Simulation in Critical Care Medicine
|
|
|
- Claire Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simulation in Critical Care Medicine Chris Brackney, DO, FACOI Assistant Professor Department of Critical Care Medicine University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Director VAPHS Surgical ICU Director VAPHS ECLS Program
2 NONE Disclosures
3 Education and Simulation Overview Task Trainers High Fidelity Simulation Simulation Integration
4 Teaching Teacher Centered (Traditional approach) Lecture based, dependent upon presenter Learn passively, absorbing concepts /taking notes Outcomes based upon essays and exams
5 The Teacher as a Manager of Resources Develops a curriculum with clear, measurable objectives Organizes a variety of learning experiences Motivates students to become self-directed learners Evaluates student performance Provides immediate feedback Stritter, J. Med. Ed. V42, pg
6 Characteristics of Adult Learners Self-directed - the teacher acts as a facilitator guiding students to knowledge rather than supplying it Goal oriented - students have predetermined goals and enjoy a curriculum that helps them attain those goals Bloom s Taxonomy
7 Characteristics of Adult Learners Relevancy oriented learning must be applicable to training them for their jobs Respected in medical education this includes voicing opinions about management and defending their judgement Motivated Require feedback Adapted from Malcolm Knowles
8 Apply Bloom s Taxonomy Utilize Various Teaching Techniques Evaluate Performance Create Educational Objectives Give Appropriate and Effective Feedback
9 Developing Educational Objectives An objective is a statement of purpose They describe specifically what the learner is to learn This includes three domains Cognitive intellect brain / the knowing Affective values heart / the feeling Psychomotor skills hands / the doing
10 Sample Educational Objectives Be able to manage unresponsive patients OR Check for pulse immediately, check blood glucose, inquire about opiate use, administer 40ug narcan, provide bag-mask ventilation if airway not protected
11 Sample Educational Objectives Manages respiratory distress OR Check respiratory rate, place pulse oximeter, start 100% non-rebreather, call for rapid response team
12 Feedback Definition Method of controlling a system by reinserting into the system the results of its performance Providing the learner with specific information about their performance to reinforce or change behavior Formative (qualitative feedback) Summative (educational outcomes)
13 Feedback Purpose The most powerful teaching tool an instructor has Provides a basis for maintaining or improving performance Provides a mechanism for assessing needs and providing learning experiences
14 Feedback Timing and Setting Established during orientation that feedback will be provided immediately following assessment Will be provided daily Should be an expected part of the learning experience
15 Characteristics of Effective Feedback Begin with clear, unambiguous, specific, achievable goals Inform the learner to expect feedback as part of the educational process Base feedback on first hand observation Delivered as a two way conversation soliciting the learners comments Must be credible to the learner
16 Characteristics of Effective Feedback Base feedback on behavior not interpretations of behavior Provide feedback privately Provide the learner with the way to succeed Do not give positive feedback before giving feedback that is intended to change behavior
17 Without Feedback In surveys one of the most frequently cited deficiencies of an educational program is the lack of feedback Failure to effectively evaluate performance Concern it will lead to an unpleasant emotional response May damage learner-teacher relationship Mistakes go uncorrected Good performance goes unreinforced Students generate their own feedback by attacking importance to unintended clues
18 I hear, and I forget I see, and I remember I do, and I understand -Confucius
19 Whole Body Simulators Is an efficient means of teaching a large group of trainees Allows trainees to experience rare, life-threatening conditions Allows trainees to make medical errors without harmful consequences to patients Enables faculty to provide feedback Permits trainees to repeat performances until educational objectives are mastered
