DIFFERENCES IN BODY POSTURE AND BALANCE IN CHILDREN OF CLASSROOM TEACHING ATTENDING AND NOT ATTENDING EXTENDED STAY
|
|
|
- Harry Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
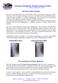
1 Research in Physical Education, Sport and Health 2014, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp ISSN(Print): ; ISSN(Online): DIFFERENCES IN BODY POSTURE AND BALANCE IN CHILDREN OF CLASSROOM TEACHING ATTENDING AND NOT ATTENDING EXTENDED STAY Mirela Milardović, Jelena Paušić, Biljana Kuzmanić University of Split, Faculty of Kinesiology, Split, Croatia, UDC: : (Original scientific paper) Abstract Proper postural child development depends on good structural and functional development of the body. Children have already affected their development and their posture in a negative way by reducing their movements and by increasing their weight at the same time. When observing the sagittal posture, the gravity line passes through these points: mid skull, mid shoulder, hip, knee, and slightly in front of the malleolus lateralis.the main objective of this paper is to determine the differences in indicators of posture in children attending extended and those children who do not attend an extended stay. The sample in this study included the students from 1st to 3rd grade of elementary school with a total number of 134. Subsamples of respondents are arranged within the first, second and third grade and subsamples of children attending an extended stay and those who do not attend it. Four variables were taken to determine the postural stability: anterior or posterior tilt of the body in relation to the gravity line, percentage of CG distributed anteriorly and posteriorly to the point of the projection of the center of the body on the surface of the palm of respondents and distance travelled point of the projection of the center of the body in the area of support expressed in millimeters. Measuring of the indicators of posture were exercised by one surveyor who set markers at specific points of the body in the sagittal examination, another surveyor carried out the shooting, and the third one did the analysis on the force platform recording within 3 seconds by setting a foot parallel to the platform in a calm and relaxed attitude. Based on the results the main hypothesis was confirmed: subsamples of respondents (children attending and those not attending extended stay) were significantly different in all postural parameters. Key Words: foot pressure distribution, elementary school children Introduction The standard posture (Latin - positura - position ) is the correct relation of different parts of the body which maintains a balance between supporting structures. The spine must have a normal curvature and lower extremities must be in an ideal position to maintain balance. When observing the sagittal posture, it is clear that gravity line passes through these points: auditory opening, acromion, and hip, slightly anterior to the epicondyle knees and slightly anterior to the lateral malleolus. Derogation from any point of the correct body posture will try to compensate for posture, and eventually will become improper posture. It is important to recognize the body points that indicate postural deviations in the growth of the individual. In recent times there is increasing dispute about the problem of overweight children s schoolbags and risks to children's health, the muscle and spinal discomfort and numbness in hands and fingers, fatigue and cervical spinal musculature which is associated with improper posture. In some European countries, the law prescribes that the weight of school bags must not exceed 10 % of the body weight of the child (Fošnarić, 2007). The younger the child, the lower acceptable load; for children who are between 6 and 7, it should not exceed 5-10 % of their body weight. If a child carries heavy burden, it will be difficult to walk faster and they will get tired easily. Conditions unwittingly exacerbate if a child carries a bag on one shoulder, in one hand or over their back all the way to their thigh. Child weakens stat - dynamics of their musculoskeletal system; there is a failure in occurrence of postural muscle which promotes the formation of inadequate posture. Hunched posture will harm the natural curvature of the spine in the long run. Postural tilt implies a movement of the head, shoulders and pelvis. The head and pelvis can tilt the 135
2 DIFFERENCES IN BODY POSTURE AND BALANCE anterior or posterior to the coronal plane. The anterior tilt of the head will result in flexion of the cervical spine and posterior slope will result in the extension. The posterior pelvic tilt results in flexion of the lumbar spine and anterior pelvic tilt results in the extension of the lumbar spine. The head and pelvis can tilt laterally; from the neutral position, shoulder blade can attain anterior slope rather than posterior slope, unless the posterior slope means the blades moving back to theneutral positionof theanteriortilt. There is an increasing number of children with incorrect posture and the research has shown that in Croatian schools in children between 6-9 years, this percentage ranges from 51-62%, (Paušić, 2005) and in boys years, from 10 to 22% (Paušić, 2007). Paušić and Kujundžić (2008) conducted a study whose objective was to determine the percentage of the weight of school bags in relation to the weight of students in some schools in Split-DalmatianCounty and therefore warn all of those concerned, that there is a problem of too heavy bags in early childhood. The weight study was carried out on a sample of 348 students attending years 1-4 and two values were established : body weight and the weight of school bags, as well as the average weight of bags in relation to body weight. The data indicated that in all years, the percentage of overweight bags in relation to students body weight is 10% higher, reaching up to %. Paušić et al. (2009) have conducted this research on 252 students attending years 1-4. The aim of the study was to determine the percentage of overweight schoolbags in relation to body weight students and to determine whether there were differences between the students of the first, second, third and fourth years. The next objective was to answer the question of whether there is a connection established by the percentage of weight of school bags in relation to body weight and intensity of pain reported by carrying schoolbags and differences between students of different years in the variable of intensity of pain. The interview with the students was conducted immediately after the measurement of body weight and weight bags and the researcher talked with all the students involved. It was concluded that the primary factor that made the bags so heavy was carrying unnecessary didactic material; the timetable was always defined, but its implementation was not always to the plan. Ultimately, we always have to think about the future growth and development of our children. Pau et al. (2010) analyzed the foot pressure in 359 children attending primary school (6-10 years of age) in a static upright posture, in order to assess the size and features that impact stemming from the relationship between the load and the foot of the substrate. The data collected showed that the school bag had a significant increase in the total reliance on the surface (10%) and that the pressure was greater on the front of the foot (20-30%). A significant shift in the average position of the feet from the pressure centre towards the front of the foot was an indication of where the body tried to compensate for its stability at an excessive load. These results suggest that heavy burden increases the risk of foot deformities and acts as an important factor in the occurrence of changes in the structure of the foot. Kellis (2001) conducted a