HEALTH PROFESSIONAL ADVICE: Pertussis (update March 2014)
|
|
|
- Anastasia Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5 March 2014 HEALTH PROFESSIONAL ADVICE: Pertussis (update March 2014) SITUATION UPDATE The Pertussis epidemic which began in May 2011 has continued without any sign of abating. In 2013 there were 791 cases of pertussis notified, including 98 notifications in <12 month olds. Tdap Immunisation for pregnant women is recommended and funded for every pregnancy from weeks gestation. Azithromycin is the first line treatment and prophylaxis for all ages and is fully funded, this is a much more convenient dosage regime and treatment duration. Pertussis is especially serious in infants under 12 months old. For every 100 infants <12 months old with whooping cough, around 70 will be hospitalised. The current public health strategy aims to protect this vulnerable cohort. Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 1 of 8
2 CURRENT INFORMATION (links provided to updated sections) Current Process for Health Professionals Investigation recommendations updated After-Hours laboratory requests Azithromycin for all ages now fully funded Roxithromycin (rulide) use Management in Primary Care & Hospitals Immunisation recommendations Resources available from ARPHS CURRENT PROCESS FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS Auckland Regional Public Health Service (ARPHS) is focussing on protecting those at greatest risk of adverse outcomes from pertussis, and promotion of pertussis immunisation. Due to the widespread nature of pertussis in the community, outbreak control is not an achievable objective currently. We are advising the sector (primary care and hospitals) in case management and high priority contact management. ARPHS continues to receive notifications (see Managing Suspected Pertussis Cases section). General Practice and hospital-based health professionals are responsible for providing the case and high priority contacts with appropriate information, advice, and treatment or prophylaxis (see link below) Individual cases and their contacts are continuing to be managed through primary care. This has been the case since the disease became epidemic and the public health priority shifted from outbreak control to the protection of those most vulnerable (under 12 month olds, pregnant, immune compromised) ARPHS can provide direct advice on high priority contacts by telephone Written information for cases, contacts, early childhood education centres, schools, and healthcare institutions is available from ARPHS: MANAGING SUSPECTED PERTUSSIS CASES Notify Investigate Treat Isolate - Advise- Immunise Notify on suspicion If your patient has a clinically compatible illness and the diagnosis is most likely pertussis, notify ARPHS. Do not wait for investigations to be completed. Inform the patient or caregiver that ARPHS has been notified and may be in contact To notify ARPHS, call (24-hour phone line) or fax with the information listed below: Fax template provided in Appendix 1 Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 2 of 8
3 Information to Supply to ARPHS when Notifying - Your details: Name, treating doctor, contact number - Case details: Name, address, age, ethnicity, NHI, occupation, contact number, pregnancy - Clinical History: Especially onset date of illness, paroxysmal cough onset date. - Laboratory tests: Any tests arranged - Immunisation Status: Dates of pertussis immunisations if available - Links to confirmed or probable cases: Including names Investigate only where necessary Investigation is NOT required for all suspected cases. ARPHS does NOT recommend testing for the following people: o Patients that meet the case definition of a cough for more than two weeks and one or more of the following: whoop, post-tussive vomiting, or apnoea o Cases that have been coughing for under 2 weeks, with an illness compatible with early whooping cough, and known contact with a case that met the case definition or with a confirmed case of pertussis (i.e. PCR, culture, or serology positive) o Symptomatic household contacts of a confirmed case of whooping cough or a case that meets the case definition Diagnostic testing should be considered ONLY if the result will alter the management of cases with high priority contacts (infants under 12 months, pregnant women, immune compromised, chronic disease), or if employment issues arise, or if requested by ARPHS Any tests believed urgent should be discussed with the appropriate pathologist Timing of Infectivity, Investigation, and Treatment First Symptoms Week Disease Phase Catarrhal Paroxysmal Infectious PCR Culture Serology Paroxysmal / Severe Cough Start Date ~5-10 days after first unwell infectious for a further 3 weeks Treat Cases Adapted from CDC: Shading indicates relative sensitivity After-Hours Laboratory Requests from Virology and Immunology PCR and serology specimens collected at community laboratories are all tested at LabPlus Specimens will be processed on the next working day Other important considerations (see diagram above) There are several laboratory tests available for the diagnosis of pertussis (see Resources) Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 3 of 8
4 o PCR nasopharyngeal swab should be performed in preference to culture o Pertussis serology is only useful later in the disease course The timing of a test impacts on its sensitivity A negative laboratory result does not necessarily rule out pertussis consider exposure, clinical compatibility, the diagnostic test performed and its timing. There is no point in requesting PCR testing if the patient has been symptomatic for more than 3 weeks. Treat Suspected Cases Early treatment may modify disease severity. Treatment reduces infectivity if started during the catarrhal phase or within three weeks of the onset of paroxysmal cough. Beyond this time it should only be considered for pregnant women in their third trimester (pg 146, Immunisation Handbook) Azithromycin is the recommended first-line treatment and a five day course is fully funded for all age groups if endorsed for the treatment or prophylaxis of pertussis (from 1 December 2012). The recommended dose varies by age and is: o Infants and children: Day 1: 10mg/kg/day in a single daily dose (max 500mg day 1); Days 2-5: 5mg/kg/day in a single daily dose (max 250mg per day) o Adults: Day 1: 500mg as a single dose; Days 2-5: 250mg once daily Erythromycin ethyl succinate (EES/E-Mycin) is also fully funded for treatment in children aged 12 months and older and in adults but must be given as a 14 day course: o Adults: 400 mg four times a day for 14 days o Children 12 months or older: 10 mg/kg/dose four times a day for 14 days (max 400mg qid) NOTE 1 : Macrolide use in pregnancy and the neonatal period has been associated with an increased risk of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Advise patients to contact their doctor if vomiting or irritability with feeding occurs. Roxithromycin (RULIDE) is NOT recommended for treatment/chemoprophylaxis of pertussis due to poor serum and tissue concentrations achieved. Alternative antibiotic regimens can be found in pg 147 of the 2011 Immunisation Handbook. Isolate Cases Cases should be advised by their GP or hospital doctor to stay away from babies, young children, pregnant women and immuno-compromised people. They should not attend early childhood education centres, school, work, and social gatherings until either: o five days of appropriate antibiotics have been completed, or o three weeks have passed since the start of the paroxysmal cough (if not taking antibiotics) Children diagnosed with pertussis are required by the Medical Officers of Health to be excluded from Early Childhood Centres/Schools as described above in accordance with the Health (Infectious and Notifiable Diseases) Regulations 1966 and/or the Education (Early Childhood Centres) Regulations Pg 146 Immunisation Handbook 2011: Macrolides taken by pregnant or breastfeeding mothers have been reported with an increased risk of infantile pyloric stenosis. The risk is presumed to be lower for azithromycin than for erythromycin; however there have been reports in the literature of pyloric stenosis in infants of women treated in pregnancy with azithromycin. Inform patients to contact their doctor if vomiting or irritability with feeding occurs. Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 4 of 8
