Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai
|
|
|
- Logan Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and verbal literacies in the context of human body systems Questionnaires, coding schemes, analysis and results Digestive System Phase 2 Part 2: Questionnaires with Scores Assignation Part 2 A Comprehension of Structure Passages Each question carries a certain number of points which are given within brackets. Questions numbers considered in the calculation of comprehension scores are marked with *. A summary of the questions considered and the total points they carry is given after the two questionnaires. Read the passages given below and answer the questions given below each of them. To answer the questions you may use words or drawings as you wish. Passage 1 Understanding of function from a structural description (therefore understanding of function) The mouth contains many teeth, one tongue and some salivary glands. We have four kinds of teeth: incisors, canines, pre molars and molars. Incisors are the front teeth, which are flat in shape. On both sides of the incisors are the long and pointed canine teeth. Any food first comes into contact with the incisors and the canines. Deeper in the jaw, behind the canines, are the pre molars. The pre molars have two points, or cusps, and are therefore called "bicuspids". Further deep inside, behind the pre molars, are a few teeth which are the last to develop. These special teeth, called molars, have four or five points, or cusps. The walls of the mouth cavity carry three pairs of salivary glands. Saliva secreted by these glands contains some active proteins, called enzymes. Some enzymes can convert starch into sugar. Other enzymes can kill bacteria. The saliva contains a lot of water and some slimy mucus. The tongue is a muscular organ. It has on its surface thousands of special structures called taste buds. There are different kinds of taste buds for sweet, salty, sour and bitter tastes. Each of these four kinds of taste buds are located in a specific region of the tongue. 1
2 a. Draw what you imagine could be the shapes of an incisor, a canine, a pre molar and a molar tooth (4) b. Draw a diagram to illustrate the position of the different kinds of teeth (1). c. From the shape and location of each kind of tooth, what can you say about its function? Answer in the table given below. Draw diagrams if necessary (12). * Type of tooth Shape of tooth Where it is located in the mouth Incisor Probable function of this tooth Canine Pre molar Molar d. What could be the use of water and mucus in the saliva? Explain. (1) * e. How does it help that the tongue is a muscular organ? What if the tongue were hard and bony? (1) * f. A piece of roti, when chewed well, tastes sweet. Why? (1) g. Can you taste all foods in all parts of the tongue? Why or why not? (1) * h. Give examples of foods which have a taste that is a combination of two or more tastes. How could you detect such a taste? (1) * i. If you cut your finger by mistake with a knife, and blood comes out of the cut, you are sometimes asked to put your finger in your mouth. Why do you think that is done? (1) Passage 2 The oesophagus is a flexible tube. This tube begins at the back of the mouth. The walls of the tube can repeatedly relax and contract to push the food along the oesophagus. The opening to the trachea lies close to the opening of the oesophagus. A flap of tissue called the epiglottis covers the trachea like a lid. 2
3 The oesophagus connects the mouth with the stomach. The walls of the stomach contain glands which secrete gastric juices, which are strongly acidic and act on the proteins. The inside of the stomach is lined with a thick layer of mucus which protects it from the action of these juices. a. Which of these words might describe the walls of the oesophagus: soft, hard, strong, flexible, bony? (2) * b. How do you think the food is pushed from the mouth to the stomach through the foodpipe? Make a drawing of it. (1) * c. Where else can you see a similar process in the human body itself? (1) * d. How might the epiglottis look like? Draw the trachea and oesophagus and show also the epiglottis in the drawing (1). e. What would happen if the epiglottis were not there? (1) * f. What do we do if food accidently lands on the epiglottis or enters the trachea? (1) * g. After reading Passage 1 and Passage 2, what is your idea of a "gland"? About how big might be the glands mentioned in Passage 1 and Passage 2? (2) * h. After reading Passage 1 and Passage 2, what is your idea of "mucus"? (1) * i. What would happen if there were no layer of mucus on the inside of the stomach? (1) * j. Draw diagrams to show what the stomach looks like and what happens inside it during digestion. (2) * Part 2 B Comprehension of Function Passages Each question carries a certain number of points which are given within brackets. Questions numbers considered in the calculation of comprehension scores are marked with *. A summary of the questions considered and the total points they carry is given after the two questionnaires. Read the passages given below and answer the questions given below each of them. To answer the questions you may use words or drawings as you wish. Passage 1 3
