BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
|
|
|
- Julius Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 21 Female Reproductive System 1 Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
2 Session Plan o Functions of female reproductive system o Ovaries Oogenesis and follicular development o Uterine tubes o Uterus o Vagina o vulva o Mammary glands Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 2
3 Female Reproductive System Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 3
4 Female Reproductive System o Organs of female reproductive system: Gonads: Ovaries Ducts: uterine (Fallopian) tubes, Supporting structures: uterus, vagina, vulva, Mammary glands Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 4
5 Female Reproductive System o Functions of female reproductive system: o Ovaries: Produce secondary oocytes and hormones, including progesterone and estrogens, inhibin, and relaxin. o Uterine tubes: Transport a secondary oocyte to the uterus and normally are the sites where fertilization occurs. o Uterus: The site of implantation of a fertilized ovum, development of the foetus during pregnancy, and labour. o Vagina: Receives the penis during sexual intercourse and is a passageway for childbirth. o Mammary glands: Synthesize, secrete, and eject milk for nourishment of the newborn. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 5
6 Female Reproductive System Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 6
7 Ovaries Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 7
8 Ovaries o The ovaries: paired unshelled almonds sized and shaped glands o Location: one on either side of the uterus. o descend to the brim of the superior portion of the pelvic cavity during the third month of development. Hilum: The point of entrance and exit for blood vessels and nerves along which the mesovarium is attached. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 8
9 Ovaries o Ligaments: maintain the ovaries position in pelvic cavity. Broad ligament: attaches to the ovaries by a doublelayered fold of peritoneum called the mesovarium. Ovarian ligament: anchors the ovaries to the uterus Suspensory ligament: attaches ovaries to the pelvic wall Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 9
10 Ovaries: Ligaments Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 10
11 Ovaries: Histology Each ovary consists of the following parts: o Germinal epithelium o Tunica albuginea o Ovarian cortex o Ovarian medulla o Ovarian follicles o A mature (Graafian) follicle o A corpus luteum Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 11
12 Ovaries: Histology Each ovary consists of the following parts: o Germinal epithelium o Tunica albuginea o Ovarian cortex o Ovarian medulla o Ovarian follicles o A mature (Graafian) follicle o A corpus luteum Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 12
13 The Ovary: Histology o Germinal epithelium: A simple epithelial covering over the ovary o Tunica albuginea: A capsule of dense connective tissue o Cortex: A region just deep to tunica, containing follicles o Medulla: A deeper region composed of connective tissue, blood vessels and lymphatics o Ovarian follicles: Consist of oocytes in various stages of development in the cortex o A mature follicle: a large, fluid filled follicle that rupture and expel its secondary oocyte, during ovulation. o A corpus luteum: contains the remnants of a mature follicle after ovulation Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 13
14 Oogenesis and Follicular Development o Oogenesis: The formation of gametes in the ovaries. Events in oogenesis: Mitosis, reduction division (Meiosis I), equatorial division (Meiosis II), and maturation o Follicular development: occurs along with oogenesis Developmental stages: Primordial, primary, secondary, and mature (Graafian) follicles, and corpus luteum and corpus albicans. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 14
15 Oogenesis and Follicular Development Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 15
16 Events in oogenesis o Mitosis: Germ cells from yolk sac migrate to ovary and become oogonia In the female fetus, oogonia divide to produce millions by mitosis but most degenerate (atresia) o Meiosis I: Some develop into primary oocytes and stop in prophase stage of meiosis I 200,000 to 2 million are present at birth 40,000 remain at puberty, but only 400 mature during a woman s life o Meiosis I resumes and Meiosis II: After puberty, each month, hormones cause Meiosis I to resume in several follicles so that Meiosis II is reached by ovulation Penetration by the sperm causes the final stages of meiosis to occur Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 16
17 Follicular Stages: Primordial follicle Primordial follicle: primary oocyte is surrounded by a single layer of flat follicular cells Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 17
18 Follicular Stages: Late primary follicle Late primary follicle: consists of a primary oocyte surrounded by several granulosa cells. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 18
