Leifer: Introduction to Maternity & Pediatric Nursing, 6th Edition
|
|
|
- Jason Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Leifer: Introduction to Maternity & Pediatric Nursing, 6th Edition Chapter 02: Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A 14-year-old boy is at the pediatric clinic for a checkup. The nurse is aware that the production of testosterone is responsible for which physical change in males during puberty? a. Stimulation of production of white cells and platelets b. Promotion of growth of small bones c. Increase in muscle mass and strength d. Decrease in production of sebaceous gland secretions ANS: C Testosterone increases muscle mass, promotes strength and growth of long bones, and enhances production of red blood cells. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 22 OBJ: 5 TOP: Male Reproductive System Assessment 2. The nurse explains that the production of sperm and secretion of hormones is regulated by the: a. testes. b. vas deferens. c. ejaculatory ducts. d. prostate gland. ANS: A The testes have two functions: manufacture of spermatozoa and secretion of androgens. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 21 OBJ: 5 TOP: Male Reproductive System 3. The nurse, speaking with a couple trying to conceive a child, reminds the patients that a factor that can decrease sperm production is: a. infrequent sexual intercourse. b. the man not being circumcised. c. the penis and testes being small. d. the testes being too warm.
2 2-2 ANS: D The scrotum is suspended away from the perineum to lower the temperature of the testes for sperm production. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 21 OBJ: 5 TOP: Male Reproductive System MSC: NCLEX: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk 4. When describing the female reproductive tract to a pregnant woman, the nurse would explain that which uterine layer is involved in implantation? a. Perimetrium b. Endometrium c. Myometrium d. Internal os The endometrium is the inner mucosal layer of the uterus that is governed by cyclical hormonal changes. It is functional during menstruation and during the implantation of a fertilized ovum. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 24 OBJ: 3 TOP: Female Reproductive System 5. A group of nursing students plans to teach a class of sixth-grade girls about menstruation. They would teach the girls that: a. menarche usually occurs around 12 years of age. b. ovulation occurs regularly from the very first cycle. c. a regular cycle is established by the third period. d. typically, menstrual flow is heavy and lasts up to 10 days. ANS: A The beginning of menstruation, called menarche, occurs at about 12 years of age. Early cycles are irregular and anovulatory. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 27 OBJ: 9 TOP: Female Reproductive Cycle and Menstruation Planning 6. A 10-year-old girl asks the nurse, What is the first sign of puberty? The correct nursing response is: a. an increase in height. b. breast development.
3 2-3 c. appearance of axillary hair. d. the first menstrual period. The first outward change of puberty in girls is the development of breasts at about 10 to 11 years of age. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 21 OBJ: 2 TOP: Puberty Female 7. Maturation of the ovarian follicle is initiated by which hormone? a. Estrogen b. Follicle-stimulating hormone c. Progesterone d. Luteinizing hormone Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the maturation of a follicle. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 27 OBJ: 9 TOP: Female Reproductive Cycle N/A 8. The statement that indicates a woman has correct information about oogenesis is: a. Women make fewer ova as they age. b. Women have all of their ova at the time they are born. c. Ova production begins at birth and continues until puberty. d. New ova are made every month from puberty to climacteric. Oogenesis (formation of immature ova) does not occur after fetal development. Females are born with about 2 million immature ova that rapidly reduce by adulthood. DIF: Cognitive Level: Analysis REF: p. 25 OBJ: 9 TOP: Female Reproductive Cycle Evaluation 9. A pregnant woman asks the nurse, Will I be able to have a vaginal delivery? The nurse would base a response on the understanding that the pelvic type most favorable for vaginal birth is: a. gynecoid. b. android. c. anthropoid. d. platypelloid.
