Epidermolysis bullosa in the medical practice of a general practitioner: a study of two cases
|
|
|
- Hilary Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pediatr Pol 2019; 94 (1): DOI: Submitted: ; Accepted: ; Published: Case report Epidermolysis bullosa in the medical practice of a general practitioner: a study of two cases Bartosz Pałdyna 1, Magdalena Pałdyna 2, Anna Charuta 1 1 Faculty of Natural Sciences, Siedlce University of Natural Sciences and Humanities, Siedlce, Poland 2 Mazovia Regional Hospital in Siedlce, Siedlce, Poland Abstract Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa is an inherited disease presenting with blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. The authors reviewed a case of siblings suffering from the disease. The first symptoms were noticed at the time of birth, and epidermolysis bullosa was suspected. The lesions appear spontaneously or as a result of a trauma, even during everyday activities connected with getting dressed or hygiene. As well as skin lesions they also have symptoms from other organs, which is a challenge for the primary care paediatrician. Children also need the constant care of specialised team of doctors. The disease is a considerable burden on the life of the whole family; therefore, social support and psychological care are also necessary. Key words: treatment, nutrition, epidermolysis bullosa, COL7A1. Introduction Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a term used to describe a group of genetically conditioned diseases of the skin and mucous membranes, characterised by the formation of blisters either as a result of mechanical trauma or spontaneously [1]. EB is a rare disease of which the incidence of occurrence is 1 : 50,000 births [2]. It is estimated that there are approximately 500,000 people suffering from different types of EB [3]. The disease is caused by a mutation in the COL7A1 gene encoding procollagen type VII, inherited as a dominant epidermolysis bullosa and recessive epidermolysis bullosa [1]. Blisters may occur in various skin layers, which has led to the division into particular EB types. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS) consists of blisters located at the keratinocyte layer of the basement membrane, junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) within lamina lucida of the basement membrane, whereas dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) occur below the lamina densa [2, 4]. The fourth type is Kindler syndrome (KS) in which blisters do not have any specific location [4]. The most severe is a type of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa inherited recessively (recessive dystrophic EB RDEB). The symptoms usually occur at birth or soon after [1]. Not only skin but also other systems and organs may be affected. Therefore, patients should be in the care of a multi-specialist team consisting of a general practitioner, a dermatologist, a nurse, a dietician, and other specialised doctors depending on the observed ailments [5]. Case study Siblings an eight-year-old girl and a six-year-old boy are in the regular care of a paediatrician. As newborns, both children were observed to develop skin maceration, Address for correspondence: Bartosz Pałdyna, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Siedlce University of Natural Sciences and Humanities, 2 Konarskiego St., Siedlce, Poland, ORCID: , bartosz.paldyna@vp.pl 58
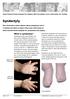
2 Epidermolysis bullosa in the medical practice of a general practitioner: a study of two cases blisters, and extensive skin losses. Molecular analysis conducted in the Medical Genetics Department of the Institute of Mother and Child in Warsaw discovered the presence of p.trp796ter mutation in both alleles of the COL7A1 gene, which confirmed the diagnosis of EB of a dystrophic type in patients. Genetic tests were also conducted in the siblings parents, and the carrier of the same mutation was found. Presently, the patients are observed to have extensive bullae of limp surface, which tend to break easily causing lesions, scars, and discolouration of the skin (Fig. 1). In the area of upper and lower limbs, distal phalangeal atrophy, nail dystrophy, contractures, and adhesions are observed (Fig. 2 and 3). Periodically, the skin of hands and feet is dry, peeling, and breaks easily when touched (Fig. 4). The lesions in the form of bullae and erosions also appear in the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The girl was hospitalised repeatedly due to infectious diseases. At the age of two months she was diagnosed with the infection of skin lesions; the culture showed increased Pseudomonas aeruginosa and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA). Then, phlegmon of the right thumb occurred, followed by phlegmon of the toes. Moreover, since the girl was two years old, anaemia related to iron deficiency was observed. At the age of four years, there were signs of insufficiency of the body mass and height (below the 3 rd percentile), at the age of five years additional swallowing difficulties, and at the age of six years narrowing of the oesophagus was observed. Ophthalmological examinations showed recurrent changes in the corneal erosions. The boy has been observed to have anaemia related to iron deficiency since he was two years old and insufficiency of the body mass and height below the 3 rd percentile. Both patients suffer from constipation and intense itching. The most frequent reasons for consultation of a doctor were the evaluation of non-healing skin lesions, infectious diseases mainly of the upper but also lower respiratory tract, inflammation of mucous membrane of the oral cavity, gastroenteritis, and conjunctivitis. The children had been vaccinated in accordance with an individual vaccination schedule. In the localisation of the injection, bullous changes with pus were observed, which usually lasted for about a month. A similar reaction was also visible after blood specimen collection or the insertion of a needle. Figure 1. Skin lesions on the back of the boy Figure 2. Distal phalangeal atrophy and nail dystrophy within the boy s hands Figure 3. Distal phalangeal atrophy and nail dystrophy within the girl s feet Figure 4. Girl s hands 59
3 Bartosz Pałdyna, Magdalena Pałdyna, Anna Charuta The siblings under the regular care of many specialised doctors, including a paediatrician, a dermatologist, a paediatric surgeon, a dentist, an ophthalmologist, an allergologist, a gastroenterologist, a neurologist, a physiotherapist, a dietician, a speech therapist, and a psychologist. The parents take care of the children and rehabilitate them on a day-to-day basis. As far as the social aspect is concerned, a lack of acceptance and lack of understanding concerning the different appearance of the children are a problem. A local treatment consists of applying special dressings, including adaptic touch dressing, silver dressings, hydrofibre dressings, hydrocolloid dressings, lipide-colloid dressings, and foam dressings; also creams and ointments including silver salts, antibiotics, and glycocorticosteroids. Daily, antihistamines are applied to relieve the itching. Multivitamin preparations and iron preparations are administered. As a result of the used supplementation the red blood cell count and the level of haemoglobin remain in the lower ranges of the norm for age. The diet is enriched by unsaturated fatty acids and high-calorific and high-protein nutrient supplements. The problem is the taste of these nutrient