Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms
|
|
|
- Kory Hensley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity oral cavity sagittal plane anatomical position frontal plane orbital cavities spinal cavity anatomy metric system pelvic cavity thoracic cavity anterior (ventral) body middle ear cavities physiology transverse plane 1. The stomach, liver, and other parts of the digestive tract are contained in the. 2. The French originated a system of measurements called the in the 1790s. 3. The is situated inside the nose. 4. The study of how living things function or work is called. 5. The surrounds and houses the spinal cord. 6. A continuous internal opening that includes the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities is called the. 7. is the study of the form or structure of all living things, including plants and animals. 8. An invisible vertical line that divides the body into left and right halves is the. 9. The opening inside the skull that holds the brain is the. 10. are found in the skull and act as chambers for transmitting and amplifying sound. 11. When someone is standing erect with arms at the sides and palms facing forward, they are in. 12. The divides the body into front and back halves. 13. The abdominal and pelvic cavities are both found in the. 14. The divides the body into top and bottom halves. 15. The internal opening that holds the reproductive and excretory organs is the. 16. The contains the heart and lungs, among other organs. 17. Openings that hold the eyes are called. 18. A(n) is an open chamber that holds the internal organs of the body. 19. Located near the back of the body, the is a continuous internal opening that includes the cranial and spinal cavities. 20. The is the opening within the mouth.
2 2 Directions: Answer the questions below on a separate sheet of paper. Studying the answers will help you prepare for the chapter test. 1. What do we call the study of the body structures we can see with our eyes? 2. What is the difference between anatomy and physiology? 3. Identify and describe the three invisible planes that divide the human body and how they divide the body. What is the direction of the movements or motions that each plane makes? 4. What are movements that do not occur in a direction of one of the three planes called? 5. Does any structure separate the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity? 6. What is the difference between gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy? 7. What separates the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity? 8. What are the four base units of the metric system? 9. In the metric system, all units (except those for time) relate by factors of 10. Why does this make conversion between units easy? 10. Common directional terms for anatomy are typically paired. Identify three pairs of directional terms. 11. What is the difference between medial and anterior? 12. What is the difference between lateral and deep? 13. What other directional terms can be used in place of anterior and posterior? 14. What is the name of the measurement system used for nonscientific purposes in the United States? 15. What is the name of the cavity located inside the mouth? 16. Which directional term means above or over? Lesson 1.1: Study Questions 17. To which part of the body do the directional terms proximal and distal refer?
3 3 Lesson 1.1: Identifying Body Cavities Directions: Label the figure with the appropriate callouts from the list provided abdominal middle ear orbital spinal cranial nasal pelvic thoracic diaphragm oral
4 4 Lesson 1.2: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. atoms homeostatic imbalance molecules positive feedback cells control center effector homeostasis homeostatic mechanisms metabolic rate metabolism negative feedback organ organ system receptor tissues 1. A(n) includes two or more organs that work together. 2. Collections of similar cells with a common function form. 3. The smallest building blocks of all living beings are. 4. Atoms combine together in different ways to form larger particles known as. 5. A(n) is a body part organized to perform a specific function and is composed of at least two different types of tissue. 6. is the state of regulated physiological balance. 7. Organ systems cooperate to maintain homeostasis through processes called. 8. is the mechanism that reverses a condition that has exceeded the normal homeostatic range and restores homeostasis. 9. further increases a condition that has exceeded the normal homeostatic range. 10. is a condition in which there is a decreased ability for the organ systems to maintain the body s internal environment within normal ranges. 11. The relates to all chemical reactions that occur within an organism to maintain life. 12. A(n) is a transmitter that senses environmental changes. 13. The unit that receives a command stimulus from the control center and causes an action to help maintain homeostasis is called a(n). 14. are tiny particles of matter. 15. The speed at which the body consumes energy is the. 16. The receives and analyzes information from sensory receptors, then sends a command stimulus to an effector to maintain homeostasis.
