Musculoskeletal Disorders affecting Musicians and Considerations for Prevention
|
|
|
- Noel Austin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Disorders affecting Musicians and Considerations for Prevention Patrice Berque BSc (Hons) MCSP SRP AACP Chartered Physiotherapist 4 Carlston Steadings, Campsie Road Torrance, Glasgow G64 4ED Tel: Mobile: patrice.berque@btinternet.com Data Protection Act 1998 Reg. No. Z You will find a full list of all references used to produce this lecture in the last few slides of this presentation. If I don t practise for one day, I know it; if I don t practise for two days, the critics know it; if I don t practise for three days, the audience knows it Ignacy Jan Paderewski. Playing-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders (PRMDs) Pain, weakness, numbness, tingling, or other symptoms that interfere with (their) ability to play (their) instrument at the level (they) are accustomed to. (Zaza et al., 1998) Impact of PRMDs on Players (Caldron et al., 1986) Musicians reported their loss of facility in playing in terms of: Loss of speed, Loss of control of major motions, Loss of control of fine motions**, Loss of power (forte)**, Loss of finger span, Other. Patrice Berque 1
2 Predisposing Factors of PRMDs Intrinsic Factors (Zaza, 1993) Predisposing Factors of PRMDs Extrinsic Factors (Zaza, 1993) Gender, Hypermobility, Age, Genetic predispositions, Size, Strength. Flexibility, Muscle tone, Physical conditioning, Underlying musculoskeletal disease, Malalignment. Change or error in one or a combination of: Technique, Instrument, Instrument group, Instrument size, Teacher, Repertoire, Increase in playing time, Practice habits, Ergonomics and technique, Posture, Holding the instrument. Grading System for Severity of Injury (Hoppmann, 1998) Grade Description 0 No Pain. 1 Pain while playing, or for a short period after playing. 2 Pain that persists for a longer period after playing. 3 Pain that progresses while playing and requires the practice session to be shortened, but resolves between sessions. 4 Pain that progresses while playing and does not totally resolve between sessions. 5 Continuous pain that markedly reduces or prevents playing. Prevalence of Medical Problems ICSOM Study (Fishbein et al., 1988) Location Side Problem Severe Problem Hand Right 9% 5% Left 14% 10% Shoulder Right 20% 13% Left 20% 11% Neck Right 21% 13% Left 22% 12% Lower Back Right 22% 13% Left 22% 11% Stage Fright 24% 16% Prevalence of Severe Musculoskeletal Problems by Instrument Group and Gender: ICSOM Study (Fishbein et al., 1988) Injury Incidence Rate of Performance-Related Hand Problems among Music Students (n=114, median age: 20) over 3 years (Manchester & Flieder, 1991) Overall 58% String 66% Woodwind 48% Brass 32% Other 60% Male 52% Female 70% Overall 8.5% Keyboard 10.4% String 9.6% Wind 2.7% Male 6.1% Female 10.9% Patrice Berque 2
3 Prevalence of Injury among Secondary School Students (Fry et al., 1987) Severity of Injury at a Canadian Music School (n=300) (Zaza, 1992) Severity % Music Students (n=98) Non-music Students (n=98) Male 49% 14% Female 63% 12% No Problem 57% Very mild (< 1 wk) 28% Mild (1 wk< < 1 mth) 4% Moderate (1 mth < < 3 mths) 7% Severe (> 3 mths) 4% BBC SSO: Edinburgh Festival 2003 (n=11) (Berque, 2003) Instrument Location Side Percentage Violin & Viola Shoulder Right 18% Left 28% Elbow Right 9% Wrist Right 9% Woodwind Hand Right 9% Brass Shoulder Both 9% Lumbar Spine Central 9% Conductor Neck Left 9% Most Common Pathologies (Caldron et al. 1986, Lockwood 1989, Nagai & Eng 1992, Elbert et al. 1998, Hoppmann 1998) Muscle-tendon unit overuse syndromes. Muscle imbalance: movement impairment syndromes. Nerve entrapment syndromes. Focal dystonia (occupational cramp): painless loss of motor control, with uncoordination of finger movement. Also affects facial muscles. Bone, joint, and bursal injuries. Overuse Syndrome: Definition Defined, in relation to playing an instrument, as: Damage that occurs when a tissue is stressed beyond its anatomic or physiological limits. (Lederman & Calabrese, 1986) Exceeding the biological limits to achieve a certain level on one or more instruments causes breakdown and soft tissue damage. (Hartsell & Tata, 1991) A condition of pain and loss of function in muscle groups and joint ligaments as a consequence of excessive or unaccustomed use. (Fry 1986, Fry 2000) Overuse Syndrome: Symptoms (Lederman & Calabrese 1986, Hoppmann 1998, Fry 2000) Pain in muscles and tendons (musculotendinous unit), ligaments. Pain is aggravated with activity, lessened by rest. Localised tenderness over the affected structures, swelling may be present. Loss of function, characterised by: loss of strength, loss of stamina, increased fatigue. Patrice Berque 3
