A hierarchical modeling approach to data analysis and study design in a multi-site experimental fmri study
|
|
|
- Chrystal Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A hierarchical modeling approach to data analysis and study design in a multi-site experimental fmri study Bo Zhou Department of Statistics University of California, Irvine Sep. 13, / 23
2 Outline 1.1 Background. 1.2 Objectives. 1.3 Experiment. 2.1 A Hierarchical Bayesian Model. 2.2 A Robust Model Using Student s t Distribution. 4.1 Results for Real Data. 4.2 Conclusions and Discussions.. 2 / 23
3 Schizophrenia 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment Schizophrenia is a neurocognitive and neuroaffective disease characterized by disordered emotional responsiveness and cognitive dysfunction, deficits in working memory, and reduced frontal and cortical brain volumes in comparison to healthy subjects (APA, 2000; Van Snellenberg, 2009; Glahn et al., 2008). 3 / 23
4 fmri 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment Due to the complexity and heterogeneity of symptoms in patients, detailed knowledge of the specific genetic, neurochemical, and neuroanatomical contributions to this disease remains elusive. Understanding the basis of this disease and other cognitive disorders has greatly increased with the use of fmri. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) can track changes in blood oxygenation in different brain areas over time which is known as the BOLD (blood-oxygen-level-dependent) signal, and thought to be correlated with changes in brain activity (DeYoe et al., 1994). 4 / 23
5 Previous Studies 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment By utilizing fmri, several studies have shown that patients diagnosed with schizophrenia display either hypo- or hyper-activation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) during working memory tasks, thus potentially localizing deficits in working memory and other executive processes to the DLPFC (Goghari et al., 2010). However, these results have not been unequivocal, and one primary concern with respect to these studies has been the low number of subjects that are generally involved in single-center fmri studies (Potkin et al., 2009). 5 / 23
6 Multi-site fmri Studies 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment To increase the sample-size of a research program, there has been an increasing interest in performing multi-site studies. The challenge in utilizing multiple-center studies is to combine the multi-site data while accounting for site-specific variability to fmri results. 6 / 23
7 Goals of Interest 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment Develop an appropriate model for partial pooling of the multi-site data while accounting for site-specific variability. Make inference on the difference in activation of the DLPFC between schizophrenic and normal subjects during the working memory task. Provide information regarding the source of variability in multi-site fmri studies which can be used to optimize experimental design in future research. 7 / 23
8 Sites 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment The fmri scanning sites were located in the following institutions: University of California at Irvine (UCI), University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), University of New Mexico, University of Iowa, University of Minnesota, Duke University/University of North Carolina, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), and Yale University. 8 / 23
9 Subjects 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment All subjects recruited for the study were between the ages of 18 and 70, did not have hearing or vision deficiencies, were fluent in English, and were capable of performing the cognitive tasks necessary for the study. Subjects included both males and non-pregnant females, and all subjects were screened for contraindications to MRI. Subjects were recruited for either a healthy comparison group or a schizophrenic/schizoaffective group. Volunteers in the healthy group did not have a first-degree relative with diagnosis of psychotic illness. Volunteers with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder had been diagnosed using DSM-IV criteria and had been clinically stable, with no significant changes in psychotropic medications in the past two months, but were excluded if they had significant extrapyramidal symptoms or tardive dyskinesia. 9 / 23
10 Cognitive Testing 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment The experiment used the Sternberg Item Recognition Paradigm (SIRP) proposed by Sternberg (1966). This test consists of an encode phase, where subjects memorize a set of target digits. This is followed by a probe phase, where the subjects are presented with single digits, called probes. During this phase, the subjects respond by indicating whether the probe is a target or not. The SIRP task involved three working memory loads of 1, 3, or 5 target digits, each presented for 6 seconds. For memory loads 1 and 3, asterisks were presented in place of extra digits so that there were still 5 presented items for each load condition. In the probe phase, the subjects were presented with 14 single digits (probes) for 2.7 seconds each. Only half of the probes were targets. Each run consisted of the three loads presented in a pseudorandom manner, with two memory sets per load. 10 / 23
11 Scanning and Preprocessing 1.1 Background 1.2 Objectives 1.3 Experiment Subjects were tested in two different sessions (visit 1 and visit 2). Each subject has 3 runs of test per visit. Each scan session lasted approximately 1.5 hours. The entire procedure was repeated 24 hours to 3 weeks later for the 2nd visit. Pre-processing was performed at UCSD in collaboration with MGH using FSL (Smith et al., 2004). A working version of the data, which consisted of the mean signal change of the activation, denoted as Y, in the left and right hemispheres of the DLPFC was compiled by UCSD for use by FBIRN investigators. 11 / 23
12 Model Structure 2.1 A Bayesian Hierarchical Model 2.2 A Robust Model Using Student s t Distribution bs 2 siteas 2 sitews bsi X hlg si hlg 2 sub µ hlg sij 2 run Y hlg sijk Figure: Schematic representation of the hierarchical Bayesian model. Nodes (in ovals) are model parameters and random variables; arrows represent dependencies between nodes. Within each box, nodes are replicated. The only observed nodes are X = (X g, X h, X l3, X l5 ) and y hlg sijk. 12 / 23
