Pediatric Radiology Update
|
|
|
- Margaret Bradley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pediatric Radiology Update Douglas Rivard, DO Vice Chairman, Radiology Dept Children s Mercy Hospital Asst Professor of Radiology University of Missouri-Kansas City
2 Objectives Review radiation biology and safety practices for pediatric imaging Discuss imaging workup of a few common presenting pediatric problems
3 Why Should We Care? Children are more sensitive to radiation than adults Children have a longer lifespan in which to manifest radiation induced injury Each exam involving ionizing radiation increases risk
4 In 2006, Americans were exposed to 7X as much ionizing radiation exposure from medical procedures than in the early 1980 s. The increase is due mostly to higher utilization of computed tomography (CT) and nuclear medicine PET/CT imaging
5 Startling Facts CT procedures have increased from 3 million procedures to 60 million procedures in only 25 years Atomic bomb survivors show statistically significant increase in cancer at doses in excess of 50 msv CT and NM PET procedures have effective dose rages of msv
6 Larson D B et al. Radiology 2011;258:
7 Typical Radiation Doses (msv) Natural background radiation 3.5 Doug Rivard, DO (2010) 4 Dental x-rays 0.09 Chest x-ray 0.01 Barium enema 8.75 CT chest/abd/pelvis 15 PET/CT 23.3
8 Equivalent Radiation Exposures Effective Dose Compared to Natural Background (3 msv/yr) Chest X-Ray 0.1 msv 10 days Mammogram 0.7 msv 3 months CT Head 2 msv 8 months CT Chest 8 msv 2 2/3 years CT Chest/Abd/Pel v 15 msv 5 years PET/CT 23 msv 7+ years
9 What do all those numbers mean? The real question from both health care professionals and patients is what do these numbers mean or what effect will they have on a health and well-being of the child. Risk vs. Benefit
10 Fatal Cancer Risk Estimated Debated May be zero May be, in children, 1 in risk from a single CT scan (your risk of getting some form of cancer is 230/1000 without any radiation) Remember, the dose you give today lasts a lifetime!
11 What Should You Be Doing? Does the facility you refer to have pediatric imaging protocols? Does your facility annually review their pediatric CT protocols? Accredited techs, board certified radiologists, ACR accredited facility?
12 Dose Reduction Strategies Reduction of technical parameters to minimum that allow for diagnostic images (kvp, mas) Iterative reconstruction techniques Image filtering/post processing software
13 How different are CT protocols? Unpublished data from CMH vs outside head CTs % lower dose at Children s Mercy Hospital compared to outside head CTs
14 Dose Reduction Strategies Image only body part needed Try to use US, MRI when possible No multiphase scanning (arterial, venous, delayed CT)
15
16 Vomiting/ Regurgitation in young children Most common cause of vomiting and regurgitation in infants is gastroesophageal reflux. These patients typically maintain normal weight and developmental milestones.
17 Natural history of infant regurgitation 47% of 1 month old infants had 1 or more daily episodes of vomiting/regurgitation, decreased to 29% at 4 mos, and 6% at 7 mos. Miyazawa et al, International Pediatrics, Spilling of feeds reached peak prevalence of 41% between 3 and 4 mos and decreased to less than 5% by 13 mos. Martin et al, Pediatrics, 2002.
18 Reflux in esophagus Stomach Upper GI study
19 Vomiting/ Regurgitation in young children Most patients do NOT require imaging with an upper GI exam as this study defines anatomy, and reflux may or may not be seen. In cases of persistent or severe regurgitation, ph probe monitoring may be helpful. Imaging should be considered if there are airway symptoms or bloody or bilious emesis.
20 ph probe in esophagus
21
22 Newborn Bilious Emesis Bilious emesis in a newborn is an emergency which should be promptly evaluated with an upper GI examination to exclude malrotation and volvulus. (SBFT is NOT required to diagnose) Patients should have an NG or OG tube placed to confirm the presence of bilious material as well as facilitating the UGI exam.
