WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics. What is Statistics and how does it relate to you?
|
|
|
- Belinda Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics Time Interval/ Unit 1: Introduction to Statistics weeks S-IC-1: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters based on a random sample from that population. S-IC-3: Recognize the purposes of and differences among sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies; explain how randomization relates to each. S-IC-6: Evaluate reports based on data. What is Statistics and how does it relate to you? Statistics is a science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data in order to make decisions. Statistics Data Population Sample Parameter Descriptive Statistics Inferential Statistics Qualitative Data Quantitative Data Levels of Measurement Observational Study Experiment Simulation Survey Census Sampling Bias Error Performance Task: Analyzing a Statistical Study Distinguish between a population and a sample Distinguish between a parameter and statistic
2 Distinguish between descriptive statistics and inferential statistics Distinguish between qualitative data and quantitative data Classify data with respect to the four levels of measurement How to design a statistical study How to collect data by doing an observational study, performing an experiment, using a simulation, or a survey How to design an experiment How to create a sample using random sampling, simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic sampling and how to identify a biased sample
3 Time Interval/ Unit 2: Descriptive Statistics weeks S-ID-1: Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots). S-ID-2: Use statistics appropriate to the shape of the data distribution to compare center (median, mean) and spread (interquartile range, standard deviation) of two or more different data sets. S-ID-3: Interpret differences in shape, center, and spread in the context of the data sets, accounting for possible effects of extreme data points (outliers). S-ID-5: Summarize categorical data for two categories in two-way frequency tables, interpret relative frequencies in the context of the data (including joint, marginal, and conditional relative frequencies). Recognize possible associations and trends in the data. S-IC-6: Evaluate reports based on data. What is descriptive statistics and how is it useful when studying data? How does descriptive statistics affect inferential statistics? Descriptive statistics is the branch of statistics that involves the organization, summarization, and display of data. Descriptive statistics is useful when making inferences about the population. Frequency Distribution Histogram Frequency Polygon Ogive Stem-and-Leaf Plot Dot Plot Time Series Plot Pie Chart Pareto Chart Mean Median Mode Distribution Shapes Range Standard Deviation Variance Empirical Rule 5 Number Summary Box Plot Percentile Z-Score Performance Task: What s the Cost of Lunch? Construct a frequency distribution including limits, midpoints, relative frequencies, cumulative frequencies, and boundaries
4 Construct frequency histograms, frequency polygons, relative frequency histograms, and ogives How to graph quantitative data sets using exploratory data analysis tools of stem-and-leaf plots and dot plots How to graph and interpret paired data sets using scatter plots and time series charts How to graph qualitative data sets using pie charts and Pareto charts How to find the mea, median, and mode of a population and a sample How to describe the shape of a distribution as symmetric, uniform, or skewed and how to compare the mean and median for each How to find the range of a data set How to find the variance and standard deviation of a population and a sample How to use the Empirical Rule to interpret standard deviation How to approximate the sample standard deviation for grouped data How to find the quartiles and interquartile range of a data set How to draw a box plot How to interpret other fractiles such as percentiles How to find and interpret the standard score (z-score)
5 Time Interval/ Unit 3: Correlation and Regression weeks S-ID-6: Represent data on two quantitative variables on a scatter plot, and describe how the variables are related. S-ID-6A: Fit a function to the data; use functions fitted to data to solve problems in the context of the data. S-ID-6B: Informally assess the fit of a function by plotting and analyzing residuals. S-ID-6C: Fit a linear function for a scatter plot that suggests a linear association. S-ID-7: Interpret the slope (rate of change) and the intercept (constant term) of a linear model in the context of the data. S-ID-8: Compute (using technology) and interpret the correlation coefficient of a linear fit. S-ID-9: Distinguish between correlation and causation. What can we use to determine the relationship between two variables? How can we make predictions using ordered pair data and scatter plots? Correlation is the relationship between two variables. A regression line is the line of best. A regression line can be used to make predictions. An error will occur when using a regression line to make predictions. Scatter plot Correlation Independent Variable Dependent Variable Correlation Coefficient Residuals Regression Line Total Deviation Explained Deviation Unexplained Deviation Coefficient of Determination Standard Error of Estimate Perforamce Task: Comparing Flight Distances vs Cost Construct a Scatter Plot Find the Correlation Coefficient Find the Equation of a Regression Line Find and Interpret the Coefficient of Determination Find and Interpret the Standard Error of Estimate
6 Time Interval/ Unit 4: Probability weeks S-CP-1: Describe events as subsets of a sample space (the set of outcomes) using characteristics (or categories) of the outcomes, or as unions, intersections, or complements of other events ( or, and, not ). S-CP-2: Understand that two events A and B are independent if the probability of A and B occurring together is the product of their probabilities, and use this characterization to determine if they are independent. S-CP-3: Understand the conditional probability of A given B as P(A and B)/P(B), and interpret independence of A and B as saying that the conditional probability of A given B is the same as the probability of A, and the conditional probability of B given A is the same as the probability of B. S-CP-4: Construct and interpret twoway frequency tables of data when two categories are associated with each object being classified. Use the two-way table as a sample space to decide if events are independent and to approximate conditional probabilities. S-CP-5: Recognize and explain the concepts of conditional probability and independence in everyday language and everyday situations. S-CP-6: Find the conditional How can we determine the probability of an event occurring? Probability is the chance an event occurs. The differences between the Counting Principal, Multiplication Rule, and Addition Rule. Probability Experiment Outcome Sample Space Event Simple Event Fundamental Counting Principal Classical Probability Empirical Probability Subjective Probability Complement of Event Conditional Probability Independent Dependent Multiplication Rule Mutually Exclusive Addition Rule Permutation Distinguishable Permutation Factorial Combination Identify the Sample Space of a probability experiment and to identify simple events Performance Task: Casino Day
