Bandura s Social Learning & Cognitive Learning Theory
|
|
|
- Lynne Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bandura s Social Learning & Cognitive Learning Theory Theories of Developmental Psychology By: Razieh Tadayon Nabavi
2 Albert Bandura He was born December 4, 1925 in a small town in northern Alberta, Canada 1949 Graduated from the University of British Columbia with a degree in Psychology Received his Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology from the University of Iowa Bandura was elected the president of the American Psychological Association Bandura became known as the Father of the Cognitive Theory Outstanding Lifetime Contribution to Psychology, American Psychological Association. 2
3 Introduction Learning is: A persisting change in human performance or performance potential as a result of the learner s interaction with the environment 1994, pp. 8-9). (Driscoll, The relatively permanent change in a person s knowledge or behavior due to experience (Mayer, 1982, p. 1040). An enduring change in behavior, or in the capacity to behave in a given fashion, which results from practice or other forms of experience (Shuell, 1986, p. 412). 3
4 Intro Learning Theories Behaviorism Social Learning Theory (SLT) Social Cognitive Learning Theory (SCLT) Albert Bandura is arguably the most eminent living psychologist. His Social Cognitive theory has influenced many areas of inquiry: education, health sciences, social policy and psychotherapy among others. 4
5 Intro SLT & SCLT are based on Observation SLT SCLT via observation, imitation, and modeling via observation understanding, predicting and changing human behavior. 5
6 Social Learning Theory SLT has become perhaps the most influential theory of learning and development. While rooted in many of the basic concepts of traditional learning theory. The theory has often been called a bridge between behaviorist learning theories and cognitive learning theories because it encompasses attention, memory, and motivation. Bandura believes that direct reinforcement could not account for all types of learning. His theory added a social element, arguing that people can learn new information and behaviors by watching other people. 6
7 General principles of SLT SLT posits that people learn from one another, via: 1. observation, 2. imitation, and 3. modeling. Learning can occur without a change in behavior. Behaviorists say that learning has to be represented by a permanent change in behavior, in contrast social learning theorists say that because people can learn through observation alone, their learning may not necessarily be shown in their performance. Learning may or may not result in a behavior change. Cognition plays a role in learning. Over the last 30 years social learning theory has become increasingly cognitive in its interpretation of human learning. 7
8 Behaviors that can be learned through modeling: Many behaviors can be learned, at least partly, through modeling. Examples that can be cited are, students can watch parents read, students can watch the demonstrations of mathematics problems, or seen someone acting bravely and a fearful situation. Aggression can be learned through models. Much research indicate that children become more aggressive when they observed aggressive or violent models. Moral thinking and moral behavior are influenced by observation and modeling. This includes moral judgments regarding right and wrong which can in part, develop through modeling. 8
9 SLT Concepts 1. People can learn through observation. (Observational Learning) 2. Mental states are important to learning. (Intrinsic Reinforcement) 3. Learning does not necessarily lead to a change in behavior. (Modeling Process) 9
10 1. Observational Learning Bandura based on his famous study "Bobo doll", demonstrated that children learn and imitate behaviors they have observed in other people. He identified three basic models of observational learning: A live model, which involves an actual individual demonstrating or acting out a behavior. A verbal instructional model, which involves descriptions and explanations of a behavior. A symbolic model, which involves real or fictional characters displaying behaviors in books, films, television programs, or online media. 10
11 2. Intrinsic Reinforcement Described as a form of internal reward, such as pride, satisfaction, and a sense of accomplishment. This also emphasis on internal thoughts and cognitions helps connect learning theories to cognitive developmental theories. Bandura noted that external, environmental reinforcement was not the only factor to influence learning and behavior. 11
12 1. Attention The person must first pay attention to the model. The more striking or different something is the more likely it is to gain our attention. Likewise, if we regard something as prestigious, attractive or like ourselves, we will take more notice. (eg. Color) 2. Retention The observer must be able to remember the behavior that has been observed. One way of increasing this is using the technique of rehearsal. Modeling Process 3. Reproduction The third condition is the ability to replicate the behavior that the model has just demonstrated. This means that the observer has to be able to replicate the action, which could be a problem with a learner who is not ready developmentally to replicate the action. 10/18/ Motivation The final necessary ingredient for modeling to occur is motivation, learners must want to demonstrate what they have learned. Remember that since these four conditions vary among individuals, different people will reproduce the same behavior differently. Reinforcement and punishment play 12 an important role in motivation.
