First Exam. Sensation and Perception. Process of Forming Sensations. Sensation and Perception. The Eye. Our perceptual experience. Mean = 57.
|
|
|
- Aubrey Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 First Exam Sensation and Perception Mean = 57.5 SD = 11 Source of human knowledge Could we know anything without our senses? Empiricists - John Locke ( ), all knowledge comes from sensory experience Nativists - Immanuel Kant ( ), knowledge cannot come from sensory experience alone, the mind has preexisting categories which organizes sensory material. Sensation and Perception Sensation vs. perception Sensation: The basic processes by which sensory organs and the nervous system respond to stimuli in the environment and form elementary psychological experiences. This tastes bitter, That sound is loud, That object is very red, Perception: The way our nervous systems organizes and interprets sensory information (sensations) to give us a perceptual experiences. The brain organizes sensory input and translates it into something meaningful. Similar to the binding problem in the previous chapter. Strong coffee, Red Hot Chilli Peppers, Apple looks ripe. Process of Forming Sensations Physical stimulus Physiological response Sensory experience Physical stimulus is the matter or energy that produces a change in a sense receptor. Each sensory receptor sensitive to different form of energy e.g., light waves, sound waves, pressure, temperature. Each sense has special cells, sensory receptors, translate physical energy into neural responses e.g., retina of eye, cochlea of the ear, touch receptors in the skin The process of converting energy of stimuli into neural impulses, which are sent to the brain is called Transduction. Our perceptual experience If we went to some other planet would we see different colors? or Was there color before an animal evolved that saw color. Doctrine of Specific Nerve Energies Neural response (action potential) itself does not reflect the characteristics of the stimulus. Our perceptions are based on the part of the brain stimulated and not on the stimulus itself Johannes Mueller What would happen if the brain were miswired? Synesthesia people who when received stimulation from one sense receives additional stimulation in another. Sound producing visual effects. Stimulating neurons manually will create a perception even if no stimulus is present. The Eye Vision Between 25 and 40 percent of human brain devoted primarily to the analysis of visual input (Gross, 1998). Cornea Responsible for initial gross focusing. Iris Controls the size of the pupil that allows light into the eye. Negative feedback system. Why do my girlfriend s pupils get larger when she looks at me? Why do her father s? Pupil opening related to visual acuity-why do high intensity lamps improve acuity.
2 Lens Transparent part of the eye which focuses light on the retina. Changes in shape of the lens to focus light at various distances known as accommodation. Old age and Presbyopia. Retina Photosensitive surface on the back of the eye. Fovea - Place on the retina of greatest acuity. Figure 18.4 The retina s reaction to light Myers: Psychology, Ninth Edition in Modules Copyright 2010 by Worth Publishers Eye movements Myopia Hyperopia Convergence Eyes converge as objects approach. Saccadic The quick darting movement of the eyes when exploring the environment. Smooth Smooth movement of the eyes which is elicited by a moving target. Nystagmus Small tremors which probably maintain image on fresh receptors. Stabilized images. Miniature slide projector attached to a contact lens moves each time the eye moves. As a result, the projected image disappears in a few seconds because it does not move on the retina. Figure 17.4 Sensory adaptation: now you see it, now you don t! Myers: Psychology, Ninth Edition in Modules Copyright 2010 by Worth Publishers
3 Snellen Notation Eagles and Hawks have more acute Vision than humans, so why is his Head upside down? Visual Receptors Rods Receptor cells on periphery of retina, responsible for black and white vision. About 150 Million of them. Very sensitive to light. Cones Receptor cell on the central part of the retina(fovea), responsible for color vision. About 7 Million of them (5-10%). Problem: How come rods which are more sensitive to light are less acute then cones? Organization of Rods and Cones Dark and light Adaptation Photons of light break down Iodopsin (cones), Rhodopsin (rods) creating a neural pulse. Purkinje Effect Rods more sensitive to blue and green, cones to reds and yellows Plane and car instrument lighting