13 Model 2.1 A Bayesian Hierarchical Model 2.2 A Robust Model Using Student s t Distribution Each run of each visit for subject i at site s, given hemisphere h, load l, and group g, are assumed to be normally distributed with a visit mean as follows, Y hlg sijk N(µhlg sij, σ2 run). The visit means are assumed to be normally distributed with a site effects and fixed effects, α hlg = X β, depending on hemisphere, load and group, µ hlg sij N(α hlg + γ hlg si, σ 2 sub ). 13 / 23
14 Model 2.1 A Bayesian Hierarchical Model 2.2 A Robust Model Using Student s t Distribution Site effects, γ hlg si, are assumed to be normally distributed with subject-specific site effects, b si, and within-subject site variance, σ 2 sitew s, and then b si itself is given a normal prior with a site-specific mean, b s, and across-subject site variance, σ 2 sitea s, γ hlg si N(b si, σ 2 sitew s ), b si N(b s, σ 2 sitea s ). 14 / 23
15 Model 2.1 A Bayesian Hierarchical Model 2.2 A Robust Model Using Student s t Distribution To build the robust model, we replace the first hierarchy of the Bayesian hierarchical model by, which is equivalent to Y hlg sijk t ν (µ hlg sij, σ2 run), Y hlg sijk N(µ hlg sij, V hlg sijk ), V hlg sijk Inv-χ 2 (ν, σrun) / 23
16 Estimates of Parameters 3.1 Results for the Real Data 3.2 Conclusions and Discussions Table: Posterior expectations and posterior intervals of the group effect, β 1, hemisphere effect, β 2, load effects, β 3 and β 4, based on the normal and t models. Normal Model t Model P. E. P. I. P. E. P. I. β (1.32,10.63) 5.10 (0.78,9.37) β (-8.10,-3.92) (-6.27,-2.27) β (1.13,6.14) 3.23 (1.11,5.37) β (6.74,11.75) 9.39 (7.23,11.60) 16 / 23
17 Estimates for Site Variability 3.1 Results for the Real Data 3.2 Conclusions and Discussions Table: Estimates of σsitew 2 s and σsitea 2 s, and the estimated conditional variance of group effects for single-center studies, Var(β 1 Y, ˆΣ s). For our multicenter study, Var(β 1 Y, ˆΣ m) = The last column shows the information e s gained by the multi-site study compared to hypothetical single-site studies. σsitew 2 s σsitea 2 s Var(β 1 Y, ˆΣ s ) e s Site % Site % Site % Site % Site % Site % Site % Site % 17 / 23
18 Efficacy of the Multi-site Study 3.1 Results for the Real Data 3.2 Conclusions and Discussions Since the measurement of interest in this case is the group effect, β 1, we use its posterior variance to compare different study designs. Let τ 2 m be the variance of the group effect based on a multi-site study, and τs 2 be the variance of group effect based on a hypothetical single-site study with the same number of subjects at site s. Then, E s = 1 τ 2 m τ 2 s measures how much precision gained or lost by the multi-site study compared to the single-site study at site s. 18 / 23
19 Efficacy of the Multi-site Study 3.1 Results for the Real Data 3.2 Conclusions and Discussions Note that it is impossible to estimate τs 2 in reality. We can, however, calculate the conditional variance of the group effect given the data Y and the corresponding estimated covariance matrix. Hence, we use the following measure of efficacy to compare the multi-site study to single-site studies. e s = 1 Var(β 1 Y, ˆΣ m ) Var(β 1 Y, ˆΣ s ). 19 / 23
20 Conclusions 3.1 Results for the Real Data 3.2 Conclusions and Discussions Schizophrenic subjects have significantly higher activation in DLPFC than that of normal subjects. The multi-center study gains information compared to the single-center study with relative large site variability and loses information compared the single-center study with relative small site variability. The relative efficacy of the multi-center study compared to single-center studies is mainly determined by across-subject site variability. 20 / 23
21 Discussions 3.1 Results for the Real Data 3.2 Conclusions and Discussions We build a hierarchical model based upon the hierarchical structure of the data. We might simplify the model by assuming exchangeability between the 6 runs of the 2 visits or make it more complex by assuming different distribution of run, visit and site variability between different groups. Thorough investigations are needed to identify potential pitfalls for theses models; that is, we need to find conditions that could lead to substantial loss of information in multi-center studies. 21 / 23
22 Discussions 3.1 Results for the Real Data 3.2 Conclusions and Discussions Our model can be extended to fmri data on the time series level, which is typically considered in fmri data analysis. For such data, we need to add one more hierarchy that capture time effects. Future research directions could be focused on more informative measure of efficacy of the multi-center study compared to single-center studies. 22 / 23
23 The project described was supported by the National Center for Research Resources and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health, through Grant UL1 TR The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. The authors also acknowledge NIH funding from P41RR / 23
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Psychometrika. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 August 25.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Psychometrika. 2013 April ; 78(2): 260 278. doi:10.1007/s11336-012-9298-9. A Hierarchical Modeling Approach to Data Analysis and Study
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Psychometrika. 2013 April ; 78(2): 260 278. doi:10.1007/s11336-012-9298-9. A Hierarchical Modeling Approach to Data Analysis and Study
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Biomarkers Workshop In Clinical Trials Imaging for Schizophrenia Trials
 Biomarkers Workshop In Clinical Trials Imaging for Schizophrenia Trials Research focused on the following areas Brain pathology in schizophrenia and its modification Effect of drug treatment on brain structure
Biomarkers Workshop In Clinical Trials Imaging for Schizophrenia Trials Research focused on the following areas Brain pathology in schizophrenia and its modification Effect of drug treatment on brain structure
Psychosocial intervention to optimal treatment to patients with schizophrenia: neurocognitive perspectives
 Psychosocial intervention to optimal treatment to patients with schizophrenia: neurocognitive perspectives TANG Tze-Chun Department of psychiatry KMUH Pharmacotherapy alone or combination with psychotherapy?
Psychosocial intervention to optimal treatment to patients with schizophrenia: neurocognitive perspectives TANG Tze-Chun Department of psychiatry KMUH Pharmacotherapy alone or combination with psychotherapy?