5 Advise Provide information sheets for patients and contacts with suspected or confirmed pertussis (see Resources) Immunise Review the immunisation status of all household members and update as necessary Pregnant women should be offered TDap Boostrix vaccine in every pregnancy. The vaccine is funded when given in the third trimester. See Resources for more information Offer immunisation to adolescent (>16 years) and adult household members who have not received an immunisation booster in the last 10 years this is not funded. Children who have had pertussis infection should still have all of their childhood pertussis immunisations as per the National Schedule MANAGING CONTACTS OF PERTUSSIS IN PRIMARY CARE & HOSPITALS ARPHS is not undertaking contact tracing for pertussis notifications Primary care is being asked to manage chemoprophylaxis for household contacts of a pertussis case and provide information to cases to distribute to their other important contacts Hospitals are being asked to manage hospital inpatient contacts of a case and provide information to other contacts (from ARPHS website) so they can discuss with their GP whether prophylaxis is indicated. GPs may have additional information regarding other high priority contacts in the family. The aim of contact management is two-fold: 1. To identify symptomatic contacts for treatment 2. To provide chemoprophylaxis with an aim of reducing the odds of infection in high priority groups (infants under 12 months, pregnant women in their 3 rd trimester, immune compromised, those with chronic disease, and their contacts) Arrange Chemoprophylaxis Advise or arrange chemoprophylaxis for the following household contacts of a case of pertussis: o all members of a household that includes: an infant under12 months old or a pregnant woman in the third trimester or household contacts under five years of age who are unimmunised or have had less than three pertussis immunisations, or individuals at risk of severe illness or complications (e.g. chronic respiratory conditions, congenital heart disease or immunodeficiency) o contacts who themselves have daily contact with infants under 12 months, pregnant women or individuals at risk of severe illness or complications (e.g. chronic respiratory conditions, congenital heart disease or immunodeficiency) e.g. through childcare or work. Prophylactic antibiotic regimens are the same as for treatment of pertussis Prophylaxis is not 100% effective. Advise contacts to: o be vigilant for symptoms and to see a GP if they develop catarrhal symptoms or cough. o stay away from babies, children under 12 months, pregnant women, and immunocompromised people, until: five days of a course of appropriate antibiotics have been completed, or three weeks have passed since last contact with the case if not taking antibiotics Provide Information for the Case to Pass on to Their Contacts Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 5 of 8
6 Advise cases/parents to let their contacts know that they have pertussis including informing: o Early childhood centres, daycares, schools, workplaces o Contacts who are aged under 12 months, partially or unimmunised children under five years, pregnant, or immune compromised o Contacts who are in daily contact with pregnant women, infants under12 months Provide cases with Information Sheets to give to their contacts (see Resources) IMMUNISATION Immunisation remains the mainstay for controlling the current outbreak. To reduce the burden of pertussis in New Zealand, and to prevent or minimise future outbreaks, consistent immunisation coverage rates of 92-94% 2 are required at each Ministry of Health reported milestone age (i.e. six months, five years, and 12 years). The most vulnerable cohort, infants under 12 months, is currently the least protected with immunisation rates of 82% across the Auckland region at six months of age (64% in Maori, 76% in Pacific) 3 Every opportunity to immunise should be taken, including active precall, recall, review of immunisation status at all paediatric consultations, and opportunistic immunisation KEY IMMUNISATION MESSAGES FOR PATIENTS On time immunisation is essential at 6 weeks, 3 months, 5 months Delay in receipt of any of the first three pertussis immunisations increases the odds of hospitalisation with pertussis in the first year of life by 4-5 times. Note: Due to waning immunity in adulthood, maternal antibodies are generally inadequate to provide protection to newborns. Boosters are essential at 4 years and 11 years Immunity following immunisation or pertussis infection wanes after 4-6 years. Boosters help maintain personal immunity through the school years, and also provide indirect protection of infants in the community who are too young to be immunised. Pregnancy (Immunisation Handbook 2011 page 24 and ARPHS website Immunisation is funded for pregnant women from 20 weeks gestation with the ideal time to give the vaccine between weeks. This booster is given to reduce the risk of the mother infecting her baby, and to provide passive protection in the first weeks of life. Consult the vaccination datasheet when considering use in pregnancy or lactation. 4 Note that Section 25 of the Medicines Act allows off-label use of medicines (including vaccines) providing that doctors have informed consent from the patient and exercise a duty of care. 5 An information sheet on Pertussis Immunisation in Pregnancy is available for patients on the ARPHS website (see Resources). Adult immunisation (Immunisation Handbook 2011 Page 142) Around 80% of infants with pertussis catch it from a parent, caregiver, or sibling. Immunisation of other family members helps provide indirect protection of those who are most vulnerable. Adult immunisation booster is not funded 6, but is recommended by the Ministry of Health for: 2 Fine PE. Herd Immunity: History, Theory, Practice. Epidemiologic Reviews. 1998: 15(2); Ministry of Health. 4 Boostrix datasheet states: Adequate human data on use during pregnancy and adequate animal reproduction studies are not available. Therefore, BOOSTRIX should be used during pregnancy only when clearly needed, and the possible advantages outweigh the possible risks for the foetus. When protection against tetanus is sought, consideration should be given to tetanus or combined diphtheria-tetanus vaccines. As with all inactivated vaccines, one does not expect harm to the foetus. See: 5 See: 6 Some employers may provide this to staff free. Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 6 of 8
7 o o o Lead maternity carers and all health care personnel working with/around infants, chronic disease (e.g. heart or respiratory) or immuno-compromised individuals Household/family contacts of newborns (including older children over 7 years and adults) Early childhood service personnel PERTUSSIS INFECTION Pertussis is a highly infectious bacterial infection spread by coughing and sneezing There are two phases of the illness: o Catarrhal Phase: Most infectious period lasting seven to 10 days. Symptoms include runny nose, fever, malaise and coughing o Paroxysmal Phase: Severe prolonged coughing episodes (paroxysms) that typically end in a whoop (inspiratory gasp), apnoea, or vomiting Pertussis occurs at any age as immunity wanes four to six years after immunisation or infection Clinical presentation varies with age and immunisation status: o Immunised children and adults typically experience a milder illness and may not whoop o Infants < six months frequently have an atypical presentation with a short catarrhal phase, gagging, gasping, or apnoea as prominent features, absence of whoop, and a prolonged paroxysmal phase Complications: Include pneumonia, neurologic complications including seizures and encephalopathy due to hypoxia, pressure complication resulting from sever coughing include rib fractures, petechial haemorrhage, pneumothorax, hernia, rectal prolapse Serious complications are most common in infants under 12 months: 65-75% hospitalised, 10% pneumonia, 20-25% apnoea, seizures ~1%, death 1-2% Incubation period: Ranges from five to 21 days Infectious period: From symptom onset (catarrhal phase, most infectious period) until three weeks after the onset of paroxysmal or severe coughing RESOURCES For Health Professionals: Pertussis: Clinical Pathway (PDF, 75 KB) Pertussis Fax Notification Template (Word, 213 KB) GP fax: FREE pertussis vaccination for pregnant women ( KB) Quick answers to frequent Tdap questions (PDF, KB) For patients and their contacts: Pertussis Fact Sheet in English and Te Reo Information for Cases Information for Contacts Pertussis Immunisation in Pregnancy For additional information on immunisation, please call the Immunisation Advisory Centre on 0800 IMMUNE ( ) or visit their website Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 7 of 8
