The Science of Psychology
|
|
|
- Myron Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Science of Psychology Module 2 Psychology s Scientific Method Module Objectives Why is Psychology a Science? What is the scientific method? Why should I believe what researchers say? How do Psychologist s design a study? Types of research Scientific psychology has four basic goals: to describe, explain, predict, and change behavior and mental processes 1
2 Psychology as a Science Psychologists must engage in careful systematic observation when studying behavior and mental processes Systematic observation is setting up our study so that we eliminate or reduce bias. We must keep our minds open but not so open that our brain falls out. (Oberg, 1995) Why can t scientists base their research off of casual, everyday observations? (AKA, People watching) 2
3 Unfortunately, casual observation is subject to bias that can distort information We tend to notice the behavior that fits our stereotypes Skepticism combines two opposing attitudes: an openness to new ideas combined with a willingness to subject these claims to scrutiny. Why is Research Conducted? The purpose of scientific research is to create new knowledge. This knowledge is applied in all areas of society to provide solutions. 3
4 How Do Scientists Collect and Evaluate Evidence? The Scientific Method is how Psychologist s gain knowledge about the mind and behavior Scientific Method in Psychology Step 1: Before research begins, a problem must be identified. Observe some phenomenon and want to know why it exists. Phenomena that psychologists study are called a variables (anything that can change). Why are more students enrolling in community colleges than in previous years? The answer to such questions are called theories. Theories seek to explain why things have happened, and they can be used to make predictions about future observations 4
5 Make a Prediction! Step 2: Develop a testable hypothesis, or a specific prediction about how one factor is related to another. Drinking excessive amounts of caffeine before the exam will increase my score how can we make this testable? What is a testable hypothesis for this nursery rhyme? What is your Hypothesis? What could help us understand why Jack and Jill fell down the hill? Perhaps we could hypothesize that fetching water causes falls. There is a correlation or a relationship between the terrain and the likelihood of falling. 5
6 Or, Perhaps Step 3- Testing through Empirical Research It s time to design the study to test a prediction (hypothesis) that is based on a theory. The hypothesis must be testable, but also operationally defined Meaning the variables are in measurable terms by defining a numerical value. 6
7 Get into groups of 3-4 and Operationally define the following -Sadness -Creativity Examples of Operational Definitions Aggressive behavior the number of times a child punches a punching bag over the course of one hour Happiness the number of times a person smiles while watching a Disney movie Intelligence a score on an IQ test Anxiety the number of pencils a student brings to an exam Was my prediction correct? Step 4- Drawing Conclusions Researchers draw conclusions about the results of the study. Did the information support or oppose their hypothesis? Don t forget this information MUST be replicated to be accepted as valid. 7
8 Evaluating the theory If the information produced in a study supports the original hypothesis it is published in the scientific community in peer-reviewed journals. The scientific community continues to debate the issue further. What s Next? Types of Psychological research Types of Psychological Research Experimental Research Descriptive Methods Correlational Research Biological Research 8
9 Descriptive Research describes events or phenomenon that already exist. This type of research can reveal important information about people s behaviors and attitudes. This research method is used to observe and record behavior without producing an explanation Naturalistic Observation A systematic observation what many people do under natural conditions, without interference. 9
10 Case Study An in-depth look at a single (unusual) individual. Case studies provide dramatic, detailed information about a person s life, but their generalizability is limited. Example of a Case Study Phineas Gage On September 13, 1848 an accidental explosion blew a tamping iron through his head. The tamping iron was 3 ½ feet long and weighed 13 pounds. The tamping iron went in under his left cheek bone and completely out through the top of his head, landing about 25 to 30 yards behind him. Phineas Gage (1848) Yes he LIVED! Most of the front part of the left side of his brain was destroyed. Afterwards he experienced serious personality changes and his friends reported that he was no longer Phineas. 10
11 Ask questions Surveys examines more people in less depth. A survey presents a standard set of questions, or items, to obtain people s self-reported attitudes or beliefs about a topic. Although these a be a great way of collecting data, they must be properly constructed. Limitations People tend to answer the questions to make them look good, rather than provide how they really feel about the topic. Or they simply lie Correlational Studies Research that examines the relationships between variables by making predictions. The purpose is to examine whether and how two variables change together. Correlation indicates the strength and direction of a relationship. It allows for prediction of one variable based on the other variable 11
12 The strength of the relationship is measured by a correlation coefficient which ranges from +1 to -1 +1: perfect positive correlation (perfect relationship) 0: no correlation (no relationship) -1: perfect negative correlation (perfect relationship) Three Types of Correlation In a positive correlation, the two factors move (or vary) in the same direction. In a negative correlation, the two factors vary in opposite directions that is, as one factor increases, the other factor decreases. Sometimes there is no relationship between two variables a zero correlation. Name that Correlation! The more you party, the lower your test grade. Negative correlation The more you study, the higher your test grade Positive correlation The amount of time a college student studies and their height in inches NO (Zero) correlation 12
13 Correlation is not causation! Just because there is a correlation between tow variables does not mean that one variable causes another. The relationship could be the result of another variable that was not studied (third-variable problem) Experimental Research This is the ONLY research design that can examine a single factor s effect on a particular behavior Experimental Method A study in which the investigator manipulates at least one variable while measuring at least one other variable. Determines a cause and effect relationship between variables and should involve random assignment of participants. 13