4 Digestion of food begins in the mouth. In our mouth we have four kinds of teeth: incisors, canines, pre molars and molars. The teeth chew the food in the following way. First the incisors break off a piece of the food. Tough foods are torn up by the canines. Next the pre molars and molars grind the food. This is how our teeth break up the food material into tiny pieces. Three pairs of salivary glands in the mouth secrete saliva. Saliva mixes with the tiny pieces of food. Active proteins, or enzymes in the saliva, help convert some starch in the food into sugar. Other enzymes in the saliva kill bacteria. Mucus and water in the saliva helps us to smoothly swallow the chewed up food. The tongue moves the food around in the mouth to mix it with the saliva. The tongue also detects the taste of the food. Taste buds in specific regions of the tongue can detect one of four different kinds of tastes: sweet, salty, sour and bitter. a. Draw what you imagine could be the shapes of an incisor, a canine, a pre molar and a molar tooth (4). * b. Draw a diagram to illustrate the action of the different kinds of teeth (4). * c. From the function of each kind of tooth, can you guess its shape and location? Answer in the table given in the next page. Draw diagrams if necessary (12). * Type of tooth Function of tooth Probable shape of this tooth Incisor Where it might be located in the mouth Canine Pre molar Molar d. What could be the use of water and mucus in the saliva? Explain. (1) e. What do you think the tongue is made of? Could the tongue have bones in it? Could it have blood vessels? Or muscle tissue? (1) * f. A piece of roti, when chewed well, tastes sweet. Why? (1) 4
5 g. Can you taste all foods in all parts of the tongue? Why or why not? (1) * h. Give examples of foods which have a taste that is a combination of two or more tastes. How could you detect such a taste? (1) i. If you cut your finger by mistake with a knife, and blood comes out of the cut, you are sometimes asked to put your finger in your mouth. Why do you think that is done? (1) Passage 2 When food is swallowed, it goes from the mouth into the oesophagus. The food is pushed along with the help of repeated contractions and relaxations of the oesophagus. The opening to the trachea lies close the opening of the oesophagus. As we swallow, a flap of tissue called the epiglottis closes over the top of the trachea. The food passes from the oesophagus to the stomach. Here, proteins are acted on by strong acids known as gastric juices, which are secreted by glands in the walls of the stomach. The mucus lining inside the stomach protects it from the action of these juices. a. Which of these words might describe the walls of the oesophagus: soft, hard, strong, flexible, bony? (2) * b. How do you think the food is pushed from the mouth to the stomach through the foodpipe? Make a drawing of it. (1) * c. Where else can you see a similar process in the human body itself? (1) * d. How might the epiglottis look like? Draw the trachea and oesophagus and show also the epiglottis in the drawing. (1) * e. What would happen if the epiglottis were not there? (1) * f. What do we do if food accidently lands on the epiglottis or enters the trachea (1)? g. After reading Passage 1 and Passage 2, what is your idea of a "gland"? About how big might be the glands mentioned in Passage 1 and Passage 2? (2) * h. After reading Passage 1 and Passage 2, what is your idea of "mucus"? (1) * i. What would happen if there were no layer of mucus on the inside of the stomach? (1) * 5
6 j. Draw diagrams to show what the stomach looks like and what happens inside it during digestion. (2) * Questions which probed understanding of Structure Function relationships for the digestive system. Only these questions were taken into account while calculating mean scores for Part 2: Part 2 a Question nos: 1c (12), 1d (1), 1e (1), 1g (1), 1h (1), 2a (2), 2b (1), 2c (1), 2e (1), 2f (1), 2g (2), 2h (1), 2i (1), 2j (2) Total: 28 Part 2 b Question nos: 1a (4), 1b (1), 1c (12), 1e (1), 1g (1), 2a (2), 2b (1), 2c (1), 2d (1), 2e (1), 2g (2), 2h (1), 2i (1), 2j (2) Total: 31 Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and verbal literacies in the context of human body systems Questionnaires, coding schemes, analysis and results Digestive System Phase 2 Part 2: Average scores, maximum scores and nature of questions Questions used in calculation of Structure Function comprehension scores are marked with *. Part 2A Q No Average Score Max score Nature of questions 1c* shape, location, function of teeth 1e* what if hard and bony tongue 1g* taste buds in tongue 1a diagrams of teeth 1b position of teeth 1f chewed roti 6