19 Follicular Stages: Secondary follicle Secondary follicle with theca interna, theca externa and antrum Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 19
20 Follicular Stages: Graafian Follicle Graafian Follicle with Zona Pellucida, Corona radiata and Antrum Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 20
21 Follicular Stages: Graafian Follicle Histology of a Graafian follicle: o Zona Pellucida clear area between oocyte and granulosa cells o Corona radiata granulosa cells attached to Zona Pellucida - still attached to oocyte at ovulation o Antrum formed by granulosa cells secreting fluid o By this time, the oocyte has reached the metaphase of Meiosis II stage and stopped developing - the first polar body has been discarded Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 21
22 Follicular Stages: Corpus Luteum and Albicans o Corpus luteum: An ovulation wound that fills in with hormonesecreting cells o Corpus albicans: A white fibrous tissue scar left after corpus luteum degenerates (when it is not needed) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 22
23 Uterine Tubes and Uterus Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 23
24 Uterine or Fallopian Tubes o Uterine Tubes: Narrow, 10cm tube extends from ovary to uterus o Three parts: Infundibulum fimbriae Ampulla Isthmus o Functions: Transport ova from ovaries to uterus The normal sites of fertilization Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 24
25 Histology of Uterine Tube Histology: 3 Layers o Mucosa: ciliated columnar epithelium with secretory cells provide nutrients o Muscularis: circular and longitudinal smooth muscle peristalsis helps move ovum down to the uterus o Serosa: outer serous membrane Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 25
26 Uterus o Shape: of an inverted pear o Size: 7.5cm long, 5cm wide and 2.5cm thick o Functions: Transport of spermatozoa, Menstruation, Implantation of a fertilized ovum, Development of a fetus during pregnancy, and labor Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 26
27 Anatomy of the Uterus o Anatomical Subdivisions: Fundus Body uterine cavity Isthmus Cervix Cervical canal Internal os External os Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 27
28 Uterus: Position o Position: anteflexion-projects anteriorly and superiorly over the urinary bladder o Ligaments: hold uterus in normal position Broad ligament, uterosacral ligaments, cardinal (lateral cervical) ligaments, round ligaments o Retroflexion: Posterior tilting of the uterus, A harmless variation of the normal position of the uterus. May occur after childbirth. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 28
29 Histology of the Uterus o Endometrium Simple columnar epithelium Stroma of connective tissue and endometrial glands stratum functionalis: shed during menstruation stratum basalis: replaces stratum functionalis each month o Myometrium 3 layers of smooth muscle o Perimetrium Visceral peritoneum Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 29
30 Blood Supply of Uterus o Arterial supply: Uterine arteries and their numerous branches Arcuate and radial arteries: Supply the myometrium Straight and spiral branches: penetrate to the endometrium spiral arteries: supply the stratum functionalis their constriction due to hormonal changes starts menstrual cycle o Venous drainage: Uterine veins Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 30
31 Blood Supply of Uterus Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 31
32 Cervical Mucus o Cervical mucus: Produced by secretory cells of the mucosa of the cervix o Contains: A mixture of water, glycoprotein, serum-type proteins, lipids, enzymes, and inorganic salts o Significance: When thin, is more receptive to sperm; When thick, forms a cervical plug that physically impedes sperm penetration Supplements the energy needs of the sperm Serve as a sperm reservoir, protect sperm from the hostile environment of the vagina, and protect sperm from phagocytes Play a role in capacitation Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 32
33 Vagina and Vulva Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 33
34 Vagina The vagina: o Size: 10cm long fibromuscular organ ending at the cervix o Location: lies between urinary bladder and rectum o The vaginal orifice: Vaginal opening to exterior o Hymen: a thin fold of vascularized mucous membrane, often partially cover the vaginal orifice. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 34
35 Vagina Functions: o a passageway for spermatozoa and the menstrual flow, o the receptacle of the penis during sexual intercourse, o the lower portion of the birth canal Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 35
36 o Mucosa: Vagina - Histology Rugae: Folds of epithelial layer Mucosa dendritic cells: Are Antigen Presenting Cells (APC) perform an immune function Glycogen: which decompose into organic acids which set up a hostile acid environment for bacteria and sperm. o Muscularis: smooth muscle layer can stretch considerably to accommodate the penis during sexual intercourse and a child during birth. o Adventitia: is loose connective tissue that binds vagina to other organs Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 36