supplements, which is often not accepted by children and causes them to consume it reluctantly, usually in an amount less than recommended. Both patients have gained weight and height, but their body mass and height still remain below the third percentile; therefore, further consultations with nutrition specialists are planned. Laxatives are administered on an ad hoc basis. Discussion EB is a disease in which skin lesions are the first observed symptoms. Widespread blisters with limp covering occur typically in distal parts of the limbs and on the back and heal of the foot, leaving scars and hipo- and hyperpigmented changes. The occurrence of milia is very common, especially on the auricles and the dorsal surfaces of hands. The course of the disease is connected with the disappearance of fingerprints, nail dystrophy, hand and foot contracture, and syndactyly [1]. Most of those symptoms were observed in the described children. Not only skin but also other systems and organs may be affected by the disease. Disorders concerning the gastrointestinal system are the most frequent. Freeman et al. claimed that 58% of patients suffer from them, and the incidence of occurrence of particular disorders differed between groups of patients depending on the particular EB type [6]. One of the most frequent ailments of all EB patients is constipation, occurring in 75% of patients. This is caused by painful defecation connected with the presence of changes in the area of the rectum; moreover, due to swallowing disorders patients are often on a diet poor in fibre, have limited physical activity, and take oral iron preparations, which intensify the symptoms [7]. Freeman et al. also observed the occurrence of gastroesophageal reflux in three out of four RDEB patients and the narrowing of the oesophagus in 66% of them [6]. Changes present in the cornea are particularly painful for patients and may lead to damage to eyes and visual impairment. It is essential to mention that external otitis and middle ear inflammation are otolaryngological complications that are most frequent pathologies of the organ of hearing in these patients. However, it may also lead to rare conditions such as narrowing or closing of the upper respiratory tract, which is a direct life-threatening condition [4]. Other pathologies include enamel defects, which together with painful ulcerations in the oral cavity, making hygiene difficult, may lead to the development of tooth decay [1]. Moreover, EB patients are in the risk group to develop congestive cardiomyopathy, nephropathy, and glomerulonephritis [4]. Malnutrition is a very serious problem the degree of which is connected with the intensity of the changes and occurs most frequently as RDEB and JEB types. It is caused by a need for an increased calorific value due to the occurrence of widespread lesions, transdermal loss of proteins, and warmth, intensifying in the case of infections [8]. Another factor is the increase in intensification of changes within the oral cavity, the throat, the oesophagus, and further parts of the digestive track, connected with painful swallowing and later with swallowing difficulties due to a progressing process of scarring of the oesophagus and its narrowing, as well as intestinal absorption disorders [4, 9]. Painful defecation, which may be accompanied by constipation, results in apathy and secondary anorexia [10]. These disorders lead to shortages of micro- and macro-elements, including zinc, magnesium, calcium, potassium, iron, vitamins: A, D, E, B1, B6, and B12, and proteins [11], which is connected with anaemia, retarded physical and sexual development, an increased risk of osteopenia and osteoporosis, as well as a greater susceptibility to infections and wound healing disorders [4, 8, 9]. Within non-healing wounds in patients with acute forms of EB, cancerous transformations may develop. Squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) occur most frequently and develop in 90% of ill people. In RDEB patients, skin cancers usually develop in the second, third, or fourth decade of life, being the main cause of deaths in the group. Hence it is necessary to control non-healing ulcers during each check-up visit and to conduct a histopathological examination when cancer is suspected [4]. EB is a very serious disease that has a negative influence on the quality of life of patients themselves and their families [4, 5, 12]. A psychological study conducted on parents of ill children indicated a significantly bigger void in life, lower sense of life control and its goals, lower life satisfaction, as well as an increased need for social support [12]. At present, patients suffering from epidermolysis bullosa can make use of symptom therapy concentrating mainly on the treatment of skin lesions and accompany- 60
4 Epidermolysis bullosa in the medical practice of a general practitioner: a study of two cases ing changes in organs. New blisters should be punctured with a sterile needle leaving the pockets of the bullae. In the case of erosions that heal fast, it is enough to apply ointment with silver nitrate or preparations containing antibiotic or glycocorticosteroid. A significantly more serious problem concerns non-healing wounds, which are connected with pain and increase the risk of infections. An important element is to evaluate the lesion and to control the infection that is preventing the healing process. Dressings are applied locally, which protect the lesion from harmful influences from the external environment and provide optimal healing conditions [4]. An integral EB symptom, significantly influencing patients quality of life, is pain [13]. Most RDEB patients estimate the pain level during the day as 5 in 1 10 scale [4]. Among measures undertaken to prevent the occurrence of lesions and to make healing faster, appropriate nutrition and the control of infections are key factors [13]. In the case of light and mild degree of ailments, paracetamol is applied as the only medicine or in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, whereas when the pain is severe opioid-based drugs are necessary [13]. To treat chronic pain, pregabalin and gabapentin may be applied as adjuvant drugs [14]. They are also ideal during neuropathic pain within damaged skin [4, 13]. It has been reported that lidocaine or morphine are effective while alleviating the pain locally; however, a lack of research concerning the absorption of the substances and their general effects limits their applicability [13]. The basis for treating itching is antihistamine II generation, and in case it is not effective hydroxyzine, doxepin, ondansetron, or gabapentin [4]. Practically, it may be essential to apply a few drugs from various groups [13]. Apart from pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy and methods of relaxation are effective techniques to relieve pain, both acute and chronic, as well as to ease itching [13]. Great progress concerning the research on the pathogenesis of EB brings hope for the development of cause-related therapy, such as a gene therapy, protein therapy, or cell therapy. All these methods aim at providing the skin with functional protein in the area of the damage, which led to the relief symptoms in experimental research and clinical pilot tests [4, 15 17]. Nutrition treatment seems to be an integral element of the therapy due to frequent malnutrition, especially in patients with acute forms of EB. Patients energetic needs are increased and comparable to the ones of patients with burns, whereas a