Department of Neurosurgery, Shinko Hospital, Kobe, Japan
|
|
|
- Ross Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
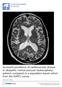
1 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 127: , 2017 Utility of MRI-based disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus scoring for predicting prognosis after surgery for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: clinical research *Narihide Shinoda, MD, Osamu Hirai, MD, Shinya Hori, MD, Kazuyuki Mikami, MD, Toshiaki Bando, MD, Daisuke Shimo, MD, Takahiro Kuroyama, MD, Yoji Kuramoto, MD, Masato Matsumoto, MD, and Yasushi Ueno, MD Department of Neurosurgery, Shinko Hospital, Kobe, Japan OBJECTIVE The presence of disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus (DESH) on brain imaging is a recognized finding of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph), but the features of DESH can vary across patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the utility of MRI-based DESH scoring for predicting prognosis after surgery. METHODS In this single-center, retrospective cohort study, the DESH score was determined by consensus between a group of neurosurgeons, neurologists, and a neuroradiologist based on the preoperative MRI findings of the patients with suspected inph. The DESH score was composed of the following 5 items, each scored from 0 to 2 (maximum score 10 points): ventriculomegaly, dilated sylvian fissures, tight high convexity, acute callosal angle, and focal sulcal dilation. The association between the DESH score and improvement of the scores on the modified Rankin Scale (mrs), inph Grading Scale (inphgs), Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), Trail Making Test-A (TMT-A), and Timed 3-Meter Up and Go Test (TUG-t) was examined. The primary end point was improvement in the mrs score at 1 year after surgery, and the secondary outcome measures were the inphgs, MMSE, TMT-A, and TUG-t scores at 1 year after surgery. Improvement was determined as improvement of 1 or more levels on mrs, 1 point on inphgs, 3 points on MMSE, a decrease of > 30% on TMT-A, and a decrease of > 10% on TUG-t. RESULTS The mean DESH score for the 50 patients (mean age 77.6 ± 5.9 years) reviewed in this study was 5.58 ± The mean rate of change in the mrs score was ± 0.93, indicating an inverse correlation between the DESH score and rate of change in the mrs score (r = ). Patients who showed no improvement in mrs score tended to have a low DESH score as well as low preoperative MMSE and TMT-A scores. There were no differences in the areas of deep white matter hyperintensity and periventricular hyperintensity on the images between patients with and without an improved mrs score (15.6% vs 16.7%, respectively; p = 1.000). The DESH score did differ significantly between patients with and without improved scores on the inphgs (6.39 ± 1.76 vs 4.26 ± 1.69, respectively; p < 0.001), MMSE (6.63 ± 1.82 vs 5.09 ± 1.93; p = 0.010), TMT-A (6.32 ± 1.97 seconds vs 5.13 ± 1.93 seconds; p = 0.042), and TUG-t (6.48 ± 1.81 seconds vs 4.33 ± 1.59 seconds; p < 0.001). CONCLUSIONS MRI-based DESH scoring is useful for the prediction of neurological improvement and prognosis after surgery for inph. KEY WORDS idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus, disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus, SINPHONI trial, ventriculoperitoneal shunt, DESH score ABBREVIATIONS DESH = disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus; inph = idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus; inphgs = inph Grading Scale; MMSE = Mini-Mental State Examination; mrs = modified Ranking Scale; SINPHONI = Study of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus on Neurological Improvement; TMT-A = Trail Making Test-A; TUG-t = Timed 3-Meter Up and Go Test. SUBMITTED April 26, ACCEPTED September 19, INCLUDE WHEN CITING Published online February 3, 2017; DOI: / JNS * Drs. Shinoda and Hirai contributed equally to this work AANS, 2017
2 Utility of the MRI-based DESH score for postoperative inph prognosis Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph), a treatable syndrome in the elderly, is characterized by the classic triad of gait disturbance, dementia, and urinary disturbance. 2 Kitagaki et al. 10 first reported the appearance of disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus (DESH) on brain imaging in 1988, and DESH is now a recognized characteristic feature of inph and itself composed of the findings of ventriculomegaly, dilated sylvian fissures, tight high convexity, acute callosal angle, and focal sulcal dilation. 1,6,8,10 In the Study of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus on Neurological Improvement (SINPHONI) trial, the diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus is supported by an MRI-based scheme, and DESH was shown on MRI to have a high positive predictive value in identifying shunt-responsive inph patients. 6 Most cases of inph have characteristic imaging findings of DESH, but a subgroup of patients has much less typical DESH findings, 17 and therefore the prognostic difference according to the nature of the imaging findings is unclear. Hashimoto et al. 6 demonstrated that the MRI features of DESH namely, ventriculomegaly, tight high-convexity and medial subarachnoid spaces, and enlarged sylvian fissures are useful for the diagnosis of inph, but they did not describe other features, particularly the callosal angle and focal sulcal dilation. Furthermore, they did not explain the prognostic difference separated by the degree of the MRI features of DESH (e.g., more typical DESH findings, better outcome). In this study, we quantitatively evaluated the appearance of DESH on MRI prior to surgery in elderly patients with inph and investigated if the resulting DESH score was useful for predicting neurological improvement and prognosis. The principal utility of this study is the potential to develop a noninvasive and easy method for predicting response to CSF diversion in patients with inph. Methods Study Design Patients with suspected inph defined as the presence of 1 or more symptoms of the classic triad of gait disturbance, cognitive impairment, and urinary symptoms underwent MRI. The resulting images were reviewed by a group of neurosurgeons, neurologists, and a neuroradiologist, who assigned a DESH score that was reached by consensus. When their opinions were divided, they discussed it again and adopted the opinion of the majority. By separating the raters and the operating surgeon, there were no factors that influenced the data. DESH Score The DESH score was composed of the following 5 items, each scored from 0 to 2 (maximum score 10): ventriculomegaly, dilated sylvian fissures, tight high convexity, acute callosal angle, and focal sulcal dilation (Table 1). TABLE 1. Summarized DESH scales Grade Definition Ventriculomegaly 0 Normal (Evans index <0.3) 1 Slight dilatation (Evans index 0.3 & 0.35) 2 Dilatation (Evans index >0.35) Dilated sylvian fissures 0 Normal or narrow 1 Slight dilatation or unilateral 2 Bilateral dilatation Tight high convexity 0 Normal or wider than normal 1 Slight compression 2 Definitive compression Acute callosal angle 0 Obtuse angle (>100 ) 1 Not acute, but not obtuse angle ( 90 & 100 ) 2 Acute angle (<90 ) Focal sulcal dilation 0 Not present 1 Some present 2 Many present Ventriculomegaly The Evans index was measured on transverse images as the ratio between the maximum diameter of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles and the maximum inner diameter of the skull in the same section. 21 Ventriculomegaly was graded as follows: 0, normal (Evans index < 0.3); 1, slight dilation (Evans index ); or 2, dilation (Evans index > 0.35). Dilated Sylvian Fissures The coronal images used for the sylvian fissure ordinal were reconstructed at the level of the central part of the brainstem and angulated along the brainstem. 25 Dilation was graded as follows: 0, normal or narrow; 1, slight dilation or unilateral; or 2, bilateral dilation. Tight High Convexity Tight high convexity was evaluated on coronal and transverse images and graded as follows 20 0, normal or wider than normal; 1, slight compression; or 2, definitive compression. Acute Callosal Angle The callosal angle measured on a coronal MR image is the angle between the lateral ventricles through the posterior commissure and perpendicular to the anteriorposterior commissure plane. 8,9 The angle was graded as 0, obtuse (> 100 ); 1, not acute or obtuse ( ); or 2, acute (< 90 ). Focal Sulcal Dilation The accumulation of CSF in focally enlarged sulci, which has previously been referred to as transport sulci, was graded as follows 7,26 0, no sulci; 1, some sulci present; or 2, many sulci present. Regardless of a high or low DESH score, patients were 1437