4 Details of the Retina Concept of a Visual Field Light Impulses produced by light Photoreceptors Receptive Fields Receptive field: The organization of bipolar cells that feed information about the light changes in the environment to the ganglion cell. Insert a microelectrode into a retinal ganglion cell: then record potentials as various stimuli are shown onto the cell Center-surround shape (a) baseline firing of cell (b) cell firing greater than baseline (c) cell firing less than baseline Mach Bands Fig. 4.10
5 Inhibition of center of visual field greatest Inhibition of center of visual field least Path of Visual Stimulation Light reaches visual receptors on the Retina Bipolar cells organize responses of receptors Ganglion cells, which form the optic nerve, organize responses of bipolar cells into receptive fields (center surround cells) Primary visual area, back of occipital lobe, receives signals from optic nerve and organize information into feature detectors. 4.2 Visual Pathway From Eye Through Brain 32 Feature Detectors Motion Detector Hubel and Wiesel Discovered cells in the visual cortex Feature Detectors that are organized so that they responded to specific features of the environment. Feature detectors can be explained by a collection of ganglion cells from the retina that are connected to one cell in the cortex so as to respond to specific stimulus features. This finding suggests we have feature detectors, specialized neurons that respond to the presence of certain simple features, such as angles and lines, which are then processed at higher levels to give us forms and objects.
6 Color Vision Our visual system sensitive to narrow band of electromagnetic radiation from 350 millimicrons (violet) to 750 millimicrons (Red) Why does your shirt look blue? Yellow? What if there is no blue or yellow wavelength shining on your shirt? What do you get when you mix blue and yellow paint? Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision Young-Helmholtz model Conjectured that color vision started at the retinal level. Retina has three types of cone receptors(red, Green, Blue) Additive versus subtractive color mixing. Additive-Each light adds its portion of the wavelength spectrum adding up to White Light Subtractive-Each pigment subtracts a portion of the wavelength that it absorbs leaving no light to reflect or black Young-Helmholtz model Problems with the Young-Helmholtz model People act as if there are four primaries, Red, Green, Blue AND YELLOW. Some color combinations make sense to us others don t. What do you get from combination of Red and Blue? Red and Yellow Green and Blue But Green and Red Yellow and Blue Color blindness tends to come in specific pairs. Red/Green and Blue/Yellow but not red/blue or yellow/green. Negative afterimages Color Blindness Test
7 He Lurks Among Us. Opponent Process Theory of Color Vision Because of these findings, Ewald Hering proposed that we perceive color in a system of paired colors. Red vs. green Yellow vs. blue White vs. black Opponent Process Cells Red /Green Stimulated experience, Red Inhibited experience, Green Blue/Yellow Stimulated experience, Blue Inhibited experience, Yellow Negative after image caused by fatigue one kind of receptor, so the opponent process cell rebounds with the other color experience.
8 Working against color constancy The ear is designed to detect and transmit sound waves to the brain. Sound waves are vibrations in the air or other medium. Sound waves vary according to frequency (pitch) and amplitude (loudness). Frequency is measured by the number of vibrations or cycles of the sound wave per second, referred to as hertz (Hz.). Human ear 15 20,000 Hz. Hearing Hearing The Ear Sound waves strike the tympanic membrane, or eardrum. The vibrations of the eardrum cause three very tiny bones, the malleus, the incus, and the stapes, (literally the hammer, anvil and stirrup) to work to make the sound waves become stronger signals. The stirrup causes the cochlea to vibrate. Sound waves create vibrations that displace hair cells along the basilar membrane within the cochlea. The Ear Hearing Hearing Loss There are two common forms of deafness. Conduction deafness results when the three special bones in the ear fail to transmit sound waves properly to the cochlea. Nerve deafness results from damage to the structures that receive and transmit the impulses - the cochlea, hair cells or auditory nerve. From ear drum to oval window, sound amplified 180 times through action of these small bones.