20 Task Trainers
21 Central Line Trainers Central Lines
22 Peripherial IV / Arterial Lines
23 Ultrasound Trainer Viamedix (CAE) X-Porte (Sonosite)
24 Bronch Mentor Bronch Mentor
25
26 Sim-ECMO Krystal Shaffer, MD Lillian Emlet, MD Christopher Brackney, DO
27 Background Gap Analysis Fellows exposed to high volume, reputable, ECMO program Pre-rotation preparation includes written manual and a 3hr on-line lecture series Fellows struggle to identify and treat common ECMO complications Purpose Serve as a training tool to educate critical care fellows on how to recognize, diagnose, and treat complications related to ECMO
28 Setup Personel Perfusionist Respiratory Therapist Bedside Nurse CCM Fellow Equipment Laerdal 3G SimMan Ventilator Ultrasound CPB Machine with tubing Red food coloring
29 ECMO photo
30 Scenario #1 - Hypovolemia Learning Objectives ID low flow rates/chatter as signs of hypovolemia Establish DDX for hypovolemia in setting of ECMO Discuss risks benefits of stopping anticoagulation
31 Scenario #2 Recirculation Learning Objectives Recognize persistant hypoxemia after VV ECMO cannulation and develop an appropriate differential diagnosis for hypoxia while on an ECMO circuit Recognize flash on ECMO cannulas and move femoral cannula back to prevent recirculation Identify PTX as a complication of ECMO cannula placement
32 Scenario #3 Obstructive Learning Objectives Correctly identify alarms on the ECMO circuit as indicative of low flow Formulate a differential diagnosis for causes of low ECMO flow and hemodynamic deterioration Reinforce concepts of diagnosis and treatment of pericardial tamponade Shock
33 Assessment Pre/Post test which mimics CCM board questions Post Simulation survey
34
35 Sim-Trach Kavita Dedhia, MD Christopher Brackney, DO David Eibling, MD
36 Horror Stories
37 Background Growing number of hospitalized patients with tracheostomies Common procedure performed by: ENT, Thoracic surgery, general surgery, and pulmonary/critical care team 2009 study by McGrath: 75% of the 453 incidents associated w/tracheostomy were associated with patient harm 6% required life saving care 15 patients died Complications and death associated with laryngectomy patients No current training at UPMC
38 NHS RESOURCES National Tracheostomy Safety Project Joint NHS project Online resources What is tracheostomy, different types of tubes Surgical procedure Emergency management of tracheostomy and laryngectomy Management of day-today needs of tracheostomy patients
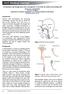
39 Emergency tracheostomy management Patent upper airway Call for airway expert help Look, listen & feel at the mouth and tracheostomy A Mapleson C system (e.g. Waters circuit ) may help assessment if available Use waveform capnography when available: exhaled carbon dioxide indicates a patent or partially patent airway No Is the patient breathing? Yes Call Resuscitation Team CPR if no pulse / signs of life Apply high flow oxygen to BOTH the face and the tracheostomy Assess tracheostomy patency Remove speaking valve or cap (if present) Remove inner tube Some inner tubes need re inserting to connect to breathing circuits Can you pass a suction catheter? No Deflate the cuff (if present) Look, listen & feel at the mouth and tracheostomy Use waveform capnography or Mapleson C if available Is the patient stable or improving? Yes Yes The tracheostomy tube is patent Perform tracheal suction Consider partial obstruction Ventilate (via tracheostomy) if not breathing Continue ABCDE assessment Tracheostomy tube partially obstructed or displaced Continue ABCDE assessment No REMOVE THE TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE Look, listen & feel at the mouth and tracheostomy. Ensure oxygen re applied to face and stoma Use waveform capnography or Mapleson C if available Call Resuscitation team CPR if no pulse / signs of life No Is the patient breathing? Yes Continue ABCDE assessment Primary emergency oxygenation Standard ORAL airway manoeuvres Cover the stoma (swabs / hand). Use: Bag valve mask Oral or nasal airway adjuncts Supraglottic airway device e.g. LMA Tracheostomy STOMA ventilation Paediatric face mask applied to stoma LMA applied to stoma Secondary emergency oxygenation Attempt ORAL intubation Prepare for difficult intubation Uncut tube, advanced beyond stoma Attempt intubation of STOMA Small tracheostomy tube / 6.0 cuffed ETT Consider Aintree catheter and fibreoptic scope / Bougie / Airway exchange catheter National Tracheostomy Safety Project. Review date 1/4/14. Feedback & resources at