significant loss of protein through the damaged skin, the constant process of regeneration, and recurring infections mean that it is necessary to increase protein by as much as 200% of the average for a given age group [9]. Due to observed shortages of vitamins and micro-elements, patients should be supplemented with multivitamin preparations when their daily intake of vitamins is lower than 150% of a suggested daily consumption for a particular age group [8]. Because of constipation, patients diets ought to contain an appropriate amount of fibre, and taking into account the increased needs for many nutrients, a good solution may be nutrient preparations containing an increased amount of insoluble dietary fibre. Gastrostomy may be essential to increase the nutrition of patients with acute forms of EB [9]. It has been used in several Polish patients with EB with good results in increasing body mass index. So far, however, the question of when gastrostomy should be applied has not been answered, whether it is before malnutrition is observed or when it is discovered. What is the optimal diet of people fed this way, and which method of applying a gastrostomy tube is the most effective in this group? These are the next questions to which answers have not yet been given [18]. Disclosure The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1. Bruckner-Tuderman L. Pęcherzowe oddzielanie się naskórka. In: Dermatologia Braun-Falco. Vol. 2, Gliński W (ed.). Cornetis, Wrocław 2008; Sobczynska-Tomaszewska A, Wertheim K, Kowalewski C, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica. From clinics to genetics. Przegl Dermatol 2009; 96: Featherstone C. Epidermolysis bullosa: from fundamental molecular biology to clinical therapies. J Invest Dermatol 2007; 127: Wertheim-Tysarowska K, Kowalewski C, Woźniak K, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa pęcherzowe oddzielanie się naskórka. Etiopatogeneza, dziedziczenie, diagnostyka, leczenie. Continuo, Wrocław El Hachem M, Zambruno G, Bourdon-Lanoy E, et al. Multicentre consensus recommendations for skin care in inherited epidermolysis bullosa. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014; 9: Freeman EB, Köglmeier J, Martinez AE, et al. Gastrointestinal complications of epidermolysis bullosa in children. Br J Dermatol 2008; 158: Fine JD, Mellerio JE. Extracutaneous manifestations and complications of inherited epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermatol 2009; 61: Haynes L. Nutrition for children with epidermolysis bullosa. Dermatol Clin 2010; 28: Zidorio APC, Dutra ES, Leão DOD, et al. Nutritional aspects of children and adolescents with epidermolysis bullosa: literature review. An Bras Dermatol 2015; 90: Haynes L. Epidermolysis bullosa. In: Clinical paediatric dietetics, Shaw V, Lawson M (eds.). 3 rd ed. Blackwell Science, Oxford 2007; Lechner Gruskay D, Honig PJ, Pereira G, et al. Nutritional and metabolic profile of children with epidermolysis bullosa. Pediatr Dermatol 1988; 5: Macik D, Kowalska-Dabrowska M. The need of social support, life attitudes and life satisfaction among parents of children suffering from epidermolysis bullosa. Przegl Dermatol 2015; 102: Goldschneider KR, Good J, Harrop E, et al. Pain care for patients with epidermolysis bullosa: best care practice guidelines. BMC Med 2014; 12:
5 Bartosz Pałdyna, Magdalena Pałdyna, Anna Charuta 14. Pope E, Lara-Corrales I, Mellerio J, et al. A consensus approach to wound care in epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermatol 2012; 67: Lees CJ, Eide C, Keene DR, et al. Patient-specific naturally gene-reverted induced pluripotent stem cells in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol 2014; 134: Tolar J, Wagner JE. Allogeneic blood and bone marrow cells for the treatment of severe epidermolysis bullosa: repair of the extracellular matrix. Lancet 2013; 382: Cutlar L, Greiser U, Wang W. Gene therapy: pursuing restoration of dermal adhesion in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol 2014; 23: Moss C; Does gastrostomy benefit patients with epidermolysis bullosa? We need to collaborate to find out. Br J Dermatol 2018; 179:
Extracutaneous manifestations of Epidermolysis Bullosa
 Extracutaneous manifestations of Epidermolysis Bullosa DEBRA International Congress Toronto 13th September 2012 Dr Anna Martinez Great Ormond Street Hospital London 400 EB: more than just skin deep Multisystemic
Extracutaneous manifestations of Epidermolysis Bullosa DEBRA International Congress Toronto 13th September 2012 Dr Anna Martinez Great Ormond Street Hospital London 400 EB: more than just skin deep Multisystemic
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE
 WHEN CHILDHOOD HURTS: EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC LYNN CLARK, RN, MS, CPNP-PC, AP-PMN CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC NOTHING TO DISCLOSE
WHEN CHILDHOOD HURTS: EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC LYNN CLARK, RN, MS, CPNP-PC, AP-PMN CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC NOTHING TO DISCLOSE
Enteral Nutrition in Children with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
 Enteral Nutrition in Children with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Virginie Colomb, MD, PhD Christine Bodemer, MD, PhD Necker Enfants Malades Hospital, Paris DebRA conference Avignon, November
Enteral Nutrition in Children with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Virginie Colomb, MD, PhD Christine Bodemer, MD, PhD Necker Enfants Malades Hospital, Paris DebRA conference Avignon, November
Mild Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Denyer EB CNS DebRA UK 2009
 Mild Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa J. Denyer EB CNS DebRA UK 2009 What is Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB)? EB is a group of inherited disorders in which the skin blisters extremely easily. There are 3 main
Mild Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa J. Denyer EB CNS DebRA UK 2009 What is Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB)? EB is a group of inherited disorders in which the skin blisters extremely easily. There are 3 main
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
DYSTROPHIC EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA (DEB)
 DYSTROPHIC EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA (DEB) 1. Introduction Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa is an umbrella term for all forms of EB, where the blisters are formed in the dermis layer of the skin. "Dystrophic"
DYSTROPHIC EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA (DEB) 1. Introduction Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa is an umbrella term for all forms of EB, where the blisters are formed in the dermis layer of the skin. "Dystrophic"
EB 2009 The DEBRA International Epidermolysis Bullosa Research Conference Vienna, 6-8 September 2009
 EB 2009 The DEBRA International Epidermolysis Bullosa Research Conference Vienna, 6-8 September 2009 Pohla-Gubo G, Riedl R, Nuess D, Bauer JW, Hintner H The DEBRA International Epidermolysis Bullosa Research
EB 2009 The DEBRA International Epidermolysis Bullosa Research Conference Vienna, 6-8 September 2009 Pohla-Gubo G, Riedl R, Nuess D, Bauer JW, Hintner H The DEBRA International Epidermolysis Bullosa Research
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Scleroderma Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS SCLERODERMA 1.1 What is it? The name scleroderma is derived from Greek and can be translated as "hard skin".