37 Vulva The vulva/pudendum: the external genitalia of the female o Components: Mons pubis Labia majora Labia minora Clitoris, vestibule Vaginal and urethral orifices Hymen Bulb of the vestibule Paraurethral (Skene s), Greater vestibular (Bartholin s) and Lesser vestibular glands Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 37
38 Vulva o Mons pubis: fatty pad over the pubic symphysis o Labia majora and minora: folds of skin encircling vestibule with the urethral and vaginal openings o Clitoris: small mass of erectile tissue o Bulb of vestibule: masses of erectile tissue just deep to the labia on either side of the vaginal orifice o Paraurethral (Skene s), Greater vestibular (Bartholin s) and Lesser vestibular glands: produce a small quantity of mucus during sexual arousal and intercourse that adds to cervical mucus and provides lubrication. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 38
39 Perineum o Perineum: The diamond-shaped area between the thighs and buttocks of both males and females that contains the external genitals and anus. urogenital triangle contains external genitals anal triangle contains anus Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 39
40 Mammary Glands Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 40
41 Mammary Glands o Mammary Glands: modified sudoriferous (sweat) glands o Consist of: Lobes lobules alveoli (milk-secreting glands) Adipose tissue Secondary tubules mammary ducts lactiferous sinuses Lactiferous ducts o Functions: synthesis of milk, secretion and ejection of milk. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 41
42 Mammary Glands Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 42
43 Mammary Glands o Breast: A hemispheric projection of variable size anterior to the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles that consist of a mammary gland. o Nipple: The pigmented projection, consist of a series of closely spaced openings of ducts called lactiferous ducts o Areola: The pigmented area around nipple that contains modified sebaceous glands. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 43
44 Fibrocystic Disease of the Breasts o Fibrocystic disease: The most common cause of a breast lump one or more cysts (fluid-filled sacs) thickening of alveoli (clusters of milk-secreting cells) develop o Cause hormonal imbalance excess of estrogen or deficiency of progesterone in the postovulatory phase result is lumpy, swollen and tender breast a week before menstruation begins Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 44
45 Homologous structures: Male and Female Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 45
46 Readings and Resources o Tortora, GJ & Derrickson, B Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 14th edn, Wiley. o Harris, P, Nagy, S & Vardaxis, N 2010, Mosby s Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing and Health Professions, 2nd edn, Mosby Elsevier. o Guyton, AC & Hall, JE 2011, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th edn, Saunders Elsevier. o Marieb, EN & Hoehn, K 2011, Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9th edn, Benjamin Cummings Pearson. o Moore, KL, Dalley, AF & Agur, AMR 2010, Clinically Orientated Anatomy, 6th edn, Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 46
47 Copyright COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the Endeavour College of Natural Health pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 47
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems. Male 11/29/2015. Male reproductive system is composed of... BIO 218 Fall Gonads (testes)
 Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Female Reproductive System
 21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
The Female Reproductive System
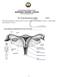 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Fig The CS of the Ovary The Ovarian Follicles a) Primordial Follicles The primordial follicles represent the stored primary oocytes of
 Chapter 19 Female Reproductive System 19.1. Introduction The female reproductive system is composed of: (1) internal organs located in the pelvic cavity consisting of the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, and
Chapter 19 Female Reproductive System 19.1. Introduction The female reproductive system is composed of: (1) internal organs located in the pelvic cavity consisting of the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, and
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Aniko Szabo Hill 1 of 12
 Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 22 Female Reproductive System 2 The Reproductive Cycle Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o The female reproductive
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 22 Female Reproductive System 2 The Reproductive Cycle Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o The female reproductive
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O.
