Berenhaut, RD, CSP, CSR Aug 28, 2017 OBJECTIVES Brief overview of newborn screening of metabolic disorders, inheritance patterns.
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when
 CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
Metabolic Changes in ASD. Norma J. Arciniegas, MD Simón E. Carlo, MD Instituto Filius
 Metabolic Changes in ASD Norma J. Arciniegas, MD Simón E. Carlo, MD Instituto Filius 12 patients 3 Autism: Ages 3/3/3.7 3 PDD: Ages 3/3/6 3 Asperger: Ages 6/7/15.1 3 Speech delay and Sensory Problems (SHL):
Metabolic Changes in ASD Norma J. Arciniegas, MD Simón E. Carlo, MD Instituto Filius 12 patients 3 Autism: Ages 3/3/3.7 3 PDD: Ages 3/3/6 3 Asperger: Ages 6/7/15.1 3 Speech delay and Sensory Problems (SHL):
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS-Please type your awesome answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What is an X-linked inheritance pattern? Use a specific example to explain the role of the father and mother in
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders. Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital
 Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks
 A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders
 Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis)
 Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES
 HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES Particular risk factors are: Advanced maternal age (e.g. Down's syndrome) Family history of inherited diseases (e.g. fragile X syndrome, Huntington's chorea) Previous child
HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES Particular risk factors are: Advanced maternal age (e.g. Down's syndrome) Family history of inherited diseases (e.g. fragile X syndrome, Huntington's chorea) Previous child
So Much More Than The PKU Test
 Newborn Metabolic Screening So Much More Than The PKU Test Sarah Viall, MSN, PPCNP BC Newborn Screening Program Coordinator Division of Genetics & Metabolism Conflicts of Interest I have no conflicts of
Newborn Metabolic Screening So Much More Than The PKU Test Sarah Viall, MSN, PPCNP BC Newborn Screening Program Coordinator Division of Genetics & Metabolism Conflicts of Interest I have no conflicts of
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM)
 Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
The spectrum and outcome of the. neonates with inborn errors of. metabolism at a tertiary care hospital
 The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
Col Rama Krishna Sanjeev Military Hospital Chennai Prof Shanmughasundaram Mehta Hospital, Chennai
 Col Rama Krishna Sanjeev Military Hospital Chennai Prof Shanmughasundaram Mehta Hospital, Chennai 11 day old male neonate admitted on 26/6 to our Hospital with c/olethargy -since day1 abnormal movements
Col Rama Krishna Sanjeev Military Hospital Chennai Prof Shanmughasundaram Mehta Hospital, Chennai 11 day old male neonate admitted on 26/6 to our Hospital with c/olethargy -since day1 abnormal movements
Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency
 Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase MCAD
Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase MCAD
THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND
 BIRTH DEFECTS 1 THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND Once there was a king who had a beautiful, large pure diamond. There was no other diamond like it in the world. One day, it became deeply scratched. The
BIRTH DEFECTS 1 THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND Once there was a king who had a beautiful, large pure diamond. There was no other diamond like it in the world. One day, it became deeply scratched. The
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Advances in Perinatal Genetics
 Advances in Perinatal Genetics Common and Not-So-Common Genetic Conditions Donna Wallerstein, MS Certified Genetic Counselor South Bay Regional Genetics Center Top 5 reasons Genetics is Important: Normal
Advances in Perinatal Genetics Common and Not-So-Common Genetic Conditions Donna Wallerstein, MS Certified Genetic Counselor South Bay Regional Genetics Center Top 5 reasons Genetics is Important: Normal
The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments
 CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE
 THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE Dr. Nadeem Qureshi M.D, FAAP, FCCM Associate Professor Pediatrics School of Medicine. St Louis University Attending Physician Pediatric Emergency
THE ED APPROACH OF THE CHILD WITH SUSPECTED METABOLIC DISEASE Dr. Nadeem Qureshi M.D, FAAP, FCCM Associate Professor Pediatrics School of Medicine. St Louis University Attending Physician Pediatric Emergency
Quick Reference Guide
 This index may help determine a clinical diagnosis. Fairly common dysmorphic features are listed with corresponding syndromes in which the characteristic is a frequent finding. The syndrome features are
This index may help determine a clinical diagnosis. Fairly common dysmorphic features are listed with corresponding syndromes in which the characteristic is a frequent finding. The syndrome features are
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities. Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD. Pediatric Genetics Team
 Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism Patricia Jones, PhD DABCC FACB UT Southwestern Medical Center Children s Medical Center Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives Justify
Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism Patricia Jones, PhD DABCC FACB UT Southwestern Medical Center Children s Medical Center Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives Justify
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP
 GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP University of New Mexico 1. General Description: UNM MFM fellows rotate through genetics during their PGY5 and PGY7 years. The PGY5 fellow
GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP University of New Mexico 1. General Description: UNM MFM fellows rotate through genetics during their PGY5 and PGY7 years. The PGY5 fellow
