9 month old with stridor, cough, low-grade fever, mild hypoxia
|
|
|
- Doreen Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9 month old with stridor, cough, low-grade fever, mild hypoxia
2
3 3 months of age CXR normal
4 Scenarios: Pregnant woman with + PPD Next steps? CXR negative, asymptomatic: treat for LTBI after delivery (INH x 9 mos). May wish to confirm with T-Spot (IGRA)
5 Tuberculosis Stephen J Swanson, MD HCMC Dept of Pediatrics 2013
6 6 year returning traveler with mild cough (Ethiopia x 3 mos)
7 6 year returning traveler with mild cough PPD+ 18mm
8 MYCOBACTERIOLOGY Non-motile, nonspore-forming, weakly Gram-positive rods; often appear bent or beaded Obligate aerobes MTB vs NTM, M. uclerans, M. leprae
9 Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Termed: Mycobacterium other than tuberculosis (MOTT), Atypical mycobacterium, Environmental mycobacterium No evidence for person-to-person transmission Environmental sources: soil, water, dust, animals MAI, M. fortuitum, M. kansasii, M. scrofulaceum, M. marinum
10 NTM - II Most common sites: adults lungs children lymph nodes, skin Granulomas often absent, AFB stains usually negative Reaction to PPD variable, usually < 10mm, wanes after months
11 Appearance over weeks to months
12 Tuberculosis Epidemiology 1/3 of world s population infected (~2 billion) WHO estimate worldwide: ~10 million annual new cases million annual deaths from TB Poor countries bear most of global TB burden (majority TB cases in Asia/Africa) ~15% of TB cases = HIV+
13 Worldwide Burden of Pediatric TB Incidence??? Prevalence??? Death Rate??? Rate of Infection??? ~ 11% of TB disease occurs in children < 15y, with 400,000 annual pediatric TB deaths
14 Challenges of M. tuberculosis Diagnosis Slow growing mycobacteria Replicates every hours Delay in culture results AFB smears not specific for MTB (suggestive) Requires specialized media & labs for growth TB drug susceptibility testing (not available overseas) Pulmonary TB may be AFB smear and culture negative (USA = 10-15% of PTB) Chronic respiratory conditions common overseas
15 Treatment Challenges with MTB Combination Therapy Required Prolonged Treatment 2 nd line TB drugs Expensive Poorly tolerated Less effective
16 Transitions in Tuberculosis Susceptible Exposed Infected Diseased Sick Diagnosed Treated Cured
17 Exposure Stages of Tuberculosis Defined by contact investigation recent (< 3 months) contact with infectious case Negative ST, physical exam, CXR Period during which skin test may be negative in infected person Children < 5 years old usually treated because disease may develop rapidly Older children, adults often not treat, but repeat skin test after exposure over
18 Infection Stages of Tuberculosis Hallmark is positive PPD Germs in the body CXR is often normal No symptoms, physical exam normal Anyone with infection should be treated when risk of dz outweighs adverse reaction to medication
19
20 Disease Stages of Tuberculosis Clinical and/or radiographic manifestations Primary: complication of initial infection Reactivation (Postprimary): disease after period of dormancy TST negative in 10 20% of all disease cases (50% of miliary or meningeal diseases)
21 Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Lungs are portal of entry in > 95% of cases Organisms in droplet land in alveoli Infectious dose is unknown Organisms are ingested by non-sensitized macrophages; intracellular replication occurs Organisms travel to regional lymph nodes via cells; lympho-hematogenous dissemination occurs CMI and delayed-type hypersensitivity generally develop in 4 12 weeks; if effective, replication is halted and infection remains subclinical
22 Lymphogenic spread of TB from Primary Pulmonary Focus (LUL)
23 Age-specific Risk for TB Disease Development following Primary Infection Age (years) Risk of disease < Pulmonary* 30 40%, TBM or miliary 10 20% Pulmonary* 10 20%, TBM or miliary 2 5 % Pulmonary* 5%, TBM or miliary 0.5 % Pulmonary* 2%, TBM or miliary < 0.5 % Pulmonary 10 20%, TBM or miliary < 0.5% *Ghon focus and/or lymph node pleural effusion or adult type TBM, tuberculous meningitis Adapted from Marais BJ, Gie RP, Schaaf HS. et al. The natural history of childhood intrathoracic TB a critical review of the literature from the pre-chemotherapy era. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2004;8:
