Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years)
|
|
|
- Matthew Shaw
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years) Yoshiharu Kawaguchi 1), Masato Nakano 1), Taketoshi Yasuda 1), Shoji Seki 1), Kayo Suzuki 1), Yasuhito Yahara 1), Hiroto Makino 1), Masahiko Kanamori 2) and Tomoatsu Kimura 1) 1) Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Toyama, Toyama, Japan 2) Department of Human Science, University of Toyama, Toyama, Japan Abstract: Introduction: In more than 20 years follow-up after cervical laminoplasty, some patients died at an early stage, within 5 years postoperatively. The details remain unclear. This study was conducted to elucidate the clinical features in patients who died at an early stage after cervical laminoplasty to determine possible preventive measures against early death after surgery. Methods: A total of 74 patients who died with the follow-up period were included. The patients were divided into two groups: patients with a short survival period (S group, died 5 years after surgery) and patients with a long survival period (L group, died >5 years after surgery). Diseases, gender, age, causes of the death, general complications before surgery, and the pre- and postoperative JOA scores were compared between the two groups. Results: Eleven patients (15%) died within 5 years after laminoplasty. The average age at death in the S group was 68.7 years which was considerably younger than that in the L group (80.2 years). The ratio of pneumonia was higher in the S group, compared to that in the L group. Postoperative JOA score in the S group was lower than that in the L group. Conclusions: 11 patients out of 74 patients (15%) died within 5 years after laminoplasty. The average age at the death in the S group was much younger than that in the L group. The postoperative JOA score in the S group was lower than that in the L group. As pneumonia was more prevalent in the S group, it might be reasonable to give the information for the protection of pneumonia after cervical laminoplasty. Keywords: cervical laminoplasty, cervical spondylosis, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament, life expectancy, cause of death, cervical spine, operative treatment Spine Surg Relat Res 2017; 1(4): Introduction Cervical laminoplasty has been indicated for treating the patients with cervical compressive myelopathy due to cervical spondylosis (CS) and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) since 1980 s. In our recent study, we analyzed the surgical outcomes of more than 20 years follow up after en bloc cervical laminoplasty and found that cervical laminoplasty is a safe procedure, because there were no patients who died due to surgical complications 1). The previous studies demonstrated that the average life expectancy from surgery to death was 13.4 ± 7.4 years 2).There was no difference in the survival rate between the CS and OPLL patients. The most frequent cause of death was malignant tumor, followed by ischemic heart disease and cerebral infarction. However, there were some patients who died at the early stage in that follow up. As the average life expectancy was 13 years, it might be reasonable to judge the early death as the death within 5 years from surgery. In the clinical point of view, it is beneficial for spinal surgeons to know the detailed information of the early death after cervical laminoplasty when therapeutic strategy is considered for the patients with compressive myelopathy. This information might also be beneficial to consider the post-operative care. This study was conducted for detecting the clinical features in patients who died at the early stage, within 5 years, after cervical laminoplasty to seek the possible preventive measures against the early death. Corresponding author: Yoshiharu Kawaguchi, zenji@med.u-toyama.ac.jp Received: April 18, 2017, Accepted: May 23, 2017 Copyright 2017 The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research 174
2 Spine Surg Relat Res 2017; 1(4): Materials and Methods Two hundred and sixteen patients underwent en bloc cervical laminoplasty for the treatment of cervical compressive myelopathy due to CS or OPLL between 1981 and 1994 at our university hospital. It was possible to follow 148 patients for more than 20 years. There were 68 surviving patients and 80 patients who had died by the time of their last follow-up. Demographic data of patients followed for more than 20 years after cervical laminoplasty are shown in Fig. 1. Clinical diagnosis was made by physical examination, plain radiography, CT, myelography, and MRI. This study was carried out using the data of patients with CS or OPLL only. Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, destructive spondyloarthropathy, spinal metastasis, and primary spinal tumors were strictly excluded. No patient in this study had a medical history of being treated for malignant tumors. En bloc laminoplasty, as proposed by Itoh and Tsuji 3,4), was utilized for the decompression of the spinal cord in all patients. The detail of this procedure was reported in previous papers 2-4). Eighty patients who had died at the last follow up were subjected to this study. There were 44 patients with CS (31 males and 13 females) and 36 patients with OPLL (30 males and 6 females). Detailed information regarding the death was obtained from the medical record in our hospital or the family members of patients. It was unclear for the family members of 5 patients (2 males with CS and 3 males with OPLL) to declare the exact year of patients death. These patients were excluded. One CS patient who committed suicide 1 year after surgery was also excluded. A total of 74 patients were subjected to this study. The patients were divided in to two groups; patients with short survival times (S group) and patients with long survive times (L group). The S group was the category of patients who died 5 years after surgery and the L group was that of patients who died >5 years after surgery. The following data was compared in the two groups. Those were diseases, gender, age, causes of the death, and general complications before surgery. The neurological evaluation was graded using the scale devised by the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA), called JOA score 5). The preoperative JOA score was compared between the S group and the L group. The rate of recovery, which indicates the degree of normalization after surgery, was calculated using the following formula: (postop. score preop. score) 100 / {17 (full score) preop. score} The postoperative score within 1 year after surgery was used for the analysis, because of the possible effect of the causes regarding the early death in the S group. The postoperative JOA score and recovery rate were also compared between the two groups. Although we obtained data for respiratory function in all the patients before surgery, however we could not access data because the surgery was carried out more than 20 years CS OPLL total survivors pa nts that d unknown males emales total CS OPLL total CS OPLL total CS OPLL total Figure 1. Demographic data of patients followed for more than 20 years after cervical laminoplasty. Results of 216 patients treated by cervical laminoplasty from 1981 to Sixty-eight patients died at the follow-up. CS: cervical spondylosis, OPLL: ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. The same figure was used in reference No. 2. ago. Most of the medical sheets did not exist in the hospital. Statistical analysis Data were presented as the mean value ± standard deviation. Fisher s exact test was used for the analysis of the gender and disease distribution between the S and L groups. The same statistics were used for the analysis of incidence regarding the causes of the death. A t-test with Welch s correction was used for the statistical analysis of the difference in mean age, JOA score, and recovery rate between the S and L groups. StatMate software version 5.01 (Japan) was used for the analysis and p<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Results Fig. 2 showed the data of when patients died after surgery. Eleven patients (15%) died within 5 years after cervical laminoplasty. These patients were in the short survival time group (S group). The detailed demographic data were shown in Table 1. There were 8 males (5 CS and 3 OPLL) and 3 females (3 CS). The average age at operation in the S group was 65.6 ± 7.7 years and the age at death was 68.7 ± 7.3 years. The average period of survival was 3.1 ± 1.3 years in the S group. Sixty-three patients were included in the long survival time group (L group). Comparison of the demographic data showed that there were no statistical differences in gender, diseases of patients, and the age at operation (Table 2). However, the age at death in the S group was lesser than that in the L group (80.2 ± 7.2 years old). As for the preoperative general complications, one patient 175
3 Spine Surg Relat Res 2017; 1(4): Number 6 5 CS OPLL (years) Figure 2. The period of death caused after cervical laminoplasty. CS: cervical spondylosis, OPLL: ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Table 1. Demographic Data of the Patients in the S Group. No. gender disease age at op. age at the death cause of the death pre op. complication 1 male OPLL pneumonia 2 male CS pneumonia DM 3 male CS cerebral infarction 4 male CS gastric cancer HT 5 male OPLL pneumonia 6 female CS brain tumor 7 female CS unknown 8 male CS lung cancer HT 9 female CS natural death HT 10 male OPLL ileus 11 male CS pneumonia CS: cervical spondylosis OPLL: ossfication of the posterior longitudinal ligament op.: operation DM: diabetes mellitus HT: hypertension Table 2. Comparison of the Data between the S Group and the L Group. S group L group p value Male/Female (n) 8/3 47/ CS/OPLL (n) 8/3 33/ age at operation (years) 65.6± ± age at death (years) 68.7± ±7.2 <0.001 (n): number CS: cervical spondylosis OPLL: ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament had non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and three patients had hypertension which was controlled by medication in the S group. No other remarkable general complications were found in the S group. The causes of death were varied (Table 3). The characteristic finding was that the ratio of pneumonia sufferers was more in the S group than in the L group. Four patients (36%) in the S group died from pneumonia, whereas 6% in the L group died from pneumonia. There was a statistical difference in ileus between the two groups, but there was only 1 patient in the S group. Malignant tumor was the common lethal disease in both groups. There was no difference in preoperative JOA score between the S and L groups. In contrast, postoperative JOA score in the S group was lower than that in the L group. 176
4 Spine Surg Relat Res 2017; 1(4): Table 3. Comparison of the Causes of the Death between the S Group and the L Group. S group (n=11) L group (n=63) p value malignant tumor 3 (27%) 20 (32%) 0.83 ischemic heart disease 0 13 (21%) 0.14 natural death 1 (9%) 10 (16%) 0.61 pneumonia 4 (36%) 4 (6%) cerebral infarction 1 (9%) 5 (8%) 0.91 ileus 1 (9%) renal failure 0 1 (1.5%) 0.68 anaplastic anemia 0 1 (1.5%) 0.68 suffocation 0 1 (1.5%) 0.68 unknown 1 (9%) 8 (13%) 0.76 However, there was no statistical difference in the recovery rate between the two groups (Table 4). Discussion This study showed that the average age at death in the S group was 68.7 years. This was much lesser than the average age of death in the L group. In recent public data published in 2013, the average life span in Japanese people was years for males and years for females. Thus, the average lifespan in the S group was also much lesser than that in the average Japanese people. It might be important for spine surgeons to know the exact reasons why the average age of death in the S group was so small, in order to consider the cautionary note before surgery. Also, it might be beneficial in the follow-up after cervical laminoplasty. There were no remarkable general complications among patients in the S group. However, pneumonia was the most frequent cause of death in this group. The current data revealed that, regarding the cause of the death, the incidence of pneumonia in the S group was higher than that in the L group. These results indicate that we must pay attention to respiratory problems, such as pneumonia, in the follow up for the patients after cervical laminoplasty. Previous studies demonstrated that cervical myelopathy impaired respiratory function 6-8). Nomura et al reported that forced vital capacity%, peak flow rate, and maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV)% in patients with cervical myelopathy was smaller than those in normal controls 6,7). Toyoda et al found that expiratory flow was impaired in patients with cervical myelopathy 8). The patients with spinal cord injury had impaired pulmonary function and frequently suffered from pneumonia 9). Analysis of the three cohorts revealed that reduced respiratory