4 Overuse Syndrome: Factors Overuse Syndrome: Factors Increase in duration and intensity of practice. Normal movements done correctly, but too many times. (Berque, 2003) Problems with playing technique. Inappropriate static position of the left wrist. (Berque, 2003) Overuse Syndrome: Factors Inappropriate static posture causing muscle tension and excessive elevation of the left shoulder, possibly due to inadequate shoulder and chin rests. (Nagai & Eng 1992, Ackermann et al. 2002) Overuse Syndrome: Factors (Palmerud et al. 1995, Hoppmann 1998, Berque & Gray 2002) Static and dynamic loading of muscles: Overstabilisation of the left shoulder joint. A significant reduction in Trapezius muscle activity was shown when using a shoulder rest compared to not using a shoulder rest. (Levy et al., 1992) (Brandfonbrener, 2000) Increased frequency of leaps on the four strings for the bowing arm. (Berque & Gray, 2002) Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Overuse Syndrome: Scale (Fry 1986, Fry 1988) Pain in one site on causal activity. Pain in multiple sites on causal activity. Pain with some other uses of the hand, tender structures demonstrable, may show pain at rest or loss of muscle function. Pain with all uses of the hand, post activity pain with minor uses, pain at rest and at night, marked physical signs of tenderness, loss of motor function (loss of response or control), weakness. Loss of capacity for use because of pain which is continuous, loss of muscle function, particularly weakness, gross physical signs. Overuse Syndrome: Conservative Treatment (Fry 1986, Fry 1988, Lederman 2002) Strategies (Grades 1,2,3): Reduction in playing time to 10-minute sessions, Increase in length and number of breaks, Control of posture and body awareness, Reduce static loading with instrument adaptations (woodwinds), Review of playing technique, Vary content of a practice session, Stop repertoire or exercises causing pain. Patrice Berque 4
5 Overuse Syndrome: Radical Rest (Fry 1986, Fry 1988, Lederman 2002) Muscle Imbalance (Mottram 1997) Strategies (Grades 4,5): Prolonged rest for several weeks until pain-free and structures are non-tender, Avoidance of pain-inducing activities, Adequate medication, Very gradual return to playing (few minutes daily), All other strategies mentioned in previous slide apply. Imbalance in scapula (shoulder blade) muscles can result in: Movement dysfunction, or abnormal movement, Causing impingement syndromes, recurrent tendinitis of some shoulder muscles, and pain. (Berque, 2003) Shoulder Anatomy Muscle Imbalance and Impingement (Sahrmann, 2002) (Berque, 2003) (Grant s Atlas, 1999) (Grant s Atlas, 1999) Muscle Imbalance and Impingement Muscle Imbalance and Impingement (Sahrmann, 2002) (Berque, 2003) (Grant s Atlas, 1999) (Berque, 2003) Patrice Berque 5
6 Muscle Imbalance Inflammation of Tendon Sheaths (Hoppmann 1998, Baron and Eaton 1998, Wynn Parry 2000) The problem is not weakness of the stability muscles, but inhibition, which means: Poor recruitment of the muscles by the higher central nervous system. Delayed recruitment timing. Altered recruitment sequencing between muscles. These stability muscles need to be recruited prior to movement to fulfil their role. (Mottram, 1997) De Quervain s syndrome affects two tendons of the thumb at wrist level. Instrumentits affected: pianist ( thumb under ), string player s bowing arm, oboe and clarinet players. Management: rest, splinting, physiotherapy, nonsteroidal drugs, corticosteroid injection. (Grant s Atlas, 1999) Hypermobility (Hoppmann 1998, Brandfonbrener 2000) Hypermobility (Hoppmann 1998, Brandfonbrener 2000) Correlation between musicians with hand and arm pain and the presence of significant joint laxity, especially of the finger and wrist joints. Benign laxity (Hypermobility Syndrome) typically affects young and female musicians, and is due to laxity in the ligaments protecting joints. (Brandfonbrener, 2000) Prevalence of 5-10% in the general population, 20% in a population of musicians. Hyperlaxity is considered as detrimental, putting the individual at increased risk of musculoskeletal complaints. Management: finger splints, exercise programme, adaptive devices, attention to technique. Nerve Entrapment Syndromes Nerve root compression in the cervical spine. Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Nerve Root Compression (Bejjani 1996, Lederman 1998, Wynn Parry 2000) Compression of nerve roots in the cervical spine. Symptoms: neck pain; radiating down the arm; pins & needles; weakness. Associated with degenerative changes. Posture related: increased neck rotation and side flexion. (Grant s Atlas, 1999) Patrice Berque 6
7 Nerve Root Compression Cervical Spine Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (Bejjani 1996, Lederman 1998, Wynn Parry 2000) (Brandfonbrener, 2000) (Grant s Atlas, 1999) Compression at the brachial plexus. Symptoms: pain on inner side of forearm, ring and little fingers, pins & needles. Causes: droopy shoulders, downward traction of the shoulder and internal rotation during prolonged playing. (Grant s Atlas, 1999) Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Lederman 1998, Wynn Parry 2000) Most common entrapment neuropathy. Not necessarily performance-related. Affecting middle-aged women more often. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Signs & Symptoms (Lederman, 1998) Common: pain; pins and needles in the hand: thumb, index and middle fingers; symptoms at night. Later stages: sensory loss and numbness; weakness and atrophy; diminished tendon reflexes. (Grant s Atlas, 1999) Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Classification (Wynn Parry, 2000) Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 1- Classical CTS unrelated to performance: abnormal nerve conduction tests. 2- CTS due to acute positional factors: only occurs when playing (flexed wrist of guitarists). 3- Pins and needles associated with swelling of flexor tendons: related to playing, relieved by rest. (Tubiana, 2000) (Grant s Atlas, 1999) Patrice Berque 7
