Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
|
|
|
- Jeffry Cole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
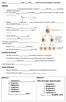
1 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, or by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called. Who is Gregor Mendel? Mendel can be called the of genetics because he made the principles of genetics that we still use today! Mendel s most important work was the research and experiments that he did by studying. These experiments helped him explain how were passed from one generation to the next. Where are these genes? Each gene controls something different, and it has a specific location on a DNA molecule. A DNA molecule that is curled or coiled up is called a, which may have more than a thousand genes on it. Your chromosomes are in the of the cell. Each species of organism has a different number of chromosomes. Every chromosome carries genes for different traits. Humans have chromosomes in a somatic cell (body cell) and in a gamete (sex cell). In body cells, chromosomes are in. The pictures below are of a. This is a picture of a test that shows human chromosomes that have been cut out and arranged in their pairs. Academy Biology 1
2 Who cares about the pairs? Mendel s research showed that there are two factors that control a trait or characteristic. He concluded that at the end of, when the gametes are produced, each sperm or egg cell has only one factor instead of two. When the gametes combine during, the offspring will then have the two factors controlling each specific trait. We now call these factors, chromosomes. One chromosome is from the mom and the other chromosome of the pair is from the dad. The pair of factors is separated during meiosis. Mendel named this process of separating the Law of. Humans have pairs of chromosomes in every cell. One characteristic of humans that can be found by looking at a karyotype is the of the baby. The first 22 pairs of chromosomes in a male and a female are the same; they are called or body chromosomes. The 23 rd pair isn t really a pair so it is labeled differently. This last two chromosomes are called the. These chromosomes decide the gender or sex of the organism. They also carry for other characteristics. The sex chromosome of the female is the chromosome. A human female has two X chromosomes in each cell. The sex chromosome only found in males is the chromosome. A human male has one chromosome and one chromosome in each cell. Look at the karyotypes from page 1. What is the sex of person A? how do you know?. What is the sex of person B? how do you know?. Academy Biology 2
3 Are more chromosomes better? It would be easy to think that having an extra chromosome or two would make a superhuman, but this in not true. Extra chromosomes, damaged chromosomes and missing chromosomes almost always cause. A karyotype can be used to find some genetic disorders that a developing baby, or may have. Doctors will use cells taken from a developing baby to see if the baby has the correct number of chromosomes. This is done with a test called. If there are too many, too few, or damaged chromosomes, then that means that there must have been a mistake in when the are formed. If the number of chromosomes is wrong, then the did not separate correctly Meiosis. The phase of meiosis when this separation happens is called. This kind of mistake in which a tetrad does not separate is called. If an egg like this (with the mutation) is fertilized, the mother may miscarry the baby or the baby may die in the first year. If the baby is born, it will have a genetic disorder. The kind of genetic disorder is determined by how many chromosomes have a mistake and which ones have the mistake. What could happen to the baby? Here are some of the possible disorders that are caused by these types of mistakes. Read the descriptions and fill in the chart below. Cri Du Chat Syndrome: This disorder results in severe mental and physical retardation. This means that the child has trouble learning and they have physical difficulties. The affected people make sounds like a cat; that is the reason for the name cri du chat, which is French for cry of the cat. A missing part of chromosome five causes this; the amount of the chromosome that is missing determines how bad the effects are. Down Syndrome: Non-disjunction in the 21 st pair of chromosomes in one of the gametes causes an extra 21 st chromosome. This causes mental retardation (trouble learning). A person born with this genetic disorder has very serious physical and mental disabilities. They may have small, round heads, shorter bodies and almond shaped eyes. They can get other diseases very easily and they do not live as long as most people. This is found in about 3 of every 2000 births. Klinefelter Syndrome: A person with this disorder has an extra sex chromosome. Non-disjunction in either the egg or the sperm causes the fertilized egg to have two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome. The Y chromosome makes this person a male. A person with this karyotype has internal male sex organs, but they are not fully developed and cannot produce sperm. They also develop a few female characteristics, such as enlarged breasts. They have above-average height (usually over 6 ft tall) and below- normal intelligence; they may even be mentally retarded (have trouble learning). Turner Syndrome: A person with this disorder is missing one of the sex chromosomes. Non-disjunction in the egg or sperm causes the fertilized egg to have only one X chromosome. There is no second sex chromosome. This baby will be a female, but her ovaries will not develop and she will be unable to have children. She will have some physical problem like being very short. Her mental abilities may also be inhibited, which means she will have trouble learning. Academy Biology 3
4 Read the descriptions from the previous page to fill in this chart. Karyotype What is the sex or gender of the person? What disorder does this person have? Academy Biology 4