9 The Cochlea Hearing Pitch Perception Adult hearing range-- between 15 and 20,000 Hz. How we hear pitch depends in part on the frequency to which we are listening. Low frequencies (up to about 100 Hz), the frequency principle. Sound waves passing through the fluid in the cochlea cause all the hair cells to vibrate, producing action potentials that are synchronized with the sound waves. Mid frequencies ( Hz), volley principle. Fewer hair cells can fire at this pace, but those that do respond in groups, called volleys, and produce action potentials. High frequencies (beyond 4000 Hz), place principle. The place or location of the hair cells stimulated by the sound waves depends on their frequency and determines frequency perception. The highest frequency sounds vibrate hair cells near the stirrup. Thresholds Absolute Threshold-point at which you can detect any stimulation to that sense organ Difference Threshold-point at which you can detect an increase in stimulation Concept of a Threshold Thresholds Early psychological researchers thought it would be relatively simple to determine the weakest possible stimuli that humans could detect. They were wrong. Absolute Threshold the minimum amount of stimulus energy that allows us to perceive a sensation Thresholds are the result of a decision-making process. 50/50 point. Subliminal Perception? Difference Threshold
10 Perception vs. Sensation Weber s Law Difference Thresholds--The size of a Just Noticeable Difference(JND) is a constant. Sensitivity of senses based on difference thresholds. Weber's Fractions: Vision Kinesthesia(weight) Pain Audition Pressure Smell Taste Perceptions result from interpreting primitive sensations from sense receptors to produce more complex forms we see as objects and events in reality. Perception interprets, elaborates and organizes our sensations to provide us with a perceptual experience. 1/60 1/50 1/30 1/10 1/7 1/4 1/3 4.2 Pathways Damage in the What Pathway Visual streams Ventral (below) stream Visual Form Agnosia-can identify color and brightness of objects but not its shape. Visual Object Agnosia-can draw shapes but cannot identify objects across occipital lobe into lower levels of temporal lobes (shape and identity) Dorsal (above) stream travels up from occipital lobe to parietal lobes (location and motion) 76 Damage in the Where Pathway Gestalt Psychology Gestalt psychology focuses on the human ability to perceive overall patterns. According to Gestalt psychologists, visual perception is an active creation, not merely the adding up of lines and movement. Figure/ ground
11 Skull or Couple at a Party Gestalt Laws Perception of form and objects Good continuation
12 Figure 17.1 What s going on here? Myers: Psychology, Ninth Edition in Modules Copyright 2010 by Worth Publishers Perception Depends on Context Who are these Guys?
13 Object Recognition Image-based object recognition-top down processing Objects you recognize are stored in memory as a template which is then compared with objects you experience on your retina-based object recognition Parts-based object recognition-bottom up processing Objects represented in memory by structural description of how what parts I needed to create the object Bottom-up versus top-down processing. Bottom up Processing Bottom-up processing progresses from individual elements to whole elements Top-down processing progresses from the whole to the individual elements. Perception Top Down processing in audition Queen s Another one bites the dust Same song backwards Lewis Carrol s Jabberwocky backwards
14 Depth Perception Our retinas are two-dimensional surfaces, but they give us very good depth perception our ability to perceive distance. Binocular cues Convergence is the degree to which our eyes must turn in to allow us to focus on a very close object. Retinal disparity, which is the difference in apparent position of an object seen by each retina. Figure 4.53 Convergence of the eyes as a cue to distance. The more this viewer must converge her eyes toward each other in order to focus on an object, the closer the object must be. Depth Perception Monocular cues Object size Linear perspective is used when parallel lines are drawn so that they converge as they approach the horizon. Detail generally objects that are closer can be seen in greater detail than those that are farther away. Interposition nearby objects will obstruct objects that are farther away. Texture gradient refers to the fact that clusters of objects will seem more densely packed the farther away the clusters are. Shadows give clues to distance depending on size and position. Motion parallax is the principle that close objects will pass by faster than distant objects.