23 Upper GI study Left pedicle line Duodenojejunal junction
24 Upper GI study Volvulus
25 Normal duodenojejunal junction (ligament of Treitz)
26 Pyloric Stenosis Common cause of early infantile intestinal obstruction. Also known as Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (HPS). Multifactorial causes suggested including: Hereditary Exposure to macrolide antibiotics (erythromycin) Abnormal myenteric plexus innervation Infantile hypergastrinemia
27 Pyloric Stenosis 2-4 cases/ 1000 live births in U.S., male:female ratio 4:1 95% diagnosed between 3 and 12 weeks of age. Nonbilious emesis which becomes projectile. May have a palpable olive on exam.
28 Pyloric Stenosis A limited abdominal ultrasound is the diagnostic study of choice. Highly sensitive and specific No radiation No sedation
29 Pyloric Ultrasound Elongated pyloric channel Thickened pyloric muscular wall
30 Pyloric Stenosis
31 Intussusception Most common cause of intestinal obstruction in children aged 3 to 36 mos., 60% < 1 y.o., 80% < 2 y.o. Majority are idiopathic. Seasonal patterns associated with gastroenteritis, possibly due to hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue in the terminal ileum. Increased incidence after some forms of rotavirus vaccine.
32 Intussusception Pathologic lead point in some cases: Meckel s diverticulum Enteric duplication cyst Lymphoma Polyps Henoch-Schonlein purpura (intramural hemorrhage)
33 Intussusception Present with sudden onset of crampy, intermittent abdominal pain with drawing-up of legs and inconsolable crying. May develop vomiting and currant-jelly stools. Diagnostic work-up includes abdominal radiographs and ultrasound. Treated with air enema reduction.
34 Supine abdomen X-ray Left decubitus X-ray
35 Abdominal Ultrasound Ileocolic intussusception
36 Air enema reduction
37 Intussusception Contraindications to enema reduction: Pneumoperitoneum Clinical peritonitis or unstable patient Surgery required for incomplete reduction, free air, multiple recurrent episodes (possible lead point). Incidental small bowel-small bowel intussusception which may be seen on US or CT is typically transient and asymptomatic.
38 Additional causes of obstruction Older infants and children: Appendicitis Adhesions Incarcerated hernia Meckel s diverticulum
39 Shadowing stone in dilated appendix Appendix Ultrasound
40 Stone within an inflamed appendix Appendicitis CT
41 Inguinal hernia noted on physical exam; Gas-filled bowel loops seen on X-Ray performed for vomiting.
42 Abnormal fluid filled structure on Pelvis CT
43 Nuclear Medicine Meckel s Scan (Tc99m-Pertechnetate) Meckel s diverticulum
44 Summary Most vomiting/ regurgitation in infants is due to reflux and does not require imaging.
45 Summary Most vomiting/ regurgitation in infants is due to reflux and does not require imaging. Bilious emesis is an emergency which should be evaluated by an upper GI study.
46 Summary Most vomiting/ regurgitation in infants is due to reflux and does not require imaging. Bilious emesis is an emergency which should be evaluated by an upper GI study. Ultrasound is an important tool in the diagnosis of pyloric stenosis and intussusception.
47 Summary Most vomiting/ regurgitation in infants is due to reflux and does not require imaging. Bilious emesis is an emergency which should be evaluated by an upper GI study. Ultrasound is an important tool in the diagnosis of pyloric stenosis and intussusception. When in doubt about the imaging work-up, consult your radiology colleagues
48 Misshapen Head Craniosynostosis Macrocephaly
49 Craniosynostosis Definition: Premature fusion of cranial sutures Synonyms: Craniostenosis, sutural synostosis, cranial dysostosis M:F = 3:1
50 Craniosynostosis Imaging Imaging is based on 3 categories: 1. Low risk- Developmentally normal or posterior flattening only Plain films (4 view skull) 2. Intermediate risk - Healthy children with head deformity CT head 3. High risk - Obviously misshapen head 3D CT needed for surgical planning
51 Craniosynostosis Incidence: 3-5 cases per 10,000 live births Sagittal 56% (1/3600) Scaphocephaly
52 Craniosynostosis Incidence: 3-5 cases per 10,000 live births Sagittal 56% (1/3600) Scaphocephaly Coronal 26% (1/7700) Brachycephaly
53 Craniosynostosis Incidence: 3-5 cases per 10,000 live births Sagittal 56% (1/3600) Scaphocephaly Coronal 26% (1/7700) Brachycephaly Metopic 8% (1/25,000) Trigonocephaly
54 Craniosynostosis: Low Risk History: Developmentally normal child with posterior flattening Coronal Sagittal Lambdoid Lambdoid Diagnosis: Normal sutures