7 probability of A given B as the fraction of B s outcomes that also belong to A, and interpret the answer in terms of the model. S-CP-7: Apply the Addition Rule, P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) P(A and B), and interpret the answer in terms of the model. S-CP-8: Apply the general Multiplication Rule in a uniform probability model, P(A and B) = P(A)P(B A) = P(B)P(A B), and interpret the answer in terms of the model. S-CP-9: Use permutations and combinations to compute probabilities of compound events and solve problems. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find the number of ways two or more events can occur Distinguish among classical probability, empirical probability, and subjective probability Find the probability of the complement of an event and how to find other probabilities using tree diagrams and the Fundamental Counting Principal Find conditional probabilities Distinguish between independent and dependent events Use the Multiplication Rule to find the probability of two events occurring in sequence Determine if two events are mutually exclusive Use the Additional Rule to find the probability of two events Find the number of ways a group of objects can be arranged in order and the number of ways to choose several objects from a group without regard to order Use the counting principal to find probabilities
8 Time Interval/ Unit 5: Probability Distributions 4.1, weeks S-MD-1: Define a random variable for a quantity of interest by assigning a numerical value to each event in a sample space; graph the corresponding probability distribution using the same graphical displays as for data distributions. S-MD-2: Calculate the expected value of a random variable; interpret it as the mean of the probability distribution. S-MD-3: Develop a probability distribution for a random variable defined for a sample space in which theoretical probabilities can be calculated; find the expected value. S-MD-4: Develop a probability distribution for a random variable defined for a sample space in which probabilities are assigned empirically; find the expected value. S-MD-5: Weight the possible outcomes of a decision by assigning probabilities to payoff values and finding expected values. S-MD-5A: Find the expected payoff for a game of chance. S-MD-5B: Evaluate and compare strategies on the basis of expected values. S-ID-6: Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize How can we interpret a probability distribution? When should we use a discrete distribution versus a continuous distribution? A probability distribution is every possible value the random variable can assume, together with its probability. Discrete probability distributions are for finite or countable possible outcomes. Continuous probability distributions are for infinite or uncountable possible outcomes, represented by the normal curve. Random Variable Discrete Continuous Probability Distribution Mean of a Random Variable Standard Deviation of a Random Variable Expected Value Normal Distribution (Curve) Standard Normal Curve Z-Score Sampling Distribution How to distinguish between discrete random variables and continuous random variables How to determine if a distribution is a probability distribution Performance Task: Birth Weights in America
9 that there are data sets for which such a procedure is not appropriate. Use calculators, spreadsheets, and tables to estimate areas under the normal curve. How to construct a discrete probability distribution and its graph and find the mean, variance, and standard deviation How to find the expected value How to interpret graphs of normal probability distributions How to interpret z-scores How to find areas under the standard normal curve How to find probabilities for normally distributed variables How to find a z-score given the area under the normal curve How to transform a z-score to an x-value How to find a specific data value of a normal distribution given the probability
10 Time Interval/ Unit 6: Sampling Distributions 5.4, 6.1, 6.3, 7.1, 7.2, 7.4, 8.4 CP: 3 weeks S-IC-2: Decide if a specified model is consistent with results from a given data-generating process, e.g., using simulation. S-IC-4: Use data from a sample survey to estimate a population mean or proportion; develop a margin of error through the use of simulation models for random sampling. S-IC-5: Use data from a randomized experiment to compare two treatments; use simulations to decide if differences between parameters are significant. S-MD-6: Use probabilities to make fair decisions (e.g., drawing by lots, using a random number generator). S-MD-7: Analyze decisions and strategies using probability concepts (e.g., product testing, medical testing, pulling a hockey goalie at the end of a game). Why are sampling distributions important? What is the purpose of hypothesis testing? A sampling distribution can be used to approximate characteristics of a population. Hypothesis testing is a process that uses a sampling distribution to test a claim about a population characteristic. Sampling Distribution Standard Error of the Mean Central Limit Theorem Point Estimate Interval Estimate Level of Confidence Critical Values Sampling Error Margin of Error Confidence Interval Hypothesis Null Hypothesis Alternative Hypothesis Level of Significance Statistic P-Value Z- Performance Task: Ahoy Mates Find sampling distributions and verify their properties. Interpret the Central Limit Theorem.
11 Apply the Central Limit Theorem to find the probability of a sample mean. Find a point estimate and a margin of error. Construct and interpret confidence intervals for the population mean and proportion. State a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. Know whether to use a one-tailed or a two-tailed statistical test. Interpret a decision based on the results of a statistical test. Find critical values for a z-test. Use rejection regions for a z-test. Find P-values and use them to test a mean and a population proportion. How to perform a z-test for the difference between two population proportions.
Statistics and Probability
 Statistics and a single count or measurement variable. S.ID.1: Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots). S.ID.2: Use statistics appropriate to the shape
Statistics and a single count or measurement variable. S.ID.1: Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots). S.ID.2: Use statistics appropriate to the shape
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data
 Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Understandable Statistics
 Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
Chapter 1: Exploring Data
 Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT. Course Description. Instructional Strategies, Learning Practices, Activities, and Experiences.
 SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Basic Introductory Statistics Grade Level(s): 11-12 Units of Credit: 1 Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles Periods
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Basic Introductory Statistics Grade Level(s): 11-12 Units of Credit: 1 Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles Periods
Business Statistics Probability
 Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
STATISTICS & PROBABILITY
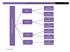 STATISTICS & PROBABILITY LAWRENCE HIGH SCHOOL STATISTICS & PROBABILITY CURRICULUM MAP 2015-2016 Quarter 1 Unit 1 Collecting Data and Drawing Conclusions Unit 2 Summarizing Data Quarter 2 Unit 3 Randomness
STATISTICS & PROBABILITY LAWRENCE HIGH SCHOOL STATISTICS & PROBABILITY CURRICULUM MAP 2015-2016 Quarter 1 Unit 1 Collecting Data and Drawing Conclusions Unit 2 Summarizing Data Quarter 2 Unit 3 Randomness
Describe what is meant by a placebo Contrast the double-blind procedure with the single-blind procedure Review the structure for organizing a memo
 Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Still important ideas
 Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous Chapters 17 & 18 - Chapter 17: Social Influences - Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions Still important ideas Contrast the measurement
Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous Chapters 17 & 18 - Chapter 17: Social Influences - Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions Still important ideas Contrast the measurement
Describe what is meant by a placebo Contrast the double-blind procedure with the single-blind procedure Review the structure for organizing a memo
 Please note the page numbers listed for the Lind book may vary by a page or two depending on which version of the textbook you have. Readings: Lind 1 11 (with emphasis on chapters 10, 11) Please note chapter
Please note the page numbers listed for the Lind book may vary by a page or two depending on which version of the textbook you have. Readings: Lind 1 11 (with emphasis on chapters 10, 11) Please note chapter
2.75: 84% 2.5: 80% 2.25: 78% 2: 74% 1.75: 70% 1.5: 66% 1.25: 64% 1.0: 60% 0.5: 50% 0.25: 25% 0: 0%
 Capstone Test (will consist of FOUR quizzes and the FINAL test grade will be an average of the four quizzes). Capstone #1: Review of Chapters 1-3 Capstone #2: Review of Chapter 4 Capstone #3: Review of
Capstone Test (will consist of FOUR quizzes and the FINAL test grade will be an average of the four quizzes). Capstone #1: Review of Chapters 1-3 Capstone #2: Review of Chapter 4 Capstone #3: Review of
Medical Statistics 1. Basic Concepts Farhad Pishgar. Defining the data. Alive after 6 months?
 Medical Statistics 1 Basic Concepts Farhad Pishgar Defining the data Population and samples Except when a full census is taken, we collect data on a sample from a much larger group called the population.
Medical Statistics 1 Basic Concepts Farhad Pishgar Defining the data Population and samples Except when a full census is taken, we collect data on a sample from a much larger group called the population.
Still important ideas
 Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 11 + 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 2, 3, and 4 Chapter 2: Cognitive Dissonance, Chapter 3: Memory and Hindsight Bias, Chapter 4: Context Dependence Still
Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 11 + 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 2, 3, and 4 Chapter 2: Cognitive Dissonance, Chapter 3: Memory and Hindsight Bias, Chapter 4: Context Dependence Still
HW 1 - Bus Stat. Student:
 HW 1 - Bus Stat Student: 1. An identification of police officers by rank would represent a(n) level of measurement. A. Nominative C. Interval D. Ratio 2. A(n) variable is a qualitative variable such that
HW 1 - Bus Stat Student: 1. An identification of police officers by rank would represent a(n) level of measurement. A. Nominative C. Interval D. Ratio 2. A(n) variable is a qualitative variable such that
Describe what is meant by a placebo Contrast the double-blind procedure with the single-blind procedure Review the structure for organizing a memo
 Please note the page numbers listed for the Lind book may vary by a page or two depending on which version of the textbook you have. Readings: Lind 1 11 (with emphasis on chapters 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 10 & 11)
Please note the page numbers listed for the Lind book may vary by a page or two depending on which version of the textbook you have. Readings: Lind 1 11 (with emphasis on chapters 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 10 & 11)
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 (emphasis on Chapter 12) Online readings: Appendix D, E & F
 Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 (emphasis on Chapter 12) Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Plous Chapters 17 & 18 Chapter 17: Social Influences Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 (emphasis on Chapter 12) Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Plous Chapters 17 & 18 Chapter 17: Social Influences Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting data to assist in making effective decisions
 Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting data to assist in making effective decisions
 Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 11 Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Plous Chapters 10, 11, 12 and 14
 Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 11 Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Plous Chapters 10, 11, 12 and 14 Still important ideas Contrast the measurement of observable actions (and/or characteristics)
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 11 Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Plous Chapters 10, 11, 12 and 14 Still important ideas Contrast the measurement of observable actions (and/or characteristics)
MTH 225: Introductory Statistics
 Marshall University College of Science Mathematics Department MTH 225: Introductory Statistics Course catalog description Basic probability, descriptive statistics, fundamental statistical inference procedures
Marshall University College of Science Mathematics Department MTH 225: Introductory Statistics Course catalog description Basic probability, descriptive statistics, fundamental statistical inference procedures
SCATTER PLOTS AND TREND LINES
 1 SCATTER PLOTS AND TREND LINES LEARNING MAP INFORMATION STANDARDS 8.SP.1 Construct and interpret scatter s for measurement to investigate patterns of between two quantities. Describe patterns such as
1 SCATTER PLOTS AND TREND LINES LEARNING MAP INFORMATION STANDARDS 8.SP.1 Construct and interpret scatter s for measurement to investigate patterns of between two quantities. Describe patterns such as
UNIT 4 ALGEBRA II TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 4
 UNIT 4 ALGEBRA II TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 4 Algebra II Unit 4 Overview: Inferences and Conclusions from Data In this unit, students see how the visual displays and summary statistics they
UNIT 4 ALGEBRA II TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 4 Algebra II Unit 4 Overview: Inferences and Conclusions from Data In this unit, students see how the visual displays and summary statistics they
2.4.1 STA-O Assessment 2
 2.4.1 STA-O Assessment 2 Work all the problems and determine the correct answers. When you have completed the assessment, open the Assessment 2 activity and input your responses into the online grading