5 What is the probability of having a boy or a girl? Many times in genetics, we can make guesses about whether or not a parent will give a certain trait to their children. To do this we use a tool called a. This is a way to show all of the possible combinations of genes from the and and chances for certain combinations happen. Meiosis produces egg in a woman and sperm in a man. Gametes have the number of chromosomes that any body cell has. The gametes then will also only have one sex chromosome. What are the possible sex chromosomes that a woman can give? or What are the possible sex chromosomes that a man can give? or An example of an empty Punnett Square is below. Follow the directions to predict (guess) how likely it is to have a boy or girl. Dad s sex chromosomes Mom s sex chromosomes 1. The sides of a Punnett Square are for what chromosomes the gametes could have. In this case, we are looking at sex chromosomes. Write in the sex chromosomes that the mother can give on the top and those from the father on the side. 2. Copy the letters from the top of the square into each of the boxes below it. 3. Copy the letters from the sides of the square into each of the boxes next to it. 4. Each of the boxes now shows a possible combination of the egg and sperm. Within all 4 boxes is every possible combination of these two parents. What are the possible combinations of sex chromosomes? How many times does each occur? How likely is it for any woman and man to have a make child? How likely is it for any woman and man to have a female child? If a woman has a baby boy, what are the chances of her having another baby boy? Explain. Academy Biology 5
6 How do certain traits get passed on? Non-sex chromosomes are called. Every regular body cell has paired (in two) autosomal chromosomes. Every sex cell has one of the paired autosomal chromosomes. The offspring receives one copy of each autosomal chromosome from each. The two autosomal chromosomes that make the pair are called chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes are the same size and shape and carry genes for the same traits. The picture below is a pair of homologous human autosomal chromosomes. The different kinds of genes that are possible for each trait are called. Every trait of an organism is decided by at least two alleles. If a trait is decided by more than two alleles, it is called. Alleles are represented by a letter. Capital letters represent alleles and lower case letters represent alleles. The trait for a dominant allele will cover or mask a trait for a. The genes of an organism make up its. We write the letters of the alleles to show this. Look at the chromosomes in the picture above. The genotype for the trait showing of this person is. Both of these alleles are. If both of the alleles are the same, for example two dominant (GG) or two recessive (gg), the genotype is called. If the alleles are different (Gg) the genotype is called, When you have a heterozygous genotype, you are a for the recessive trait. This person s genotype is. The way that an organism looks is called its. If B represents the trait for brown eyes, and b represents the trait for blue eyes, what is the phenotype of this person? Academy Biology 6
7 List the genotypes of each of the plants: List the phenotypes of each of the plants: Describe the genotype of each of the plants using the following terms: Homozygous, Heterozygous If it is Homozygous, write whether it is Dominant or Recessive If plants 1 and 3 reproduced, what would be the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? - Start by completing this Punnett Square. Possible genotypes Possible phenotypes Academy Biology 7
8 A B C D E F Follow the directions provided. To fill in the chart, you will have to make some Punnett Squares. Use the space at the bottom of the page to make them. A B C D E F Academy Biology 8
9 Name: Date: Period: Punnett Square Problems Write the possible genotypes and the genotypic ratios (fractions) each Punnett Square below. Academy Biology 9
10 Use Punnett Squares to help you predict (guess) the genotypes and phenotypes from each of the crosses shown below. Complete each section of the chart. Cross Genotypes of parents Phenotypes of Parents Punnett Square Genotypic Ratios Phenotypic Ratios Green (GG) peas X Yellow (gg) peas Green (Gg) peas X Yellow (gg) peas Green (Gg) peas X Green (Gg) peas Green (GG) peas X Green (GG) peas Green (GG) peas X Yellow (gg) peas Academy Biology 10
11 Are some traits more common in boys than girls? Like autosomes, the sex chromosomes also carry genes for certain traits. The figure below shows some of the traits that are controlled by the on the sex chromosomes. Label the sex chromosomes as either male or female. How many genes decide whether or not a female has dry skin? How many genes decide whether or not a male has dry skin? The Y chromosome does not have ALL of the genes that the X chromosome has. In autosomes, recessive genes are needed for the recessive trait to show. This is different in sex chromosomes. One sex-linked trait shown above is color blindness. This trait is on an X of the sex chromosome. We write X c for recessive or X C for dominant. We use the X to show that it is found on the X sex chromosome. The dominant trait is normal color vision and the recessive trait is red-green color blindness. In order for a female to be colorblind, she must have the genotype In order for a male to be colorblind, he must have the genotype.. Academy Biology 11
12 Let s look at muscular dystrophy, another recessive sex-linked disorder, weakens and destroys muscle tissue. You are a genetic counselor and you have to tell each of these couples the chance that they will have children with this disorder. Figure out the probability (chance of this happening) using Punnett squares. SHOW YOUR WORK! Remember- THERE IS NO GENE FOR THIS TRAIT ON THE Y CHROMOSOME. 1.) Healthy father and homozygous dominant mother 2.) Father with MD and heterozygous mother 3.) Healthy father and mother with MD 4.) Healthy father and heterozygous mother 5.) Father with MD and mother with MD 6.) Father with MD and homozygous dominant mother Couple # 1. Punnett square Genotypic ratios (fractions) Phenotypic ratios (fractions) Who has a bigger chance of having a recessive sex-linked genetic disorder, a male or female? Why? Academy Biology 12
13 How do we know if we could pass a trait to our children? When Mendel did his studies on genetics, he cross-pollinated (mixed) different pea plants. Using a green pea plant and a yellow (gg) plant, he could find out the genotype of a yellow pea plant. Since a green pea plant could have a genotype of or, how could he use this figure out the genotype of a yellow pea plant? The study of human genetics is different, we can t do a test-cross and as many experiments as we can with plants or small animals. When geneticists mate (reproduce) fruit flies, they control which ones mate with others. We cannot do this with humans. The study of human genetics depends a lot on the study of the family history of disorders and traits. A is a diagram, which shows how a particular trait is passed through a family from one to the next. Some of the symbols that are used in a pedigree chart are: Pedigree I looks at the dimples trait through three generations of a family. 1. What do the Roman Numerals stand for? 2. What symbols do we use for marriage and mating? 3. What symbol do we use for children? 4. What do the numbers stand for? Academy Biology 13