55 Craniosynostosis: Intermediate Risk History: Developmentally delayed child with parieto-occipital flattening Diagnosis: Plagiocephaly (parieto-occipital flattening, but no craniosynostosis
56 Craniosynostosis: High Risk History: Child with obvious abnormally shaped head Diagnosis: Sagittal synostosis Diagnosis: Lambdoid synostosis
57 Craniosynostosis Risk Category Low risk developmentally normal and posterior or posterolateral flattening only Intermediate risk children who don t clearly fit into the low or high risk group High risk developmentally abnormal and/or obvious head deformity almost certainly needing surgery Imaging No imaging, or 4-view skull (plain films) Low-dose head CT Standard head CT with 3D reformations This approach to imaging craniosynostosis and posterior plagiocephaly reduces both unnecessary imaging and radiation exposure
58
59 Imaging macrocephaly Definition: Head greater than 95% If the head circumference levels out no imaging If the head growth rate continues to increase or developmental abnormality, do imaging Imaging approach: US is used if the child is less than 6 months or if they still have an open fontanelle CT is used if the child is greater than 6 months and no fontanelle MRI if associated neurological symptoms
60 Macrocephaly: developmentally normal child with open fontanelle History: Normal subarachnoid space contains vessels Diagnosis: Benign enlarged subarachnoid spaces
61 Benign enlarged subarachnoid spaces (BESS) Usually presents between 3 months and 3 years of age (esp. 6-18mo) Most common cause of macrocephaly in a developmentally normal child Parents often have big head Resolves spontaneously
62 Macrocephaly in a neurologically abnormal child 4-month-male with macrocephaly and lethargy Diagnosis: Choroid plexus papilloma
63 Imaging macrocephaly Clinical presentation and age Developmentally normal infant/child with open fontanelle Developmentally normal infant/child with closed fontanelle Developmentally abnormal infant/child with open or closed fontanelle Imaging approach Head ultrasound CT or MRI MRI
64
65 Imaging Torticollis: Based on Infant with torticollis: age and history Most often due to fibromatosis coli (hematoma of sternocleidomastoid muscle) More common in forceps delivery Sonography is diagnostic Rx: Physical therapy or surgical release Beyond young infants the work up depends on history
66 Torticollis: Beyond infants History of isolated torticollis (no trauma) Usually rotatory subluxation (self-limiting, due to muscle spasm) No imaging needed unless persistent after a week or 2 of conservative treatment Isolated, persistent do CT then consider dynamic scan with head in neutral, right, and left positions History of trauma Plain films or CT without contrast History of sore throat/signs of infection CT with contrast History of torticollis with neurological signs MRI
67 Infantile Torticollis Hx: 6-week-male with torticollis and forceps delivery Normal right sternocleidomastoid muscle(scm) Diagnosis: Fibromatosis coli Hematoma left SCM
68 Isolated Torticollis in a child History: 10-year-male awakened with neck stuck to left 1.5weeks ago; No response to conservative treatment Coronal image demonstrates asymmetry between C1 and C2 Notice abnormal widening between C1 and dens widens with head turning to the left (toward torticollis) C1 C2 C1 Notice normalization of distance between C1 and dens with head turning to the right (away from torticollis)
69 Isolated persistent torticollis: Diagnosis: Rotatory Fixation Abnormal alignment with head turning right C1 C2 Note C1 is looking a different direction than C2-C7
70 Torticollis with fever Axial CT neck demonstrates fluid pockets both on the right and at midline History: 1- year-female with sore throat and difficulty swallowing Lateral view of the neck demonstrates prevertebral swelling of soft tissues Diagnosis: Peritonsillar and retropharyngeal infection
71 Torticollis with neurological symptoms History: 1- yr-female with persistent torticollis & scratching of the left arm Diagnosis: Spinal cord astrocytoma
72 Imaging torticollis based on history Clinical history and age < 3 months; asymptomatic except for torticollis > 3 months; asymptomatic except for torticollis Any age with history of trauma Any age with symptoms of infection Any age with neurological symptoms Initial imaging approach Ultrasound No imaging; conservative Rx 1-2 weeks; Persistent symptoms CT without contrast CT without contrast CT with IV contrast MRI
73
74 Summary Radiation is associated with increased lifetime risk of cancer Children are much more sensitive to radiation than adults Imaging strategies should take these into consideration