2.4.1 STA-O Assessment 2 Work all the problems and determine the correct answers. When you have completed the assessment, open the Assessment 2 activity and input your responses into the online grading
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis I
 Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis I JULY 2011 Afsaneh Yazdani Preface What is Statistics? Preface What is Statistics? Science of: designing studies or experiments, collecting data Summarizing/modeling/analyzing
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis I JULY 2011 Afsaneh Yazdani Preface What is Statistics? Preface What is Statistics? Science of: designing studies or experiments, collecting data Summarizing/modeling/analyzing
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 4 Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Online readings: Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13
 Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 4 Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Online readings: Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 4 Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Online readings: Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods
PRINCIPLES OF STATISTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF STATISTICS STA-201-TE This TECEP is an introduction to descriptive and inferential statistics. Topics include: measures of central tendency, variability, correlation, regression, hypothesis
PRINCIPLES OF STATISTICS STA-201-TE This TECEP is an introduction to descriptive and inferential statistics. Topics include: measures of central tendency, variability, correlation, regression, hypothesis
Statistics. Nur Hidayanto PSP English Education Dept. SStatistics/Nur Hidayanto PSP/PBI
 Statistics Nur Hidayanto PSP English Education Dept. RESEARCH STATISTICS WHAT S THE RELATIONSHIP? RESEARCH RESEARCH positivistic Prepositivistic Postpositivistic Data Initial Observation (research Question)
Statistics Nur Hidayanto PSP English Education Dept. RESEARCH STATISTICS WHAT S THE RELATIONSHIP? RESEARCH RESEARCH positivistic Prepositivistic Postpositivistic Data Initial Observation (research Question)
AP Psych - Stat 2 Name Period Date. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 AP Psych - Stat 2 Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In a set of incomes in which most people are in the $15,000
AP Psych - Stat 2 Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In a set of incomes in which most people are in the $15,000
Chapter 1 Where Do Data Come From?
 Chapter 1 Where Do Data Come From? Understanding Data: The purpose of this class; to be able to read the newspaper and know what the heck they re talking about! To be able to go to the casino and know
Chapter 1 Where Do Data Come From? Understanding Data: The purpose of this class; to be able to read the newspaper and know what the heck they re talking about! To be able to go to the casino and know
AP Statistics. Semester One Review Part 1 Chapters 1-5
 AP Statistics Semester One Review Part 1 Chapters 1-5 AP Statistics Topics Describing Data Producing Data Probability Statistical Inference Describing Data Ch 1: Describing Data: Graphically and Numerically
AP Statistics Semester One Review Part 1 Chapters 1-5 AP Statistics Topics Describing Data Producing Data Probability Statistical Inference Describing Data Ch 1: Describing Data: Graphically and Numerically
Chapter 2 Organizing and Summarizing Data. Chapter 3 Numerically Summarizing Data. Chapter 4 Describing the Relation between Two Variables
 Tables and Formulas for Sullivan, Fundamentals of Statistics, 4e 014 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Organizing and Summarizing Data Relative frequency = frequency sum of all frequencies Class midpoint:
Tables and Formulas for Sullivan, Fundamentals of Statistics, 4e 014 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Organizing and Summarizing Data Relative frequency = frequency sum of all frequencies Class midpoint:
V. Gathering and Exploring Data
 V. Gathering and Exploring Data With the language of probability in our vocabulary, we re now ready to talk about sampling and analyzing data. Data Analysis We can divide statistical methods into roughly
V. Gathering and Exploring Data With the language of probability in our vocabulary, we re now ready to talk about sampling and analyzing data. Data Analysis We can divide statistical methods into roughly
Statistical Methods Exam I Review
 Statistical Methods Exam I Review Professor: Dr. Kathleen Suchora SI Leader: Camila M. DISCLAIMER: I have created this review sheet to supplement your studies for your first exam. I am a student here at
Statistical Methods Exam I Review Professor: Dr. Kathleen Suchora SI Leader: Camila M. DISCLAIMER: I have created this review sheet to supplement your studies for your first exam. I am a student here at
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables.
 bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
Population. Sample. AP Statistics Notes for Chapter 1 Section 1.0 Making Sense of Data. Statistics: Data Analysis:
 Section 1.0 Making Sense of Data Statistics: Data Analysis: Individuals objects described by a set of data Variable any characteristic of an individual Categorical Variable places an individual into one
Section 1.0 Making Sense of Data Statistics: Data Analysis: Individuals objects described by a set of data Variable any characteristic of an individual Categorical Variable places an individual into one
STATISTICS AND RESEARCH DESIGN
 Statistics 1 STATISTICS AND RESEARCH DESIGN These are subjects that are frequently confused. Both subjects often evoke student anxiety and avoidance. To further complicate matters, both areas appear have
Statistics 1 STATISTICS AND RESEARCH DESIGN These are subjects that are frequently confused. Both subjects often evoke student anxiety and avoidance. To further complicate matters, both areas appear have
AP Psych - Stat 1 Name Period Date. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 AP Psych - Stat 1 Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In a set of incomes in which most people are in the $15,000
AP Psych - Stat 1 Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In a set of incomes in which most people are in the $15,000
Section 1: Exploring Data
 Section 1: Exploring Data The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics TAC 111.47(c). 1.01 Introduction to Statistics 1.02 Statistics and Parameters
Section 1: Exploring Data The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics TAC 111.47(c). 1.01 Introduction to Statistics 1.02 Statistics and Parameters
List of Figures. List of Tables. Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition
 List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
AP Stats Review for Midterm
 AP Stats Review for Midterm NAME: Format: 10% of final grade. There will be 20 multiple-choice questions and 3 free response questions. The multiple-choice questions will be worth 2 points each and the
AP Stats Review for Midterm NAME: Format: 10% of final grade. There will be 20 multiple-choice questions and 3 free response questions. The multiple-choice questions will be worth 2 points each and the
CHAPTER 3 Describing Relationships
 CHAPTER 3 Describing Relationships 3.1 Scatterplots and Correlation The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Reading Quiz 3.1 True/False 1.