13 SLT perspectives The SLT perspective of reinforcement and punishment (R&P) are as follow: Indirect effects on learning and they are not the sole or main cause; Influence the extent to which an individual exhibits a behavior that has been learned; Influences expectation of reinforcement on cognitive processes that promote learning; Attention pays a critical role in learning and; Attention is influenced by the expectation of reinforcement. 13
14 Social Cognitive Learning Theory (SCLT) SCLT is a learning theory based on the ideas that people learn by watching what others do, and that human thought processes are central to understanding personality. SCLT provides a framework for understanding, predicting and changing human behavior. SCLT places a heavy focus on cognitive concepts. His theory focuses on how children and adults operate cognitively on their social experiences and how these cognitions then influence behavior and development 14
15 Basic Assumptions of SCLT People can learn by observing others. Learning is an internal process that may or may not result in a behavior change; Learning can occur without a change in behavior (Observation without imitation); Behavior is directed toward particular goals; Behavior eventually becomes self-regulated; Cognition plays a role in learning; and Reinforcement and punishment have indirect rather than direct effects on learning and behavior. 10/18/
16 Cognitive Features on SCLT There are five Cognitive Features that influence behavior in SCLT: 1. Expectations of future consequences & responses based on current situation/s; 2. Vicarious experiences of others consequences; 3. Expectations about future consequences affect how we cognitively process of new information; 4. Expectations affect decisions about how to behavior; and 5. Nonoccurrence of expected consequences have effects 16
17 Phenomena of SCLT There are four features for phenomena on SCLT as follow: 1. Observational Learning Effect Acquiring new behavior from model 2. Response Facilitation Effect Increased frequency of learned behavior after model is reinforced for same behavior 3. Response Inhibition Effect Decreased frequency of learned behavior after observing punished model 4. Response Disinhibition Effect Return of inhibited response after observing model behave that adverse consequences 17
18 Internal principle of SCLT- Triadic Reciprocality The SCLT defines human behavior as a triadic, dynamic, and reciprocal interaction of personal factors, behavior, and the environment These three fundamentals work in a reciprocal nature. 10/18/
19 Internal principle of SCLT- Self efficacy It lies at the center of SCLT and shows that: Beliefs about one s ability or capacity to execute a behavior successfully People tend to engage in activities based on their sense of competence &/or past success Self efficacy affects on Behavior & Cognition in 4 ways: 1. Activity choice 2. Goal setting 3. Effort & persistence 4. Learning & achievement People with high efficacy are more likely to view difficult tasks as something to be mastered rather than something to be avoided. People with weak efficacy more likely to avoid challenging tasks and they also focus on personal failings and negative outcomes. 19
20 Self regulation and SCLT Self-regulation has come to be more emphasized in SLT but in SCLT Self-regulation is when the individual has his own ideas about what is appropriate or inappropriate behavior and chooses actions accordingly. Promoting self-regulation can be an important technique. This is usually done by teaching the individual to reward himself after doing the needed behavior. 20
21 21
22 The Linking between SLT and SCLT In 1986, Bandura renamed his SLT, Social Cognitive Learning Theory (SCLT), as better description of what he had been advocating since the 1960's. The Social Cognitive learning Theory (SCLT) stemmed from the Social Learning Theory (SLT). 22
23 Strengths and Weaknesses of SLT Broken down into two categories: 1. Positive Reinforcement The action mimicked by the observer is a positive one, therefore the action may be reward able or commended by others. 2. Punishment The action mimicked by the observer is negative and may offend or harm others, thereby leading to a form of punishment. Basically the main strength & weakness of Social/Observational learning depends on the model. If the model is producing a behavior that is appropriate, responsible and positive overall, the observer will mimic that positive good behavior. So, as future educators, we need to be constantly aware of how we present ourselves and of our actions. If Bandura's theory is correct, that means the things we do are under constant watch by our students. 23
24 Strengths of SCLT 1. Accumulated an impressive research record 2. Concerned with important human social behaviors 3. An evolving theory that is open to change 4. Focused on important theoretical issues, e.g., role of reward in learning, the stability of behavior 5. Reasonable view of people and concern with the social implications of the theory 24
25 Limitations of SCLT: The theory's comprehensiveness and complexity make it difficult to operationalize ; Many applications of the SCT focus on one or two constructs, such as self-efficacy, while ignoring the others. 25
26 Limitations of SCLT cont 1. Not a fully systematized, unified theory; loosely organized 2. Controversial issues: Is reinforcement necessary for both learning and performance? Is self-efficacy just another outcome expectancy? Why are some self-efficacy expectancies stable and others susceptible to rapid change? If self-efficacy expectancies are situation specific, how do they relate to broader personality? Why are some self-efficacy beliefs apparently unrelated to behavior, e.g., stop smoking? Relies on self-reports excessively 26
27 Limitations of SCLT cont 3. Neglected areas: Maturation and changes over the lifespan ignored Minimal attention to motivation, conflict, and emotion 4. Findings are preliminary Are cognitive processes the basic concepts of personality? Are modeling and guided participation able to handle many psychological problems? 27
28 Conclusion The SLT theory has often been called a bridge between behaviorist learning theories and cognitive learning theories because it encompasses attention, memory, and motivation. Bandura's SLT places a heavy focus on cognitive concepts. Albert Bandura is arguably the most eminent living psychologist. His Social Cognitive theory has influenced many areas of inquiry: education, health sciences, social policy and psychotherapy among others. 28
29 Conclusion cont Social cognitive theory has its roots in American behaviorism, but Bandura extends radical behaviorism to include cognitive factors in his account of social learning. Bandura has tried to use cognitive theory to solve a number of global problems. Such as environmental conservation, poverty, soaring population growth and etc. (Michael & John; 2010). 29
Title: Bandura s Social Learning Theory & Social Cognitive Learning Theory
 Theories of Developmental Psychology Title: Bandura s Social Learning Theory & Social Cognitive Learning Theory Razieh Tadayon Nabavi 2011-2012 Table of content Father of the Cognitive Theory... 3 Introduction...
Theories of Developmental Psychology Title: Bandura s Social Learning Theory & Social Cognitive Learning Theory Razieh Tadayon Nabavi 2011-2012 Table of content Father of the Cognitive Theory... 3 Introduction...
CHAPTER 10. The Dynamics of the Personality: SCLT View of Learning THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH. part 2
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH part 2 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 All behaviour is acquired through learning Important differences between social cognitive views of learning
CHAPTER 10 THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH part 2 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 All behaviour is acquired through learning Important differences between social cognitive views of learning
Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches
 Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches What is Learning o What Learning Is and Is Not Learning - a relatively permanent influence on behavior, knowledge, and thinking skills that comes about
Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches What is Learning o What Learning Is and Is Not Learning - a relatively permanent influence on behavior, knowledge, and thinking skills that comes about
Innate? Learned? Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Aggression and Violence. What is violence?
 Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING
 Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Site: University of the Philippines Open University: Course: EDS_103_1T_2015-16- Theories of Learning Book: Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Printed by: Reyes
Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Site: University of the Philippines Open University: Course: EDS_103_1T_2015-16- Theories of Learning Book: Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Printed by: Reyes
Theories of Personality Bandura: Social Cognitive Theory
 Theories of Personality Bandura: Social Cognitive Theory Chapter 17 Feist, J., & Feist, R. J., & Roberts, T. A. (2013). Theories of personality (8th ed.). NY:McGraw-Hill. Outline Overview of Social Cognitive
Theories of Personality Bandura: Social Cognitive Theory Chapter 17 Feist, J., & Feist, R. J., & Roberts, T. A. (2013). Theories of personality (8th ed.). NY:McGraw-Hill. Outline Overview of Social Cognitive
Learning. Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning.
