Original paper Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, no. 3,
|
|
|
- Cory Harrell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original paper Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, no. 3, DOI: /mu zsu Reproducibility in pelvic floor biometric parameters of nulliparous women assessed by translabial three-dimensional ultrasound using Omniview reformatting technique. Zsuzsanna Ilona Katalin Jármy-Di Bella 1, Edward Araujo Júnior 2, Claudinei Alves Rodrigues 1, Luiza Torelli 1, Wellington P. Martins 3, Antonio Fernandes Moron 2, Manoel João Batista Castello Girão 1 1 Department of Gynecology, Paulista School of Medicine Federal University of São Paulo (EPM-UNIFESP), São Paulo-SP, 2 Department of Obstetrics, Paulista School of Medicine Federal University of São Paulo (EPM-UNI- FESP), São Paulo-SP, 3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo (DGO-FMRP-USP), Ribeirão Preto-SP, Brazil. Abstract Aim: To assess the reproducibility of pelvic floor biometric parameters by translabial three-dimensional ultrasound compared with the OmniView reformatting technique. Material and methods: We performed a prospective cross-sectional study involving 47 nulliparous women without symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction. The hiatal area and right pubovisceral muscle width measurements were performed in the axial plane using both 3D ultrasound in the rendering mode and OmniView techniques. To determine the occurrence of standardized error between examiners and the two sonographic methods, the paired t-test was used. The intra- and inter-observer reliability and agreement were estimated by concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) and limits of agreement, respectively. Results: We did not observe significant statistical differences among both measurements performed by the first examiner, both examiners and both methods in the assessment of the hiatal area; however, the measurements of the right pubovisceral muscle were significantly lower using OmniView. The intra-observer reliability was good in the evaluation of all pelvic floor parameters; however, the inter-observer reliability was good only to the 3D rendering mode (CCC=0.87). The intra-observer agreement was good in the assessment of all pelvic floor parameters; however, the inter-observer agreement was found to be good only when 3DUS in the rendering mode was used (<±15%). Conclusion: Both 3D ultrasound in the rendering mode and OmniView reformatting techniques were concordant in the assessment of pelvic floor parameters; however, the 3D ultrasound rendering in the mode demonstrated better inter-observer reliability and agreement. Keywords: Pelvic floor, nulliparous, rendering mode, three-dimensional ultrasound, omniview Introduction Received Accepted Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, No 3, Corresponding author: Prof. Edward Araujo Júnior, PhD Department of Obstetrics, Paulista School of Medicine Federal University of São Paulo EPM-UNIFESP) Rua Belchior de Azevedo, 156 apto. 111 Torre Vitoria, São Paulo SP, Brazil, CEP Phone / Fax: araujojred@terra.com.br Currently, the three-dimensional ultrasound (3DUS) is a common method used to assess the anatomy and function of the pelvic floor structures, and it is used mainly in urogenital dysfunctions, such as genital prolapse and urinary incontinence. It was first described by Khullar et al [1] using an endovaginal probe and the focus was on the observation of urethra and paraurethral structures. After 10 years, Dietz et al published the first paper using the translabial 3D convex probe to assess the pelvic floor in women [2]. The advantage of this modern equipment makes it possible to observe and analyze the dimensions of the pubic symphysis, urethra, bladder, bladder neck, vagina, anorectal angle, and pubovisceral muscles. The inter-observer reproducibility of the pelvic floor biometric parameters at rest, during pelvic floor muscle contraction, and during the Valsalva maneuver using the
2 346 Zsuzsanna Ilona Katalin Jármy-Di Bella et al Reproducibility in pelvic floor biometric parameters of nulliparous women translabial 3DUS has been proved both in acquisition and off-line analysis [3,4]. In addition, the translabial 3DUS is a technique that can be learnt in a short time period [4]. OmniView (GE Medical System, Zipf, Austria) is a software application for 3DUS that allows interrogation of volume datasets and simultaneous display of up to three independent (non-orthogonal) planes by manually drawing line, curve, polyline, or trace from any direction or angle [5]. The first line (yellow), the second line (fuchsia), and the third line (turquoise) should be applied to the region of interest, achieving non-orthogonal planes simultaneously displayed on 3D volume multiplanar rendering [6]. This technology has been applied in obstetrics to assess the fetal hard and soft palates [6], central nervous system [5], heart [7], and spine [8]. In gynecology, the OmniView has been used to assess the location of intrauterine devices [9]. Recently, Youssef et al [10] proved good reproducibility of the pelvic hiatal area measurement using OmniView software in nulliparous asymptomatic and in women with symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction. A high agreement was shown between OmniView and 3DUS in the rendering mode. The objective of this study was to assess the reproducibility of OmniView and 3DUS in the rendering mode in the assessment of hiatal area and right pubovisceral muscle width measurements of the pelvic floor of nulliparous women. Material and methods This was a prospective cross-sectional study that involved 47 nulliparous asymptomatic healthy women between July 2013 and July This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Federal University of São Paulo. The consent form was signed by all volunteer patients included in this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) age between 18 and 35 years, 2) body mass index (BMI) between 20 and 25 Kg/m 2, 3) absence of symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction. 3DUS assessment of the pelvic floor was performed with the patient in the lithotomy position with hips flexed and abducted, after voiding, using a Voluson 730 Expert (General Electric Medical System, Zipf, Austria) equipment with a convex volumetric probe (RAB 4 8L). All 3D volume scans were acquired at rest with an acquisition angle of 85 degrees. Only one 3D pelvic floor volume dataset was acquired for each patient, and transferred to a personal computer. The ultrasound exams were performed by only one examiner (ZIKJB) with four years experience in 3DUS of the pelvic floor. The pelvic floor volume datasets were assessed offline using a 4D View version 10.0 (General Electric Medical System, Zipf, Austria). The hiatal area was measured on the plane of minimum hiatal dimension, which was referenced as mid-sagittal, comprising the area between the posterior region of the pubic symphysis and the anterior and posterior borders of the muscles of the levator ani, including the anorectal muscle (pubovisceral muscle). This transverse section in the axial plane enabled measurements of the hiatal dimension, such as area and transverse and anteroposterior diameters, as described by Dietz et al [11]. The thickness of the pubovisceral muscle was standardized in the axial plane and we chose the right pubovisceral width to define it. The measurement of pubovisceral muscle was performed in the place of the maximum width of the muscle. After this, the same measurements with the OmniView were performed.the line from the OmniView was drawn along the plane of least pelvic hiatal dimensions between the posterior margin of the symphysis pubis and the anterior margin of the puborectalis muscle, where it defines the anorectal angle, including a thickness of 3 to 10 mm. The plane of hiatal dimensions was automatically displayed on the right hand side. The trace method was then used to measure the hiatal area and right thickens pubovisceral muscle (fig 1). The measurements, hiatal area in cm 2 and width of the right pubovisceral muscle in cm were performed by two blinded experienced examiners (ZIKJB and CAR). The first examiner repeated a new measurement 7 days later, either with the 3DUS in the rendering mode or by the OmniView technique to assess the intra-observer reproducibility. Statistical analysis The statistical analysis was performed by one of the authors (WPM) using a Graph Pad Prism version 6.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) and Stata Fig 1. Ominiview reformatting technique: a) The line of Ominiview is drawn between the posterior margin of the symphysis pubis and the anterior margin of pubovisceral muscle with a thickness between 3 to 10 mm; b) The rendering mode image in the axial plane showing the hiatal area and right pubovisceral muscle measurements.