40 Emergency laryngectomy management Call for airway expert help Look, listen & feel at the mouth and laryngectomy stoma A Mapleson C system (e.g. Waters circuit ) may help assessment if available Use waveform capnography whenever available: exhaled carbon dioxide indicates a patent or partially patent airway No Is the patient breathing? Yes Call Resuscitation Team CPR if no pulse / signs of life Apply high flow oxygen to laryngectomy stoma If any doubt whether patient has a laryngectomy, apply oxygen to face also* Assess laryngectomy stoma patency Most laryngectomy stomas will NOT have a tube in situ Remove stoma cover (if present) Remove inner tube (if present ) Some inner tubes need re inserting to connect to breathing circuits Do not remove a tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP) prosthesis Can you pass a suction catheter? No Deflate the cuff (if present) Look, listen & feel at the laryngectomy stoma or tube Use waveform capnography or Mapleson C if available Is the patient stable or improving? Yes Yes The laryngectomy stoma is patent Perform tracheal suction Consider partial obstruction Ventilate via stoma if not breathing Continue ABCDE assessment Continue ABCDE assessment No REMOVE THE TUBE FROM THE LARYNGECTOMY STOMA if present Look, listen & feel at the laryngectomy stoma. Ensure oxygen is re applied to stoma Use waveform capnography or Mapleson C if available Call Resuscitation Team CPR if no pulse / signs of life No Is the patient breathing? Yes Continue ABCDE assessment Primary emergency oxygenation Secondary emergency oxygenation Laryngectomy stoma ventilation via either Paediatric face mask applied to stoma LMA applied to stoma Attempt intubation of laryngectomy stoma Small tracheostomy tube / 6.0 cuffed ETT Consider Aintree catheter and fibreoptic scope / Bougie / Airway exchange catheter Laryngectomy patients have an end stoma and cannot be oxygenated via the mouth or nose *Applying oxygen to the face and stoma is the default emergency action for all patients with a tracheostomy National Tracheostomy Safety Project. Review date 1/4/14. Feedback & resources at
41 Targeted LEARNERS Critical Care Physicians and Fellows Other professionals involved in the care of both tracheostomy and laryngectomy patients Hospitalists ER physicians General surgeons Nurses Respiratory therapists
42 Pre-course PowerPoint Viewed online on own time prior to course Key Learning Points Anatomy of tracheotomy, laryngectomy Role of different types of trach tubes Cuffed vs uncuffed Inner cannula vs no inner canula Fenestrated vs non fenestrated Normal vs extended length proximal vs distal Manufacturers, sizing of tubes Pluging, decannulation, speaking valve use Tracheostomy complications Difficult tracheostomy/laryngectomy algorithm Management of trach displacement DO NOT INTUBATE LARYNGECTOMY PATIENT Know when to intubate!
43 Course Components Examine multiple different tracheostomy tubes Practice intubating using surgical laryngoscope Fellows already familiar with standard scopes and Glide Scope High fidelity scenarios Displaced tracheostomy Plugged laryngectomy tube
44 HIGH FIDELITY Simulation Scenarios Displaced Tracheostomy tube scenario Tube occluded with tape, slipped under chest flap Airway blocked with tape to make reinsertion difficult May leave small aperature if goal is reinsertion Patient wheezing, coughing, desating Goal is to recognize tube not in airway Secure airway by bag-mask and intubation If bag trach, sats will crash in 1 minute due to pneumothorax Laryngectomy senario Plugged laryngectomy tube (use Gorilla glue) Tape over larynx, set tongue to maximum pressure Patient wheezing, coughing, desating Goal is to recognize and remove laryngectomy tube If Attempted oral intubation will crash immediately
45 Scenario Video
46 Post-Course Survey Administered 8 months following course All respondents strongly positive All had encountered similar event in 8 months All thought useful in addressing event All thought scenarios most useful part.