8 Management of CTS (Spinner & Amadio, 2000) Management of CTS (Spinner & Amadio, 2000) Modification of activity: more neutral wrist. Splinting. Steroid injection. Surgery. (Spinner & Amadio, 2000) (Spinner & Amadio, 2000) (Bejjani et al. 1996, Elbert et al. 1998, Lederman 2002, Brandfonbrener et al. 2004, Frucht 2004) Painless motor disorder. Loss of fine motor control/coordination of individual finger movements. Usually involving 3 rd to 5 th digits. Seen in pianists, wind players, guitarists, string players, pipers. Thought to be associated with many hours of daily practice. Affecting between 5% and 14% of musicians. (Bejjani et al. 1996, Elbert et al. 1998, Pantev et al. 2001) Related to other conditions associated with prolonged performance of rapid, alternating, and/or forceful movements of the digits (typing, data processing ). Movements of some fingers of a hand become involuntarily linked to those of others. No clear cause, no physiological mechanism determined (idiopathic). Treatments: temporary and palliative. Prevalence per Instrument (Tubiana & Chamagne 2000, Brandfonbrener et al. 2004, Frucht 2004) Piano: right hand mainly. Guitar: right hand more often than left. Violin and viola: left hand mainly. Cello: left hand mainly. Flute: left hand mainly. Oboe and clarinet: right hand more often than left. (Sakai, 2006) (Tubiana & Chamagne, 2000) Patrice Berque 8
9 Use-dependent Central Nervous System Plasticity (Elbert et al., 1995) Cortical territory occupied by the representation of the left hand digits in string players has expanded. (Ackermann & Adams, 2005) (Tubiana, 2000) String players exhibit a use-dependent enlargement of portions of the somatosensory map in cortical representational zones of the digits of the left hand, which are used intensively to play the instrument. Neurological Changes (Elbert et al.,1998) Fusion of Cortical Representations (Elbert et al., 1998) Extensive simultaneous stimulation of the digits and other types of prolonged, unusual types of sensory input can produce a use-dependent reorganisation of digital receptive fields. Study Results (Elbert et al., 1998) Reduced distance between the representational zones of the digits in primary somatosensory cortex for the affected hand of dystonic musicians. Fusion of cortical digital receptive fields. Fusion also occurred in the cortex opposite the non-dystonic hand in 4 of 7 musicians studied. Treatment Options (Elbert et al. 1998, Byl 2004) If cortical digital fusion is the cause of dystonia: Intervention to break apart the fusion may be effective. Sensory relearning: extensive practice in tactile discriminations with individual fingers. Patrice Berque 9
10 Treatment Options (Elbert et al. 1998, Byl 2004) Dystonia is a disturbance of motor production: Extensive practice in making discrete individual finger movements. In combination with constraint-induced movement therapy. The normal spine has 4 curvatures: Cervical lordosis, Thoracic kyphosis, Lumbar lordosis, Sacral kyphosis. Normal Posture (Kapandji, 2000) Posture and Disc Pathology Posture and Back Pain (Nordin & Schecter-Weiner, 2001) (Green et al., 2000) (Kapandji, 2000) (Kapandji, 2000) Posture and Breathing Sitting Posture and Back Pain (Norris & Dommerholt, 1998) (Kapandji, 2000) (Green et al., 2000) Forward-sloping seat to avoid: flattening of lumbar spine, strain on back muscles and ligaments, diminished breathing capacity. Wedge cushion. Exercise programme, frequent breaks, body awareness. (PhysioMed, 2003) Patrice Berque 10
11 Prevention: Posture Correction Prevention: Posture Correction (Kapandji, 2000) (Perrin, 1999) (Dommerholt, 2000) (Dommerholt, 2000) Prevention: Posture Correction Prevention: Posture Correction (Bros & Papillon, 2001) (Green et al., 2000) (Green et al., 2000) (Bros & Papillon, 2001) Hand Posture (Glenn Gould s Hand) Prevention: Hand Posture (Green et al., 2000) (Tubiana, 2000) (Brown, 2000) (Wilson, 2000) Patrice Berque 11
12 Return to Play Schedule (Norris, 1996) Level Play Rest Play Rest Play Rest Play Rest Play Ergonomics: Instrument Modifications (Norris & Dommerholt, 1998) String players: Orthoses: Custom moulding of shoulder and chin rests, tailpiece centred chin rest. Instrument supports: Voelkow rest for violin, angled end pin for cello. Instrument modifications: viola, guitar. Adapt size of instrument to anatomical features of the musician. (Norris, 2000) Ergonomics: Instrument Modifications (Norris & Dommerholt, 1998) Woodwind players: Orthoses for better hand positioning: right thumb and left index rests for the flute. Instrument supports: neck strap, end pin for English Horn, adjustable-height post for clarinet and flute, angled staple for oboe, vertical post for bassoon. Instrument modifications: angled-head flute, key extensions for the flute. (Norris, 2000) There is no generalizable data for guidance on healthy practice, nor can there be a formula dictating how many times a phrase can be safely repeated over a specific time period. Common sense and sensitivity to one s body is the only gauge for determining a safe number of repetitions. However, it is clear from all data on musicians that because practice sessions are times of risk it is incumbent on teachers to discuss and guide their students in practicing techniques. (Brandfonbrener, 2000) Prevention: Practice Habits (Fry 1986, Nagai & Eng 1992, Zaza 1994, Norris 1996, Zaza & Farewell 1997) Musical neuro-muscular warm-up **, Stretches can be used as a cool-down, but need to be appropriately performed, Inclusion of breaks every minutes during practice sessions**, Pacing: gradual increase of practice before concerts, recitals, competitions, Variety of content of the practice session: styles of music, types of exercises, Cognitive rehearsal: away from the instrument, Body awareness and control techniques: Alexander, Feldenkreis, Yoga, Stress and anxiety management. References Ackermann BJ, Adams R, Marshall E (2002) The Effect of Scapula Taping on Electromyographic Activity and Musical Performance in Professional Violinists. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy. Vol.48: Ackermann BJ, Adams R (2005) Finger Movement Discrimination in Focal Hand Dystonia: Case Study of a Cellist. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.20: Agur AMR, Lee MJ (1999) Grant s Atlas of Anatomy. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Barron OA, Eaton RG (1998) The Upper Limb of the Performing Artist. In: Sataloff RT, Brandfonbrener AG, Lederman RJ ed. Textbook of Performing Arts Medicine. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press, pp Bejjani FJ, Kaye GM, Benham M (1996) Musculoskeletal and Neuromuscular Conditions of Instrumental Musicians. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Vol. 77(4): Berque P, Gray H (2002) The Influence of Neck-Shoulder Pain on Trapezius Muscle Activity among Professional Violin and Viola Players: An Electromyographic Study. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.17: Branfonbrener AG (2000) Epidemiology and Risk Factors. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Brandfonbrener AG, Robson C (2004) Review of 113 Musicians with Focal Hand Dystonia Seen Between 1985 and 2002 at a Clinic for Peforming Arts. Dystonia 4: Advances in Neurology. Vol.94: Patrice Berque 12
13 References Bros C, Papillon M (2001) La Main du Pianiste: Méthode d Education Posturale Progressive. Montauban, France: Alexitère Editions. Brown S (2000) Promoting A Healthy Keyboard Technique. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Byl NN (2004) May Result from Aberrant Neuroplasticity. Dystonia 4: Advances in Neurology. Vol.94: Caldron PH, Calabrese LH, Clough JD, Lederman RJ, Williams G, Leatherman J (1986) A Survey of Musculoskeletal Problems Encountered in High-Level Musicians. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.1(4): Dommerholt J (2000) Posture. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Elbert T, Pantev C, Wienbruch C, Rockstroh B, Taub E (1995) Increased Cortical Representation of the Fingers of the Left Hand in String Players. Science. Vol.270(5234): Elbert T, Candia V, Altenmüller E, Rau H, Sterr A, Rockstroh B, Pantev C, Taub E (1998) Alteration of Digital Representations in Somatosensory Cortex in Focal Hand Dystonia. Neuroreport. Vol.9: Fishbein M, Middlestadt SE, Ottati V, Straus S, Ellis A (1988) Medical Problems among ICSOM Musicians: Overview of a National Survey. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.3(1):1-8. References Frucht SJ (2004) Focal Task-Specific Dystonia in Musicians. Dystonia 4: Advances in Neurology. Vol.94: Fry HJH (1986) Incidence of Overuse Syndrome in the Symphony Orchestra. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.1(2): Fry HJH (1987) Prevalence of Overuse (Injury) Syndrome in Australian Music Schools. British Journal of Industrial Medicine. Vol.44(1): Fry HJH (1988) The Treatment of Overuse Syndrome in Musicians. Result in 175 Patients. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. Vol.81: Fry HJH (2000) Overuse Syndrome. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Green JA, Champagne P, Tubiana R (2000) Prevention. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Hartsell HD, Tata GE (1991) A Retrospective Survey of Music-related Musculoskeletal Problems Occurring in Undergraduate Music Students. Physiotherapy Canada. Vol. 43(1): Hoppmann RA (1998) Musculoskeletal Problems in Instrumental Musicians. In: Sataloff RT, Brandfonbrener AG, Lederman RJ ed. Textbook of Performing Arts Medicine. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press, pp Kapandji AI (2000) Anatomy of the Spine. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Lederman RJ, Calabrese LH (1986) Overuse Syndromes in Instrumentalists. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.1(1):7-11. References Lederman RJ (1998) Neurological Problems of Performing Artists. In: Sataloff RT, Brandfonbrener AG, Lederman RJ ed. Textbook of Performing Arts Medicine. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press, pp Lederman RJ (2002) Neuromuscular Problems in Musicians. The Neurologist. Vol.8: Levy CE, Lee WA, Brandfonbrener AG, Press J, Levy AE (1992) Electromyographic Analysis of Muscular Activity in the Upper Extremity Generated by Supporting a Violin with and without a Shoulder Rest. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.7(4): Lockwood AH (1989) Medical Problems of Musicians. The New England Journal of Medicine. Vol.320(4): Manchester RA, Flieder D (1991) Further Observations on the Epidemiology of Hand Injuries in Music Students. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.6(1): Mottram SL (1997) Dynamic Stability of the Scapula. Manual Therapy. Vol.2(3): Nagai L, Eng J (1992) Overuse Injuries Incurred by Musicians. Physiotherapy Canada. Vol.44(1): Nordin M, Schecter-Weiner S (2001) Biomechanics of the Lumbar Spine. In: Nordin M, Frankel VH ed. Basic Biomechanics of the Musculoskeletal System. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, pp Norris RN (1996) Return to Play after Injury: Strategies to Support a Musician s Recovery. Work. Vol.7: References Norris RN, Dommerholt J (1998) Applied Ergonomics: Adaptive Equipment and Instrument Modification for Musicians. In: Sataloff RT, Brandfonbrener AG, Lederman RJ ed. Textbook of Performing Arts Medicine. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press, pp Norris RN (2000) Applied Ergonomics. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Palmerud G, Kadefors R, Sporrong H, Jarvholm U, Herberts P, Hogfors C, Peterson B (1995) Voluntary Redistribution of Muscle Activity in Human Shoulder Muscles. Ergonomics. Vol.38(4): Pantev C, Engelien A, Candia V, Elbert T (2001) Representational Cortex in Musicians- Plastic Alterations in Response to Musical Practice. Annals of New York Academy of Sciences, pp Perrin P (1999) Analyse des Principales Fautes Posturales chez les Guitaristes. Médecine des Arts. Vol.30: Sahrmann SA (2002) Diagnosis and Treatment of Movement Impairment Syndromes. St Louis, USA: Mosby, pp Sakai N (2006) Slow-Down Exercise for the Treatment of in Pianists. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.21: Spinner RJ, Amadio PC (2000) Compression Neuropathies of the Upper Extremity. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp References Tubiana R (2000) Musician s Focal Dystonia. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Tubiana R, Chamagne P (2000) Prolonged Rehabilitation Treatment of Musician s Focal dystonia. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Wilson FR (2000) Glenn Gould s Hand. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Wynn Parry C (2000) Clinical Approaches. In: Tubiana R, Amadio PC ed. Medical Problems of the Instrumentalist Musician. London: Martin Dunitz, pp Zaza C (1992) Playing-Related Health Problems at a Canadian Music School. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.7: Zaza C (1993) Prevention of Musicians' Playing-related Health Problems: Rationale and Recommendations for Action. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.8(4): Zaza C (1994) Research-based Prevention for Musicians. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. Vol.9(1):3-6. Zaza C, Farewell VT (1997) Musicians' Playing-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders: An Examination of Risk Factors. American Journal of Industrial Medicine. Vol.32: Zaza C (1998) Playing-related Musculoskeletal Disorders in Musicians: a Systematic Review of Incidence and Prevalence. Canadian Medical Association Journal. Vol.158(8): Patrice Berque 13
14 THE END Thank You Patrice Berque 14
RESEARCH INTO ALEXANDER TEACHING METHODOLOGY & EXPLAINING THE ALEXANDER TECHNIQUE TO CLINICIANS & SCIENTISTS
 RESEARCH INTO ALEXANDER TEACHING METHODOLOGY & EXPLAINING THE ALEXANDER TECHNIQUE TO CLINICIANS & SCIENTISTS PSYCHO-PHYSICAL RE-EDUCATION: AN INTRODUCTION TO COGNITIVE-MOTOR SYSTEM-LEVEL CAUSES OF PERFORMANCE-RELATED
RESEARCH INTO ALEXANDER TEACHING METHODOLOGY & EXPLAINING THE ALEXANDER TECHNIQUE TO CLINICIANS & SCIENTISTS PSYCHO-PHYSICAL RE-EDUCATION: AN INTRODUCTION TO COGNITIVE-MOTOR SYSTEM-LEVEL CAUSES OF PERFORMANCE-RELATED
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM
 TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS)
 Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
Head and scapular posture in flutists: A pilot controlled study
 International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-94-90306-02-1 The Author 2011, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Head and scapular posture in flutists: A pilot controlled study Ziliane L.
International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-94-90306-02-1 The Author 2011, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Head and scapular posture in flutists: A pilot controlled study Ziliane L.
Table of contents. Actsafe Performing Arts Safety Primers
 Actsafe Performing Arts Safety Primers This book is one in a series of Performing Arts Safety Primers that also includes: The Performing Arts Safety Primer Dancers and MSI Table of contents Introduction...4
Actsafe Performing Arts Safety Primers This book is one in a series of Performing Arts Safety Primers that also includes: The Performing Arts Safety Primer Dancers and MSI Table of contents Introduction...4
Official Definition. Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
 Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Dimensional Requirements. Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways.
 Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Muscular Skeletal Disorders
 Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Focal task-specific dystonia (FTSD) affecting musicians
 A Combination of Constraint-Induced Therapy and Motor Control Retraining in the Treatment of Focal Hand Dystonia in Musicians A Long-term Follow-up Study Patrice Berque, BSc (Hons), MCSP, Heather Gray,
A Combination of Constraint-Induced Therapy and Motor Control Retraining in the Treatment of Focal Hand Dystonia in Musicians A Long-term Follow-up Study Patrice Berque, BSc (Hons), MCSP, Heather Gray,
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre
 Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Influence of musculoskeletal dysfunction and pain on performance excellence
 International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-94-90306-01-4 The Author 2009, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Influence of musculoskeletal dysfunction and pain on performance excellence
International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-94-90306-01-4 The Author 2009, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Influence of musculoskeletal dysfunction and pain on performance excellence
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence
 Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference.
 Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Alteration of digital representations in somatosensory cortex in focal hand dystonia
 Clinical Neuroscience 0 0 0 0 0 p Website publication November NeuroRepor t, () FOCAL hand dystonia involves a loss of motor control of one or more digits; it is associated with the repetitive, synchronous
Clinical Neuroscience 0 0 0 0 0 p Website publication November NeuroRepor t, () FOCAL hand dystonia involves a loss of motor control of one or more digits; it is associated with the repetitive, synchronous
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Acute Services Division. Information for patients. Carpal Tunnel. Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary
 Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Ergonomics in Sonography
 Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Changing the Brain through Therapy for Musicians Hand Dystonia
 Changing the Brain through Therapy for Musicians Hand Dystonia VICTOR CANDIA, a,b JAUME ROSSET-LLOBET, b THOMAS ELBERT, c AND ALVARO PASCUAL-LEONE d a Collegium Helveticum, ETH-Zentrum/STW, Schmelzbergstrasse
Changing the Brain through Therapy for Musicians Hand Dystonia VICTOR CANDIA, a,b JAUME ROSSET-LLOBET, b THOMAS ELBERT, c AND ALVARO PASCUAL-LEONE d a Collegium Helveticum, ETH-Zentrum/STW, Schmelzbergstrasse
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
Chiropractic Glossary
 Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Author. Published. Conference Title. Copyright Statement. Downloaded from. Link to published version. Griffith Research Online. Lonsdale, Karen Anne
 Physical Considerations for Teaching Beginner Flutists Author Lonsdale, Karen Anne Published 2010 Conference Title Physical Considerations for Teaching Beginner Flutists Copyright Statement 2010 National
Physical Considerations for Teaching Beginner Flutists Author Lonsdale, Karen Anne Published 2010 Conference Title Physical Considerations for Teaching Beginner Flutists Copyright Statement 2010 National
Richard Dobrusin DO FACOFP
 Richard Dobrusin DO FACOFP Define Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Describe the Mechanisms of Dysfunction List Diagnostic tests for (TOS) Understand (TOS) referral patterns Discuss Treatment Options Definition:
Richard Dobrusin DO FACOFP Define Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Describe the Mechanisms of Dysfunction List Diagnostic tests for (TOS) Understand (TOS) referral patterns Discuss Treatment Options Definition:
2/3/2017. Discuss findings of latest research of psychoneur0 immunology
 Jan Idzikowski, PA C Discuss findings of latest research of psychoneur0 immunology of music Introduce the concept of the athletic musician Outline types of injuries musicians sustain Discuss prevention
Jan Idzikowski, PA C Discuss findings of latest research of psychoneur0 immunology of music Introduce the concept of the athletic musician Outline types of injuries musicians sustain Discuss prevention
Comparative study of epidemiological inquiries of the Musicians Upper Limb disorders.
 Comparative study of epidemiological inquiries of the Musicians Upper Limb disorders. SHORT TITLE: Comparison of epidemiological studies on Musician s Upper Limb disorders. AUTHORS: Ioannis Ignatiadis
Comparative study of epidemiological inquiries of the Musicians Upper Limb disorders. SHORT TITLE: Comparison of epidemiological studies on Musician s Upper Limb disorders. AUTHORS: Ioannis Ignatiadis
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome
 NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome What is carpal tunnel? The carpal tunnel refers to an area at the base of the wrist which contains bones, nerves,
NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome What is carpal tunnel? The carpal tunnel refers to an area at the base of the wrist which contains bones, nerves,
Chiropractic Healthcare
 ebook 2 Chiropractic Healthcare Four symptoms explained Introduction 3 Chapter 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 4 Chapter 2 Common Shoulder Pain Issues 8 Chapter 3 Headaches and Chiropractic Care 14 Chapter 4
ebook 2 Chiropractic Healthcare Four symptoms explained Introduction 3 Chapter 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 4 Chapter 2 Common Shoulder Pain Issues 8 Chapter 3 Headaches and Chiropractic Care 14 Chapter 4
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Relax, Reset, Repeat: Tuning up Posture for Performance. Catherine Holt, Matt Kubalski, Peggy Miller, Sarah O Reilly, Molly Vogel
 Relax, Reset, Repeat: Tuning up Posture for Performance Catherine Holt, Matt Kubalski, Peggy Miller, Sarah O Reilly, Molly Vogel Learning Objectives 1. Internalize and value the importance of proper body
Relax, Reset, Repeat: Tuning up Posture for Performance Catherine Holt, Matt Kubalski, Peggy Miller, Sarah O Reilly, Molly Vogel Learning Objectives 1. Internalize and value the importance of proper body
The Evolution of Human s? Objectives. Agenda. Defining Ergonomics. History of Ergonomics. Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer.
 Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
OMT FOR THE PERFORMING ARTIST
 OMT FOR THE PERFORMING ARTIST Sajid A. Surve, DO Associate Professor, UNTHSC-TCOM Co-Director, UNT Texas Center for Performing Arts Health http://tcpah.unt.edu Occupation History for the Performer Pertinent
OMT FOR THE PERFORMING ARTIST Sajid A. Surve, DO Associate Professor, UNTHSC-TCOM Co-Director, UNT Texas Center for Performing Arts Health http://tcpah.unt.edu Occupation History for the Performer Pertinent
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
Avoiding Discomfort and Injury in Young String Players:
 Avoiding Discomfort and Injury in Young String Players: A Stretching Activity Guide by Joshua Russell and Paul Higgins String educators are becoming increasingly aware of the health and wellness issues
Avoiding Discomfort and Injury in Young String Players: A Stretching Activity Guide by Joshua Russell and Paul Higgins String educators are becoming increasingly aware of the health and wellness issues
FOCAL HAND DYSTONIA in musicians is a set of conditions
 1342 Sensory Motor Retuning: A Behavioral Treatment for Focal Hand Dystonia of Pianists and Guitarists Victor Candia, MA, Thomas Schäfer, Edward Taub, PhD, Harald Rau, PhD, Eckart Altenmüller, MD, Brigitte
1342 Sensory Motor Retuning: A Behavioral Treatment for Focal Hand Dystonia of Pianists and Guitarists Victor Candia, MA, Thomas Schäfer, Edward Taub, PhD, Harald Rau, PhD, Eckart Altenmüller, MD, Brigitte
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection
 The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Musicians Medicine: Musculoskeletal Problems in String Players
 Review Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:155-160 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.3.155 Musicians Medicine: Musculoskeletal Problems in String Players Han-Sung Lee, Ho Youn Park, MD, Jun
Review Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:155-160 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.3.155 Musicians Medicine: Musculoskeletal Problems in String Players Han-Sung Lee, Ho Youn Park, MD, Jun
Risk Management Department. Office Ergonomics
 Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
ACTIVE AGING.
 Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Functional Well-Being. Neck, Shoulders and Wrist
 Functional Well-Being Neck, Shoulders and Wrist 1 Neck Definition and Structure Your neck (cervical spine) is made up of 7 vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper torso. 2 Causes of Neck Pain
Functional Well-Being Neck, Shoulders and Wrist 1 Neck Definition and Structure Your neck (cervical spine) is made up of 7 vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper torso. 2 Causes of Neck Pain
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job
 Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Wellness for Accordionists. Presented by Rachel Quirbach, MTI AAA Festival 2018 Alexandria, Virginia 12 July 2018
 Wellness for Accordionists Presented by Rachel Quirbach, MTI AAA Festival 2018 Alexandria, Virginia 12 July 2018 The Blurb Being an accordionist can take a significant physical and mental toll on your
Wellness for Accordionists Presented by Rachel Quirbach, MTI AAA Festival 2018 Alexandria, Virginia 12 July 2018 The Blurb Being an accordionist can take a significant physical and mental toll on your
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
The Reasons We Experience Pain
 Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
ACUTE CARE SHOULDER PROGRAM
 POST-OPERATIVE ACUTE CARE SHOULDER PROGRAM PASSIVE RANGE OF MOTION (PROM) Performed during the period of 0 to 6 weeks after surgery. (Or at the discretion of your Physician and Therapist.) The success
POST-OPERATIVE ACUTE CARE SHOULDER PROGRAM PASSIVE RANGE OF MOTION (PROM) Performed during the period of 0 to 6 weeks after surgery. (Or at the discretion of your Physician and Therapist.) The success
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
WRITING SUB-TEST TEST BOOKLET
 PHYSAMPLE01 WRITING SUB-TEST TEST BOOKLET INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES You must write your answer for the Writing sub-test in the Writing Answer Booklet. You must NOT remove OET material from the test room.
PHYSAMPLE01 WRITING SUB-TEST TEST BOOKLET INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES You must write your answer for the Writing sub-test in the Writing Answer Booklet. You must NOT remove OET material from the test room.
Focal Hand Dystonia Affecting Musicians. Part II: An Overview Of Current Rehabilitative Treatment
 Focal Hand Dystonia Affecting Musicians. Part II: An Overview Of Current Rehabilitative Treatment Techniques Katherine Butler BAp(Sc) Occupational Therapy, AHT (BAHT), A MusA(Flute) The Princess Grace
Focal Hand Dystonia Affecting Musicians. Part II: An Overview Of Current Rehabilitative Treatment Techniques Katherine Butler BAp(Sc) Occupational Therapy, AHT (BAHT), A MusA(Flute) The Princess Grace
Computer Ergonomics. Static Efforts
 Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Carpal tunnel syndrome
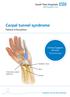 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Repetitive Upper Limb Tasks. Introductions. ' Crown Copyright Health & Safety Laboratory. 1. Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist.
 Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you
 Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations
 Preventing workrelated upper limb disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations Aims of the programme - To increase awareness of work-related upper limb disorders (WRULDs) associated
Preventing workrelated upper limb disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations Aims of the programme - To increase awareness of work-related upper limb disorders (WRULDs) associated
Beginning of Process: Development of the Office Ergonomics program.
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
Injury Prevention What Can Music Teachers Do? Research in performing arts medicine has demonstrated that approximately 25% of music
 1 Injury Prevention What Can Music Teachers Do? Abstract Research in performing arts medicine has demonstrated that approximately 25% of music students experience a playing-related injury 1. Since musicians
1 Injury Prevention What Can Music Teachers Do? Abstract Research in performing arts medicine has demonstrated that approximately 25% of music students experience a playing-related injury 1. Since musicians
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
Disc injury is a common source of neck pain associated with radiation of pain into the upper back, shoulder, and arm.
 Disc Injury - Neck, Shoulder, and Arm Pain Disc injury is a common source of neck pain associated with radiation of pain into the upper back, shoulder, and arm. Intervertebral Discs, located between the
Disc Injury - Neck, Shoulder, and Arm Pain Disc injury is a common source of neck pain associated with radiation of pain into the upper back, shoulder, and arm. Intervertebral Discs, located between the
CS, IT Occupational Hazard
 CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment
 Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
RECIPES FOR RATINGS !!! A. FIBROMYALGIA: 0% WPI P. 569 B. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME 0% WPI P. 569 C. MYOFASCIAL PAIN SYNDROME 0% WPI P.
 RECIPES FOR RATINGS 1. THE "0% WPI" RATINGS A. FIBROMYALGIA: 0% WPI P. 569 B. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME 0% WPI P. 569 C. MYOFASCIAL PAIN SYNDROME 0% WPI P. 569 D. TENDINITIS OF UPPER EXTREMITY 0% WPI P.