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Final Report 2017 Authors: Affiliations: Title of Project: Background:
 Final Report 2017 Authors: Dr Gershon Spitz, Ms Abbie Taing, Professor Jennie Ponsford, Dr Matthew Mundy, Affiliations: Epworth Research Foundation and Monash University Title of Project: The return of
Final Report 2017 Authors: Dr Gershon Spitz, Ms Abbie Taing, Professor Jennie Ponsford, Dr Matthew Mundy, Affiliations: Epworth Research Foundation and Monash University Title of Project: The return of
Functional MRI Mapping Cognition
 Outline Functional MRI Mapping Cognition Michael A. Yassa, B.A. Division of Psychiatric Neuro-imaging Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Why fmri? fmri - How it works Research
Outline Functional MRI Mapping Cognition Michael A. Yassa, B.A. Division of Psychiatric Neuro-imaging Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Why fmri? fmri - How it works Research
Supplemental Data. Inclusion/exclusion criteria for major depressive disorder group and healthy control group
 1 Supplemental Data Inclusion/exclusion criteria for major depressive disorder group and healthy control group Additional inclusion criteria for the major depressive disorder group were: age of onset of
1 Supplemental Data Inclusion/exclusion criteria for major depressive disorder group and healthy control group Additional inclusion criteria for the major depressive disorder group were: age of onset of
Bayesian Models for Combining Data Across Subjects and Studies in Predictive fmri Data Analysis
 Bayesian Models for Combining Data Across Subjects and Studies in Predictive fmri Data Analysis Thesis Proposal Indrayana Rustandi April 3, 2007 Outline Motivation and Thesis Preliminary results: Hierarchical
Bayesian Models for Combining Data Across Subjects and Studies in Predictive fmri Data Analysis Thesis Proposal Indrayana Rustandi April 3, 2007 Outline Motivation and Thesis Preliminary results: Hierarchical
Using mixture priors for robust inference: application in Bayesian dose escalation trials
 Using mixture priors for robust inference: application in Bayesian dose escalation trials Astrid Jullion, Beat Neuenschwander, Daniel Lorand BAYES2014, London, 11 June 2014 Agenda Dose escalation in oncology
Using mixture priors for robust inference: application in Bayesian dose escalation trials Astrid Jullion, Beat Neuenschwander, Daniel Lorand BAYES2014, London, 11 June 2014 Agenda Dose escalation in oncology
Bayesian Models for Combining Data Across Domains and Domain Types in Predictive fmri Data Analysis (Thesis Proposal)
 Bayesian Models for Combining Data Across Domains and Domain Types in Predictive fmri Data Analysis (Thesis Proposal) Indrayana Rustandi Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University March 26,
Bayesian Models for Combining Data Across Domains and Domain Types in Predictive fmri Data Analysis (Thesis Proposal) Indrayana Rustandi Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University March 26,
Accepted to MICCAI Sources of Variability in MEG
 Accepted to MICCAI 27 Sources of Variability in MEG Wanmei Ou, Polina Golland, and Matti Hämäläinen 2 Department of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, MIT, USA 2 Athinoula A. Martinos
Accepted to MICCAI 27 Sources of Variability in MEG Wanmei Ou, Polina Golland, and Matti Hämäläinen 2 Department of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, MIT, USA 2 Athinoula A. Martinos
Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications.
 Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011
 Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011 I. Purpose Drawing from the profile development of the QIBA-fMRI Technical Committee,
Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011 I. Purpose Drawing from the profile development of the QIBA-fMRI Technical Committee,
Estimating drug effects in the presence of placebo response: Causal inference using growth mixture modeling
 STATISTICS IN MEDICINE Statist. Med. 2009; 28:3363 3385 Published online 3 September 2009 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).3721 Estimating drug effects in the presence of placebo response:
STATISTICS IN MEDICINE Statist. Med. 2009; 28:3363 3385 Published online 3 September 2009 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).3721 Estimating drug effects in the presence of placebo response:
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Bayesian hierarchical modelling
 Bayesian hierarchical modelling Matthew Schofield Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Otago Bayesian hierarchical modelling Slide 1 What is a statistical model? A statistical model:
Bayesian hierarchical modelling Matthew Schofield Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Otago Bayesian hierarchical modelling Slide 1 What is a statistical model? A statistical model:
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University
 Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
The Effects of Autocorrelated Noise and Biased HRF in fmri Analysis Error Rates
 The Effects of Autocorrelated Noise and Biased HRF in fmri Analysis Error Rates Ariana Anderson University of California, Los Angeles Departments of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences David Geffen School
The Effects of Autocorrelated Noise and Biased HRF in fmri Analysis Error Rates Ariana Anderson University of California, Los Angeles Departments of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences David Geffen School
Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning
 Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning John Gabrieli Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Institute for Medical Engineering & Sciences McGovern Institute for Brain Sciences MIT Levels of Analysis
Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning John Gabrieli Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Institute for Medical Engineering & Sciences McGovern Institute for Brain Sciences MIT Levels of Analysis
NeuroImage 53 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. NeuroImage. journal homepage:
 NeuroImage 53 (2010) 119 131 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Multi-site characterization of an fmri working memory paradigm: Reliability
NeuroImage 53 (2010) 119 131 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Multi-site characterization of an fmri working memory paradigm: Reliability
WinBUGS : part 1. Bruno Boulanger Jonathan Jaeger Astrid Jullion Philippe Lambert. Gabriele, living with rheumatoid arthritis
 WinBUGS : part 1 Bruno Boulanger Jonathan Jaeger Astrid Jullion Philippe Lambert Gabriele, living with rheumatoid arthritis Agenda 2 Introduction to WinBUGS Exercice 1 : Normal with unknown mean and variance
WinBUGS : part 1 Bruno Boulanger Jonathan Jaeger Astrid Jullion Philippe Lambert Gabriele, living with rheumatoid arthritis Agenda 2 Introduction to WinBUGS Exercice 1 : Normal with unknown mean and variance