14 5. The genes for dimples are on autosomes. Are dimples a dominant or recessive trait? How can you tell? Even though Jane and Joe Smith have dimples, their daughter, Clarissa, does not. Joe s dad has dimples, but his mother and sister Grace do not. Jane s dad, Mr. Renaldo, her brother Jorge, and her sister Emily do not have dimples, but her mother does. 6. Write the name of each person in the pedigree below. I-1. II-2. I-2. II-3. I-3. II-4. I-4. II-5. II-1. III-1. Think about the pedigree below that shows cystic fibrosis, a recessive autosomal disorder. How many generations does this pedigree represent? What does it mean if the shape is half colored in? Is the gene for cystic fibrosis dominant or recessive? How can you tell? Write in the genotypes of the family members in the pedigree. Who married a homozygous dominant person? In which generation does the first case of cystic fibrosis appear? Who was born with it? Academy Biology 14
15 Complete the pedigree chart exercise below. The man and woman in the first step (first generation) of the pedigree chart are both red-green colorblind. Remember that red-green colorblindness is a recessive trait carried on the X sex-chromosome. All of the people who marry into this family are NOT colorblind and are NOT carriers for being colorblind. 1. You must decide what the symbols of the chart will be. Write all of the symbols in a key (box) under the chart. 2. Complete the pedigree chart below. Use the symbols you made in the key to show the genotype of each of the family members. You will need to do Punnett squares to figure out these genotypes. Show the Punnett squares in the space below the chart. Academy Biology 15
16 Are all genes that decide traits either dominant or recessive? Certain traits like freckles or dimples are caused by dominant alleles. Only one parent has to have the dominant allele, because there only needs to be dominant gene for the trait to show. Draw a Punnett square below to show what kind of alleles the parents must have to make a child with more than five fingers per hand. Five fingers on a hand is a recessive trait. Explain how this shows what the parents genotypes must be. Some traits are neither totally nor totally. When this happens, When this happens, the trait does not follow the usual Law of Dominance. We call this. If there is one dominant and one recessive gene, then usually only the gene is seen. Incomplete dominance will not show either trait. In incomplete dominance, the phenotype of the organism is a mixture of both of the genes. Because neither trait is recessive, both alleles are written as capital letters. Try the examples below. Academy Biology 16
17 When there are two dominant genes, and the phenotype is a mixture of the two dominant traits, it is called. There are other cases in which both traits show because they are both dominant, but the traits do not mix together. This is called. Sickle-cell anemia is a dangerous genetic disorder. Red blood cells carry through your body. The shape of sickle red blood cells is different from the shape of normal red blood cells. The sickle cells do not carry enough oxygen to body parts. Their shape also makes it difficult for them to move through blood vessels, which causes. R is the gene for round (regular) cell shape and R is the gene for sickle cell shape. Put checkmarks in the table to show the cell shape that goes with each genotype listed. What are the genotypes from the chart above? 1.) 3.) 4.) What are the phenotypes shown in the chart above? 1.) 2.) 3.) When genes are codominant, what do you notice about the phenotype of the organism? The genes for human blood type are also codominant. Complete the chart with the possible genes that a person with each of the following blood types could have. Blood Type A B O AB Possible genes Or Or Which of the blood types show regular dominance? How do you know? What blood types show codominance? How do you know? What possible blood types could a child have if the parents blood types were A and B? Use a separate sheet of paper to show all of the possible Punnett squares. Academy Biology 17
18 Baby Mix Up Four newborn babies are born in the hospital at the same time. Clumsy Clara the nurse ran was about to give each of the babies a wristband with that child s name on it, but she dropped the wristbands and they got out of order. She looked at the charts with the blood types of all four babies and their parents. Please help her figure out which baby belongs to which family. The baby s blood types are luckily all different. There is one baby with each: Baby A = blood type A Baby B = blood type B Baby C = blood type AB Baby D = blood type O The parents blood types are as follows: The Gonzalez parents: blood types O and O The Johnson parents: blood types O and A The Rogers parents: blood types AB and B The Smith parents: blood types O and AB Show your Punnett Squares below. Write the last name of each baby below. Baby A is a. Baby B is a. Baby C is a. Baby D is a. Academy Biology 18
19 If every gamete has half of the chromosomes, why are siblings so different? Mendel s research also showed that offspring could get one trait without necessarily getting another. For example, some children may have brown hair and blue eyes, or they may have brown hair and brown eyes. He concluded that the alleles (genes) for different traits are not always connected. The Law of Independent Assortment says that alleles for different traits are separated into gametes. That means that they do not go together; they go one by one. The phase of Meiosis when crossing over occurs is called. This is when changes can happen in the genes or alleles of each gamete. How likely is it for a person to have TWO TRAITS? So far, we have only done crosses for one trait at a time. For instance whether or not the child will be able to roll his tongue. This is called a cross. What if someone is interested in finding out the chances for their child to have two traits like brown hair and brown eyes? We would have to do a Punnett Square to show all of the possible genotypes. This gets a little more complicated. A cross with two traits is called a cross and a cross for three traits is called a tri-hybrid cross. Let s pretend to mate a pair of hamsters. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the following cross? Black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Short fur (A) is dominant over long fur (a). Rough coat (R) is dominant over smooth coat (r). Gene Information Heterozygous black and heterozygous short fur X heterozygous black and heterozygous short fur Genotypes of Parents: X Gamete Possibilities: Punnett Square: X Genotype & Phenotype Ratios: Academy Biology 19
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
GENETICS NOTES. Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16
 GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism.
 Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
Meiosis and Genetics
 Meiosis and Genetics Humans have chromosomes in each cell What pattern do you notice in the human karyotype (a technique that organizes chromosomes by type and size)? Humans are diploid 1 Gametes are produced
Meiosis and Genetics Humans have chromosomes in each cell What pattern do you notice in the human karyotype (a technique that organizes chromosomes by type and size)? Humans are diploid 1 Gametes are produced
Genetics Unit Outcomes
 Genetics Unit Outcomes In the cell division unit, you learned that chromosomes come in pairs and that humans have 46 chromosomes in each of their body cells. You receive one of each chromosome from dad
Genetics Unit Outcomes In the cell division unit, you learned that chromosomes come in pairs and that humans have 46 chromosomes in each of their body cells. You receive one of each chromosome from dad
Class *GENETIC NOTES & WORKSHEETS
 Name Class *GENETIC NOTES & WORKSHEETS DAY 1: Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary A. Genetics- Study of B. Heredity- The passing on of characteristics (traits) from to C. Trait A particular that can vary from
Name Class *GENETIC NOTES & WORKSHEETS DAY 1: Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary A. Genetics- Study of B. Heredity- The passing on of characteristics (traits) from to C. Trait A particular that can vary from
Unit 5 Review Name: Period:
 Unit 5 Review Name: Period: 1 4 5 6 7 & give an example of the following. Be able to apply their meanings: Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive Genotype Phenotype Haploid Diploid Sex chromosomes
Unit 5 Review Name: Period: 1 4 5 6 7 & give an example of the following. Be able to apply their meanings: Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive Genotype Phenotype Haploid Diploid Sex chromosomes
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY
 GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics ACP BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics ACP BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
Mendelian Genetics. Vocabulary. M o l e c u l a r a n d M e n d e l i a n G e n e t i c s
 Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary Genotype: o Capital letter = allele o Lowercase letter = allele o Ex AA, Aa, aa Phenotype: o Ex green, yellow Homozygous: o Homozygous dominant: o Homozygous recessive: Heterozygous:
Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary Genotype: o Capital letter = allele o Lowercase letter = allele o Ex AA, Aa, aa Phenotype: o Ex green, yellow Homozygous: o Homozygous dominant: o Homozygous recessive: Heterozygous:
Mendelian Genetics. Activity. Part I: Introduction. Instructions
 Activity Part I: Introduction Some of your traits are inherited and cannot be changed, while others can be influenced by the environment around you. There has been ongoing research in the causes of cancer.
Activity Part I: Introduction Some of your traits are inherited and cannot be changed, while others can be influenced by the environment around you. There has been ongoing research in the causes of cancer.
Genes and Inheritance
 Genes and Inheritance Variation Causes of Variation Variation No two people are exactly the same The differences between people is called VARIATION. This variation comes from two sources: Genetic cause
Genes and Inheritance Variation Causes of Variation Variation No two people are exactly the same The differences between people is called VARIATION. This variation comes from two sources: Genetic cause
Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE
 Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE MEIOSIS is specialized cell division resulting in cells with the genetic material of the parents Sex cells called have exactly set of chromosomes, this
Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE MEIOSIS is specialized cell division resulting in cells with the genetic material of the parents Sex cells called have exactly set of chromosomes, this
Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes. Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Genetics. The study of heredity. Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel (mid 1800 s) Developed set of laws that explain how heredity works
 Genetics The study of heredity Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel (mid 1800 s) Developed set of laws that explain how heredity works Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel original pea plant (input) offspring
Genetics The study of heredity Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel (mid 1800 s) Developed set of laws that explain how heredity works Father of Genetics: Gregor Mendel original pea plant (input) offspring
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity
 Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Genetics, Mendel and Units of Heredity ¾ Austrian monk and naturalist. ¾ Conducted research in Brno, Czech Republic from 1856-1863 ¾ Curious about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. Gregor
Name Class Date. Review Guide. Genetics. The fundamental principles of genetics were first discovered by. What type of plant did he breed?.
 Name Class Date Review Guide Genetics The fundamental principles of genetics were first discovered by. What type of plant did he breed?. True-breeding parental plants are called the generation. Their hybrid
Name Class Date Review Guide Genetics The fundamental principles of genetics were first discovered by. What type of plant did he breed?. True-breeding parental plants are called the generation. Their hybrid
Mendelian Genetics. Biology 3201 Unit 3
 Mendelian Genetics Biology 3201 Unit 3 Recall: Terms Genetics is a branch of biology dealing with the principles of variation and inheritance in animals and plants. Heredity the passing of traits from
Mendelian Genetics Biology 3201 Unit 3 Recall: Terms Genetics is a branch of biology dealing with the principles of variation and inheritance in animals and plants. Heredity the passing of traits from
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
Biology Unit 7 Genetics 7:1 Genetics
 Biology Unit 7 Genetics 7:1 Genetics Gregor Mendel: Austrian monk Studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants His work was not recognized until the 20 th century Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated
Biology Unit 7 Genetics 7:1 Genetics Gregor Mendel: Austrian monk Studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants His work was not recognized until the 20 th century Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated
GENETICS - NOTES-
 GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts
 Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance
 Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
.the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next.