8 Appendix 1: PERTUSSIS NOTIFICATION TEMPLATE: Please complete and fax to (09) or Tel: Thank you. Reporting GP: GP Practice: Tel No: Name of Case: NHI: Case Tel No: Current Address of Case: Date of Birth: Male or Female (Circle one): Coryzal/catarrhal prodrome (URTI symptoms and nonspecific cough Date of Onset: Paroxysmal cough (coughing fits) Inspiratory whoop Post-tussive vomiting or apnoea In GP s view is this a clinically compatible illness? Laboratory Investigations: Hospitalised Infection Control notified Vaccination History (6wks, 3mths, 5mths, 4yrs, 11yrs and Boostrix): Antibiotics Prescribed: Azithromycin for 5 days Or Erythromycin for 14 days Other If yes, Date of Onset: PCR Date: Culture Date: Serology Date: Age appropriately immunised (Circle one): Partially immunised Too young Unimmunised Information incomplete Unknown/uncertain Boostrix given in last 5yrs Date prescribed: Date prescribed: Name of antibiotic: Pregnant Number of weeks: Attendance at school, pre-school or childcare Name: Staff of healthcare/early childhood facilities Occupation: Exclusion Advice given ARPHS information for case and contacts given Household Contacts: Anyone symptomatic Anyone less than 1 yr old Anyone Pregnant 3 rd trimester Anyone immuno-compromised Unimmunised or Partially Immunised Please visit our website at for further pertussis information and resources. Auckland Regional Public Health - Page 8 of 8
Health Professionals Advice: Summer
 Health Professionals Advice: Summer 2013-2014 SITUATION UPDATE The Pertussis epidemic which began in May 2011 has continued all year, without any sign of abating. Between 1 January and 10 December 2013
Health Professionals Advice: Summer 2013-2014 SITUATION UPDATE The Pertussis epidemic which began in May 2011 has continued all year, without any sign of abating. Between 1 January and 10 December 2013
Health Professionals Advice: Pertussis 7 June, 2012
 Health Professionals Advice: Pertussis 7 June, 2012 SITUATION UPDATE Since 1 January 2012 there have been 322 cases of pertussis notified and over 1,500 contacts requiring follow up. Of concern, two recent
Health Professionals Advice: Pertussis 7 June, 2012 SITUATION UPDATE Since 1 January 2012 there have been 322 cases of pertussis notified and over 1,500 contacts requiring follow up. Of concern, two recent
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women
 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
Pertussis. Information for Physicians. Disease Information. Diagnostic Testing of Suspect Cases. Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program
 September 2007 Pertussis Disease Information Incubation Period: 7-10 days; rarely up to 21 days Infectious Period: From prodrome (early symptom) onset to 3 weeks after cough onset. Patients are considered
September 2007 Pertussis Disease Information Incubation Period: 7-10 days; rarely up to 21 days Infectious Period: From prodrome (early symptom) onset to 3 weeks after cough onset. Patients are considered
FACTS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FACTS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) General Questions About Pertussis What is pertussis? Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person sneezes or coughs
FACTS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) General Questions About Pertussis What is pertussis? Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person sneezes or coughs
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Pertussis. This document should be read in conjunction with this DISCLAIMER
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Pertussis Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Pertussis Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Objectives 3/3/2017. Disease Reporting in Georgia: The School Nurse s Role. Georgia Department of Public Health
 Disease Reporting in Georgia: The School Nurse s Role Presentation to: Georgia s School Nurses Presented by: Ebony S. Thomas, MPH Date: Friday, March 10, 2017 Objectives Describe the school nurse s role
Disease Reporting in Georgia: The School Nurse s Role Presentation to: Georgia s School Nurses Presented by: Ebony S. Thomas, MPH Date: Friday, March 10, 2017 Objectives Describe the school nurse s role
Frequently Asked Questions Pertussis (Whooping Cough) in the School Setting
 Frequently Asked Questions Pertussis (Whooping Cough) in the School Setting General information What is pertussis? Who can get pertussis? What are the symptoms of pertussis? How soon do symptoms of pertussis
Frequently Asked Questions Pertussis (Whooping Cough) in the School Setting General information What is pertussis? Who can get pertussis? What are the symptoms of pertussis? How soon do symptoms of pertussis
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
 TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
Maternal vaccination
 Maternal vaccination (Gary) Edwin Reynolds Immunisation Advisory Centre (IMAC) 0.1FTE University of Auckland Medical Advisor / General Practitioner Vaccinology / Immunology General Practitioner 0.1FTE
Maternal vaccination (Gary) Edwin Reynolds Immunisation Advisory Centre (IMAC) 0.1FTE University of Auckland Medical Advisor / General Practitioner Vaccinology / Immunology General Practitioner 0.1FTE
Prince Edward Island Guidelines for the Management and Control of Pertussis
 Prince Edward Island Guidelines for the Management and Control of Pertussis November 2015 Table of Contents 1. General Guidelines... 2 1.1 Clinical Presentation... 3 1.2 Epidemiology... 4 2. Diagnosis...
Prince Edward Island Guidelines for the Management and Control of Pertussis November 2015 Table of Contents 1. General Guidelines... 2 1.1 Clinical Presentation... 3 1.2 Epidemiology... 4 2. Diagnosis...
Policy Objective. This policy applies to all staff employed by NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde and locum staff on fixed term contracts.
 1 of 9 Policy Objective To ensure that Healthcare Workers are aware of the actions and precautions necessary to minimise the risk of outbreaks and the importance of diagnosing patients clinical conditions
1 of 9 Policy Objective To ensure that Healthcare Workers are aware of the actions and precautions necessary to minimise the risk of outbreaks and the importance of diagnosing patients clinical conditions
Don t delay Immunise for. Whooping Cough. Immunisation is FREE. weeks months. months
 Don t delay Immunise for Whooping Cough Immunisation is FREE 6 3 weeks months 5 months What is whooping cough? Whooping cough (Pertussis) is a highly contagious bacterial infection that is spread by coughing
Don t delay Immunise for Whooping Cough Immunisation is FREE 6 3 weeks months 5 months What is whooping cough? Whooping cough (Pertussis) is a highly contagious bacterial infection that is spread by coughing
Pertussis Testing and Treatment Guidelines
 Chicago Department of Public Health City of Chicago Rahm Emanuel, Mayor Pertussis Testing and Treatment Guidelines Date: August 1, 2012 To: Immunization Program Chicago Department of Public Health Bechara
Chicago Department of Public Health City of Chicago Rahm Emanuel, Mayor Pertussis Testing and Treatment Guidelines Date: August 1, 2012 To: Immunization Program Chicago Department of Public Health Bechara
Announcements. Please mute your phones and DO NOT place us on hold. Press *6 to mute your phone.