function was the most important risk factor of pneumonia 10). Thus, it is speculated that the impaired respiratory function due to cervical myelopathy results in the fatal pneumonia at the early stage after cervical laminoplasty. JOA score was established to evaluate neurological status Table 4. Comparison of the JOA Score and Recovery Rate between the S Group and the L Group. S group L group p value pre op. JOA score 8.1± ± post op. JOA score 11.2± ± Recovery rate (%) 39.5± ± op.: operation in patients with cervical myelopathy 5) and it is commonly used in clinical practice. This score includes the items for checking motor function of upper and lower extremities, sensory function of the whole body, and bladder function. In this study, postoperative JOA score in the S group was lower than that in the L group. This is an interesting result, because postoperative neurological status might be related to life expectancy. However, this JOA score system has no item to evaluate respiratory function. In our study, there was no data regarding the pre- and post-operative patients respiratory function. Previous study showed that MVV% was significantly correlated with postoperative recovery of the JOA score 7). Unsatisfactory post-operative recovery, including impaired recovery of respiratory function, might be related to the early death in the S group. Although severity of neurological dysfunction is correlated with respiratory dysfunction 11), it is impossible to know the respiratory dysfunction only using JOA score. Respiratory dysfunction is caused by phrenic nerve insufficiency, weakness of respiratory muscles, and loss of intercostal tonus. Based on these dysfunctions, patients frequently have difficulty in deep breathing and experience cough. There was a case report describing diaphragmatic paralysis due to cervical spondylotic myelopathy 12). Some patients with respiratory dysfunction have severe sputum and suffer from aspiration pneumonia. Therefore, it might be beneficial to evaluate respiratory function before performing cervical laminoplasty. Breathing condition, ability to cough, the existence of severe sputum, and the level of diaphragm by X-P are the concrete checking points before surgery. Cervical laminoplasty brings about the recovery of the neurological status in patients with cervical myelopathy. A previous study revealed that cervical laminoplasty improved respiratory function in elderly patients with cervical myelopathy 13). Thus, cervical laminoplasty might reduce the risk of postoperative pneumonia. However, we consider that surgery is not a direct protective measure for pneumonia. A new system to protect streptococcus pneumonia has been introduced in Japan since Vaccination against streptococcus pneumonia is recommended in elderly people every 5 years of age over 65 years old. The information regarding the vaccination should be given to the elderly patients who have cervical laminoplasty. Other protective measures, such as gargle, hand-washing, tooth brushing, and cessation of smoking, are strictly advised to the patients before surgery 177
5 Spine Surg Relat Res 2017; 1(4): and at the follow-up after surgery. This study has several limitations. Firstly, this is a retrospective study with case series. We were not able to obtain any data from 68 patients who did not follow-up. Secondly, the responsible levels of cervical myelopathy were unclear. Most of them had multilevel spinal cord compression due to CS or OPLL. Thirdly, the data of pre- and post-operative respiratory functions were not evaluated in this study. This data is useful for the important message regarding the prevention of pneumonia. However, this data could not be accessed because the operation was performed more than 20 years ago. Fourthly, the causes of death were based on the medical sheets and answers to questions from family members of the patients. The real cause of death was partly unclear. In addition, the cause of pneumonia was unclear. If pneumonia was caused by streptococcus, vaccination might be effective for prevention. In conclusion, 11 out of 74 patients (15%) died within 5 years after laminoplasty. The average age of patients at the time of death in the short survival time group was 68.7 years, which was much lesser than that in the long survival time group. The postoperative JOA score in the S group was lower than that in the L group. The ratio of pneumonia occurrence was greater in the short survival time group, compared to that in the long survival time group. It might be reasonable to give the information for the protection from pneumonia after cervical laminoplasty. Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Source of financial support: Yoshiharu Kawaguchi is a chief contributor who got a grant from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan: Committee for Study of Ossification of Spinal Ligament and Committee for Research and Development of Therapies for Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. Acknowledgements: The work reported in this article was supported by grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan: Committee for Study of Ossification of Spinal Ligament and Committee for Research and Development of Therapies for Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. References 1. Kawaguchi Y, Nakano M, Yasuda T, et al. More than 20 years of follow-up after en bloc cervical laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(20): Kawaguchi Y, Nakano M, Yasuda T, et al. Life expectancy after cervical en bloc laminoplasty: Analysis of data following more than 20 years. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(7): Ito T, Tsuji H. Technical improvements and results of laminoplasty for compressive myelopathy in the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10(8): Tsuji H. Laminoplasty for patients with compressive myelopathy due to so-called spinal canal stenosis in cervical and thoracic regions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1982;7(1): Kato S, Oshima Y, Oka H, et al. Comparison of the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) score and modified JOA (mjoa) score for the assessment of cervical myelopathy: a multicenter observational study. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e doi: / journal.pone ecollection Nomura T, Tani T, Kitaoka K, et al. A subclinical impairment of ventilatory function in cervical spondylotic mylopathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(7): Nomura T, Tani T, Ikeuchi M, et al. Maximum voluntary ventilation as a sensitive measure to monitor the ventilatory function in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spinal Cord. 2012;50(4): doi: /sc Epub 2012 Jan Toyoda H, Nakamura H, Konishi S, et al. Does chronic cervical myelopathy affect respiratory function? J Neurosurg Spine Sep;1(2): Linn WS, Adkins RH, Gong H Jr, et al. Pulmonary function in chronic spinal cord injury: A cross-sectional survey of 222 southern California adult outpatients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000;81 (6): Yende S, Alvarez K, Loehr L, et al. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study; Cardiovascular Health Study; Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Epidemiology and long-term clinical and biologic risk factors for pneumonia in community-dwelling older Americans. Analysis of three cohorts. Chest. 2013;144(3): doi: /chest Ishibe T, Takahashi S. Respiratory dysfunction in patients with chronic-onset cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) ;27(20): Hayashi D, Kihara S, Hoshimaru M, et al. Diaphragmatic paralysis caused by cervical spondylosis. Case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(5): Yanaka K, Noguchi S, Asakawa H, et al. Laminoplasty improves respiratory function in elderly patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2001;41(10):488-92; discussion 493. Spine Surgery and Related Research is an Open Access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view the details of this license, please visit ( nc nd/4.0/). 178
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki 3), Masatsune Yamagata 1), Yoshikazu Ikeda 1), Fumitake Nakajima 1)
 Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy in 60 consecutive patients with cervical ossi cation of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Laminoplasty Improves Respiratory Function in Elderly Patients With Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 41, 488 493, 2001 Laminoplasty Improves Respiratory Function in Elderly Patients With Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Kiyoyuki YANAKA*, **, ShozoNOGUCHI*, HiroyukiASAKAWA*, and
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 41, 488 493, 2001 Laminoplasty Improves Respiratory Function in Elderly Patients With Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Kiyoyuki YANAKA*, **, ShozoNOGUCHI*, HiroyukiASAKAWA*, and
Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Spine Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine
 Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring with Tce-MEP for cervical laminoplasty
 Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring with Tce-MEP for cervical laminoplasty Nobuhiro Tanaka 1, 2), Kazuyoshi Nakanishi 2), Naosuke Kamei 2), Toshio Nakamae 2), Shinji Kotaka 2), Yoshinori Fujimoto 1),
Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring with Tce-MEP for cervical laminoplasty Nobuhiro Tanaka 1, 2), Kazuyoshi Nakanishi 2), Naosuke Kamei 2), Toshio Nakamae 2), Shinji Kotaka 2), Yoshinori Fujimoto 1),
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics
 Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up
 Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy. Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86
 Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
 Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Introduction SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Cervical Kyphotic Deformity after Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament with Normal Sagittal Spinal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Cervical Kyphotic Deformity after Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament with Normal Sagittal Spinal
Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting cervical stenosis (tandem spinal stenosis): a retrospective analysis of 565 cases
 Yamada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0765-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting
Yamada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0765-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting
Original Investigation. Byung-Wan CHOI. INTRODUCTION Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament ABSTRACT
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy
 Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy Department of Spinal Surgery 1), Brain Attack Center Ota Memorial Hospital,
Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy Department of Spinal Surgery 1), Brain Attack Center Ota Memorial Hospital,
Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis
 Original Article Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis D. Agrawal, B. S. Sharma, A. Gupta, V. S. Mehta Department of
Original Article Efficacy and results of expansive laminoplasty in patients with severe cervical myelopathy due to cervical canal stenosis D. Agrawal, B. S. Sharma, A. Gupta, V. S. Mehta Department of
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a
 WScJ 4: 1-5, 2013 Functional Evaluation Using the Modified Japanese Orthopedic Association Score (mjoa) for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy by Age, Gender, and Type of Disease Parisa Azimi 1*, Sohrab Shahzadi
WScJ 4: 1-5, 2013 Functional Evaluation Using the Modified Japanese Orthopedic Association Score (mjoa) for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy by Age, Gender, and Type of Disease Parisa Azimi 1*, Sohrab Shahzadi
Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire (JOACMEQ): part 4. Establishment of equations for severity scores
 J Orthop Sci (2008) 13:25 31 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1194-2 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire (JOACMEQ): part 4. Establishment of equations for
J Orthop Sci (2008) 13:25 31 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1194-2 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire (JOACMEQ): part 4. Establishment of equations for
Department of Neurological Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
 online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
Minamide A*, Yoshida M*, Yamada H*, Hashizume H*, NakagawaY*, Iwasaki H*, Tsutsui S*, Hiroyuki Oka H**.
 Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome
 Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion
 Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
Abstract Study Design Systematic review. Weerasak Singhatanadgige 1 Worawat Limthongkul 1 Frank Valone III 2 Wicharn Yingsakmongkol 1 K.