4 2-4 ANS: A The gynecoid pelvis is the typical female pelvis and is most favorable for vaginal birth. DIF: Cognitive Level: Analysis REF: p. 25 OBJ: 8 TOP: Female Reproductive System MSC: NCLEX: Health Promotion and Maintenance: Prevention and Early Detection of Disease 10. A mother is anxious about her ability to breastfeed after her child is born because of her small breast size. An important point to teach her is that: a. milk is produced in ducts and lobules regardless of breast size. b. supplementing breastfeeding with formula allows the infant to receive adequate nutrition. c. breast size can be increased with exercise. d. drinking extra milk during pregnancy allows breasts to produce adequate amounts of milk. ANS: A Breast size does not influence the ability to secrete milk. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 27 OBJ: 6 TOP: Female Reproductive System MSC: NCLEX: Psychosocial Integrity: Psychosocial Adaptation 11. The nurse explains that the decrease in estrogen and progesterone during the menstrual cycle is responsible for: a. degeneration of the corpus luteum. b. ovulation. c. follicle maturation. d. shedding of the endometrium. ANS: D The fall in estrogen and progesterone causes the endometrium to break down, resulting in menstruation. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 27 OBJ: 9 TOP: Female Reproductive Cycle 12. The nurse assisting with pelvic inlet measurements on a pregnant woman is aware that the measurement that provides information about whether or not the woman can deliver vaginally is:
5 2-5 a. diagonal conjugate. b. obstetric conjugate. c. transverse diameter. d. anteroposterior diameter. This measurement determines if the fetus can pass through the birth canal. DIF: Cognitive Level: Analysis REF: p. 26 OBJ: 8 TOP: Female Reproductive System MSC: NCLEX: Health Promotion and Maintenance: Prevention and Early Detection of Disease 13. The nurse has explained menstruation to a 13-year-old girl. The statement that indicates the girl needs additional education is: a. Periods last about 5 days. b. My cycle should get regular in 6 months. c. I should expect heavy bleeding with clots. d. Periods come about every 4 weeks. ANS: C Clots are not normally seen in menstrual discharge. A normal menstrual flow is 30 to 40 ml blood and 30 to 50 ml serous fluid. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 27 OBJ: 9 TOP: Female Reproductive Cycle Evaluation 14. A mother asks the nurse, When will I know my child has entered puberty? Based on an understanding of changes associated with puberty, the nurse states: a. When your daughter has her first period. b. You ll recognize puberty by the mood swings. c. The child becomes interested in the opposite sex. d. Secondary sex characteristics, such as pubic hair, appear. ANS: D Puberty begins when the secondary sex characteristics appear. Puberty ends when mature sperm are formed in the male and when regular menstrual cycles occur in the female. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 20 OBJ: 2 TOP: Puberty
6 When planning to teach couples about the physiology of the sex act, the nurse would state that: a. Fertilization of an ovum requires penetration by several sperm. b. An ovum must be fertilized within 24 hours of ovulation. c. It takes 4 to 5 days for sperm to reach the fallopian tubes. d. Sperm live for only 24 hours following ejaculation. Following ovulation, the egg lives for only 24 hours. Sperm must be available during that time if fertilization is to occur. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 29 OBJ: 6 TOP: Physiology of the Sex Act Planning 16. A newly married couple tells the nurse they would like to wait a few years before starting a family. The statement made by the man that indicates an understanding about sexual activity and pregnancy is: a. My wife can t get pregnant if I withdraw before climax. b. A man can secrete semen before ejaculation. c. If we don t have intercourse very often, my wife won t get pregnant. d. It is safe to ejaculate outside the vagina. Semen may be secreted during sexual intercourse before ejaculation. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 22 OBJ: 4 TOP: Male Reproductive System Evaluation MSC: NCLEX: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk 17. The nurse who is aware that the diagonal conjugate is 12 centimeters knows that the obstetric conjugate is centimeters. a. 10 to 10.5 b. 11 to 11.5 c to 13 d. 14 to 14.5 ANS: A The obstetric conjugate is approximately 1.5 to 2 centimeters shorter than the diagonal conjugate. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 26 OBJ: 8 TOP: Obstetric Conjugate MSC: NCLEX: Health Promotion and Maintenance: Prevention and Early Detection of Disease