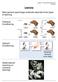 Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Learning Chapter Module 21 Observational Learning Module 21: Observational Learning
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Learning Chapter Module 21 Observational Learning Module 21: Observational Learning
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn?
 Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
SAMPLE 3 - ASSESSMENT CRITERIA AND LEARNING OUTCOMES
 SAMPLE 3 - ASSESSMENT CRITERIA AND LEARNING OUTCOMES PSYCHOLOGY Behaviourism and social learning theory are two perspectives of psychology; discuss how they explain learning: PK1/3/AA/11G (2014-15 VERSION)
SAMPLE 3 - ASSESSMENT CRITERIA AND LEARNING OUTCOMES PSYCHOLOGY Behaviourism and social learning theory are two perspectives of psychology; discuss how they explain learning: PK1/3/AA/11G (2014-15 VERSION)
Module 30. Learning by Observation
 Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Psychological Foundations of Curriculum. Kevin Thompson
 Psychological Foundations of Curriculum Kevin Thompson Focusing Questions 1. In what ways do psychological foundations enable curriculum workers (teachers, supervisors, and curriculum developers) to perform
Psychological Foundations of Curriculum Kevin Thompson Focusing Questions 1. In what ways do psychological foundations enable curriculum workers (teachers, supervisors, and curriculum developers) to perform
Chapter 11: Behaviorism: After the Founding
 Chapter 11: Behaviorism: After the Founding Dr. Rick Grieve PSY 495 History and Systems Western Kentucky University 1 Operationism Operationism: : the doctrine that a physical concept can be defined in
Chapter 11: Behaviorism: After the Founding Dr. Rick Grieve PSY 495 History and Systems Western Kentucky University 1 Operationism Operationism: : the doctrine that a physical concept can be defined in
EPSY 6304 Jaime H. García, Ph.D. Marie D. Lara 11/25/2013
 EPSY 6304 Jaime H. García, Ph.D. Marie D. Lara 11/25/2013 What distinguishes Albert Bandura s Social Cognitive Learning Theory from many others is that he created one of the grand theories that is still
EPSY 6304 Jaime H. García, Ph.D. Marie D. Lara 11/25/2013 What distinguishes Albert Bandura s Social Cognitive Learning Theory from many others is that he created one of the grand theories that is still
Topic Page: Social cognitive theory
 Topic Page: Social cognitive theory Definition: social cognitive theory from Dictionary of Psychological Testing, Assessment and Treatment Term for theories of social learning - the term stresses the cognitive
Topic Page: Social cognitive theory Definition: social cognitive theory from Dictionary of Psychological Testing, Assessment and Treatment Term for theories of social learning - the term stresses the cognitive
Com 400 Dr. Raz. Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research
 Com 400 Dr. Raz Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research Review Theory an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events Some guiding questions What are different ways to study
Com 400 Dr. Raz Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research Review Theory an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events Some guiding questions What are different ways to study
CHAPTER TWELVE. MISCHEL AND BANDURA: Cognitive Social Learning Theory 10/14/08. Personality Psychology. Chapter Overview.
 Personality Psychology Psychology 370 Sheila K. Grant, Ph.D. Professor California State University, Northridge CHAPTER TWELVE MISCHEL AND BANDURA: Cognitive Social Learning Theory Chapter Overview TRAITS
Personality Psychology Psychology 370 Sheila K. Grant, Ph.D. Professor California State University, Northridge CHAPTER TWELVE MISCHEL AND BANDURA: Cognitive Social Learning Theory Chapter Overview TRAITS
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II
 THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 111
 Dikran J. Martin Psychology 111 Name:. Date:. Lecture Series: Chapter 16 Motivation, Thought, and Behavior: The Social Learning Theories Pages:19 TEXT: Funder, David C., (2000). The Personality Puzzle
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 111 Name:. Date:. Lecture Series: Chapter 16 Motivation, Thought, and Behavior: The Social Learning Theories Pages:19 TEXT: Funder, David C., (2000). The Personality Puzzle
Learning Approaches. Classical Conditioning Conditioned Stimulus (CS)... Conditioned Response (CR)... Acquisition... Extinction...
 Reading: H & O Chapters 9, 10, 11 Terms you should know. J. B. Watson Pavlov Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Conditioned Response
Reading: H & O Chapters 9, 10, 11 Terms you should know. J. B. Watson Pavlov Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Conditioned Response
CHAPTER 10. Background THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH. part 1. Background. Background. Social Cognitive Learning Theory
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH part 1 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 Social Cognitive Learning Theory Agrees with behaviouristically-oriented theories that behaviour is learnt Differs
CHAPTER 10 THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH part 1 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 Social Cognitive Learning Theory Agrees with behaviouristically-oriented theories that behaviour is learnt Differs
Observational Learning. The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224).
 LP 6E observational learning 1 Observational Learning The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224). Observational learning LP 6E observational
LP 6E observational learning 1 Observational Learning The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224). Observational learning LP 6E observational
About Social Cognitive Theory
 SOME CURRENT MOTIVATION CONSTRUCTS INTEREST and ENJOYMENT TASK VALUE GOALS (Purposes for doing) INTRINSIC vs EXTRINSIC MOTIVATION EXPECTANCY BELIEFS SELF-EFFICACY SELF-CONCEPT (Self-Esteem) OUTCOME EXPECTATIONS
SOME CURRENT MOTIVATION CONSTRUCTS INTEREST and ENJOYMENT TASK VALUE GOALS (Purposes for doing) INTRINSIC vs EXTRINSIC MOTIVATION EXPECTANCY BELIEFS SELF-EFFICACY SELF-CONCEPT (Self-Esteem) OUTCOME EXPECTATIONS
Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality. Copyright Allyn & Bacon (2009)
 Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality Roots in Gestalt Psychology Human beings seek meaning in their environments We organize the sensations we receive into meaningful perceptions Complex stimuli
Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality Roots in Gestalt Psychology Human beings seek meaning in their environments We organize the sensations we receive into meaningful perceptions Complex stimuli
Behavior Change Theories
 Behavior Change Theories Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD, FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Behavioral change theories These theories explain the reasons behind alterations in individuals' behavioral patterns.