study where the aim was to examine the pressure distribution of the body weight on the foot in preschool boys with upright posture, during lowering and walking. Fourteen healthy boys performed five activities (standing on one leg, standing on both feet, landing in a squat on one and both legs and walking) on the platform of Musgrave system. Eight points of view were considered in analyzing the results taken: analysis of variance (ANOVA) shows that, in total, the pressure of the foot during the descent was significantly higher compared to the total pressure developed during standing on one leg or both legs and the contact during walking (p<0.05). Multivariate analysis of variance showed that the foot pressures were significantly greater during the descent on the other point of view and walking compared with pressures while standing on both legs (p<0.05). Standing and walking phases were not entirely important positions in this observation. The aim of this study was to determine whether there were differences in body posture in children attending an extended stay (breakfast club and after school club) and those children who do not, but go to school and carry their bag every day, in order to highlight the problem and assist in their healthy growth and development. Material & methods The study included 134 students in years 1-3. The respondents were observed within the first, second and third year, those attending an extended stay and those who did not. The first class included 45 children, 26 of whom were attending an extended stay and 19 who did not. The second class included 42, 18 of which attended an extended stay and 24 did not. The third class included 47 children, 34 of them attended an extended stay and 13 who did not attend. Subsample of children attending an extended stay within each class were not wearing school bags and had daily physical activity within the 2 hours of afternoon rest. The students needed their parents approval for participating in this study and signed 136
3 M. Milardović et al. agreement was needed for performing further measurements as well as their approval for their children s photographs to be taken and used in this study. In order to determine the postural stability four variables had to be considered. Variable BODTIL shows the anterior or posterior tilt of the body in relation to gravity line which is estimated by taking pictures of posture and angle of inclination of the line, using computer program PostureZone Analyser Version ( Phillip Geary DC, MSc ). The following three variables were estimated by tensiometric platform Footscan( RsScan, Inc., UK): ANT% - the percentage of body gravity is distributed anterior to the point of projection of the body center of gravity on the surface of the support of the respondents. The value is expressed in percentages and the total percentage is 100%; it refers to the sum of the values of two variables ANT% and POS%. POS% - the percentage of body gravity is distributed posterior to the point of projection of the body center of gravity on the surface of the support of the respondents. The value is expressed in percentages and the total percentage is 100%; it refers to the sum of values of two variables %ANT and %POS. PCTT - distance travelled point projection of the center of gravity in the area of support, expressed in millimetres (mm). Data collection was carried out within one working day and 134 school children from years 1-3 took part. Children were arranged in different subcategories according to whether they attended an extended stay in school or not. It is important to note that the measurement was performed at the end of the school year when the children were already adjusted to school regime (carrying a school bag). Measuring indicators of body posture was performed by an assessor who set markers at specific points of the body in the sagittal review, another surveyor carried out picture taking and the third performed analysis using the platform of Footscan, ( RsScan, Inc., UK) recording within 3 seconds, setting foot parallel to the platform in a calm and relaxed attitude. Photography was done in the sagittal examination by placing markers in order from head to toe, to very specific areas of the body, using method of photography analysis of subjects within the computer software Posture Zone Analyser Version (Phillip Geary DC, MSc), which proved to be highly reliable (Paušić, 2010). After all the children had been measured and the data stored, the processing of the obtained data started. The data processing began by analyzing photos of the children within the computer software PostureZone Analyser Version (Phillip Geary DC, MSc). For each photo the assessors have set lines that match the description of the variables obtained. In this way, six reference lines were detected and for this study the line that represented the deviation of body posture towards gravity line was taken as the reference (representative) line. The results of reference lines were entered into the matrix of data, which were subsequently processed in the statistical program Statistica 7.0 (StatSoft, Inc. 2004). Then, they analyzed the data obtained on the platform of Footscan (RsScan, Inc. UK) and for each of the children were taken three data (anterior ANT and posterior POS percentage of the body mass centre distributed from the point of projection on the surface of the respondent s palm and the distance travelled from the point of projection of the body mass line within the area of support, expressed in millimetres, PCTT). The results were analyzed by descriptive statistics and the following values were obtained: AS - mean, SD - standard deviation, min. - Minimum score, max. - the maximum score and histogram display for all reference points. The Kolmogorov - Smirnov normality test was used and it showed the following parameters: d max - p - MANOVA - a test that compares the independent categorical variables and more continuous dependent variables, most often used for comparison of several groups with respect to the more continuous variables. Results and Discussion Kolmogorov - Smirnov test indicated the assessment of normal distribution of all measurement tests and, except in the third variable PCTT class (the distance travelled based on body mass) which were not normally distributed variables, did not deviate significantly from the normal distribution, because the greatest discrepancies between the theoretical and the cumulative proportion (D max) were lower than limits of deviation (0.23). These results indicated the relevance of the tests. The data obtained were transformed into descriptive statistics in order to obtain the basic values of the actual situation. Within the subsample of subjects in all years, the biggest difference between the subsample of children attending an extended stay and those who did not attend, was found inside PCTT variables (the distance travelled based on body mass). The position of the projection of the body mass centre, for the children in Year 1 who did not attend an extended stay, at a standstill, was 80 mm, while the children who attended the extended stay was 39 mm. The other parameters of postural stability were not significantly different. In the subsample of children attending Year 2 and subsample of children who did not attend extended stay, 137