24
25 Skin Testing, Infection, and Disease TST takes 3 weeks to 3 months to turn positive after infection Risk of disease after untreated infection Normal adults: 5 10 % in lifetime; (half of risk in first 2 3 years) HIV infected adults: 5 10% per year Infants: 40-50% in initial 1 2 years Older children (5 15 years): 2 10%
26 TST (PPD) False Negative? False Positive
27 TST (PPD) False Negative? Window Period Extremes of age (neonate, elderly) Steroids Co-occuring viral infections (i.e., influenza) Recent live vaccines HIV Malnourished Extrapulmonary/ miliary TB Improper Technique Inexperienced reader Reader Bias And for no explanation! False Positive BCG Environmental NTB Allergic reaction to components (peaks at 24 48h)
28 Induration Size = Positive TST > 5 mm HIV coinfection Immune compromise Recent contact to infectious TB case Abnormal CXR, suspected dz > 10 mm Foreign borne, highrisk country Drug user HR congregate setting Children < 4 years No risk factors: > 15mm
29 BCG Vaccines Negligible effect on TB epidemiology Does not prevent infection Little effect on reactivation disease Major use is to prevent life-threatening forms of TB in infants and children Most studies, 80-90% of PPD reactivity lost within 5 years after newborn BCG vaccination
30 Interferon-γRelease Assays Detects IFN-γafter lympocyte stimulation with MTB proteins More specific than TST, equal sensitivity Not influenced by NTM, BCG Lower IGRA sensitivity in immunocompromised May be more sensitive in recent infection Not well studied in young kids (< 4 years) Preferred test in older kids, refugees/immigrants
31 Clinical and Radiographic Manifestations of Childhood Pulmonary TB Paucity of signs and symptoms relative to CXR findings In U.S., up to 50% children with pulmonary TB have few or no symptoms Infants more symptomatic: fever, cough, focal wheezing, respiratory distress Predominance of hilar and/or mediastinal adenopathy (not always seen on plain film) Any lobe of lung involved; 25% multilobar Local pleural reaction/effusion is common Collapse consolidation or segmental pattern most common Obstructive signs/symptoms with endobronchial lesions Not contagious
32 8-month-old girl with obstructive hyperaeration of the right lower lobe, large hilar nodes compressing RLL bronchi TB should be considered inpatients with hyperaeration of unknown etiolgy
33 9 month old
34
35 2 months later on 4 drug therapy
36 RUL pulmonary TB, Subcarinal node, bronchial obstruction
37 Fever and Cough in 12 year old
38 12 year old CXR Widened mediastinum Hilar adenopathy Compression of L mainstem bronchus
39 Sept 2006
40 Dec 2006
41 Aorticopulmonary Node
42 Subcarinal Node L Mainstem compression
43 RML Syndrome
44 RML Syndrome - TB
45 14 yo with PTB: 2 findings
46
47 Right pleural effusion and R pulmonary bleb
48 1 year old with pulmonary TB
49 Pulmonary TB
50
51 School age boy CXR
52 Cambodian 4 year old
53 When to suspect TB in kids CXR much worse than clinical picture Wheeze, cough not responsive to albuterol Failure to thrive, reduced playfulness Don t expect fevers, night-time sweats, significant cough, upper lobe (reactivated) disease, or +PPD in pediatric TB cases
54 Diagnosis of TB in children Clinical/epi: gold standard AFB stains: positive < 10% of cases AFB culture: 3 early a.m. gastric aspirates All children: 20 40% of cases Infants: up to 75% of cases CSF, pleural fluid: ~25% of cases PCR:? Sensitivity, specificity 80-90%
55 Diagnosis of TB adults Proper sputum collections Best collected in early AM 2 nd sputum smear increases AFB smear yield by 13% 3 rd sputum smear 4% At least 2 quality sputa samples recommended (3 in settings where TB culture not readily available)
56 Complications of Primary Childhood Pulmonary TB Progressive local disease cavitation Obstructive emphysema Pericardial or esophageal perforation from subcarinal nodes Sudden death asphyxia, bleed Bronchiectasis Calcification takes at least 6 months