 Announcements Register for the Epi-Tech Trainings: 1. Log-on or Request log-on ID/password: https://tiny.army.mil/r/zb8a/cme 2. Register for Epi-Tech Surveillance Training: Confirm attendance: https://tiny.army.mil/r/dvrgo/epitechfy14
Announcements Register for the Epi-Tech Trainings: 1. Log-on or Request log-on ID/password: https://tiny.army.mil/r/zb8a/cme 2. Register for Epi-Tech Surveillance Training: Confirm attendance: https://tiny.army.mil/r/dvrgo/epitechfy14
Whooping cough vaccine for pregnant women
 Whooping cough vaccine for pregnant women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
Whooping cough vaccine for pregnant women What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a highly contagious illness that can be life threatening. The disease is most serious
Pertussis Toolkit for Schools
 Pertussis Toolkit for Schools Burlington County Health Department December 2012 1 CONTENTS What to do if you suspect a case of pertussis in your school 3 Pertussis reporting form 5 Pertussis Fact sheet
Pertussis Toolkit for Schools Burlington County Health Department December 2012 1 CONTENTS What to do if you suspect a case of pertussis in your school 3 Pertussis reporting form 5 Pertussis Fact sheet
CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health. Learn About Pertussis PERTUSSIS
 CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health PERTUSSIS Learn About Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is an extremely contagious respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It can be especially
CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health PERTUSSIS Learn About Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is an extremely contagious respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It can be especially
Immunise against whooping cough. Protect baby and you
 Immunise against whooping cough Protect baby and you What is whooping cough? Whooping cough (pertussis) is a serious disease caused by bacteria that are easily spread by coughing and sneezing. How serious
Immunise against whooping cough Protect baby and you What is whooping cough? Whooping cough (pertussis) is a serious disease caused by bacteria that are easily spread by coughing and sneezing. How serious
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives. August 2014
 Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives August 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Key Message There is a lot
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives August 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Key Message There is a lot
The Epidemiology of Pertussis and Timeliness of Pertussis Immunisation in New Zealand
 The Epidemiology of Pertussis and Timeliness of Pertussis Immunisation in New Zealand A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Public Health Georgia Deane University
The Epidemiology of Pertussis and Timeliness of Pertussis Immunisation in New Zealand A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Public Health Georgia Deane University
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers
 Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers April 2016 Health Protection Scotland is a division of NHS National Services Scotland.
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers April 2016 Health Protection Scotland is a division of NHS National Services Scotland.
A PERTUSSIS EPIDEMIC IN NSW: HOW EPIDEMIOLOGY REFLECTS VACCINATION POLICY
 A PERTUSSIS EPIDEMIC IN NSW: HOW EPIDEMIOLOGY REFLECTS VACCINATION POLICY Julia Brotherton and Jeremy McAnulty Communicable Diseases Branch NSW Department of Health Pertussis has traditionally been considered
A PERTUSSIS EPIDEMIC IN NSW: HOW EPIDEMIOLOGY REFLECTS VACCINATION POLICY Julia Brotherton and Jeremy McAnulty Communicable Diseases Branch NSW Department of Health Pertussis has traditionally been considered
Advice for residential institutions, early childhood education centres. and schools on managing. cases and outbreaks of influenza
 Auckland Regional Public Health Service Cornwall Complex, Floor 2, Building 15 Greenlane Clinical Centre, Auckland Private Bag 92 605, Symonds Street, Auckland 1150, New Zealand Telephone: 09 623 4600
Auckland Regional Public Health Service Cornwall Complex, Floor 2, Building 15 Greenlane Clinical Centre, Auckland Private Bag 92 605, Symonds Street, Auckland 1150, New Zealand Telephone: 09 623 4600
PERTUSSIS. Introduction
 PERTUSSIS Introduction Pertussis (whooping cough) is a highly contagious acute respiratory tract infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. It is spread by aerosol droplets. Neither vaccination
PERTUSSIS Introduction Pertussis (whooping cough) is a highly contagious acute respiratory tract infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. It is spread by aerosol droplets. Neither vaccination
Boostrix version 1. Elements for a Public Summary. Overview of disease epidemiology. Pertussis Epidemiology
 Boostrix 2.1.2015 version 1 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Pertussis Epidemiology Pertussis (whooping cough), which is caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria,
Boostrix 2.1.2015 version 1 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Pertussis Epidemiology Pertussis (whooping cough), which is caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria,
Coughing up the Facts on Pertussis Emerging Trends and Communication Efforts
 Coughing up the Facts on Pertussis Emerging Trends and Communication Efforts Alison Patti, MPH, CHES National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Coughing up the Facts on Pertussis Emerging Trends and Communication Efforts Alison Patti, MPH, CHES National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Protecting Infants and Children from Pertussis and Influenza
 September 23, 2016 Paulomi Shah, DO, FAAP Pediatrician, Medical Director Children s Medical Services, Sonoma County Alan Shotkin, MD, FAAP Neonatologist, Medical Director Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Protecting
September 23, 2016 Paulomi Shah, DO, FAAP Pediatrician, Medical Director Children s Medical Services, Sonoma County Alan Shotkin, MD, FAAP Neonatologist, Medical Director Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Protecting
Addressing an Epidemic: The Clinicians Role in Preventing Pertussis
 Welcome! Addressing an Epidemic: The Clinicians Role in Preventing Pertussis Mark Sawyer, MD. FAAP Presented by: California Department of Public Health Co-sponsor: California Immunization Coalition Joint
Welcome! Addressing an Epidemic: The Clinicians Role in Preventing Pertussis Mark Sawyer, MD. FAAP Presented by: California Department of Public Health Co-sponsor: California Immunization Coalition Joint
Pertussis Control in New Zealand How can we do better?