3 N. Shinoda et al. included in the study if they satisfied the inclusion criteria stated below. Participants and Protocol The study was approved by the institutional review board and adhered to the principles set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki. It was performed as a retrospective, single-center cohort study to examine the 1-year outcome in inph patients who received a ventriculoperitoneal shunt with the Codman-Hakim programmable valve (CSF shunt valve, Codman, a Johnson & Johnson Co.) at our institution between April 2007 and March The initial pressure for the shunt system was set according to the patient s height and body mass index based on the estimated hydrostatic pressure and intraabdominal pressure. 14,15 The criteria for patient selection were determined in reference to the SINPHONI trial. 6 The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) age 60 years or older; 2) presence of 1 or more symptoms of the triad (gait disturbance, cognitive impairment, and urinary symptoms), which were measurable on inphgs 13 ; 3) MRI features of inph, with ventriculomegaly indicated by an Evans index score of > 0.3 on MRI 11 ; 4) the absence of known disorders causing ventriculomegaly; 5) normal CSF content (protein 50 mg/dl and cell count 3 cells/ml) and pressure ( 20 cm H 2 O); and 6) positive response on the CSF tap test. 24 The exclusion criteria were: 1) the presence of a musculoskeletal, cardiopulmonary, renal, hepatic, or mental disorder that would make it difficult to evaluate changes in symptoms; 2) obstacles to 1-year follow-up; and 3) bleeding diathesis or taking anticoagulant medication. In addition, we performed SPECT in patients with a Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) score of less than 20 and excluded other differential diseases, including Alzheimer s disease. Outcome Measures According to both the inph guidelines 19 and Guideline for management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: second edition, 16 improvement was determined as improvement of 1 or more levels on mrs, 1 points on the inph grading scale, 3 points on MMSE, a decrease of greater than 30% on TMT-A, and a decrease of greater than 10% on TUG-t. The primary end point was improvement in the mrs score 23 at 1 year after surgery, and the secondary outcome measures were the inphgs, 27 MMSE, 4 TMT-A, 5 and TUG-t 18 scores at 1 year after surgery. We examined the association between the DESH score and an improved score for these 5 measures at 1 year after surgery. In addition, we investigated leukoaraiosis on MR images, deep white matter hyperintensity, and periventricular hyperintensity, which are reported to be associated with the risk factors for vascular diseases such as hypertension and smoking. 3,12 Statistical Analysis The analysis was performed using R statistical software (Foundation for Statistical Computing). Statistical significance was examined using the Student t-test, and the correlation coefficients were tested using Microsoft Excel (version 2016; Microsoft Corp.). Results Patient Population The flow chart for this study is shown in Fig. 1. Of the 110 preregistered patients, 10 patients had a diagnosis of Alzheimer s disease or other disease as determined by SPECT and assessment of cognitive function, and 45 patients did not fulfill the CSF inclusion criteria or had positive findings on a tap test. Of the 55 patients who proceeded to registration, 5 withdrew (1 patient each due to traumatic intracranial hemorrhage, acute ischemic stroke, or aggravation of cirrhosis, and 2 patients were lost to follow-up), leaving 50 patients for analysis. Baseline Data The baseline data for the 50 patients are summarized in Table 2. Almost all patients were older than 70 years of age (mean age 77.6 ± 5.9 years [± SD]). The objective symptoms on inphgs were gait disturbance in 94% patients, cognitive impairment in 82% of patients, urinary symptoms in 64% of patients, and the classic triad in 48% of patients. On MRI review, the Evans index typically demonstrated a slight dilation (Evans index ), and, in most cases, the callosal angle was 100. The mean DESH score was 5.58 ± 2.01 (range 2 10) and showed a normal distribution (Fig. 2). Clinical Outcomes The mean initial valve pressure of the ventriculoperitoneal shunt was 14.5 ± 3.5 cm H 2 O, and 8 patients needed TABLE 2. Background characteristics and preoperative status of 50 patients with suspected inph Characteristic Value Demographics Mean age, yrs 77.6 ± 5.9 (61 87) Male sex 33 (66) Symptoms present Triad of symptoms 24 (48) Gait + cognitive impairment 13 (26) Gait + urinary symptom 6 (12) Cognitive impairment + urinary symptom 2 (4) Gait impairment only 4 (8) Cognitive impairment only 2 (4) Urinary symptom only 0 Lumbar puncture finding Mean CSF pressure, cm H 2 O 13.3 ± 1.92 ( ) MRI findings Mean Evans index, % 33.2 ± 2.8 Mean callosal angle, 91.7 ± 13.1 Mean DESH score 5.58 ± 2.01 Data are presented as the mean ± SD (range) or number (%) of patients. 1438
4 Utility of the MRI-based DESH score for postoperative inph prognosis FIG. 1. Flow chart for this study from the initial screening to the final analysis. to have the pressure readjusted throughout the follow-up period. At 1 year after surgery, the mean mrs score improved from 2.54 ± 0.76 to 2.02 ± 1.17 (p = 0.010). The improvement rate defined as a 1 or more levels of improvement on mrs was 64.0%, and the mean rate of change in the mrs score was 0.50 ± 0.93 (range 2 to 2) (Fig. 3A and B), indicating an inverse correlation between the DESH score and the rate of change in the mrs score (r = ; Fig. 4). FIG. 2. Distribution map of the DESH scores. 1439
5 N. Shinoda et al. FIG. 3. Distribution maps of the mrs scores before and 1 year after surgery (A) and the rate of change in mrs scores (B). Table 3 compares the preoperative scores between the patients with an improved mrs score (n = 32; 64.0%) and those without an improved mrs score (n = 18; no change in 10 patients and aggravation in 8 patients). There were marked significant differences between patients with and without improvement in relation to the DESH score (6.50 ± 2.0 vs 3.94 ± 1.5, respectively; p < 0.001) and preoperative MMSE score (23.7 ± 3.5 vs 17.7 ± 3.0; p < 0.001), as well as a difference in the preoperative TMT-A score (159.5 ± 49.2 vs ± 51.8; p = 0.020). On the other hand, no differences were found in relation to leukoaraiosis on the MR images between patients with and without improved mrs scores (15.6% vs 16.7%; p = 1.000). Thus, patients with an improved mrs score tended to have low preoperative DESH, MMSE, and TMT-A scores. All the secondary outcomes showed significant improvement at 1 year after surgery (Table 4). The mean inphgs score improved from 6.00 ± 1.93 to 5.00 ± 2.85 (p = 0.043), MMSE improved from ± 4.02 to ± 4.53 (p = 0.047), TMT-A improved from ± 69.4 seconds to ± 59.8 seconds (p = 0.049), and TUG-t improved from 27.5 ± 11.3 seconds to 21.1 ± 10.1 seconds (p = 0.046). As for the overall improvements after surgery, 62.0% of patients had an improved inphgs score of 1 or higher, 32.0% had an improved MMSE score of 3 or higher, 30% had a decreased TMT-A time, and 58.0% had FIG. 4. Inverse correlation between DESH score and the rate of change in mrs score (r = ). a greater than 10% decrease on TUG-t. Furthermore, there was a significant difference in the DESH score between patients with and without an improved inphgs score (DESH score 6.39 ± 1.76 vs 4.26 ± 1.69; p < 0.001), MMSE (DESH score 6.63 ± 1.82 vs 5.09 ± 1.93; p = 0.010), TMT- A (DESH score 6.32 ± 1.97 vs 5.13 ± 1.93; p = 0.042), and TUG-t (DESH score 6.48 ± 1.81 vs 4.33 ± 1.59; p < 0.001) (Table 5). Based on these findings, the DESH score appears to have a strong association with the mrs, inphgs, MMSE, TMT-A, and TUG-t scores. Discussion The improvement rate of 1 or more levels on mrs was 64.0% in our cohort, which is similar to the rate of 69.0% reported by the SINPHONI trial. 