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Scleroderma Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS SCLERODERMA 1.1 What is it? The name scleroderma is derived from Greek and can be translated as "hard skin".
A REPORT OF TWO CASES OF SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA OF THE HAND IN PATIENTS WITH EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA DYSTROPHICA
 Basrah Journal Case Report Of Surgery A REPORT OF TWO CASES OF SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA OF THE HAND IN PATIENTS WITH EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA DYSTROPHICA MB,ChB, Assist. Prof., FICMS, Consultant Orthopaedic
Basrah Journal Case Report Of Surgery A REPORT OF TWO CASES OF SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA OF THE HAND IN PATIENTS WITH EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA DYSTROPHICA MB,ChB, Assist. Prof., FICMS, Consultant Orthopaedic
Epidermolysis bullosa Report from observation charts
 Orofacial function of persons having Epidermolysis bullosa Report from observation charts The survey comprises 20 observation charts. Estimated occurrence: 50:000 000 inhabitants. Etiology: There are both
Orofacial function of persons having Epidermolysis bullosa Report from observation charts The survey comprises 20 observation charts. Estimated occurrence: 50:000 000 inhabitants. Etiology: There are both
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
 EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA Definition Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a term used to describe a group of rare mainly hereditary, chronic, non-inflammatory diseases of skin and mucous membranes. EB is characterized
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA Definition Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a term used to describe a group of rare mainly hereditary, chronic, non-inflammatory diseases of skin and mucous membranes. EB is characterized
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports
 Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2015; 3(9B):896-900 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2015; 3(9B):896-900 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Galen ( A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing
 Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Eating Disorders. About more than Food Teena
 Eating Disorders About more than Food Teena Eating Disorders: About More than Food What are eating disorders? The eating disorders anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder, and their
Eating Disorders About more than Food Teena Eating Disorders: About More than Food What are eating disorders? The eating disorders anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder, and their
Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.]
![Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.] Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.]](/thumbs/83/87846749.jpg) University of Groningen Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa Gostynski, Antoni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa Gostynski, Antoni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Severe generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (Hallopeau-Siemen s) : a case report Iffat Hassan, Mohammad Abid Keen Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2013;5:e190
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Severe generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (Hallopeau-Siemen s) : a case report Iffat Hassan, Mohammad Abid Keen Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2013;5:e190
Nutrition. Chapter 45. Reada Almashagba
 Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
Unit 4: Contemporary Nutrition Issues. Malnutrition (Undernutrition)
 Unit 4: Contemporary Nutrition Issues Malnutrition (Undernutrition) Syllabus Link: What is Undernutrition? Undernutrition: A condition that occurs when an individual s diet is lacking one or more nutrients.
Unit 4: Contemporary Nutrition Issues Malnutrition (Undernutrition) Syllabus Link: What is Undernutrition? Undernutrition: A condition that occurs when an individual s diet is lacking one or more nutrients.
السكري للداء مرافقة فقاعات diabeticorum= Bullosis
 1 / 6 Bullosis diabeticorum Bullous disease of diabetes (bullosis diabeticorum) is a distinct, spontaneous, noninflammatory, blistering condition of acral skin unique to patients with diabetes mellitus.
1 / 6 Bullosis diabeticorum Bullous disease of diabetes (bullosis diabeticorum) is a distinct, spontaneous, noninflammatory, blistering condition of acral skin unique to patients with diabetes mellitus.
list of speciality types
 Descriptions of Speciality Types GENERAL PRACTITIONER GENERAL PRACTITIONER GP or family practitioner (FP) Family doctor A medical practitioner whose practice is not limited to any specific branch of medicine
Descriptions of Speciality Types GENERAL PRACTITIONER GENERAL PRACTITIONER GP or family practitioner (FP) Family doctor A medical practitioner whose practice is not limited to any specific branch of medicine
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Life and death of a butterfly child born in a resourcelimited
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Life and death of a butterfly child born in a resourcelimited country January 2017 Alfonso Deliz O, Berger TM, Gubler D, Rundu State Hospital (ADO, BTM), Rundu, Namibia, The
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Life and death of a butterfly child born in a resourcelimited country January 2017 Alfonso Deliz O, Berger TM, Gubler D, Rundu State Hospital (ADO, BTM), Rundu, Namibia, The
The Adult hand and EB Rachel Box Clinical Specialist St Thomas Hospital
 The Adult hand and EB Rachel Box Clinical Specialist St Thomas Hospital All types of EB affect the Hand. Patients treated often have Junctional, Dystrophic or Recessive Dystrophic EB. Skin, mucosal linings
The Adult hand and EB Rachel Box Clinical Specialist St Thomas Hospital All types of EB affect the Hand. Patients treated often have Junctional, Dystrophic or Recessive Dystrophic EB. Skin, mucosal linings
Familial Mediterranean Fever
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
Interesting Case Series. A rapid response to matrix therapy with RGTA in severe epidermolysis bullosa
 Interesting Case Series A rapid response to matrix therapy with RGTA in severe epidermolysis bullosa Al Malaq, Ali*; Barritault Denis** * King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh KSA,
Interesting Case Series A rapid response to matrix therapy with RGTA in severe epidermolysis bullosa Al Malaq, Ali*; Barritault Denis** * King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh KSA,
Nutrition Competency Framework (NCF) March 2016
 K1 SCIENCES understanding of the basic sciences in relation to nutrition Framework (NCF) March 2016 1. Describe the functions of essential nutrients, and the basis for the biochemical demand for energy
K1 SCIENCES understanding of the basic sciences in relation to nutrition Framework (NCF) March 2016 1. Describe the functions of essential nutrients, and the basis for the biochemical demand for energy
TYPES OF DOCTORS. Dermatologist - This is a doctor that treats any ailment related to the skin and its appendages such as hair, nails etc.