3 version 11.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA). Initially, the normality distribution using the D Agostino-Pearson omnibus test was assessed. The mean ± standard deviation of participant characteristics, such as age, height, weight, BMI, hiatal area, and right pubovisceral muscle width measurements were performed. To determine the occurrence of standardized error (consistently higher or lower measurements) between examiners and the 3DUS in the rendering mode and OmniView techniques, the related values for the same measurements were compared between the measurements and methods using the paired t-test. The intra- and inter-observer reliability was estimated by the concordance correlation coefficient (CCC), being the estimative accuracy assessed by their respective 95% confidence intervals (CI). The intra- and inter-observer agreement was estimated by the limits of agreement (LoA) of the relative differences and also by Bland-Altman plots. The interpretation of the results of reliability and agreement was performed according to a recent publication on this subject [12]. Results A random selection of 47 nulliparous women who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were included in the final statistical analysis. The mean age was years old, Med Ultrason 2016; 18(3): the mean height was cm, the mean weight was kg, and the mean BMI was 22.9±2.8 kg/m². There was no difference between the two measurements performed by the first examiner, the measurements performed between both examiners, and also between both methods (3DUS in the rendering mode and OmniView ) regarding the systematic error of the hiatal area measurement. Although a systematic error between the examiners was not observed, a slight significant difference between OmniView and 3DUS in the rendering mode techniques regarding the right pubovisceral muscle width which was smaller in the OmniView method was identified (Table I). In the evaluation of intra- and inter-observer reliability, despite the intra-observer reliability was reasonable (CCC ), the inter-observer reliability was very poor (CCC ), except for the measurement of the hiatal area using the 3DUS in the rendering mode, with CCC = 0.87 (Table II). The results for the agreement analysis were consistent with data from the reliability analysis (Table III, figures 2 5). The intra-observer differences were usually lower than ± 15%; however, the values were higher for inter-observer differences, reaching approximately ± 40% variation only by repeat testing. The exception was the hiatal area measurement by 3DUS in the rendering mode, where the difference of measurements between the examiners was usually less than ± 15%. Table I. Evaluation of the systematic errors between the examiners measurements and between the methods (3DUS in the rendering mode and Omniview ). Examiner 1A Examiner 1B Examiner 2 p (1A vs. 1B) p (1A vs. 2) Hiatal Area (cm²) Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD 3DUS in the rendering mode Omniview Comparison 3DUS vs. Omniview Right Pubovisceral Muscle Width (cm) 3DUS in the rendering mode Omniview Comparison 3DUS vs. Omniview <0.001 <0.001 p values determined by paired t-tests. SD: standard deviation.examiner 1A first measurement performed by first examiner. Examiner 1B second measurement performed by first examiner. Examiner 2 measurement performed by second examiner. Table II. Assessment of intra- and inter-observer reliability by concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) and their respective 95% confidence intervals (CI). Intra-observer Inter-observer Hiatal Area CCC 95% CI CCC 95% CI 3DUS in the rendering mode Omniview Right Pubovisceral Muscle Width 3DUS in the rendering mode Omniview
4 348 Zsuzsanna Ilona Katalin Jármy-Di Bella et al Reproducibility in pelvic floor biometric parameters of nulliparous women Table III. Assessment of intra and inter-observer agreement by the estimation of mean difference and the limits of agreement (LoA). Intra-observer Inter-observer Hiatal Area MD (%) LoA (%) MD (%) LoA (%) 3DUS in the rendering mode to to 18.3 Omniview to to 28.7 Right Pubovisceral Muscle Width 3DUS in the rendering mode to to 40.5 Omniview to to 39.1 MD = mean difference; LoA = limits of agreement Fig 2. The Bland-Altman plot of (a) intra- and (b) inter-observer reproducibility of hiatal area measurement using the 3DUS in the rendering mode. Fig 4. The Bland-Altman plot of (a) intra- and (b) inter-observer reproducibility of hiatal area measurement using the Omniview reformatting technique. Fig 3. The Bland-Altman plot of (a) intra- and (b) inter-observer reproducibility of the right pubovisceral muscle width measurement using the 3DUS in the rendering mode. Fig 5. The Bland-Altman plot of (a) intra- and (b) inter-observer reproducibility of right pubovisceral muscle width measurement using the Omniview reformatting technique. Discussions In this study, we assessed the reproducibility of 3DUS in the rendering mode and OmniView techniques to assess pelvic floor parameters. We observed that both techniques are concordant; however, the 3DUS in the rendering mode demonstrated better inter-observer reliability and agreement. In this study we preferred to use CCC to assess the reliability instead of intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) which is usually applied to pelvic floor parameters [3,4,13]. We preferred the CCC because there are several models for ICC choosing the most appropriate method could be complicated and because ICC is only valid when analysis of variance assumptions are present, which is frequently not the case [14]. According to Martins and Nastri, a good/moderate reliability/agreement of ultrasound measurements is obtained with ICC/ CCC of and LoA of approximately 5% 10%. This method may be applied for the purpose of research,
5 but must be employed with caution in clinical practice [12]. Majida et al [9] used a translabial 3DUS in the rendering mode to assess the reproducibility of hiatal area and thickness of pubovisceral muscle in 17 healthy women at rest, contraction, and during Valsalva maneuver. They observed a good inter-observer reliability (ICC = 0.92) and inter-observer agreement LoA approximately ±18% to the hiatal area at rest; however, the thickness of pubovisceral muscle at rest demonstrated poor inter-observer reliability (ICC ). In our study, we obtained similar results with a good inter-observer reliability (CCC=0.87) and inter-observer agreement LoA ( 13.5%18.3%) to the hiatal area at rest; however, poor reliability and agreement to the thickness of the right pubovisceral muscle, CCC=0.44 and LoA approximately ±35%, respectively, using the 3DUS in the rendering mode, was noted. We believe that this poor reproducibility of the thickness of pubovisceral muscle is a consequence of the difficulty to obtain clear and well-defined edges of the pubovisceral muscle in the translabial 3DUS in the rendering mode. Besides the pubovisceral muscle presents irregular edges, hindering the location of its maximum measurement. In a study using endovaginal 3DUS in the rendering mode, Yang et al [13] assessed the pelvic floor parameters of 59 nulliparous Chinese women. They observed better inter-observer reproducibility of the pubovisceral muscle area (ICC=0.78) than the hiatal area (ICC=0.63), probably because of the use of a higher frequency probe (RIC 5 9W), allowing better quality of pubovisceral muscle edges. In our study, we did not use the transvaginal approach, because it is a more invasive technique. Furthermore, the transabdominal approach allows a higher scanning window, enabling all edges of pubvisceral muscle to be included in the 3D volume dataset. Siafarikas et al [4] performed a study to analyze the learning curve for acquiring translabial 3D volume datasets of the pelvic floor to improve the inter-observer reproducibility. This prospective study involved 22 women in whom the 3D volumes were acquired by two examiners (inexperienced and experienced). After the training, 20 volumes acquired by experienced examiners were analyzed offline by an inexperienced examiner to assess the levator hiatus dimensions. The inter-observer reliability study showed reasonable ICC values (ICC ) for all levator hiatus measurements except the pubic arc (ICC=0.67). This study proved that the learning curve of the translabial 3DUS in the rendering mode is quick and effective. In our study, the acquisition of 3D volume datasets were performed by only one experienced sonographer and the offline analysis were performed by another experienced operator. Med Ultrason 2016; 18(3): Recently, Youssef et al [10] assessed the reproducibility of OmniView for pelvic hiatal area measurement at rest and agreement with the 3DUS in the rendering mode. They evaluated 124 nulliparous asymptomatic women and 118 women with symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction. They