Decoding the Representation of Code in the Brain: An fmri Study of Code Review and Expertise
 Decoding the Representation of Code in the Brain: An fmri Study of Code Review and Expertise Benjamin Floyd, Tyler Santander, University of Virginia University of Michigan University of Michigan Looking
Decoding the Representation of Code in the Brain: An fmri Study of Code Review and Expertise Benjamin Floyd, Tyler Santander, University of Virginia University of Michigan University of Michigan Looking
Neuroimaging in Clinical Practice
 Neuroimaging in Clinical Practice John Gabrieli Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences & Martinos Imaging Center at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research, MIT Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner
Neuroimaging in Clinical Practice John Gabrieli Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences & Martinos Imaging Center at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research, MIT Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan. Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1
 The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
Geography of the Forehead
 5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
Application of Bayesian Extrapolation in Pediatric Drug Development Program
 Application of Bayesian Extrapolation in Pediatric Drug Development Program May Mo, Amy Xia Amgen Regulatory-Industry Statistics Workshop Sep 13, 2018 Washington, DC Disclaimer: The views expressed herein
Application of Bayesian Extrapolation in Pediatric Drug Development Program May Mo, Amy Xia Amgen Regulatory-Industry Statistics Workshop Sep 13, 2018 Washington, DC Disclaimer: The views expressed herein
Memory-Augmented Active Deep Learning for Identifying Relations Between Distant Medical Concepts in Electroencephalography Reports
 Memory-Augmented Active Deep Learning for Identifying Relations Between Distant Medical Concepts in Electroencephalography Reports Ramon Maldonado, BS, Travis Goodwin, PhD Sanda M. Harabagiu, PhD The University
Memory-Augmented Active Deep Learning for Identifying Relations Between Distant Medical Concepts in Electroencephalography Reports Ramon Maldonado, BS, Travis Goodwin, PhD Sanda M. Harabagiu, PhD The University
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders
 Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Prediction of Successful Memory Encoding from fmri Data
 Prediction of Successful Memory Encoding from fmri Data S.K. Balci 1, M.R. Sabuncu 1, J. Yoo 2, S.S. Ghosh 3, S. Whitfield-Gabrieli 2, J.D.E. Gabrieli 2 and P. Golland 1 1 CSAIL, MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA
Prediction of Successful Memory Encoding from fmri Data S.K. Balci 1, M.R. Sabuncu 1, J. Yoo 2, S.S. Ghosh 3, S. Whitfield-Gabrieli 2, J.D.E. Gabrieli 2 and P. Golland 1 1 CSAIL, MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Table 1. Summary of PET and fmri Methods. What is imaged PET fmri BOLD (T2*) Regional brain activation. Blood flow ( 15 O) Arterial spin tagging (AST)
 Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
Bayesian Hierarchical Models for Fitting Dose-Response Relationships
 Bayesian Hierarchical Models for Fitting Dose-Response Relationships Ketra A. Schmitt Battelle Memorial Institute Mitchell J. Small and Kan Shao Carnegie Mellon University Dose Response Estimates using
Bayesian Hierarchical Models for Fitting Dose-Response Relationships Ketra A. Schmitt Battelle Memorial Institute Mitchell J. Small and Kan Shao Carnegie Mellon University Dose Response Estimates using
MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience
 MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience School of Psychological Sciences Faculty of Medical & Human Sciences Module Information *Please note that this is a sample guide to modules. The exact
MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience School of Psychological Sciences Faculty of Medical & Human Sciences Module Information *Please note that this is a sample guide to modules. The exact
Bayesian approaches to handling missing data: Practical Exercises
 Bayesian approaches to handling missing data: Practical Exercises 1 Practical A Thanks to James Carpenter and Jonathan Bartlett who developed the exercise on which this practical is based (funded by ESRC).
Bayesian approaches to handling missing data: Practical Exercises 1 Practical A Thanks to James Carpenter and Jonathan Bartlett who developed the exercise on which this practical is based (funded by ESRC).
Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using Linear Discriminative Analysis and Quadratic Discriminative Analysis
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
Whose Choice is it Anyway? Montague's Experimental Results
 Reference: McClure, SM, Li, J, Tomlin, D, Cypert, KS, Montague, LM, Montague, RM (2004) Neural correlates of behavioral preference for culturally familiar drinks. Neuron 44:379-387. The main goal of the
Reference: McClure, SM, Li, J, Tomlin, D, Cypert, KS, Montague, LM, Montague, RM (2004) Neural correlates of behavioral preference for culturally familiar drinks. Neuron 44:379-387. The main goal of the
ERA: Architectures for Inference
 ERA: Architectures for Inference Dan Hammerstrom Electrical And Computer Engineering 7/28/09 1 Intelligent Computing In spite of the transistor bounty of Moore s law, there is a large class of problems
ERA: Architectures for Inference Dan Hammerstrom Electrical And Computer Engineering 7/28/09 1 Intelligent Computing In spite of the transistor bounty of Moore s law, there is a large class of problems
AUTOMATING NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE DIAGNOSIS USING STRUCTURAL MR BRAIN SCAN FEATURES
 AUTOMATING NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE DIAGNOSIS USING STRUCTURAL MR BRAIN SCAN FEATURES ALLAN RAVENTÓS AND MOOSA ZAIDI Stanford University I. INTRODUCTION Nine percent of those aged 65 or older and about one
AUTOMATING NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE DIAGNOSIS USING STRUCTURAL MR BRAIN SCAN FEATURES ALLAN RAVENTÓS AND MOOSA ZAIDI Stanford University I. INTRODUCTION Nine percent of those aged 65 or older and about one
Human Connectome: Developmental Patterns and Brain Maps
 Human Connectome: Developmental Patterns and Brain Maps Len Matheson, PhD Faithful Brain Research Foundation Neurorehabilitation Psychologist Author: Your Faithful Brain: Designed for so much more! Overview
Human Connectome: Developmental Patterns and Brain Maps Len Matheson, PhD Faithful Brain Research Foundation Neurorehabilitation Psychologist Author: Your Faithful Brain: Designed for so much more! Overview
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Individual Differences in Texture Discrimination
 Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Individual Differences in Texture Discrimination Timothy N. Rubin (trubin@uci.edu) Michael D. Lee (mdlee@uci.edu) Charles F. Chubb (cchubb@uci.edu) Department of Cognitive