14 Experimental Design Variables are a condition or characteristic that is subject to change. There are two types of variables in every study: Independent variable: Factor that is manipulated Dependent variable: Behavior/variable that is measured Variables Independent Variable is the variable is purposefully manipulated by the experimenter to see what changes happen. This is done to see how the other variables will be effected. What will happen if? Dependent Variable is the behavior that is measured because it is expected to change. Outcome or effect If I move all of my front row students to the back, what will happen? 14
15 Identify the Variable Independent and Dependent? Developmental psychologists want to know if exposing children to differing amounts of public television improves their reading skills. IV-the amount of public television watched DV- change in reading skills Name the Variables! A clinical psychologist is interested in how heart rate is affected by viewing a violent film as opposed to a nonviolent film IV- film type (violent or nonviolent) DV- change in heart rate Try another one Cognitive psychologists are interested in what types of diagrams are easiest for people to remember IV-Types of Diagrams DV- Effect on memory 15
16 OK, Last One An industrial/organizational psychologist tests to see if wearing name tags makes employees happier with their work IV- Wearing name tags DV- Happiness at work Who will you study? Participants in a study are individuals in an experiment whose behaviors are observed. The sample All have something in common which is based on what the researcher is testing Participants are randomly assigned to one of two groups: 1. The Control Group-(Comparison group) This group does not receive the independent variable It does not receive the treatment 2. The Experimental Group- receives new treatment This group receives the independent variable 16
17 Cautions about research Validity refers to the soundness of the conclusions a researcher draws from an experiment External Validity- The degree to which an experiment actually reflects the real-world issues it is supposed to address Internal validity- The degree to which changes in the DV are due to the manipulation if the IV Ethics in Research Being part of a research study can potentially lead to unintended consequences for the participants. Safeguards are required to protect participant rights. Ethics in Research Participants must be advised about the purpose and conditions of the study- up front. Participants cannot be coerced into doing something psychologically or physically harmful, or that violates standards of decency At the end of the study, participants must go through debriefing Psychology has a long history of controversial that experiments that would now be considered UNETHICAL. 17
18 Next Class Biopsychology How is the nervous system organized? How do brain chemicals influence our behavior? 18
The Science of Psychology
 The Science of Psychology Module 2 Psychology s Scientific Method Module Objectives Why is Psychology a Science? What is the scientific method? Why should I believe what researchers say? How do Psychologist
The Science of Psychology Module 2 Psychology s Scientific Method Module Objectives Why is Psychology a Science? What is the scientific method? Why should I believe what researchers say? How do Psychologist
Why do Psychologists Perform Research?
 PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
Introduction to Research Methods
 Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
Module 2/3 Research Strategies: How Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY 8 th Edition in Modules Module 2/3 Research Strategies: How Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions 1 The Need for Psychological Science Psychologists, like all scientists, use the scientific
Myers PSYCHOLOGY 8 th Edition in Modules Module 2/3 Research Strategies: How Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions 1 The Need for Psychological Science Psychologists, like all scientists, use the scientific
Audio: In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2
 Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
9/24/2014 UNIT 2: RESEARCH METHODS AND STATISTICS RESEARCH METHODS RESEARCH METHODS RESEARCH METHODS
 RESEARCH METHODS UNIT 2: RESEARCH METHODS AND STATISTICS 8-10% of AP Exam Case Studies A case study is an in-depth study of one person. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history
RESEARCH METHODS UNIT 2: RESEARCH METHODS AND STATISTICS 8-10% of AP Exam Case Studies A case study is an in-depth study of one person. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history
AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology
 AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology 1. In the opening vignette, to what was Alicia's condition linked? The death of her parents and only brother 2. What did Pennebaker s study
AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology 1. In the opening vignette, to what was Alicia's condition linked? The death of her parents and only brother 2. What did Pennebaker s study
PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH DESIGN & METHODS AP PSYCHOLOGY: CHAPTER 2
 PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH DESIGN & METHODS AP PSYCHOLOGY: CHAPTER 2 Bellwork: Why do we need Psychological Research? What were your thoughts.. Hindsight Bias I knew it all along phenomenon Examples.. 2 groups..
PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH DESIGN & METHODS AP PSYCHOLOGY: CHAPTER 2 Bellwork: Why do we need Psychological Research? What were your thoughts.. Hindsight Bias I knew it all along phenomenon Examples.. 2 groups..
UNIT II: RESEARCH METHODS
 THINKING CRITICALLY WITH PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE UNIT II: RESEARCH METHODS Module 4: The Need for Psychological Science Module 5: Scientific Method and Description Module 6: Correlation and Experimentation
THINKING CRITICALLY WITH PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE UNIT II: RESEARCH METHODS Module 4: The Need for Psychological Science Module 5: Scientific Method and Description Module 6: Correlation and Experimentation
Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with Psychological Science
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers The Need for Psychologists, like all scientists, use the scientific method to construct
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers The Need for Psychologists, like all scientists, use the scientific method to construct
In this chapter we discuss validity issues for quantitative research and for qualitative research.