observed that the OmniView showed good intra- and inter-observer reliability (ICC=0.926 and 0.930, respectively) and agreement (LoA ±13.6 and ±12.6, respectively) in asymptomatic women. In addition, they observed a good intermethod agreement (ICC=0.917). In our study, we observed a good intra-observer and a poor inter-observer reliability and agreement using the OmniView reformatting technique. We believe that the poor inter-observer reproducibility is a consequence of the absent learning curve for the second examiner that is proved for the 3DUS in the rendering mode [4]. As both examiners presented great experience in the 3DUS in the rendering mode, the inter-observer reliability, and agreement to the hiatal area measurement was good. Ominiview reformatting technique, despite several applications in gynecology and obstetrics area, is a new technique in the assessment of pelvic floor and more experience is necessary before clinical practice application. Conclusion In summary, both 3DUS in the rendering mode and the OmniView techniques were concordant in the assessment of pelvic floor parameters; however, the 3DUS in the rendering mode showed better inter-observer reliability and agreement. Conflict of interest: none References 1. Khullar V, Salvatore S, Cardozo LD. Three dimensional ultrasound of the urethra and urethral pressure profiles. Int Urogynecol J 1994; 5: Dietz HP. Ultrasound imaging of the pelvic floor. Part II: three-dimensional or volume imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: Majida M, Braekken IH, Umek W, Bø K, Saltyte Benth J, Ellstrøm Engh M. Interobserver repeatability of threeand four-dimensional transperineal ultrasound assessment of pelvic floor muscle anatomy and function. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009; 33: Siafarikas F, Staer-Jensen J, Braekken IH, Bø K, Engh ME. Learning process for performing and analyzing 3D/4D transperineal ultrasound imaging and interobserver reliability study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: Tonni G, Lituania M. OmniView algorithm: a novel 3-dimensional sonographic technique in the study of the fetal 349
6 350 Zsuzsanna Ilona Katalin Jármy-Di Bella et al Reproducibility in pelvic floor biometric parameters of nulliparous women hard and soft palates. J Ultrasound Med 2012; 31: Rizzo G, Capponi A, Pietrolucci ME, et al. An algorithm based on OmniView technology to reconstruct sagittal and coronal plane of the fetal brain from volume datasets acquired by three-dimensional ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 38: Yeo L, Romero R, Jodicke C, et al. Four-chamber view and swing technique (FAST) echo: a novel and simple algorithm to visualize standard fetal echocardiographic planes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: Martinez LH, Araujo Júnior E, Simioni C, Nardozza LM, Moron AF. Reference ranges for vertebral body areas of the fetal lumbosacral spine on 3-dimensional sonography using volume contrast imaging with OmniView. J Ultrasound Med 2012; 31: Paladini D, Di Spiezio Sardo A, Coppola C, Zizolfi B, Pastore G, Nappi C. Ultrasound assessment of the Essure contraceptive devices: is three-dimensional ultrasound really needed? J Minim Invasive Gynecol 2015; 22: Youssef A, Montaguti E, Sanlorenzo O, et al. A new simple technique for 3-dimensional sonographic assessment of the pelvic floor muscles. J Ultrasound Med 2015; 34: Dietz HP, Shek C, Clarke B. Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus by three-dimensional pelvic floor ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: Martins WP, Nastri CO. Interpreting reproducibility results for ultrasound measurements. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: Yang JM, Yang SH, Huang WC. Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus in nulliparous Chinese women. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 28: Chen CC, Barnhart HX. Comparison of ICC and CCC for assessing agreement for data without and with replications. Comput Stat Data Anal 2008; 53:
Learning process for performing and analyzing 3D/4D transperineal ultrasound imaging and interobserver reliability study
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 312 317 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11192 Learning process for performing and analyzing 3D/4D transperineal ultrasound
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 312 317 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11192 Learning process for performing and analyzing 3D/4D transperineal ultrasound
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning
 Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
Guide to Pelvic Floor Multicompartment Scanning These guidelines have been prepared by Giulio A. Santoro, MD, PhD, Head Pelvic Floor Unit, Section of Anal Physiology and Ultrasound, Coloproctology Service,
Measuring echogenicity and area of the puborectalis muscle: method and reliability
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 44: 481 485 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13409 Measuring echogenicity and area of the puborectalis muscle: method
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 44: 481 485 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13409 Measuring echogenicity and area of the puborectalis muscle: method
Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus by three-dimensional pelvic floor ultrasound
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 580 585 Published online 10 May 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1899 Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 580 585 Published online 10 May 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1899 Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus
Ballooning of the levator hiatus
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 676 680 Published online 12 May 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5355 Ballooning of the levator hiatus H. P. DIETZ*, C. SHEK*,
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 676 680 Published online 12 May 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5355 Ballooning of the levator hiatus H. P. DIETZ*, C. SHEK*,
Is pelvic organ support different between young nulliparous African and Caucasian women?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2016; 47: 774 778 Published online 2 May 2016 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.15811 Is pelvic organ support different between young nulliparous
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2016; 47: 774 778 Published online 2 May 2016 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.15811 Is pelvic organ support different between young nulliparous
Original Article Efficacy of 3D ultrasound on diagnosis of women pelvic flour dysfunction
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):16523-16528 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028796 Original Article Efficacy of 3D ultrasound on diagnosis of women pelvic flour dysfunction Aifang Chen 1*, Yingzi Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):16523-16528 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0028796 Original Article Efficacy of 3D ultrasound on diagnosis of women pelvic flour dysfunction Aifang Chen 1*, Yingzi Zhang
Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus in nulliparous Chinese women
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 28: 710 716 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.3825 Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus in nulliparous
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 28: 710 716 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.3825 Biometry of the pubovisceral muscle and levator hiatus in nulliparous
TEST-RETEST RELIABILITY OF PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE CONTRACTION. Ingeborg Hoff BRÆKKEN, PhD student, Msci, PT, Manual therapist 1
 TEST-RETEST RELIABILITY OF PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE CONTRACTION MEASURED BY 4D ULTRASOUND Ingeborg Hoff BRÆKKEN, PhD student, Msci, PT, Manual therapist 1 Memona MAJIDA, Consultant gynaecologist 2 Marie Ellström
TEST-RETEST RELIABILITY OF PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE CONTRACTION MEASURED BY 4D ULTRASOUND Ingeborg Hoff BRÆKKEN, PhD student, Msci, PT, Manual therapist 1 Memona MAJIDA, Consultant gynaecologist 2 Marie Ellström
Pelvic floor function in elite nulliparous athletes
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 81 85 Published online 14 May 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.4027 Pelvic floor function in elite nulliparous athletes J. A.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 81 85 Published online 14 May 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.4027 Pelvic floor function in elite nulliparous athletes J. A.