 Cardiologist - A cardiologist is certified to treat any problem dealing with heart diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Dentist - Any dental problem from tooth decay to dentures to retainers are handled
Cardiologist - A cardiologist is certified to treat any problem dealing with heart diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Dentist - Any dental problem from tooth decay to dentures to retainers are handled
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Majeed Syndrome Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS MAJEED 1.1 What is it? Majeed syndrome is a rare genetic disease. Affected children suffer from Chronic
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Majeed Syndrome Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS MAJEED 1.1 What is it? Majeed syndrome is a rare genetic disease. Affected children suffer from Chronic
Cystic Fibrosis. Parkland College. Monica Rahman Parkland College. Recommended Citation
 Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2013 Cystic Fibrosis Monica Rahman Parkland College Recommended Citation Rahman, Monica, "Cystic Fibrosis" (2013). A with Honors Projects. 98. http://spark.parkland.edu/ah/98
Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2013 Cystic Fibrosis Monica Rahman Parkland College Recommended Citation Rahman, Monica, "Cystic Fibrosis" (2013). A with Honors Projects. 98. http://spark.parkland.edu/ah/98
REPORT OF EXPERIENCES:
 REPORT OF EXPERIENCES: Non Adherent Dressings in Fragile Skin Conditions: The Use of Soft Silicone Coated Polyurethane Foam Dressing (Mepilex ) in Hereditary and Acquired Bullous Skin Diseases. Hauke Schumann
REPORT OF EXPERIENCES: Non Adherent Dressings in Fragile Skin Conditions: The Use of Soft Silicone Coated Polyurethane Foam Dressing (Mepilex ) in Hereditary and Acquired Bullous Skin Diseases. Hauke Schumann
Chapter 6, Part Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Dental Care and Health An Update. Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI
 Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
Nutrient Assessment Chart
 Vitamin A Assessment Chart Chicken skin on backs of arms Chronic acne Dry eyes Food allergies Poor night vision Recurrent infections and colds Reduced hair growth in children Ulcers B Vitamins Afternoon
Vitamin A Assessment Chart Chicken skin on backs of arms Chronic acne Dry eyes Food allergies Poor night vision Recurrent infections and colds Reduced hair growth in children Ulcers B Vitamins Afternoon
Changes in the management of children with Cystic Fibrosis. Caroline Murphy & Deirdre O Donovan CF Nurses
 Changes in the management of children with Cystic Fibrosis Caroline Murphy & Deirdre O Donovan CF Nurses What Is Cystic Fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that primarily affects
Changes in the management of children with Cystic Fibrosis Caroline Murphy & Deirdre O Donovan CF Nurses What Is Cystic Fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that primarily affects
PLEASE COMPLETE ALL SECTIONS OF THIS FORM
 PLEASE COMPLETE ALL SECTIONS OF THIS FORM Patient Name: Date of Birth: Referring Doctor? (Name, telephone number and address) Chief Complaint: Why have you come here? How did it start? What are the symptoms?
PLEASE COMPLETE ALL SECTIONS OF THIS FORM Patient Name: Date of Birth: Referring Doctor? (Name, telephone number and address) Chief Complaint: Why have you come here? How did it start? What are the symptoms?
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
Management of the complications of myeloma and side-effects of treatment Christine Morris Clinical Nurse Specialist in Myeloma Royal Derby Hospital
 Management of the complications of myeloma and side-effects of treatment Christine Morris Clinical Nurse Specialist in Myeloma Royal Derby Hospital Common problems in myeloma Myeloma-related complications/symptoms
Management of the complications of myeloma and side-effects of treatment Christine Morris Clinical Nurse Specialist in Myeloma Royal Derby Hospital Common problems in myeloma Myeloma-related complications/symptoms
University of Groningen. The Pain Quality Assessment Scale for epidermolysis bullosa Schrader, Nicholas; Yuen, Wing Y; Jonkman, Marcel F.
 University of Groningen The Pain Quality Assessment Scale for epidermolysis bullosa Schrader, Nicholas; Yuen, Wing Y; Jonkman, Marcel F. Published in: Acta dermato-venereologica DOI: 10.2340/00015555-2827
University of Groningen The Pain Quality Assessment Scale for epidermolysis bullosa Schrader, Nicholas; Yuen, Wing Y; Jonkman, Marcel F. Published in: Acta dermato-venereologica DOI: 10.2340/00015555-2827
Hyper IgE Syndrome. IDF US Information: Hyper IgE Syndrome. Definition of Hyper IgE Syndrome
 Hyper IgE Syndrome Definition of Hyper IgE Syndrome Hyper-IgE syndrome (HIES) is a complex primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a spectrum of abnormalities related to the immune system, bones,
Hyper IgE Syndrome Definition of Hyper IgE Syndrome Hyper-IgE syndrome (HIES) is a complex primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a spectrum of abnormalities related to the immune system, bones,
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE
 SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
- Conclusion: This study confirmed the very good acceptability and efficacy of Urgotul in the treatment of skin lesions in patients with EB.