5 5 Directions: Answer the questions below on a separate sheet of paper. Studying the answers will help you prepare for the chapter test. 1. Which two body systems initiate the majority of the body s homeostatic responses? 2. What three elements do all homeostatic control mechanisms have in common? 3. Does positive feedback increase or decrease disruptive influences? 4. Diabetes can cause homeostatic imbalances, leading to serious side effects. Give at least two examples of the side effects related to homeostatic imbalances in diabetics. 5. What are the four basic types of tissues? 6. What is the primary function of the respiratory system? 7. Which body system pumps the heart and moves the body? 8. What is the name of the tube through which food enters the stomach? 9. Which is part of the cardiovascular system, the brain or the heart? 10. List the structures of the digestive system in the order by which they receive food. 11. What do endocrine glands secrete? Lesson 1.2: Study Questions 12. Identify the main organs and structures of both the male and female reproductive systems. 13. Which disease associated with aging can occur with homeostatic imbalances? 14. What are the two general activities associated with metabolism? 15. How can drinking too much water during activity be dangerous? 16. Name two conditions that can result from inadequate water intake.
6 6 Lesson 1.2: The Human Organ Systems Directions: Match the organ system with its organs and function by writing the appropriate letters next to each organ system. Organs Function 1. Urinary system 2. Cardiovascular system 3. Muscular system 4. Digestive system 5. Endocrine system 6. Integumentary system 7. Sensory system 8. Reproductive systems 9. Lympathic system 10. Skeletal system 11. Respiratory system 12. Nervous system Organs A. layers of skin B. bones, cartilage, ligaments C. cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscle D. brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors E. eyes, ears, organs of smell and taste F. endocrine glands G. lungs, nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea H. heart, blood vessels I. lymphatic vessels and nodes J. esophagus, stomach, intestines K. kidneys, bladder L. testes, scrotum, penis; ovaries, uterus, vagina Function a. breaks down foods for absorption of nutrients by the body b. protects, eliminates waste, helps regulate body temperature c. returns body fluids to the bloodstream d. secretes hormones e. supports body, protects organs, produces blood cells f. enables production of offspring g. enables vision, hearing, smell, and taste h. receives and interprets sensory input, directs body movements, includes memory, emotions, cognition i. removes nitrogen-containing wastes from blood j. transports oxygen and nutrients to the body s cells and removes waste products k. pumps the heart, helps move materials through the digestive tract, moves the body l. delivers oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from blood
7 7 Lesson 1.3: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. bending 2. combined loading 3. compression 4. elastic 5. force 6. kinetics 7. mass 8. net force 9. pressure 10. shear 11. stress 12. tension 13. torque 14. torsion 15. weight A. a force that acts along a surface and perpendicular to the length of a structure B. the simultaneous action of two or more kinds of forces C. force equal to the gravitational acceleration exerted on the mass of an object D. push or pull exerting influence on a structure E. the analysis of the actions of forces F. the rotary effect of a force G. the amount of matter that an object contains H. a response occurring when force is removed and the structure resumes its original shape and size I. the single force that results from the total of all forces acting on a structure at a given time J. force distributed over a certain area K. the distribution of force inside a structure L. a pulling force creating stress in the structure to which it is applied M. a loading pattern that can make a structure twist around its length N. a combination of off-center forces that creates a pattern of loading O. a squeezing force that causes compression in the object absorbing the force
8 8 Directions: Answer the questions below on a separate sheet of paper. Studying the answers will help you prepare for the chapter test. 1. What are three types of directional force distributions that act on the body? 2. The amount of deformation caused by a given force depends upon what factor? 3. Describe how compression and tension differ. 4. What is a chronic, or stress injury? 5. How does the amount of stress created vary between a force acting on a small surface and a force acting over a larger surface? 6. Acceleration and deformation are the two potential effects when a force acts on an object. Describe them. 7. Will a heavier object have greater acceleration than a smaller object? Why or why not? 8. What factors influence whether an injury occurs when an external force is applied to the human body? 9. What does it mean when the body s response to a force is plastic? 10. What kind of injury is an acute injury? 11. How are pressure and stress quantified? 12. How is knowledge of kinetic concepts useful? 13. Which three factors can be used to describe force? 14. Give two examples of forces the human body commonly encounters. 15. What is net force? Lesson 1.3: Study Questions 16. What is the rotary effect of the force called when a force causes a structure to rotate?