7 1h* examples of food, comb of tastes 2j* structure of stomach, function 2a* describe walls of oesophagus 2f* effect of food landing on epiglottis 2c* peristalsis in other organs 1d* role of water and mucus in saliva 2d looks of epiglottis 2h* idea of "mucus" 2e* what if epiglottis not there 2b* drawing of food pushed through food pipe 2i* what if no mucus 1i fn of saliva when finger cut 2g* role of gland Part 2B Q No Score Max score Nature of questions 1d role of water and mucus in saliva 1e* what if hard and bony tongue 1c* shape, location, function of teeth 1g* taste buds in tongue 1a* diagrams of teeth 2h* idea of "mucus" 2b* drawing of food pushed through food pipe 2c* peristalsis in other organs 2f effect of food landing on epiglottis 2i* what if no mucus 2j* structure of stomach, function 1f chewed roti 2a* describe walls of oesophagus 1h examples of food, comb of tastes 2e* what if epiglottis not there 2d* looks of epiglottis 2g* role of gland 1i fn of saliva when finger cut 1b* action of teeth Part 2a Q No 1c 1e 1g 1a 1b 1f 1h Criteria for expected responses largely depends on prior content knowledge, shape and location given in passage quite intuitive, some imagination, helps to have knowledge of function of tongue, prior knowledge given in passage, some prior knowledge of appearance, the problem would be to convert into a diagram given in passage, also from personal experience, difficulty with translating into diagram chewed roti, inferencing, but not from passage personal experience, no inferencing involved 7
8 2j 2a 2f 2c 1d 2d 2h 2e 2b 2i 1i 2g shape from prior knowledge, part of function also given in passage (in terms of secreting gastric juices), but not why? flexible part given directly in the passage, strong from inferencing shape and location of epiglottis there in passage from prior knowledge of respiratory, circulatory systems from prior knowledge is there in passage, but converting into a diagram, and relative knowledge with respect to trachea and oesophagus cumulative understanding from description in passage 1 and 2, question requiring inferencing knowledge of location of epiglottis, some imagination, visualisation description given in passage, problem in converting into a diagram, before that understanding what the terms mean, its consequence from content in passage, substracting effect of mucus in stomach from content in passage, but could be done from prior knowledge, experience inferencing from 1 and 2, also understanding role of gland Part 2b Q No 1d 1e 1c 1g 1a 2h 2b 2c 2f 2i 2j 1f 2a 1h 2e 2d 2g 1i 1b Criteria for expected responses can be directly taken from the passage quite intuitive, some imagination, helps to have knowledge of function of tongue, largely depends on prior content knowledge, function given in passage can be directly taken from the passage inferenced from passage, even if not known earlier only function of teeth described in passage, if no prior knowledge, inferencing is required from function to structure, easy if prior knowledge is there, diagrams cumulative understanding from description in passage 1 and 2, question requiring inferencing description given in passage, problem in converting into a diagram, before that understanding what the terms mean, its consequence from prior knowledge of respiratory, circulatory systems function of epiglottis there in passage, inference about the effect of food landing on it can be made from content in passage, subtracting effect of mucus in stomach shape from prior knowledge, part of function also given in passage (in terms of secreting gastric juices), but not why it secretes chewed roti, inferencing, but not from passage flexible' part given directly in the passage, 'strong' from inferencing personal experience, no inferencing involved can be inferred from function of epiglottis given in passage; knowledge of location of epiglottis also required, some imagination, visualisation is there in passage, but converting into a diagram, and relative knowledge with respect to trachea and oesophagus inferencing from 1 and 2, also understanding of role of gland from two different functions, requires comprehension and inferencing from some content in passage, but could be done from prior knowledge, experience difficulty compared with its equivalent question in Part 2a with translating into function diagrams 8
9 Effect of content on comprehension of "structure" and "function" passages Mean scores and (s.d.) 2A (Structure version) 2B (Function version) Significance Mann Whitney U Passage 1 (mouth) 0.69 (0.20) 0.67 (0.19) N.S. Passage 2 (oesophagus 0.36 (0.23) 0.47 (0.24) z = 2.0, p < 0.05 and stomach) Significance Wilcoxon Signed ranks z = 5.7, p = 0.00 z = 3.7, p =
Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human body systems Questionnaires, coding schemes, analysis and results
 Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