47 Course was incredibly helpful! This course is very pertinent and useful. Understanding how to trouble shoot new trachs and why to prefer intubation in those case Never before knew the difference between a Shiley, Bivona, etc. tubes Overall, a very helpful course. Also, appropriate length/depth. Other comments? None... just that we need more training like this
48 SAVE-ME Mechanical Ventilator Simulator John Hotchkiss, MD Chris Brackney, DO
49 SAVE-ME tool comprises Simulation model Non-linear, multicompartment mechanics and gas exchange modules Acid/base and hemodynamic modules Dynamically responsive virtual patient population COPD, asthma, acute lung injury, restriction, pneumonia Represent major categories of acute respiratory failure Modules providing real-time learner debriefing Conventional metrics Metrics based on practice patterns Algorithms providing real-time learner guidance At this point in time, your patient has the following problems At this time, you should consider these changes for your patient
50 Initial presentation of standardized patient case
51 Oops bad choice
52 Interventions have corrected ph
53 Interventions have corrected ph and SaO2
54 Acidosis, hypoxia, and hypotension repaired: Learner commits to settings
55 New virtual patient is immediately presented
56 Freeware tool has garnered an international audience Simulator ranked # 1 on Bing search and #2 on Google search Generating ~ 20 unique downloads per day spanning 98 countries; pace is accelerating
57 Practice patterns show statistical characteristics of spoken languages
58 Evidence of cognitive conceptual clustering is readily apparent
59
60 Your Being Sued! When bad things happen to good doctors Deanna Blisard, MD
61 Purpose The goal of the workshop is to offer the Critical Care fellows the opportunity to participate in a mock medical malpractice lawsuit that would provide a basic understanding of the litigation process. At the end of the workshop, the fellows should be able to: Have a general understanding of the procedural aspects of a malpractice case Recognize the pitfalls inherent in poor documentation and communication and the potential consequences of both at trial Better defend their actions in litigation Document more intelligently
62 A Longitudinal Curriculum! Video Actual case involving previous fellow and a failed reintubation Video was made recreating the attempted reintubation The video was viewed by fellows and used for documentation exercise Viewed in October Deposition Notes collected and reviewed and one fellow selected Fellow underwent mock deposition with real lawyers Co-fellows were in the audience observing Held in April Mock trial Standardized Patients (SPs) played the defendant, plaintiff expert, and defense expert Scripted testimony and real lawyers Fellows acted as jury and deliberated
63 Documentation Video Recreation of the failed re-intubation using Critical Care program directors and VA Pittsburgh simulation fellows Key moments time-stamped with actual times documented in the patient chart Fellows viewed the video as part of their difficult airway workshop (embedded into their known curriculum), and asked to document what transpired
64
65 Mock Deposition One fellow was selected to be deposed Received a redacted copy of the initial complaint and a letter from the insurance company stating he was being sued Actual lawyers deposed the fellow using the redacted chart Facilitated debriefing and Q&A session after the deposition with faculty, lawyers, and the VP of Risk Management
66 Mock Trial Scripted from the actual patient chart, depositions, and expert witness summaries Standardized Patients (SP) used to play the part of defendant and expert witnesses Fellows acted as jurors, deliberated the case, and rendered a verdict Fellows were unable to come to a unanimous decision but favored acquittal 9-4 Actual case settled by UPMC
67 Future Goals and Applications Documentation checklist in process: Delphi model utilizing local critical care faculty to provide feedback on key aspects of fellow documentation 2 nd year fellows to play roles in future mock trials Real-life experience being an expert witness Increase fidelity and reality for fellows Possible affiliation/collaboration with Pitt Law School Mediation vs Mock Trial Most are mediated and settled before getting to a trial
68 VAPHS Center for Medical Product End-user Testing Jamie L. Estock, MA Director Human Factors Psychologist Co-Director, Inter-professional Patient Safety Fellowship David E. Eibling, MD Associate Director Assistant Chief of Surgery Co-Director, Inter-professional Patient Safety Fellowship