 702 Review Article GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Outcomes following or Fusion in Patients with Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: A Systematic Review Weerasak Singhatanadgige
702 Review Article GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Outcomes following or Fusion in Patients with Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: A Systematic Review Weerasak Singhatanadgige
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
Yoshifumi Kudo, 1 Tomoaki Toyone, 1 Toshiyuki Shirahata, 1 Tomoyuki Ozawa, 1 Akira Matsuoka, 1 Yoichi Jin, 2 and Katsunori Inagaki 1. 1.
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1250810, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1250810 Case Report A Case of Successful Foraminotomy for Severe Bilateral C5 Palsy following Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1250810, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1250810 Case Report A Case of Successful Foraminotomy for Severe Bilateral C5 Palsy following Posterior
Is high T-1 slope a significant risk factor for developing interlaminar bony fusion after cervical laminoplasty? A retrospective cohort study
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 27:627 632, 2017 Is high T-1 slope a significant risk factor for developing interlaminar bony fusion after cervical laminoplasty? A retrospective cohort study Takeshi
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 27:627 632, 2017 Is high T-1 slope a significant risk factor for developing interlaminar bony fusion after cervical laminoplasty? A retrospective cohort study Takeshi
Op e n-d o o r laminoplasty was developed by Hirabayashi. Risk factors for closure of lamina after open-door laminoplasty.
 J Neurosurg Spine 9:530 537, 2008 Risk factors for closure of lamina after open-door laminoplasty Clinical article Mo r i o Ma t s u m o t o, M.D., 1 Ko ta Wata n a b e, M.D., 2 Ta k a s h i Ts u j i,
J Neurosurg Spine 9:530 537, 2008 Risk factors for closure of lamina after open-door laminoplasty Clinical article Mo r i o Ma t s u m o t o, M.D., 1 Ko ta Wata n a b e, M.D., 2 Ta k a s h i Ts u j i,
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery,Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine,Nagoya,Japan 2
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Central Cord Syndrome: Does early surgical intervention improve neurological outcome
 Central Cord Syndrome: Does early surgical intervention improve neurological outcome Ciara Stevenson, Jonathan Warnock, Suzanne Maguire, Niall Eames Department of Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery, Royal
Central Cord Syndrome: Does early surgical intervention improve neurological outcome Ciara Stevenson, Jonathan Warnock, Suzanne Maguire, Niall Eames Department of Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery, Royal
Hiroshi Takahashi, 1 2 Yasuchika Aoki, 1 Arata Nakajima, 1. Masato Sonobe, 1 Fumiaki Terajima, 1 Masahiko Saito, 1 Masahiro Inoue, 1
 Reversible axonal damage is remarkable in patients with acutely worsening symptoms of compression myelopathy: analysis of human cerebrospinal fluid samples 1 Hiroshi Takahashi, 1 2 Yasuchika Aoki, 1 Arata
Reversible axonal damage is remarkable in patients with acutely worsening symptoms of compression myelopathy: analysis of human cerebrospinal fluid samples 1 Hiroshi Takahashi, 1 2 Yasuchika Aoki, 1 Arata
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI /s
 Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
How cervical alignment and thoracic inlet angle affect on postoperative spinal cord alignment after laminoplasty?
 How cervical alignment and thoracic inlet angle affect on postoperative spinal cord alignment after laminoplasty? Shinya Kato, Hisanori Mihara Department of Orthopaedics Surgery, Yokohama Hodogaya Central
How cervical alignment and thoracic inlet angle affect on postoperative spinal cord alignment after laminoplasty? Shinya Kato, Hisanori Mihara Department of Orthopaedics Surgery, Yokohama Hodogaya Central
Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire: Part 3. Determination of reliability
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:321 326 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1131-4 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire: Part 3. Determination of reliability Mitsuru
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:321 326 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1131-4 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire: Part 3. Determination of reliability Mitsuru
S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA
 AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine
 J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 567-574 ORIGINAL STUDY Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma? Kyung-Jin Song, Chan-Il Park, Do-Yeon Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Kwang-Bok
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 567-574 ORIGINAL STUDY Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma? Kyung-Jin Song, Chan-Il Park, Do-Yeon Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Kwang-Bok
UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA
 UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA REPORT OF 4 SURGICAL CASES Yujiro Takeshita*, Kota Miyoshi**, Tomoaki Kitagawa** *Department of Orthopaedic and Spine Surgery, University of Tokyo, Japan
UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA REPORT OF 4 SURGICAL CASES Yujiro Takeshita*, Kota Miyoshi**, Tomoaki Kitagawa** *Department of Orthopaedic and Spine Surgery, University of Tokyo, Japan
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging
 Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Disclosures. Introduction. Purpose. Pulmonary Function and Complications in Patients with Cervical Myelopathy and Myelomalacia
 Pulmonary Function and Complications in Patients with Cervical Myelopathy and Myelomalacia Jeremy D. Shaw, MD, MS; Juli Martha, MPH; Ling Li, MSPH; David J. Hunter, MD, PhD; Brian Kwon, MD; Tal Rencus,
Pulmonary Function and Complications in Patients with Cervical Myelopathy and Myelomalacia Jeremy D. Shaw, MD, MS; Juli Martha, MPH; Ling Li, MSPH; David J. Hunter, MD, PhD; Brian Kwon, MD; Tal Rencus,
Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine Fuculty of Medical Sciences University of Fukui
 Quantitative analysis and prognostic value of changes in spinal cord signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine
Quantitative analysis and prognostic value of changes in spinal cord signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine
Kazunari Takeuchi Æ Toru Yokoyama Æ Atsushi Ono Æ Takuya Numasawa Æ Kanichiro Wada Æ Taito Itabashi Æ Satoshi Toh
 Eur Spine J (2008) 17:415 420 DOI 10.1007/s00586-007-0553-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitation of activities of daily living accompanying reduced neck mobility after laminoplasty preserving or reattaching the
Eur Spine J (2008) 17:415 420 DOI 10.1007/s00586-007-0553-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitation of activities of daily living accompanying reduced neck mobility after laminoplasty preserving or reattaching the
Morphological Patterns of the Anterior Median Fissure in the Cervical Spinal Cord Evaluated by Computed Tomography After Myelography
 Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients
 Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis
 Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Introduction SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
Spinal Cord (2005) 43, & 2005 International Spinal Cord Society All rights reserved /05 $
 (2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
(2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
We performed CT myelography in 38 patients
 Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Complex Spine Symposium January 12th, Balgrist University Hospital
 DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with and without Instrumentation
 Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.18 Research Article Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with without Instrumentation ABSTRACT Sanjay
Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.18 Research Article Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with without Instrumentation ABSTRACT Sanjay
Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
Cervical Open-Door Laminoplasty by Hydroxyapatite Implant Insertion Without Suturing
 Neurospine 2018;15(4):362-367. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836106.053 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yoshifumi Kawanabe https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2251-0293
Neurospine 2018;15(4):362-367. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836106.053 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yoshifumi Kawanabe https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2251-0293
PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY
 PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY Shota Takenaka*, Noboru Hosono, Yoshihiro Mukai, Kosuke Tateishi, Takeshi Fuji Osaka Kosei-nenkin
PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY Shota Takenaka*, Noboru Hosono, Yoshihiro Mukai, Kosuke Tateishi, Takeshi Fuji Osaka Kosei-nenkin
ASJ. Significance of Stabilometry for Assessing Postoperative Body Sway in Patients with Cervical Myelopathy. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine The J 217;11(5):763-769 efficacy of stabilometry https://doi.org/1.414/asj.217.11.5.763 for cervical myelopathy 763 Significance of Stabilometry
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine The J 217;11(5):763-769 efficacy of stabilometry https://doi.org/1.414/asj.217.11.5.763 for cervical myelopathy 763 Significance of Stabilometry
Recent Surgical Methods of Double-door Laminoplasty of the Cervical Spine (Kurokawa s Method)
 TECHNICAL NOTE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Recent Surgical Methods of Double-door Laminoplasty of the Cervical Spine (Kurokawa s Method) Shigeru Hirabayashi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Teikyo
TECHNICAL NOTE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Recent Surgical Methods of Double-door Laminoplasty of the Cervical Spine (Kurokawa s Method) Shigeru Hirabayashi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Teikyo
ASJ. Magnification Error in Digital Radiographs of the Cervical Spine Against Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Key words: Professional Med J 2018;25(8): CERVICAL LAMINOPLASTY
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4872 1. MBBS Post graduate Trainee, 2. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 3. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 4. MBBS Honorary Researcher, 5. MBBS, FCPS
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4872 1. MBBS Post graduate Trainee, 2. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 3. MBBS, FCPS Associate Professor 4. MBBS Honorary Researcher, 5. MBBS, FCPS
Respiratory Dysfunction in Craniovertebral Junction Pathology: A Pulmonary Function Test Correlation
 Alok M Uppar et al Original ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1152 Respiratory Dysfunction in Craniovertebral Junction Pathology: A Pulmonary Function Test Correlation 1 Alok M Uppar, 2 George C Vilanilam,
Alok M Uppar et al Original ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1152 Respiratory Dysfunction in Craniovertebral Junction Pathology: A Pulmonary Function Test Correlation 1 Alok M Uppar, 2 George C Vilanilam,
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 J Neurosurg Spine 13:319 323, 2010 Using the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity ratio and clinical manifestations to assess the prognosis of patients with cervical ossification of
J Neurosurg Spine 13:319 323, 2010 Using the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity ratio and clinical manifestations to assess the prognosis of patients with cervical ossification of
Influence of hinge position on the effectiveness of opendoor expansive laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 . 6. Influence of hinge position on the effectiveness of opendoor expansive laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy WAN Jun, XU Tian-tong*, SHEN Qing-feng, LI Hui-nan and XIA Ying-peng Abstract
. 6. Influence of hinge position on the effectiveness of opendoor expansive laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy WAN Jun, XU Tian-tong*, SHEN Qing-feng, LI Hui-nan and XIA Ying-peng Abstract
It is recommended that preoperative SEPs be considered. Clinical prognostic indicators of surgical outcome in cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 J Neurosurg Spine 11:000 000, 11:112 118, 2009 Clinical prognostic indicators of surgical outcome in cervical spondylotic myelopathy La n g s t o n T. Ho l ly, M.D., 1 Pa u l G. Ma t z, M.D., 2 Pa u l