4 DIFFERENCES IN BODY POSTURE AND BALANCE average value of the projection of the body mass centre was significantly different from the subsample of children attending an extended stay. It was 91mm for the children who did not and 32mm for the children who attended an extended stay. The other three indicators were not significantly different. In the children in Year 3, statistically significant differences were also found between the subsample of children who attended and those children who did not attend an extended stay, in PCTT variables as in previous school years. The indicator value of postural stability in the subsample who attended extended stay was 38mm while in the subsample who did not attend was 73mm. All variables between the subsample of children who attended and those who did not attend an extended stay were taken as a collective assessment of postural stability. According to multivariate analysis of variance, the two subsamples were statistically different in PCTT variable, while others contributed to it (Table 1). Table 1. Multivariate analysis of the variables indicators in postural stability in children in Year 1, within the subsample of children who attended and those who did not attend extended stay (school hours including breakfast and after school club Regular stay n=19 Extended stay n=25 AS Min Max SD AS Min Max SD F p PCTT 80,61 58,00 122,00 17,26 39,29 21,00 133,00 27,18 33,531 0,000 %ANT 36,53 20,00 60,00 13,02 35,92 19,00 48,00 7,95 0,321 0,574 %POS 61,37 32,00 80,00 14,69 64,08 52,00 81,00 7,95 0,003 0,956 NAGTIJ -1,72-3,40-0,60 0,93-1,56-2,90-0,20 0,72 0,421 0,519 Wilks'λ = F = DF1 = 4 df2 = 38 p = On the basis of Table 1, subsamples of respondents (children attending and not attending an extended stay) were significantly different in all postural indicators in Year 1. There was also a statistically significant difference (p) variables within PCTT subsample of children in Year 2 in those who attended and the ones who did not attend extended stay, while within the variable ANT%, POS% and BODTIL, there was no statistically significant difference. Subsamples of respondents (the children attending and not attending an extended stay) were statistically, significantly different in all postural indicators in Year 2 (Table 2). Table 2. Multivariate analysis of the variables indicate postural stability in children in Year 2, within the subsample of children who attended and those who did not attend extended stay (school hours including breakfast and after school club). Regular stayn=24 Extended stay n=18 F p AS Min Max SD AS Min Max SD PCTT 91,75 73,00 128,00 14,71 32,44 20,00 64,00 11,61 199,07 0,000 %ANT 36,29 19,00 60,00 11,58 39,33 11,00 55,00 11,18 0,731 0,397 %POS 63,71 40,00 81,00 11,58 60,67 45,00 89,00 11,18 0,732 0,398 NAGTIJ -2,30-4,90 0,90 1,32-2,28-7,80-0,20 1,68 0,011 0,974 Wilks'λ=0,159 F=66,57 df1=3 df2=38 p=0,000 Table 3 also confirmed the same significant difference within the subsample of children in Year 3 between the children who attend and those who do not attend extended stay in PCTT variables. Subsamples of respondents (children attending and not attending an extended stay) are statistically significantly different in all postural indicators in Year
5 M. Milardović et al. Table 3. Multivariate analysis of the variables indicate postural stability in children in Year 3, within the subsample of children who attended and those who did not attend extended stay (school hours including breakfast and after school club). PCTT %ANT %POS NAGTIJ Regular stayn=13 Extended stay n=33 F p AS Min Max SD AS Min Max SD 73,58 61,00 90,00 10,07 38,28 22,00 111,00 23,65 5,280 0,026 44,62 21,00 69,00 14,96 42,52 22,00 73,00 11,85 0,252 0,617 55,38 31,00 79,00 14,96 57,48 27,00 78,00 11,85 0,252 0,617-2,31-4,00 0,20 1,19-2,54-6,20-0,20 1,24 0,323 0,572 Wilks'λ=0,502 F=13,2 df1=3 df2=40 p=0,000 Through the subsample of children who attend all the three years, the same crucial statistical indicator of postural stability (PCTT) appears. All children after Year 3, cease to be entitled to the extended stay in Croatia. The research was performed in Year 4 in the same school, but is not taken as a direct sub sample in this study. It is interesting to note that the average value of the projection center of the body mass, as a common value of the children attending and those not attending an extended stay was 79. From this, stems the conclusion that in children who have not entered the system of extended stays in school, this parameter is weaker. It should longitudinally follow and record children who start the system, in order to assess the speed of weakening their postural stability. The results of descriptive statistics showed dominantly better postural stability in a group of extended stay, because they were not subject to the additional load (carrying a school bag). Subsamples of respondents (children who attended and those who did not attend extended stay) were statistically significantly different in all postural parameters. Conclusions Children who were in the system of extended stay had better postural stability. School bags present quite a heavy load, in addition to carrying unnecessary didactic material, which first weakens postural stability and later on, causes bigger deformities. In Croatia, the children from the extended stay after Year 3 join the regular school system. This study showed statistically significant differences in the subsample of children who attend school, but do not attend an extended stay, in the variable projection of the center of body mass (for Year 1 and 2-100% and in Year 3-98%). The conclusion is that there is a great need for the continuation of extended stay in our system of education even after Year 3, which would lead to improving the health status and functional problems in children. Acknowledgements Research was conducted in collaboration with the Agency for Education of Republic of Croatia and Primary School Spinut in Split. References: Fošnarič, S., & Delčnjak Smrečnik, I. (2007). Physical overburdening of pupils with the weigh of school bags during the period of passing from eight year primary school to nine year primary school. Informatologia, 40(3), Kellis, E. (2001). Plantar pressure distribution during barefoot standing, walking and landing in preschool boys. Gait and Posture 14 (2001) Pau, M., Corona, F., Leban, B., Pau, M. (2010). Effects of backpack carriage on foot ground relationship in children during upright stance. Gait & Posture 33 (2011) Paušić, J. (2005). Procjenepromjenetjelesnogdržanjaudjece životnedobiodsedam do devet godina. Magistarski rad. Kineziološki fakultet, Sveučilišta u Zagrebu, Zagreb. Paušić, J. (2007). Konstrukcija i vrednovanje mjernih postupaka za procjenu tjelesnog držanja u dječaka dobi od 10 do 13 godina. Doktorska disertacija. Kineziološki fakultet Sveučilišta u Zagrebu. Paušić, J., Kujundžić, H. (2008). Težina školske torbe u djece razredne nastave. U B. Maleš (ur.), Proceedings of the 3 nd International Conference Contemporary Kinesiology, Mostar, (str ). Split: Kineziološki fakultet. Paušić, J., Kujundžić, H., Mihalj, N. (2009). Povezanost bolnog sindroma kralješnice i težine školske torbe u djece razredne nastave. U B. Neljak (ur.), Zbornik radova 18. Ljetne škole kineziologa Republike Hrvatske, Poreč, (str ). Zagreb: Hrvatski kineziološki savez. Paušić, J., Pedišić, Z., Dizdar, D. (2010). Reliability of a photographic method for assessing standing posture of elementary school students. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics, 33 (6),
6 DIFFERENCES IN BODY POSTURE AND BALANCE Corresponding Author Biljana Kuzmanić, PhD student Faculty of Kinesiology, Split, Croatia,
POSTURAL STATUS MODEL YOUNGER SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN (Preliminary communication)
 120 Activities in Physical Education and Sport 2014, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp.120-124 POSTURAL STATUS MODEL YOUNGER SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN (Preliminary communication) Dejan Ilić and Saša Đurić University of Belgrade,
120 Activities in Physical Education and Sport 2014, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp.120-124 POSTURAL STATUS MODEL YOUNGER SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN (Preliminary communication) Dejan Ilić and Saša Đurić University of Belgrade,
POSTURE ANALYSIS. What is good posture?