6 Our findings suggest that a high DESH score has an important positive predictive value in relation to neurological improvement after surgery for inph, in turn suggesting that MRI-based DESH scoring has diagnostic utility. A previous multicenter, prospective cohort study found an MRI-based diagnostic scheme highly useful and concluded that the DESH sign tight high convexity, medial TABLE 3. Comparison of preoperative scores between patients with and without an improved mrs score after surgery Variable Improvement in mrs Score (n = 32) No Improvement in mrs Score (n = 18)* p Value DESH score 6.50 ± ± 1.5 <0.001 inphgs score 5.68 ± ± MMSE score 23.7 ± ± 3.0 <0.001 TMT-A, sec ± ± TUG-t, sec 27.0 ± ± DWMH or PVH on MRI 5 (15.6) 3 (16.7) DWMH = deep white matter hyperintensity; PVH = periventricular hyperintensity. Data are presented as the mean ± SD or number (%) of patients. * No change was observed in 10 patients, and aggravation was observed in 8 patients. Determined using the Student t-test. Determined using the Fisher exact test. 1440
6 Utility of the MRI-based DESH score for postoperative inph prognosis TABLE 4. Comparison of secondary outcomes between preoperative status and 1-year postoperative status Variable Before Surgery 1 Yr After Surgery p Value* inphgs score 6.00 ± ± MMSE score ± ± TMT-A, secs ± ± TUG-t, secs 27.5 ± ± Data are shown as the mean ± SD. * p values were calculated using the Student t-test. subarachnoid spaces, and enlarged sylvian fissures with ventriculomegaly is valuable for the diagnosis of inph. 6 We assigned the DESH score on the basis of 5 parameters, each of which was scored simply from 0 to 2 for a maximum of 10 points: ventriculomegaly, dilated sylvian fissures, tight high convexity, acute callosal angle, and focal sulcal dilation. These 5 features mentioned above are very important in diagnosing inph, but we must be aware of their correlations. Ishii et al. 9 reported that the Evans index correlated well with the relative volume of the enlarged ventricle systems and sylvian fissures, and it correlated inversely with the relative volume of the sulci at the high convexity and midline. The callosal angle also showed a good negative correlation with the relative volume of the ventricle systems and sylvian fissures, and it correlated positively with the relative volume of the sulci at the high convexity and midline. In addition, Virhammar et al. 25 reported that the callosal angle correlated with focal sulcal dilation (r = -0.28), and they concluded that a small callosal angle, wide temporal horns, and the occurrence of disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus were significant predictors of a positive shunt outcome. In our study, leukoaraiosis was not related to improvement after surgery. A previous study showed that this parameter was a negative factor associated with the clinical improvement of inph; 21 however, a recent study reported that patients must not be excluded from shunt surgery on the basis of leukoaraiosis findings because patients with severe leukoaraiosis had a positive outcome rate similar to that of the entire sample. 22 There may be room for debate about this result, but the presence of leukoaraiosis on MRI does not predict a poor outcome of surgery and therefore should be used as an exclusion criterion for shunting. Our study examined both the usefulness of the DESH score that followed an MRI-based diagnostic scheme and the beneficial effect of shunt surgery on inph after 1 year. The diagnosis of inph is established in terms of response to surgery, and the efficacy of surgery depends on the diagnostic accuracy. 6 Therefore, the more accurate the diagnosis is, the more efficacious the treatment will be. Our study suggests a strong association between the DESH score and prognosis after surgery. MRI-based DESH scoring appears to be a useful objective method as it allows an easy and quantitative evaluation for predicting prognosis. Limitations These enrollment criteria were based solely on the SINPHONI trial. 6 This study was a single-center, retrospective cohort study, and it was exploratory. So we will TABLE 5. Comparison of the DESH scores between patients with and without improved scores after surgery Test No. of Patients (n = 50) DESH Score* p Value inphgs Improvement ± 1.76 <0.001 No improvement ± 1.69 MMSE Improvement ± No improvement ± 1.93 TMT-A Improvement ± No improvement ± 1.93 TUG-t Improvement ± 1.81 <0.001 No improvement ± 1.59 * Data are presented as the mean ± SD. p values were calculated using the Student t-test. need to conduct a prospective investigation to confirm the accuracy of our results. The cohort was relatively small because of the strict differential diagnosis and the robust inclusion criteria we used before registration by assessing cognitive function and performing SPECT. However, this is the first study to evaluate the utility of MRI-based DESH scoring for predicting prognosis after surgery, and it suggests the method is promising and that further study is warranted. Conclusions A typical, high DESH score had a positive predictive value for neurological improvement after surgery for inph. The DESH score does appear to be useful for the prediction of neurological improvement and prognosis after surgery. References 1. Adachi M, Kawanami T, Ohshima F, Kato T: Upper midbrain profile sign and cingulate sulcus sign: MRI findings on sagittal images in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus, Alzheimer s disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Radiat Med 24: , Adams RD, Fisher CM, Hakim S, Ojemann RG, Sweet WH: Symptomatic occult hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal-fluid pressure: a treatable syndrome. N Engl J Med 273: , Bradley WG Jr, Whittemore AR, Watanabe AS, Davis SJ, Teresi LM, Homyak M: Association of deep white matter infarction with chronic communicating hydrocephalus: implications regarding the possible origin of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 12:31 39, Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR: Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12: , Gordon NG: The Trail Making Test in neuropsychological diagnosis. J Clin Psychol 28: , Hashimoto M, Ishikawa M, Mori E, Kuwana N: Diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus is supported by MRI-based scheme: a prospective cohort study. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 7:18, Holodny AI, George AE, de Leon MJ, Golomb J, Kalnin AJ, 1441