75 Summary When in doubt what the best test to order is CONSULT A RADIOLOGIST!!
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success
 Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently
 Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound. Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound
 Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING
 GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
Good morning! July 24, 2014
 Good morning! July 24, 2014 Prep #1 A 2-year-old boy presents to your office with a 2-day history of swelling of the right eye. He has been otherwise well. There are scattered insect bites on his body,
Good morning! July 24, 2014 Prep #1 A 2-year-old boy presents to your office with a 2-day history of swelling of the right eye. He has been otherwise well. There are scattered insect bites on his body,
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases. Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT)
 Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR
 Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Emory University Financial disclosures: AIM (American Imaging Management) radiation protection advisory
Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Emory University Financial disclosures: AIM (American Imaging Management) radiation protection advisory
ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN. Carlos J. Sivit M.D.
 ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN Carlos J. Sivit M.D. ACUTE ABDOMEN Clinical condition characterized by severe abdominal pain developing over several hours ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN Common childhood complaint
ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN Carlos J. Sivit M.D. ACUTE ABDOMEN Clinical condition characterized by severe abdominal pain developing over several hours ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN Common childhood complaint
Pediatric Bowel Obstruction
 Pediatric Bowel Obstruction Matt Zerden, Harvard Medical School III Patient 1 16 year old presents with severe, episodic abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Questionable abdominal mass in RLQ Previous
Pediatric Bowel Obstruction Matt Zerden, Harvard Medical School III Patient 1 16 year old presents with severe, episodic abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Questionable abdominal mass in RLQ Previous
Craniosynostosis. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Craniosynostosis Diagnosis and Treatment 2015 For more information about the Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program ABOUT The Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program takes a multidisciplinary approach to treating
Craniosynostosis Diagnosis and Treatment 2015 For more information about the Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program ABOUT The Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program takes a multidisciplinary approach to treating
Pediatric abdominal emergencies In the first year of life
 Common Pediatric abdominal emergencies In the first year of life Kristian Stien Thomassen Section of Pediatric Radiology Dept. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Understand the
Common Pediatric abdominal emergencies In the first year of life Kristian Stien Thomassen Section of Pediatric Radiology Dept. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Understand the
Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly
 Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly Andrew Jea MD MHA FAAP Professor and Chief Section of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Department of Neurosurgery Indiana University School of Medicine
Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly Andrew Jea MD MHA FAAP Professor and Chief Section of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Department of Neurosurgery Indiana University School of Medicine
Disclosure of Commercial Interest
 Evidence Based Imaging: Getting the Right Study for Your Patient Johanne E. Dillon, MD, FAAP Pediatric Radiology UK HealthCare Assistant Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Kentucky College
Evidence Based Imaging: Getting the Right Study for Your Patient Johanne E. Dillon, MD, FAAP Pediatric Radiology UK HealthCare Assistant Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Kentucky College
Paediatric surgical emergencies. Mani Thyagarajan BWCH
 Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts. David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology
 Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
6/23/2017. What do you see? skull fracture
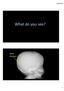 What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
Objectives. Pediatric Mortality. Another belly pain. Gastroenteritis. Spewing & Pooing Child 4/18/16
 Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Prevention Diagnosis