 Chapter 8 Validity of Research Results (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) In this chapter we discuss validity issues for
Chapter 8 Validity of Research Results (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) In this chapter we discuss validity issues for
OVERVIEW OF RESEARCH METHODS II. Lecturer: Dr. Paul Narh Doku Contact: Department of Psychology, University of Ghana
 OVERVIEW OF RESEARCH METHODS II Lecturer: Dr. Paul Narh Doku Contact: pndoku@ug.edu.gh Department of Psychology, University of Ghana Session Overview This session will present an overview of several non-experimental
OVERVIEW OF RESEARCH METHODS II Lecturer: Dr. Paul Narh Doku Contact: pndoku@ug.edu.gh Department of Psychology, University of Ghana Session Overview This session will present an overview of several non-experimental
The degree to which a measure is free from error. (See page 65) Accuracy
 Accuracy The degree to which a measure is free from error. (See page 65) Case studies A descriptive research method that involves the intensive examination of unusual people or organizations. (See page
Accuracy The degree to which a measure is free from error. (See page 65) Case studies A descriptive research method that involves the intensive examination of unusual people or organizations. (See page
Introduction to PSYCHOLOGY
 Introduction to PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY The scientific study of behavior and the mental process. What are the characteristics of an excellent Psychologist? How do psychologists think? I feel myself a naturalist
Introduction to PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY The scientific study of behavior and the mental process. What are the characteristics of an excellent Psychologist? How do psychologists think? I feel myself a naturalist
Psych 1Chapter 2 Overview
 Psych 1Chapter 2 Overview After studying this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: 1) What are five characteristics of an ideal scientist? 2) What are the defining elements of
Psych 1Chapter 2 Overview After studying this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: 1) What are five characteristics of an ideal scientist? 2) What are the defining elements of
2 Critical thinking guidelines
 What makes psychological research scientific? Precision How psychologists do research? Skepticism Reliance on empirical evidence Willingness to make risky predictions Openness Precision Begin with a Theory
What makes psychological research scientific? Precision How psychologists do research? Skepticism Reliance on empirical evidence Willingness to make risky predictions Openness Precision Begin with a Theory
1. What is the difference between positive and negative correlations?
 1. What is the difference between positive and negative correlations? 2. Can correlations make predictions? 3. Can correlations prove causation? 4. What are illusory correlations? We can take data from
1. What is the difference between positive and negative correlations? 2. Can correlations make predictions? 3. Can correlations prove causation? 4. What are illusory correlations? We can take data from
Final Exam: PSYC 300. Multiple Choice Items (1 point each)
 Final Exam: PSYC 300 Multiple Choice Items (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three fundamental features of science? a. empirical questions b. public knowledge c. mathematical equations
Final Exam: PSYC 300 Multiple Choice Items (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three fundamental features of science? a. empirical questions b. public knowledge c. mathematical equations
Human intuition is remarkably accurate and free from error.
 Human intuition is remarkably accurate and free from error. 3 Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy of their beliefs. 4 Case studies are particularly useful because of the similarities we
Human intuition is remarkably accurate and free from error. 3 Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy of their beliefs. 4 Case studies are particularly useful because of the similarities we
9 research designs likely for PSYC 2100
 9 research designs likely for PSYC 2100 1) 1 factor, 2 levels, 1 group (one group gets both treatment levels) related samples t-test (compare means of 2 levels only) 2) 1 factor, 2 levels, 2 groups (one
9 research designs likely for PSYC 2100 1) 1 factor, 2 levels, 1 group (one group gets both treatment levels) related samples t-test (compare means of 2 levels only) 2) 1 factor, 2 levels, 2 groups (one
PSYC1024 Clinical Perspectives on Anxiety, Mood and Stress
 PSYC1024 Clinical Perspectives on Anxiety, Mood and Stress LECTURE 1 WHAT IS SCIENCE? SCIENCE is a standardised approach of collecting and gathering information and answering simple and complex questions
PSYC1024 Clinical Perspectives on Anxiety, Mood and Stress LECTURE 1 WHAT IS SCIENCE? SCIENCE is a standardised approach of collecting and gathering information and answering simple and complex questions
Research Strategies: How Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions. Module 2
 Research Strategies: How Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions Module 2 How Do Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions? The Scientific Method Goals and Tools of Psychology Description Correlation Experimentation
Research Strategies: How Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions Module 2 How Do Psychologists Ask and Answer Questions? The Scientific Method Goals and Tools of Psychology Description Correlation Experimentation
RESEARCH METHODS: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE
 RESEARCH METHODS: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE TODAY S OBJECTIVE Explain basic methods of psychological research. IMPORTANT KEY TERMS Variable: anything that can change Theory: broad idea or set of closely
RESEARCH METHODS: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE TODAY S OBJECTIVE Explain basic methods of psychological research. IMPORTANT KEY TERMS Variable: anything that can change Theory: broad idea or set of closely
Clever Hans the horse could do simple math and spell out the answers to simple questions. He wasn t always correct, but he was most of the time.