69 MISSION Facilitate the safest use of medical products in the delivery of care to Veterans
70 APPROACH Conduct human factors evaluations to measure product safety in situations that mirror the real clinical practice settings Leverage high-fidelity simulation Involve a representative set of users Incorporate real-world scenarios
71 APPROACH Measure the effects of interface design on user decisions and actions with the goal of maximizing performance and minimizing errors
72 PSCI GOALS 1. Advise the purchase of the safest medical products across VHA 2. Identify and mitigate safety issues before products are used on Veterans 3. Inform the future design, development, and approval of safe medical products
73 Completed Evaluations Decision Completed HF Evaluations Purchasing Which product has the fewest use-related hazards? Automated Chest Compression (ACC) Devices Implementation/Use How can we mitigate use-related hazards associated with the products? External Defibrillators Design How can we design products to reduce/eliminate use-related hazards? Intravenous Medication Labels
74 Interruption Time (seconds) ACC Device Evaluation OBJECTIVE Identify whether an ACC device would be safe and beneficial for use at VA Pittsburgh METHODS Simulated resuscitation scenario involving an unconscious 45-year-old man in cardiac arrest RESULTS Device Application AutoPulse LUCAS 2 IMPACT Prevented the purchase of an unwarranted device resulting in improved patient care and cost savings
75 Estock JL, Curinga HK, Li A, Grieve LB, Brackney CR. Comparison of chest compression interruption times across 2 automated devices: a randomized, crossover simulation study. Am J Emerg Med Jan;34(1): PMID:
76 Medication Label Evaluation OBJECTIVE Quantify the impact of label design on medication safety in a realistic, high-stress, clinical situation METHODS Operating room scenario involving an unexpected vascular injury and incorrectly stocked lidocaine bag 100% RESULTS Correct Medication Selection IMPACT VA Pittsburgh redesigned the labels placed on operating room medications compounded in-house 80% 60% 40% 40% 63% 20% 0% Current Label Redesigned Label
77 The End
Tracheostomy and laryngectomy airway emergencies: an overview for medical and nursing staff
 2013 Medical Journal Tracheostomy and laryngectomy airway emergencies: an overview for medical and nursing staff Steven Lobaz 1 and Paul Bush 2 1 ST6 and 2 Consultant Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive
2013 Medical Journal Tracheostomy and laryngectomy airway emergencies: an overview for medical and nursing staff Steven Lobaz 1 and Paul Bush 2 1 ST6 and 2 Consultant Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive
Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Coeditor/author. Associate Science Editor, American Heart Association
 Tracheotomy Challenges for airway specialists Elizabeth H. Sinz, MD Professor of Anesthesiology & Neurosurgery Associate Dean for Clinical Simulation Disclosures Coeditor/author Associate Science Editor,
Tracheotomy Challenges for airway specialists Elizabeth H. Sinz, MD Professor of Anesthesiology & Neurosurgery Associate Dean for Clinical Simulation Disclosures Coeditor/author Associate Science Editor,
Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients. Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA
 Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA Learning Objectives Define common terms identified with total (laryngectomy)
Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA Learning Objectives Define common terms identified with total (laryngectomy)
TRACHEOSTOMY EMERGENCIES
 TRACHEOSTOMY EMERGENCIES MODULE: AIRWAY TARGET: ALL ANAESTHETISTS, INTENSIVISTS, ED & ACUTE PHYSICIANS, FOUNDATION DOCTORS BACKGROUND: Around 16% of ICU patients may have a tracheostomy. Life- threatening
TRACHEOSTOMY EMERGENCIES MODULE: AIRWAY TARGET: ALL ANAESTHETISTS, INTENSIVISTS, ED & ACUTE PHYSICIANS, FOUNDATION DOCTORS BACKGROUND: Around 16% of ICU patients may have a tracheostomy. Life- threatening
*gurgle* *snore* *slaver* Tracheostomy Emergencies with Trachy Tracey Helen Lyall ACCP LUHT 03/06/2016
 *gurgle* *snore* *slaver* Tracheostomy Emergencies with Trachy Tracey Helen Lyall ACCP LUHT 03/06/2016 Learning objectives Describe the difference in anatomy between a tracheotomy and a laryngectomy Understand
*gurgle* *snore* *slaver* Tracheostomy Emergencies with Trachy Tracey Helen Lyall ACCP LUHT 03/06/2016 Learning objectives Describe the difference in anatomy between a tracheotomy and a laryngectomy Understand
Emergency)tracheostomy)management)/)Patent)upper)airway)