15
16 Optical Illusions An optical illusion is a misinterpretation of a visual stimulus. It may be because of the way our brains process visual images in an attempt to make veridical judgments. Perceptual Constancies Color: Tendency to perceive object color as stable even under conditions of changing illumination Shape: We recognize an object as having the same shape although we may view it in a different angle, at a different distance... Size: Objects do not differ in size when viewed from different distances Our visual system is organized to give us true perceptions. Size Constancy Some illusions based on misinterpretation of depth
17 Table Top Illusion Wheel illusion
18 Does the sex of these people differ?
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Sensing and Perceiving Our World
 PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
The Perceptual Experience
 Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Sensation and Perception. A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations
 I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
SENSES: VISION. Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014
 SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation. Date Period. 1) sensation. 2) perception. 3) bottom-up processing. 4) top-down processing
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Sensation and Perception. Chapter 6
 Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
Dikran J. Martin. Psychology 110. Name: Date: Making Contact with the World around Us. Principal Features
 Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 3 Sensation and Perception: Pages: 31 Making Contact with the World around Us TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition).
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 3 Sensation and Perception: Pages: 31 Making Contact with the World around Us TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition).
l3;~~?~~~,'0~'~~t~t:~:~~~~~~~~~~!,1
 112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Vision Seeing is in the mind
 1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds. Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
 Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Consciousness and Blindsight
 Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Unit 4 Practice. PSYCHOLOGY SECTION I Time-- Minutes Questions, Unit 4 Practice/Quiz
 PSYCHOLOGY SECTION I Time-- Minutes Questions, Unit 4 Practice/Quiz Unit 4 Practice Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions.
PSYCHOLOGY SECTION I Time-- Minutes Questions, Unit 4 Practice/Quiz Unit 4 Practice Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions.
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
SENSATION & PERCEPTION
 SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II
 Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Chapter 5 Test Review. Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line
 Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014
 Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014 AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014 AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Unit 4 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. Kinesthesis refers to the A) process of organizing and interpreting sensory information. B) diminished sensitivity to an unchanging stimulus. C) quivering eye movements that enable the retina
Name: Date: 1. Kinesthesis refers to the A) process of organizing and interpreting sensory information. B) diminished sensitivity to an unchanging stimulus. C) quivering eye movements that enable the retina
A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception E. Overload
 Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition
 Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition Sensation the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition Sensation the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
The Basic Senses and What They Detect. Energy senses Vision (electromagnetic energy light waves)
 The Basic Senses and What They Detect Energy senses Vision (electromagnetic energy light waves) LP 4B Color Perception 1 Hearing (sound waves) LP 4B Color Perception 2 Chemical senses Smell (airborne chemical
The Basic Senses and What They Detect Energy senses Vision (electromagnetic energy light waves) LP 4B Color Perception 1 Hearing (sound waves) LP 4B Color Perception 2 Chemical senses Smell (airborne chemical
STUDY GUIDE: Sensation and Perception Psychology, Myers, 8 th ed.
 STUDY GUIDE: Sensation and Perception Psychology, Myers, 8 th ed. 1. Frequency is to pitch as is to. A) wavelength; loudness B) amplitude; loudness C) wavelength; intensity D) amplitude; intensity 2. The
STUDY GUIDE: Sensation and Perception Psychology, Myers, 8 th ed. 1. Frequency is to pitch as is to. A) wavelength; loudness B) amplitude; loudness C) wavelength; intensity D) amplitude; intensity 2. The
6. The term gestalt means A. grouping B. sensation C. perception D. whole Correct Answer:- D.
 1. Each time you see you car, it projects a different image on the retinas of your eyes, yet you do not perceive it as changing. This is because of B. retinal disparity C. perceptual constancy D. figure-ground
1. Each time you see you car, it projects a different image on the retinas of your eyes, yet you do not perceive it as changing. This is because of B. retinal disparity C. perceptual constancy D. figure-ground
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Senses are transducers. Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What?