1 ANIMALS Digestive System Oral Cavity and Esophagus.notebook January 06, 2016
 The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
Digestion. Final Products of Digestion Carbohydrates Disaccharides (sucrose, maltose) Proteins Short polypeptides Individual amino acids
 Digestion Process has three stages: 1. Physical Digestion: mechanical process of breaking down the food. Knives and forks, teeth grinding and tearing 2. Chemical Digestion: enzymes and stomach acid breaks
Digestion Process has three stages: 1. Physical Digestion: mechanical process of breaking down the food. Knives and forks, teeth grinding and tearing 2. Chemical Digestion: enzymes and stomach acid breaks
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
Digestion is a process in which the complex food we eat is broken down in to simple, soluble, substances which our body is able to use.
 KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
The Digestive Process Begins
 Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells.
 Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
Digestive System Anatomy
 Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
The Digestive System. 1. The Mouth. 2. Epiglottis and Esophagus. 3. The Stomach. 4. The Small Intestine
 The Digestive System Name: The digestive system has 3 main functions. First, it breaks down food into smaller nutrients that the body can use. Secondly, these nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Thirdly,
The Digestive System Name: The digestive system has 3 main functions. First, it breaks down food into smaller nutrients that the body can use. Secondly, these nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Thirdly,
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
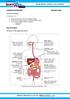 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
Digestive System. Physical and breakdown begins. : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic
 SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Monday, October Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page.
 1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
Primary Function. 1. Ingestion: food enters the system
 Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
"The Digestive Process Begins" and "Final Digestion and Absorption" excerpts
 Read the following two passages about how the human digestive system processes food. Then answer the questions based on the text. "The Digestive Process Begins" and "Final Digestion and Absorption" excerpts
Read the following two passages about how the human digestive system processes food. Then answer the questions based on the text. "The Digestive Process Begins" and "Final Digestion and Absorption" excerpts
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
Digestive System. 1) Learn about the major organs in the digestive system. 2) Learn the locations of the major organs in the digestive system
 Digestive System 1) Learn about the major organs in the digestive system 2) Learn the locations of the major organs in the digestive system Teachers' notes Subject Topic Title Grade(s) Cross curricular
Digestive System 1) Learn about the major organs in the digestive system 2) Learn the locations of the major organs in the digestive system Teachers' notes Subject Topic Title Grade(s) Cross curricular
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Essential Standard. 5.PCH.4 Understand body systems and organs, functions, and their care. Clarifying Objective
 Essential Standard 5.PCH.4 Understand body systems and organs, functions, and their care. Clarifying Objective 5.PCH.4.1 Summarize the functions of the organs which make up the digestive system. CCSS.Math.Content.5.MD.A.1
Essential Standard 5.PCH.4 Understand body systems and organs, functions, and their care. Clarifying Objective 5.PCH.4.1 Summarize the functions of the organs which make up the digestive system. CCSS.Math.Content.5.MD.A.1
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
4/8/16. Digestive System. When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy
 When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
The Digestive System. Functions of the Digestive System
 The Digestive System THINK ABOUT IT When you re hungry, your whole body needs food. But the only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So, how does food get to the rest
The Digestive System THINK ABOUT IT When you re hungry, your whole body needs food. But the only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So, how does food get to the rest
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Contents. Section 1: The Circulatory System. Section 2: The Digestive System. Section 3: The Excretory System. Section 4: The Endocrine System
 Contents Section 1: The Circulatory System 1. The Heart... 2 2. The Blood Vessels.... 6 3. The Blood.... 10 4. Quiz 1.... 14 Section 2: The Digestive System 5. The Mouth and Esophagus.... 15 6. The Stomach....