7 N. Shinoda et al. Cooper PR: Focal dilation and paradoxical collapse of cortical fissures and sulci in patients with normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 89: , Ishii K, Kanda T, Harada A, Miyamoto N, Kawaguchi T, Shimada K, et al: Clinical impact of the callosal angle in the diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur Radiol 18: , Ishii K, Soma T, Shimada K, Oda H, Terashima A, Kawasaki R: Automatic volumetry of the cerebrospinal fluid space in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 3: , Kitagaki H, Mori E, Ishii K, Yamaji S, Hirono N, Imamura T: CSF spaces in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: morphology and volumetry. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19: , Klinge P, Marmarou A, Bergsneider M, Relkin N, Black PM: Outcome of shunting in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus and the value of outcome assessment in shunted patients. Neurosurgery 57 (3 Suppl):S40 S52, ii v, Krauss JK, Droste DW, Vach W, Regel JP, Orszagh M, Borremans JJ, et al: Cerebrospinal fluid shunting in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus of the elderly: effect of periventricular and deep white matter lesions. Neurosurgery 39: , Kubo Y, Kazui H, Yoshida T, Kito Y, Kimura N, Tokunaga H, et al: Validation of grading scale for evaluating symptoms of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 25:37 45, Miyake H, Kajimoto Y, Tsuji M, Ukita T, Tucker A, Ohmura T: Development of a quick reference table for setting programmable pressure valves in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 48: , Miyake H, Ohta T, Kajimoto Y, Nagao K: New concept for the pressure setting of a programmable pressure valve and measurement of in vivo shunt flow performed using a microflowmeter. Technical note. J Neurosurg 92: , Mori E, Ishikawa M, Kato T, Kazui H, Miyake H, Miyajima M, et al: Guideline for management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: second edition. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 52: , Mostafa T, Craven C, Patel NA, Dyson EW, Matloob SA, Chari A et al: DESH negative normal pressure hydrocephalus: can patients still benefit from shunt insertion? Fluids Barriers CNS 12 (Suppl 1):O52, Podsiadlo D, Richardson S: The timed Up & Go : a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 39: , Relkin N, Marmarou A, Klinge P, Bergsneider M, Black PM: Diagnosing idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 57 (3 Suppl):S4 S16, ii v, Sasaki M, Honda S, Yuasa T, Iwamura A, Shibata E, Ohba H: Narrow CSF space at high convexity and high midline areas in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus detected by axial and coronal MRI. Neuroradiology 50: , Toma AK, Holl E, Kitchen ND, Watkins LD: Evans index revisited: the need for an alternative in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 68: , Tullberg M, Jensen C, Ekholm S, Wikkelsø C: Normal pressure hydrocephalus: vascular white matter changes on MR images must not exclude patients from shunt surgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22: , van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J: Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19: , Virhammar J, Cesarini KG, Laurell K: The CSF tap test in normal pressure hydrocephalus: evaluation time, reliability and the influence of pain. Eur J Neurol 19: , Virhammar J, Laurell K, Cesarini KG, Larsson EM: Preoperative prognostic value of MRI findings in 108 patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35: , Wikkelsö C, Andersson H, Blomstrand C, Matousek M, Svendsen P: Computed tomography of the brain in the diagnosis of and prognosis in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neuroradiology 31: , Zemack G, Romner B: Adjustable valves in normal-pressure hydrocephalus: a retrospective study of 218 patients. Neurosurgery 51: , 2002 Disclosures The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper. Author Contributions Conception and design: Shinoda. Acquisition of data: Shinoda. Analysis and interpretation of data: Shinoda, Hirai. Drafting the article: Shinoda. Critically revising the article: Shinoda. Reviewed submitted version of manuscript: Shinoda. Approved the final version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors: Shinoda. Statistical analysis: Shinoda. Administrative/technical/material support: all authors. Study supervision: Hirai, Ueno. Correspondence Narihide Shinoda, Department of Neurosurgery, Shinko Memorial Hospital, Wakinohama-cho, Chuo-ku, Kobe, Hyogo , Japan. shinoda.narihide@shinkohp.or.jp. 1442
Published July 10, 2014 as /ajnr.A4046
 Published July 10, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4046 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Preoperative Prognostic Value of MRI Findings in 108 Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus J. Virhammar, K. Laurell,
Published July 10, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4046 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Preoperative Prognostic Value of MRI Findings in 108 Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus J. Virhammar, K. Laurell,
Alternate Methods: Pros and Cons (With a Focus on NPH)
 Alternate Methods: Pros and Cons (With a Focus on NPH) William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor and Chair Department of Radiology University of California, San Diego Alternate Imaging Methods for
Alternate Methods: Pros and Cons (With a Focus on NPH) William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor and Chair Department of Radiology University of California, San Diego Alternate Imaging Methods for
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is an
 J Neurosurg 120:178 184, 2014 AANS, 2014 The callosal angle measured on MRI as a predictor of outcome in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Clinical article Johan Virhammar, M.D., 1 Katarina Laurell,
J Neurosurg 120:178 184, 2014 AANS, 2014 The callosal angle measured on MRI as a predictor of outcome in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Clinical article Johan Virhammar, M.D., 1 Katarina Laurell,
Supplementary webappendix
 Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kazui H, Miyajima M, Mori E, Ishikawa
Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kazui H, Miyajima M, Mori E, Ishikawa
Utility of radiologic imaging in the diagnosis and follow up of normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Utility of radiologic imaging in the diagnosis and follow up of normal pressure hydrocephalus Poster No.: C-0312 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Rodríguez, D. Marquina, A. Mir Torres,
Utility of radiologic imaging in the diagnosis and follow up of normal pressure hydrocephalus Poster No.: C-0312 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Rodríguez, D. Marquina, A. Mir Torres,
John H. Woo, MD Associate Professor, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center October 28, 2016
 John H. Woo, MD Associate Professor, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center October 28, 2016 Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Bulk model (traditional) Production:
John H. Woo, MD Associate Professor, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center October 28, 2016 Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Bulk model (traditional) Production:
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph),
 clinical article J Neurosurg 125:1483 1492, 2016 One-year outcome in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: comparison of lumboperitoneal shunt to ventriculoperitoneal shunt Masakazu Miyajima,
clinical article J Neurosurg 125:1483 1492, 2016 One-year outcome in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: comparison of lumboperitoneal shunt to ventriculoperitoneal shunt Masakazu Miyajima,
Natural history of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus
 DOI 10.1007/s10143-011-0316-7 REVIEW Natural history of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Ahmed K. Toma & Simon Stapleton & Marios C. Papadopoulos & Neil D. Kitchen & Laurence D. Watkins Received:
DOI 10.1007/s10143-011-0316-7 REVIEW Natural history of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Ahmed K. Toma & Simon Stapleton & Marios C. Papadopoulos & Neil D. Kitchen & Laurence D. Watkins Received:
First identified in 1965,5 idiopathic normal pressure. focus Neurosurg Focus 41 (3):E2, 2016
 neurosurgical focus Neurosurg Focus 41 (3):E2, 2016 Timing of surgical treatment for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: association between treatment delay and reduced short-term benefit Sharif
neurosurgical focus Neurosurg Focus 41 (3):E2, 2016 Timing of surgical treatment for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: association between treatment delay and reduced short-term benefit Sharif
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35771 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Walter Miguel Title: Ventricular dilatation in aging and dementia Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35771 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Walter Miguel Title: Ventricular dilatation in aging and dementia Issue
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126: , 2017