57 TB Pleural Effusion in Pediatrics Primarily adolescents uncommon before age 5, rare before age 2 Usually unilateral, can be bilateral Rare in miliary disease Usually abrupt onset: fever, chest pain, SOB Thoracentesis: several hundred WBCs, high protein, glucose < 39, AFB negative, culture positive 30-60%
58 5-year-old boy with massive left pleural effusion caused by tuberculosis. B: Patient 6 years later with a normal chest film and no physical complaint
59 Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
60 Extrapulmonary disease by site in adults and children
61 Miliary (Disseminated) TB in childhood Early complication of primary infection 1-2 mm opacities, aggregates of macrophages, lymphs w/ necrosis Most common in infants, recent after infection Protean manifestations FUO common, rapid breathing, wt loss Insiduous or explosive presentation CXR usually normal initially, then classic. LUNGS CTA! TST negative 50% Other findings: HSM, LAD, cutaneous Dx: gastric aspirate, bronchoscopy, bone marrow, urine cx
62 Miliary TB = extrapulmonary TB!
63 Miliary TB: 1-2 mm rounded opacities throughout all lung fields
64 Miliary TB
65 Miliary TB
66 Miliary TB Up close
67 Multiple Bullae, Pleural Thickening
68 Lymphadenitis Caused by MTB Most often unilateral; may be bilateral CXR usually normal Usually indolent onset of enlarged, fixed, matted nodes in anterior chains, submandibular Submental, occipital, axillary, supraclavicular nodes less often Absence of systemic findings, minimal tenderness Often progress, break down with sinus tracts Major Ddx: NTM, malignancy
69
70
71 Weeks to months
72 NTM vs TB Lymphadenitis NTM TB Age: 1 5 any Residence: rural urban TB risk factors: no yes CXR: negative 10% positive TST (mm) 0 15mm >10 15mm NEVER do incision & drainage Surgical excision diagnostic & curative for NTM (if complete excision)
73 7 year old male with a 2-month history of increasing lumbar pain and 5 day history of difficulty walking, vomiting, and progressive somnolence
74 Pott s Disease
75
76 Skeletal TB Lymphohematogenous spread or direct extension from paravertebral node WBC normal Skeletal TB: young > old children (intense blood flow) Adults: 6mos 3 years after primary TB Vertebrae (~50%)> knee > hip S/sxs: night cries, restless sleep, gait changes, lowgrade fever, gibbus deformity, reflex changes, clonus
77
78
79
80 L3 L5
81 76 yo presenting with abdominal TB presenting as GI bleed. Miliary TB.
82 76 yo - Miliary
83 Miliary 76 yo
84 44yo 20 kg wt loss. HIV-negative
85
86
87
88
89
90
91 Erythema Induratum
92 Copyright 2006 American Academy of Pediatrics
93 Primary Cutaneous TB
94
95 TB verucosa cutis
96
97 Treatment of TB Disease in Children Pulmonary INH, RIF x 6 mos + PZA for first 2 mos Add ETH initially if risk of INH resistance DOT INH resistant: RIF + PZA+ETH for 9 mos MDR depends on susceptibility; at least 18mos CNS, Disseminated Usually start with 4 drugs Usual length 9 12 months Once daily initially, may use twice weekly later Steroids: meningitis, endobronchial, miliary with alveolar block, pericardial with construction, vertebral with spinal root involvement
98 Practical Aspects of TB Management Preganancy: INH, Rif, EMB. PZA avoided. DOT from beginning! 1 st line drugs administered together Do not split dosing lower efficacy GI upset common early in treatment (r/o hepatitis). Administer with food rather than split dosing. Asymptomatic ALT increase (<3x normal) okay with INH/RIF Never add single drug to failing regimen. Pyridoxine (B6) supplementation to prevent INH-associated peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy (small children, malnourished, pregnant, alcoholics, diabetes, renal dz)
99 Scenarios: 2 month infant, mother has active pulmonary TB. Infant is breastfed next steps? Contagious vs noncontagious diseases? - Hilar adenopathy only? - Smear positive? Any treatment? - Household members? Infant: examine carefully - TST/CXR at 3 mos & possibly 6 mos time - ALWAYS start INH x 3 mos [window period] - If TST, CXR, exam all normal at 3 mos, can stop INH - Continues breastfeeding?