 Genetics .the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next. The chromosomes are contained in the nucleus of the cell. Genes and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made of: Gene:
Genetics .the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next. The chromosomes are contained in the nucleus of the cell. Genes and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made of: Gene:
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment. Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment Student name: Author: Megan Kitchens School: SHAW HIGH SCHOOL Printed: Monday January 30, 2017 1 In fruit flies, the gray body color (G) is dominant
Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: HS Genetics Assessment Student name: Author: Megan Kitchens School: SHAW HIGH SCHOOL Printed: Monday January 30, 2017 1 In fruit flies, the gray body color (G) is dominant
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance
 Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Your Vocabulary words-- write into your journal:
 HUMAN INHERITANCE Your Vocabulary words-- write into your journal: 1. Multiple alleles: three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait. 2. Sex chromosomes: these carry genes that determine
HUMAN INHERITANCE Your Vocabulary words-- write into your journal: 1. Multiple alleles: three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait. 2. Sex chromosomes: these carry genes that determine
Labrador Coat Color Similar to coat color in mice: Black lab is BxEx Yellow lab is xxee Chocolate lab is bbex Probable pathway:
 Honors Genetics 1. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) German monk at the Augustine Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno (today in the Czech Republic). He was a gardener, teacher and priest. Mendel conducted experiments
Honors Genetics 1. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) German monk at the Augustine Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno (today in the Czech Republic). He was a gardener, teacher and priest. Mendel conducted experiments
Mendel and Heredity. Chapter 12
 Mendel and Heredity Chapter 12 Objectives: 1.) Differentiate between genotype and phenotype 2.)Differentiate between genes and alleles. 3.) Differentiate between dominant and recessive alleles. 4.) Explain
Mendel and Heredity Chapter 12 Objectives: 1.) Differentiate between genotype and phenotype 2.)Differentiate between genes and alleles. 3.) Differentiate between dominant and recessive alleles. 4.) Explain
Genetics Honors NOtes 2017 SHORT p2.notebook. May 26, 2017
 Do Now A man and woman want to predict the chances of their offspring having dimples. The woman is heterozygous for dimples and the man does not have dimples. What is the chance of having a child with
Do Now A man and woman want to predict the chances of their offspring having dimples. The woman is heterozygous for dimples and the man does not have dimples. What is the chance of having a child with
Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011
 Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents in appearance.
Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents in appearance.
Mendelian Genetics. Gregor Mendel. Father of modern genetics
 Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel Father of modern genetics Objectives I can compare and contrast mitosis & meiosis. I can properly use the genetic vocabulary presented. I can differentiate and gather data
Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel Father of modern genetics Objectives I can compare and contrast mitosis & meiosis. I can properly use the genetic vocabulary presented. I can differentiate and gather data
14.1 Human Chromosomes pg
 14.1 Human Chromosomes pg. 392-397 Lesson Objectives Identify the types of human chromosomes in a karotype. Describe the patterns of the inheritance of human traits. Explain how pedigrees are used to study
14.1 Human Chromosomes pg. 392-397 Lesson Objectives Identify the types of human chromosomes in a karotype. Describe the patterns of the inheritance of human traits. Explain how pedigrees are used to study
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3
 Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
2. Circle the genotypes in the table that are homozygous. Explain how the two different homozygous genotypes result in different phenotypes.
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Mendel and Heredity. Chapter 12
 Mendel and Heredity Chapter 12 12.1 Objectives: 1.) summarize the importance of Mendel s experiments 2.)Differentiate between genes and alleles. 3.) Explain that alleles determine what physical traits
Mendel and Heredity Chapter 12 12.1 Objectives: 1.) summarize the importance of Mendel s experiments 2.)Differentiate between genes and alleles. 3.) Explain that alleles determine what physical traits
Normal enzyme makes melanin (dark pigment in skin and hair) Defective enzyme does not make melanin
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Human Inheritance Lesson 4
 Human Inheritance Lesson 4 May 10 6:55 PM What are some patterns of human inheritance? What are the functions of the sex chromosomes? May 10 6:56 PM 1 I. What are some patterns of human inheritance A.
Human Inheritance Lesson 4 May 10 6:55 PM What are some patterns of human inheritance? What are the functions of the sex chromosomes? May 10 6:56 PM 1 I. What are some patterns of human inheritance A.
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Remember DNA RNA Protein Traits DNA contains the code for proteins (protein synthesis remember?) Proteins determine our traits Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 Father of Genetics Studied
Introduction to Genetics Remember DNA RNA Protein Traits DNA contains the code for proteins (protein synthesis remember?) Proteins determine our traits Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 Father of Genetics Studied
Extra Review Practice Biology Test Genetics
 Mendel fill in the blanks: Extra Review Practice Biology Test Genetics Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied genetics primarily using plants. He started with plants that produced offspring with only
Mendel fill in the blanks: Extra Review Practice Biology Test Genetics Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied genetics primarily using plants. He started with plants that produced offspring with only
40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12
 40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12 1. I am available after school on Wed. and Thurs. this week. 2. Quiz Friday over genetic material 3. Last day to turn in
40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12 1. I am available after school on Wed. and Thurs. this week. 2. Quiz Friday over genetic material 3. Last day to turn in
Inheritance. Children inherit traits from both parents.