Contents Section 1: The Circulatory System 1. The Heart... 2 2. The Blood Vessels.... 6 3. The Blood.... 10 4. Quiz 1.... 14 Section 2: The Digestive System 5. The Mouth and Esophagus.... 15 6. The Stomach....
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013
 ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
What is the major site of digestion? If you answered stomach, you missed it! The correct answer is small intestine.
 DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p )
 10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p411 418) Learning Goal: Label and explain the anatomy of the Digestive System See text p411 Fig.10.6: Label "Organs of Digestive System": See text p411 Fig.10.6:
10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p411 418) Learning Goal: Label and explain the anatomy of the Digestive System See text p411 Fig.10.6: Label "Organs of Digestive System": See text p411 Fig.10.6:
Body Systems. Unit. Key Words. In this unit you will learn to: cell. function. system. convert. circulate
 Unit 1 Body Systems Key Words cell chest function system convert circulate In this unit you will learn to: describe the levels of biological organization. identify the basic structures and functions of
Unit 1 Body Systems Key Words cell chest function system convert circulate In this unit you will learn to: describe the levels of biological organization. identify the basic structures and functions of
The Digestive System Exam Questions
 The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Healthy eating reading comprehension
 Name:... Date:... Read each text carefully and answer the questions. Sometimes the answers can be found in the text, other times you must work out the answer by what is being suggested by the author. The
Name:... Date:... Read each text carefully and answer the questions. Sometimes the answers can be found in the text, other times you must work out the answer by what is being suggested by the author. The
The Digestive System: Basics. WedNesday October 24th All organisms need energy to survive. > Use energy to reproduce, grow, and repair
 WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
The Digestive System. Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1
 The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
The anatomy of the digestive tract
 4. The digestive system 4.1 The organs in the digestive tract 4.1.2 The anatomy of the digestive tract THE MOUTH The digestive tract is simply all the organs that are instrumental in digestion. It starts
4. The digestive system 4.1 The organs in the digestive tract 4.1.2 The anatomy of the digestive tract THE MOUTH The digestive tract is simply all the organs that are instrumental in digestion. It starts
Biology: 4. The Digestive System
 Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
HETEROTROPHS cannot make their own food like Autotrophs(Plants). They must get their nutrition from their surrounding environment.
 HETEROTROPHS cannot make their own food like Autotrophs(Plants). They must get their nutrition from their surrounding environment. 1 Heterotrophic organisms are most bacteria, some protists, and ALL fungi
HETEROTROPHS cannot make their own food like Autotrophs(Plants). They must get their nutrition from their surrounding environment. 1 Heterotrophic organisms are most bacteria, some protists, and ALL fungi
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out how your body processes food. Mouth The teeth in your mouth are involved in the first stage of digestion. Teeth are used
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out how your body processes food. Mouth The teeth in your mouth are involved in the first stage of digestion. Teeth are used
The Digestive System CP Biology
 The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
Structure and Function of Cells, Organs and Organ Systems 1
 I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
Rebel Biology - Nutrition. organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities. carbs, proteins. vitamins, water,
 Rebel Biology - Nutrition organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities the most important ones are fats, carbs, proteins vitamins, water, these either provide direct value(fats/carbs/proteins)
Rebel Biology - Nutrition organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities the most important ones are fats, carbs, proteins vitamins, water, these either provide direct value(fats/carbs/proteins)
4 th primary. 2 nd term 1 Science
 2 nd term 1 Science A-Choose: Model Answer (work sheet) 1-16 2-pharynx 3-stomach 4-seven meters 5-stomach. 6-digestive system. 7-lung 8-respiration 9-nose 10-hair and mucus. 11-organs 12-cell 13-chloroplast
2 nd term 1 Science A-Choose: Model Answer (work sheet) 1-16 2-pharynx 3-stomach 4-seven meters 5-stomach. 6-digestive system. 7-lung 8-respiration 9-nose 10-hair and mucus. 11-organs 12-cell 13-chloroplast
The function of the digestive system is to break down
 Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