100 Mom has active disease, suspected contagious Contact-household tracing Mother infant separated until mother confirmed non-contagious (~2 weeks of tx, smear neg) Infant careful physical exam Started on INH (high risk of disseminated TB) TST/CXR 3 mos and possibly 6 mos INH stopped at 3 months of well
101 Congenital TB
102
Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011
 TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Smith, MD, MPH July 19, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Smith, MD, MPH July 19, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Intensive Houston, Texas. Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith. November 12, 2009
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017
 Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures
Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH April 6, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH April 6, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, Pediatric TB Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH March 8, 2012
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH March 8, 2012 Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH March 8, 2012 Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children
 Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital (TCH) Estimated TB incidence
Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital (TCH) Estimated TB incidence
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016
 Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
TUBERCULOSIS. By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi
 TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
TB in Children. Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012
 TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease. Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015
 Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 2-5, 2011 Pediatric TB Jeffrey Starke, MD August 5, 2011 Jeffrey Starke, MD has the following disclosures to make: Is on a data safety monitoring board for Hoffman
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 2-5, 2011 Pediatric TB Jeffrey Starke, MD August 5, 2011 Jeffrey Starke, MD has the following disclosures to make: Is on a data safety monitoring board for Hoffman
Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey
 Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey Helen Aguila, MD NJMS Global TB Institute December 15, 2011 This presentation is in part adapted from Pediatric Tuberculosis by Ann Loeffler, MD : Francis
Management of Pediatric Tuberculosis in New Jersey Helen Aguila, MD NJMS Global TB Institute December 15, 2011 This presentation is in part adapted from Pediatric Tuberculosis by Ann Loeffler, MD : Francis
3/25/2012. numerous micro-organismsorganisms
 Congenital & Neonatal TB A Case of Tuberculosis Congenital or Acquired? Felicia Dworkin, MD NYC DOHMH Bureau TB Control World TB Day March 23, 2012 Congenital TB: acquired by the fetus during pregnancy
Congenital & Neonatal TB A Case of Tuberculosis Congenital or Acquired? Felicia Dworkin, MD NYC DOHMH Bureau TB Control World TB Day March 23, 2012 Congenital TB: acquired by the fetus during pregnancy
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012 An Introduction to Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH August 10, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012 An Introduction to Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH August 10, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance. Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012
 TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012 Objectives: 1. Explain the steps for diagnosing latent and active TB role of interferon-gamma release
TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012 Objectives: 1. Explain the steps for diagnosing latent and active TB role of interferon-gamma release
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010
 Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
At the end of this session, participants will be able to:
 Advanced Concepts in Pediatric Tuberculosis: Infection Control, Source Case and Contact Investigation Ana M. Alvarez, M.D. Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University
Advanced Concepts in Pediatric Tuberculosis: Infection Control, Source Case and Contact Investigation Ana M. Alvarez, M.D. Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University
TUBERCULOSIS. Pathogenesis and Transmission
 TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
Pediatric TB Theresa Barton, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas December 8-10, 2009 Pediatric TB Theresa Barton, MD December 9, 2009 Pediatric Tuberculosis Tess Barton, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UT Southwestern
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas December 8-10, 2009 Pediatric TB Theresa Barton, MD December 9, 2009 Pediatric Tuberculosis Tess Barton, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UT Southwestern
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE
 DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB Nurse Case Management
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 2-4, 2011 Pediatric TB Andrea T. Cruz, MD, MPH March 2, 2011 Andrea Cruz, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 2-4, 2011 Pediatric TB Andrea T. Cruz, MD, MPH March 2, 2011 Andrea Cruz, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Treatment of TB Infection Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD April 7, 2015