CHAPTER 3 Describing Relationships 3.1 Scatterplots and Correlation The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Reading Quiz 3.1 True/False 1.
PRINTABLE VERSION. Quiz 1. True or False: The amount of rainfall in your state last month is an example of continuous data.
 Question 1 PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 1 True or False: The amount of rainfall in your state last month is an example of continuous data. a) True b) False Question 2 True or False: The standard deviation is
Question 1 PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 1 True or False: The amount of rainfall in your state last month is an example of continuous data. a) True b) False Question 2 True or False: The standard deviation is
Slide 1 - Introduction to Statistics Tutorial: An Overview Slide notes
 Slide 1 - Introduction to Statistics Tutorial: An Overview Introduction to Statistics Tutorial: An Overview. This tutorial is the first in a series of several tutorials that introduce probability and statistics.
Slide 1 - Introduction to Statistics Tutorial: An Overview Introduction to Statistics Tutorial: An Overview. This tutorial is the first in a series of several tutorials that introduce probability and statistics.
NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY TUTORIAL 1
 NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY TUTORIAL 1 REVIEW FROM BIOSTATISTICS I AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD Data Management and Analysis AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD - Data Management and Analysis 1 DATA TYPES/ MEASUREMENT SCALES Categorical:
NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY TUTORIAL 1 REVIEW FROM BIOSTATISTICS I AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD Data Management and Analysis AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD - Data Management and Analysis 1 DATA TYPES/ MEASUREMENT SCALES Categorical:
Frequency distributions
 Applied Biostatistics distributions Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://www-users.york.ac.uk/~mb55/ Types of data Qualitative data arise when individuals may fall into
Applied Biostatistics distributions Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://www-users.york.ac.uk/~mb55/ Types of data Qualitative data arise when individuals may fall into
Biostatistics. Donna Kritz-Silverstein, Ph.D. Professor Department of Family & Preventive Medicine University of California, San Diego
 Biostatistics Donna Kritz-Silverstein, Ph.D. Professor Department of Family & Preventive Medicine University of California, San Diego (858) 534-1818 dsilverstein@ucsd.edu Introduction Overview of statistical
Biostatistics Donna Kritz-Silverstein, Ph.D. Professor Department of Family & Preventive Medicine University of California, San Diego (858) 534-1818 dsilverstein@ucsd.edu Introduction Overview of statistical
What you should know before you collect data. BAE 815 (Fall 2017) Dr. Zifei Liu
 What you should know before you collect data BAE 815 (Fall 2017) Dr. Zifei Liu Zifeiliu@ksu.edu Types and levels of study Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics How to choose a statistical test
What you should know before you collect data BAE 815 (Fall 2017) Dr. Zifei Liu Zifeiliu@ksu.edu Types and levels of study Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics How to choose a statistical test
Stats 95. Statistical analysis without compelling presentation is annoying at best and catastrophic at worst. From raw numbers to meaningful pictures
 Stats 95 Statistical analysis without compelling presentation is annoying at best and catastrophic at worst. From raw numbers to meaningful pictures Stats 95 Why Stats? 200 countries over 200 years http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jbksrlysojo
Stats 95 Statistical analysis without compelling presentation is annoying at best and catastrophic at worst. From raw numbers to meaningful pictures Stats 95 Why Stats? 200 countries over 200 years http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jbksrlysojo
Chapter 1: Explaining Behavior
 Chapter 1: Explaining Behavior GOAL OF SCIENCE is to generate explanations for various puzzling natural phenomenon. - Generate general laws of behavior (psychology) RESEARCH: principle method for acquiring
Chapter 1: Explaining Behavior GOAL OF SCIENCE is to generate explanations for various puzzling natural phenomenon. - Generate general laws of behavior (psychology) RESEARCH: principle method for acquiring
Six Sigma Glossary Lean 6 Society
 Six Sigma Glossary Lean 6 Society ABSCISSA ACCEPTANCE REGION ALPHA RISK ALTERNATIVE HYPOTHESIS ASSIGNABLE CAUSE ASSIGNABLE VARIATIONS The horizontal axis of a graph The region of values for which the null
Six Sigma Glossary Lean 6 Society ABSCISSA ACCEPTANCE REGION ALPHA RISK ALTERNATIVE HYPOTHESIS ASSIGNABLE CAUSE ASSIGNABLE VARIATIONS The horizontal axis of a graph The region of values for which the null
Lecture Outline. Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I. Purpose of Descriptive Statistics. Purpose of Descriptive Statistics
 Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics University of Washington Lecture 3: Overview of Descriptive Statistics October 3, 2005 Lecture Outline Purpose
Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics University of Washington Lecture 3: Overview of Descriptive Statistics October 3, 2005 Lecture Outline Purpose
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences Midterm Test February 2016
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences Midterm Test February 2016 STAB22H3 Statistics I, LEC 01 and LEC 02 Duration: 1 hour and 45 minutes Last Name: First Name:
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences Midterm Test February 2016 STAB22H3 Statistics I, LEC 01 and LEC 02 Duration: 1 hour and 45 minutes Last Name: First Name:
Biostatistics for Med Students. Lecture 1
 Biostatistics for Med Students Lecture 1 John J. Chen, Ph.D. Professor & Director of Biostatistics Core UH JABSOM JABSOM MD7 February 14, 2018 Lecture note: http://biostat.jabsom.hawaii.edu/education/training.html
Biostatistics for Med Students Lecture 1 John J. Chen, Ph.D. Professor & Director of Biostatistics Core UH JABSOM JABSOM MD7 February 14, 2018 Lecture note: http://biostat.jabsom.hawaii.edu/education/training.html
Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques)
 Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques) Dr Judy Sheard Senior Lecturer Co-Director, Computing Education Research Group Monash University judy.sheard@monash.edu
Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques) Dr Judy Sheard Senior Lecturer Co-Director, Computing Education Research Group Monash University judy.sheard@monash.edu
M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points Total 60
 M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points 1-10 10 11 3 12 4 13 3 14 10 15 14 16 10 17 7 18 4 19 4 Total 60 Multiple choice questions (1 point each) For questions
M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points 1-10 10 11 3 12 4 13 3 14 10 15 14 16 10 17 7 18 4 19 4 Total 60 Multiple choice questions (1 point each) For questions
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2009 AP Statistics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2009 free-response questions for AP Statistics were written by the Chief Reader, Christine Franklin of
Student Performance Q&A: 2009 AP Statistics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2009 free-response questions for AP Statistics were written by the Chief Reader, Christine Franklin of
Research Methods in Forest Sciences: Learning Diary. Yoko Lu December Research process
 Research Methods in Forest Sciences: Learning Diary Yoko Lu 285122 9 December 2016 1. Research process It is important to pursue and apply knowledge and understand the world under both natural and social
Research Methods in Forest Sciences: Learning Diary Yoko Lu 285122 9 December 2016 1. Research process It is important to pursue and apply knowledge and understand the world under both natural and social
Pitfalls in Linear Regression Analysis
 Pitfalls in Linear Regression Analysis Due to the widespread availability of spreadsheet and statistical software for disposal, many of us do not really have a good understanding of how to use regression
Pitfalls in Linear Regression Analysis Due to the widespread availability of spreadsheet and statistical software for disposal, many of us do not really have a good understanding of how to use regression
DOWNLOAD PDF SUMMARIZING AND INTERPRETING DATA : USING STATISTICS
 Chapter 1 : Summarizing Numerical Data Sets Worksheets Stem and Leaf Activity Sheets with Answers. Students first create the stem and leaf plot. Then they use it to answer questions. This is a great way
Chapter 1 : Summarizing Numerical Data Sets Worksheets Stem and Leaf Activity Sheets with Answers. Students first create the stem and leaf plot. Then they use it to answer questions. This is a great way
Data, frequencies, and distributions. Martin Bland. Types of data. Types of data. Clinical Biostatistics
 Clinical Biostatistics Data, frequencies, and distributions Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://martinbland.co.uk/ Types of data Qualitative data arise when individuals
Clinical Biostatistics Data, frequencies, and distributions Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://martinbland.co.uk/ Types of data Qualitative data arise when individuals
LOTS of NEW stuff right away 2. The book has calculator commands 3. About 90% of technology by week 5
 1.1 1. LOTS of NEW stuff right away 2. The book has calculator commands 3. About 90% of technology by week 5 1 Three adventurers are in a hot air balloon. Soon, they find themselves lost in a canyon in
1.1 1. LOTS of NEW stuff right away 2. The book has calculator commands 3. About 90% of technology by week 5 1 Three adventurers are in a hot air balloon. Soon, they find themselves lost in a canyon in
Table of Contents. Plots. Essential Statistics for Nursing Research 1/12/2017
 Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
Lesson 1: Distributions and Their Shapes
 Lesson 1 Name Date Lesson 1: Distributions and Their Shapes 1. Sam said that a typical flight delay for the sixty BigAir flights was approximately one hour. Do you agree? Why or why not? 2. Sam said that
Lesson 1 Name Date Lesson 1: Distributions and Their Shapes 1. Sam said that a typical flight delay for the sixty BigAir flights was approximately one hour. Do you agree? Why or why not? 2. Sam said that
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL CORE SUBJECT
 Grade: 11/12 Core Subject Title: Statistics and Probability No. of Hours/Semester: 80 hours/semester Prerequisite: Core Subject Description: At the end of the course, the students must know how to find
Grade: 11/12 Core Subject Title: Statistics and Probability No. of Hours/Semester: 80 hours/semester Prerequisite: Core Subject Description: At the end of the course, the students must know how to find
Observational studies; descriptive statistics
 Observational studies; descriptive statistics Patrick Breheny August 30 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Biostatistical Methods I (BIOS 5710) 1 / 38 Observational studies Association versus causation
Observational studies; descriptive statistics Patrick Breheny August 30 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Biostatistical Methods I (BIOS 5710) 1 / 38 Observational studies Association versus causation
Student name: SOCI 420 Advanced Methods of Social Research Fall 2017
 SOCI 420 Advanced Methods of Social Research Fall 2017 EXAM 1 RUBRIC Instructor: Ernesto F. L. Amaral, Assistant Professor, Department of Sociology Date: October 12, 2017 (Thursday) Section 904: 2:20 3:35pm
SOCI 420 Advanced Methods of Social Research Fall 2017 EXAM 1 RUBRIC Instructor: Ernesto F. L. Amaral, Assistant Professor, Department of Sociology Date: October 12, 2017 (Thursday) Section 904: 2:20 3:35pm
UNIT V: Analysis of Non-numerical and Numerical Data SWK 330 Kimberly Baker-Abrams. In qualitative research: Grounded Theory
 UNIT V: Analysis of Non-numerical and Numerical Data SWK 330 Kimberly Baker-Abrams In qualitative research: analysis is on going (occurs as data is gathered) must be careful not to draw conclusions before
UNIT V: Analysis of Non-numerical and Numerical Data SWK 330 Kimberly Baker-Abrams In qualitative research: analysis is on going (occurs as data is gathered) must be careful not to draw conclusions before
*A Case of Possible Discrimination (Spotlight Task)
 *A Case of Possible Discrimination (Spotlight Task) This activity is adapted by one of the authors, Christine Franklin, from Navigating through Data Analysis in Grades 9-12, Burrill, Gail, Christine Franklin,
*A Case of Possible Discrimination (Spotlight Task) This activity is adapted by one of the authors, Christine Franklin, from Navigating through Data Analysis in Grades 9-12, Burrill, Gail, Christine Franklin,
MATH 1040 Skittles Data Project