 Prevention and Management of Positional Skull Deformities in Infants John Persing, MD, Hector James, MD, Jack Swanson, MD, John Kattwinkel, MD, Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on
Prevention and Management of Positional Skull Deformities in Infants John Persing, MD, Hector James, MD, Jack Swanson, MD, John Kattwinkel, MD, Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS
 DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment
 1 I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment II. Author Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Indiana University Department of Radiology Riley Hospital for Children 702 Barnhill Rd., Rm 1053b
1 I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment II. Author Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Indiana University Department of Radiology Riley Hospital for Children 702 Barnhill Rd., Rm 1053b
Topics for discussion. Pediatric General Surgery. Physiology. Surgical Newborns. Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction
 Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
 A Sonographic walk-through: Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Tara K. Cielma, RDMS, RDCS, RVT, RT(S) Anjum N. Bandarkar, MD, Adebunmi O. Adeyiga, MD, Diagnostic Imaging and Radiology, Children s
A Sonographic walk-through: Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Tara K. Cielma, RDMS, RDCS, RVT, RT(S) Anjum N. Bandarkar, MD, Adebunmi O. Adeyiga, MD, Diagnostic Imaging and Radiology, Children s
Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C
 Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C Texas Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric General Surgery Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Objectives 1. Define Pediatric Surgical
Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C Texas Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric General Surgery Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Objectives 1. Define Pediatric Surgical
Overview. Imaging Indications. Paediatric Radiation Safety 2015/03/12. Paediatric radiation safety General guidelines Protocols
 Overview Paediatric radiation safety General guidelines Protocols Paediatric Radiation Safety Paediatric patients are unique Children are more susceptible to radiation induced cancer than adults Younger
Overview Paediatric radiation safety General guidelines Protocols Paediatric Radiation Safety Paediatric patients are unique Children are more susceptible to radiation induced cancer than adults Younger
3/30/18. Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery. Disclosure Information. Objectives
 Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery A Scenario Based Approach to Interpretation for the Pediatric Nurse and Provider presented by Elizabeth A. Paton, DNP, RN-BC, PNP-A, PPCNP-BC, CPEN, FAEN Disclosure
Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery A Scenario Based Approach to Interpretation for the Pediatric Nurse and Provider presented by Elizabeth A. Paton, DNP, RN-BC, PNP-A, PPCNP-BC, CPEN, FAEN Disclosure
created by high-voltage devices Examples include medical and dental x-rays, light, microwaves and nuclear energy
 What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
In children 3 months to 3 years of age intussusception is
 Baird Mallory, MD, 1 and Yale Popowich, MD 2 In children 3 months to 3 years of age intussusception is one of the most common causes of a distal small bowel obstruction. It is often associated with intermittent
Baird Mallory, MD, 1 and Yale Popowich, MD 2 In children 3 months to 3 years of age intussusception is one of the most common causes of a distal small bowel obstruction. It is often associated with intermittent
Objectives: Resources:
 Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy?
 January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL. (615)
 RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL www.vanderbiltchildrens.com RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL EXAM PROTOCOL QUESTIONS? Please call: DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY (X-RAY) Pager (615) 835-1714 CT (615) 936-4920 MRI (615) 936-4933
RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL www.vanderbiltchildrens.com RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL EXAM PROTOCOL QUESTIONS? Please call: DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY (X-RAY) Pager (615) 835-1714 CT (615) 936-4920 MRI (615) 936-4933
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Chapter Outline. Structural defects. Obstructive disorders. Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 98. Cleft lip and cleft palate
 Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Interpret clinical and laboratory tests to identify conditions that require surgical intervention, including:
 Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
PEDIATRIC GI EMERGENCIES. AGE-RELATED DIAGNOSIS Early Infancy EXAMINATION TIPS PEDIATRIC ABDOMINAL PAIN. How Common Is It?