 Treatment of TB Infection Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD April 7, 2015 Tuberculosis Infection Diagnosis and Treatment April 7, 2015 El Paso, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has
Treatment of TB Infection Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD April 7, 2015 Tuberculosis Infection Diagnosis and Treatment April 7, 2015 El Paso, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has
Pediatric TB Radiology: It s Not Black and White Part 2
 Experiencing technical difficulties? Please call Adobe Connect for technical assistance at 1-800-422-3623 Pediatric TB Radiology: It s Not Black and White Part 2 June 18, 2018 A National Webinar June 18,
Experiencing technical difficulties? Please call Adobe Connect for technical assistance at 1-800-422-3623 Pediatric TB Radiology: It s Not Black and White Part 2 June 18, 2018 A National Webinar June 18,
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 2013
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 2013 Tuberculosis in Children Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH October 16, 2013 Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 2013 Tuberculosis in Children Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH October 16, 2013 Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses
 Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children H Simon Schaaf
 Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital (TCH) Estimated TB incidence
Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital (TCH) Estimated TB incidence
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS. Objectives. Children are not just small adults. Pediatric Tuberculosis 1
 PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 4: Tuberculosis
 Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Errors in Dx and Rx of TB
 Errors in Dx and Rx of TB David Schlossberg, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Temple University School of Medicine Medical Director, TB Control Program Philadelphia Department of Public Health TB Still a
Errors in Dx and Rx of TB David Schlossberg, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Temple University School of Medicine Medical Director, TB Control Program Philadelphia Department of Public Health TB Still a
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS
 PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
Recognizing MDR-TB in Children. Ma. Cecilia G. Ama, MD 23 rd PIDSP Annual Convention February 2016
 Recognizing MDR-TB in Children Ma. Cecilia G. Ama, MD 23 rd PIDSP Annual Convention 17-18 February 2016 Objectives Review the definitions and categorization of drugresistant tuberculosis Understand the
Recognizing MDR-TB in Children Ma. Cecilia G. Ama, MD 23 rd PIDSP Annual Convention 17-18 February 2016 Objectives Review the definitions and categorization of drugresistant tuberculosis Understand the
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis. Topics for Discussion. Life Cycle of M. tuberculosis
 What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Microbiology Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Microbiology Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011
 Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB, or NOT TB? A Tough Question in Kids!
 TB, or NOT TB? A Tough Question in Kids! Brian Lee, MD Pediatric Tuberculosis Program Division of Infectious Diseases Ken Martin, MD Division of Radiology Overview Illustrate the range of clinical scenarios
TB, or NOT TB? A Tough Question in Kids! Brian Lee, MD Pediatric Tuberculosis Program Division of Infectious Diseases Ken Martin, MD Division of Radiology Overview Illustrate the range of clinical scenarios
has the following disclosures to make:
 CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH September 22, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management September 22 24, 2015 San Antonio. TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Annie Kizilbash
CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH September 22, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management September 22 24, 2015 San Antonio. TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Annie Kizilbash
MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS IN NEONATES AND YOUNG INFANTS
 MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS IN NEONATES AND YOUNG INFANTS A Bekker FIDSSA Conference, 2017 OUTLINE Case Perinatal TB Approach to the TB-exposed newborn MOM AND BABY S Born by NVD at peripheral hospital
MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS IN NEONATES AND YOUNG INFANTS A Bekker FIDSSA Conference, 2017 OUTLINE Case Perinatal TB Approach to the TB-exposed newborn MOM AND BABY S Born by NVD at peripheral hospital
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!!
 Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!! DECLARATION No relevant conflicts of interest to declare OVERVIEW Burden of disease & epidemiology Pathogenesis (not
Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!! DECLARATION No relevant conflicts of interest to declare OVERVIEW Burden of disease & epidemiology Pathogenesis (not
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis. Topics for Discussion. Global Impact of TB
 What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active TB Screening
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist
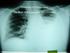 Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012
 TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
Dr Francis Ogaro MTRH ELDORET
 Dr Francis Ogaro MTRH ELDORET TB in children often severe, disseminated and can progress rapidly and with poor outcome TB diagnosis in children has relied on clinical, imaging, microscopy and TST findings.