Hierarchical Bayesian Modeling of Individual Differences in Texture Discrimination Timothy N. Rubin (trubin@uci.edu) Michael D. Lee (mdlee@uci.edu) Charles F. Chubb (cchubb@uci.edu) Department of Cognitive
SMART Clinical Trial Designs for Dynamic Treatment Regimes
 SMART Clinical Trial Designs for Dynamic Treatment Regimes Bibhas Chakraborty Centre for Quantitative Medicine, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore bibhas.chakraborty@duke-nus.edu.sg MCP Conference
SMART Clinical Trial Designs for Dynamic Treatment Regimes Bibhas Chakraborty Centre for Quantitative Medicine, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School, Singapore bibhas.chakraborty@duke-nus.edu.sg MCP Conference
Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation
 Introduction (tdcs) is a non-invasive form of brain stimulation similar to transcranial magnetic stimulation, but instead of using magnets, it uses a lowintensity, constant current applied through scalp
Introduction (tdcs) is a non-invasive form of brain stimulation similar to transcranial magnetic stimulation, but instead of using magnets, it uses a lowintensity, constant current applied through scalp
Frontal Contributions to Memory Encoding Before and After Unilateral Medial Temporal Lobectomy
 Frontal Contributions to Memory Encoding Before and After Unilateral Medial Temporal Lobectomy Jeff Ojemann, MD Department of Neurological Surgery University of Washington Children s Hospital & Regional
Frontal Contributions to Memory Encoding Before and After Unilateral Medial Temporal Lobectomy Jeff Ojemann, MD Department of Neurological Surgery University of Washington Children s Hospital & Regional
Object recognition and hierarchical computation
 Object recognition and hierarchical computation Challenges in object recognition. Fukushima s Neocognitron View-based representations of objects Poggio s HMAX Forward and Feedback in visual hierarchy Hierarchical
Object recognition and hierarchical computation Challenges in object recognition. Fukushima s Neocognitron View-based representations of objects Poggio s HMAX Forward and Feedback in visual hierarchy Hierarchical
Neuroimaging and Assessment Methods
 Psych 2200, Lecture 5 Experimental Design and Brain Imaging Methods Tues Sept 15, 2015 Revised TA office hours (Sam), today 4-5p, and wed 11:30-1:30. I will not have office hours this thurs but you should
Psych 2200, Lecture 5 Experimental Design and Brain Imaging Methods Tues Sept 15, 2015 Revised TA office hours (Sam), today 4-5p, and wed 11:30-1:30. I will not have office hours this thurs but you should
Experimental Design I
 Experimental Design I Topics What questions can we ask (intelligently) in fmri Basic assumptions in isolating cognitive processes and comparing conditions General design strategies A few really cool experiments
Experimental Design I Topics What questions can we ask (intelligently) in fmri Basic assumptions in isolating cognitive processes and comparing conditions General design strategies A few really cool experiments
Experimental Design. Outline. Outline. A very simple experiment. Activation for movement versus rest
 Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
Brain Imaging Investigation of the Impairing Effect of Emotion on Cognition
 Brain Imaging Investigation of the Impairing Effect of Emotion on Cognition Gloria Wong 1,2, Sanda Dolcos 1,3, Ekaterina Denkova 1, Rajendra A. Morey 4,5, Lihong Wang 4,5, Nicholas Coupland 1, Gregory
Brain Imaging Investigation of the Impairing Effect of Emotion on Cognition Gloria Wong 1,2, Sanda Dolcos 1,3, Ekaterina Denkova 1, Rajendra A. Morey 4,5, Lihong Wang 4,5, Nicholas Coupland 1, Gregory
An Introduction to Bayesian Statistics
 An Introduction to Bayesian Statistics Robert Weiss Department of Biostatistics UCLA Fielding School of Public Health robweiss@ucla.edu Sept 2015 Robert Weiss (UCLA) An Introduction to Bayesian Statistics
An Introduction to Bayesian Statistics Robert Weiss Department of Biostatistics UCLA Fielding School of Public Health robweiss@ucla.edu Sept 2015 Robert Weiss (UCLA) An Introduction to Bayesian Statistics
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues. Outline. Starting Points. Starting Points
 Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Practical Bayesian Design and Analysis for Drug and Device Clinical Trials
 Practical Bayesian Design and Analysis for Drug and Device Clinical Trials p. 1/2 Practical Bayesian Design and Analysis for Drug and Device Clinical Trials Brian P. Hobbs Plan B Advisor: Bradley P. Carlin
Practical Bayesian Design and Analysis for Drug and Device Clinical Trials p. 1/2 Practical Bayesian Design and Analysis for Drug and Device Clinical Trials Brian P. Hobbs Plan B Advisor: Bradley P. Carlin
Problem Set #8 Rad 226
 Problem Set #8 1. J-editing. In class, we discussed J-editing for the doublet resonance of lactate. Other in vivo peaks (e.g. GABA) are more complicated (triplets, quartets, etc.). In this problem, we
Problem Set #8 1. J-editing. In class, we discussed J-editing for the doublet resonance of lactate. Other in vivo peaks (e.g. GABA) are more complicated (triplets, quartets, etc.). In this problem, we
functional MRI everything you always wanted to know, but never dared to MD PhD
 functional MRI everything you always wanted to know, but never dared to ask @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant
functional MRI everything you always wanted to know, but never dared to ask @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant
Neuroscience, University of Notre Dame. Postdoctoral Scholar Advisors: Dr. Bradley S. Gibson, Dr. Nathan Rose
 PEDRO SZTYBEL, PhD Dept. of Psychology-University of Notre Dame Haggar Hall, Room 204 Notre Dame, IN 46556 Phone: (415) 385-0584 Email: psztybel@nd.edu EDUCATION & TRAINING 2017-Present Psychology & Neuroscience,
PEDRO SZTYBEL, PhD Dept. of Psychology-University of Notre Dame Haggar Hall, Room 204 Notre Dame, IN 46556 Phone: (415) 385-0584 Email: psztybel@nd.edu EDUCATION & TRAINING 2017-Present Psychology & Neuroscience,
The previous three chapters provide a description of the interaction between explicit and
 77 5 Discussion The previous three chapters provide a description of the interaction between explicit and implicit learning systems. Chapter 2 described the effects of performing a working memory task
77 5 Discussion The previous three chapters provide a description of the interaction between explicit and implicit learning systems. Chapter 2 described the effects of performing a working memory task
Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics
 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'18 85 Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics Bing Liu 1*, Xuan Guo 2, and Jing Zhang 1** 1 Department
Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'18 85 Bayesian Bi-Cluster Change-Point Model for Exploring Functional Brain Dynamics Bing Liu 1*, Xuan Guo 2, and Jing Zhang 1** 1 Department
FUNCTIONAL MRI CORRELATES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS DURING AUDITORY ODDBALL TASK AND RESTING STATE. Joseph James Shaffer Jr.