 PEDIATRIC ABDOMINAL PAIN How Common Is It? PEDIATRIC GI EMERGENCIES Ghazala Q. Sharieff, MD 5% of unscheduled visits 2% of patients are admitted 1% need operative intervention EXAMINATION TIPS Palpate
PEDIATRIC ABDOMINAL PAIN How Common Is It? PEDIATRIC GI EMERGENCIES Ghazala Q. Sharieff, MD 5% of unscheduled visits 2% of patients are admitted 1% need operative intervention EXAMINATION TIPS Palpate
VOMITING. Tan Lay Zye
 VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception
 Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
Research Article Human Anatomy Case Report Bathrocephaly: a case report of a head shape associated with a persistent mendosal suture
 IJAE Vol. 119, n. 3: 263-267, 2014 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research Article Human Anatomy Case Report Bathrocephaly: a case report of a head shape associated with a persistent mendosal
IJAE Vol. 119, n. 3: 263-267, 2014 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research Article Human Anatomy Case Report Bathrocephaly: a case report of a head shape associated with a persistent mendosal
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Pediatrics Donald L. Renfrew, MD
 This free educational material is provided by 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 Donald L. Renfrew, MD This chapter briefly reviews pediatric imaging. Because of the nature of the diseases
This free educational material is provided by 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 Donald L. Renfrew, MD This chapter briefly reviews pediatric imaging. Because of the nature of the diseases
Sonographic Appearances of Common Gut Pathology in Paediatric Patients: Comparison with Plain Abdominal Radiography
 3668 Radiographer Text 1/4/04 2:57 PM Page 11 The Radiographer vol. 51: 11-17 Sonographic Appearances of Common Gut Pathology in Paediatric Patients: Comparison with Plain Abdominal Radiography Lino Piotto
3668 Radiographer Text 1/4/04 2:57 PM Page 11 The Radiographer vol. 51: 11-17 Sonographic Appearances of Common Gut Pathology in Paediatric Patients: Comparison with Plain Abdominal Radiography Lino Piotto
Effective Utilization of Imaging. John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging
 Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST
 CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST IDENTIFICATION DATA ผ ป วยเด กชายไทย อาย 13 ว น เช อชาต ไทย ส ญชาต ไทย ภ ม ล าเนา จ งหว ด อ ท ยธาน เข าร บการร กษาท รพ.มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวรว
CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST IDENTIFICATION DATA ผ ป วยเด กชายไทย อาย 13 ว น เช อชาต ไทย ส ญชาต ไทย ภ ม ล าเนา จ งหว ด อ ท ยธาน เข าร บการร กษาท รพ.มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวรว
Hernia. emoryhealthcare.org
 Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Document Title: Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain/Abdominal Emergencies. Author(s): Joseph House (University of Michigan), MD 2012
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain/Abdominal Emergencies Author(s): Joseph House (University of Michigan), MD 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted,
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain/Abdominal Emergencies Author(s): Joseph House (University of Michigan), MD 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted,
Pediatric Surgery MUHC MCH Siste. Objectives of Training
 Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
of Trauma Assembly 27 th Page 1
 Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS
 JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus
 A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Pediatric Imaging Studies: Congenital and Acquired Diagnoses
 Pediatric Imaging Studies: Congenital and Acquired Diagnoses Robin Foster MD FAAP FACEP Division Chief Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at Virginia Commonwealth University Health
Pediatric Imaging Studies: Congenital and Acquired Diagnoses Robin Foster MD FAAP FACEP Division Chief Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at Virginia Commonwealth University Health
Radiology of GI system diseases
 GI Cycle - Lecture 12 436 Teams Radiology of GI system diseases Objectives 1. 2. 3. To know common GIT Pathologies presentation. To understand step wise approach in requesting GIT Radiology Investigations.
GI Cycle - Lecture 12 436 Teams Radiology of GI system diseases Objectives 1. 2. 3. To know common GIT Pathologies presentation. To understand step wise approach in requesting GIT Radiology Investigations.
Arteriogram An X-ray of an artery after the injection of dye.
 A Abscess A localized collection of pus in any part of the body, usually surrounded by inflamed tissue. Anesthetic An agent that causes loss of sensation with or without the loss of consciousness. Angiography,
A Abscess A localized collection of pus in any part of the body, usually surrounded by inflamed tissue. Anesthetic An agent that causes loss of sensation with or without the loss of consciousness. Angiography,
Pediatric radiology. Varga Edit. Semmelweis University MR Research Center Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pediatrics
 Pediatric radiology Varga Edit Semmelweis University MR Research Center Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pediatrics Modalities radiograpy (x-ray, fluoroscopy) ultrasound computer tomography (CT)
Pediatric radiology Varga Edit Semmelweis University MR Research Center Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pediatrics Modalities radiograpy (x-ray, fluoroscopy) ultrasound computer tomography (CT)
Neurosurgery. Neurosurgery
 Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Telephone Numbers: Appointment: 202-476-3020 Fax: 202-476-3091 Administration: 202-476-3020 Evenings and Weekends: 202-476-5000 Robert Keating, MD, Chief The Division
Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Telephone Numbers: Appointment: 202-476-3020 Fax: 202-476-3091 Administration: 202-476-3020 Evenings and Weekends: 202-476-5000 Robert Keating, MD, Chief The Division
X-ray Corner. Imaging of the Small Bowel. Pantongrag-Brown L. Case 1. A 63-year-old man presented with abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