Dr Francis Ogaro MTRH ELDORET TB in children often severe, disseminated and can progress rapidly and with poor outcome TB diagnosis in children has relied on clinical, imaging, microscopy and TST findings.
TB Nurse Case Management Waukesha, Wisconsin March 31 April 2, Pediatric TB Michelle Hulse, MD April 1, 2009
 TB Nurse Case Management Waukesha, Wisconsin March 31 April 2, 2009 Pediatric TB Michelle Hulse, MD April 1, 2009 Pediatric Tuberculosis HNTC Nurse Case Management Course April 1, 2009 Waukesha, Wisconsin
TB Nurse Case Management Waukesha, Wisconsin March 31 April 2, 2009 Pediatric TB Michelle Hulse, MD April 1, 2009 Pediatric Tuberculosis HNTC Nurse Case Management Course April 1, 2009 Waukesha, Wisconsin
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Algorithmic Approaches to Child TB Management in Resource-limited Settings
 Algorithmic Approaches to Child TB Management in Resource-limited Settings Steve Graham Centre for International Child Health University of Melbourne Department of Paediatrics Royal Children s Hospital
Algorithmic Approaches to Child TB Management in Resource-limited Settings Steve Graham Centre for International Child Health University of Melbourne Department of Paediatrics Royal Children s Hospital
Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012
 Moving Past the Basics of Tuberculosis Phoenix, Arizona May 8-10, 2012 Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012 Carla Chee, MHS has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Moving Past the Basics of Tuberculosis Phoenix, Arizona May 8-10, 2012 Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012 Carla Chee, MHS has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease. Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2014
 What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2014 The Critical First Step Consider TB in the Differential 1. Risks
What you need to know about diagnosing and treating TB: a preventable, fatal disease Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2014 The Critical First Step Consider TB in the Differential 1. Risks
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk
 Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis
 Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Pediatric Tuberculosis
 Pediatric Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH April 7, 2016 TB Intensive April 5 8, 2016 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to
Pediatric Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH April 7, 2016 TB Intensive April 5 8, 2016 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department
 Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department Elaine Darnall, RN, BSN, CIC TB Nurse Consultant Illinois Dept of Public Health March 21, 2018 Elaine Darnall has disclosed that there is no actual or
Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department Elaine Darnall, RN, BSN, CIC TB Nurse Consultant Illinois Dept of Public Health March 21, 2018 Elaine Darnall has disclosed that there is no actual or
Interpretation of Chest Radiographs Paul Christensen, MD 10/21/09. Diagnostic Evaluation. Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation.
 Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
The Origin of Swine Flu
 How the Heck Do You Diagnose Tuberculosis in Children, Anyway? Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor and Vice Chairman of Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas USA The Origin of Swine Flu MAIN
How the Heck Do You Diagnose Tuberculosis in Children, Anyway? Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor and Vice Chairman of Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas USA The Origin of Swine Flu MAIN
The diagnosis of active TB
 The diagnosis of active TB Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Martha Ainslie Relationships with commercial interests: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Boehringer Ingelheim Mitigating Potential Bias I have
The diagnosis of active TB Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Martha Ainslie Relationships with commercial interests: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Boehringer Ingelheim Mitigating Potential Bias I have
Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus. Lana Kay Tyer, RN MSN WA State Department of Health TB Nurse Consultant
 Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus Lana Kay Tyer, RN MSN WA State Department of Health TB Nurse Consultant Learning Objectives Understand the impact of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) on TB infection
Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus Lana Kay Tyer, RN MSN WA State Department of Health TB Nurse Consultant Learning Objectives Understand the impact of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) on TB infection
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 29-December 2, 2011
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 29-December 2, 2011 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR November 30, 2011 Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR has the following disclosures to make: No
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 29-December 2, 2011 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR November 30, 2011 Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR has the following disclosures to make: No