 POSTURE ANALYSIS What is good posture? Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing or sitting. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit
POSTURE ANALYSIS What is good posture? Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing or sitting. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit
WHY BASIC HIP FLEXOR STRETCHES DON'T ALWAYS WORK
 WHY BASIC HIP FLEXOR STRETCHES DON'T ALWAYS WORK Do you do a daily stretching routine only to find that your muscles tighten back up throughout the day? Do you continue to stretch your hamstrings but still
WHY BASIC HIP FLEXOR STRETCHES DON'T ALWAYS WORK Do you do a daily stretching routine only to find that your muscles tighten back up throughout the day? Do you continue to stretch your hamstrings but still
DB HAMMER CURL: 1-LEG SUPPORTED ALT- ARM + ISO-HOLD
 DB HAMMER CURL: 1-LEG SUPPORTED ALT- ARM + ISO-HOLD The single-leg supported alternating-arm DB hammer curl with iso-hold requires you to maintain a stable position on one leg while performing a biceps
DB HAMMER CURL: 1-LEG SUPPORTED ALT- ARM + ISO-HOLD The single-leg supported alternating-arm DB hammer curl with iso-hold requires you to maintain a stable position on one leg while performing a biceps
Quads (machines) Cable Lunge
 Cable Lunge Cable Lunge 1) Stand with feet hip width apart and a cable attached around your waist. Take left leg and step back approximately 2 feet standing on the ball of the foot. 2) Start position:
Cable Lunge Cable Lunge 1) Stand with feet hip width apart and a cable attached around your waist. Take left leg and step back approximately 2 feet standing on the ball of the foot. 2) Start position:
Posture. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE
 UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE 1. WHY IS POSTURE IMPORTANT? The term posture is used to describe how your body is positioned when you're sitting, standing and lying down. Proper posture is important
UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE 1. WHY IS POSTURE IMPORTANT? The term posture is used to describe how your body is positioned when you're sitting, standing and lying down. Proper posture is important
Lower Body. Exercise intensity moderate to high.
 Lower Body Lower Body Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goals of strengthening the lower body. Along with increasing strength of the leg muscles this workout will
Lower Body Lower Body Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goals of strengthening the lower body. Along with increasing strength of the leg muscles this workout will
ORTOVOX NAKED SHEEP EXERCISES TRAINING SESSION 1
 TRAINING SESSION OPEN DOORS DESCRIPTION PICTURE PICTURE PICTURE COUCH STRETCH Bring your knee as close as possible to the wall and straighten upper body backward; you need to be able to activate your glutes
TRAINING SESSION OPEN DOORS DESCRIPTION PICTURE PICTURE PICTURE COUCH STRETCH Bring your knee as close as possible to the wall and straighten upper body backward; you need to be able to activate your glutes
The BioMechanics Method
 The BioMechanics Method EXERCISE SOLUTIONS FOR CHRONIC PAIN The Fundamentals of Structural Assessment End of Section Self-Check There are many things that can make conducting a structural assessment more
The BioMechanics Method EXERCISE SOLUTIONS FOR CHRONIC PAIN The Fundamentals of Structural Assessment End of Section Self-Check There are many things that can make conducting a structural assessment more
CERTIFIED WEIGHTLIFTING PERFORMANCE COACH. Notebook THE SQUAT
 CERTIFIED WEIGHTLIFTING PERFORMANCE COACH Notebook THE SQUAT THE SQUAT Squatting as a part of Olympic weightlifting cannot be overlooked. It will be a large part of any good training program, but also
CERTIFIED WEIGHTLIFTING PERFORMANCE COACH Notebook THE SQUAT THE SQUAT Squatting as a part of Olympic weightlifting cannot be overlooked. It will be a large part of any good training program, but also
Inside or Outside you can get it done
 Inside or Outside you can get it done April 21, 2008 An understanding of Strength The definition of strength usually pertains to an amount of force that can be produced maximally by muscles in a single
Inside or Outside you can get it done April 21, 2008 An understanding of Strength The definition of strength usually pertains to an amount of force that can be produced maximally by muscles in a single
BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES
 63 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES Rafael F. Escamilla, Tracy M. Lowry, Daryl C. Osbahr, and
63 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES Rafael F. Escamilla, Tracy M. Lowry, Daryl C. Osbahr, and
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions
 Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist. Concept ENGSTRÖM
 FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
Home Workout with Household Items
 Home Workout Home Workout with Household Items Introduction This home routine is created for women and men to workout while they are at home. It incorporates the use of household items to imitate weights
Home Workout Home Workout with Household Items Introduction This home routine is created for women and men to workout while they are at home. It incorporates the use of household items to imitate weights
Weight Loss Interval (Beginner)
 Program for BP Fitness Center Introduction Weight Loss Interval (Beginner) This is a full body interval workout. Keep your heart rate up to safe levels by not resting between exercises. Please workout
Program for BP Fitness Center Introduction Weight Loss Interval (Beginner) This is a full body interval workout. Keep your heart rate up to safe levels by not resting between exercises. Please workout
Posture. Posture Evaluation. Good Posture. Correct Posture. Postural Analysis. Endomorphs
 Posture Posture Evaluation Martha Macht Sliwinski PT PhD The alignment and positioning of the body in relation to gravity, center of mass and base of support The physical therapist uses posture tests and
Posture Posture Evaluation Martha Macht Sliwinski PT PhD The alignment and positioning of the body in relation to gravity, center of mass and base of support The physical therapist uses posture tests and
Hip Flexor Stretch. Glute Stretch. Hamstring stretch
 STATIC FLEXIBILITY STRETCHES Hip Flexor Stretch If the iliopsoas is tight, back pain may be present. Extended periods of the seated position can harbor tight hip flexors. Be sure to have a mat or towel
STATIC FLEXIBILITY STRETCHES Hip Flexor Stretch If the iliopsoas is tight, back pain may be present. Extended periods of the seated position can harbor tight hip flexors. Be sure to have a mat or towel