J Neurosurg Spine 11:000 000, 11:112 118, 2009 Clinical prognostic indicators of surgical outcome in cervical spondylotic myelopathy La n g s t o n T. Ho l ly, M.D., 1 Pa u l G. Ma t z, M.D., 2 Pa u l
Comparison of staged reconstruction with extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) adult thoracolumbar kyphoscoliotic deformity
 Comparison of staged reconstruction with extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) and multilevel corrective PLIF/TLIF for adult thoracolumbar kyphoscoliotic deformity Hidetoshi Yamaguchi, MD; Tokumi Kanemura,MD,
Comparison of staged reconstruction with extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) and multilevel corrective PLIF/TLIF for adult thoracolumbar kyphoscoliotic deformity Hidetoshi Yamaguchi, MD; Tokumi Kanemura,MD,
Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD
 CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
The Effect of Age on the Benefits of Early Decompression for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 The Effect of Age on the Benefits of Early Decompression for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Publish date: September 20, 2018 Authors: David J. Kusin, MD Uri M. Ahn, MD Nicholas U. Ahn, MD Author Affiliation
The Effect of Age on the Benefits of Early Decompression for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Publish date: September 20, 2018 Authors: David J. Kusin, MD Uri M. Ahn, MD Nicholas U. Ahn, MD Author Affiliation
Junming Cao, Yongsheng Lin, Xiangbei Qi, Zhihong Wang, Yipeng Yang, Hehuan Xia, Bin Xu
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):741-746 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067327 Original Article Effect of intramedullary signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images on prognosis in patients
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):741-746 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067327 Original Article Effect of intramedullary signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images on prognosis in patients
Radiographic Dimensional Analysis of Open Door Laminoplasty with Plate in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Radiographic Dimensional Analysis of Open Door Laminoplasty with Plate in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Woo-Kie Min,MD,PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine,
Radiographic Dimensional Analysis of Open Door Laminoplasty with Plate in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Woo-Kie Min,MD,PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine,
ASJ. Risk Factor Analysis for C5 Palsy after Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 298 Satoshi Clinical Baba et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.2.298 Risk Factor Analysis for C5 Palsy after Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
Asian Spine Journal 298 Satoshi Clinical Baba et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.2.298 Risk Factor Analysis for C5 Palsy after Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
Author(s) Hiroyuki. Issue Date Right.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Surgical Treatment of dialysis-asso Baba, Hideo; Tagami, Atsushi; Adach Hiroyuki Acta Medica Nagasakiensia, 56(1), p Issue Date 2011-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25386
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Surgical Treatment of dialysis-asso Baba, Hideo; Tagami, Atsushi; Adach Hiroyuki Acta Medica Nagasakiensia, 56(1), p Issue Date 2011-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25386
John E. O Toole, Marjorie C. Wang, and Michael G. Kaiser
 Hypothermia and Human Spinal Cord Injury: Updated Position Statement and Evidence Based Recommendations from the AANS/CNS Joint Section on Disorders of the Spine Peripheral Nerves John E. O Toole, Marjorie
Hypothermia and Human Spinal Cord Injury: Updated Position Statement and Evidence Based Recommendations from the AANS/CNS Joint Section on Disorders of the Spine Peripheral Nerves John E. O Toole, Marjorie
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a progressive
 literature review J Neurosurg Spine 24:77 99, 2016 A systematic review of clinical and surgical predictors of complications following surgery for degenerative cervical myelopathy Lindsay Tetreault, BSc,
literature review J Neurosurg Spine 24:77 99, 2016 A systematic review of clinical and surgical predictors of complications following surgery for degenerative cervical myelopathy Lindsay Tetreault, BSc,
Appendix: Diagnostic Criteria for OPLL and Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm
 Appendix: Diagstic Criteria for OPLL and Diagsis and Treatment Algorithm Diagstic Criteria for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine (Proposed by the Committee for Development
Appendix: Diagstic Criteria for OPLL and Diagsis and Treatment Algorithm Diagstic Criteria for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine (Proposed by the Committee for Development
Comparative Effectiveness of Different Types of Cervical Laminoplasty
 Systematic Review 105 Comparative Effectiveness of Different Types of Cervical Laminoplasty John G. Heller 1 Annie L. Raich 2 Joseph R. Dettori 2 K. Daniel Riew 3 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Emory
Systematic Review 105 Comparative Effectiveness of Different Types of Cervical Laminoplasty John G. Heller 1 Annie L. Raich 2 Joseph R. Dettori 2 K. Daniel Riew 3 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Emory
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto
 Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels Page 1 of 13 Cervical Posterior Decompression
National Imaging Associates, Inc. CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels Page 1 of 13 Cervical Posterior Decompression
Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 328103, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/328103 Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 328103, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/328103 Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case
SURGICAL COMPLICATIONS OF CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY
 OBJECTIVE SURGICAL COMPLICATIONS OF CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY Matamalas A, Plano X, Pellisé F,García de Frutos A, Casamitjana J. Spine Unit. Hospital Vall d Hebrón. Barcelona To assess the rate of
OBJECTIVE SURGICAL COMPLICATIONS OF CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY Matamalas A, Plano X, Pellisé F,García de Frutos A, Casamitjana J. Spine Unit. Hospital Vall d Hebrón. Barcelona To assess the rate of