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 28 The Reproductive System Organs include: testes, ductus deferens, epididymis, ejaculatory ducts, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 28 The Reproductive System Organs include: testes, ductus deferens, epididymis, ejaculatory ducts, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
The Reproductive System
 The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 24
 primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Lab Activity 33. Anatomy of the Reproductive System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 33 Anatomy of the Reproductive System Portland Community College BI 233 Scrotum Sac of skin and superficial fascia that hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis Contains
Lab Activity 33 Anatomy of the Reproductive System Portland Community College BI 233 Scrotum Sac of skin and superficial fascia that hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis Contains
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
~ Bobbitt Laboratories Human Female Genital Organs 1308 RAINEY STREET BURLINGTON, N. C
 56-6935 Human Female Genital Organs ~ Bobbitt Laboratories 1308 RAINEY STREET BURLINGTON, N. C. 27215 Printed in U.S.A. 1974 Bobbitt Laboratories, Inc. BB169357402/356-6935 Human Female Genital Organs
56-6935 Human Female Genital Organs ~ Bobbitt Laboratories 1308 RAINEY STREET BURLINGTON, N. C. 27215 Printed in U.S.A. 1974 Bobbitt Laboratories, Inc. BB169357402/356-6935 Human Female Genital Organs
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Lecture 28, The Reproductive System
 Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology
 Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia. Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska
 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The reproductive system is designed to perpetuate the species
27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The reproductive system is designed to perpetuate the species
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Dr. Abdal-jabbar F. Al-Rubai'y, M.B.Ch.B, M.Sc, Ph.D (UK)
 The female reproductive system Oviducts: The oviducts are two muscular tubes of great motility, 10-12 cm in length. It can be divided into 4 portions by gross inspection: The infundibulum: it lies next
The female reproductive system Oviducts: The oviducts are two muscular tubes of great motility, 10-12 cm in length. It can be divided into 4 portions by gross inspection: The infundibulum: it lies next
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
2 - male hormones/ female system
 2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
Embryology Lecture # 4
 1 Quick Review: Oogenesis : - Oogonia start appear in the ovary when the age of the fetus 1 is th (5 week). - Then the Oogonia transformed into 1ry Oocyte. - 1ry Oocyte is surrounded by a follicle (cover).
1 Quick Review: Oogenesis : - Oogonia start appear in the ovary when the age of the fetus 1 is th (5 week). - Then the Oogonia transformed into 1ry Oocyte. - 1ry Oocyte is surrounded by a follicle (cover).
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
 Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Reproductive structures that have erectile tissue include
Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Reproductive structures that have erectile tissue include
HUMAN REPRODUCTION SYSTEM
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION SYSTEM The human reproductive system usually involves internal fertilization by sexual intercourse. During this process, the male inserts his erect penis into the female's vagina and
HUMAN REPRODUCTION SYSTEM The human reproductive system usually involves internal fertilization by sexual intercourse. During this process, the male inserts his erect penis into the female's vagina and
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16 Name Identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter 2) The renal pyramid is indicated by letter 3) The fibrous capsule is indicated by letter
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16 Name Identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter 2) The renal pyramid is indicated by letter 3) The fibrous capsule is indicated by letter
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23
 AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
Chapter 27 The Reproductive System. MDufilho
 Chapter 27 The Reproductive System 1 Figure 27.19 Events of oogenesis. Before birth Meiotic events 2n Oogonium (stem cell) Mitosis Follicle development in ovary Follicle cells Oocyte 2n Primary oocyte
Chapter 27 The Reproductive System 1 Figure 27.19 Events of oogenesis. Before birth Meiotic events 2n Oogonium (stem cell) Mitosis Follicle development in ovary Follicle cells Oocyte 2n Primary oocyte
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Physiology of Male Reproductive System
 Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
 MOCK TEST I (HUMAN REPRODUCTION) 1. In human transfer of sperms into female genital tract is called as 1) Fertilization 2) Implantation 3) Insemination 4) Gestation 2. In male human scrotum maintains the
MOCK TEST I (HUMAN REPRODUCTION) 1. In human transfer of sperms into female genital tract is called as 1) Fertilization 2) Implantation 3) Insemination 4) Gestation 2. In male human scrotum maintains the
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
link full dowload:
 link full dowload: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-maternity-nursingan-introductory-text-11th-edition-by-gloria-leifer Leifer: Maternity Nursing: An Introductory Text, 11th Edition Chapter
link full dowload: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-maternity-nursingan-introductory-text-11th-edition-by-gloria-leifer Leifer: Maternity Nursing: An Introductory Text, 11th Edition Chapter
Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1
 Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1 Reproductive System Introduction 1. Functions: a. Procreation b. Bonding between sexes 2. Gonads: a. Male-testes b. Female-ovaries Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive
Bio 182- Ecology Unit Outline 1 Reproductive System Introduction 1. Functions: a. Procreation b. Bonding between sexes 2. Gonads: a. Male-testes b. Female-ovaries Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Bio 104 Reproductive System