 Clever Hans the horse could do simple math and spell out the answers to simple questions. He wasn t always correct, but he was most of the time. While a team of scientists, veterinarians, zoologists and
Clever Hans the horse could do simple math and spell out the answers to simple questions. He wasn t always correct, but he was most of the time. While a team of scientists, veterinarians, zoologists and
The Research Enterprise in Psychology Chapter 2
 The Research Enterprise in Psychology Chapter 2 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including
The Research Enterprise in Psychology Chapter 2 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including
RESEARCH FUNDAMENTALS
 RESEARCH FUNDAMENTALS What do psychologists study? The ABCs (emotion) E.g., emotional reactions to stimuli, ideas, and oneself, emotional disorders, manipulating emotions, etc Behavior E.g., behavioral
RESEARCH FUNDAMENTALS What do psychologists study? The ABCs (emotion) E.g., emotional reactions to stimuli, ideas, and oneself, emotional disorders, manipulating emotions, etc Behavior E.g., behavioral
8/17/2012. Social Psychology: An Empirical Science. Social Psychology: An Empirical Science. Chapter 2
 Chapter 2 Methodology: How Social Psychologists Do Research Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Social Psychology: An Empirical Science Fundamental
Chapter 2 Methodology: How Social Psychologists Do Research Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Social Psychology: An Empirical Science Fundamental
Research. how we figure stuff out. Methods
 Research how we figure stuff out Methods Penny in the Glass Activity Let s Make A Deal! One volunteer is needed for a chance to win $1,334,499! Let s Make A Deal Shows Us That: Human Intuition is highly
Research how we figure stuff out Methods Penny in the Glass Activity Let s Make A Deal! One volunteer is needed for a chance to win $1,334,499! Let s Make A Deal Shows Us That: Human Intuition is highly
AP Psychology Ch. 01 Psych Science & Stats Study Guide
 Name: Period: 1. Which of the following best describes the hindsight bias? A) Events seem more predictable before they have occurred. B) Events seem more predictable after they have occurred. C) A person's
Name: Period: 1. Which of the following best describes the hindsight bias? A) Events seem more predictable before they have occurred. B) Events seem more predictable after they have occurred. C) A person's
Chapter 1: Thinking Like a Scientist
 Chapter 1: Thinking Like a Scientist MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A psychologist from the research area might study brain organization or the chemical messengers used in the nervous system. 2. A psychologist from
Chapter 1: Thinking Like a Scientist MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A psychologist from the research area might study brain organization or the chemical messengers used in the nervous system. 2. A psychologist from
CHAPTER 1 Understanding Social Behavior
 CHAPTER 1 Understanding Social Behavior CHAPTER OVERVIEW Chapter 1 introduces you to the field of social psychology. The Chapter begins with a definition of social psychology and a discussion of how social
CHAPTER 1 Understanding Social Behavior CHAPTER OVERVIEW Chapter 1 introduces you to the field of social psychology. The Chapter begins with a definition of social psychology and a discussion of how social
Conducting Research. Research Methods Chapter 1. Descriptive Research Methods. Conducting Research. Case Study
 Research Methods Chapter 1 Conducting Research Goals of Psychology Describe Explain Predict Control Pitfalls of intuition and common sense explanations: Hindsight bias, overconfidence Remember psychology
Research Methods Chapter 1 Conducting Research Goals of Psychology Describe Explain Predict Control Pitfalls of intuition and common sense explanations: Hindsight bias, overconfidence Remember psychology
What is Psychology? Science versus Intuition 1 a. What is psychology? (from text) b. Note the revision from class:
 Lilienfeld et al. Chapter 1: Psychology and Scientific Thinking: A Framework for Everyday Life p. 1 of 12 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college- level courses.
Lilienfeld et al. Chapter 1: Psychology and Scientific Thinking: A Framework for Everyday Life p. 1 of 12 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college- level courses.
Research Methods. Observational Methods. Correlation - Single Score. Basic Methods. Elaine Blakemore. Title goes here 1. Observational.
 Research Methods Basic Methods Observational Experimental Observational Methods Observes behavior as it occurs in the real world One important observational method is correlation Correlation observes a
Research Methods Basic Methods Observational Experimental Observational Methods Observes behavior as it occurs in the real world One important observational method is correlation Correlation observes a
Chapter 1: Thinking critically with. Introduction
 Chapter 1: Thinking critically with psychological science Introduction Fact or Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkable accurate and free from error. 2. Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy
Chapter 1: Thinking critically with psychological science Introduction Fact or Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkable accurate and free from error. 2. Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Science stems from the empirical movement and thus observation, as well as measurement and description are crucial. The deterministic assumptions of science lead scientists
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Science stems from the empirical movement and thus observation, as well as measurement and description are crucial. The deterministic assumptions of science lead scientists
INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY SUMMARY 1 ABDULLAH ALZIBDEH Introduction In this lecture, we discuss the definitions of psychology and behavior. We also discuss the approaches in psychology and the scientific
INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY SUMMARY 1 ABDULLAH ALZIBDEH Introduction In this lecture, we discuss the definitions of psychology and behavior. We also discuss the approaches in psychology and the scientific
THE RESEARCH ENTERPRISE IN PSYCHOLOGY
 THE RESEARCH ENTERPRISE IN PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 2 Mr. Reinhard Winston Churchill High School Adapted from: Psychology: Themes and Variations by Wayne Weiten, 9 th edition Looking for laws Psychologists share
THE RESEARCH ENTERPRISE IN PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 2 Mr. Reinhard Winston Churchill High School Adapted from: Psychology: Themes and Variations by Wayne Weiten, 9 th edition Looking for laws Psychologists share
Psychology: The Science
 Psychology: The Science How Psychologists Do Research Ex: While biking, it seems to me that drivers of pick up trucks aren t as nice as car drivers. I make a hypothesis or even develop a theory that p/u
Psychology: The Science How Psychologists Do Research Ex: While biking, it seems to me that drivers of pick up trucks aren t as nice as car drivers. I make a hypothesis or even develop a theory that p/u
Psychology - MR. CALLAWAY Mundy s Mill High School Unit RESEARCH METHODS
 Psychology - MR. CALLAWAY Mundy s Mill High School Unit 2.1 - RESEARCH METHODS Intro to Research How do psychologists ask & answer questions? Differentiate types of research with regard to purpose, strengths,
Psychology - MR. CALLAWAY Mundy s Mill High School Unit 2.1 - RESEARCH METHODS Intro to Research How do psychologists ask & answer questions? Differentiate types of research with regard to purpose, strengths,
Chapter Eight: Multivariate Analysis
 Chapter Eight: Multivariate Analysis Up until now, we have covered univariate ( one variable ) analysis and bivariate ( two variables ) analysis. We can also measure the simultaneous effects of two or