 Have you ever been told you have your mother s eyes or your father s smile? Have you ever noticed you share your grandfather s eye color or possibly your grandmother s curly hair, and yet your parents
Have you ever been told you have your mother s eyes or your father s smile? Have you ever noticed you share your grandfather s eye color or possibly your grandmother s curly hair, and yet your parents
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares
 Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Genetics. *** Reading Packet
 Genetics *** Reading Packet 5.4 Mendel and His Peas Learning Objectives Describe Mendel's first genetics experiments. Introduction Why do you look like your family? For a long time people understood that
Genetics *** Reading Packet 5.4 Mendel and His Peas Learning Objectives Describe Mendel's first genetics experiments. Introduction Why do you look like your family? For a long time people understood that
Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS
 Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS Chapter Summary In order to study the transmission of human genetic traits to the next generation, a different method of operation had to be adopted. Instead
Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS Chapter Summary In order to study the transmission of human genetic traits to the next generation, a different method of operation had to be adopted. Instead
Gregor Mendel. What is Genetics? the study of heredity
 Gregor Mendel What is Genetics? the study of heredity Gregor Mendel s Peas Pollen: plant s sperm Egg Cells: plants reproductive cells Fertilization: joining of pollen + egg cells develops into embryo in
Gregor Mendel What is Genetics? the study of heredity Gregor Mendel s Peas Pollen: plant s sperm Egg Cells: plants reproductive cells Fertilization: joining of pollen + egg cells develops into embryo in
Genes and Inheritance (11-12)
 Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents.
 Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Remember DNA RNA Protein Traits DNA contains the code for proteins (protein synthesis remember?) Proteins determine our traits Remember Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 Father of Genetics
Introduction to Genetics Remember DNA RNA Protein Traits DNA contains the code for proteins (protein synthesis remember?) Proteins determine our traits Remember Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 Father of Genetics
Review Packet for Genetics and Meiosis
 Name: Date: Block: 1 Review Packet for Genetics and Meiosis Directions: Answer the questions and where indicated, draw a Punnett square and show all work! 1. Who was Gregor Mendel? Where did he live and
Name: Date: Block: 1 Review Packet for Genetics and Meiosis Directions: Answer the questions and where indicated, draw a Punnett square and show all work! 1. Who was Gregor Mendel? Where did he live and
Puzzling Pedigrees. Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits?
 Name: Puzzling Pedigrees Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits? Studying inheritance in humans is more difficult than studying inheritance in fruit flies
Name: Puzzling Pedigrees Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits? Studying inheritance in humans is more difficult than studying inheritance in fruit flies
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes
 Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
Hope you all had a wonderful weekend! Today we are finally getting into Genetics!
 Hope you all had a wonderful weekend! Today we are finally getting into Genetics! To prepare for class today, please do the following: Grab one of the activity worksheets off the front table. Widow s Peak
Hope you all had a wonderful weekend! Today we are finally getting into Genetics! To prepare for class today, please do the following: Grab one of the activity worksheets off the front table. Widow s Peak
draw and interpret pedigree charts from data on human single allele and multiple allele inheritance patterns; e.g., hemophilia, blood types
 Specific Outcomes for Knowledge Students will: 30 C2.1k describe the evidence for dominance, segregation and the independent assortment of genes on different chromosomes, as investigated by Mendel 30 C2.2k
Specific Outcomes for Knowledge Students will: 30 C2.1k describe the evidence for dominance, segregation and the independent assortment of genes on different chromosomes, as investigated by Mendel 30 C2.2k
B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and relate that theory to Gregor Mendel s principles of genetics
 B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and relate that theory to Gregor Mendel s principles of genetics The Chromosome theory of inheritance is a basic principle in biology that states genes
B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and relate that theory to Gregor Mendel s principles of genetics The Chromosome theory of inheritance is a basic principle in biology that states genes
Pre-AP Biology Unit 7 Genetics Review Outline
 Unit 7 Genetics Review Outline Pre-AP Biology 2017-2018 LT 1 - I can explain the relationships among alleles, genes, chromosomes, genotypes, and phenotypes. This target covers application of the vocabulary
Unit 7 Genetics Review Outline Pre-AP Biology 2017-2018 LT 1 - I can explain the relationships among alleles, genes, chromosomes, genotypes, and phenotypes. This target covers application of the vocabulary
By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES
 Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
Genetics Practice Questions:
 Genetics Practice Questions: 1. Define the following Vocabulary Words: Fertilization fusion of a haploid nucleus of an egg cell and a haploid nucleus of a sperm cell haploid-- a nucleus containing a single
Genetics Practice Questions: 1. Define the following Vocabulary Words: Fertilization fusion of a haploid nucleus of an egg cell and a haploid nucleus of a sperm cell haploid-- a nucleus containing a single
Human Genetics Notes:
 Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses:
 Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses: 2.5 Genetics Objectives 2.5.6 Genetic Inheritance 2.5.10.H Origin of the Science of genetics 2.5.11 H Law of segregation 2.5.12 H Law of independent assortment 2.5.13.H Dihybrid
Chapter 17 Genetics Crosses: 2.5 Genetics Objectives 2.5.6 Genetic Inheritance 2.5.10.H Origin of the Science of genetics 2.5.11 H Law of segregation 2.5.12 H Law of independent assortment 2.5.13.H Dihybrid
PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS
 PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS GENETICS TERMS AND VOCABULARY DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the molecule that codes for our traits. CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus
PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS GENETICS TERMS AND VOCABULARY DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the molecule that codes for our traits. CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus
Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages )
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
Mendelian Genetics. You are who you are due to the interaction of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism.