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up
 HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
Mendelian Inheritance Patterns
 Genetic Disorders What is a karyotype? A. A karyotype is the functional unit of heredity B. A karyotype is the gene s observable characteristic in an individual C. A karyotype is the degree to which an
Genetic Disorders What is a karyotype? A. A karyotype is the functional unit of heredity B. A karyotype is the gene s observable characteristic in an individual C. A karyotype is the degree to which an
Red flags for clinical practice - guidance on indicators that your patient may have a genetic condition
 Red flags for clinical practice - guidance on indicators that your patient may have a genetic condition General red flags for clinical practice One or more of these red flags that may indicate a high genetic
Red flags for clinical practice - guidance on indicators that your patient may have a genetic condition General red flags for clinical practice One or more of these red flags that may indicate a high genetic
Lab Activity 36. Principles of Heredity. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Metabolic Pathway. Digestion and Fasting. How is Expanded Newborn Screening Different? MS/MS. The body is a factory.
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism The body is a factory. Inborn errors of metabolism are rare genetic disorders in which the body cannot properly turn food into energy. The disorders are usually caused by defects
Inborn Errors of Metabolism The body is a factory. Inborn errors of metabolism are rare genetic disorders in which the body cannot properly turn food into energy. The disorders are usually caused by defects
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies
 Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
For Your Baby s Health Department of Health
 Newborn Screening For Your Baby s Health Department of Health Why is my baby tested? To help make sure your baby will be as healthy as possible. The blood test provides important information about your
Newborn Screening For Your Baby s Health Department of Health Why is my baby tested? To help make sure your baby will be as healthy as possible. The blood test provides important information about your
Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information
 Jame5. L.Jma5, ~reuiry Medical Conditions Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information I Not Listed later Children with medical conditions which
Jame5. L.Jma5, ~reuiry Medical Conditions Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information I Not Listed later Children with medical conditions which
Hths 2231 Laboratory 3 Genetics
 Watch Movie: Cystic Fibrosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-5 Activity #1: Under Lab 3 Click on activity 1 Click on Tour of the Basics Do all 6 What is exercises Activity
Watch Movie: Cystic Fibrosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-5 Activity #1: Under Lab 3 Click on activity 1 Click on Tour of the Basics Do all 6 What is exercises Activity
Recognizing Genetic Red Flags in Clinical Evaluations
 Recognizing Genetic Red Flags in Clinical Evaluations ACGME Sub-competencies / Developmental Milestones Addressed Patient Care: Gather essential and accurate information about the patient; Make informed
Recognizing Genetic Red Flags in Clinical Evaluations ACGME Sub-competencies / Developmental Milestones Addressed Patient Care: Gather essential and accurate information about the patient; Make informed
Routine Newborn Screening, Testing the Newborn Inherited Metabolic Disorders Update August 2015
 Routine Newborn Screening, Testing the Newborn Inherited Metabolic Disorders Update August 2015 Metabolic birth defects can cause physical problems, mental retardation and, in some cases, death. It is
Routine Newborn Screening, Testing the Newborn Inherited Metabolic Disorders Update August 2015 Metabolic birth defects can cause physical problems, mental retardation and, in some cases, death. It is
Genetic Disorders. n A genetic disorder is an abnormality
 + GENETIC DISORDERS + Genetic Disorders n A genetic disorder is an abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from a small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of an
+ GENETIC DISORDERS + Genetic Disorders n A genetic disorder is an abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from a small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of an
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
Genetic Diseases. SCPA202: Basic Pathology
 Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Genetic Disorders and Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Genetic Disorders and Inborn Errors of Metabolism - Abnormalities of morphogenesis: Malformation: intrinsically abnormal
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Genetic Disorders and Inborn Errors of Metabolism - Abnormalities of morphogenesis: Malformation: intrinsically abnormal
7 Medical Genetics. Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobinopathies. Protein and Gene Structure. and Biochemical Genetics
 SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
Genetic Disorders. PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders. Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test
 Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Genetic Disorders PART ONE: Detecting Genetic Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Karyotype Triple Screen Blood Test Amniocentesis A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus
Objectives See course web page for full objectives Read : , (not Bayes theorem section)
 An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
Approach to the Genetic Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders
 Approach to the Genetic Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders Dr Wendy Jones MBBS MRCP Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery What is a genetic diagnosis?