9 9 Lesson 1.4: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. scientific method 2. statistical inference 3. scientific theory 4. research question 5. data 6. science 7. statistical significance 8. scientific research hypothesis A. systematically collected and recorded observations B. a question to be answered or a problem to be solved in a research study C. a systematic process that creates new knowledge and organizes it into a form of testable explanations and predictions about an aspect of our universe D. a systematic process that can be used to answer questions or find solutions to problems E. an educated guess about what the outcome of a study will be F. an explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on rigorously tested, repeatedly confirmed research G. the practice of generalizing the findings of a research study to a large population H. an interpretation of statistical data indicating that the results of a study can legitimately be generalized to the population represented in the study sample
10 10 Directions: Answer the questions below on a separate sheet of paper. Studying the answers will help you prepare for the chapter test. 1. What is used to answer questions or find solutions to problems in many scientific fields? 2. Identify the seven steps of the scientific method. 3. What is another term for an educated guess? 4. Measuring height and weight are examples of which type of research? 5. How does experimental research differ from descriptive and comparative research? 6. What are some safety concerns you should consider when conducting research in the lab? 7. What is the difference between a scientific research hypothesis and a scientific theory? 8. What are the two types of data? Lesson 1.4: Study Questions 9. What distinguishes an educated guess versus a hunch or a feeling? 10. What are the five criteria for planning the organization of a study? 11. How can research be evaluated for objectivity? 12. How can a researcher feel confident that statistical inference is accurate for his or her research? 13. In order to derive conclusions from the results of a study, researchers must relate the conclusion back to which part of the study? 14. Roman physician Galen learned a great deal about the human body from dissecting animals. Which of his notions about the human body proved true? 15. What correct observations did Vesalius make about the heart, liver, and blood vessels? 16. Which scientific tool was refined by both Robert Hooke and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek? 17. Scientific discoveries made by NASA have contributed to the development of many products related to anatomy and physiology, as well as the environment. Name four of these products.
11 11 Lesson 1.4: Using the Scientific Method Directions: The scientific method can be used to answer questions relating to nearly any question or problem in your daily life. For this activity, identify a research question from your daily life or from things or people around you. Using the steps of the scientific method, identify the research question, then formulate and test your hypothesis. Report the steps of your exploration in the spaces below. Step 1: Identifying a Research Question Step 2: Formulating One or More Hypotheses Step 3: Planning the Organization of the Study Step 4: Collecting the Data Step 5: Analyzing and Evaluating the Data with Statistical Tools Step 6: Interpreting and Discussing the Results Step 7: Deriving Conclusions from the Results
12 12 Chapter 1: Analyzing Body Movements Directions: Using the Internet, find and print five action shots from five different sports. Analyze each image to determine the athlete s motion, and what plane of the body is involved in the movement. Then, fill in the details of each image in the table below. An example is provided for your reference. Sport Action What s Moving? Plane(s) Involved in Movement tennis Serena Williams uses a backhand stroke to return the ball to her opponent. upper body rotates; arms move as part of her backhand stroke; feet are planted transverse plane Compare and contrast the planes and most common movements between two of the sports you chose. Did any sports require similar movements?
13 13 Chapter 1 Lab Investigation: The Language of Anatomy Purpose In this investigation you will practice identifying body planes and directional terms. Materials your textbook, your body Procedure Follow the directions below and refer to your textbook as needed to answer the questions. Body Planes 1. Stand in anatomical position. A. Your feet point in which direction? B. Your thumbs point in which direction? C. Your fingers point in which direction? D. Your palms face which direction? 2. With your palm open and your thumb pointing up, use your right index finger to follow a sagittal plane on your body. As you do this, which direction (right or left) does your palm face? 3. With your palm open and your thumb pointing up, use your right index finger to follow a frontal plane on your body. As you do this, which direction (front or back) does your palm face? 4. With your palm open and your thumb pointing away from your body, use your right little finger to follow a transverse plane on your body. As you do this, which direction (up or down) does your palm face? Sagittal plane Transverse plane Frontal plane Directional Terms 1. Place your left index finger on the tip of your nose. A. List a body part that is superior to your nose. B. List a body part that is inferior to your nose. C. List a body part that is lateral to your nose. D. List a body part that is posterior to the tip of your nose. E. Is there a body part medial to the tip of your nose? F. Is there any body part that is anterior to the tip of your nose?