Behavior Change Theories Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD, FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Behavioral change theories These theories explain the reasons behind alterations in individuals' behavioral patterns.
Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement. reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited
 OPERANT CONDITIONING Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement CONTINUOUS REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited pro: necessary for initial
OPERANT CONDITIONING Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement CONTINUOUS REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited pro: necessary for initial
Goals of Diabetes Education Train the Trainer
 Goals of Diabetes Education Train the Trainer Phil Unsworth Diabetes Education Nurse Facilitator Novo Nordisk Date of preparation: June 2016 UK/DB/0616/0125 Goals of Diabetes Education Training the Trainer
Goals of Diabetes Education Train the Trainer Phil Unsworth Diabetes Education Nurse Facilitator Novo Nordisk Date of preparation: June 2016 UK/DB/0616/0125 Goals of Diabetes Education Training the Trainer
MEDIA RESEARCH -2: FROM LIMITED EFFECTS to ACTIVE INTERPRETATION and SOCIAL LEARNING
 MEDIA RESEARCH -2: FROM LIMITED EFFECTS to ACTIVE INTERPRETATION and SOCIAL LEARNING Limited Effects Paradigms Reinforcement Theories of Media Influence Joseph Klapper CBS Television: Director of Social
MEDIA RESEARCH -2: FROM LIMITED EFFECTS to ACTIVE INTERPRETATION and SOCIAL LEARNING Limited Effects Paradigms Reinforcement Theories of Media Influence Joseph Klapper CBS Television: Director of Social
Five Misconceptions of Behavior Analysis 1) It ignores consciousness, feelings, and states of mind. 2) It neglects innate endowment and argues all
 Five Misconceptions of Behavior Analysis 1) It ignores consciousness, feelings, and states of mind. 2) It neglects innate endowment and argues all behavior is acquired in the lifetime of the individual
Five Misconceptions of Behavior Analysis 1) It ignores consciousness, feelings, and states of mind. 2) It neglects innate endowment and argues all behavior is acquired in the lifetime of the individual
CONCEPT OF PROSOCIAL BEHAVIOR
 FAQ CONCEPT OF PROSOCIAL BEHAVIOR 1Q: Explain prosocial behavior, helping behavior and altruism. What is the difference between helping behavior and altruism? Ans: As the word indicates, prosocial behavior
FAQ CONCEPT OF PROSOCIAL BEHAVIOR 1Q: Explain prosocial behavior, helping behavior and altruism. What is the difference between helping behavior and altruism? Ans: As the word indicates, prosocial behavior
The Role of Modeling and Feedback in. Task Performance and the Development of Self-Efficacy. Skidmore College
 Self-Efficacy 1 Running Head: THE DEVELOPMENT OF SELF-EFFICACY The Role of Modeling and Feedback in Task Performance and the Development of Self-Efficacy Skidmore College Self-Efficacy 2 Abstract Participants
Self-Efficacy 1 Running Head: THE DEVELOPMENT OF SELF-EFFICACY The Role of Modeling and Feedback in Task Performance and the Development of Self-Efficacy Skidmore College Self-Efficacy 2 Abstract Participants
Learning. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice.
 Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice. What is Learning? Learning is the process that allows us to adapt (be flexible) to the changing conditions
Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice. What is Learning? Learning is the process that allows us to adapt (be flexible) to the changing conditions
E Cog Sci II -- Plass New York University
 Overview Situated Cognition Theoretical conceptions of human nature can influence what people actually become. 2001-2005, Jan L. Plass 1 Psychological Theory Examples of theories Psychodynamic theory (inner
Overview Situated Cognition Theoretical conceptions of human nature can influence what people actually become. 2001-2005, Jan L. Plass 1 Psychological Theory Examples of theories Psychodynamic theory (inner
Social Cognitive Theory
 Epistemological Review Social Cognitive Theory By Douglas Valentine INTRODUCTION/BACKGROUND Social Cognitive Theory is a very recognizable learning theory. It is one that most of us have seen in use in
Epistemological Review Social Cognitive Theory By Douglas Valentine INTRODUCTION/BACKGROUND Social Cognitive Theory is a very recognizable learning theory. It is one that most of us have seen in use in
Psychological Perspectives. Unit 11
 Psychological Perspectives Unit 11 What is Psychology? What is Psychology?? Psychology is the science of the mind. So what are Psychological Perspectives? Psychological perspectives are ways of investigating
Psychological Perspectives Unit 11 What is Psychology? What is Psychology?? Psychology is the science of the mind. So what are Psychological Perspectives? Psychological perspectives are ways of investigating
Chapter 17 Therapy and Change
 Chapter 17 Therapy and Change Section 1 What is Psychotherapy? Psychotherapy is a general term for the several approaches used by mental health professionals to treat psychological disorders. Objectives
Chapter 17 Therapy and Change Section 1 What is Psychotherapy? Psychotherapy is a general term for the several approaches used by mental health professionals to treat psychological disorders. Objectives
Psychology. November 6, 2018.