Abstract. Introduction
 Original article doi:10.1111/codi.12740 Assessment of pubovisceral muscle defects and levator hiatal dimensions in women with faecal incontinence after vaginal delivery: is there a correlation with severity
Original article doi:10.1111/codi.12740 Assessment of pubovisceral muscle defects and levator hiatal dimensions in women with faecal incontinence after vaginal delivery: is there a correlation with severity
Inter- and intraobserver reliability for diagnosing levator ani changes on magnetic resonance imaging
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 347 352 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12462 Inter- and intraobserver reliability for diagnosing levator ani changes
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 347 352 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12462 Inter- and intraobserver reliability for diagnosing levator ani changes
How can we measure bladder volumes in women with advanced pelvic organ prolapse?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 215; 46: 233 238 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14678 How can we measure bladder volumes in women with advanced pelvic organ
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 215; 46: 233 238 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14678 How can we measure bladder volumes in women with advanced pelvic organ
Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength Ghazaleh Rostaminia, MD, Jennifer Peck, PhD, Lieschen Quiroz, MD, S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD Received December 4,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength Ghazaleh Rostaminia, MD, Jennifer Peck, PhD, Lieschen Quiroz, MD, S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD Received December 4,
Why are some women with pelvic floor dysfunction unable to contract their pelvic floor muscles?
 Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2013; 53: 574 579 DOI: 10.1111/ajo.12133 Original Article Why are some women with pelvic floor dysfunction unable to contract their pelvic
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2013; 53: 574 579 DOI: 10.1111/ajo.12133 Original Article Why are some women with pelvic floor dysfunction unable to contract their pelvic
New imaging method for assessing pelvic floor biomechanics
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 201 205 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5219 New imaging method for assessing pelvic floor biomechanics I. THYER*,
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 201 205 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5219 New imaging method for assessing pelvic floor biomechanics I. THYER*,
A. FALKERT, A. WILLMANN, E. ENDRESS, P. MEINT and B. SEELBACH-GÖBEL ABSTRACT
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 204 209 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11214 Three-dimensional ultrasound of pelvic floor: is there a correlation
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 204 209 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.11214 Three-dimensional ultrasound of pelvic floor: is there a correlation
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging. Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague)
 Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 740925, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/740925 Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles Laila Najjari,
BioMed Research International, Article ID 740925, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/740925 Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles Laila Najjari,
USING AN INVERSE METHOD TO OBTAIN THE MATERIAL PARAMETERS OF THE MOONEY-RIVLIN CONSTITUTIVE MODEL FOR PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES
 Congresso de Métodos Numéricos em Engenharia 2015 Lisboa, 29 de Junho a 2 de Julho, 2015 APMTAC, Portugal, 2015 USING AN INVERSE METHOD TO OBTAIN THE MATERIAL PARAMETERS OF THE MOONEY-RIVLIN CONSTITUTIVE
Congresso de Métodos Numéricos em Engenharia 2015 Lisboa, 29 de Junho a 2 de Julho, 2015 APMTAC, Portugal, 2015 USING AN INVERSE METHOD TO OBTAIN THE MATERIAL PARAMETERS OF THE MOONEY-RIVLIN CONSTITUTIVE
Association between ICS POP-Q coordinates and translabial ultrasound findings: implications for definition of normal pelvic organ support
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 216; 47: 36368 Published online 29 January 216 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14872 Association between ICS POP-Q coordinates and translabial
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 216; 47: 36368 Published online 29 January 216 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.14872 Association between ICS POP-Q coordinates and translabial
Minimal criteria for the diagnosis of avulsion of the puborectalis muscle by tomographic ultrasound
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:699 704 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1329-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimal criteria for the diagnosis of avulsion of the puborectalis muscle by tomographic ultrasound Hans Peter Dietz &
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:699 704 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1329-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimal criteria for the diagnosis of avulsion of the puborectalis muscle by tomographic ultrasound Hans Peter Dietz &
Modern methods of imaging in urogynecology when do we really need them?