 Heredity Chapter 3 3:1 Genetics Mendelian Genetics You are who you are due to the interaction of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that
Heredity Chapter 3 3:1 Genetics Mendelian Genetics You are who you are due to the interaction of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity
 Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
UNIT IV. Chapter 14 The Human Genome
 UNIT IV Chapter 14 The Human Genome UNIT 2: GENETICS Chapter 7: Extending Medelian Genetics I. Chromosomes and Phenotype (7.1) A. Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype 1. Most human traits
UNIT IV Chapter 14 The Human Genome UNIT 2: GENETICS Chapter 7: Extending Medelian Genetics I. Chromosomes and Phenotype (7.1) A. Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype 1. Most human traits
Unit 5: Genetics Notes
 Unit 5: Genetics Notes https://goo.gl/fgtzef Name: Period: Test Date: Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Date Warm-ups 3-4 Mendelian Genetics Notes 5-6 Mendelian Genetics Lets Practice 7 Monohybrid
Unit 5: Genetics Notes https://goo.gl/fgtzef Name: Period: Test Date: Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Date Warm-ups 3-4 Mendelian Genetics Notes 5-6 Mendelian Genetics Lets Practice 7 Monohybrid
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits.
 Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation MAIN IDEA:
Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation MAIN IDEA:
Introduction to Genetics
 DAY 2 Introduction to Genetics Heredity Passing of traits from parents to their young The branch of biology that studies heredity is genetics. Trait Characteristic that is inherited Gregor Mendel Austrian
DAY 2 Introduction to Genetics Heredity Passing of traits from parents to their young The branch of biology that studies heredity is genetics. Trait Characteristic that is inherited Gregor Mendel Austrian
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1
 Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Science Olympiad Heredity
 Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
Mendelian Genetics. 7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping Genes can be mapped to specific locations on chromosomes.
 7 Extending CHAPTER Mendelian Genetics GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. 7.2 Complex
7 Extending CHAPTER Mendelian Genetics GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. 7.2 Complex
Guided Notes: Simple Genetics
 Punnett Squares Guided Notes: Simple Genetics In order to determine the a person might inherit, we use a simple diagram called a o Give us of an offspring having particular traits Pieces of the Punnett
Punnett Squares Guided Notes: Simple Genetics In order to determine the a person might inherit, we use a simple diagram called a o Give us of an offspring having particular traits Pieces of the Punnett
Genetic Variation Junior Science
 2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
Fundamentals of Genetics
 Fundamentals of Genetics For thousands of years people have known that living things somehow pass on some type of information to their offspring. This was very clear in things that humans selected to breed
Fundamentals of Genetics For thousands of years people have known that living things somehow pass on some type of information to their offspring. This was very clear in things that humans selected to breed
UNIT 6 GENETICS 12/30/16
 12/30/16 UNIT 6 GENETICS III. Mendel and Heredity (6.3) A. Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics 1. Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. 2. Genetics is the study of biological
12/30/16 UNIT 6 GENETICS III. Mendel and Heredity (6.3) A. Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics 1. Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. 2. Genetics is the study of biological
Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3
 Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3 Genetics = the study of heredity by which traits are passed from parents to offspring Page. 227 Heredity = The passing of genes/traits
Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3 Genetics = the study of heredity by which traits are passed from parents to offspring Page. 227 Heredity = The passing of genes/traits
Genetics All somatic cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Genes contained in each pair of chromosomes
 Chapter 6 Genetics and Inheritance Lecture 1: Genetics and Patterns of Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic
Chapter 6 Genetics and Inheritance Lecture 1: Genetics and Patterns of Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic
Genetics and Heredity Notes
 Genetics and Heredity Notes I. Introduction A. It was known for 1000s of years that traits were inherited but scientists were unsure about the laws that governed this inheritance. B. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
Genetics and Heredity Notes I. Introduction A. It was known for 1000s of years that traits were inherited but scientists were unsure about the laws that governed this inheritance. B. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
Inheritance. What is inheritance? What are genetics? l The genetic characters transmitted from parent to offspring, taken collectively
 Genetics Interest Grabber Look at your classmates. Note how they vary in the shape of the front hairline, the space between the two upper front teeth, and the way in which the ear lobes are attached. Make
Genetics Interest Grabber Look at your classmates. Note how they vary in the shape of the front hairline, the space between the two upper front teeth, and the way in which the ear lobes are attached. Make
Lesson Overview Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview 14.1 Human Chromosomes Human Genome To find what makes us uniquely human, we have to explore the human genome, which is the full set of genetic information carried in our DNA. This DNA
Lesson Overview 14.1 Human Chromosomes Human Genome To find what makes us uniquely human, we have to explore the human genome, which is the full set of genetic information carried in our DNA. This DNA
The Modern Genetics View
 Inheritance Mendelian Genetics The Modern Genetics View Alleles are versions of a gene Gene for flower color Alleles for purple or white flowers Two alleles per trait 2 chromosomes, each with 1 gene The
Inheritance Mendelian Genetics The Modern Genetics View Alleles are versions of a gene Gene for flower color Alleles for purple or white flowers Two alleles per trait 2 chromosomes, each with 1 gene The
Question 2: Which one of the following is the phenotypic monohybrid ratio in F2 generation? (a) 3:1 (b) 1:2:1 (c) 2:2 (d) 1:3 Solution 2: (a) 3 : 1
 Class X Genetics Biology A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option) Which one of the following has the smallest number of chromosomes? (a) Onion (b) Mouse (c) Monkey (d) Ascaris (d)
Class X Genetics Biology A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option) Which one of the following has the smallest number of chromosomes? (a) Onion (b) Mouse (c) Monkey (d) Ascaris (d)
Section Objectives: Pedigrees illustrate inheritance. Pedigrees illustrate inheritance
 What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
Human Heredity: The genetic transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring.