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:2002 2009, 2017 Disability risk or unimproved symptoms following shunt surgery in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: post hoc analysis of SINPHONI-2
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:2002 2009, 2017 Disability risk or unimproved symptoms following shunt surgery in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: post hoc analysis of SINPHONI-2
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Eide and Pripp FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS
 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS Increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients compared to a population-based cohort from the HUNT3 survey Eide and Pripp
FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS Increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients compared to a population-based cohort from the HUNT3 survey Eide and Pripp
CSF Spaces in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Morphology and Volumetry
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1277 1284, August 1998 CSF Spaces in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Morphology and Volumetry Hajime Kitagaki, Etsuro Mori, Kazunari Ishii, Shigeru Yamaji, Nobutsugu
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1277 1284, August 1998 CSF Spaces in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Morphology and Volumetry Hajime Kitagaki, Etsuro Mori, Kazunari Ishii, Shigeru Yamaji, Nobutsugu
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
subdural hematoma : SDH
 Dementia Japan 26 : 343-348, 2012 343 85 NPH NPH Masaya Oda 1, Masanori Hiji 1, Hijiri Ito 1, Yuishin Izumi 1,2 1 728-0001 605-20 Department of Neurology, Mifukai Vihara Hananosato Hospital 605-20 Yamaga
Dementia Japan 26 : 343-348, 2012 343 85 NPH NPH Masaya Oda 1, Masanori Hiji 1, Hijiri Ito 1, Yuishin Izumi 1,2 1 728-0001 605-20 Department of Neurology, Mifukai Vihara Hananosato Hospital 605-20 Yamaga
Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases-
 Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases- Mitsuru SEIDA, Umeo ITO, Shuichi TOMIDA, Shingo YAMAZAKI and Yutaka INABA* Department
Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases- Mitsuru SEIDA, Umeo ITO, Shuichi TOMIDA, Shingo YAMAZAKI and Yutaka INABA* Department
Falling and Forgetting
 Falling and Forgetting Dr TC Chan Dr LW Chu Inter-hosipital Geriatric Meeting 29-5-2009 Case 1 Mr A 86/M ADL-I Walk unaided Live with family Non smoker non drinker Good past health Attend A&E 10/2008 due
Falling and Forgetting Dr TC Chan Dr LW Chu Inter-hosipital Geriatric Meeting 29-5-2009 Case 1 Mr A 86/M ADL-I Walk unaided Live with family Non smoker non drinker Good past health Attend A&E 10/2008 due
ORIGINAL PAPER. Faculty of Physical Therapy, Mahidol University, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand 2
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 53 60, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.1.53 ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of spinal tap test on the performance of sit-to-stand, walking, and turning in patients with idiopathic normal pressure
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 53 60, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.1.53 ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of spinal tap test on the performance of sit-to-stand, walking, and turning in patients with idiopathic normal pressure
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:359 367, 2016 A double-blind randomized trial on the clinical effect of different shunt valve settings in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus Dan Farahmand, MD, 1
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:359 367, 2016 A double-blind randomized trial on the clinical effect of different shunt valve settings in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus Dan Farahmand, MD, 1
Citation for the original published paper (version of record):
 http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Johansson, E., Ambarki, K.,
http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Johansson, E., Ambarki, K.,
Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgical Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
 J Neurosurg 52:371-377, 1980 Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Results of shunting in 62 patients PETER McL. BLACK, M.D., PH.D. Neurosurgical Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
J Neurosurg 52:371-377, 1980 Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Results of shunting in 62 patients PETER McL. BLACK, M.D., PH.D. Neurosurgical Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
N ormal pressure hydrocephalus was first described by
 PAPER Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus B Kahlon, G Sundbärg, S Rehncrona... See end of article
PAPER Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus B Kahlon, G Sundbärg, S Rehncrona... See end of article
The Challenges of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
 CE/CME The Challenges of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus A Case-Based Review Freddi Segal-Gidan, PA, PhD Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is one of the few reversible causes of dementia. Unfortunately,
CE/CME The Challenges of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus A Case-Based Review Freddi Segal-Gidan, PA, PhD Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is one of the few reversible causes of dementia. Unfortunately,
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
Confusional state. Digit Span. Mini Mental State Examination MMSE. confusional state MRI
 10 304 29 3 confusional state MRI 29 3 304 311 2009 Key Words memory test attention brain region causative disease subcortical dementia 1 Confusional state Digit Span 1 1 5 4 Mini Mental State Examination
10 304 29 3 confusional state MRI 29 3 304 311 2009 Key Words memory test attention brain region causative disease subcortical dementia 1 Confusional state Digit Span 1 1 5 4 Mini Mental State Examination
Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report
 Neurosurg Focus 7 (4):Article 5, 1999 Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report Akira Watanabe, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 7 (4):Article 5, 1999 Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report Akira Watanabe, M.D.,
CASE REPORT. Jackson Hayes, Marie Roguski and Ron I Riesenburger *
 Hayes et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:393 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Rapid resolution of an acute subdural hematoma by increasing the shunt valve pressure in
Hayes et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:393 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Rapid resolution of an acute subdural hematoma by increasing the shunt valve pressure in
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Hydrocephalus 1/16/2015. Hydrocephalus. Functions of Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Flow of CSF
 Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
arcuate fasciculus of patients with aphasia caused by acute cerebral infarct.progress in Rehabilitation Medicine 1: ,2016
 英文論文 2016 1. Miyake H : Shunt Devices for the Treatment of Adult Hydrocephalus:Recent Progress and Characteristics Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 56 No.4:274-283 2016 2. Koyama T, Domen K:Reduced diiffusion tensor
英文論文 2016 1. Miyake H : Shunt Devices for the Treatment of Adult Hydrocephalus:Recent Progress and Characteristics Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 56 No.4:274-283 2016 2. Koyama T, Domen K:Reduced diiffusion tensor
The classic teaching is that cerebrospinal fluid is formed primarily. CSF Flow in the Brain in the Context of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
 REVIEW ARTICLE CSF Flow in the Brain in the Context of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus W.G. Bradley Jr ABSTRACT SUMMARY: CSF normally flows back and forth through the aqueduct during the cardiac cycle. During