RECIPES FOR RATINGS 1. THE "0% WPI" RATINGS A. FIBROMYALGIA: 0% WPI P. 569 B. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME 0% WPI P. 569 C. MYOFASCIAL PAIN SYNDROME 0% WPI P. 569 D. TENDINITIS OF UPPER EXTREMITY 0% WPI P.
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Upper Cross Syndrome: Assessment & Management in Family Practice HKDU Symposium Dec 2014
 Upper Cross Syndrome: Assessment & Management in Family Practice HKDU Symposium Dec 2014 Dr. Ngai Ho Yin Allen Family Medicine Specialist PGDipMusculoskeletal Medicine MBBS(HK), DCH(London), DFM(CUHK),
Upper Cross Syndrome: Assessment & Management in Family Practice HKDU Symposium Dec 2014 Dr. Ngai Ho Yin Allen Family Medicine Specialist PGDipMusculoskeletal Medicine MBBS(HK), DCH(London), DFM(CUHK),
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs
 KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
 Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players.
 Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
IMPACT OF EXCESSIVE COMPUTER USE ON GLOBAL HEALTH STATE
 Marathon IMPACT OF EXCESSIVE COMPUTER USE ON GLOBAL HEALTH STATE Andreea VOINEA 1 Abstract The computer has become indispensable for many of us, but together with all the advantages that it offers longtime
Marathon IMPACT OF EXCESSIVE COMPUTER USE ON GLOBAL HEALTH STATE Andreea VOINEA 1 Abstract The computer has become indispensable for many of us, but together with all the advantages that it offers longtime
3/10/17 Spinal a Injury 1
 Spinal Injury 1 'Paralysed' Watmough vows he'll have the backbone for Game Two after treatment for neck injury Watmough will have cortisone injected into his spine this morning to speed up the recovery
Spinal Injury 1 'Paralysed' Watmough vows he'll have the backbone for Game Two after treatment for neck injury Watmough will have cortisone injected into his spine this morning to speed up the recovery
Protect Your Neuromusculoskeletal and Vocal Health Every Day
 Protect Your Neuromusculoskeletal and Vocal Health Every Day Information and Recommendations for Student Musicians Student Guide National Association of Schools of Music Performing Arts Medicine Association
Protect Your Neuromusculoskeletal and Vocal Health Every Day Information and Recommendations for Student Musicians Student Guide National Association of Schools of Music Performing Arts Medicine Association
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
Mid-Thoracic Dysfunction: A Key Perpetuating Factor of Pain in the Locomotor System
 Mid-Thoracic Dysfunction: A Key Perpetuating Factor of Pain in the Locomotor System Dysfunction involving excessive T4-T8 kyphosis is common. Symptoms arising from regions at a distance to the mid-thoracic
Mid-Thoracic Dysfunction: A Key Perpetuating Factor of Pain in the Locomotor System Dysfunction involving excessive T4-T8 kyphosis is common. Symptoms arising from regions at a distance to the mid-thoracic
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity
 Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Carpal Tunnel: How To Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: How To Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome By Ace McCloud
 Carpal Tunnel: How To Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: How To Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome By Ace McCloud If searching for the book Carpal Tunnel: How To Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: How To Prevent Carpal
Carpal Tunnel: How To Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: How To Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome By Ace McCloud If searching for the book Carpal Tunnel: How To Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: How To Prevent Carpal
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents
 Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment
 Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Suprascapular nerve entrapment is an uncommon nerve condition in the shoulder, causing pain and weakness. It involves compression of the suprascapular nerve at the top or
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Suprascapular nerve entrapment is an uncommon nerve condition in the shoulder, causing pain and weakness. It involves compression of the suprascapular nerve at the top or
Dentalelle Tutoring. Exercise Needs. For the Dental Hygienist
 Dentalelle Tutoring Exercise Needs For the Dental Hygienist Work-related Injuries Epidemiological studies during the past decade have demonstrated a high incidence of work-related shoulder injuries among
Dentalelle Tutoring Exercise Needs For the Dental Hygienist Work-related Injuries Epidemiological studies during the past decade have demonstrated a high incidence of work-related shoulder injuries among
BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS
 BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS Description Proximal biceps tendon tendinitis and tenosynovitis is characterized by pain at the front of the shoulder and upper arm caused by inflammation
BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS Description Proximal biceps tendon tendinitis and tenosynovitis is characterized by pain at the front of the shoulder and upper arm caused by inflammation
Hemiplegic Shoulder Power Point for staff education sessions
 Appendix B Hemiplegic Shoulder Power Point for staff education sessions Jennifer Curry Physiotherapist, London Health Sciences Centre www.swostroke.ca Acknowledgements Maria Lung BSc (PT), MSc Train the
Appendix B Hemiplegic Shoulder Power Point for staff education sessions Jennifer Curry Physiotherapist, London Health Sciences Centre www.swostroke.ca Acknowledgements Maria Lung BSc (PT), MSc Train the
Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
 Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Symptoms and Signs Thumb, index, middle, and radial aspect of ring finger Hand Pain Paresthesia Numbness Pins
Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Symptoms and Signs Thumb, index, middle, and radial aspect of ring finger Hand Pain Paresthesia Numbness Pins
260- OFFICE ERGONOMICS
 260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE)
 Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology
 Physical Therapy Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology Scott Behjani, DPT, OCS Introduction Prevalence 1-year incidence of first-episode LBP ranges from
Physical Therapy Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology Scott Behjani, DPT, OCS Introduction Prevalence 1-year incidence of first-episode LBP ranges from