Outcomes of Secondary Laminoplasty for Patients with Unsatisfactory Results after Anterior Multilevel Cervical Surgery
 online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.1.36 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 57 (1) : 36-41, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical
online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.1.36 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 57 (1) : 36-41, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical
Radiculopathy of C-5 after anterior decompression for cervical myelopathy
 J Neurosurg Spine 3:210 217, 2005 Radiculopathy of C-5 after anterior decompression for cervical myelopathy MINORU IKENAGA, M.D., PH.D., JITSUHIKO SHIKATA M.D., PH.D., AND CHIAKI TANAKA M.D., PH.D. Department
J Neurosurg Spine 3:210 217, 2005 Radiculopathy of C-5 after anterior decompression for cervical myelopathy MINORU IKENAGA, M.D., PH.D., JITSUHIKO SHIKATA M.D., PH.D., AND CHIAKI TANAKA M.D., PH.D. Department
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 J Neurosurg Spine 19:431 435, 2013 AANS, 2013 Upper cervical cord compression due to a C-1 posterior arch in a patient with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and a kyphotic cervical spine
J Neurosurg Spine 19:431 435, 2013 AANS, 2013 Upper cervical cord compression due to a C-1 posterior arch in a patient with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and a kyphotic cervical spine
Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis
 29 29 33 Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis Author Institution Sreedharan Namboothiri Kovai Medical Center and Hospitals, Coimbatore,
29 29 33 Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis Author Institution Sreedharan Namboothiri Kovai Medical Center and Hospitals, Coimbatore,
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
CMEARTICLE * * * Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed
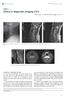 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE?
 FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
Treatment for thoracic ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament with posterior circumferential decompression: complications and managements
 Yang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0489-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Treatment for thoracic ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament with
Yang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0489-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Treatment for thoracic ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament with
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
Novel Classification System of Cervical Myelopathy Based on Symptomatology
 Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Neurology and Neuroscience DOI: 10.21767/2171-6625.1000277 Novel Classification System of Cervical Myelopathy Based on Symptomatology Hisanori
Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Neurology and Neuroscience DOI: 10.21767/2171-6625.1000277 Novel Classification System of Cervical Myelopathy Based on Symptomatology Hisanori
The Incidence Of An Epidural Hematoma Following Cervical Spine Surgery
 The Incidence Of An Epidural Hematoma Following Cervical Spine Surgery Gregory D. Schroeder, MD, Alan S. Hilibrand MD, Paul Arnold, MD, David Fish, MD, Jeffrey C. Wang, MD, Jeffrey L. Gum, MD, Zachary
The Incidence Of An Epidural Hematoma Following Cervical Spine Surgery Gregory D. Schroeder, MD, Alan S. Hilibrand MD, Paul Arnold, MD, David Fish, MD, Jeffrey C. Wang, MD, Jeffrey L. Gum, MD, Zachary
Unanswered Questions. Laminoplasty is best
 Laminoplasty is best Wellington K. Hsu, MD Clifford C. Raisbeck Distinguished Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Research Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Northwestern University Feinberg School
Laminoplasty is best Wellington K. Hsu, MD Clifford C. Raisbeck Distinguished Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Research Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Northwestern University Feinberg School
Contributing factors affecting the prognosis surgical outcome for thoracic OLF
 Eur Spine J (2006) 15: 485 491 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0903-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sung Uk Kuh Young Soo Kim Yong Eun Cho Byung Ho Jin Keun Su Kim Young Sul Yoon Dong Kyu Chin Contributing factors affecting
Eur Spine J (2006) 15: 485 491 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0903-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sung Uk Kuh Young Soo Kim Yong Eun Cho Byung Ho Jin Keun Su Kim Young Sul Yoon Dong Kyu Chin Contributing factors affecting
Jing Tao Zhang 1, Lin Feng Wang 1, Yue Ju Liu 2, Jun Ming Cao 1, Jie Li 1, Shuai Wang 1 and Yong Shen 1*
 Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Case Report Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma with 2-Stage Total en bloc Spondylectomy after Marked Response to Molecular Target Drugs
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 916501, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/916501 Case Report Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma with 2-Stage Total en bloc Spondylectomy after Marked
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 916501, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/916501 Case Report Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma with 2-Stage Total en bloc Spondylectomy after Marked
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries. Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital
 A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire (JOACMEQ): Part 2. Endorsement of the alternative item
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:241 248 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1119-0 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire (JOACMEQ): Part 2. Endorsement of the alternative
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:241 248 DOI 10.1007/s00776-007-1119-0 Original article Japanese Orthopaedic Association Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation Questionnaire (JOACMEQ): Part 2. Endorsement of the alternative
Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty
 CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic resonance imaging study evidence
 See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