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL
 ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Functional Movement Test. Deep Squat
 Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Side Split Squat. The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time
 GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
TPW 's Upper Back Menu
 TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
Norfolk Public Schools: Back Safety in the Workplace. By: Arianne Conley RN, BSN
 Norfolk Public Schools: Back Safety in the Workplace By: Arianne Conley RN, BSN arianneconley@yahoo.com Back Safety & Lifting Training Objectives: Risk Factors - Occupational Back Injury Prevention Principles
Norfolk Public Schools: Back Safety in the Workplace By: Arianne Conley RN, BSN arianneconley@yahoo.com Back Safety & Lifting Training Objectives: Risk Factors - Occupational Back Injury Prevention Principles
anchor point. Essentially, the more the body is parallel to the floor, the more difficult the exercise. The third set of pictures shows two common
 ST BOWLER SQUAT The bowler squat performed with a suspension trainer is a great little single leg squat/hinge combo! The suspension trainer assists with balance and I believe makes the exercise more effective.
ST BOWLER SQUAT The bowler squat performed with a suspension trainer is a great little single leg squat/hinge combo! The suspension trainer assists with balance and I believe makes the exercise more effective.
Dynamic slings and optimal 3D function
 Dynamic slings and optimal 3D function Abstract Trish Wisbey-Roth Olympic/Specialist Sports Physiotherapist (FACP), Masters of Sport Physiotherapy (AIS/UC) Active Rehabilitation Consultant Layered over
Dynamic slings and optimal 3D function Abstract Trish Wisbey-Roth Olympic/Specialist Sports Physiotherapist (FACP), Masters of Sport Physiotherapy (AIS/UC) Active Rehabilitation Consultant Layered over
POSTURAL ANALYSIS. Posture is the attitude of the body. Good Posture = maximum efficiency with minimum effort
 POSTURAL ANALYSIS A Postural Analysis should be undertaken on a client prior to each occasion a treatment is performed. It can vary from an extensive total body analysis to just a specific problem area.
POSTURAL ANALYSIS A Postural Analysis should be undertaken on a client prior to each occasion a treatment is performed. It can vary from an extensive total body analysis to just a specific problem area.
Osteoporosis Exercise:
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
BeBalanced! total body training
 BeBalanced! von Manuela Böhme made in switzerland 1 sponsored by As a therapy and training device, the AIREX Balance-pad Elite covers a large spectrum of possible applications. Thanks to its destabilising
BeBalanced! von Manuela Böhme made in switzerland 1 sponsored by As a therapy and training device, the AIREX Balance-pad Elite covers a large spectrum of possible applications. Thanks to its destabilising
Older Adult Advanced
 Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
DEEP SQUAT. Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet
 APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Sportlyzer s Core Exercises
 Sportlyzer s Core Exercises Core training exercises are as important part of your training schedule as your endurance training. You need it to support your everyday running and improve your racing results.
Sportlyzer s Core Exercises Core training exercises are as important part of your training schedule as your endurance training. You need it to support your everyday running and improve your racing results.
Older Adult Beginner
 Older Adult Beginner Older Adult - Beginners Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women over the age of 55. These individuals may have joint pain, muscular pain, new to a workout routine,
Older Adult Beginner Older Adult - Beginners Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women over the age of 55. These individuals may have joint pain, muscular pain, new to a workout routine,
NDIPE Dictionary of Visual Terms
 NDIPE Dictionary of Visual Terms One of the challenges of the indoor activity is knowing terms used by the staff and fellow members. As a potential member of the NDIPE, you are expected to have a firm
NDIPE Dictionary of Visual Terms One of the challenges of the indoor activity is knowing terms used by the staff and fellow members. As a potential member of the NDIPE, you are expected to have a firm
Chicago Chiropractic & Sports Injury Centers Dr. Alden Clendenin DC, CCSP
 Cervical Lordotic Traction The soft forward [lordotic] curve at the middle of the cervical spine is critical as a shock absorber for the full weight of the head. Loss of cervical lordosis, often called
Cervical Lordotic Traction The soft forward [lordotic] curve at the middle of the cervical spine is critical as a shock absorber for the full weight of the head. Loss of cervical lordosis, often called
Top 35 Lower Body Exercises
 Top 35 Lower Body Exercises Calf Raise - Single Leg Stand on one leg, toes on edge of box Ankle hanging below toes Hold something for support Lift & lower body by extending the ankle of the stance leg
Top 35 Lower Body Exercises Calf Raise - Single Leg Stand on one leg, toes on edge of box Ankle hanging below toes Hold something for support Lift & lower body by extending the ankle of the stance leg
THE GREAT EIGHT. Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13
 THE GREAT EIGHT Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13 ABOUT THE GREAT EIGHT Exercises that is! Eight GREAT exercises. By now you should have opened your Master Trainer elog Book (see Welcome section)
THE GREAT EIGHT Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13 ABOUT THE GREAT EIGHT Exercises that is! Eight GREAT exercises. By now you should have opened your Master Trainer elog Book (see Welcome section)
Board Positions. Skill progression from beginner to advanced: 2 Half Balls 1 Half Ball 1 Half Ball and 1 Ball 2 Balls 1 Ball
 Feet facing forward on bolts General athletic stance for pushing and pulling Feet facing at an angle Movement transition for rotational and agility Wide in-line stance Simulate forward weight shift running
Feet facing forward on bolts General athletic stance for pushing and pulling Feet facing at an angle Movement transition for rotational and agility Wide in-line stance Simulate forward weight shift running
2017 COS ANNUAL MEETING AND EXHIBITION HOME EXERCISES
 UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
9 PROGRESSED YOGA HIP
 MY ACEACCOUNT ACE Professional ResourcesExpert Articles9 Progressed Yoga Hip Opener Postures 9 PROGRESSED YOGA HIP OPENER POSTURES /2/2015 Yoga is an ideal form of exercise to open tight and stiff hips.