 Pertussis Control in New Zealand How can we do better? 1 Conflict of interest In the past I have received support for vaccine work, clinical trials, presentation of papers and conference attendance from
Pertussis Control in New Zealand How can we do better? 1 Conflict of interest In the past I have received support for vaccine work, clinical trials, presentation of papers and conference attendance from
Summary of Key Points
 Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Pertussis September 2015 1 Background l Pertussis (whooping cough), caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis, was one of the most common
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Pertussis September 2015 1 Background l Pertussis (whooping cough), caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis, was one of the most common
Pertussis. Gary Reubenson 10 September 2014
 Pertussis Gary Reubenson 10 September 2014 Conflicts of Interest Sanofi Local Conference support Study sponsor Pfizer Local & International Conference Support Speakers fee Abbvie Speakers fee Overview
Pertussis Gary Reubenson 10 September 2014 Conflicts of Interest Sanofi Local Conference support Study sponsor Pfizer Local & International Conference Support Speakers fee Abbvie Speakers fee Overview
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Pertussis Epidemiology Pertussis (whooping cough), which is caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria, is an easily spread respiratory
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Pertussis Epidemiology Pertussis (whooping cough), which is caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria, is an easily spread respiratory
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives
 Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives August 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Background As you will be
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives August 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Background As you will be
Surveillance, Reporting and Control of Influenza and Pertussis. Steve Fleming, EdM Hillary Johnson, MHS Epidemiologists Immunization Program, MDPH
 Surveillance, Reporting and Control of Influenza and Pertussis Steve Fleming, EdM Hillary Johnson, MHS Epidemiologists Immunization Program, MDPH Disclosures The speaker has no financial interest or conflict
Surveillance, Reporting and Control of Influenza and Pertussis Steve Fleming, EdM Hillary Johnson, MHS Epidemiologists Immunization Program, MDPH Disclosures The speaker has no financial interest or conflict
Protecting the Innocent Bystander The Importance of Vaccination During Pregnancy
 Disclosures Protecting the Innocent Bystander The Importance of Vaccination During Pregnancy Judy Guzman-Cottrill, DO Professor of Pediatrics Division of Infectious Diseases Oregon Health & Science University
Disclosures Protecting the Innocent Bystander The Importance of Vaccination During Pregnancy Judy Guzman-Cottrill, DO Professor of Pediatrics Division of Infectious Diseases Oregon Health & Science University
Global and National Trends in Vaccine Preventable Diseases. Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office.
 Global and National Trends in Vaccine Preventable Diseases Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office Global mortality 2008 Children under 5 years of age 1.5 million deaths due to vaccine preventable
Global and National Trends in Vaccine Preventable Diseases Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office Global mortality 2008 Children under 5 years of age 1.5 million deaths due to vaccine preventable
er of Cas ses Numb Mid 1940s: Whole cell pertussis vaccine developed *2010 YTD 2008: Tdap pphase- in for grades 6-12 started
 Pertussis Update Stephanie Schauer, PhD Epidemiologist Wisconsin Immunization Program November 16, 2010 Pertussis Caused by bacterium Bordetella pertussis Highly communicable, with secondary attack rate
Pertussis Update Stephanie Schauer, PhD Epidemiologist Wisconsin Immunization Program November 16, 2010 Pertussis Caused by bacterium Bordetella pertussis Highly communicable, with secondary attack rate
Vaccination against pertussis(whooping cough)
 Vaccination against pertussis(whooping cough) Vaccination now recommended from 16 weeks of pregnancy An update for registered healthcare practitioners February 2018 additions and/or revisions of any kind
Vaccination against pertussis(whooping cough) Vaccination now recommended from 16 weeks of pregnancy An update for registered healthcare practitioners February 2018 additions and/or revisions of any kind
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PERTUSSIS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PERTUSSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PERTUSSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits
PERTUSSIS The Unpredictable Burden of Disease. Lawrence D. Frenkel, MD, FAAP AAP/Novartis Grand Rounds Webinar February 7, 2013
 PERTUSSIS The Unpredictable Burden of Disease Lawrence D. Frenkel, MD, FAAP AAP/Novartis Grand Rounds Webinar February 7, 2013 Pertussis Agent Bordetella pertussis Nonmotile, fastidious, gram-negative,
PERTUSSIS The Unpredictable Burden of Disease Lawrence D. Frenkel, MD, FAAP AAP/Novartis Grand Rounds Webinar February 7, 2013 Pertussis Agent Bordetella pertussis Nonmotile, fastidious, gram-negative,
2013 About Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
 2013 About Pertussis (Whooping Cough) Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious and often serious disease, especially in young children. 1,2 In adolescents and adults it
2013 About Pertussis (Whooping Cough) Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious and often serious disease, especially in young children. 1,2 In adolescents and adults it
Pedro Plans-Rubió 1,4 Encarna Navas. Angela Domínguez 3,4 Mireia Jané
 PharmacoEconomics Open https://doi.org/10.1007/s41669-018-0081-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reduction of Direct Health Costs Associated with Pertussis Vaccination with Acellular Vaccines in Children Aged
PharmacoEconomics Open https://doi.org/10.1007/s41669-018-0081-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reduction of Direct Health Costs Associated with Pertussis Vaccination with Acellular Vaccines in Children Aged
Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis. DTaP/DT and Tdap/Td Vaccines
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis DTaP/DT and Tdap/Td Vaccines Jean C. Smith, MD, MPH Medical Officer
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis DTaP/DT and Tdap/Td Vaccines Jean C. Smith, MD, MPH Medical Officer
Pertussis: Clinical Review and Colorado s Epidemic
 Pertussis: Clinical Review and Colorado s Epidemic Today s Speakers: Robert Brayden, MD, Professor of Pediatrics, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Children s Hospital Colorado Lisa Miller, MD,
Pertussis: Clinical Review and Colorado s Epidemic Today s Speakers: Robert Brayden, MD, Professor of Pediatrics, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Children s Hospital Colorado Lisa Miller, MD,
MEASLES HEALTH ALERT/ADVISORY. Date: February 5, Dear Colleague:
 MEASLES HEALTH ALERT/ADVISORY Date: February 5, 2019 Dear Colleague: Details of situation: Five measles cases, four between the ages of 12 to 21 months, have been reported in three different counties within
MEASLES HEALTH ALERT/ADVISORY Date: February 5, 2019 Dear Colleague: Details of situation: Five measles cases, four between the ages of 12 to 21 months, have been reported in three different counties within
Immunisation Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 10 February (minutes for web publishing)
 Immunisation Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 10 February 2014 (minutes for web publishing) Immunisation Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology
Immunisation Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 10 February 2014 (minutes for web publishing) Immunisation Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology
Dr Emma Best. Paediatric Infectious Diseases Consultant Starship Children s Hospital
 Dr Emma Best Paediatric Infectious Diseases Consultant Starship Children s Hospital Vaccine preventable diseases Dr Emma Best Senior Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics, University of Auckland Paediatric
Dr Emma Best Paediatric Infectious Diseases Consultant Starship Children s Hospital Vaccine preventable diseases Dr Emma Best Senior Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics, University of Auckland Paediatric
Pertussis Outbreak Investigation Report. Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health
 Pertussis Outbreak Investigation Report Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Department of Health April 2014 Table of Contents Summary... 1 Acronyms... 1 Introduction... 2 1. Outbreak epidemiology...
Pertussis Outbreak Investigation Report Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Department of Health April 2014 Table of Contents Summary... 1 Acronyms... 1 Introduction... 2 1. Outbreak epidemiology...