 www.journalofwoundcare.com Using Urgotul dressing for the management of epidermolysis bullosa skin lesions VOL 14, NO 10, November 2005 Objective: To evaluate the acceptability, tolerance and efficacy
www.journalofwoundcare.com Using Urgotul dressing for the management of epidermolysis bullosa skin lesions VOL 14, NO 10, November 2005 Objective: To evaluate the acceptability, tolerance and efficacy
Cystic Fibrosis. Information for Caregivers
 Cystic Fibrosis Information for Caregivers Arkansas Children s Hospital is an accredited Cystic Fibrosis Care Center by the National Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Cystic Fibrosis: Information for Caregivers
Cystic Fibrosis Information for Caregivers Arkansas Children s Hospital is an accredited Cystic Fibrosis Care Center by the National Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Cystic Fibrosis: Information for Caregivers
E09 PEG. Expires end of March 2018 VITALITY.CO.UK
 VITALITY.CO.UK E09 PEG Expires end of March 2018 You can get more information and share your experiences at www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org eidohealthcare.com
VITALITY.CO.UK E09 PEG Expires end of March 2018 You can get more information and share your experiences at www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org eidohealthcare.com
CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY
 IMPORTANT NEW UPDATE A Summary of the Report of the DMD Care Considerations Working Group Intended for US healthcare professionals only. CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Full article
IMPORTANT NEW UPDATE A Summary of the Report of the DMD Care Considerations Working Group Intended for US healthcare professionals only. CARE CONSIDERATIONS FOR DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Full article
Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet
 Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future Introduction This leaflet is about pressure ulcers and includes information about what they are what can cause them and how they
Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future Introduction This leaflet is about pressure ulcers and includes information about what they are what can cause them and how they
Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet
 Further information about the content, reference sources or production of this leaflet can be obtained from the Patient Information Centre. Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet This information
Further information about the content, reference sources or production of this leaflet can be obtained from the Patient Information Centre. Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet This information
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis
 Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Appropriate prescribing of specialist infant formula feeds
 Appropriate Prescribing of Specialist Infant Formula Feeds Purpose of the guidance These guidelines aim to assist GPs and Health Visitors with information on the appropriate use of infant formula that
Appropriate Prescribing of Specialist Infant Formula Feeds Purpose of the guidance These guidelines aim to assist GPs and Health Visitors with information on the appropriate use of infant formula that
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Skin lesions & Abrasions
 Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Hip Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 riginator: Anne Flavall Professional Development Lead, Mr Marsh and Mr Quraishi Orthopaedic Consultant Surgeons Date: March 2012 Version: 2 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00611 Hip Fracture
riginator: Anne Flavall Professional Development Lead, Mr Marsh and Mr Quraishi Orthopaedic Consultant Surgeons Date: March 2012 Version: 2 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00611 Hip Fracture
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease:
 Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
1 ANIMALS Digestive System Oral Cavity and Esophagus.notebook January 06, 2016
 The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
Western Health Specialist Clinics Access & Referral Guidelines
 Western Health Specialist Clinics Access & Referral Guidelines Paediatric Medicine Clinics at Western Health: Western Health operates the following Specialist Clinic services for patients who require assessment
Western Health Specialist Clinics Access & Referral Guidelines Paediatric Medicine Clinics at Western Health: Western Health operates the following Specialist Clinic services for patients who require assessment
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST
 COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
Tissues. Definition. A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function.
 Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels.
 Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis, how is it treated, and will it go away?
 Panelists What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis, how is it treated, and will it go away? Bradley A. Becker, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics and Internal Medicine Division of Allergy and Immunology Saint Louis
Panelists What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis, how is it treated, and will it go away? Bradley A. Becker, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics and Internal Medicine Division of Allergy and Immunology Saint Louis
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science
 CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Basic Nutrition - Biol 209 3 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION Appropriate
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Basic Nutrition - Biol 209 3 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION Appropriate
Janice Scott MS, RD, CSP, LD Clinical Nutrition Manager Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children
 Janice Scott MS, RD, CSP, LD Clinical Nutrition Manager Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children Nutrition and Disability are intimately linked. Malnutrition can directly cause or contribute to disability
Janice Scott MS, RD, CSP, LD Clinical Nutrition Manager Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children Nutrition and Disability are intimately linked. Malnutrition can directly cause or contribute to disability
Case Report: Rapidly Healing Epidermolysis Bullosa Wound After Ablative Fractional Resurfacing
 Case Report: Rapidly Healing Epidermolysis Bullosa Wound After Ablative Fractional Resurfacing Andrew C. Krakowski, MD a,b, Pedram Ghasri, MD c Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) is a devastating
Case Report: Rapidly Healing Epidermolysis Bullosa Wound After Ablative Fractional Resurfacing Andrew C. Krakowski, MD a,b, Pedram Ghasri, MD c Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) is a devastating
Treating your leg ulcer
 Page 1 of 7 Treating your leg ulcer Introduction The information in this leaflet will answer many questions you may have about your leg ulcer. If you have any further questions about your condition or
Page 1 of 7 Treating your leg ulcer Introduction The information in this leaflet will answer many questions you may have about your leg ulcer. If you have any further questions about your condition or
Table Clinical Features Related to Level of Spinal Cord Injury. Level of Spinal Cord Damage. Associated Clinical Features. respiratory paralysis
 Table 17.1. Clinical Features Related to Level of Spinal Cord Injury Level of Spinal Cord Damage C1 to C4 C4 to C5 C5 to C6 C6 to C7 T11 to T12 T12 to L1 S3 to S5 Associated Clinical Features Death secondary
Table 17.1. Clinical Features Related to Level of Spinal Cord Injury Level of Spinal Cord Damage C1 to C4 C4 to C5 C5 to C6 C6 to C7 T11 to T12 T12 to L1 S3 to S5 Associated Clinical Features Death secondary
The recommended protocol is for all patients suffering from diabetes to have yearly foot checks. This was checking the foot pulses and doing
 Foot disease is a common long-term complication of diabetes. There are different types of foot disease caused by diabetes, but they all stem from a similar process. Raised blood sugar for a prolonged amount
Foot disease is a common long-term complication of diabetes. There are different types of foot disease caused by diabetes, but they all stem from a similar process. Raised blood sugar for a prolonged amount
Dr Saleem Taibjee. Consultant Dermatologist & Dermatopathologist
 Dr Saleem Taibjee saleem.taibjee@dchft.nhs.uk Consultant Dermatologist & Dermatopathologist Case S14-10797 and S15-4023 F50. Previous blistering, now marked milia on dorsum of hands. 4mm punch biopsy The
Dr Saleem Taibjee saleem.taibjee@dchft.nhs.uk Consultant Dermatologist & Dermatopathologist Case S14-10797 and S15-4023 F50. Previous blistering, now marked milia on dorsum of hands. 4mm punch biopsy The
Approximately 25% of people develop shingles during their lifetime, with the majority of cases occurring in those over 50 years of age.