Chapter Eight: Multivariate Analysis Up until now, we have covered univariate ( one variable ) analysis and bivariate ( two variables ) analysis. We can also measure the simultaneous effects of two or
Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research Steps in Nonexperimental Research
 Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) Nonexperimental research is needed because
Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) Nonexperimental research is needed because
Educational Psychology
 Educational Psychology Introduction/Research Methods Daniel H. Tingstrom, Ph.D. Department of Psychology Box 5025 Univ. of Southern Mississippi Hattiesburg, MS 39406-5025 1 My Background??? 2 B = E x B
Educational Psychology Introduction/Research Methods Daniel H. Tingstrom, Ph.D. Department of Psychology Box 5025 Univ. of Southern Mississippi Hattiesburg, MS 39406-5025 1 My Background??? 2 B = E x B
Psychological Research
 Introduction Psychologists do more than just wonder about human behavior: they conduct research to understand exactly why people think, feel, and behave the way they do. Like other scientists, psychologists
Introduction Psychologists do more than just wonder about human behavior: they conduct research to understand exactly why people think, feel, and behave the way they do. Like other scientists, psychologists
Introduction Stanovich, Chapter 1
 Introduction Stanovich, Chapter 1 A. Exercises 1. Write a brief characterization of each of the following professionals: A. Psychologist B. Astrologist C. Scientist 2. List the most interesting psychologist
Introduction Stanovich, Chapter 1 A. Exercises 1. Write a brief characterization of each of the following professionals: A. Psychologist B. Astrologist C. Scientist 2. List the most interesting psychologist
2.2 Psychologists Use Descriptive, Correlational, and Experimental Research Designs to Understand Behavior LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Ruble, D., & Martin, C. (1998). Gender development. In W. Damon (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology (5th ed., pp. 933 1016). New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons. Popper, K. R. (1959). The logic of scientific
Ruble, D., & Martin, C. (1998). Gender development. In W. Damon (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology (5th ed., pp. 933 1016). New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons. Popper, K. R. (1959). The logic of scientific
Conducting Research. Research Methods Chapter 1. Descriptive Research Methods. Conducting Research
 Research Methods Chapter 1 Conducting Research Goals of Psychology Describe Explain Predict Control Pitfalls of intuition and common sense explanations: Hindsight bias, overconfidence Remember psychology
Research Methods Chapter 1 Conducting Research Goals of Psychology Describe Explain Predict Control Pitfalls of intuition and common sense explanations: Hindsight bias, overconfidence Remember psychology
Skills Center Psychology Practice Exam II
 1.) The scientific method always a. begins with observation and ends with generation of a hypothesis. b. begins with generation of a hypothesis and ends with systematic observation. c. begins and ends
1.) The scientific method always a. begins with observation and ends with generation of a hypothesis. b. begins with generation of a hypothesis and ends with systematic observation. c. begins and ends
Unit 1 History and Methods Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with Psychological Science
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Unit 1 History and Methods Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Fact vs. Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkably accurate
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Unit 1 History and Methods Chapter 1 Thinking Critically with James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Fact vs. Falsehood 1. Human intuition is remarkably accurate
Asking and answering research questions. What s it about?
 2 Asking and answering research questions What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 24 54) Social psychologists strive to reach general conclusions by developing scientific theories about why people behave
2 Asking and answering research questions What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 24 54) Social psychologists strive to reach general conclusions by developing scientific theories about why people behave
(an intro to AP Biology)
 (an intro to AP Biology) 1. How does being science literate benefit you and your community? 2. What is the most critical element in the process of doing science? 3. What is meant by the phrase the fuel
(an intro to AP Biology) 1. How does being science literate benefit you and your community? 2. What is the most critical element in the process of doing science? 3. What is meant by the phrase the fuel
Chapter Eight: Multivariate Analysis
 Chapter Eight: Multivariate Analysis Up until now, we have covered univariate ( one variable ) analysis and bivariate ( two variables ) analysis. We can also measure the simultaneous effects of two or
Chapter Eight: Multivariate Analysis Up until now, we have covered univariate ( one variable ) analysis and bivariate ( two variables ) analysis. We can also measure the simultaneous effects of two or
ISC- GRADE XI HUMANITIES ( ) PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 2- Methods of Psychology
 ISC- GRADE XI HUMANITIES (2018-19) PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 2- Methods of Psychology OUTLINE OF THE CHAPTER (i) Scientific Methods in Psychology -observation, case study, surveys, psychological tests, experimentation
ISC- GRADE XI HUMANITIES (2018-19) PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 2- Methods of Psychology OUTLINE OF THE CHAPTER (i) Scientific Methods in Psychology -observation, case study, surveys, psychological tests, experimentation
Psychology UNIT 1: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE. Core
 Core provides a solid overview of the field's major domains: methods, biopsychology, cognitive and developmental psychology, and variations in individual and group behavior. By focusing on significant
Core provides a solid overview of the field's major domains: methods, biopsychology, cognitive and developmental psychology, and variations in individual and group behavior. By focusing on significant
Scientific Method in Biology
 Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can lead to scientific questions. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture
Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can lead to scientific questions. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture
Critical Thinking and Reading Lecture 15
 Critical Thinking and Reading Lecture 5 Critical thinking is the ability and willingness to assess claims and make objective judgments on the basis of well-supported reasons. (Wade and Tavris, pp.4-5)
Critical Thinking and Reading Lecture 5 Critical thinking is the ability and willingness to assess claims and make objective judgments on the basis of well-supported reasons. (Wade and Tavris, pp.4-5)
DIABETES EDUCATION PROMPT DECK
 DIABETES EDUCATION PROMPT DECK Copyright 2011. American Association of Diabetes Educators. All rights reserved. Sponsored by GENERAL DIABETES INFORMATION HEALTHY EATING BEING ACTIVE MONITORING USING THE
DIABETES EDUCATION PROMPT DECK Copyright 2011. American Association of Diabetes Educators. All rights reserved. Sponsored by GENERAL DIABETES INFORMATION HEALTHY EATING BEING ACTIVE MONITORING USING THE
What is Science? The pics are used for education purposes only
 What is Science? Science is one of many ways to investigate and understand the world around us. It is a search for knowledge through observation, description, identification, and experimental investigation.