HIV prevalance in TB cases
 TUBERCULOSIS HIV prevalance in TB cases Top 5 AIDS indicative diseases; EUR, 2003 58% 35% 25% 11% 7% TB HIV wasting s. Candidiasis Rec. pneumonia HIV encephal. 26% 25% 31% 31% 16% 8% 7% 16% 14% 10% TB
TUBERCULOSIS HIV prevalance in TB cases Top 5 AIDS indicative diseases; EUR, 2003 58% 35% 25% 11% 7% TB HIV wasting s. Candidiasis Rec. pneumonia HIV encephal. 26% 25% 31% 31% 16% 8% 7% 16% 14% 10% TB
CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT]
![CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT]](/thumbs/89/99628771.jpg) CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] QUESTION: : Which children in the United States should get a tuberculin skin test? Do questionnaires really work? Jeffrey
CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] QUESTION: : Which children in the United States should get a tuberculin skin test? Do questionnaires really work? Jeffrey
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome. Dr. Lesego Mawela
 Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Dr. Lesego Mawela TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION IRIS Case Epidermiology Pathogenesis of IRIS Risk factors for IRIS Epidemiology of IRIS Health system burden of IRIS
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Dr. Lesego Mawela TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION IRIS Case Epidermiology Pathogenesis of IRIS Risk factors for IRIS Epidemiology of IRIS Health system burden of IRIS
10/3/2017. Updates in Tuberculosis. Global Tuberculosis, WHO 2015 report. Objectives. Disclosures. I have nothing to disclose
 Disclosures Updates in Tuberculosis I have nothing to disclose Chris Keh, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, Division of Infectious Diseases, UCSF TB Controller, TB Prevention and Control Program, Population
Disclosures Updates in Tuberculosis I have nothing to disclose Chris Keh, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, Division of Infectious Diseases, UCSF TB Controller, TB Prevention and Control Program, Population
Diagnosis and Medical Management of TB Disease. Quratulian Annie Kizilbash, MD, MPH March 17, 2015
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of TB Disease Quratulian Annie Kizilbash, MD, MPH March 17, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management March 17 19, 2015 San Antonio, Texas EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Quratulian
Diagnosis and Medical Management of TB Disease Quratulian Annie Kizilbash, MD, MPH March 17, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management March 17 19, 2015 San Antonio, Texas EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Quratulian
Tuberculosis in Primary Care COC GTA Spring Symposium Dr Elizabeth Rea April 2013
 Tuberculosis in Primary Care COC GTA Spring Symposium Dr Elizabeth Rea April 2013 1 TB in Toronto - risk groups Diagnosis of active TB LTBI diagnosis and management Infection control 2 TB in Toronto Case
Tuberculosis in Primary Care COC GTA Spring Symposium Dr Elizabeth Rea April 2013 1 TB in Toronto - risk groups Diagnosis of active TB LTBI diagnosis and management Infection control 2 TB in Toronto Case
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis in Adolescents Andrea T. Cruz, MD, MPH Sections of Infectious Diseases & Emergency Medicine October 14, 2013
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis in Adolescents Andrea T. Cruz, MD, MPH Sections of Infectious Diseases & Emergency Medicine October 14, 2013
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Diagnosis of TB in Children. Dr Jacquie Narotso Oliwa
 Diagnosis of TB in Children Dr Jacquie Narotso Oliwa 1 Objectives To identify the common clinical presentations of TB in children Overview of diagnostic measures To understand a simplified approach to
Diagnosis of TB in Children Dr Jacquie Narotso Oliwa 1 Objectives To identify the common clinical presentations of TB in children Overview of diagnostic measures To understand a simplified approach to
Contact Follow-Up and Treatment of LTBI in Households of Infectious Cases in Pakistan
 Contact Follow-Up and Treatment of LTBI in Households of Infectious Cases in Pakistan 17 th Annual Conference, The Union-North American Region, Vancouver, Canada. 28 February 2013 Farhana Amanullah Director
Contact Follow-Up and Treatment of LTBI in Households of Infectious Cases in Pakistan 17 th Annual Conference, The Union-North American Region, Vancouver, Canada. 28 February 2013 Farhana Amanullah Director
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Strategies for Detection and Management
 Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Strategies for Detection and Management Patrick T. Dowling MD,MPH Professor and Chair Dept of Family Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pri-Med March 29 2014 Pdowling@mednet.ucla.edu
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) Strategies for Detection and Management Patrick T. Dowling MD,MPH Professor and Chair Dept of Family Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Pri-Med March 29 2014 Pdowling@mednet.ucla.edu
Tuberculosis. Objectives. Tuberculosis in children is usually spead from an adult with untreated pulmonary tuberculosis.