 Archives of Perinatal Medicine 23(2), 77 81, 2017 ORIGINAL PAPER Modern methods of imaging in urogynecology when do we really need them? GRZEGORZ SURKONT, EDYTA WLAŹLAK Abstract Imaging is more often used
Archives of Perinatal Medicine 23(2), 77 81, 2017 ORIGINAL PAPER Modern methods of imaging in urogynecology when do we really need them? GRZEGORZ SURKONT, EDYTA WLAŹLAK Abstract Imaging is more often used
Constriction of the levator hiatus during instruction of pelvic floor or transversus abdominis contraction: a 4D ultrasound study
 DOI 10.1007/s00192-008-0719-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Constriction of the levator hiatus during instruction of pelvic floor or transversus abdominis contraction: a 4D ultrasound study Kari Bø & Ingeborg H. Brækken
DOI 10.1007/s00192-008-0719-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Constriction of the levator hiatus during instruction of pelvic floor or transversus abdominis contraction: a 4D ultrasound study Kari Bø & Ingeborg H. Brækken
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND
 PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
PELVIC FLOOR ULTRASOUND How, When, Why Part 1: Phyllis Glanc MD Sunnybrook Health Science Center University of Toronto Phyllis.Glanc@sunnybrook.ca www.phyllisglanc.com (current exact handout) Disclosures
Long-term follow-up of sacrocolpopexy mesh implants at two time intervals at least 1 year apart using 4D transperineal ultrasound
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2017; 49: 398 403 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.15891 Long-term follow-up of sacrocolpopexy mesh implants at two time intervals
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2017; 49: 398 403 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.15891 Long-term follow-up of sacrocolpopexy mesh implants at two time intervals
Axial Plane Imaging. Hans Peter Dietz. Levator Ani Complex
 6 Axial Plane Imaging Hans Peter Dietz Levator Ani Complex It is only very recently that imaging of the levator ani has become feasible using translabial ultrasound. The inferior aspects of the levator
6 Axial Plane Imaging Hans Peter Dietz Levator Ani Complex It is only very recently that imaging of the levator ani has become feasible using translabial ultrasound. The inferior aspects of the levator
Vincent Letouzey, MD, PhD
 How to protect the perineum and prevent obstetric perineal trauma Standards of OASIS diagnosis: Primary (clinical) and Secondary (ultrasound) Vincent Letouzey, MD, PhD Obst/Gyne Dept Nîmes University Hospital
How to protect the perineum and prevent obstetric perineal trauma Standards of OASIS diagnosis: Primary (clinical) and Secondary (ultrasound) Vincent Letouzey, MD, PhD Obst/Gyne Dept Nîmes University Hospital
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, K., Hilde, G., Stær-Jensen, J., Brækken, I. H. (2011). Can the Paula method facilitate co-contraction of the
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, K., Hilde, G., Stær-Jensen, J., Brækken, I. H. (2011). Can the Paula method facilitate co-contraction of the
Diagnosis of cystocele type by clinical examination and pelvic floor ultrasound
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 39: 710 714 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10156 Diagnosis of cystocele type by clinical examination and pelvic floor
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 39: 710 714 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10156 Diagnosis of cystocele type by clinical examination and pelvic floor
Use of a visual analog scale for evaluation of bother from pelvic organ prolapse
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 693 697 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13222 Use of a visual analog scale for evaluation of bother from pelvic organ
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 693 697 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13222 Use of a visual analog scale for evaluation of bother from pelvic organ
Camila Garcia de Carvalho 15:30 16:00 Break None 16:00 16:45 Live scans: functional evaluation using translabial Zsuzsanna Jarmi Di Bella
 W35: Clinical, biomechanical and functional evaluation of pelvic floor in female athletes. A multidisciplinary approach. Workshop Chair: Maita Poli de Araujo, Brazil 21 October 2014 14:00-18:00 Start End
W35: Clinical, biomechanical and functional evaluation of pelvic floor in female athletes. A multidisciplinary approach. Workshop Chair: Maita Poli de Araujo, Brazil 21 October 2014 14:00-18:00 Start End
Does levator ani injury affect cystocele type?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2010; 36: 618 623 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.7712 Does levator ani injury affect cystocele type? V. H. EISENBERG*, V.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2010; 36: 618 623 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.7712 Does levator ani injury affect cystocele type? V. H. EISENBERG*, V.
How common is pelvic floor muscle atrophy after vaginal childbirth?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 3 Published online 2 December 2013 in Wiley Online Library wileyonlinelibrary.com. DOI: 10.1002/uog.12543 How common is pelvic floor muscle atrophy after vaginal childbirth?
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 3 Published online 2 December 2013 in Wiley Online Library wileyonlinelibrary.com. DOI: 10.1002/uog.12543 How common is pelvic floor muscle atrophy after vaginal childbirth?
Three-dimensional transperineal ultrasound for imaging mesh implants following sacrocolpopexy
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 459 465 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13303 Three-dimensional transperineal ultrasound for imaging mesh implants
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 459 465 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13303 Three-dimensional transperineal ultrasound for imaging mesh implants
Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture
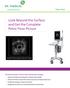 Pelvic Floor Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture Endovaginal ultrasound. Levator ani defect seen on the right side (arrows). A=anus, B=bladder, LA=levator ani, U=urethra.
Pelvic Floor Look Beyond the Surface and Get the Complete Pelvic Floor Picture Endovaginal ultrasound. Levator ani defect seen on the right side (arrows). A=anus, B=bladder, LA=levator ani, U=urethra.
Ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary system in women after Burch colposuspension
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: 58 64 Ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary system in Blackwell Original Paper Science, Ltd women after Burch colposuspension A. MARTAN, J. MASATA, M. HALASKA and
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: 58 64 Ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary system in Blackwell Original Paper Science, Ltd women after Burch colposuspension A. MARTAN, J. MASATA, M. HALASKA and
Research Article Ultrasound Thickness of Bladder Wall in Continent and Incontinent Women and Its Correlation with Cystometry
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 684671, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/684671 Research Article Ultrasound Thickness of Bladder Wall in Continent and Incontinent Women and Its Correlation
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 684671, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/684671 Research Article Ultrasound Thickness of Bladder Wall in Continent and Incontinent Women and Its Correlation
Urogynaecology. Introduction. G Hilde, a,b J Stær-Jensen, b F Siafarikas, b,c K Gjestland, b M Ellstr om Engh, b,c KBø a,b
 DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12321 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology How well can pelvic floor muscles with major defects contract? A cross-sectional comparative study 6 weeks after delivery using transperineal 3D/4D
DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12321 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology How well can pelvic floor muscles with major defects contract? A cross-sectional comparative study 6 weeks after delivery using transperineal 3D/4D
Three-Dimensional Ultrasonographic Bladder Volume Measurement
 Article Three-Dimensional Ultrasonographic Bladder Volume Measurement Reliability of the Virtual Organ Computer-Aided Analysis Technique Using Different Rotation Steps Chitkasaem Suwanrath, MD, MMedSci,
Article Three-Dimensional Ultrasonographic Bladder Volume Measurement Reliability of the Virtual Organ Computer-Aided Analysis Technique Using Different Rotation Steps Chitkasaem Suwanrath, MD, MMedSci,
Levator trauma is associated with pelvic organ prolapse
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01751.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology Levator trauma is associated with pelvic organ prolapse HP Dietz, a JM Simpson b a Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01751.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology Levator trauma is associated with pelvic organ prolapse HP Dietz, a JM Simpson b a Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging (EAUS) W44, 30 August :00-18:00
 Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging (EAUS) W44, 30 August 2011 14:00-18:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:10 Introduction: Pre-test,
Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging (EAUS) W44, 30 August 2011 14:00-18:00 Start End Topic Speakers 14:00 14:10 Introduction: Pre-test,
Special Thank You NO DISCLOSURES. Objectives. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Role of Ultrasound Text
 Special Thank You Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Role of Ultrasound Phyllis Glanc Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center Department Medical Imaging Associate Professor, University of Toronto phyllis.glanc@sunnybrook.ca