What is Science? Science is one of many ways to investigate and understand the world around us. It is a search for knowledge through observation, description, identification, and experimental investigation.
Between Fact and Fiction: Artifacts and Ethics in Social Research. Toh Wah Seng ABSTRACT
 Between Fact and Fiction: Artifacts and Ethics in Social Research by Toh Wah Seng ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to raise awareness among new researchers on the importance of recognizing the effect
Between Fact and Fiction: Artifacts and Ethics in Social Research by Toh Wah Seng ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to raise awareness among new researchers on the importance of recognizing the effect
Reliability and Validity
 Reliability and Validity Why Are They Important? Check out our opening graphics. In a nutshell, do you want that car? It's not reliable. Would you recommend that car magazine (Auto Tester Weakly) to a
Reliability and Validity Why Are They Important? Check out our opening graphics. In a nutshell, do you want that car? It's not reliable. Would you recommend that car magazine (Auto Tester Weakly) to a
Conducting Research in the Social Sciences. Rick Balkin, Ph.D., LPC-S, NCC
 Conducting Research in the Social Sciences Rick Balkin, Ph.D., LPC-S, NCC 1 Why we do research Improvement Description Explanation Prediction R. S. Balkin, 2008 2 Theory Explanation of an observed phenomena
Conducting Research in the Social Sciences Rick Balkin, Ph.D., LPC-S, NCC 1 Why we do research Improvement Description Explanation Prediction R. S. Balkin, 2008 2 Theory Explanation of an observed phenomena
Lecture Preview Psychology: From Inquiry to Understanding 2/e. The Need for Good Research Design. The Need for Good Research Design
 Psychology: From Inquiry to Understanding 2/e Scott O. Lilienfeld Steven Jay Lynn Laura Namy Nancy J. Woolf Chapter Two Research Methods: Safeguards against Error Prepared by Caleb W. Lack This multimedia
Psychology: From Inquiry to Understanding 2/e Scott O. Lilienfeld Steven Jay Lynn Laura Namy Nancy J. Woolf Chapter Two Research Methods: Safeguards against Error Prepared by Caleb W. Lack This multimedia
What is the Scientific Method?
 Scientific Method What is the Scientific Method? It s a way to solve/explain a problem or natural phenomenon, while removing human bias and opinion. It is a critical procedure that allows validity and
Scientific Method What is the Scientific Method? It s a way to solve/explain a problem or natural phenomenon, while removing human bias and opinion. It is a critical procedure that allows validity and
PSY 205 Module 3 Supplement. Comparing Correlation, Ex post facto, and Experimental Approaches to Research
 PSY 205 Module 3 Supplement Comparing Correlation, Ex post facto, and Experimental Approaches to Research As you have seen in this module, there are many ways to do research in psychology. Now let s carefully
PSY 205 Module 3 Supplement Comparing Correlation, Ex post facto, and Experimental Approaches to Research As you have seen in this module, there are many ways to do research in psychology. Now let s carefully
Prologue/Chapter 1. What is Psychology?
 Prologue/Chapter 1 Introduction and Research Methods What is Psychology? The science of behavior and mental processes Behavior observable actions of a person or animal Mind thoughts, feelings, sensations,
Prologue/Chapter 1 Introduction and Research Methods What is Psychology? The science of behavior and mental processes Behavior observable actions of a person or animal Mind thoughts, feelings, sensations,
Beware of Confounding Variables
 Beware of Confounding Variables If I wanted to prove that smoking causes heart issues, what are some confounding variables? The object of an experiment is to prove that A causes B. A confounding variable
Beware of Confounding Variables If I wanted to prove that smoking causes heart issues, what are some confounding variables? The object of an experiment is to prove that A causes B. A confounding variable
INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY. Radwan Banimustafa
 INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY Radwan Banimustafa At the end of this Chapter you should be able to: Understand the scope of psychology Different perspectives in psychology The scientific research method in
INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY Radwan Banimustafa At the end of this Chapter you should be able to: Understand the scope of psychology Different perspectives in psychology The scientific research method in
CAUTIONS ABOUT THE PRACTICE EXAM
 Dr. Michael Passer Psych 209, U. of Washington CAUTIONS ABOUT THE PRACTICE EXAM DEAR STUDENT: This practice tests consists of questions from past exams. By taking this practice test, you should gain an
Dr. Michael Passer Psych 209, U. of Washington CAUTIONS ABOUT THE PRACTICE EXAM DEAR STUDENT: This practice tests consists of questions from past exams. By taking this practice test, you should gain an
Making Your Treatment Work Long-Term
 Making Your Treatment Work Long-Term How to keep your treatment working... and why you don t want it to fail Regardless of the particular drugs you re taking, your drugs will only work when you take them.
Making Your Treatment Work Long-Term How to keep your treatment working... and why you don t want it to fail Regardless of the particular drugs you re taking, your drugs will only work when you take them.
Question: What steps do scientists follow in conducting scientific research?
 Section 1: Conducting Research Question: What steps do scientists follow in conducting scientific research? In psychology, assumptions must be supported by evidence. STEPS IN SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH 1. Form
Section 1: Conducting Research Question: What steps do scientists follow in conducting scientific research? In psychology, assumptions must be supported by evidence. STEPS IN SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH 1. Form
ID# Exam 1 PS306, Spring 2005
 ID# Exam 1 PS306, Spring 2005 OK, take a deep breath. CALM. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Think of a point as a minute, so a 10-point question should take you about 10 minutes.
ID# Exam 1 PS306, Spring 2005 OK, take a deep breath. CALM. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Think of a point as a minute, so a 10-point question should take you about 10 minutes.