Approach to the Genetic Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders Dr Wendy Jones MBBS MRCP Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery What is a genetic diagnosis?
Summary. Syndromic versus Etiologic. Definitions. Why does it matter? ASD=autism
 Summary It is becoming clear that multiple genes with complex interactions underlie autism spectrum (ASD). A small subset of people with ASD, however, actually suffer from rare single-gene Important to
Summary It is becoming clear that multiple genes with complex interactions underlie autism spectrum (ASD). A small subset of people with ASD, however, actually suffer from rare single-gene Important to
PEDIATRIC MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 Division of Otolaryngology Main Phone: 847 504-3300 Main Fax: 847 504-3305 Mihir Bhayani, MD Judy L. Chen, MD Mark E. Gerber, MD, FACS, FAAP Joseph Raviv, MD Ilana Seligman, MD, FACS, FAAP Michael J. Shinners,
Division of Otolaryngology Main Phone: 847 504-3300 Main Fax: 847 504-3305 Mihir Bhayani, MD Judy L. Chen, MD Mark E. Gerber, MD, FACS, FAAP Joseph Raviv, MD Ilana Seligman, MD, FACS, FAAP Michael J. Shinners,
Gene Expression and Mutation
 Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When
 UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the summary of product characteristics and package leaflets
 Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the summary of product characteristics and package leaflets Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the Summary of Product Characteristics and package
Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the summary of product characteristics and package leaflets Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the Summary of Product Characteristics and package
Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye. Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine
 Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine Why Make A Syndrome Diagnosis? Why did it happen? What does the future hold? How can you treat/manage it?
Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine Why Make A Syndrome Diagnosis? Why did it happen? What does the future hold? How can you treat/manage it?
Introduction to Organic Acidemias. Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.
 Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
Patterns of Single-Gene Inheritance Cont.
 Genetic Basis of Disease Patterns of Single-Gene Inheritance Cont. Traditional Mechanisms Chromosomal disorders Single-gene gene disorders Polygenic/multifactorial disorders Novel mechanisms Imprinting
Genetic Basis of Disease Patterns of Single-Gene Inheritance Cont. Traditional Mechanisms Chromosomal disorders Single-gene gene disorders Polygenic/multifactorial disorders Novel mechanisms Imprinting
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine
 Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
Urea Cycle Defects. Dr Mick Henderson. Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust. MetBioNet IEM Introductory Training
 Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
Neurofibromatosis type 1 and RASopathies
 Neurofibromatosis type 1 and RASopathies Dawn Siegel, MD Medical College of Wisconsin American Academy of Dermatology San Diego, CA February 19 th, 2018 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 NF1- diagnostic criteria
Neurofibromatosis type 1 and RASopathies Dawn Siegel, MD Medical College of Wisconsin American Academy of Dermatology San Diego, CA February 19 th, 2018 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 NF1- diagnostic criteria
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition
 Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Disorder name: Argininemia / Arginase deficiency Acronym: ARG 1 deficiency
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet
 Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet Website:www.tipn.org.tw Telephone:(02)85962050 Ext. 401-403 Service line:(02)85962065 Fax:(02)85962067
Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet Website:www.tipn.org.tw Telephone:(02)85962050 Ext. 401-403 Service line:(02)85962065 Fax:(02)85962067
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Fetal & Neonatal Pathology Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Self-Directed Reading Topics
Fetal & Neonatal Pathology Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Self-Directed Reading Topics
LOW CITRULLINE AS A MARKER FOR THE PROXIMAL UREA CYCLE DEFECTS EXPERIENCE OF THE NEW ENGLAND NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM
 LOW CITRULLINE AS A MARKER FOR THE PROXIMAL UREA CYCLE DEFECTS EXPERIENCE OF THE NEW ENGLAND NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Inderneel Sahai, MD, FACMG Newborn Screening and Genetic Testing Symposium Oct 2014