REVIEW ARTICLE CSF Flow in the Brain in the Context of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus W.G. Bradley Jr ABSTRACT SUMMARY: CSF normally flows back and forth through the aqueduct during the cardiac cycle. During
Outcomes of chronic subdural hematoma with preexisting comorbidities causing disturbed consciousness
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:1042 1046, 2017 Outcomes of chronic subdural hematoma with preexisting comorbidities causing disturbed consciousness *Yasuaki Abe, MD, Keisuke Maruyama, MD, PhD, Shigeomi
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:1042 1046, 2017 Outcomes of chronic subdural hematoma with preexisting comorbidities causing disturbed consciousness *Yasuaki Abe, MD, Keisuke Maruyama, MD, PhD, Shigeomi
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
 Nuclear Medicine Review 2015, 18, 2: 84 88 DOI: 10.5603/NMR.2015.0020 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Early brain perfusion improvement after ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery in patients with
Nuclear Medicine Review 2015, 18, 2: 84 88 DOI: 10.5603/NMR.2015.0020 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Early brain perfusion improvement after ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery in patients with
Visual Rating Scale Reference Material. Lorna Harper Dementia Research Centre University College London
 Visual Rating Scale Reference Material Lorna Harper Dementia Research Centre University College London Background The reference materials included in this document were compiled and used in relation to
Visual Rating Scale Reference Material Lorna Harper Dementia Research Centre University College London Background The reference materials included in this document were compiled and used in relation to
Dual-task related gait changes after CSF tapping: a new way to identify idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Allali et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2013, 10:117 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Open Access Dual-task related gait changes after CSF tapping: a new
Allali et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2013, 10:117 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Open Access Dual-task related gait changes after CSF tapping: a new
Psychology, 3 Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology,
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 115 124) QUANTITATIVE CEREBRAL ANATOMY
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 115 124) QUANTITATIVE CEREBRAL ANATOMY
HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI, M.D., PH.D., TAKEO TANISHIMA, M.D., PH.D., Clinical Material and Methods
 J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus.
 Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. Kahlon, Babar; Sundbärg, Göran; Rehncrona, Stig Published in:
Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. Kahlon, Babar; Sundbärg, Göran; Rehncrona, Stig Published in:
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Prevalence of Schizophrenia in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus RESEARCH HUMAN CLINICAL STUDIES
 RESEARCH HUMAN CLINICAL STUDIES Vasco Vanhala, BMed Antti Junkkari, MD, PhD Ville E. Korhonen, BMed Mitja I. Kurki, PhD Mikko Hiltunen, PhD Tuomas Rauramaa, MD, PhD Ossi Nerg, MD # Anne M. Koivisto, MD,
RESEARCH HUMAN CLINICAL STUDIES Vasco Vanhala, BMed Antti Junkkari, MD, PhD Ville E. Korhonen, BMed Mitja I. Kurki, PhD Mikko Hiltunen, PhD Tuomas Rauramaa, MD, PhD Ossi Nerg, MD # Anne M. Koivisto, MD,
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Counting-backward test for executive function in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Acta Neurol Scand 2012: 126: 279 286 DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2012.01644.x Ó 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Counting-backward test for executive function in idiopathic normal
Acta Neurol Scand 2012: 126: 279 286 DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2012.01644.x Ó 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Counting-backward test for executive function in idiopathic normal
Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset Shusuke Yamamoto, MD, Satoshi Hori, MD, PhD,
CLINICAL ARTICLE Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset Shusuke Yamamoto, MD, Satoshi Hori, MD, PhD,
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Lumbar infusion test in normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Acta Neurol Scand 2005: 111: 379 384 DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2005.00417.x Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Lumbar infusion test in normal pressure hydrocephalus Kahlon
Acta Neurol Scand 2005: 111: 379 384 DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2005.00417.x Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Lumbar infusion test in normal pressure hydrocephalus Kahlon
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN
 Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
inph is a syndrome characterized by the triad of gait disturbance,
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hattori T. Yuasa S. Aoki R. Sato H. Sawaura T. Mori H. Mizusawa Altered Microstructure in Corticospinal Tract in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Comparison with Alzheimer
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hattori T. Yuasa S. Aoki R. Sato H. Sawaura T. Mori H. Mizusawa Altered Microstructure in Corticospinal Tract in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Comparison with Alzheimer
Department of Neurosurgery, Showa University School of Medicine; and 2 Tokyo Midtown Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Detection rates and sites of unruptured intracranial aneurysms according to sex and age: an analysis of MR angiography based brain examinations of 4070 healthy Japanese adults Yohichi
CLINICAL ARTICLE Detection rates and sites of unruptured intracranial aneurysms according to sex and age: an analysis of MR angiography based brain examinations of 4070 healthy Japanese adults Yohichi
A change in brain white matter after shunt surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a tract based spatial statistics study
 DOI 10.1186/s12987-016-0048-8 Fluids and Barriers of the CNS RESEARCH Open Access A change in brain white matter after shunt surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a tract based spatial statistics
DOI 10.1186/s12987-016-0048-8 Fluids and Barriers of the CNS RESEARCH Open Access A change in brain white matter after shunt surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a tract based spatial statistics
Received: 15 September 2014 /Accepted: 20 November 2014 /Published online: 6 December 2014 # Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2014
 Neuroradiology (2015) 57:269 274 DOI 10.1007/s00234-014-1472-6 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY Quantification of structural cerebral abnormalities on MRI 18 months after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in
Neuroradiology (2015) 57:269 274 DOI 10.1007/s00234-014-1472-6 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY Quantification of structural cerebral abnormalities on MRI 18 months after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2
 Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
MR Imaging of the Hippocampus in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Correlations with Cortical Alzheimer s Disease Confirmed by Pathologic Analysis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:409 414, February 2000 MR Imaging of the Hippocampus in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Correlations with Cortical Alzheimer s Disease Confirmed by Pathologic Analysis Sakari Savolainen,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:409 414, February 2000 MR Imaging of the Hippocampus in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Correlations with Cortical Alzheimer s Disease Confirmed by Pathologic Analysis Sakari Savolainen,
ventriculography compared, those with mass lesions involving the cerebral hemispheres were excluded.