 Human Heredity: The genetic transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring. Karyotype : picture of the actual chromosomes arranged in pairs, paired and arranged from largest to smallest. Human
Human Heredity: The genetic transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring. Karyotype : picture of the actual chromosomes arranged in pairs, paired and arranged from largest to smallest. Human
Name Period. Keystone Vocabulary: genetics fertilization trait hybrid gene allele Principle of dominance segregation gamete probability
 Name Period BIO B2 GENETICS (Chapter 11) You should be able to: 1. Describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (dominant, recessive, co- dominant, incomplete dominance, sex- linked, polygenic
Name Period BIO B2 GENETICS (Chapter 11) You should be able to: 1. Describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (dominant, recessive, co- dominant, incomplete dominance, sex- linked, polygenic
Genetics & Heredity 11/16/2017
 Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
How do genes influence our characteristics?
 Genetics Supplement 1 This activity will focus on the question: How do genes contribute to the similarities and differences between parents and their children? This question can be divided into two parts:
Genetics Supplement 1 This activity will focus on the question: How do genes contribute to the similarities and differences between parents and their children? This question can be divided into two parts:
Mendelian Genetics. KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units.
 KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics. Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. Genetics is the
KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics. Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. Genetics is the
Pedigrees: Genetic Family History
 Pedigrees: Genetic Family History - Women are represented with a. - Men are represented with a. - Affected individuals are (individuals who express the trait). C B A D If this is you who are The other
Pedigrees: Genetic Family History - Women are represented with a. - Men are represented with a. - Affected individuals are (individuals who express the trait). C B A D If this is you who are The other
Bell Work 3/8/18. Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis?
 Bell Work 3/8/18 Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis? Bell Work: 3/9/18 Complete the pre-assessment on your Anchor Activity Unit 6 sheet.
Bell Work 3/8/18 Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis? Bell Work: 3/9/18 Complete the pre-assessment on your Anchor Activity Unit 6 sheet.
UNIT III (Notes) : Genetics : Mendelian. (MHR Biology p ) Traits are distinguishing characteristics that make a unique individual.
 1 UNIT III (Notes) : Genetics : endelian. (HR Biology p. 526-543) Heredity is the transmission of traits from one generation to another. Traits that are passed on are said to be inherited. Genetics is
1 UNIT III (Notes) : Genetics : endelian. (HR Biology p. 526-543) Heredity is the transmission of traits from one generation to another. Traits that are passed on are said to be inherited. Genetics is
Unit B2, B2.7. Cell division and inheritance. Stage 1. Ovary. Cell Q. Cell P. Cell R. Cell S. 7 Embryo A B C
 Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
11-1: Introduction to Genetics
 11-1: Introduction to Genetics The Work of Gregor Mendel Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Genetics Vocabulary Genetics The study of heredity. Heredity The passing of physical characteristics from parents
11-1: Introduction to Genetics The Work of Gregor Mendel Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Genetics Vocabulary Genetics The study of heredity. Heredity The passing of physical characteristics from parents
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis. (Sections 11-3,11-4;)
 MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
HEREDITY. def: the passing of traits from parent to offspring.
 Genetics & Heredity HEREDITY def: the passing of traits from parent to offspring. GENETICS def: The study of heredity. *The Father of Genetics* (1822-1884) Occupation: Monk Subjects Studied: Botany (*study
Genetics & Heredity HEREDITY def: the passing of traits from parent to offspring. GENETICS def: The study of heredity. *The Father of Genetics* (1822-1884) Occupation: Monk Subjects Studied: Botany (*study
5Which one of the following occurs in meiosis, but not mitosis?
 Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
Patterns of Heredity Genetics
 Patterns of Heredity Genetics DO NOW Hand in outlines (my desk) Pick up tests from back table and review them. We will be going over the zipgrade and the short answer together. Save your questions for
Patterns of Heredity Genetics DO NOW Hand in outlines (my desk) Pick up tests from back table and review them. We will be going over the zipgrade and the short answer together. Save your questions for
Patterns in Inheritance. Chapter 10
 Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
Gregor Mendel Father of Genetics
 Genetics and Mendel Gregor Mendel Father of Genetics Gregor Mendel First person to trace characteristics of living things Augustinian Monk Lived and worked in an Austrian monastery in the mid-1800s Parents
Genetics and Mendel Gregor Mendel Father of Genetics Gregor Mendel First person to trace characteristics of living things Augustinian Monk Lived and worked in an Austrian monastery in the mid-1800s Parents