Special Thank You Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Role of Ultrasound Phyllis Glanc Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center Department Medical Imaging Associate Professor, University of Toronto phyllis.glanc@sunnybrook.ca
The prevalence of major abnormalities of the levator ani in urogynaecological patients
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00819.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology The prevalence of major abnormalities of the levator ani in urogynaecological patients HP Dietz, a AB Steensma b a
DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00819.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Urogynaecology The prevalence of major abnormalities of the levator ani in urogynaecological patients HP Dietz, a AB Steensma b a
NEWER DIMENSIONS IN THE EVALUATION OF PELVIC PATHOLOGY BY TRANSPERINEAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY S. C. Sanjay 1, N. Krishnappa 2, Anil Kumar Shukla 3
 NEWER DIMENSIONS IN THE EVALUATION OF PELVIC PATHOLOGY BY TRANSPERINEAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY S. C. Sanjay 1, N. Krishnappa 2, Anil Kumar Shukla 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. C. Sanjay, N. Krishnappa, Anil
NEWER DIMENSIONS IN THE EVALUATION OF PELVIC PATHOLOGY BY TRANSPERINEAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY S. C. Sanjay 1, N. Krishnappa 2, Anil Kumar Shukla 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: S. C. Sanjay, N. Krishnappa, Anil
Sonography-based Automated Volume Count (SonoAVC): an efficient and reproducible method of follicular assessment
 GE Healthcare Sonography-based Automated Volume Count (SonoAVC): an efficient and reproducible method of follicular assessment Todd D. Deutch, MD Clinical Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Fellow
GE Healthcare Sonography-based Automated Volume Count (SonoAVC): an efficient and reproducible method of follicular assessment Todd D. Deutch, MD Clinical Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Fellow
Does childbirth alter the reflex pelvic floor response to coughing?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol (2012) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10083 Does childbirth alter the reflex pelvic floor response to coughing? H. P. DIETZ,
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol (2012) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10083 Does childbirth alter the reflex pelvic floor response to coughing? H. P. DIETZ,
Levator hiatal area as a risk factor for cystocele recurrence after surgery: a prospective study
 DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.13340 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology Levator hiatal area as a risk factor for cystocele recurrence after surgery: a prospective study TFM Vergeldt, a KJB Notten, b M Weemhoff, c SMJ
DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.13340 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology Levator hiatal area as a risk factor for cystocele recurrence after surgery: a prospective study TFM Vergeldt, a KJB Notten, b M Weemhoff, c SMJ
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Int Urogynecol J. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 December 06.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J. 2011 December ; 22(12): 1491 1495. doi:10.1007/s00192-011-1458-4. URETHRAL CLOSURE PRESSURES AMONG PRIMIPAROUS WOMEN
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J. 2011 December ; 22(12): 1491 1495. doi:10.1007/s00192-011-1458-4. URETHRAL CLOSURE PRESSURES AMONG PRIMIPAROUS WOMEN
Iraqi JMS. Perineal Ultrasound for Evaluating Bladder Neck and Urethra in Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqi_jms_alnahrain @yahoo.com http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Perineal Ultrasound for Evaluating Bladder Neck and Urethra
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqi_jms_alnahrain @yahoo.com http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Perineal Ultrasound for Evaluating Bladder Neck and Urethra
An Introduction to 4D View TM (Version 5.0)
 9 An Introduction to 4D View TM (Version 5.0) Hans Peter Dietz This book includes a DVD that contains a version of the software 4D View (version 5.0), courtesy of GE Medical, Kretz Ultrasound, Zipf, Austria.
9 An Introduction to 4D View TM (Version 5.0) Hans Peter Dietz This book includes a DVD that contains a version of the software 4D View (version 5.0), courtesy of GE Medical, Kretz Ultrasound, Zipf, Austria.
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness. Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne
 Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound- Atlas and Textbook by Hans Peter Dietz MD PhD
 Pelvic Floor Ultrasound- Atlas and Textbook by Hans Peter Dietz MD PhD is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. This means you can use, distribute,
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound- Atlas and Textbook by Hans Peter Dietz MD PhD is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. This means you can use, distribute,
Vision of a new dimension
 Samsung Medison, an affiliate of Samsung Electronics, is a global medical company founded in 1985. With a mission to bring health and well-being to people's lives, the company manufactures diagnostic ultrasound
Samsung Medison, an affiliate of Samsung Electronics, is a global medical company founded in 1985. With a mission to bring health and well-being to people's lives, the company manufactures diagnostic ultrasound
Laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy: how low does the mesh go?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2017; 49: 404 408 Published online 7 February 2017 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.15882 Laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy: how low does the mesh
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2017; 49: 404 408 Published online 7 February 2017 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.15882 Laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy: how low does the mesh
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2742-2750 Role of dynamic MRI in assessment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in Females Nada Ahmed Hussein, Naglaa Hussein Shebrya, Nermeen
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2742-2750 Role of dynamic MRI in assessment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in Females Nada Ahmed Hussein, Naglaa Hussein Shebrya, Nermeen
State of the art: an integrated approach to pelvic floor ultrasonography
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 381 396 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8816 State of the art: an integrated approach to pelvic floor ultrasonography
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 381 396 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8816 State of the art: an integrated approach to pelvic floor ultrasonography
The pelvic floor muscles (PFM) form
 Correlation of Digital Palpation and Transabdominal Ultrasound for Assessment of Pelvic Floor Muscle Contraction Amir Massoud Arab, PT, PhD 1 ; Roxana Bazaz Behbahani, PT, BSc 2 ; Leila Lorestani, PT,
Correlation of Digital Palpation and Transabdominal Ultrasound for Assessment of Pelvic Floor Muscle Contraction Amir Massoud Arab, PT, PhD 1 ; Roxana Bazaz Behbahani, PT, BSc 2 ; Leila Lorestani, PT,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Judith A. Thompson & Peter B. O Sullivan & N. Kathryn Briffa & Patricia Neumann
 Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
IUGA Fellowship 2013 Final Report
 IUGA Fellowship 2013 Final Report Award Recipient: Andrea C. Santiago, M.D. (Philippines) Dates of Fellowship: June 1, 2013- May 31, 2014 Host Site: University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Host:
IUGA Fellowship 2013 Final Report Award Recipient: Andrea C. Santiago, M.D. (Philippines) Dates of Fellowship: June 1, 2013- May 31, 2014 Host Site: University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Host:
Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor. Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole
 Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole Pelvic Floor 1. Sacrospinous Ligament 2. Levator Ani A Puborectalis B. Pubococcygeus C. Iliococcygeus 3.
Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole Pelvic Floor 1. Sacrospinous Ligament 2. Levator Ani A Puborectalis B. Pubococcygeus C. Iliococcygeus 3.
Introital ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract symptoms following anti-incontinence surgery using a synthetic midurethral tape
 International Urogynecology Journal https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-018-3837-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introital ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract symptoms following anti-incontinence surgery
International Urogynecology Journal https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-018-3837-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introital ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract symptoms following anti-incontinence surgery
Is levator avulsion a predictor of cystocele recurrence following anterior vaginal mesh placement?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 230 234 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12433 Is levator avulsion a predictor of cystocele recurrence following anterior
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 230 234 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12433 Is levator avulsion a predictor of cystocele recurrence following anterior
IUGA : Introduction: Pre-test, Course objectives, clinical (Max 1000 words) and rationale for pelvic floor imaging S.