 FUNCTIONAL MRI CORRELATES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS DURING AUDITORY ODDBALL TASK AND RESTING STATE Joseph James Shaffer Jr. Dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina
FUNCTIONAL MRI CORRELATES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS DURING AUDITORY ODDBALL TASK AND RESTING STATE Joseph James Shaffer Jr. Dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina
Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Stroke Patients After Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Therapy: A Pilot Study
 Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Stroke Patients After Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Therapy: A Pilot Study N. Kinany 1,3,4(&), C. Pierella 1, E. Pirondini 3,4, M. Coscia 2, J. Miehlbradt 1, C. Magnin
Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Stroke Patients After Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Therapy: A Pilot Study N. Kinany 1,3,4(&), C. Pierella 1, E. Pirondini 3,4, M. Coscia 2, J. Miehlbradt 1, C. Magnin
Advances in Clinical Neuroimaging
 Advances in Clinical Neuroimaging Joseph I. Tracy 1, PhD, ABPP/CN; Gaelle Doucet 2, PhD; Xaiosong He 2, PhD; Dorian Pustina 2, PhD; Karol Osipowicz 2, PhD 1 Department of Radiology, Thomas Jefferson University,
Advances in Clinical Neuroimaging Joseph I. Tracy 1, PhD, ABPP/CN; Gaelle Doucet 2, PhD; Xaiosong He 2, PhD; Dorian Pustina 2, PhD; Karol Osipowicz 2, PhD 1 Department of Radiology, Thomas Jefferson University,
Analysis of left-censored multiplex immunoassay data: A unified approach
 1 / 41 Analysis of left-censored multiplex immunoassay data: A unified approach Elizabeth G. Hill Medical University of South Carolina Elizabeth H. Slate Florida State University FSU Department of Statistics
1 / 41 Analysis of left-censored multiplex immunoassay data: A unified approach Elizabeth G. Hill Medical University of South Carolina Elizabeth H. Slate Florida State University FSU Department of Statistics
MITELMAN, SHIHABUDDIN, BRICKMAN, ET AL. basic necessities of life, including food, clothing, and shelter. Compared to patients with good-outcome schiz
 Article MRI Assessment of Gray and White Matter Distribution in Brodmann s Areas of the Cortex in Patients With Schizophrenia With Good and Poor Outcomes Serge A. Mitelman, M.D. Lina Shihabuddin, M.D.
Article MRI Assessment of Gray and White Matter Distribution in Brodmann s Areas of the Cortex in Patients With Schizophrenia With Good and Poor Outcomes Serge A. Mitelman, M.D. Lina Shihabuddin, M.D.