MY ACEACCOUNT ACE Professional ResourcesExpert Articles9 Progressed Yoga Hip Opener Postures 9 PROGRESSED YOGA HIP OPENER POSTURES /2/2015 Yoga is an ideal form of exercise to open tight and stiff hips.
Ergonomics: Optimizing human well-being & system performance
 Ergonomics: Optimizing human well-being & system performance Protecting your back is not a luxury When you re healthy you can participate and enjoy life Leisure activities-enjoy going for a run Household
Ergonomics: Optimizing human well-being & system performance Protecting your back is not a luxury When you re healthy you can participate and enjoy life Leisure activities-enjoy going for a run Household
Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture
 Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture Sitting: weight of the body is transferred to a supporting area 1.Main Contact points (seat) Ischial tuberosities Soft tissues 2. Secondary contact points (other)
Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture Sitting: weight of the body is transferred to a supporting area 1.Main Contact points (seat) Ischial tuberosities Soft tissues 2. Secondary contact points (other)
An overview of posture
 An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
Pilates for Runners: Core Strength and Flexibility for Increased Efficiency and Injury Prevention
 Pilates for Runners: Core Strength and Flexibility for Increased Efficiency and Injury Prevention Helen Buehler 9/20/15 Flow Studio // Chicago // 2015 Running is the most natural and accessible form of
Pilates for Runners: Core Strength and Flexibility for Increased Efficiency and Injury Prevention Helen Buehler 9/20/15 Flow Studio // Chicago // 2015 Running is the most natural and accessible form of
Posture and Body Mechanics
 Posture and Body Mechanics Making a difference in people s lives Probility Physical Therapy Posture and Body Mechanics Table of Contents LIFTING Correct Lifting Posture... 2 Lifting Objects The Half Kneel
Posture and Body Mechanics Making a difference in people s lives Probility Physical Therapy Posture and Body Mechanics Table of Contents LIFTING Correct Lifting Posture... 2 Lifting Objects The Half Kneel
Quads (medicine ball)
 Saggital Front Reach Saggital Front Reach 1) Start position: Stand with feet hip width apart. Hold medicine ball or dumbbell at waist. 2) Step forward 2-3 feet with the heel striking first and lean torso
Saggital Front Reach Saggital Front Reach 1) Start position: Stand with feet hip width apart. Hold medicine ball or dumbbell at waist. 2) Step forward 2-3 feet with the heel striking first and lean torso
Transformational Posture for a healthier back. Evolution of corrective training Leslee Bender
 Transformational Posture for a healthier back Evolution of corrective training Leslee Bender Our society Low back injuries and pain costs us $$$ healthcare Most postural problems are due to injuries in
Transformational Posture for a healthier back Evolution of corrective training Leslee Bender Our society Low back injuries and pain costs us $$$ healthcare Most postural problems are due to injuries in
Mindful yoga for stress movement practice
 Mindful yoga for stress movement practice The following sequence is more or less what we practised in the workshop. You can do it all if you have time, or if you just have a few minutes do one or two poses
Mindful yoga for stress movement practice The following sequence is more or less what we practised in the workshop. You can do it all if you have time, or if you just have a few minutes do one or two poses
Avoiding Discomfort and Injury in Young String Players:
 Avoiding Discomfort and Injury in Young String Players: A Stretching Activity Guide by Joshua Russell and Paul Higgins String educators are becoming increasingly aware of the health and wellness issues
Avoiding Discomfort and Injury in Young String Players: A Stretching Activity Guide by Joshua Russell and Paul Higgins String educators are becoming increasingly aware of the health and wellness issues
Static Back. Instructions: Purpose: Hold this ecise for 05 min. prepared for Pain Free Posture MN
 1 Static Back Hold this ecise for 05 min. 1. Lie on your back with your legs up over a block or chair 2. Place your arms out to the sides at 45 degrees from your body with palms up 3. Relax your upper
1 Static Back Hold this ecise for 05 min. 1. Lie on your back with your legs up over a block or chair 2. Place your arms out to the sides at 45 degrees from your body with palms up 3. Relax your upper
A B C. Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow
 Session Two A B C Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow Will be based on your group of participants. Ensure that your lesson plan content links to objectives What is the reason for prep?
Session Two A B C Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow Will be based on your group of participants. Ensure that your lesson plan content links to objectives What is the reason for prep?
Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design
 PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts
 The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts Assessment details NAME D.O.B. DIAGNOSIS DATE OF ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT CENTRE NAME OF ASSESSOR Notes CHAILEY HERITAGE CLINICAL SERVICES Beggars Wood Road
The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts Assessment details NAME D.O.B. DIAGNOSIS DATE OF ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT CENTRE NAME OF ASSESSOR Notes CHAILEY HERITAGE CLINICAL SERVICES Beggars Wood Road
VIPR and Power plate EXERCISE - 1 EXERCISE Fitness Professionals Ltd 2011 Job No. 2968
 FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint
 Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
Presuming all the above symptoms are not present, pain is more likely to be mechanical and caused by a sprain, strain or poor posture.
 Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR.
 Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
Connecting the Core. Rationale. Physiology. Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS. Athletes have been inundated with terminology
 Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Snow Angels on Foam Roll
 Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back
 the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
PREPARED FOR. Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016. REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr.
 Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
Michelle Felzmann Page 1
 Functional Fascia for Group Fitness Presented By: Michelle Felzmann Let's get out of our box in group fitness and try something new! Learn new exercise sequences that are designed to train the fascial
Functional Fascia for Group Fitness Presented By: Michelle Felzmann Let's get out of our box in group fitness and try something new! Learn new exercise sequences that are designed to train the fascial
THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE
 THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE Postural Tips To Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence BY DR. AARON LEBAUER, PT, DPT 2 P a g e Disclaimer The information in this book is not a replacement
THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE Postural Tips To Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence BY DR. AARON LEBAUER, PT, DPT 2 P a g e Disclaimer The information in this book is not a replacement
Evaluating Fundamental
 12 Locomotor Lab 12.1 Evaluating Fundamental Skills Purpose Practice in learning to observe and evaluate locomotor skills from video performance. Procedures Listed below are several websites showing children
12 Locomotor Lab 12.1 Evaluating Fundamental Skills Purpose Practice in learning to observe and evaluate locomotor skills from video performance. Procedures Listed below are several websites showing children
The core of the MIHP Think Tank message is based around Five (5) Key Facts About Your Body s Design:
 Lesson 1 THE FIVE KEY FACTS ABOUT YOUR BODY S DESIGN The design of the human body is so complete, so complex in its interrelationships, so prepared for its world of motion that it allows for its function
Lesson 1 THE FIVE KEY FACTS ABOUT YOUR BODY S DESIGN The design of the human body is so complete, so complex in its interrelationships, so prepared for its world of motion that it allows for its function
Posture and balance. Center of gravity. Dynamic nature of center of gravity. John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017
 Posture and balance John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017 Center of gravity The center of gravity (COG) of the human body lies approximately at the level of the second sacral vertebrae (S2), anterior to
Posture and balance John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017 Center of gravity The center of gravity (COG) of the human body lies approximately at the level of the second sacral vertebrae (S2), anterior to
GFM Platform Exercise Manual
 GFM Platform Exercise Manual STEPHEN NEWHART, CSCS*D What is Whole Body Vibration? Body vibration is delivered through a variety of machines, including the most recent inclusion of whole body vibration
GFM Platform Exercise Manual STEPHEN NEWHART, CSCS*D What is Whole Body Vibration? Body vibration is delivered through a variety of machines, including the most recent inclusion of whole body vibration
American Council on Exercise
 American Council on Exercise February 23, 2015 Fitnovatives Blog Exercise Progressions for Clients Who Are Overweight or Are Affected by Obesity While there is no single right way to train clients who
American Council on Exercise February 23, 2015 Fitnovatives Blog Exercise Progressions for Clients Who Are Overweight or Are Affected by Obesity While there is no single right way to train clients who
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed.
 Session 1 Details Cardio - Choose one of the following Elliptical Slow to Moderate Cardio Intervals (1) Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed. Treadmill
Session 1 Details Cardio - Choose one of the following Elliptical Slow to Moderate Cardio Intervals (1) Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed. Treadmill
2002 Physioball Supplement
 2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
Body Mechanics--Posture, Alignment & Core
 Body Mechanics--Posture, Alignment & Core Proper Alignment Proper body alignment allows you to safely perform different tasks throughout the day, and to do so in a way that does not require you to exert
Body Mechanics--Posture, Alignment & Core Proper Alignment Proper body alignment allows you to safely perform different tasks throughout the day, and to do so in a way that does not require you to exert
How To Achieve Your Best Plumb Line
 How To Achieve Your Best Plumb Line Created by Allison Oswald DPT, WCS, CPT Doctor of Physical Therapy Women s Certified Specialist Certified Pilates Teacher & Owner of Plumb Line Pilates and Physical
How To Achieve Your Best Plumb Line Created by Allison Oswald DPT, WCS, CPT Doctor of Physical Therapy Women s Certified Specialist Certified Pilates Teacher & Owner of Plumb Line Pilates and Physical
Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique.
 Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique. Lying on back: Hip Crossover: Arms out in T position, feet flat on the floor, knees
Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique. Lying on back: Hip Crossover: Arms out in T position, feet flat on the floor, knees
Preventative Exercises for the Achilles
 Preventative Exercises for the Achilles Outline 1. Toe walk x 15 each foot 2. Feet out walk x 15 each foot 3. Feet in walk x 15 each foot 4. Ankle in walk x 10 each foot 5. Ankle out walk x 10 each foot
Preventative Exercises for the Achilles Outline 1. Toe walk x 15 each foot 2. Feet out walk x 15 each foot 3. Feet in walk x 15 each foot 4. Ankle in walk x 10 each foot 5. Ankle out walk x 10 each foot
20/40 Yard Dash. Mile Run/Walk
 Objective Testing In addition to the Functional Movement Test, which offers subjective evaluation of a range of movement skills, Learn to Move Academy suggests an objective testing component to obtain
Objective Testing In addition to the Functional Movement Test, which offers subjective evaluation of a range of movement skills, Learn to Move Academy suggests an objective testing component to obtain
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual
 Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Ergonomics Seminar. Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller
 Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
Follow the instructions below and students will be moving in no time: 1. Utilize the hallways for an indoor fitness trail.
 indoor Fitness breaks Indoor physical activity is a challenge for many schools. Winter weather can trap students and staff inside for months at a time. Lack of space and lack of time also contribute to
indoor Fitness breaks Indoor physical activity is a challenge for many schools. Winter weather can trap students and staff inside for months at a time. Lack of space and lack of time also contribute to
Lower Extremity Physical Performance Testing. Return to Function (Level I): Core Stability
 Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
PILATES AS A TOOL TO AID IN THE TREATMENT OF MILD TO
 PILATES AS A TOOL TO AID IN THE TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATE SCOLIOSIS BETH NICKS FEBRUARY 16, 2014 SANTA BARBARA 2013-2014 ABSTRACT: Scoliosis is a spinal condition characterized by the appearance of
PILATES AS A TOOL TO AID IN THE TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATE SCOLIOSIS BETH NICKS FEBRUARY 16, 2014 SANTA BARBARA 2013-2014 ABSTRACT: Scoliosis is a spinal condition characterized by the appearance of
National Strength Program for Young Players
 Australian Baseball Federation National Strength Program for Young Players A critical foundation of Long Term Athletic Development Introduction These circuits are designed to build some basic strength,
Australian Baseball Federation National Strength Program for Young Players A critical foundation of Long Term Athletic Development Introduction These circuits are designed to build some basic strength,
Today s session. Common Problems in Rehab. Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist. physiofitness.com.au facebook.
 Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist physiofitness.com.au facebook.com/physiofitness Today s session Essential list for the lower body Rehab starting point Focussing on activation,
Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist physiofitness.com.au facebook.com/physiofitness Today s session Essential list for the lower body Rehab starting point Focussing on activation,
Copyrighted Material. Do not duplicate.
 THAT IS THE EASY PART Copyrighted Material. Do not duplicate. JOHN TSCHIDA - UNIVERSITY OF ST. THOMAS HITTING Our Goal in Hitting: Consistently Achieve Maximum Force with Minimal Effort!! 1) Force: Bat
THAT IS THE EASY PART Copyrighted Material. Do not duplicate. JOHN TSCHIDA - UNIVERSITY OF ST. THOMAS HITTING Our Goal in Hitting: Consistently Achieve Maximum Force with Minimal Effort!! 1) Force: Bat
DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam
 DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam 1. What is NOT a concept or training principle of the DVRT System? A. Addressing specific needs of the client. B. Mixing simplicity with complexity. C. Progressive
DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam 1. What is NOT a concept or training principle of the DVRT System? A. Addressing specific needs of the client. B. Mixing simplicity with complexity. C. Progressive
The Secrets to Good Posture
 The Secrets to Good Posture Postural Tips to Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence Brought to You by Your Therapists at: JOHNS CREEK LOCATION LAWRENCEVILLE LOCATION Tel: 770-623-0105
The Secrets to Good Posture Postural Tips to Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence Brought to You by Your Therapists at: JOHNS CREEK LOCATION LAWRENCEVILLE LOCATION Tel: 770-623-0105
FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREENING TEST
 FUNCTIONA MOVEMENT SCEENING TEST This movement screening test has been developed by Federation University for the use by Sporting Pathway Program staff to indicate athlete competency for injury prevention
FUNCTIONA MOVEMENT SCEENING TEST This movement screening test has been developed by Federation University for the use by Sporting Pathway Program staff to indicate athlete competency for injury prevention
MSE Exercise 1: Box Push Up. Repeat: start with 10 build up to 30 and move to ¾ Push Up
 MSE Exercise 1: Box Push Up Repeat: start with 10 build up to 30 and move to ¾ Push Up Kneel on all fours with the hands a little wider than shoulder width apart. Push your hips forwards so that the weight
MSE Exercise 1: Box Push Up Repeat: start with 10 build up to 30 and move to ¾ Push Up Kneel on all fours with the hands a little wider than shoulder width apart. Push your hips forwards so that the weight
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Lower body modeling with Plug-in Gait
 Lower body modeling with Plug-in Gait This section describes lower body modeling with Plug?in Gait. It covers the following information: Outputs from Plug-in Gait lower body model Marker sets for Plug-in
Lower body modeling with Plug-in Gait This section describes lower body modeling with Plug?in Gait. It covers the following information: Outputs from Plug-in Gait lower body model Marker sets for Plug-in
 Introduction 1/1 To build better athletes, start with the basics. The exercises here may seem familiar, but they represent the foundation on which you will build strength, mobility, speed, and power. And
Introduction 1/1 To build better athletes, start with the basics. The exercises here may seem familiar, but they represent the foundation on which you will build strength, mobility, speed, and power. And
Return to Play/Duty Testing. Robb Rogers CSCS, MSCC
 Return to Play/Duty Testing Robb Rogers CSCS, MSCC Problem: How to determine readiness for return to competition/duty for high speed athletes Cybex testing...? Bar Back Squat...? Single Leg Testing...?
Return to Play/Duty Testing Robb Rogers CSCS, MSCC Problem: How to determine readiness for return to competition/duty for high speed athletes Cybex testing...? Bar Back Squat...? Single Leg Testing...?
Day 1 exercise progressions and key coaching points
 England Athletics movement skills for running, jumping and throwing Day 1 exercise progressions and key coaching points Double leg squat o Feet at hip distance apart and toes turned slightly out if required
England Athletics movement skills for running, jumping and throwing Day 1 exercise progressions and key coaching points Double leg squat o Feet at hip distance apart and toes turned slightly out if required
Flexible Fitness. Kevin J. Kula
 Flexible Fitness Contract/Relax (PNF) Principles Move into stretch so that it is slightly uncomfortable but not painful Contract muscle into resistance: either band or wall/floor on the inhale Move deeper
Flexible Fitness Contract/Relax (PNF) Principles Move into stretch so that it is slightly uncomfortable but not painful Contract muscle into resistance: either band or wall/floor on the inhale Move deeper
Bodycode body-type analysis manual. Skeleton Scan Part. Patent Application Patent Brand Application 바디코드
 Bodycode body-type analysis manual Skeleton Scan Part Patent Application Patent -2016-0007505 Brand Application 바디코드 40-2016-0002444 Contents Ⅰ Front Analysis 3~7p Ⅱ Kneebend Analysis 8~9p Ⅲ Side Analysis
Bodycode body-type analysis manual Skeleton Scan Part Patent Application Patent -2016-0007505 Brand Application 바디코드 40-2016-0002444 Contents Ⅰ Front Analysis 3~7p Ⅱ Kneebend Analysis 8~9p Ⅲ Side Analysis