 Laura Boren MATH 1040 Data Project For our project in MATH 1040 everyone in the class was asked to buy a 2.17 individual sized bag of skittles and count the number of each color of candy in the bag. The
Laura Boren MATH 1040 Data Project For our project in MATH 1040 everyone in the class was asked to buy a 2.17 individual sized bag of skittles and count the number of each color of candy in the bag. The
Organizing Data. Types of Distributions. Uniform distribution All ranges or categories have nearly the same value a.k.a. rectangular distribution
 Organizing Data Frequency How many of the data are in a category or range Just count up how many there are Notation x = number in one category n = total number in sample (all categories combined) Relative
Organizing Data Frequency How many of the data are in a category or range Just count up how many there are Notation x = number in one category n = total number in sample (all categories combined) Relative
Ecological Statistics
 A Primer of Ecological Statistics Second Edition Nicholas J. Gotelli University of Vermont Aaron M. Ellison Harvard Forest Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Contents
A Primer of Ecological Statistics Second Edition Nicholas J. Gotelli University of Vermont Aaron M. Ellison Harvard Forest Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Contents
Chapter 23. Inference About Means. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Inference About Means Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Getting Started Now that we know how to create confidence intervals and test hypotheses about proportions, it d be nice to be able
Chapter 23 Inference About Means Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Getting Started Now that we know how to create confidence intervals and test hypotheses about proportions, it d be nice to be able
9 research designs likely for PSYC 2100
 9 research designs likely for PSYC 2100 1) 1 factor, 2 levels, 1 group (one group gets both treatment levels) related samples t-test (compare means of 2 levels only) 2) 1 factor, 2 levels, 2 groups (one
9 research designs likely for PSYC 2100 1) 1 factor, 2 levels, 1 group (one group gets both treatment levels) related samples t-test (compare means of 2 levels only) 2) 1 factor, 2 levels, 2 groups (one
q2_2 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 q2_2 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. A sporting goods retailer conducted a customer survey to determine its customers primary reason
q2_2 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. A sporting goods retailer conducted a customer survey to determine its customers primary reason
Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics Variables A variable is a characteristic or condition that can change or take on different values. Most research begins with a general question about the relationship
Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics Variables A variable is a characteristic or condition that can change or take on different values. Most research begins with a general question about the relationship
Basic Statistics 01. Describing Data. Special Program: Pre-training 1
 Basic Statistics 01 Describing Data Special Program: Pre-training 1 Describing Data 1. Numerical Measures Measures of Location Measures of Dispersion Correlation Analysis 2. Frequency Distributions (Relative)
Basic Statistics 01 Describing Data Special Program: Pre-training 1 Describing Data 1. Numerical Measures Measures of Location Measures of Dispersion Correlation Analysis 2. Frequency Distributions (Relative)
Statistics Guide. Prepared by: Amanda J. Rockinson- Szapkiw, Ed.D.
 This guide contains a summary of the statistical terms and procedures. This guide can be used as a reference for course work and the dissertation process. However, it is recommended that you refer to statistical
This guide contains a summary of the statistical terms and procedures. This guide can be used as a reference for course work and the dissertation process. However, it is recommended that you refer to statistical
STATISTICS 8 CHAPTERS 1 TO 6, SAMPLE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 STATISTICS 8 CHAPTERS 1 TO 6, SAMPLE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Circle the best answer. This scenario applies to Questions 1 and 2: A study was done to compare the lung capacity of coal miners to the lung
STATISTICS 8 CHAPTERS 1 TO 6, SAMPLE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Circle the best answer. This scenario applies to Questions 1 and 2: A study was done to compare the lung capacity of coal miners to the lung
In This Section An Introductory Example Obesity in America
 In This Section An Introductory Example Obesity in America Example 5: Estimating the Density of the Earth A Classical Study The Investigatory Process at Level C Formulating Questions Example 6: Linear
In This Section An Introductory Example Obesity in America Example 5: Estimating the Density of the Earth A Classical Study The Investigatory Process at Level C Formulating Questions Example 6: Linear
1.4 - Linear Regression and MS Excel
 1.4 - Linear Regression and MS Excel Regression is an analytic technique for determining the relationship between a dependent variable and an independent variable. When the two variables have a linear
1.4 - Linear Regression and MS Excel Regression is an analytic technique for determining the relationship between a dependent variable and an independent variable. When the two variables have a linear
Part 1. Online Session: Math Review and Math Preparation for Course 5 minutes Introduction 45 minutes Reading and Practice Problem Assignment
 Course Schedule PREREQUISITE (Pre-Class) Advanced Education Diagnostic Test 10 minutes Excel 2007 Exercise SECTION 1. (Completed before face-to-face sections begin) (2 hours) Part 1. Online Session: Math
Course Schedule PREREQUISITE (Pre-Class) Advanced Education Diagnostic Test 10 minutes Excel 2007 Exercise SECTION 1. (Completed before face-to-face sections begin) (2 hours) Part 1. Online Session: Math
On the purpose of testing:
 Why Evaluation & Assessment is Important Feedback to students Feedback to teachers Information to parents Information for selection and certification Information for accountability Incentives to increase
Why Evaluation & Assessment is Important Feedback to students Feedback to teachers Information to parents Information for selection and certification Information for accountability Incentives to increase
Examining Relationships Least-squares regression. Sections 2.3