 IUGA WS 7 Workshop Outline Chairman: S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD (USA) IUGA Title of workshop Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging IU(EA (EAUS)
IUGA WS 7 Workshop Outline Chairman: S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD (USA) IUGA Title of workshop Comprehensive 3D Pelvic Floor Ultrasonography with emphasis on endovaginal (EVUS) and endoanal imaging IU(EA (EAUS)
The relationship between postpartum levator ani muscle avulsion and signs and symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction
 DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12666 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology The relationship between postpartum levator ani muscle avulsion and signs and symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction K van Delft, a AH Sultan, a R
DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12666 www.bjog.org Urogynaecology The relationship between postpartum levator ani muscle avulsion and signs and symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction K van Delft, a AH Sultan, a R
Both the middle and distal sections of the urethra may be regarded as optimal targets for outside in transobturator tape placement
 DOI 10.1007/s00345-014-1261-1 Original Article Both the middle and distal sections of the urethra may be regarded as optimal targets for outside in transobturator tape placement Michał Bogusiewicz Marta
DOI 10.1007/s00345-014-1261-1 Original Article Both the middle and distal sections of the urethra may be regarded as optimal targets for outside in transobturator tape placement Michał Bogusiewicz Marta
M. OTCENASEK*, L. KROFTA*, V. BACA, R. GRILL, E. KUCERA*, H. HERMAN*, I. VASICKA*, J. DRAHONOVSKY* and J. FEYEREISL*
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 29: 692 696 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.4030 Bilateral avulsion of the puborectal muscle: magnetic resonance imaging-based
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 29: 692 696 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.4030 Bilateral avulsion of the puborectal muscle: magnetic resonance imaging-based
Morphometry of the Pelvic Floor Muscles in Women With and Without Provoked Vestibulodynia Using 4D Ultrasound
 776 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAIN Morphometry of the Pelvic Floor Muscles in Women With and Without Provoked Vestibulodynia Using 4D Ultrasound Mélanie Morin, PT, PhD,* Sophie Bergeron, PhD, Samir Khalifé, MD,
776 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAIN Morphometry of the Pelvic Floor Muscles in Women With and Without Provoked Vestibulodynia Using 4D Ultrasound Mélanie Morin, PT, PhD,* Sophie Bergeron, PhD, Samir Khalifé, MD,
Abstract. Introduction. RBMOnline - Vol 18. No Reproductive BioMedicine Online; on web 26 March 2009
 RBMOnline - Vol 18. No 5. 2009 658-663 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/3762 on web 26 March 2009 Article Automated follicle tracking improves measurement reliability in patients
RBMOnline - Vol 18. No 5. 2009 658-663 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/3762 on web 26 March 2009 Article Automated follicle tracking improves measurement reliability in patients
Sonocubic fine: new three-dimensional ultrasound software to the screening of congenital heart diseases
 Araujo Júnior SPECIAL E, et al. - Sonocubic ARTICLE fine: new three-dimensional ultrasound Sonocubic fine: new three-dimensional ultrasound Sonocubic fine: novo software de ultrassonografia tridimensional
Araujo Júnior SPECIAL E, et al. - Sonocubic ARTICLE fine: new three-dimensional ultrasound Sonocubic fine: new three-dimensional ultrasound Sonocubic fine: novo software de ultrassonografia tridimensional
EFFECT OF SPINAL MANIPULATION ON PELVIC FLOOR FUNCTIONAL CHANGES IN PREGNANT AND NONPREGNANT WOMEN: A PRELIMINARY STUDY
 EFFECT OF SPINAL MANIPULATION ON PELVIC FLOOR FUNCTIONAL CHANGES IN PREGNANT AND NONPREGNANT WOMEN: A PRELIMINARY STUDY Heidi Haavik, BSc (Chiro), PhDip (Science), PhD, a Bernadette A. Murphy, DC, MSc,
EFFECT OF SPINAL MANIPULATION ON PELVIC FLOOR FUNCTIONAL CHANGES IN PREGNANT AND NONPREGNANT WOMEN: A PRELIMINARY STUDY Heidi Haavik, BSc (Chiro), PhDip (Science), PhD, a Bernadette A. Murphy, DC, MSc,
Doctor s assessment and evaluation of the pelvic floor in antenatal and postpartum women: routine or???
 Doctor s assessment and evaluation of the pelvic floor in antenatal and postpartum women: routine or??? Dr Barry O Reilly Head of department of Urogynaecology Cork University Maternity Hospital Ireland
Doctor s assessment and evaluation of the pelvic floor in antenatal and postpartum women: routine or??? Dr Barry O Reilly Head of department of Urogynaecology Cork University Maternity Hospital Ireland
Aetiology 1998 Bump & Norton Theoretical model
 Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers. This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions.
 Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions. This lesson was derived from pages 33 through 42 in the textbook: Ultrasound Transducers Ultrasound Transducers
Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions. This lesson was derived from pages 33 through 42 in the textbook: Ultrasound Transducers Ultrasound Transducers
Comparison Of Accuracy Of Prostate Model Volume Measurement Between 2 Dimensional And 3 Dimensional Ultrasonography.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 2 Comparison Of Accuracy Of Prostate Model Volume Measurement Between 2 Dimensional And 3 Dimensional Ultrasonography. S Park, S Hwang Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 2 Comparison Of Accuracy Of Prostate Model Volume Measurement Between 2 Dimensional And 3 Dimensional Ultrasonography. S Park, S Hwang Citation
GE Healthcare. Accomplish more. Voluson 730
 GE Healthcare Accomplish more. Voluson 730 Demand m In the fast-paced environment of today s clinical practice, you require the right tools to help you see more and do more every day. From routine 2D imaging
GE Healthcare Accomplish more. Voluson 730 Demand m In the fast-paced environment of today s clinical practice, you require the right tools to help you see more and do more every day. From routine 2D imaging
P. SLADKEVICIUS and L. VALENTIN ABSTRACT
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 318 327 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12289 Intra- and interobserver agreement when describing adnexal masses using
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 318 327 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12289 Intra- and interobserver agreement when describing adnexal masses using
Pelvic Floor Exercise. Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist
 Pelvic Floor Exercise Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist Treatment for urinary incontinence Pelvic floor muscle exercise (Kegel, 1948) Bladder retraining Behaviour modification Treatment for urinary incontinence
Pelvic Floor Exercise Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist Treatment for urinary incontinence Pelvic floor muscle exercise (Kegel, 1948) Bladder retraining Behaviour modification Treatment for urinary incontinence
Association between Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of the Pelvic Floor and de novo Stress Urinary Incontinence after Vaginal Delivery
 Original Article Genitourinary Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.715 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):715-723 Association between Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings
Original Article Genitourinary Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.715 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):715-723 Association between Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings
Value of UVJ-M in the diagnosis of SUI in late pregnancy and postpartum
 1772 Value of UVJ-M in the diagnosis of SUI in late pregnancy and postpartum GUIXIN ZHANG 1, WEI JIANG 1, QUANWEI GUO 2 and QUANRONG GUO 3 Departments of 1 Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2 Ultrasonography,
1772 Value of UVJ-M in the diagnosis of SUI in late pregnancy and postpartum GUIXIN ZHANG 1, WEI JIANG 1, QUANWEI GUO 2 and QUANRONG GUO 3 Departments of 1 Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2 Ultrasonography,
Ultrasound Characteristics of Patients with Urinary Stress Incontinence with or without Genital Prolapse
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.10.691 Voiding Dysfunction Ultrasound Characteristics of Patients with Urinary Stress Incontinence with or without Genital Prolapse Vesna S. Antovska
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.10.691 Voiding Dysfunction Ultrasound Characteristics of Patients with Urinary Stress Incontinence with or without Genital Prolapse Vesna S. Antovska
Neither Dr. Geri Hewitt nor Dr. Richard Wood have any disclosures.