Whooping. pregnancy. Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby. the safest way to protect yourself and your baby
 Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby the safest way to protect yourself and your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who
Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby the safest way to protect yourself and your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who
Pregnant? There are many ways to help protect you and your baby. Immunise against: Flu (Influenza) Whooping cough (Pertussis) German measles (Rubella)
 Pregnant? There are many ways to help protect you and your baby Immunise against: Flu (Influenza) Whooping cough (Pertussis) German measles (Rubella) mmunisation This leaflet describes the vaccinations
Pregnant? There are many ways to help protect you and your baby Immunise against: Flu (Influenza) Whooping cough (Pertussis) German measles (Rubella) mmunisation This leaflet describes the vaccinations
Pertussis: Trends, Prevention and Challenges Flor M. Munoz, MD Associate Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases
 Pertussis: Trends, Prevention and Challenges Flor M. Munoz, MD Associate Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Disclosure I do not have any relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Page 1 xxx00.#####.ppt
Pertussis: Trends, Prevention and Challenges Flor M. Munoz, MD Associate Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Disclosure I do not have any relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Page 1 xxx00.#####.ppt
MICHAEL PARK A RUDOLF STEINER SCHOOL
 MICHAEL PARK A RUDOLF STEINER SCHOOL 9 November 2011 Dear Parents/Caregivers, Re: English Measles To help contain an outbreak of English measles at Michael Park School, please contact me on 525 8995 or
MICHAEL PARK A RUDOLF STEINER SCHOOL 9 November 2011 Dear Parents/Caregivers, Re: English Measles To help contain an outbreak of English measles at Michael Park School, please contact me on 525 8995 or
keyword: hepatitis Hepatitis
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: hepatitis Hepatitis Key reviewers: Dr Susan Taylor, Microbiologist, Diagnostic Medlab, Auckland Dr Tim Blackmore, Infectious Diseases Physician and Microbiologist, Wellington Hospital,
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: hepatitis Hepatitis Key reviewers: Dr Susan Taylor, Microbiologist, Diagnostic Medlab, Auckland Dr Tim Blackmore, Infectious Diseases Physician and Microbiologist, Wellington Hospital,
IMMUNISATION POLICY. Explanation: It is imperative that children are kept safe and healthy at all times in the centre environment.
 IMMUNISATION POLICY Aim: Immunisation is a simple, safe and effective way of protecting people against harmful diseases before they come into contact with them in the community. Immunisation not only protects
IMMUNISATION POLICY Aim: Immunisation is a simple, safe and effective way of protecting people against harmful diseases before they come into contact with them in the community. Immunisation not only protects
Pertussis: An Emerging Infection. Holly K. Ehrke. Ferris State University
 Running head: PERTUSSIS AN EMERGING INFECTION 1 Pertussis: An Emerging Infection Holly K. Ehrke Ferris State University PERTUSSIS AN EMERGING INFECTION 2 Abstract Pertussis is a highly contagious disease
Running head: PERTUSSIS AN EMERGING INFECTION 1 Pertussis: An Emerging Infection Holly K. Ehrke Ferris State University PERTUSSIS AN EMERGING INFECTION 2 Abstract Pertussis is a highly contagious disease
Pertussis. West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System
 Pertussis Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program : 304-558-5358 or 800-423-1271 in Fax: 304-558-8736 Investigation Information
Pertussis Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program : 304-558-5358 or 800-423-1271 in Fax: 304-558-8736 Investigation Information
MITIGATING PERTUSSIS:
 MITIGATING PERTUSSIS: WHAT PERINATAL SERVICE COORDINATORS CAN DO Figure 1 Figure 1: Pictures of San Diego family who lost baby to pertussis. Retrieved August 18 th, 2016 from: http://abcnews.go.com/lifestyle/heartbroken-family-hopes-babys-death-whooping-cough-raises/story?id=40956756
MITIGATING PERTUSSIS: WHAT PERINATAL SERVICE COORDINATORS CAN DO Figure 1 Figure 1: Pictures of San Diego family who lost baby to pertussis. Retrieved August 18 th, 2016 from: http://abcnews.go.com/lifestyle/heartbroken-family-hopes-babys-death-whooping-cough-raises/story?id=40956756
flu vaccination DRAFT The WINTER 2018/19 Who should have it and why Includes information for children and pregnant women mmunisation
 flu vaccination Who should have it and why The WINTER 2018/19 Includes information for children and pregnant women The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2018/19 Flu mmunisation Helping to protect everyone, every
flu vaccination Who should have it and why The WINTER 2018/19 Includes information for children and pregnant women The flu vaccination 1 Winter 2018/19 Flu mmunisation Helping to protect everyone, every
Considerations for Public Health on Pertussis Case and Contact Management
 Considerations for Public Health on Pertussis Case and Contact Management September 2015 History of Pertussis and Immunization Pertussis outbreaks tend to be cyclical in nature, with increased disease
Considerations for Public Health on Pertussis Case and Contact Management September 2015 History of Pertussis and Immunization Pertussis outbreaks tend to be cyclical in nature, with increased disease
Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox
 Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox Noelle Bessette, MPH Surveillance Specialist New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Chickenpox Caused
Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox Noelle Bessette, MPH Surveillance Specialist New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Chickenpox Caused
Quote. These are my principles. If you don t like them I have others. Groucho Marx
 Quote These are my principles. If you don t like them I have others. Groucho Marx Analysis of the Auckland 2014 Measles Outbreak Indicates that Adolescents and Young Adults could Benefit from Catch up
Quote These are my principles. If you don t like them I have others. Groucho Marx Analysis of the Auckland 2014 Measles Outbreak Indicates that Adolescents and Young Adults could Benefit from Catch up
Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox
 Chickenpox Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox Noelle Bessette, MPH Surveillance Specialist New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Caused
Chickenpox Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox Noelle Bessette, MPH Surveillance Specialist New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Caused
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality rev Jan 2018
 rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Influenza A, B or C virus BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Transmission occurs via droplet spread. After a person infected with influenza coughs, sneezes, or talks, influenza
rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Influenza A, B or C virus BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Transmission occurs via droplet spread. After a person infected with influenza coughs, sneezes, or talks, influenza
Meningococcal. Disease. Know the. symptoms. Don t wait talk to your doctor or nurse
 Meningococcal Disease Know the symptoms Don t wait talk to your doctor or nurse Meningococcal disease Meningococcal disease is an infection caused by a bacteria, and can lead to two very serious illnesses:
Meningococcal Disease Know the symptoms Don t wait talk to your doctor or nurse Meningococcal disease Meningococcal disease is an infection caused by a bacteria, and can lead to two very serious illnesses:
Background: Pertussis
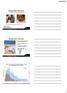 MITIGATING PERTUSSIS: WHAT PERINATAL SERVICE COORDINATORS CAN DO Figure 1 Figure 1: Pictures of San Diego family who lost baby to pertussis. Retrieved August 18 th, 2016 from: http://abcnews.go.com/lifestyle/heartbroken-family-hopes-babys-death-whooping-cough-raises/story?id=40956756
MITIGATING PERTUSSIS: WHAT PERINATAL SERVICE COORDINATORS CAN DO Figure 1 Figure 1: Pictures of San Diego family who lost baby to pertussis. Retrieved August 18 th, 2016 from: http://abcnews.go.com/lifestyle/heartbroken-family-hopes-babys-death-whooping-cough-raises/story?id=40956756
FAQ S ABOUT MAXWELL HEALTH S WORKPLACE FLU VACCINATION SERVICE
 THE DISEASE - INFLUENZA FACTS 2017 Influenza the disease Influenza can be a serious illness with severe effects including hospitalisation, complications and even death. Influenza is not just a 'bad cold'.