14 14 2. Standing in anatomical position, place your left index finger on the anterior surface of your right elbow. A. List a body part that is distal to your right elbow. B. List a body part that is proximal to your right elbow. C. List a body part that is lateral to your right elbow. D. List a body part that is medial to your right elbow. 3. Place your right index finger on your left collarbone. A. List a body part that is medial to your left collarbone. B. List a body part that is lateral to your left collarbone. C. List a body part that is deep to your left collarbone. 4. Place your left index finger on your left cheek. A. List a body part that is anterior to your left cheek. B. List a body part that is posterior to your left cheek. C. List a body part that is medial to your left cheek. 5. Place your left index finger on your belly button. A. List a body part that is lateral to your belly button. B. List a body part that is deep to your belly button. C. List a body part that is superior to your belly button. D. List a body part that is inferior to your belly button. 6. Place your right index finger on your left knee. A. List a body part that is superior to your left knee. B. List a body part that is distal to your left knee. C. List a body part that is proximal to your left knee. Conclusions 1. Which body plane divides the body into left and right halves? 2. Which body plane divides the body into top and bottom halves? 3. Which body plane divides the body into front and back halves? 4. Circle the body parts listed below that are divided into two pieces by a mid sagittal plane: nose, mouth, left eye, right leg, belly button, heart, right lung, left kidney 5. Circle the body parts listed below that are divided into two pieces by a frontal plane through the middle of the body: belly button, right lung, left kidney, nose, heart, left eye, brain, left leg 6. Circle the body parts listed below that are divided into two pieces by a transverse plane through the abdomen: brain, stomach, kidney, right leg, left arm, left eye, nose Select the correct word from the two choices and write it in the blank to the right. 7. Your head is (superior, inferior) to your neck. 8. Your thumb is (medial, lateral) to your fingers. 9. Your belly button is (superficial, deep) to your intestines. 10. Your forearm is (distal, proximal) to your hand. 11. Your sternum is (anterior, posterior) to your spinal cord.
15 15 Chapter 1 Practice Test Completion: Carefully read the following statements. Write the term that completes the statement in the spaces provided. 1. is the state of regulated physiological balance. 2. The study of how living things function or work is called. 3. is the single force that results from the total of all forces acting on a structure at a given time. 4. Generalizing the findings of a research study to a large population is called. 5. The speed at which the body consumes energy is the. True/False: Indicate whether each statement below is true or false by circling either T or F. T F 6. The chin is inferior to the trunk. T F 7. Combined loading is the simultaneous action of two or more kinds of forces. T F 8. The rotary effect of a force is called torque. T F 9. Data is a systematic process that can be used to answer questions or solve problems. T F 10. Collections of similar cells with a common function are called effectors. Multiple Choice: Circle the correct answer. 11. Which of the following is not true of the metric system? A. It can be used in many countries. C. Its measurements depend on gravity. B. It is easy to convert. D. It is organized around four base units. 12. The smallest building blocks of all living beings are. A. data C. tissues B. organs D. cells 13. Sagittal plane movements. A. mean there is no movement B. go forward and backward 14. The trachea is an organ of the system. A. digestive B. cardiovascular 15. Stress is quantified in the same way as. A. pressure B. acceleration C. go sideways D. move rotationally C. skeletal D. respiratory C. torsion D. deformation
16 16 Matching: Match each key term to its definition by writing the letter of the definition in the spaces provided. 16. metabolic rate 17. kinetics 18. anatomy 19. anterior (ventral) cavity 20. scientific theory 21. force 22. homeostatic imbalance 23. research question 24. organ system 25. bending A. a condition in which there is a decreased ability for the organ systems to maintain the body s internal environment within normal ranges B. a question to be answered or a problem to be solved in a research study C. push or pull exerting influence on a structure D. the study of the form or structure of all living things, including plants and animals E. two or more organs that work together F. a combination of off-center forces that creates a pattern of loading G. the analysis of the actions of forces H. the speed at which the body consumes energy I. an explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on rigorously tested, repeatedly confirmed research J. a continuous internal opening that includes the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Art Labeling: Locate each of the following items on the drawing by placing the corresponding letter on the blanks provided. 26. thoracic cavity 27. abdominopelvic cavity 28. cranial cavity 29. orbital cavity B. D. E. 30. spinal cavity 31. nasal cavity 32. anterior (ventral) cavity 33. pelvic cavity F. 34. diaphragm 35. posterior (dorsal) cavity A. C. G. J. I. H. Short Answer: Answer the following questions using what you have learned in this chapter. 36. Explain how homeostasis works. 37. Explain the factors that influence whether or not the application of an external force causes injury to the human body.