LOW CITRULLINE AS A MARKER FOR THE PROXIMAL UREA CYCLE DEFECTS EXPERIENCE OF THE NEW ENGLAND NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Inderneel Sahai, MD, FACMG Newborn Screening and Genetic Testing Symposium Oct 2014
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Yunis-Varon syndrome
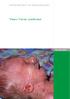 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
Pedigree Analysis. Genetic disorders. Dominant inheritance. Recessive inheritance. Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits. X-linked recessive inheritance
 Genetic disorders 4.2 Errors During Meiosis 5.3 Following Patterns of Human nheritance Pedigree Analysis 2005 Lee Bardwell Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits Autosomal traits are caused by genes on autosomes
Genetic disorders 4.2 Errors During Meiosis 5.3 Following Patterns of Human nheritance Pedigree Analysis 2005 Lee Bardwell Autosomal vs. sex-linked traits Autosomal traits are caused by genes on autosomes
Unit 3: DNA and Genetics Module 9: Human Genetics
 Unit 3: DNA and Genetics Module 9: Human Genetics NC Essential Standard: 3.2 Understand how the environment, and /or the interaction of alleles, influences the expression of genetic traits. 3.3.3 Evaluate
Unit 3: DNA and Genetics Module 9: Human Genetics NC Essential Standard: 3.2 Understand how the environment, and /or the interaction of alleles, influences the expression of genetic traits. 3.3.3 Evaluate
Disorder name: Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Acronym: SCID
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Other Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues surrounding
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Other Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues surrounding
Inborn Error Of Metabolism :
 Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Genetic Counseling Who, What, Where, When, Why, & How. Kate Zellmer, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Aurora Health Care
 Genetic Counseling Who, What, Where, When, Why, & How Kate Zellmer, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Aurora Health Care Genetics is rapidly becoming a central organizing principle in medical practice.
Genetic Counseling Who, What, Where, When, Why, & How Kate Zellmer, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Aurora Health Care Genetics is rapidly becoming a central organizing principle in medical practice.
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE
 CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010
 Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Genetics Questions: There are 15 questions in total. The answers can be found on the accompanying document
 Page 1 Genetics Questions: These questions are aimed at medical and allied health professionals and they are designed to show where genetics has a role in clinical practice. There are 15 questions in total
Page 1 Genetics Questions: These questions are aimed at medical and allied health professionals and they are designed to show where genetics has a role in clinical practice. There are 15 questions in total
Amino Acid Disorders. Disorder name: Tyrosinemia, type 1. What is tyrosinemia 1? Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Case 1B. 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21)
 Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Human Genetic Mutations
 Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. The chromosomes
WHO Growth Grids/ 2012 Risk Changes. Diane Traver Joyce Bryant
 WHO Growth Grids/ 2012 Risk Changes Diane Traver Joyce Bryant Overview CDC vs WHO Growth Charts- Why Change? Transition from
WHO Growth Grids/ 2012 Risk Changes Diane Traver Joyce Bryant Overview CDC vs WHO Growth Charts- Why Change? Transition from
Chapter Objectives 9/21/2017. Chapter 6 Biological Aspects and the Promises of Prevention. 8 points possible
 Chapter 6 Biological Aspects and the Promises of Prevention Quiz 1. List 3 types of Down Syndrome. 8 points possible 2. A person diagnosed with Down Syndrome has an increased risk of dementia. 3.Name the
Chapter 6 Biological Aspects and the Promises of Prevention Quiz 1. List 3 types of Down Syndrome. 8 points possible 2. A person diagnosed with Down Syndrome has an increased risk of dementia. 3.Name the
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style. Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA
 ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
Chromosome Disease. The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental
 Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