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 203-211 Computerized tomography (the EMAI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography J. GAWLER, G. H. DU BOULAY,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 203-211 Computerized tomography (the EMAI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography J. GAWLER, G. H. DU BOULAY,
Aqueductal CSF stroke volume (ACSV) measured by
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Scollato P. Gallina B. Gautam G. Pellicanò C. Cavallini R. Tenenbaum N. Di Lorenzo Changes in Aqueductal CSF Stroke Volume in Shunted Patients with Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Scollato P. Gallina B. Gautam G. Pellicanò C. Cavallini R. Tenenbaum N. Di Lorenzo Changes in Aqueductal CSF Stroke Volume in Shunted Patients with Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Focused ultrasound (FUS) thalamotomy was recently. FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 44 (2):E5, 2018
 NEUROSURGICAL FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 44 (2):E5, 2018 Predicting lesion size during focused ultrasound thalamotomy: a review of 63 lesions over 3 clinical trials Aaron E. Bond, MD, PhD, and W. Jeffrey Elias,
NEUROSURGICAL FOCUS Neurosurg Focus 44 (2):E5, 2018 Predicting lesion size during focused ultrasound thalamotomy: a review of 63 lesions over 3 clinical trials Aaron E. Bond, MD, PhD, and W. Jeffrey Elias,
Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Association of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase with disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid-space in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Nishida et al. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 214, 11:9 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS RESEARCH Open Access Association of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase with disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid-space
Nishida et al. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 214, 11:9 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS RESEARCH Open Access Association of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase with disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid-space
Morphometric Study of the Midsagittal MR Imaging Plane in Cases of Hydrocephalus and Atrophy and in Normal Brains
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1674 1679, October 2001 Morphometric Study of the Midsagittal MR Imaging Plane in Cases of Hydrocephalus and Atrophy and in Normal Brains Yoram Segev, Ur Metser, Liana Beni-Adani,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1674 1679, October 2001 Morphometric Study of the Midsagittal MR Imaging Plane in Cases of Hydrocephalus and Atrophy and in Normal Brains Yoram Segev, Ur Metser, Liana Beni-Adani,
Serial Mini-Mental Status Examination to Evaluate Cognitive Outcome in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2015;11(1):6-10 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2015.11.1.6 Serial Mini-Mental Status Examination to Evaluate Cognitive Outcome in
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2015;11(1):6-10 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2015.11.1.6 Serial Mini-Mental Status Examination to Evaluate Cognitive Outcome in
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Neurosurgery. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2006 January 25.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neurosurgery. 2004 September ; 55(3): 582 593. DECREASES IN VENTRICULAR VOLUME CORRELATE WITH DECREASES IN VENTRICULAR PRESSURE IN
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neurosurgery. 2004 September ; 55(3): 582 593. DECREASES IN VENTRICULAR VOLUME CORRELATE WITH DECREASES IN VENTRICULAR PRESSURE IN
Two computerized methods used to analyze intracranial pressure B waves: comparison with traditional visual interpretation
 J Neurosurg 94:392 396, 2001 Two computerized methods used to analyze intracranial pressure B waves: comparison with traditional visual interpretation ANDERS EKLUND, MSC.E.P., AINA ÅGREN-WILSSON, M.D.,
J Neurosurg 94:392 396, 2001 Two computerized methods used to analyze intracranial pressure B waves: comparison with traditional visual interpretation ANDERS EKLUND, MSC.E.P., AINA ÅGREN-WILSSON, M.D.,
Chronic Subdural Hematoma Following Maxillofacial Fracture: Report of 2 Cases
 Shimane J. Med. Sci., Vol.35 pp.15-19, 2018 Chronic Subdural Hematoma Following Maxillofacial Fracture: Report of 2 Cases Takashi KOIKE 1,2, Takahiro KANNO 2, Masaaki KARINO 2, Aya YOSHINO 2, Joji SEKINE
Shimane J. Med. Sci., Vol.35 pp.15-19, 2018 Chronic Subdural Hematoma Following Maxillofacial Fracture: Report of 2 Cases Takashi KOIKE 1,2, Takahiro KANNO 2, Masaaki KARINO 2, Aya YOSHINO 2, Joji SEKINE
Increased Intracranial Volume: A Clue to the Etiology of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus?
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1479 1484, October 2004 Increased Intracranial Volume: A Clue to the Etiology of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus? William G. Bradley, Francis G. Safar, Claudia Hurtado,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1479 1484, October 2004 Increased Intracranial Volume: A Clue to the Etiology of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus? William G. Bradley, Francis G. Safar, Claudia Hurtado,
Efficacy of Lumboperitoneal Shunting in Patients with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.18702-16.1 Received: 17.08.2016 / Accepted: 17.09.2016 Published Online: 14.11.2016 Turk Neurosurg 28(1):62-66, 2018 Original Investigation Efficacy of Lumboperitoneal Shunting
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.18702-16.1 Received: 17.08.2016 / Accepted: 17.09.2016 Published Online: 14.11.2016 Turk Neurosurg 28(1):62-66, 2018 Original Investigation Efficacy of Lumboperitoneal Shunting
Don t lose your life to NPH.