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide
 Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition
 Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: ext. 6049
 Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13
 CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
The Human Body: An Orientation
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Systemic The study of anatomy by body systems
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology
 is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology
 Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Chapters 1 & 2 A. Intro to Studies of the Human Body
 Chapters 1 & 2 A. Intro to Studies of the Human Body a. Anatomy the study of body structure -tomy means cutting or dissecting b. Physiology The study of body function; based on a Latin term meaning nature
Chapters 1 & 2 A. Intro to Studies of the Human Body a. Anatomy the study of body structure -tomy means cutting or dissecting b. Physiology The study of body function; based on a Latin term meaning nature
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
THE HUMAN BODY. study of the structure of living organisms. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: studying the structure of the heart.
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
Biology Anatomy and Physiology I. Learn and Understand. What is Biology? bios = life -ology = study of
 Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
The HUMAN BODY. Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY
 The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
study of body structure & Physiology study of body function
 study of body structure & Physiology study of body function Medical Words Made up of Latin, Greek, French, German, Dutch, Scandinavian, Italian, English, etc.. Common Medical Roots, Prefixes & Suffixes
study of body structure & Physiology study of body function Medical Words Made up of Latin, Greek, French, German, Dutch, Scandinavian, Italian, English, etc.. Common Medical Roots, Prefixes & Suffixes
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed.
 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth, and the hottest on record, with temperatures
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth, and the hottest on record, with temperatures
Date Lab Pd. Lecture Notes (57)
 Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units
 hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
Anatomy & Physiology. Next >> COURSE 1 MODULE 1
 Anatomy & Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology course introduces the structure and function of the human body. You will read about the cells, tissues and membranes that make up our bodies and how our
Anatomy & Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology course introduces the structure and function of the human body. You will read about the cells, tissues and membranes that make up our bodies and how our
1. Define Anatomy and Physiology-
 Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
NOSE GOES. What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent?
 1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224. Reem Alkhamis 3 rd floor/ office # 113
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Reem Alkhamis Email: ralkhamis@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office # 113 Lecture 1: The Human Body (an orienta=on) 1. An overview of anatomy and physiology 2. Levels of structural
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Reem Alkhamis Email: ralkhamis@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office # 113 Lecture 1: The Human Body (an orienta=on) 1. An overview of anatomy and physiology 2. Levels of structural
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy---Study of Structure Gross anatomy Systemic anatomy Regional anatomy Microscopic anatomy Physiology---Study of Function Neurophysiology Muscle physiology Respiratory Renal
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy---Study of Structure Gross anatomy Systemic anatomy Regional anatomy Microscopic anatomy Physiology---Study of Function Neurophysiology Muscle physiology Respiratory Renal
Figure 1.2. Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5) Umbilical region. Answer: C. 6) Right hypochondriac. Answer: B
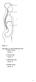 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Organization of the Body Chapter 1. Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden
 Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