 8 Tuberculosis Objectives When you have completed this unit you should be able to: Give reasons why tuberculosis is an important and dangerous disease. Describe primary tuberculous infection of the lung.
8 Tuberculosis Objectives When you have completed this unit you should be able to: Give reasons why tuberculosis is an important and dangerous disease. Describe primary tuberculous infection of the lung.
Contact Investigation and Prevention in the USA
 Contact Investigation and Prevention in the USA George D. McSherry, MD Division of Infectious Disease Penn State Children s Hospital Pediatric Section TB Center of Excellence Rutgers Global Tuberculosis
Contact Investigation and Prevention in the USA George D. McSherry, MD Division of Infectious Disease Penn State Children s Hospital Pediatric Section TB Center of Excellence Rutgers Global Tuberculosis
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
Pediatric TB Basics and Evaluation and Management of Exposed Neonates
 Pediatric TB Basics and Evaluation and Management of Exposed Neonates Ann M. Loeffler, MD Randall Children s Hospital, Portland OR & Curry International TB Center, Oakland CA September, 2017 No Disclosures
Pediatric TB Basics and Evaluation and Management of Exposed Neonates Ann M. Loeffler, MD Randall Children s Hospital, Portland OR & Curry International TB Center, Oakland CA September, 2017 No Disclosures
TB in the Patient with HIV
 TB in the Patient with HIV Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD May 11, 2017 TB Intensive May 9 12, 2017 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD, has the following disclosures to
TB in the Patient with HIV Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD May 11, 2017 TB Intensive May 9 12, 2017 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD, has the following disclosures to
Managing the Patients Response to TB Treatment
 Managing the Patients Response to TB Treatment Barbarah Martinez, RN, BSN September 13, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Barbarah Martinez, RN, BSN has
Managing the Patients Response to TB Treatment Barbarah Martinez, RN, BSN September 13, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Barbarah Martinez, RN, BSN has
New Tuberculosis Guidelines. Jason Stout, MD, MHS
 New Tuberculosis Guidelines Jason Stout, MD, MHS Two New Sets of Guidelines Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Clinical Infectious Diseases 2016; 63(7): e147-e195 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Adults
New Tuberculosis Guidelines Jason Stout, MD, MHS Two New Sets of Guidelines Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Clinical Infectious Diseases 2016; 63(7): e147-e195 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Adults
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
New Approaches to the Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents
 New Approaches to the Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine [With great thanks to Andrea
New Approaches to the Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine [With great thanks to Andrea
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Treatment of Pediatric TB Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. November 13, 2009 MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Treatment of Pediatric TB Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. November 13, 2009 MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
European Respiratory Society Congress Barcelona President Award. Dr Walther Guerrero Ciquero
 TUBERCULOSIS Homework European Respiratory Society Congress Barcelona 2010 President Award Dr Walther Guerrero Ciquero ERS will continue to honour his memory through a Fellowship bearing his name. Stop
TUBERCULOSIS Homework European Respiratory Society Congress Barcelona 2010 President Award Dr Walther Guerrero Ciquero ERS will continue to honour his memory through a Fellowship bearing his name. Stop
Tuberculosis What you need to know. James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director
 Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Mycobacteriology William H. Benjamin, Jr.
 Mycobacteriology William H. Benjamin, Jr. William H. Benjamin, PhD Department of Pathology UAB 1 Mycobacteria sp. Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) Mycolic acids (C78-91) Waxes Obligate aerobes Slow growing days
Mycobacteriology William H. Benjamin, Jr. William H. Benjamin, PhD Department of Pathology UAB 1 Mycobacteria sp. Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) Mycolic acids (C78-91) Waxes Obligate aerobes Slow growing days