 1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
AP Psychology Review Chapter 04: Sensation and Perception
 AP Psychology Review Chapter 04: Sensation and Perception 1. What is perception? The process by which the brain organizes and interprets sensation 2. Which senses allow for sensation at a distance? Vision
AP Psychology Review Chapter 04: Sensation and Perception 1. What is perception? The process by which the brain organizes and interprets sensation 2. Which senses allow for sensation at a distance? Vision
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 Module 19 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions
Module 19 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions
Practice Test Questions
 Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Sensation & Perception Unit Guide
 ΨAP METEA VALLEY PSYCHOLOGY Sensation & Perception Unit Guide Essential Questions What is the difference between sensation and perception, and how are they related? What are the basic sensory concepts
ΨAP METEA VALLEY PSYCHOLOGY Sensation & Perception Unit Guide Essential Questions What is the difference between sensation and perception, and how are they related? What are the basic sensory concepts
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
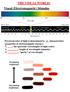 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
Answer: B difficulty: 2 conceptual Goal 3: Critical Thinking Skills in Psychology
 Chapter Test 1. The concepts of sensation and perception are different because a. perception is something that happens to your sense organs and neurons; sensation is something that happens to you b. sensation
Chapter Test 1. The concepts of sensation and perception are different because a. perception is something that happens to your sense organs and neurons; sensation is something that happens to you b. sensation
Psychology Unit 3 Test
 1 Choose the best answer. (2 pts each). Psychology Unit 3 Test 1. In bright light, the iris and the pupil to control the amount of light entering the eye. a. expands; constricts b. constricts; expands
1 Choose the best answer. (2 pts each). Psychology Unit 3 Test 1. In bright light, the iris and the pupil to control the amount of light entering the eye. a. expands; constricts b. constricts; expands
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6
 Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 Basic Principles Basic Principles Sensation- how sensory receptors and your nervous system receive stimuli I hear, I see Perception- the process of organizing and interpreting
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 Basic Principles Basic Principles Sensation- how sensory receptors and your nervous system receive stimuli I hear, I see Perception- the process of organizing and interpreting
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of response by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of response by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
The Sense Organs 10/13/2016. The Human Eye. 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina. The eye is made up of three layers:
 The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
c. finding it difficult to maintain your balance when you have an ear infection
 Sensory and Perception Quiz- Reynolds Fall 2015 1. The inner ear contains receptors for: a. audition and kinesthesis. b. kinesthesis and the vestibular sense. c. audition and the vestibular sense. d. audition,
Sensory and Perception Quiz- Reynolds Fall 2015 1. The inner ear contains receptors for: a. audition and kinesthesis. b. kinesthesis and the vestibular sense. c. audition and the vestibular sense. d. audition,
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION Vision
 DEMIDEC~ AP Psychology Cram Kit I 20 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION Vision Posterior chamber Retina Zonular fibres VISUAL SENSATION LET THE SUNSHINE IN Ins Pupil Lens Cornea Anterior chamber (aqueous humour)
DEMIDEC~ AP Psychology Cram Kit I 20 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION Vision Posterior chamber Retina Zonular fibres VISUAL SENSATION LET THE SUNSHINE IN Ins Pupil Lens Cornea Anterior chamber (aqueous humour)
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world