A Bayesian Account of Reconstructive Memory
 Hemmer, P. & Steyvers, M. (8). A Bayesian Account of Reconstructive Memory. In V. Sloutsky, B. Love, and K. McRae (Eds.) Proceedings of the 3th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Mahwah,
Hemmer, P. & Steyvers, M. (8). A Bayesian Account of Reconstructive Memory. In V. Sloutsky, B. Love, and K. McRae (Eds.) Proceedings of the 3th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Mahwah,
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
November/December 2008 The Brain Unveiled A new imaging method offers a spectacular view of neural structures. By Emily Singer
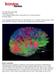 November/December 2008 The Brain Unveiled A new imaging method offers a spectacular view of neural structures. By Emily Singer A new imaging method that offers an unprecedented view of complex neural structures
November/December 2008 The Brain Unveiled A new imaging method offers a spectacular view of neural structures. By Emily Singer A new imaging method that offers an unprecedented view of complex neural structures
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Functional Connectivity and the Neurophysics of EEG. Ramesh Srinivasan Department of Cognitive Sciences University of California, Irvine
 Functional Connectivity and the Neurophysics of EEG Ramesh Srinivasan Department of Cognitive Sciences University of California, Irvine Outline Introduce the use of EEG coherence to assess functional connectivity
Functional Connectivity and the Neurophysics of EEG Ramesh Srinivasan Department of Cognitive Sciences University of California, Irvine Outline Introduce the use of EEG coherence to assess functional connectivity
Discriminative Analysis for Image-Based Studies
 Discriminative Analysis for Image-Based Studies Polina Golland 1, Bruce Fischl 2, Mona Spiridon 3, Nancy Kanwisher 3, Randy L. Buckner 4, Martha E. Shenton 5, Ron Kikinis 6, Anders Dale 2, and W. Eric
Discriminative Analysis for Image-Based Studies Polina Golland 1, Bruce Fischl 2, Mona Spiridon 3, Nancy Kanwisher 3, Randy L. Buckner 4, Martha E. Shenton 5, Ron Kikinis 6, Anders Dale 2, and W. Eric
Small-area estimation of mental illness prevalence for schools
 Small-area estimation of mental illness prevalence for schools Fan Li 1 Alan Zaslavsky 2 1 Department of Statistical Science Duke University 2 Department of Health Care Policy Harvard Medical School March
Small-area estimation of mental illness prevalence for schools Fan Li 1 Alan Zaslavsky 2 1 Department of Statistical Science Duke University 2 Department of Health Care Policy Harvard Medical School March
Bayesian graphical models for combining multiple data sources, with applications in environmental epidemiology
 Bayesian graphical models for combining multiple data sources, with applications in environmental epidemiology Sylvia Richardson 1 sylvia.richardson@imperial.co.uk Joint work with: Alexina Mason 1, Lawrence
Bayesian graphical models for combining multiple data sources, with applications in environmental epidemiology Sylvia Richardson 1 sylvia.richardson@imperial.co.uk Joint work with: Alexina Mason 1, Lawrence
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Modelling Spatially Correlated Survival Data for Individuals with Multiple Cancers
 Modelling Spatially Correlated Survival Data for Individuals with Multiple Cancers Dipak K. Dey, Ulysses Diva and Sudipto Banerjee Department of Statistics University of Connecticut, Storrs. March 16,
Modelling Spatially Correlated Survival Data for Individuals with Multiple Cancers Dipak K. Dey, Ulysses Diva and Sudipto Banerjee Department of Statistics University of Connecticut, Storrs. March 16,
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS. specifications
 NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
Selection of Linking Items
 Selection of Linking Items Subset of items that maximally reflect the scale information function Denote the scale information as Linear programming solver (in R, lp_solve 5.5) min(y) Subject to θ, θs,
Selection of Linking Items Subset of items that maximally reflect the scale information function Denote the scale information as Linear programming solver (in R, lp_solve 5.5) min(y) Subject to θ, θs,
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
FUNCTIONAL MRI IN EPILEPSY December 6 th 2013
 FUNCTIONAL MRI IN EPILEPSY December 6 th 2013 Matthias J Koepp, MD, PhD UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure
FUNCTIONAL MRI IN EPILEPSY December 6 th 2013 Matthias J Koepp, MD, PhD UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure
Design for Targeted Therapies: Statistical Considerations
 Design for Targeted Therapies: Statistical Considerations J. Jack Lee, Ph.D. Department of Biostatistics University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Outline Premise General Review of Statistical Designs
Design for Targeted Therapies: Statistical Considerations J. Jack Lee, Ph.D. Department of Biostatistics University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Outline Premise General Review of Statistical Designs
Why does language set up shop where it does?
 Why does language set up shop where it does? Does modality affect the functional neuroanatomy of language? For example, the M350 and the N400 localize in the vicinity of auditory cortex. Is that just an
Why does language set up shop where it does? Does modality affect the functional neuroanatomy of language? For example, the M350 and the N400 localize in the vicinity of auditory cortex. Is that just an
Brian A. Coffman, PhD
 Brian A. Coffman, PhD Research Instructor Department of Psychiatry University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital Pittsburgh, PA Dr. Brian Coffman is a Research Instructor
Brian A. Coffman, PhD Research Instructor Department of Psychiatry University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital Pittsburgh, PA Dr. Brian Coffman is a Research Instructor
Dynamic Causal Modeling
 Dynamic Causal Modeling Hannes Almgren, Frederik van de Steen, Daniele Marinazzo daniele.marinazzo@ugent.be @dan_marinazzo Model of brain mechanisms Neural populations Neural model Interactions between
Dynamic Causal Modeling Hannes Almgren, Frederik van de Steen, Daniele Marinazzo daniele.marinazzo@ugent.be @dan_marinazzo Model of brain mechanisms Neural populations Neural model Interactions between
Clinical Applications of fmri
 Clinical Applications of fmri Benjamin M. Hampstead, Ph.D., ABPP/CN Associate Professor Department of Psychiatry University of Michigan VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System No Disclosures or Conflicts Hampstead
Clinical Applications of fmri Benjamin M. Hampstead, Ph.D., ABPP/CN Associate Professor Department of Psychiatry University of Michigan VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System No Disclosures or Conflicts Hampstead