 Emergency)tracheostomy)management)/)Patent)upper)airway) Call,for,airway,expert,help,,Look,,listen,&,feel,at,the,mouth,and,tracheostomy) A)Mapleson)C)system)(e.g.) Waters)circuit ))may)help)assessment)if)available)
Emergency)tracheostomy)management)/)Patent)upper)airway) Call,for,airway,expert,help,,Look,,listen,&,feel,at,the,mouth,and,tracheostomy) A)Mapleson)C)system)(e.g.) Waters)circuit ))may)help)assessment)if)available)
Other methods for maintaining the airway (not definitive airway as still unprotected):
 Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Jefferson Tower Task Trainer List
 Jefferson Tower Task Trainer List Table of Contents Blue Phantom Ultrasound Central Line Training Model 2 Blue Phantom Femoral Vascular Access Training Model 3 Blue Phantom Thoracentesis Ultrasound Training
Jefferson Tower Task Trainer List Table of Contents Blue Phantom Ultrasound Central Line Training Model 2 Blue Phantom Femoral Vascular Access Training Model 3 Blue Phantom Thoracentesis Ultrasound Training
HeartCode PALS. PALS Actions Overview > Legend. Contents
 HeartCode PALS PALS Actions Overview > Legend Action buttons (round buttons) Clicking a round button initiates an action. Clicking this button, for example, checks the child s carotid pulse. Menu buttons
HeartCode PALS PALS Actions Overview > Legend Action buttons (round buttons) Clicking a round button initiates an action. Clicking this button, for example, checks the child s carotid pulse. Menu buttons
Airway Management Essentials Self-Study Guide
 Airway Management Essentials Self-Study Guide Fourth Quarter 2010 Self-Study Guide Learning Objectives Cognitive Domain 1. Describe the various conditions that cause concern during treatment in the field
Airway Management Essentials Self-Study Guide Fourth Quarter 2010 Self-Study Guide Learning Objectives Cognitive Domain 1. Describe the various conditions that cause concern during treatment in the field
Foundations of Critical Care Nursing Course. Tracheostomy Workbook
 Foundations of Critical Care Nursing Course Tracheostomy Workbook 1 Key Reference: Dawson D (2014) Essential principles:trachepstomy care in the adult patient, Nursing in Critical Care, Vol 19, 2 p.63-72.
Foundations of Critical Care Nursing Course Tracheostomy Workbook 1 Key Reference: Dawson D (2014) Essential principles:trachepstomy care in the adult patient, Nursing in Critical Care, Vol 19, 2 p.63-72.
Changing tracheostomy tubes
 Changing tracheostomy tubes Changing the tracheostomy tube should be a multidisciplinary decision. The first change should always be performed or supervised by a suitably trained member of the medical
Changing tracheostomy tubes Changing the tracheostomy tube should be a multidisciplinary decision. The first change should always be performed or supervised by a suitably trained member of the medical
Competency 1: General principles and equipment required to safely manage a patient with a tracheostomy tube.
 Competency 1: General principles and equipment required to safely manage a patient with a tracheostomy tube. Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
Competency 1: General principles and equipment required to safely manage a patient with a tracheostomy tube. Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
Kevin K. Nunnink Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Program
 PATIE NT I N FO R M ATI O N Kevin K. Nunnink Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Program A family s guide to understanding this specialized treatment for cardiac and pulmonary complications Saint Luke
PATIE NT I N FO R M ATI O N Kevin K. Nunnink Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Program A family s guide to understanding this specialized treatment for cardiac and pulmonary complications Saint Luke
Learning Station Competency Checklists
 Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Advanced Airway Management. University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track
 Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
EMERGENCY CARE. Advanced Patient Simulators 116 CALL US TOLL FREE AT
 EMERGENCY CARE Advanced Patient Simulators 116 CALL US TOLL FREE AT 800.882.6655 Our Code Blue III ALS training simulators allow you to teach high-performance, quality CPR by providing you with real-time
EMERGENCY CARE Advanced Patient Simulators 116 CALL US TOLL FREE AT 800.882.6655 Our Code Blue III ALS training simulators allow you to teach high-performance, quality CPR by providing you with real-time
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Scenario title. Pear Shaped- prepare for intubation on the ward. Designed for (specific group) ICU MET team. Scenario Design team.