Student Success Guide
 Student Success Guide TO ACCOMPANY WHAT IS LIFE? A GUIDE TO BIOLOGY WITH PHYSIOLOGY Third Edition by Jay Phelan Meredith S. Norris, M.S. Jennifer M. Warner, Ph.D. Department of Biology The University of
Student Success Guide TO ACCOMPANY WHAT IS LIFE? A GUIDE TO BIOLOGY WITH PHYSIOLOGY Third Edition by Jay Phelan Meredith S. Norris, M.S. Jennifer M. Warner, Ph.D. Department of Biology The University of
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Images
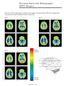 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Images Each set of PET images below contains four images of a human brain. The four images show cross-sections taken at different levels of the brain. Set 1 Set 2 a b
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Images Each set of PET images below contains four images of a human brain. The four images show cross-sections taken at different levels of the brain. Set 1 Set 2 a b
Social Research (Complete) Agha Zohaib Khan
 Social Research (Complete) Agha Zohaib Khan What is Research? Research is the systematic process of collecting and analysing information (data) in order to increase our understanding of the phenomenon
Social Research (Complete) Agha Zohaib Khan What is Research? Research is the systematic process of collecting and analysing information (data) in order to increase our understanding of the phenomenon
Module 30. Learning by Observation
 Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Theory. = an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events.
 Definition Slides Hindsight Bias = the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it. Also known as the I knew it all along phenomenon. Critical Thinking = thinking that
Definition Slides Hindsight Bias = the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it. Also known as the I knew it all along phenomenon. Critical Thinking = thinking that
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Introduction to Research Methods
 Introduction to Research Methods 8-10% of the AP Exam Psychology is an empirical discipline. Psychologists develop knowledge by doing research. Research provides guidance for psychologists who develop
Introduction to Research Methods 8-10% of the AP Exam Psychology is an empirical discipline. Psychologists develop knowledge by doing research. Research provides guidance for psychologists who develop
MODULE 3 APPRAISING EVIDENCE. Evidence-Informed Policy Making Training
 MODULE 3 APPRAISING EVIDENCE Evidence-Informed Policy Making Training RECAP OF PREVIOUS DAY OR SESSION MODULE 3 OBJECTIVES At the end of this module participants will: Identify characteristics of basic
MODULE 3 APPRAISING EVIDENCE Evidence-Informed Policy Making Training RECAP OF PREVIOUS DAY OR SESSION MODULE 3 OBJECTIVES At the end of this module participants will: Identify characteristics of basic
OBSERVATION METHODS: EXPERIMENTS
 OBSERVATION METHODS: EXPERIMENTS Sociological Research Methods Experiments Independent variable is manipulated, and the dependent variable respond to the manipulation. e.g. Eating a chocolate bar prior
OBSERVATION METHODS: EXPERIMENTS Sociological Research Methods Experiments Independent variable is manipulated, and the dependent variable respond to the manipulation. e.g. Eating a chocolate bar prior
What Constitutes a Good Contribution to the Literature (Body of Knowledge)?
 What Constitutes a Good Contribution to the Literature (Body of Knowledge)? Read things that make good contributions to the body of knowledge. The purpose of scientific research is to add to the body of
What Constitutes a Good Contribution to the Literature (Body of Knowledge)? Read things that make good contributions to the body of knowledge. The purpose of scientific research is to add to the body of
Lesson 11 Correlations
 Lesson 11 Correlations Lesson Objectives All students will define key terms and explain the difference between correlations and experiments. All students should be able to analyse scattergrams using knowledge
Lesson 11 Correlations Lesson Objectives All students will define key terms and explain the difference between correlations and experiments. All students should be able to analyse scattergrams using knowledge
Chapter 2 Methodology: How Social Psychologists Do Research
 Chapter 2 Methodology: How Social Psychologists Do Research Methodology Social Psychology: An Empirical Science Empirical research allows us to test the validity of personal observations and folk wisdom.
Chapter 2 Methodology: How Social Psychologists Do Research Methodology Social Psychology: An Empirical Science Empirical research allows us to test the validity of personal observations and folk wisdom.
Do not copy, post, or distribute
 1 CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Define science and the scientific method. 2. Describe six steps for engaging in the scientific method. 3. Describe five nonscientific methods of acquiring knowledge. 4.
1 CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Define science and the scientific method. 2. Describe six steps for engaging in the scientific method. 3. Describe five nonscientific methods of acquiring knowledge. 4.
Correlation and Causation. Phil 12: Logic and Decision Making Winter 2010 UC San Diego 2/17/2010
 Correlation and Causation Phil 12: Logic and Decision Making Winter 2010 UC San Diego 2/17/2010 First paper Due Friday 2/19 by noon (beginning of lecture) If you want to turn it in early: put in envelope
Correlation and Causation Phil 12: Logic and Decision Making Winter 2010 UC San Diego 2/17/2010 First paper Due Friday 2/19 by noon (beginning of lecture) If you want to turn it in early: put in envelope
What is a Science? As an occupation, an individual who practices, applies or studies the sciences.