 63 Lecture Outline: Reproductive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 22, 23] I. Introduction A. Primary sex characteristics Male Female B. Secondary sex characteristics Male: 9 14 yrs. Reproductive development
63 Lecture Outline: Reproductive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 22, 23] I. Introduction A. Primary sex characteristics Male Female B. Secondary sex characteristics Male: 9 14 yrs. Reproductive development
11/15/2017. Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System. Reproductive Organs of the Male, Sagittal View
 Reproductive System What is sex? Biological science perspective Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce gametes (sex cells): sperm and ova Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males)
Reproductive System What is sex? Biological science perspective Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce gametes (sex cells): sperm and ova Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males)
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Chapter Five. Female Sexual Anatomy
 Chapter Five Female Sexual Anatomy Agenda Discuss Female Sexual & Reproductive System Describe Female Maturation Cycle Discuss Female Reproductive and Sexual Health The Female Sexual and Reproductive System
Chapter Five Female Sexual Anatomy Agenda Discuss Female Sexual & Reproductive System Describe Female Maturation Cycle Discuss Female Reproductive and Sexual Health The Female Sexual and Reproductive System
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male Reproductive System I. Overview A. gonads organs producing sex cells (gametes) = B. support for gonads = C. ducts for storage and transport
 Male Reproductive System I. Overview A. gonads organs producing sex cells (gametes) = B. support for gonads = C. ducts for storage and transport (epididymis, ductus deferens(vas deferens), ejaculatory
Male Reproductive System I. Overview A. gonads organs producing sex cells (gametes) = B. support for gonads = C. ducts for storage and transport (epididymis, ductus deferens(vas deferens), ejaculatory
Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review Rachel Ledden Paper for Bachelors in Science January 20, 2018
 Running head: 1 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review Rachel Ledden Paper for Bachelors in Science January 20, 2018 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review 2 The reproductive cycle
Running head: 1 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review Rachel Ledden Paper for Bachelors in Science January 20, 2018 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review 2 The reproductive cycle
The reproductive lifespan
 The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
The Reproductive System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II The Reproductive System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapters
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II The Reproductive System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapters
10 Reproductive System
 Chapter 10 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System -The male reproductive system consists of the penis, testes, scrotum, a series of ducts (epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts, and urethra),
Chapter 10 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System -The male reproductive system consists of the penis, testes, scrotum, a series of ducts (epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts, and urethra),
Anatomy of Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
The Female and Male External Genitalia. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 15 The Reproductive Systems and Human Development. ANATOMY Loulousis
 Chapter 15 The Reproductive Systems and Human Development ANATOMY Loulousis Overview Main job ensure continuation of the human species Gonads in all sexually reproducing organisms Aid in sexual reproduction
Chapter 15 The Reproductive Systems and Human Development ANATOMY Loulousis Overview Main job ensure continuation of the human species Gonads in all sexually reproducing organisms Aid in sexual reproduction
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
**Confirm identifications with instructor.
 AP2 Lab 10 - THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS (1 st week) Note: All these instructions are based on using the genitalia from the smaller, light colored torsos and those on freestanding display stands. A. Female
AP2 Lab 10 - THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS (1 st week) Note: All these instructions are based on using the genitalia from the smaller, light colored torsos and those on freestanding display stands. A. Female
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Embryology 3. Spermatogenesis:
 Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
Embryology 3 Spermatogenesis: The 2 testis in males are each divided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa forming 250 lobule and in each lobule there are 1 to 4 seminefrous tubule ( so almost
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology. Basic Structure of the Human Body. Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology
 Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Science Honors: Human Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1: The Reproductive System
 Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Vocabulary The reproductive system ensures continuity of the species by producing offspring. Male and female gonads produce both gametes
Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Vocabulary The reproductive system ensures continuity of the species by producing offspring. Male and female gonads produce both gametes
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM GROUP 3 CHAPTER 28 QUESTIONS AMANDA HUYNH, TUYEN PHAM, NGOC VU, AND ELBA
 ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM GROUP 3 CHAPTER 28 QUESTIONS AMANDA HUYNH, TUYEN PHAM, NGOC VU, AND ELBA 1. Which hormone initiates the changes in puberty? A. FSH (initiates follicular growth)
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM GROUP 3 CHAPTER 28 QUESTIONS AMANDA HUYNH, TUYEN PHAM, NGOC VU, AND ELBA 1. Which hormone initiates the changes in puberty? A. FSH (initiates follicular growth)
Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester
 Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