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Historical controls in clinical trials: the meta-analytic predictive approach applied to over-dispersed count data
 Historical controls in clinical trials: the meta-analytic predictive approach applied to over-dispersed count data Sandro Gsteiger, Beat Neuenschwander, and Heinz Schmidli Novartis Pharma AG Bayes Pharma,
Historical controls in clinical trials: the meta-analytic predictive approach applied to over-dispersed count data Sandro Gsteiger, Beat Neuenschwander, and Heinz Schmidli Novartis Pharma AG Bayes Pharma,
Final Report. Title of Project: Quantifying and measuring cortical reorganisation and excitability with post-stroke Wii-based Movement Therapy
 Final Report Author: Dr Penelope McNulty Qualification: PhD Institution: Neuroscience Research Australia Date: 26 th August, 2015 Title of Project: Quantifying and measuring cortical reorganisation and
Final Report Author: Dr Penelope McNulty Qualification: PhD Institution: Neuroscience Research Australia Date: 26 th August, 2015 Title of Project: Quantifying and measuring cortical reorganisation and
Memory Scanning for Words Versus Categories z
 JOURNAL OF VERBAL LEARNING AND VERBAL BEHAVIOR 10, 522-527 (1971) Memory Scanning for Words Versus Categories z JAMES F. JUOLA AND R. C. ATKINSON Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305 Two groups
JOURNAL OF VERBAL LEARNING AND VERBAL BEHAVIOR 10, 522-527 (1971) Memory Scanning for Words Versus Categories z JAMES F. JUOLA AND R. C. ATKINSON Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305 Two groups
Computational and Predictive Models for Medical Image Analysis Yi Hong, Computer Science, University of Georgia
 Neural White Matter Distinctions in Biologically Classified Psychosis Courtney Burton, B.S. Jackson, D.A. Parker, E.S. Gershon, M.S. Keshavan, G.D. Pearlson, C.A. Tamminga, B.A. Clementz, and J.E. McDowell,
Neural White Matter Distinctions in Biologically Classified Psychosis Courtney Burton, B.S. Jackson, D.A. Parker, E.S. Gershon, M.S. Keshavan, G.D. Pearlson, C.A. Tamminga, B.A. Clementz, and J.E. McDowell,
Cancer Treatment Using Multiple Chemotheraputic Agents Subject to Drug Resistance
 Cancer Treatment Using Multiple Chemotheraputic Agents Subject to Drug Resistance J. J. Westman Department of Mathematics University of California Box 951555 Los Angeles, CA 90095-1555 B. R. Fabijonas
Cancer Treatment Using Multiple Chemotheraputic Agents Subject to Drug Resistance J. J. Westman Department of Mathematics University of California Box 951555 Los Angeles, CA 90095-1555 B. R. Fabijonas
Aging, cognitive-motor function, and tcs. Brad Manor, PhD. October 31, 2017 LEASE DO NOT COPY
 Aging, cognitive-motor function, and tcs Brad Manor, PhD October 31, 2017 Disclosures - NIH / NIA - Michael J. Fox Foundation - U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation - Marcus Applebaum Research Award
Aging, cognitive-motor function, and tcs Brad Manor, PhD October 31, 2017 Disclosures - NIH / NIA - Michael J. Fox Foundation - U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation - Marcus Applebaum Research Award
Source Memory is not Properly Differentiated from Object Memory in Early Schizophrenia An fmri study using virtual reality
 Source Memory is not Properly Differentiated from Object Memory in Early Schizophrenia An fmri study using virtual reality Colin S. Hawco, PhD Lisa Buchy Michael Bodnar, Sarah Izadi, Jennifer Dell Elce,
Source Memory is not Properly Differentiated from Object Memory in Early Schizophrenia An fmri study using virtual reality Colin S. Hawco, PhD Lisa Buchy Michael Bodnar, Sarah Izadi, Jennifer Dell Elce,
Gianluca Baio. University College London Department of Statistical Science.
 Bayesian hierarchical models and recent computational development using Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation, with applications to pre-implantation genetic screening in IVF Gianluca Baio University
Bayesian hierarchical models and recent computational development using Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation, with applications to pre-implantation genetic screening in IVF Gianluca Baio University
Multivariate Multilevel Models
 Multivariate Multilevel Models Getachew A. Dagne George W. Howe C. Hendricks Brown Funded by NIMH/NIDA 11/20/2014 (ISSG Seminar) 1 Outline What is Behavioral Social Interaction? Importance of studying
Multivariate Multilevel Models Getachew A. Dagne George W. Howe C. Hendricks Brown Funded by NIMH/NIDA 11/20/2014 (ISSG Seminar) 1 Outline What is Behavioral Social Interaction? Importance of studying
Outline. Hierarchical Hidden Markov Models for HIV-Transmission Behavior Outcomes. Motivation. Why Hidden Markov Model? Why Hidden Markov Model?
 Hierarchical Hidden Markov Models for HIV-Transmission Behavior Outcomes Li-Jung Liang Department of Medicine Statistics Core Email: liangl@ucla.edu Joint work with Rob Weiss & Scott Comulada Outline Motivation
Hierarchical Hidden Markov Models for HIV-Transmission Behavior Outcomes Li-Jung Liang Department of Medicine Statistics Core Email: liangl@ucla.edu Joint work with Rob Weiss & Scott Comulada Outline Motivation
Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition
 Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition Charles F. Cadieu, Ha Hong, Daniel L. K. Yamins, Nicolas Pinto, Diego Ardila, Ethan A. Solomon, Najib
Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition Charles F. Cadieu, Ha Hong, Daniel L. K. Yamins, Nicolas Pinto, Diego Ardila, Ethan A. Solomon, Najib
MEA DISCUSSION PAPERS
 Inference Problems under a Special Form of Heteroskedasticity Helmut Farbmacher, Heinrich Kögel 03-2015 MEA DISCUSSION PAPERS mea Amalienstr. 33_D-80799 Munich_Phone+49 89 38602-355_Fax +49 89 38602-390_www.mea.mpisoc.mpg.de
Inference Problems under a Special Form of Heteroskedasticity Helmut Farbmacher, Heinrich Kögel 03-2015 MEA DISCUSSION PAPERS mea Amalienstr. 33_D-80799 Munich_Phone+49 89 38602-355_Fax +49 89 38602-390_www.mea.mpisoc.mpg.de
Mapping Cognitive and Motivational Domains Across Levels of Analysis: Challenges and Opportunities for Target Specification
 Mapping Cognitive and Motivational Domains Across Levels of Analysis: Challenges and Opportunities for Target Specification Robert M Bilder, PhD Michael E. Tennenbaum Family Professor, and Chief of Medical
Mapping Cognitive and Motivational Domains Across Levels of Analysis: Challenges and Opportunities for Target Specification Robert M Bilder, PhD Michael E. Tennenbaum Family Professor, and Chief of Medical
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs
 Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