7 The nurse uses a diagram to demonstrate the fimbriae, which: a. are the passageway for the sperm to meet the ovum. b. is the site of fertilization. c. are fingerlike projections that capture the ovum. d. propel the egg through the fallopian tube. ANS: C Fimbriae are the fingerlike projections from the infundibulum that capture the ovum at ovulation and conduct it into the fallopian tube. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 25 OBJ: 6 TOP: Fimbriae 19. The nurse explains to a 12-year-old patient that nocturnal emissions (wet dreams) are characterized by: a. a drop in testosterone level. b. sexual stimulation. c. absence of sperm in ejaculate. d. association with violent dreams. ANS: C Nocturnal emissions occur without sexual stimulation and contain no sperm. Testosterone levels are constant until midlife. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 21 OBJ: 2 TOP: Nocturnal Emissions 20. The nurse explains to a pregnant patient who expects to breastfeed that the portions of the breast that secrete milk are the: a. lactiferous sinuses. b. lobes. c. Montgomery s glands. d. alveoli. ANS: D The alveoli secrete milk. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 27 OBJ: 6 TOP: Milk Secretion KEY: Nursing Process Step: 21. The nurse explains that the sperm are nourished by secretions from the:
8 2-8 a. vas deferens. b. epididymis. c. Cowper s glands. d. scrotum. ANS: C The Cowper s gland secretions nourish the sperm. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 22 OBJ: 4 TOP: Cowper s Gland 22. The nurse clarifies that puberty ends for a male when: a. facial hair is evident. b. erections can be sustained. c. ejaculate is greater than 5 ml. d. mature sperm form. ANS: D Puberty ends for a male when mature sperm are formed by the testes. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 20 OBJ: 2 TOP: End of Puberty 23. The nurse explains that sperm can remain viable in the female reproductive tract for as long as: a. 12 hours. b. 1 day. c. 2 days. d. 4 days. ANS: D Sperm can remain viable in the reproductive tract of the female for as long as 4 to 5 days. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 29 OBJ: 7 TOP: Viability of Sperm 24. The nurse encourages the members of a prenatal class to seriously consider breastfeeding because, in addition to nourishment for the infant, breast milk provides:
9 2-9 a. maternal antibodies. b. stimulus for red blood cell production. c. endorphins that soothe the infant. d. hormones that stimulate growth. ANS: A Breast milk provides maternal antibodies to the infant that give the child acquired immunity from some diseases for several months. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 26 OBJ: 4 TOP: Properties of Breast Milk MSC: NCLEX: Health Promotion and Maintenance: Prevention and Early Detection of Disease MULTIPLE RESPONSE 25. The nurse conducting a sex education class for junior high students describes some cultural rites celebrating the entry to adulthood. Which would be included? Select all that apply. a. Bar mitzvah b. Displays of bravery c. Receiving part of their inheritance d. Ritual circumcision e. Displays of self-defense ANS: A, B, D, E Some cultures celebrate the entry to adulthood with rites such as displays of strength, bravery, self-reliance, and self-defense. Ritual circumcisions and bar and bat mitzvahs are also entry rites to adulthood. Lack of such rituals can sometimes confuse young people because there is no evidence of acceptance as an adult. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 20 OBJ: 2 TOP: Rites of Passage 26. By reading a pregnant patient s history and physical, the nurse recognizes what information that might indicate the need for a cesarean delivery? Select all that apply. a. History of childhood rickets b. Immobile coccyx c. Prepregnant weight of 100 pounds d. Avid horse rider e. Pelvic fracture 3 years ago
10 2-10 ANS: A, B, E Pelvic conditions that might predispose to a cesarean delivery are childhood rickets, pelvic fracture, and immobile coccyx. DIF: Cognitive Level: Analysis REF: p. 26 OBJ: 8 TOP: Pelvic Conditions Predisposing Cesarean Delivery Assessment MSC: NCLEX: Health Promotion and Maintenance: Prevention and Early Detection of Disease 27. The nurse explains that the fallopian tubes have which function(s)? Select all that apply. a. Passage for sperm to meet ova b. Passage for ovum to uterus c. Safe environment for zygote d. Restriction for only one ovum to enter uterus e. Site for fertilization ANS: A, B, C, E The fallopian tube provides passage for both sperm and ova, offering an optimum place for fertilization and a safe environment for the zygote. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 25 OBJ: 6 TOP: Function of Fallopian Tubes 28. Using a diagram, the nurse points out which bones that are part of the pelvis? Select all that apply. a. Two innominates b. Obstetric conjugate c. Sacrum d. Perimetrium e. Coccyx ANS: A, B, E The bones of the pelvis are two innominates, the sacrum, and the coccyx. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 25 OBJ: 8 TOP: Bones of the Pelvis 29. The nurse explains that testosterone is responsible for males exceeding females in which aspect(s)? Select all that apply. a. Strength