 Psychology November 6, 2018. Today s Chunks of Learning. Chunk 1: Finishing up with the neo-freudians. Chunk 2: The Behaviorists. Chunk 1: Freud and the neo-freudians. Horney. Horney was interested in
Psychology November 6, 2018. Today s Chunks of Learning. Chunk 1: Finishing up with the neo-freudians. Chunk 2: The Behaviorists. Chunk 1: Freud and the neo-freudians. Horney. Horney was interested in
Robin Seim. Social Learning Theory
 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 1 Robin Seim Social Learning Theory May 17, 2014 EDUC 532 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 2 The social learning theory was derived by Albert Bandura in attempt to understand why people act
SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 1 Robin Seim Social Learning Theory May 17, 2014 EDUC 532 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 2 The social learning theory was derived by Albert Bandura in attempt to understand why people act
Aggression. Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental. Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz. Biological Theories
 Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental Aggression Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz Biological Theories Environmental Theories 1. Frustration/aggression 2. Theory of aggressive cues Cognitive Associationist
Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental Aggression Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz Biological Theories Environmental Theories 1. Frustration/aggression 2. Theory of aggressive cues Cognitive Associationist
Learned Helplessness
 LP 5E 1 Learned Helplessness Dogs were classically conditioned to associate a tone to the pain of an electric shock. In order to do this, the dogs were harnessed and could not avoid electric shocks. It
LP 5E 1 Learned Helplessness Dogs were classically conditioned to associate a tone to the pain of an electric shock. In order to do this, the dogs were harnessed and could not avoid electric shocks. It
Evaluate sociocultural explanations of the origins of violence. Lynn
 Evaluate sociocultural explanations of the origins of violence Lynn Evaluate: Assess the value by explaining strengths and limitations Social Learning theory (1977) Bandura suggests that people learn to
Evaluate sociocultural explanations of the origins of violence Lynn Evaluate: Assess the value by explaining strengths and limitations Social Learning theory (1977) Bandura suggests that people learn to
Best Practices for Coaching the Ego-Oriented Athlete
 Best Practices for Coaching the Ego-Oriented Athlete Charlotte R. Stith, M.S. Health and Human Performance Oklahoma State University Timothy Baghurst, Ph.D. Health and Human Performance Oklahoma State
Best Practices for Coaching the Ego-Oriented Athlete Charlotte R. Stith, M.S. Health and Human Performance Oklahoma State University Timothy Baghurst, Ph.D. Health and Human Performance Oklahoma State
Psychological Approach to Comparative Education Aneela Farooq Afshan Nisar
 Psychological Approach to Comparative Education Aneela Farooq Afshan Nisar Psychology Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behaviour. Psychology is a multifaceted discipline and includes
Psychological Approach to Comparative Education Aneela Farooq Afshan Nisar Psychology Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behaviour. Psychology is a multifaceted discipline and includes
Solutions Learning and Cognition The Design of the Mind Link full download:
 Solutions Learning and Cognition The Design of the Mind Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/solutions-learning-and-cognition-the-design-ofthe-mind/ Multiple Choice 1. The study of learning
Solutions Learning and Cognition The Design of the Mind Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/solutions-learning-and-cognition-the-design-ofthe-mind/ Multiple Choice 1. The study of learning
Week 1 reading material Mani Masuria
 CBT move-on Week 1 reading material Mani Masuria [M.Masuria@tacc.ac.uk] What is CBT? Cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapeutic treatment that helps patients to understand their thoughts
CBT move-on Week 1 reading material Mani Masuria [M.Masuria@tacc.ac.uk] What is CBT? Cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapeutic treatment that helps patients to understand their thoughts
Entertaining Violence or Violent Entertainment? Mapping the Media Violence Controversy
 Entertaining Violence or Violent Entertainment? Mapping the Media Violence Controversy The media violence controversy basically centers around the questions of effects: Does watching violent media make
Entertaining Violence or Violent Entertainment? Mapping the Media Violence Controversy The media violence controversy basically centers around the questions of effects: Does watching violent media make
Social Learning. The concept of social learning. Introduction
 15 Social Learning Introduction In this chapter, social learning is explained. Learning through observation, identification and imitation is discussed. In observational learning, four interrelated sub-processes
15 Social Learning Introduction In this chapter, social learning is explained. Learning through observation, identification and imitation is discussed. In observational learning, four interrelated sub-processes
Module 2 Unit 2. This is an OPTIONAL READING: SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY.
 Module 2 Unit 2 This is an OPTIONAL READING: SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY. Boeree, G. (2006). Albert Bandura. Retrieved from http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/bandura.html. [7 p.] A L B E R T B A NDUR A 1925 -
Module 2 Unit 2 This is an OPTIONAL READING: SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY. Boeree, G. (2006). Albert Bandura. Retrieved from http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/bandura.html. [7 p.] A L B E R T B A NDUR A 1925 -
Organizational Behaviour
 Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Perception The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private
Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Perception The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private
Using Your Brain -- for a CHANGE Summary. NLPcourses.com
 Using Your Brain -- for a CHANGE Summary NLPcourses.com Table of Contents Using Your Brain -- for a CHANGE by Richard Bandler Summary... 6 Chapter 1 Who s Driving the Bus?... 6 Chapter 2 Running Your Own
Using Your Brain -- for a CHANGE Summary NLPcourses.com Table of Contents Using Your Brain -- for a CHANGE by Richard Bandler Summary... 6 Chapter 1 Who s Driving the Bus?... 6 Chapter 2 Running Your Own
*Taken from the old syllabus. The new (2019) syllabus may have changes.
 I was a student at an IB school in Australia for my senior schooling. One of the subjects I took was Psychology at Higher Level (HL), and I finished with a 7. I was also getting consistent 7s throughout
I was a student at an IB school in Australia for my senior schooling. One of the subjects I took was Psychology at Higher Level (HL), and I finished with a 7. I was also getting consistent 7s throughout
I. Content Presentation. II. Learning Situation. IV. Reflection. III. Observation
 I. Content Presentation II. Learning Situation III. Observation IV. Reflection Defining Learning Definition of Behaviorism Three earlier behaviorists and their contributions Ivan Pavlov B.F. Skinner E.L.
I. Content Presentation II. Learning Situation III. Observation IV. Reflection Defining Learning Definition of Behaviorism Three earlier behaviorists and their contributions Ivan Pavlov B.F. Skinner E.L.
Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) then and now
 Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) then and now Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) is a classic study demonstrating the acquisition of aggression through social learning. It is summarised in the box opposite. Bandura
Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) then and now Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) is a classic study demonstrating the acquisition of aggression through social learning. It is summarised in the box opposite. Bandura
Learning. How do we learn behaviors from our direct and indirect experiences? What are the implications of learning theories for our everyday lives?