 Name: 1 Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world 1 Distinguish between sensation and perception. Include as part of your answer
Name: 1 Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world 1 Distinguish between sensation and perception. Include as part of your answer
Our Senses & the World CHAPTER 4. Sensations & Senses. Characteristics (continued) Characteristics (continued) Characteristics of All Senses
 CHAPTER 4 Sensations & Senses Our Senses & the World Characteristics of All Senses RECEPTION: Accessory Structures-modify the energy created by something in the person s environment Characteristics TRANSDUCTION:
CHAPTER 4 Sensations & Senses Our Senses & the World Characteristics of All Senses RECEPTION: Accessory Structures-modify the energy created by something in the person s environment Characteristics TRANSDUCTION:
Study Guide Chapter 5
 Name: Date: 1. Superman's eyes used, while his brain used. A) perception; sensation B) top-down processing; bottom-up processing C) bottom-up processing; top-down processing D) sensory adaptation; subliminal
Name: Date: 1. Superman's eyes used, while his brain used. A) perception; sensation B) top-down processing; bottom-up processing C) bottom-up processing; top-down processing D) sensory adaptation; subliminal
Psychology Session 9 Sensation and Perception
 Psychology Session 9 Sensation and Perception Date: November 4 th, 2016 Course instructor: Cherry Chan Mothercraft College Agenda 1. Sensation and perception 2. Vision 3. Perceptual organization 4. Sound
Psychology Session 9 Sensation and Perception Date: November 4 th, 2016 Course instructor: Cherry Chan Mothercraft College Agenda 1. Sensation and perception 2. Vision 3. Perceptual organization 4. Sound
PROGRESS TEST 1. Multiple-Choice Questions. a. wavelength; loudness b. amplitude; loudness c. wavelength; intensity d. amplitude; intensity
 136 Chapter 5 Sensation The receptors for this sense are located in the and --------------~ --------------~ of the inner ear. PROGRESS TEST 1 Multiple-Choice Questions Circle your answers to the following
136 Chapter 5 Sensation The receptors for this sense are located in the and --------------~ --------------~ of the inner ear. PROGRESS TEST 1 Multiple-Choice Questions Circle your answers to the following
Sensory Physiology. Sensory Range Varies. Introduction to the Special Senses. How do we sense the world around us?
 Sensory Physiology How do we sense the world around us? We do not see things as they are; we see things as we are. --Anais Nin Anais Nin, French author 1903-1977 Sensory Range Varies Introduction to the
Sensory Physiology How do we sense the world around us? We do not see things as they are; we see things as we are. --Anais Nin Anais Nin, French author 1903-1977 Sensory Range Varies Introduction to the
Chapter 29 The Senses
 Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind
 Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind Copyright Allyn & Bacon 2007 Sensation and Perception Sensation The awareness of properties of an object or event when a sensory receptor is stimulated
Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind Copyright Allyn & Bacon 2007 Sensation and Perception Sensation The awareness of properties of an object or event when a sensory receptor is stimulated
Vision. The Eye External View. The Eye in Cross-Section
 Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 3 Chapter Overview I. Worksheets II. Introduction III. Sensation III. Perception IV. Pass in your Work Sheets V. Review I. Worksheets: See Handout Packet II. Introduction A. Define sensation B.
Chapter 3 Chapter Overview I. Worksheets II. Introduction III. Sensation III. Perception IV. Pass in your Work Sheets V. Review I. Worksheets: See Handout Packet II. Introduction A. Define sensation B.
Sensation and Perception
 Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Sensation is the process of using senses to detect or sense information from the environment Your eyes detect light waves, your ears detect sound waves, your
Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Sensation is the process of using senses to detect or sense information from the environment Your eyes detect light waves, your ears detect sound waves, your
is the clear, transparent part at the front of the eye. It allows light to enter the eye and it also refracts (focuses) the light onto the retina.