 ÜNZÜLE ALPASLAN WHAT IS SHINGLES? Shingles is an infection of an individual nerve and the skin surface that is supplied by the nerve; it is caused by the varicella-zoster virus - the same virus that causes
ÜNZÜLE ALPASLAN WHAT IS SHINGLES? Shingles is an infection of an individual nerve and the skin surface that is supplied by the nerve; it is caused by the varicella-zoster virus - the same virus that causes
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Chapter 14 Outline. Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders. Dental Caries. Dental Caries. Prevention. Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders
 Chapter 14 Outline Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Dental caries Prevention Gingivitis Prevention Tooth hypersensitivity Pathophysiology Treatment 2 Hygiene-Related
Chapter 14 Outline Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Dental caries Prevention Gingivitis Prevention Tooth hypersensitivity Pathophysiology Treatment 2 Hygiene-Related
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. UNUSUAL OCCURRENCE OF EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. UNUSUAL OCCURRENCE OF EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
Health Benefits of Vitamin B5
 Health Benefits of Vitamin B5 Vitamin B5, or pantothenic acid, is involved in many different functions of the body. It helps convert food into energy and it also helps the body use proteins and fats. Vitamin
Health Benefits of Vitamin B5 Vitamin B5, or pantothenic acid, is involved in many different functions of the body. It helps convert food into energy and it also helps the body use proteins and fats. Vitamin
Papa Syndrome (Piogenic Arthritis, Pioderma, Gancrenosum and Acne)
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/ie/intro Papa Syndrome (Piogenic Arthritis, Pioderma, Gancrenosum and Acne) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PAPA 1.1 What is it? The acronym PAPA stands for Pyogenic
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/ie/intro Papa Syndrome (Piogenic Arthritis, Pioderma, Gancrenosum and Acne) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PAPA 1.1 What is it? The acronym PAPA stands for Pyogenic
A rare case of skin blistering and esophageal stenosis in the course of epidermolysis bullosa - case report and literature review
 Michalak et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:47 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0771-5 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of skin blistering and esophageal stenosis in the course of epidermolysis
Michalak et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:47 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0771-5 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of skin blistering and esophageal stenosis in the course of epidermolysis
DIFFERENT SCARS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT
 DIFFERENT SCARS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT Dr R. Newaj Specialist Dermatologist MBBCh (Wits) FCDerm (SA) Arwyp medical centre, Kemptonpark and Intercare Irene, Centurion COMMON CAUSES OF WOUNDS AND INJURIES
DIFFERENT SCARS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT Dr R. Newaj Specialist Dermatologist MBBCh (Wits) FCDerm (SA) Arwyp medical centre, Kemptonpark and Intercare Irene, Centurion COMMON CAUSES OF WOUNDS AND INJURIES
Kelly procedure. How does the urinary system work? What is a Kelly procedure and why does my child need one?
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Kelly procedure This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains the Kelly procedure used
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Kelly procedure This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains the Kelly procedure used
Etiology, Assessment and Treatment
 Etiology, Assessment and Treatment Andrew Tinsley MD, MS Associate Director of IBD Center Assistant Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Abbvie Janssen Nestle 1 To review the prevalence
Etiology, Assessment and Treatment Andrew Tinsley MD, MS Associate Director of IBD Center Assistant Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Abbvie Janssen Nestle 1 To review the prevalence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Nutrition support in adults: oral supplements, enteral and parenteral feeding.