 Don t lose your life to NPH. NPH The little-known neurological disorder that affects more than one in every two hundred adults over 55. Never heard of NPH? Well, you re not alone. NPH, or Normal Pressure
Don t lose your life to NPH. NPH The little-known neurological disorder that affects more than one in every two hundred adults over 55. Never heard of NPH? Well, you re not alone. NPH, or Normal Pressure
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Satoh M. 1, Ishikawa H. 1, Meguro K. 1,2, Kasuya M. 1, Ishii H. 3, and Yamaguchi S. 2
 CYRIC Annual Report 2009 VIII 15. Occipital Glucose Metabolic Decrease by Donepezil Treatment Correlated with the Improvement of Visual Hallucinations in Dementia with Lewy Bodies: the Osaki-Tajiri Project
CYRIC Annual Report 2009 VIII 15. Occipital Glucose Metabolic Decrease by Donepezil Treatment Correlated with the Improvement of Visual Hallucinations in Dementia with Lewy Bodies: the Osaki-Tajiri Project
PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY. Reversible. dementias Blackwell Science Ltd
 138 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Reversible dementias JUNE 2002 139 Gunhild Waldemar Memory Disorders Research Unit, Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100
138 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Reversible dementias JUNE 2002 139 Gunhild Waldemar Memory Disorders Research Unit, Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100
In some patients with pituitary macroadenoma, visual acuity
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
How to read the report
 Dear Client, This is your second opinion report. How to read the report 1. Always consult your findings with your doctor. 2. Please bear in mind that the report is based only on the information you provide
Dear Client, This is your second opinion report. How to read the report 1. Always consult your findings with your doctor. 2. Please bear in mind that the report is based only on the information you provide
EVects of transient and persistent cerebrospinal fluid drainage on sleep disordered breathing in patients with idiopathic adult hydrocephalus syndrome
 J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998;65:497 501 497 Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Umea University Hospital, Sweden B Kristensen J Malm T Rabben Correspondence to: Dr Bo Kristensen, Department of Clinical
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998;65:497 501 497 Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Umea University Hospital, Sweden B Kristensen J Malm T Rabben Correspondence to: Dr Bo Kristensen, Department of Clinical
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Common Misdiagnosis of a Common Neurological Disorder How Are We Misdiagnosing Essential Tremor? Samay Jain, MD; Steven E. Lo, MD; Elan D. Louis, MD, MS Background: As a common neurological
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Common Misdiagnosis of a Common Neurological Disorder How Are We Misdiagnosing Essential Tremor? Samay Jain, MD; Steven E. Lo, MD; Elan D. Louis, MD, MS Background: As a common neurological
MR Differential Diagnosis of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus and Alzheimer Disease: Significance of Perihippocampal Fissures
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:813 819, May 1998 MR Differential Diagnosis of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus and Alzheimer Disease: Significance of Perihippocampal Fissures Andrei I. Holodny, Robert Waxman, Ajax
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:813 819, May 1998 MR Differential Diagnosis of Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus and Alzheimer Disease: Significance of Perihippocampal Fissures Andrei I. Holodny, Robert Waxman, Ajax
Yoji Kuramoto, Daisuke Shimo, Shinya Hori, Kazuyuki Mikami, Toshiaki Bando, Takahiro Kuroyama, Narihide Shinoda, and Yasushi Ueno
 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0095 A Case of Vertebro-vertebral Arteriovenous Fistula Clinically Diagnosed as Segmental Arterial Mediolysis Complicated by Celiac Artery Aneurysm Suspected in a State of Impending
DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0095 A Case of Vertebro-vertebral Arteriovenous Fistula Clinically Diagnosed as Segmental Arterial Mediolysis Complicated by Celiac Artery Aneurysm Suspected in a State of Impending
Quantitative analysis for a cube copying test
 86 99 103 2010 Original Paper Quantitative analysis for a cube copying test Ichiro Shimoyama 1), Yumi Asano 2), Atsushi Murata 2) Naokatsu Saeki 3) and Ryohei Shimizu 4) Received September 29, 2009, Accepted
86 99 103 2010 Original Paper Quantitative analysis for a cube copying test Ichiro Shimoyama 1), Yumi Asano 2), Atsushi Murata 2) Naokatsu Saeki 3) and Ryohei Shimizu 4) Received September 29, 2009, Accepted
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Over the last few decades, endoscopic third ventriculostomy
 clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:734 738, 2016 Long-term follow-up of endoscopic third ventriculostomy performed in the pediatric population Matthew G. Stovell, MBBS, 1 Rasheed Zakaria, MA, BMBCh,
clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:734 738, 2016 Long-term follow-up of endoscopic third ventriculostomy performed in the pediatric population Matthew G. Stovell, MBBS, 1 Rasheed Zakaria, MA, BMBCh,
Transient Bilateral Oculomotor Nerve. Palsy (TOP) Associated with Ruptured. Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm: A Case Report
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Insights in Neurosurgery ISSN 2471-9633 DOI: 10.21767/2471-9633.100012 Abstract Transient Bilateral Oculomotor Nerve Palsy (TOP) Associated with Ruptured
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Insights in Neurosurgery ISSN 2471-9633 DOI: 10.21767/2471-9633.100012 Abstract Transient Bilateral Oculomotor Nerve Palsy (TOP) Associated with Ruptured
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING
 ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with
 Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY
 Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
A discussion of the optimal treatment of intracranial aneurysm rupture in elderly patients
 A discussion of the optimal treatment of intracranial aneurysm rupture in elderly patients C. Liu Neurology Department, The Central Hospital of Luoyang Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Luoyang City,
A discussion of the optimal treatment of intracranial aneurysm rupture in elderly patients C. Liu Neurology Department, The Central Hospital of Luoyang Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Luoyang City,
Normal pressure hydrocephalus is a reversible cause of dementia,
 Published December 0, 0 as 0.374/ajnr.A3368 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Differential Diagnosis of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus by MRI Mean Diffusivity Histogram Analysis M. Ivkovic, B. Liu, F. Ahmed, D. Moore,
Published December 0, 0 as 0.374/ajnr.A3368 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Differential Diagnosis of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus by MRI Mean Diffusivity Histogram Analysis M. Ivkovic, B. Liu, F. Ahmed, D. Moore,
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has the potential to
 Frequency and Location of Microbleeds in Patients With Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage Gudrun Roob, MD; Anita Lechner, MD; Reinhold Schmidt, MD; Erich Flooh, MSc; Hans-Peter Hartung, MD; Franz Fazekas,
Frequency and Location of Microbleeds in Patients With Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage Gudrun Roob, MD; Anita Lechner, MD; Reinhold Schmidt, MD; Erich Flooh, MSc; Hans-Peter Hartung, MD; Franz Fazekas,
Infusion studies in clinical practice. Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London
 Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms
 33 Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms Isao NAITO, M.D., Shin TAKATAMA, M.D., Naoko MIYAMOTO, M.D., Hidetoshi SHIMAGUCHI, M.D., and Tomoyuki IWAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
33 Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms Isao NAITO, M.D., Shin TAKATAMA, M.D., Naoko MIYAMOTO, M.D., Hidetoshi SHIMAGUCHI, M.D., and Tomoyuki IWAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
Evaluation of Preventive Care Program for Cognitive Function Decline among Community-dwelling Frail Elderly People A Pilot Study
 Journal of Japan Academy of Community Health Nursing Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 87 92, 2007 Evaluation of Preventive Care Program for Cognitive Function Decline among Community-dwelling Frail Elderly People A
Journal of Japan Academy of Community Health Nursing Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 87 92, 2007 Evaluation of Preventive Care Program for Cognitive Function Decline among Community-dwelling Frail Elderly People A
We have previously reported good clinical results
 J Neurosurg 113:48 52, 2010 Gamma Knife surgery as sole treatment for multiple brain metastases: 2-center retrospective review of 1508 cases meeting the inclusion criteria of the JLGK0901 multi-institutional
J Neurosurg 113:48 52, 2010 Gamma Knife surgery as sole treatment for multiple brain metastases: 2-center retrospective review of 1508 cases meeting the inclusion criteria of the JLGK0901 multi-institutional