 Senses- Vision Light is a small part (1/70th) of the total electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The EM band extends from radio waves at one extreme to x-rays at the other. The eye detects light and converts
Senses- Vision Light is a small part (1/70th) of the total electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The EM band extends from radio waves at one extreme to x-rays at the other. The eye detects light and converts
Chapter 18. The Senses SENSORY RECEPTION. Introduction: Superhuman Senses. Introduction: Superhuman Senses
 Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Sensation. I. Basic Concepts II. Characteristics of Sensory Systems III. The Visual System
 Sensation I. Basic Concepts II. Characteristics of Sensory Systems III. The Visual System Sensation The process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies
Sensation I. Basic Concepts II. Characteristics of Sensory Systems III. The Visual System Sensation The process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies
Sensation and Perception
 1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
Biological Bases of Behavior. 6: Vision
 Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 5 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 5 1 Chapter in Review 1. Sensing is the process by which our sense organs receive raw physical or chemical energy from the natural world; perception occurs when our brains organize
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 5 1 Chapter in Review 1. Sensing is the process by which our sense organs receive raw physical or chemical energy from the natural world; perception occurs when our brains organize
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Unit IV Sensation Perception
 Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Unit IV Sensation Perception Module 16: Basic Principles of Sensation and Perception Module 17: Influences of Perception Module 18: Vision Module 19: Visual Organization and Interpretation Module 20: Hearing
Sensa:on vs. Percep:on
 Chapter 4: Sensa:on & Percep:on Sensa:on vs. Percep:on Sensa&on the detec:on of physical energy by the sense organs Percep&on the brain s sor:ng out, interpreta:on, and analysis of raw sensory inputs (s&mulus)
Chapter 4: Sensa:on & Percep:on Sensa:on vs. Percep:on Sensa&on the detec:on of physical energy by the sense organs Percep&on the brain s sor:ng out, interpreta:on, and analysis of raw sensory inputs (s&mulus)
Introduction to Physiological Psychology
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy. (the part that s visible to us!)
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION
 SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
PSYC& Lilienfeld et al. - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How We Sense and Conceptualize the World Study Guide
 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
Sensation Sensation bottom-down processing Perception top-down processing Psychophysics absolute threshold signal detection theory subliminal
 1 Sensation To represent the world in our heads we must detect physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals (sensation) and we must select, organize and interpret our sensations
1 Sensation To represent the world in our heads we must detect physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals (sensation) and we must select, organize and interpret our sensations
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception 1 Chapters 4 of the required textbook Introduction to Psychology International Edition bv James Kalat (2010) 9 th Edition EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter,
Sensation and Perception 1 Chapters 4 of the required textbook Introduction to Psychology International Edition bv James Kalat (2010) 9 th Edition EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter,
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences
 BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Sensation & Perception Unit Guide MV AP Psych
 ΨAP METEA VALLEY PSYCHOLOGY Sensation & Perception Unit Guide MV AP Psych 2017-18 Essential Questions What is the difference between sensation and perception, and how are they related? What are the basic
ΨAP METEA VALLEY PSYCHOLOGY Sensation & Perception Unit Guide MV AP Psych 2017-18 Essential Questions What is the difference between sensation and perception, and how are they related? What are the basic
4: Sensation and Perception
 STUDY GUIDE ANSWERS 4: Sensation and Perception Introduction 1. prosopagnosia 2. sensation; perception 3. bottom-up processing; top-downprocessing 4. selective attention 5. cocktail party effect; inattentional
STUDY GUIDE ANSWERS 4: Sensation and Perception Introduction 1. prosopagnosia 2. sensation; perception 3. bottom-up processing; top-downprocessing 4. selective attention 5. cocktail party effect; inattentional
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2004
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2004 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Multiple-choice questions are worth one point each, other questions
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2004 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Multiple-choice questions are worth one point each, other questions
-Detect heat or cold and help maintain body temperature
 Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
What do we perceive?
 THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
Special Senses. Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others
 Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction
 Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception I INTRODUCTION A. SENSATION 1. The process by which our sensory receptors respond to light, sound, odor, textures, and taste and transmit that information to the brain. 2. Our
Sensation and Perception I INTRODUCTION A. SENSATION 1. The process by which our sensory receptors respond to light, sound, odor, textures, and taste and transmit that information to the brain. 2. Our
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, which you ll acknowledge when you turn in your exam. Each multiple-choice question is worth 1 point and the value of the other
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, which you ll acknowledge when you turn in your exam. Each multiple-choice question is worth 1 point and the value of the other
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