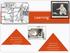 Learning How do we learn behaviors from our direct and indirect experiences? What are the implications of learning theories for our everyday lives? How do we learn? For the next few minutes brainstorm
Learning How do we learn behaviors from our direct and indirect experiences? What are the implications of learning theories for our everyday lives? How do we learn? For the next few minutes brainstorm
The Science of Leadership
 4--Why Transformational Leadership Works 1 The Science of Leadership WHY TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP WORKS by Joseph H. Boyett, Ph.D. Boyett & Associates EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Transformational leaders are
4--Why Transformational Leadership Works 1 The Science of Leadership WHY TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP WORKS by Joseph H. Boyett, Ph.D. Boyett & Associates EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Transformational leaders are
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow Learning? What s that? A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice. Note that learning is NOT the same as
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow Learning? What s that? A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice. Note that learning is NOT the same as
Chapter 01: The Study of the Person
 Chapter 01: The Study of the Person MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the psychological triad? a. behavior c. psychological health b. thoughts d. feelings C DIF: Easy REF: The Study
Chapter 01: The Study of the Person MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the psychological triad? a. behavior c. psychological health b. thoughts d. feelings C DIF: Easy REF: The Study
International School of Turin
 International School of Turin Adapted from the IB PSE scope and sequence Personal, Social and Physical Education Scope and Sequence Identity An understanding of our own beliefs, values, attitudes, experiences
International School of Turin Adapted from the IB PSE scope and sequence Personal, Social and Physical Education Scope and Sequence Identity An understanding of our own beliefs, values, attitudes, experiences
Lesson 12. Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior
 Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
Developmental Theories
 Developmental Theories The Relationship between a Theory and Research What is a theory? An explanation of what, how or why. In development, it explains change in us over time A guideline for future research,
Developmental Theories The Relationship between a Theory and Research What is a theory? An explanation of what, how or why. In development, it explains change in us over time A guideline for future research,
CORE THEORY - NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION - SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY
 CORE THEORY - NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION - SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Social Learning Theory explanation of Non- Verbal Communication Social learning theory (SLT) starts with the idea that we observe and imitate
CORE THEORY - NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION - SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Social Learning Theory explanation of Non- Verbal Communication Social learning theory (SLT) starts with the idea that we observe and imitate
What is Psychology? McGraw-Hill
 What is Psychology? DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Psy.D., PhD (PMHN), Ph.D. (Psychology), Ed.D., Sc.D., RN, PGD H/P No.: 056882733 URL: www.ifeet.org Personal URL: www.arnelsalgado.com Member: Sigma Theta
What is Psychology? DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Psy.D., PhD (PMHN), Ph.D. (Psychology), Ed.D., Sc.D., RN, PGD H/P No.: 056882733 URL: www.ifeet.org Personal URL: www.arnelsalgado.com Member: Sigma Theta
Exam 3. Multiple Choice. Please select the best response to each question. (3 points each)
 Name: Exam 3 Multiple Choice. Please select the best response to each question. (3 points each) 1. Which of the following is not true of basic-level concepts? A. They are between subordinate and superordinate
Name: Exam 3 Multiple Choice. Please select the best response to each question. (3 points each) 1. Which of the following is not true of basic-level concepts? A. They are between subordinate and superordinate
Personality. Unit 3: Developmental Psychology
 Personality Unit 3: Developmental Psychology Personality Personality: The consistent, enduring, and unique characteristics of a person. There are many personality theories that provide a way of organizing
Personality Unit 3: Developmental Psychology Personality Personality: The consistent, enduring, and unique characteristics of a person. There are many personality theories that provide a way of organizing
Chapter 7. Learning From Experience
 Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
V. List the major objectives of the proposed minor and describe its chief features briefly.
 I. School: Science Department: Psychology II. Proposed Minor: Health Psychology III. Related Major: Psychology IV. Projected Date of Implementation: Fall 2013 V. List the major objectives of the proposed
I. School: Science Department: Psychology II. Proposed Minor: Health Psychology III. Related Major: Psychology IV. Projected Date of Implementation: Fall 2013 V. List the major objectives of the proposed
Why do Psychologists Perform Research?
 PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
Unit 5: Learning. Topic: Operant Conditioning
 Unit 5: Learning Topic: Operant Conditioning 1874-1949 key name Edward THORNDIKE Proposed the Law of Effect behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely conducted puzzle box experiments on
Unit 5: Learning Topic: Operant Conditioning 1874-1949 key name Edward THORNDIKE Proposed the Law of Effect behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely conducted puzzle box experiments on
3. MAIN THEORIES ON ACQUISITION AND DEVELOPMENT DEL LANGUAGE. 3.1 LEARNING THEORIES: WATSON AND SKINNER OPERANT CONDITIONING
 SEC 3 Page 1 of 9 3. MAIN THEORIES ON ACQUISITION AND DEVELOPMENT DEL LANGUAGE. 3.1 LEARNING THEORIES: WATSON AND SKINNER OPERANT CONDITIONING By the 1920s John B. Watson had left academic psychology and
SEC 3 Page 1 of 9 3. MAIN THEORIES ON ACQUISITION AND DEVELOPMENT DEL LANGUAGE. 3.1 LEARNING THEORIES: WATSON AND SKINNER OPERANT CONDITIONING By the 1920s John B. Watson had left academic psychology and
Personality Theories HUMANISTIC APPROACH
 Personality Theories HUMANISTIC APPROACH Humanistic Theories: Rejects biological determinism & emphasizes free will and personal growth, and the ability to choose our own destiny. Kurt Cobain Cobain showed
Personality Theories HUMANISTIC APPROACH Humanistic Theories: Rejects biological determinism & emphasizes free will and personal growth, and the ability to choose our own destiny. Kurt Cobain Cobain showed
ADULT-CHILD-OF-AN-ALCOHOLIC (ACA) TRAITS
 ADULT-CHILD-OF-AN-ALCOHOLIC (ACA) TRAITS BEHAVIORAL DEFINITIONS 1. Has a history of being raised in an alcoholic home, which resulted in having experienced emotional abandonment, role confusion, abuse,