THE DISEASE - INFLUENZA FACTS 2017 Influenza the disease Influenza can be a serious illness with severe effects including hospitalisation, complications and even death. Influenza is not just a 'bad cold'.
Immunization Update Richard M. Lampe M.D.
 Immunization Update 2012 Richard M. Lampe M.D. Immunization Update List the Vaccines recommended for Health Care Personnel Explain why Health Care Personnel are at risk Recognize the importance of these
Immunization Update 2012 Richard M. Lampe M.D. Immunization Update List the Vaccines recommended for Health Care Personnel Explain why Health Care Personnel are at risk Recognize the importance of these
Communicable Disease Update; Vol. 16 (1), February 2017
 Communicable Disease Update; Vol. 16 (1), February 017 Item Type Other Authors Health Service Executive (HSE) South (South East), Department of Public Health Publisher Health Service Executive (HSE) South
Communicable Disease Update; Vol. 16 (1), February 017 Item Type Other Authors Health Service Executive (HSE) South (South East), Department of Public Health Publisher Health Service Executive (HSE) South
NOVEL INFLUENZA A (H1N1) Swine Flu
 Introduction Definitions Influenza-like Illness Emergency Department Assessment Anitiviral Medication Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) Dosing Infection Control Issues Staff Exposure References Introduction This guideline
Introduction Definitions Influenza-like Illness Emergency Department Assessment Anitiviral Medication Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) Dosing Infection Control Issues Staff Exposure References Introduction This guideline
Flu. is a killer. If you are at risk you should have your free flu vaccination every year.
 Flu is a killer. If you are at risk you should have your free flu vaccination every year. What is flu? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. It is not
Flu is a killer. If you are at risk you should have your free flu vaccination every year. What is flu? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. It is not
Pertussis. Faculty/Presenter Disclosure. Disclosure of Commercial Support. Mitigating Potential Bias. True Case 07/10/2013 DISCLOSURE
 Pertussis Outbreaks first described in the 16th Century Major cause of childhood fatality prior to vaccination Alan Kaplan Chair, Respiratory Medicine Group of College of Family Physicians of Canada Thanks
Pertussis Outbreaks first described in the 16th Century Major cause of childhood fatality prior to vaccination Alan Kaplan Chair, Respiratory Medicine Group of College of Family Physicians of Canada Thanks
It s all about the Whoop
 It s all about the Whoop Pertussis On Campus By Rebecca DiSaia Minus, MSN, RN, CNL Hear what Whooping cough sounds like Stages of Pertussis Catarrhal Stage Paroxysmal Stage Convalescent Stage (Recovery)
It s all about the Whoop Pertussis On Campus By Rebecca DiSaia Minus, MSN, RN, CNL Hear what Whooping cough sounds like Stages of Pertussis Catarrhal Stage Paroxysmal Stage Convalescent Stage (Recovery)
VACCINE PREVENTABLE DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY
 VACCINE PREVENTABLE DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY The Twenty-Second Annual Massachusetts Immunization Action Partnership Pediatric Immunization Skills Building Conference October 12, 2017 Marija PopStefanija, MPH,
VACCINE PREVENTABLE DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY The Twenty-Second Annual Massachusetts Immunization Action Partnership Pediatric Immunization Skills Building Conference October 12, 2017 Marija PopStefanija, MPH,
Immunisation Update for Occupational Health
 Immunisation Update for Occupational Health Dr Gayatri Amirthalingam Immunisation, Hepatitis & Blood Safety department Public Health England 29 th April 2016 Session Outline Epidemiology of vaccine preventable
Immunisation Update for Occupational Health Dr Gayatri Amirthalingam Immunisation, Hepatitis & Blood Safety department Public Health England 29 th April 2016 Session Outline Epidemiology of vaccine preventable
10/29/2015. Communicable Disease Outbreaks: Methods of Control. Objectives. Review of the Basics
 Communicable Disease Outbreaks: Methods of Control Brian Hartl, MPH Epidemiology Supervisor Kent County Health Department Objectives Contact Tracing Pharmaceutical Interventions Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions
Communicable Disease Outbreaks: Methods of Control Brian Hartl, MPH Epidemiology Supervisor Kent County Health Department Objectives Contact Tracing Pharmaceutical Interventions Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions
Pertussis Surveillance Examples from Europe
 Pertussis Surveillance Examples from Europe Johannes G. Liese Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University Childrens Hospital Julius-Maximilians-University, Würzburg, Germany 1 2 Pertussis Surveillance
Pertussis Surveillance Examples from Europe Johannes G. Liese Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University Childrens Hospital Julius-Maximilians-University, Würzburg, Germany 1 2 Pertussis Surveillance
Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments.
 Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Vaccine-Preventable Disease (VPD) Investigations in Kansas Chelsea Raybern, Advanced Epidemiologist Mychal Davis, Epidemiologist Amie Worthington,
Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Vaccine-Preventable Disease (VPD) Investigations in Kansas Chelsea Raybern, Advanced Epidemiologist Mychal Davis, Epidemiologist Amie Worthington,
Classification: official 1
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
Whooping cough. If you are pregnant you should get vaccinated to protect your baby
 Whooping cough If you are pregnant you should get vaccinated to protect your baby Cases of whooping cough are on the increase by getting the vaccine while pregnant you can protect your baby There were
Whooping cough If you are pregnant you should get vaccinated to protect your baby Cases of whooping cough are on the increase by getting the vaccine while pregnant you can protect your baby There were
The Continued Need for Immunizations in Top Ten Causes of Death in the U.S., 1900 vs Common Questions about Vaccines
 The Continued Need for Immunizations in 2016 Stephanie Schauer, Ph.D. Program Manager, Immunization Program April 13, 2016 Ten Great Public Health Achievements United States, 1900-1999 MMWR 1999 Control
The Continued Need for Immunizations in 2016 Stephanie Schauer, Ph.D. Program Manager, Immunization Program April 13, 2016 Ten Great Public Health Achievements United States, 1900-1999 MMWR 1999 Control
The Continued Need for Immunizations in 2016
 The Continued Need for Immunizations in 2016 Stephanie Schauer, Ph.D. Program Manager, Immunization Program April 13, 2016 Wisconsin Department of Health Services Ten Great Public Health Achievements United
The Continued Need for Immunizations in 2016 Stephanie Schauer, Ph.D. Program Manager, Immunization Program April 13, 2016 Wisconsin Department of Health Services Ten Great Public Health Achievements United
Prevent Measles Example of Fact sheet for health workers in Fiji
 Prevent Measles Example of Fact sheet for health workers in Fiji This example of a practical fact sheet can be adapted in other Pacific Island countries and territories to help raise awareness and prevent
Prevent Measles Example of Fact sheet for health workers in Fiji This example of a practical fact sheet can be adapted in other Pacific Island countries and territories to help raise awareness and prevent
HEALTH ADVISORY: MEASLES EXPOSURES IN NEW YORK STATE
 December 11, 2018 To: Health Care Providers, Hospitals, Emergency Departments, Dental Providers, and Local Health Departments From: New York State Department of Health, Bureau of Immunization HEALTH ADVISORY:
December 11, 2018 To: Health Care Providers, Hospitals, Emergency Departments, Dental Providers, and Local Health Departments From: New York State Department of Health, Bureau of Immunization HEALTH ADVISORY:
PERTUSSIS REPORT. November 2013
 PERTUSSIS REPORT Data contained within this monthly report is based on information recorded on EpiSurv by public health service staff as at 12 December 213. Changes made to EpiSurv data after this date
PERTUSSIS REPORT Data contained within this monthly report is based on information recorded on EpiSurv by public health service staff as at 12 December 213. Changes made to EpiSurv data after this date
SURVEILLANCE, REPORTING AND CONTROL OF VACCINE-PREVENTABLE DISEASES: WORKING TOGETHER TO CONTROL THE SPREAD
 SURVEILLANCE, REPORTING AND CONTROL OF VACCINE-PREVENTABLE DISEASES: WORKING TOGETHER TO CONTROL THE SPREAD Adult Immunization Conference April 10, 2018 Nancy Harrington nancy.harrington@dph.state.ma.us
SURVEILLANCE, REPORTING AND CONTROL OF VACCINE-PREVENTABLE DISEASES: WORKING TOGETHER TO CONTROL THE SPREAD Adult Immunization Conference April 10, 2018 Nancy Harrington nancy.harrington@dph.state.ma.us
Vaccine Preventable Diseases. Overview MEASLES 4/8/2015. Amy Schwartz, MPH Immunization Surveillance Coordinator North Dakota Department of Health
 Vaccine Preventable Diseases Amy Schwartz, MPH Immunization Surveillance Coordinator North Dakota Department of Health Measles Mumps Pertussis Meningococcal Disease Polio Rubella Hepatitis A Overview MEASLES
Vaccine Preventable Diseases Amy Schwartz, MPH Immunization Surveillance Coordinator North Dakota Department of Health Measles Mumps Pertussis Meningococcal Disease Polio Rubella Hepatitis A Overview MEASLES
Get Up-to-Date. With Tdap. You can make a difference. Increase Tdap vaccination rates among your adolescent and adult patients
 You can make a difference Get Up-to-Date Increase Tdap vaccination rates among your adolescent and adult patients With Tdap Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis counseling guide Identify: Proactively
You can make a difference Get Up-to-Date Increase Tdap vaccination rates among your adolescent and adult patients With Tdap Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis counseling guide Identify: Proactively
APEC Guidelines Immunizations
 Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
immunisation in New Zealand
 This appendix details the history of. Section A1.1 is a brief summary of when each vaccine was introduced to the National Immunisation Schedule (the Schedule). This summary includes vaccines which were
This appendix details the history of. Section A1.1 is a brief summary of when each vaccine was introduced to the National Immunisation Schedule (the Schedule). This summary includes vaccines which were
The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues. Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office.
 The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office : Dates vaccines introduced into the Irish immunisation schedule Vaccine 1937-1999 Date introduced
The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office : Dates vaccines introduced into the Irish immunisation schedule Vaccine 1937-1999 Date introduced
Clinical Guidance for 2009 H1N1 Influenza and Seasonal Influenza. Barbara Wallace, MD New York State Department of Health (Updated 10/8/09)
 Clinical Guidance for 2009 H1N1 Influenza and Seasonal Influenza Barbara Wallace, MD New York State Department of Health (Updated 10/8/09) 1 Outline Clinical assessment Diagnostic testing Antiviral medications
Clinical Guidance for 2009 H1N1 Influenza and Seasonal Influenza Barbara Wallace, MD New York State Department of Health (Updated 10/8/09) 1 Outline Clinical assessment Diagnostic testing Antiviral medications
Objectives. Immunity. Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children 12/22/2015
 Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children Bertha P. Rojas, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident South Miami Hospital Objectives Understand the definition of herd immunity Identify vaccine-preventable
Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children Bertha P. Rojas, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident South Miami Hospital Objectives Understand the definition of herd immunity Identify vaccine-preventable
Pertussis Epidemiology and Vaccine Impact in the United States
 Pertussis Epidemiology and Vaccine Impact in the United States Stacey Martin, MSc Epidemiology Team Lead Meningitis and Vaccine Preventable Diseases Branch Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Presented
Pertussis Epidemiology and Vaccine Impact in the United States Stacey Martin, MSc Epidemiology Team Lead Meningitis and Vaccine Preventable Diseases Branch Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Presented
Flu. Flu is a killer. Flu vaccination
 Flu Flu is a killer Flu vaccination 2015-16 Why is flu serious? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. There are outbreaks every year, usually in winter.
Flu Flu is a killer Flu vaccination 2015-16 Why is flu serious? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. There are outbreaks every year, usually in winter.
If you are not sure if your child is up to date with their MMR, please check with your GP.
 Please reply to: Tha Han E-mail: tha.han@enfield.gov.uk Phone: Textphone: Fax: My Ref: Your Ref: Date: 19 th June 2018 Dear Parent(s) / Guardian(s) Measles in Enfield I am writing to tell you that a number
Please reply to: Tha Han E-mail: tha.han@enfield.gov.uk Phone: Textphone: Fax: My Ref: Your Ref: Date: 19 th June 2018 Dear Parent(s) / Guardian(s) Measles in Enfield I am writing to tell you that a number
Year 7 immunisation. Parent Consent Form
 Year 7 immunisation Boostrix an immunisation to boost your child's protection against tetanus, diphtheria and whooping cough (pertussis) Parent Consent Form Please sign and return the form to school. COOK
Year 7 immunisation Boostrix an immunisation to boost your child's protection against tetanus, diphtheria and whooping cough (pertussis) Parent Consent Form Please sign and return the form to school. COOK
Department of Health. Year 8. vaccination program. Important information for parents and students
 Department of Health Year 8 vaccination program Important information for parents and students Contents Why immunise? 1 Vaccination program 1 Schedule of vaccinations 2 Vaccination records 2 Vaccine safety
Department of Health Year 8 vaccination program Important information for parents and students Contents Why immunise? 1 Vaccination program 1 Schedule of vaccinations 2 Vaccination records 2 Vaccine safety