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Nutrition support in adults: oral supplements, enteral and parenteral feeding. 1.1 Short title Nutrition support 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Nutrition support in adults: oral supplements, enteral and parenteral feeding. 1.1 Short title Nutrition support 2 Background a) The National
Novel and recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Chinese patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa
 Case Report Novel and recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Chinese patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa K.J. Zhu*, C.Y. Zhu*, Y. Zhou and Y.M. Fan Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital
Case Report Novel and recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Chinese patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa K.J. Zhu*, C.Y. Zhu*, Y. Zhou and Y.M. Fan Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital
Skin Integrity and Wound Care
 Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Syndactyly. What is syndactyly? Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: localised and generalised types
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: localised and generalised types This leaflet explains about the localised and generalised
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: localised and generalised types This leaflet explains about the localised and generalised
Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease
 Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease What Is a Lysosome? Millions of tiny units called cells make up the human body. Each cell has its own job to keep the body running. Within each cell, there are organelles,
Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease What Is a Lysosome? Millions of tiny units called cells make up the human body. Each cell has its own job to keep the body running. Within each cell, there are organelles,
Types of Wisdom Teeth Positions
 The Wise Guide to Wisdom Teeth Extraction H. Ryan Kazemi, DMD 11 Types of Wisdom Teeth Positions Erupted: The tooth has completely emerged through the gum tissue and is visible. This occurs when there
The Wise Guide to Wisdom Teeth Extraction H. Ryan Kazemi, DMD 11 Types of Wisdom Teeth Positions Erupted: The tooth has completely emerged through the gum tissue and is visible. This occurs when there
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
 Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment We all know that a healthy immune system is good. But, do you know that an overactive immune system can cause certain conditions like Psoriasis? Read on to find
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment We all know that a healthy immune system is good. But, do you know that an overactive immune system can cause certain conditions like Psoriasis? Read on to find
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cholangitis What is primary biliary cholangitis? Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease. When a person has PBC, the immune
Primary Biliary Cholangitis What is primary biliary cholangitis? Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease. When a person has PBC, the immune
IMPORTANT INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY TO THE BREAST AND/OR CHEST WALL AREA
 Breast Info 1 IMPORTANT INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY TO THE BREAST AND/OR CHEST WALL AREA Your doctors have recommended radiation treatments to the breast and/or
Breast Info 1 IMPORTANT INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY TO THE BREAST AND/OR CHEST WALL AREA Your doctors have recommended radiation treatments to the breast and/or
Eye Care for EB Patients Strategies to prevent blistering, scarring and vision loss
 Eye Care for EB Patients Strategies to prevent blistering, scarring and vision loss DEBRA Care Conference 7.23.18 Vicki M. Chen, MD Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology New England Eye Center Tufts Medical
Eye Care for EB Patients Strategies to prevent blistering, scarring and vision loss DEBRA Care Conference 7.23.18 Vicki M. Chen, MD Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology New England Eye Center Tufts Medical
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe
 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems; the
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems; the
Propolis is a nutrient-rich substance made by honey bees. It is a resinous substance gathered from deciduous tree bark and leaves.
 Propolis is a nutrient-rich substance made by honey bees. It is a resinous substance gathered from deciduous tree bark and leaves. Used as a healing agent for many centuries it has the ability to provide
Propolis is a nutrient-rich substance made by honey bees. It is a resinous substance gathered from deciduous tree bark and leaves. Used as a healing agent for many centuries it has the ability to provide
CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION
 GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC
 COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC 1 NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC BURNS PATIENTS Aims of Nutritional Support in Burns To promote optimal wound healing To maintain lean body mass To
COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC 1 NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC BURNS PATIENTS Aims of Nutritional Support in Burns To promote optimal wound healing To maintain lean body mass To
Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD), or Hyper IGD Syndrome
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD), or Hyper IGD Syndrome Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS MKD 1.1 What is it? Mevalonate kinase deficiency is a genetic disease.
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD), or Hyper IGD Syndrome Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS MKD 1.1 What is it? Mevalonate kinase deficiency is a genetic disease.
1.0 Presenting complaint: Onset 1.1 When it started? 1.2 How did it start? Progress 1.3 Has the problem increased /decreased so far?
 Case history Sr. No. Name Sex M / F Age Marital Status B / S / M / W Occupation Date 1.0 Presenting complaint: Onset 1.1 When it started? 1.2 How did it start? Progress 1.3 Has the problem increased /decreased
Case history Sr. No. Name Sex M / F Age Marital Status B / S / M / W Occupation Date 1.0 Presenting complaint: Onset 1.1 When it started? 1.2 How did it start? Progress 1.3 Has the problem increased /decreased
Information on CTD (Carnitine Transporter Deficiency)
 Information on CTD (Carnitine Transporter Deficiency) This fact sheet provides information for individuals with CTD, their family and friends, and other interested groups. We hope that this fact sheet
Information on CTD (Carnitine Transporter Deficiency) This fact sheet provides information for individuals with CTD, their family and friends, and other interested groups. We hope that this fact sheet
Unit 2: Animals on the land
 GCSE Animal Nutrition Unit 2: Animals on the land For first teaching from September 2013 For first award in Summer 2015 Animal Nutrition Learning Outcomes At the end of this unit students should be able
GCSE Animal Nutrition Unit 2: Animals on the land For first teaching from September 2013 For first award in Summer 2015 Animal Nutrition Learning Outcomes At the end of this unit students should be able
Having a PEG tube inserted
 Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Unit title: Human Health and Nutrition
 Unit title: Human Health and Nutrition Unit code: F/601/0234 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit provides an understanding of the fundamental role of nutrients in maintaining health in relation
Unit title: Human Health and Nutrition Unit code: F/601/0234 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit provides an understanding of the fundamental role of nutrients in maintaining health in relation
Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/za_gb/intro Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PFAPA 1.1 What is it? PFAPA stands for Periodic Fever Adenitis Pharyngitis
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/za_gb/intro Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PFAPA 1.1 What is it? PFAPA stands for Periodic Fever Adenitis Pharyngitis
Lamellar ichthyosis What Is ichthyosis? Classification of Lamellar Ichthyosis What is Lamellar Ichthyosis? What are the signs?
 Lamellar ichthyosis What Is ichthyosis? Ichthyosis describes dry, thickened, scaly or flaky skin. There are at least 28 different ichthyosis subtypes, which are mainly inherited (have a genetic cause).
Lamellar ichthyosis What Is ichthyosis? Ichthyosis describes dry, thickened, scaly or flaky skin. There are at least 28 different ichthyosis subtypes, which are mainly inherited (have a genetic cause).
B1 Question 1 Foundation
 B1 Question 1 Foundation The nucleus controls the activities of a cell. The instructions for how an organism develops i.e. the genes are found in the nuclei of its cells B1 Question 2 Foundation The genes
B1 Question 1 Foundation The nucleus controls the activities of a cell. The instructions for how an organism develops i.e. the genes are found in the nuclei of its cells B1 Question 2 Foundation The genes