ADULT-CHILD-OF-AN-ALCOHOLIC (ACA) TRAITS BEHAVIORAL DEFINITIONS 1. Has a history of being raised in an alcoholic home, which resulted in having experienced emotional abandonment, role confusion, abuse,
Topic 4: Learning Theories
 Edexcel Psychology A-level Topic 4: Learning Theories Notes Part 1 The Learning Approach: Behaviourism A01 Introduction and Assumptions: The behaviourist approach is an approach to explaining behaviour
Edexcel Psychology A-level Topic 4: Learning Theories Notes Part 1 The Learning Approach: Behaviourism A01 Introduction and Assumptions: The behaviourist approach is an approach to explaining behaviour
COURSE SYNOPSIS COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 PSYCHOLOGY OF SOCIAL & INTERPERSONAL BEHAVIOR FEM4103 3 (3+0) SEMESTER : 1 ST /2014-2015 PJJ LECTURER : ASSOC. PROF. DR. RUMAYA JUHARI OFFICE : 1 ST FLOOR BLOK A, FEM CONTACT NO : 03-89467089 E-MAIL :
PSYCHOLOGY OF SOCIAL & INTERPERSONAL BEHAVIOR FEM4103 3 (3+0) SEMESTER : 1 ST /2014-2015 PJJ LECTURER : ASSOC. PROF. DR. RUMAYA JUHARI OFFICE : 1 ST FLOOR BLOK A, FEM CONTACT NO : 03-89467089 E-MAIL :
I Shouldn t Have to Tell em That. Executive Functioning Deficits that Create Behavioral Challenges for Children and Teens
 I Shouldn t Have to Tell em That Executive Functioning Deficits that Create Behavioral Challenges for Children and Teens AGENDA Behavioral Challenges Challenges and Diagnostic Categories New Ways of Understanding:
I Shouldn t Have to Tell em That Executive Functioning Deficits that Create Behavioral Challenges for Children and Teens AGENDA Behavioral Challenges Challenges and Diagnostic Categories New Ways of Understanding:
History and Approaches CHAPTER
 History and Approaches CHAPTER J :.-.. - n ;..., "".. =:1 KEY TERMS Wilhelm Wundt Psychoanalytic theory Biopsychology (or (1832-1920) John Watson neuroscience) Introspection (1878-1958) perspective Structuralism
History and Approaches CHAPTER J :.-.. - n ;..., "".. =:1 KEY TERMS Wilhelm Wundt Psychoanalytic theory Biopsychology (or (1832-1920) John Watson neuroscience) Introspection (1878-1958) perspective Structuralism
Personal identity is cultural identity. Culture is a powerful organizer of
 Thomas (Culture) 4682-01.qxd 4/15/2005 5:56 PM Page 1 1 Framework Personal identity is cultural identity. Culture is a powerful organizer of people s lives. How we view ourselves and who we are as individuals
Thomas (Culture) 4682-01.qxd 4/15/2005 5:56 PM Page 1 1 Framework Personal identity is cultural identity. Culture is a powerful organizer of people s lives. How we view ourselves and who we are as individuals
Learning Theories - Behaviourism -
 Learning Theories - Behaviourism - Kimberley A. Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/257e-570 Office Hour: Thursdays 2-3pm Office: S302 Outline What is Learning? Classical Conditioning
Learning Theories - Behaviourism - Kimberley A. Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/257e-570 Office Hour: Thursdays 2-3pm Office: S302 Outline What is Learning? Classical Conditioning
Behaviorism: An essential survival tool for practitioners in autism
 Behaviorism: An essential survival tool for practitioners in autism What we re going to do today 1. Review the role of radical behaviorism (RB) James M. Johnston, Ph.D., BCBA-D National Autism Conference
Behaviorism: An essential survival tool for practitioners in autism What we re going to do today 1. Review the role of radical behaviorism (RB) James M. Johnston, Ph.D., BCBA-D National Autism Conference
Explanatory Style. How come you didn t get the project completed? Stable Internal Global. Associated with depression. Unstable External Specific
 LP 3D: Social Cog part2 1 Explanatory Style People s negative inferences about the causes of their experiences can make depression more likely. According to helplessness theory, individuals who are prone
LP 3D: Social Cog part2 1 Explanatory Style People s negative inferences about the causes of their experiences can make depression more likely. According to helplessness theory, individuals who are prone
Personality. Announcements. Psychodynamic Approach 10/31/2012. Psychodynamic: Structure of Personality Ego
 Announcements Extra Credit due November 8 Personality Enduring patterns of how people adapt to the world Characteristic style of behaving, thinking, and feeling Consistent over time and across situations
Announcements Extra Credit due November 8 Personality Enduring patterns of how people adapt to the world Characteristic style of behaving, thinking, and feeling Consistent over time and across situations
Chapter 11 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions
 Chapter 11 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions As you review the various in this chapter, especially the strengths and weaknesses of each, make notes on the tables at the end of this document to use
Chapter 11 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions As you review the various in this chapter, especially the strengths and weaknesses of each, make notes on the tables at the end of this document to use
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following movements is not considered to have fostered an early interest in the investigation of learning processes? (a) evolutionary theory (b) rationalism (c)
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following movements is not considered to have fostered an early interest in the investigation of learning processes? (a) evolutionary theory (b) rationalism (c)
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. us grow, both personally and intellectually. It provides an objective base for
 U l i n n u h a 1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of Study Literature is written expression designed to engage readers emotionally as well as intellectually, with the major genres being fiction, poetry,
U l i n n u h a 1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of Study Literature is written expression designed to engage readers emotionally as well as intellectually, with the major genres being fiction, poetry,
Classical conditioning or classical learning theory
 Learning theories These theories see criminality as normal learned behaviour. Some behaviour is instinctive and is possessed by an individual at birth; the possession of this is determined by biological
Learning theories These theories see criminality as normal learned behaviour. Some behaviour is instinctive and is possessed by an individual at birth; the possession of this is determined by biological
Theories of Learning
 Theories of Learning Learning Classical conditioning Classical conditioning in real life Operant conditioning Operant conditioning in real life Learning and the mind Watson s Extreme Environmentalism Give
Theories of Learning Learning Classical conditioning Classical conditioning in real life Operant conditioning Operant conditioning in real life Learning and the mind Watson s Extreme Environmentalism Give
NEGOTIATION SEVENTH EDITION
 NEGOTIATION SEVENTH EDITION ROY J. LEWICKI DAVID M. SAUNDERS BRUCE BARRY 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution
NEGOTIATION SEVENTH EDITION ROY J. LEWICKI DAVID M. SAUNDERS BRUCE BARRY 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution
Test Name: Psych1Test2SP b. complexity Feedback: The complexity of light is related to our perception of saturation.