11 2-11 b. Height c. Mental concentration d. Hematocrit levels e. Agility ANS: A, B, D DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 25 OBJ: 2 TOP: Effects of Testosterone COMPLETION 30. When the nurse reads in the history and physical of a pregnant patient that she has a platypelloid pelvis, the nurse is aware that this pelvis has a narrow diameter, making a vaginal birth unlikely. ANS: anteroposterior The platypelloid pelvis is very narrow from front to back (anteroposterior). The shape of this pelvis makes vaginal delivery unlikely. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: pp , Figure 2-5 OBJ: 8 TOP: Platypelloid Pelvis Assessment MSC: NCLEX: Health Promotion and Maintenance: Prevention and Early Detection of Disease 31. In males the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and the luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary stimulate testosterone production in the cells of the testes. ANS: Leydig The Leydig cells in the testes are stimulated by the FSH and LH to produce testosterone. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge REF: p. 22 OBJ: 2 TOP: Leydig Cells N/A OTHER 32. The nurse outlines the phases of the sexual response. Arrange the phases in order of occurrence. a. Nipples become erect. b. Involuntary muscle spasms occur.
12 2-12 c. Engorgement resolves. d. Heart rate slows. e. Skin flushes. ANS: A, E, B, C, D DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: p. 29 OBJ: 2 TOP: Sexual Response MSC: NCLEX: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
link full dowload:
 link full dowload: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-maternity-nursingan-introductory-text-11th-edition-by-gloria-leifer Leifer: Maternity Nursing: An Introductory Text, 11th Edition Chapter
link full dowload: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-maternity-nursingan-introductory-text-11th-edition-by-gloria-leifer Leifer: Maternity Nursing: An Introductory Text, 11th Edition Chapter
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
 Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Reproductive structures that have erectile tissue include
Test Bank for Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition by Leifer Chapter 02: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Reproductive structures that have erectile tissue include
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Growing up. W Worksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts
 3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
2 - male hormones/ female system
 2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
The Female Reproductive System
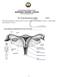 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Physiology of Male Reproductive System
 Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Lecture 28, The Reproductive System
 Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Transformation Information elearning Kit Combined Program Lesson Plan Page 1. LESSON TITLE: Combined Program
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O.
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank
 Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
Unit 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive System Test Bank Objective 6.01 Describe the basic functions of the reproductive system. 1. Which of the following is a function of the reproductive system? a. Production
Chapter 18. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
 MOCK TEST I (HUMAN REPRODUCTION) 1. In human transfer of sperms into female genital tract is called as 1) Fertilization 2) Implantation 3) Insemination 4) Gestation 2. In male human scrotum maintains the
MOCK TEST I (HUMAN REPRODUCTION) 1. In human transfer of sperms into female genital tract is called as 1) Fertilization 2) Implantation 3) Insemination 4) Gestation 2. In male human scrotum maintains the
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth
 Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine
 1 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine INTRODUCTION Fertility changes with age. Both males and females become fertile in
1 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine INTRODUCTION Fertility changes with age. Both males and females become fertile in
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
Puberty and Reproduction
 Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
40a A&P: Reproductive System
 40a A&P: Reproductive System 40a A&P: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
40a A&P: Reproductive System 40a A&P: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3:
 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