 Gynecological Considerations in Patients with Cloacal Malformations: From Antenatal Diagnosis through Evaluation to Final Reconstruction Geri Hewitt, MD and Richard J. Wood, MD Center for Colorectal and
Gynecological Considerations in Patients with Cloacal Malformations: From Antenatal Diagnosis through Evaluation to Final Reconstruction Geri Hewitt, MD and Richard J. Wood, MD Center for Colorectal and
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop
 Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 January 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009 February ; 20(2): 171 175. doi:10.1007/ s00192-008-0738-0. The Cough Game : Are there
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009 February ; 20(2): 171 175. doi:10.1007/ s00192-008-0738-0. The Cough Game : Are there
K. SVABIK, A. MARTAN, J. MASATA, R. EL-HADDAD and P. HUBKA ABSTRACT
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 365 371 Published online 11 March 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13305 Comparison of vaginal mesh repair with sacrospinous vaginal
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2014; 43: 365 371 Published online 11 March 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.13305 Comparison of vaginal mesh repair with sacrospinous vaginal
Test-Retest Reliability of an Instrumented Speculum for Measuring Vaginal Closure Force
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 26:858 863 (2007) Test-Retest Reliability of an Instrumented Speculum for Measuring Vaginal Closure Force J.M. Miller, 1,4 * y J.A. Ashton-Miller, 2{ D. Perruchini, 3 and J.O.L.
Neurourology and Urodynamics 26:858 863 (2007) Test-Retest Reliability of an Instrumented Speculum for Measuring Vaginal Closure Force J.M. Miller, 1,4 * y J.A. Ashton-Miller, 2{ D. Perruchini, 3 and J.O.L.
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
Prospective evaluation of automated follicle monitoring in 58 in vitro fertilization cycles: follicular volume as a new indicator of oocyte maturity
 Prospective evaluation of automated follicle monitoring in 58 in vitro fertilization cycles: follicular volume as a new indicator of oocyte maturity Adela Rodrıguez-Fuentes, M.D., a Jairo Hernandez, Ph.D.,
Prospective evaluation of automated follicle monitoring in 58 in vitro fertilization cycles: follicular volume as a new indicator of oocyte maturity Adela Rodrıguez-Fuentes, M.D., a Jairo Hernandez, Ph.D.,
KEYWORDS: cystocele; laparoscopic Burch colposuspension; ultrasound cystourethrography; urodynamic stress incontinence; voiding function
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 289 295 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1838 Dynamic morphological changes in the anterior vaginal wall before
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 289 295 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1838 Dynamic morphological changes in the anterior vaginal wall before
Ultrasonic Assessment of the Internal Urethral Sphincter in Stress Urinary Incontinence
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 2 Number 1 Ultrasonic Assessment of the Internal Urethral Sphincter in Stress Urinary Incontinence I Kandil, A El Hemaly, M Radwan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 2 Number 1 Ultrasonic Assessment of the Internal Urethral Sphincter in Stress Urinary Incontinence I Kandil, A El Hemaly, M Radwan Citation
Does delayed child-bearing increase the risk of levator injury in labour?
 Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2007; 47: 491 495 Blackwell Publishing Asia Original Article Delayed child-bearing and levator injury Does delayed child-bearing increase
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2007; 47: 491 495 Blackwell Publishing Asia Original Article Delayed child-bearing and levator injury Does delayed child-bearing increase
Original Article Evaluation of levator ani with no defect on elastography in women with POP
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(6):10204-10212 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0008463 Original Article Evaluation of levator ani with no defect on elastography in women with POP Meng Xie 1,4*, Xuyin Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(6):10204-10212 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0008463 Original Article Evaluation of levator ani with no defect on elastography in women with POP Meng Xie 1,4*, Xuyin Zhang
The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence Compared to Urodynamic Studies
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 231-23 7, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 231-23 7, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation
 3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
The Urethral Motion Profile Before and After Suburethral Sling Placement
 The Urethral Motion Profile Before and After Suburethral Sling Placement Ka Lai Shek,* Varisara Chantarasorn and Hans Peter Dietz From the Nepean Clinical School, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
The Urethral Motion Profile Before and After Suburethral Sling Placement Ka Lai Shek,* Varisara Chantarasorn and Hans Peter Dietz From the Nepean Clinical School, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
3D ultrasound applied to abdominal aortic aneurysm: preliminary evaluation of diameter measurement accuracy
 3D ultrasound applied to abdominal aortic aneurysm: preliminary evaluation of diameter measurement accuracy Poster No.: C-0493 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. LONG
3D ultrasound applied to abdominal aortic aneurysm: preliminary evaluation of diameter measurement accuracy Poster No.: C-0493 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. LONG
Birth Trauma. H. P. Dietz. University of Sydney, Nepean Campus. Penrith, Australia
 Birth Trauma H. P. Dietz University of Sydney, Nepean Campus Penrith, Australia Procedures in US (2010): 1.6 Prolapse Urinary Incontinence Fecal Incontinence Prolapse 200.000 Urinary Incontinence 120.000
Birth Trauma H. P. Dietz University of Sydney, Nepean Campus Penrith, Australia Procedures in US (2010): 1.6 Prolapse Urinary Incontinence Fecal Incontinence Prolapse 200.000 Urinary Incontinence 120.000
The significance of urethral hyperechogenicity in female lower urinary tract symptoms
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 67 71 Published online 8 June 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1067 The significance of urethral hyperechogenicity in female
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 67 71 Published online 8 June 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1067 The significance of urethral hyperechogenicity in female
Can the rectovaginal septum be visualized by transvaginal three-dimensional ultrasound?
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 348 352 Published online 10 January 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8896 Can the rectovaginal septum be visualized by transvaginal
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 348 352 Published online 10 January 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8896 Can the rectovaginal septum be visualized by transvaginal
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