 Examining Relationships Least-squares regression Sections 2.3 The regression line A regression line describes a one-way linear relationship between variables. An explanatory variable, x, explains variability
Examining Relationships Least-squares regression Sections 2.3 The regression line A regression line describes a one-way linear relationship between variables. An explanatory variable, x, explains variability
IAPT: Regression. Regression analyses
 Regression analyses IAPT: Regression Regression is the rather strange name given to a set of methods for predicting one variable from another. The data shown in Table 1 and come from a student project
Regression analyses IAPT: Regression Regression is the rather strange name given to a set of methods for predicting one variable from another. The data shown in Table 1 and come from a student project
UF#Stats#Club#STA#2023#Exam#1#Review#Packet# #Fall#2013#
 UF#Stats#Club#STA##Exam##Review#Packet# #Fall## The following data consists of the scores the Gators basketball team scored during the 8 games played in the - season. 84 74 66 58 79 8 7 64 8 6 78 79 77
UF#Stats#Club#STA##Exam##Review#Packet# #Fall## The following data consists of the scores the Gators basketball team scored during the 8 games played in the - season. 84 74 66 58 79 8 7 64 8 6 78 79 77
Knowledge discovery tools 381
 Knowledge discovery tools 381 hours, and prime time is prime time precisely because more people tend to watch television at that time.. Compare histograms from di erent periods of time. Changes in histogram
Knowledge discovery tools 381 hours, and prime time is prime time precisely because more people tend to watch television at that time.. Compare histograms from di erent periods of time. Changes in histogram
1 Version SP.A Investigate patterns of association in bivariate data
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Statistics and Probability Target
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Statistics and Probability Target
Outline. Practice. Confounding Variables. Discuss. Observational Studies vs Experiments. Observational Studies vs Experiments
 1 2 Outline Finish sampling slides from Tuesday. Study design what do you do with the subjects/units once you select them? (OI Sections 1.4-1.5) Observational studies vs. experiments Descriptive statistics
1 2 Outline Finish sampling slides from Tuesday. Study design what do you do with the subjects/units once you select them? (OI Sections 1.4-1.5) Observational studies vs. experiments Descriptive statistics
Empirical Knowledge: based on observations. Answer questions why, whom, how, and when.
 INTRO TO RESEARCH METHODS: Empirical Knowledge: based on observations. Answer questions why, whom, how, and when. Experimental research: treatments are given for the purpose of research. Experimental group
INTRO TO RESEARCH METHODS: Empirical Knowledge: based on observations. Answer questions why, whom, how, and when. Experimental research: treatments are given for the purpose of research. Experimental group
Undertaking statistical analysis of
 Descriptive statistics: Simply telling a story Laura Delaney introduces the principles of descriptive statistical analysis and presents an overview of the various ways in which data can be presented by
Descriptive statistics: Simply telling a story Laura Delaney introduces the principles of descriptive statistical analysis and presents an overview of the various ways in which data can be presented by
1. Introduction a. Meaning and Role of Statistics b. Descriptive and inferential Statistics c. Variable and Measurement Scales
 N. Setyaningsih 1. Introduction a. Meaning and Role of Statistics b. Descriptive and inferential Statistics c. Variable and Measurement Scales 2. Organizing Data for Meaningful Representations a. Frequency
N. Setyaningsih 1. Introduction a. Meaning and Role of Statistics b. Descriptive and inferential Statistics c. Variable and Measurement Scales 2. Organizing Data for Meaningful Representations a. Frequency
CP Statistics Sem 1 Final Exam Review
 Name: _ Period: ID: A CP Statistics Sem 1 Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A particularly common question in the study
Name: _ Period: ID: A CP Statistics Sem 1 Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A particularly common question in the study
Quizzes (and relevant lab exercises): 20% Midterm exams (2): 25% each Final exam: 30%
 1 Intro to statistics Continued 2 Grading policy Quizzes (and relevant lab exercises): 20% Midterm exams (2): 25% each Final exam: 30% Cutoffs based on final avgs (A, B, C): 91-100, 82-90, 73-81 3 Numerical
1 Intro to statistics Continued 2 Grading policy Quizzes (and relevant lab exercises): 20% Midterm exams (2): 25% each Final exam: 30% Cutoffs based on final avgs (A, B, C): 91-100, 82-90, 73-81 3 Numerical
Summary & Conclusion. Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
 Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research and design 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 2. Univariate
Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research and design 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 2. Univariate
manipulation influences other variables, the researcher is conducting a(n)
 Math 1342 Finals Review Selective Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) If a researcher manipulates one of the variables and tries to
Math 1342 Finals Review Selective Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) If a researcher manipulates one of the variables and tries to
Survey research (Lecture 1) Summary & Conclusion. Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.
 Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Survey research (Lecture 1)
 Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Statistics: Making Sense of the Numbers
 Statistics: Making Sense of the Numbers Chapter 9 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including
Statistics: Making Sense of the Numbers Chapter 9 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including
Distributions and Samples. Clicker Question. Review
 Distributions and Samples Clicker Question The major difference between an observational study and an experiment is that A. An experiment manipulates features of the situation B. An experiment does not
Distributions and Samples Clicker Question The major difference between an observational study and an experiment is that A. An experiment manipulates features of the situation B. An experiment does not
Choosing a Significance Test. Student Resource Sheet
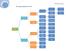 Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