 Test Name: Psych1Test2SP2012 1. b. complexity The complexity of light is related to our perception of saturation. 2. a. a secondary punisher. This is an example of a learned or secondary punisher, a low
Test Name: Psych1Test2SP2012 1. b. complexity The complexity of light is related to our perception of saturation. 2. a. a secondary punisher. This is an example of a learned or secondary punisher, a low
Awareness, Love and Light. Our Story
 Awareness, Love and Light Our Story Our mind likes to create a story about ourselves that we can tell to others The story helps define our sense of self and explain our life experiences The story can also
Awareness, Love and Light Our Story Our mind likes to create a story about ourselves that we can tell to others The story helps define our sense of self and explain our life experiences The story can also
COGNITIVE BEHAVIOUR MODIFICATION
 UNIT 3 Structure COGNITIVE BEHAVIOUR MODIFICATION 3.0 Introduction 3.1 Objectives 3.2 Techniques of 3.2.1 Self Instructional Technique 3.2.2 Self Inoculation Technique 3.2.3 Self Management Technique 3.2.4
UNIT 3 Structure COGNITIVE BEHAVIOUR MODIFICATION 3.0 Introduction 3.1 Objectives 3.2 Techniques of 3.2.1 Self Instructional Technique 3.2.2 Self Inoculation Technique 3.2.3 Self Management Technique 3.2.4
Highlights of what you may have learned from General Psychology 202?
 Highlights of what you may have learned from General Psychology 202? LP 11A intro 1 Psychology of Learning: There is a tendency to use punishments. o What are the problems with using punishments? o What
Highlights of what you may have learned from General Psychology 202? LP 11A intro 1 Psychology of Learning: There is a tendency to use punishments. o What are the problems with using punishments? o What
Trust in Relationships
 Trust in Relationships Diamond Management Consulting Page 2 Trust in Relationships Is trust easier to destroy than to build? Cooperation and conflict management research of the last 30 years assumes the
Trust in Relationships Diamond Management Consulting Page 2 Trust in Relationships Is trust easier to destroy than to build? Cooperation and conflict management research of the last 30 years assumes the
A person s unique long-term pattern of thinking, emotion, and behavior; the consistency of who you are, have been, and will become
 Chapter 12 A person s unique long-term pattern of thinking, emotion, and behavior; the consistency of who you are, have been, and will become Hereditary aspects of personality, including sensitivity, moods,
Chapter 12 A person s unique long-term pattern of thinking, emotion, and behavior; the consistency of who you are, have been, and will become Hereditary aspects of personality, including sensitivity, moods,
Stories. For C h a n g e
 FRAMING Stories For C h a n g e Stories By Nat Kendall-Taylor / Chief Executive Officer at Frameworks Institute spring & summer 2017 33/74 29/80 S T O R Y T E L L I N G is all the rage in nonprofit communications.
FRAMING Stories For C h a n g e Stories By Nat Kendall-Taylor / Chief Executive Officer at Frameworks Institute spring & summer 2017 33/74 29/80 S T O R Y T E L L I N G is all the rage in nonprofit communications.
Chapter 9. Behavior Therapy. Four Aspects of Behavior Therapy. Exposure Therapies. Therapeutic Techniques. Four Aspects of Behavior Therapy
 Chapter 9 Behavior Therapy A set of clinical procedures relying on experimental findings of psychological research Behavior Therapy Based on principles of learning that are systematically applied Treatment
Chapter 9 Behavior Therapy A set of clinical procedures relying on experimental findings of psychological research Behavior Therapy Based on principles of learning that are systematically applied Treatment
Chapter 9. Behavior Therapy
 Chapter 9 Behavior Therapy 0 Behavior Therapy A set of clinical procedures relying on experimental findings of psychological research Based on principles of learning that are systematically applied Treatment
Chapter 9 Behavior Therapy 0 Behavior Therapy A set of clinical procedures relying on experimental findings of psychological research Based on principles of learning that are systematically applied Treatment
CHAPTER 7: Achievement motivation, attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence. Practice questions - text book pages
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 7: Achievement motivation, attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence Practice questions - text book pages 111-112 1) Which one of the following best explains achievement
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 7: Achievement motivation, attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence Practice questions - text book pages 111-112 1) Which one of the following best explains achievement
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Michael Arloski, Ph.D., PCC, CWP. Lessons From Albert Bandura For Wellness Coaches
 Michael Arloski, Ph.D., PCC, CWP Lessons From Albert Bandura For Wellness Coaches Michael Arloski, Ph.D., PCC, CWP Self- efficacy or belief in one s ability to perform determines whether behavior will
Michael Arloski, Ph.D., PCC, CWP Lessons From Albert Bandura For Wellness Coaches Michael Arloski, Ph.D., PCC, CWP Self- efficacy or belief in one s ability to perform determines whether behavior will
The Power of Feedback
 The Power of Feedback 35 Principles for Turning Feedback from Others into Personal and Professional Change By Joseph R. Folkman The Big Idea The process of review and feedback is common in most organizations.
The Power of Feedback 35 Principles for Turning Feedback from Others into Personal and Professional Change By Joseph R. Folkman The Big Idea The process of review and feedback is common in most organizations.