 THAI J 42 Imaging of the Small Bowel GASTROENTEROL 2015 X-ray Corner Imaging of the Small Bowel Pantongrag-Brown L Small bowel is the longest tubular organ in the body, about 18-22 feet. It is anchored
THAI J 42 Imaging of the Small Bowel GASTROENTEROL 2015 X-ray Corner Imaging of the Small Bowel Pantongrag-Brown L Small bowel is the longest tubular organ in the body, about 18-22 feet. It is anchored
 Page 1 of 5 Patient Safety: Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate the
Page 1 of 5 Patient Safety: Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate the
George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon
 George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon Health and Sciences University. Portland, OR Nothing
George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon Health and Sciences University. Portland, OR Nothing
Dr Prashant Jain. Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital
 Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
ACUTE ABDOMEN. Dr. M Asadi. Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS. Assistant Professor of General Surgery
 ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
Estimating Risks from CT Scans - in the Context of CT Scan Benefits
 Estimating Risks from CT Scans - in the Context of CT Scan Benefits David J. Brenner Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@cumc.columbia.edu There is no question that
Estimating Risks from CT Scans - in the Context of CT Scan Benefits David J. Brenner Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@cumc.columbia.edu There is no question that
n Make tremendous difference in patients lives: n Diagnosing or excluding disease and injury n Evaluating response to therapy
 Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
The Children s Hospital Intussusception and its treatment Information for parents
 The Children s Hospital Intussusception and its treatment Information for parents What is intussusception? Intussusception occurs when one part of the bowel slides into another part of bowel, like a telescope,
The Children s Hospital Intussusception and its treatment Information for parents What is intussusception? Intussusception occurs when one part of the bowel slides into another part of bowel, like a telescope,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
GI Grand Rounds. A A Lifetime of Abdominal Pain 12/9/2004 Tim Edwards
 GI Grand Rounds A A Lifetime of Abdominal Pain 12/9/2004 Tim Edwards PMH Aug 25, 1992 4 year old male presents to a pediatric gastroenterologist for primary complaint of anorexia, intermittent abdominal
GI Grand Rounds A A Lifetime of Abdominal Pain 12/9/2004 Tim Edwards PMH Aug 25, 1992 4 year old male presents to a pediatric gastroenterologist for primary complaint of anorexia, intermittent abdominal
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1-
 Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiation Dose in Pediatric Imaging
 Radiation Dose in Pediatric Imaging A Brief History of Radiology Dose: Why Does It Matter? Measuring Exposure and Dose Deterministic Effects Stochastic Effects Common Exams: What is the Risk? Reducing
Radiation Dose in Pediatric Imaging A Brief History of Radiology Dose: Why Does It Matter? Measuring Exposure and Dose Deterministic Effects Stochastic Effects Common Exams: What is the Risk? Reducing
GI POTPOURRI. What is the best diagnostic test? Presentation #1: Vomiting. I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures GI POTPOURRI Andi Marmor, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics UCSF, San Francisco General Hospital Presentation #1: Vomiting Caraway, a 3 week old boy, is brought to your walk-in clinic
I have no disclosures GI POTPOURRI Andi Marmor, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics UCSF, San Francisco General Hospital Presentation #1: Vomiting Caraway, a 3 week old boy, is brought to your walk-in clinic
Imaging for Pediatric Trauma and the Acute Patient What to Order When
 Imaging for Pediatric Trauma and the Acute Patient What to Order When Paula Shultz, MD Pediatric Radiologist Central Oregon Radiology Associates November 8, 2013 5 yr old male involved in multicar accident,
Imaging for Pediatric Trauma and the Acute Patient What to Order When Paula Shultz, MD Pediatric Radiologist Central Oregon Radiology Associates November 8, 2013 5 yr old male involved in multicar accident,
A Perf-ect Differential
 A Perf-ect Differential Carolyn Marcus, MD Disclosure of Financial Relationships Husband works as in-house legal counsel at Sanofi Case Presentation 6 year old boy with a history of constipation presents
A Perf-ect Differential Carolyn Marcus, MD Disclosure of Financial Relationships Husband works as in-house legal counsel at Sanofi Case Presentation 6 year old boy with a history of constipation presents
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC
 Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
Case Report Intestinal Malrotation: A Rare Cause of Small Intestinal Obstruction
 Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 453128, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/453128 Case Report Intestinal Malrotation: A Rare Cause of Small Intestinal Obstruction Mesut Sipahi, 1 Kasim Caglayan,
Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 453128, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/453128 Case Report Intestinal Malrotation: A Rare Cause of Small Intestinal Obstruction Mesut Sipahi, 1 Kasim Caglayan,
The Gastrointestinal Tract
 CHAPTER 10 The Gastrointestinal Tract INTRODUCTION Although sonography may not always be the modality of choice for the detection of all gastrointestinal abnormalities, it does provide a noninvasive, nonionizing
CHAPTER 10 The Gastrointestinal Tract INTRODUCTION Although sonography may not always be the modality of choice for the detection of all gastrointestinal abnormalities, it does provide a noninvasive, nonionizing
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of ongoing back pain, six weeks of conservative
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of ongoing back pain, six weeks of conservative
Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice?
 Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice? JILL MILLER, MD PEM ATTENDING CHKD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PEDIATRICS, EVMS Objectives Review the literature to answer
Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice? JILL MILLER, MD PEM ATTENDING CHKD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PEDIATRICS, EVMS Objectives Review the literature to answer
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
Cancer Risks from CT Scans: Now We Have Data What Next?
 Cancer Risks from CT Scans: Now We Have Data What Next? David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@columbia.edu There is no question that CT has
Cancer Risks from CT Scans: Now We Have Data What Next? David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@columbia.edu There is no question that CT has
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of
Ultrasound of: Appendicitis Intussusception Pyloric Stenosis
 Ultrasound of: Appendicitis Intussusception Pyloric Stenosis Andrew Phelps MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Radiology UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital No Disclosures Take Home Message Appendicitis occurs
Ultrasound of: Appendicitis Intussusception Pyloric Stenosis Andrew Phelps MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Radiology UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital No Disclosures Take Home Message Appendicitis occurs
Advances in Emergency Imaging
 Hampton Symposium,, October 16 th, 2010 Advances in Emergency Imaging Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital
Hampton Symposium,, October 16 th, 2010 Advances in Emergency Imaging Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital
Management of Common Paediatric Surgical G.I. Problems
 Management of Common Paediatric Surgical G.I. Problems Dr. Loh Ser Kheng Dale Lincoln Senior Consultant Department of Paediatric Surgery National University Hospital National University Health System Tongue
Management of Common Paediatric Surgical G.I. Problems Dr. Loh Ser Kheng Dale Lincoln Senior Consultant Department of Paediatric Surgery National University Hospital National University Health System Tongue
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Steven Aaron Ross, M.D. Pediatric Radiologist El Paso Imaging Consultants El Paso Children s Hospital
 Steven Aaron Ross, M.D. Pediatric Radiologist El Paso Imaging Consultants El Paso Children s Hospital I will prescribe regimens for the good of my patients according to my ability and my judgment and never
Steven Aaron Ross, M.D. Pediatric Radiologist El Paso Imaging Consultants El Paso Children s Hospital I will prescribe regimens for the good of my patients according to my ability and my judgment and never
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526)
 RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Triangle Edition October 2009 VOL. 11, NO. 10. Wake Radiology Expands Pediatric Imaging
 Triangle Edition October 2009 VOL. 11, NO. 10 Wake Radiology Expands Pediatric Imaging cover story Wake Radiology Expands Pediatric Imaging Practice Dedicated s Staff New Stand alone Outpatient Office
Triangle Edition October 2009 VOL. 11, NO. 10 Wake Radiology Expands Pediatric Imaging cover story Wake Radiology Expands Pediatric Imaging Practice Dedicated s Staff New Stand alone Outpatient Office
Gastro- Intestinal Bleeding in Children
 Gastro- Intestinal Bleeding in Children Upper G1 Bleeding. Lower G1 Bleeding. Upper G1 Bleeding :- Presentation : Hematemesis Causes :- Neonate reflux esophagitis (dark, small amount) PyLoric stenosis
Gastro- Intestinal Bleeding in Children Upper G1 Bleeding. Lower G1 Bleeding. Upper G1 Bleeding :- Presentation : Hematemesis Causes :- Neonate reflux esophagitis (dark, small amount) PyLoric stenosis