 LP 1B: Scientific Attitudes 1 What is a Science? The word science can be used in different ways and contexts such as the following: Scientific Knowledge: Scientist: Scientific Process: As a body of scientific
LP 1B: Scientific Attitudes 1 What is a Science? The word science can be used in different ways and contexts such as the following: Scientific Knowledge: Scientist: Scientific Process: As a body of scientific
3 CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF STATISTICS
 3 CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF STATISTICS In this chapter, we examine the conceptual foundations of statistics. The goal is to give you an appreciation and conceptual understanding of some basic statistical
3 CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF STATISTICS In this chapter, we examine the conceptual foundations of statistics. The goal is to give you an appreciation and conceptual understanding of some basic statistical
Psychological Science
 Chapter 2 Psychological Science Psychologists aren t the only people who seek to understand human behavior and solve social problems. Philosophers, religious leaders, and politicians, among others, also
Chapter 2 Psychological Science Psychologists aren t the only people who seek to understand human behavior and solve social problems. Philosophers, religious leaders, and politicians, among others, also
Science is a way of learning about the natural world by observing things, asking questions, proposing answers, and testing those answers.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 The Nature of Science and Scientific Inquiry Online resources: www.science.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe9/centre.html Remember to ask your teacher whether your classroom
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 The Nature of Science and Scientific Inquiry Online resources: www.science.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe9/centre.html Remember to ask your teacher whether your classroom
NAME: East Carolina University PSYC Developmental Psychology. Dr. Ironsmith & Dr. Eppler
 Module 1, Page 1 NAME: East Carolina University PSYC 3206 -- Developmental Psychology Dr. Ironsmith & Dr. Eppler Study Questions for Chapter 1: Understanding Life-Span Human Development Sigelman & Rider
Module 1, Page 1 NAME: East Carolina University PSYC 3206 -- Developmental Psychology Dr. Ironsmith & Dr. Eppler Study Questions for Chapter 1: Understanding Life-Span Human Development Sigelman & Rider
Higher Psychology RESEARCH REVISION
 Higher Psychology RESEARCH REVISION 1 The biggest change from the old Higher course (up to 2014) is the possibility of an analysis and evaluation question (8-10) marks asking you to comment on aspects
Higher Psychology RESEARCH REVISION 1 The biggest change from the old Higher course (up to 2014) is the possibility of an analysis and evaluation question (8-10) marks asking you to comment on aspects
STA630 Research Methods Solved MCQs By
 STA630 Research Methods Solved MCQs By http://vustudents.ning.com 31-07-2010 Quiz # 1: Question # 1 of 10: A one tailed hypothesis predicts----------- The future The lottery result The frequency of the
STA630 Research Methods Solved MCQs By http://vustudents.ning.com 31-07-2010 Quiz # 1: Question # 1 of 10: A one tailed hypothesis predicts----------- The future The lottery result The frequency of the
Scientific Method in Biology
 Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture contaminated with mold. Discuss
Scientific Method in Biology Observations Observations are a critical component of science, because they can. Example: Alexander Fleming s observations on a bacterial culture contaminated with mold. Discuss
Research has long suggested that 21 days is all it takes to start a new habit.
 Research has long suggested that 21 days is all it takes to start a new habit. 2 Introduction It s normal to feel a tad stressed from time to time. Life can be stressful. We all worry about things like
Research has long suggested that 21 days is all it takes to start a new habit. 2 Introduction It s normal to feel a tad stressed from time to time. Life can be stressful. We all worry about things like
Psychology 12th Edition Wade TEST BANK Full download at:
 Psychology 12th Edition Wade TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/psychology-12th-edition-wade-test-bank/ Psychology 12th Edition Wade SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/psychology-12th-edition-wade-solutions-manual/
Psychology 12th Edition Wade TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/psychology-12th-edition-wade-test-bank/ Psychology 12th Edition Wade SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/psychology-12th-edition-wade-solutions-manual/
EX-POST FACTO STUDIES
 EX-POST FACTO STUDIES Select people who already have the characteristic of study Compare them to people who do not have that characteristic Subject Variable A characteristic of interest in the participants
EX-POST FACTO STUDIES Select people who already have the characteristic of study Compare them to people who do not have that characteristic Subject Variable A characteristic of interest in the participants
CSC2130: Empirical Research Methods for Software Engineering
 CSC2130: Empirical Research Methods for Software Engineering Steve Easterbrook sme@cs.toronto.edu www.cs.toronto.edu/~sme/csc2130/ 2004-5 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial
CSC2130: Empirical Research Methods for Software Engineering Steve Easterbrook sme@cs.toronto.edu www.cs.toronto.edu/~sme/csc2130/ 2004-5 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial
Controlled Variables: these are Variables in the experiment that you keep the same (YOU MAKE SURE THEY DON T CHANGE)
 Name: Date: Incoming 7 th Grade Summer Science Assignment Due September 12, 2018 What is the Experimental Design? Some Helpful Vocabulary Experimental Design- describes the manner in which you test your
Name: Date: Incoming 7 th Grade Summer Science Assignment Due September 12, 2018 What is the Experimental Design? Some Helpful Vocabulary Experimental Design- describes the manner in which you test your
Chapter 11. Experimental Design: One-Way Independent Samples Design
 11-1 Chapter 11. Experimental Design: One-Way Independent Samples Design Advantages and Limitations Comparing Two Groups Comparing t Test to ANOVA Independent Samples t Test Independent Samples ANOVA Comparing
11-1 Chapter 11. Experimental Design: One-Way Independent Samples Design Advantages and Limitations Comparing Two Groups Comparing t Test to ANOVA Independent Samples t Test Independent Samples ANOVA Comparing
Depression awareness. Bayside Academy Parent Workshop - October 2, 2017
 Depression awareness Bayside Academy Parent Workshop - October 2, 2017 Lauren Alexander 6th Grade (Last Names Lo-Z) and 8th Grade Counselor LAAlexander@smfcsd.net John-Michael Gomez Mental Health Clinician
Depression awareness Bayside Academy Parent Workshop - October 2, 2017 Lauren Alexander 6th Grade (Last Names Lo-Z) and 8th Grade Counselor LAAlexander@smfcsd.net John-Michael Gomez Mental Health Clinician