 Scenario title Pear Shaped- prepare for intubation on the ward Designed for (specific group) ICU MET team Scenario Design team Name Maurice Le Guen Cameron Knott Organisation Austin Hospital Date of creation
Scenario title Pear Shaped- prepare for intubation on the ward Designed for (specific group) ICU MET team Scenario Design team Name Maurice Le Guen Cameron Knott Organisation Austin Hospital Date of creation
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS)
 TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
MASTER SYLLABUS
 MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 A. Academic Division: Health Science B. Discipline: Respiratory Care C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2490 Practicum IV D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters, BBA, RRT, RCP Assistant
MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 A. Academic Division: Health Science B. Discipline: Respiratory Care C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2490 Practicum IV D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters, BBA, RRT, RCP Assistant
All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies
 Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Interfacility Protocol Protocol Title:
 Interfacility Protocol Protocol Title: Mechanical Ventilator Monitoring & Management Original Adoption Date: 05/2009 Past Protocol Updates 05/2009, 12/2013 Date of Most Recent Update: March 23, 2015 Medical
Interfacility Protocol Protocol Title: Mechanical Ventilator Monitoring & Management Original Adoption Date: 05/2009 Past Protocol Updates 05/2009, 12/2013 Date of Most Recent Update: March 23, 2015 Medical
Tracheostomy Sim Course
 Patients Name: Robert Smith Patients Age / DOB: 45 year old gentleman on medical ward Major Medical Problem Displaced tracheostomy tube Learning Goal Medical Early recognition of displaced tracheostomy
Patients Name: Robert Smith Patients Age / DOB: 45 year old gentleman on medical ward Major Medical Problem Displaced tracheostomy tube Learning Goal Medical Early recognition of displaced tracheostomy
TRACHEOSTOMY CARE. Tracheostomy- Surgically created hole that extends from the neck skin into the windpipe or trachea.
 1 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE Definitions: Trachea-Windpipe Tracheostomy- Surgically created hole that extends from the neck skin into the windpipe or trachea. Outer Cannula- The outer part of a trach tube. Usually
1 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE Definitions: Trachea-Windpipe Tracheostomy- Surgically created hole that extends from the neck skin into the windpipe or trachea. Outer Cannula- The outer part of a trach tube. Usually
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses
 Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
WSCC EMT CLASS SEVIERVILLE EXAM 1 STUDY GUIDE 1. Describe what is needed for good eye protection. Are prescription eye glasses adequate?
 1. Describe what is needed for good eye protection. Are prescription eye glasses adequate? 2. What kind of report must be given to officially transfer patient care at the hospital? 3. What is subcutaneous
1. Describe what is needed for good eye protection. Are prescription eye glasses adequate? 2. What kind of report must be given to officially transfer patient care at the hospital? 3. What is subcutaneous
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Improving pediatric outcomes. SimJunior. Laerdal Pediatric Simulation Solutions
 Improving pediatric outcomes Laerdal Pediatric Simulation Solutions Realistic Pediatric Simulation Why simulation matters Building self-confidence Partnering to improve pediatric outcomes Caring for pediatric
Improving pediatric outcomes Laerdal Pediatric Simulation Solutions Realistic Pediatric Simulation Why simulation matters Building self-confidence Partnering to improve pediatric outcomes Caring for pediatric
FAILED INTUBATION DURING RSI: PLAN A, C & D
 FAILED INTUBATION DURING RSI: PLAN A, C & D MODULE: NOVICE & AIRWAY TARGET: NOVICE INITIAL ASSESSMENT OF COMPETENCY ALL ANAESTHETISTS BACKGROUND: Management of the Can t Intubate, Can t Ventilate situation
FAILED INTUBATION DURING RSI: PLAN A, C & D MODULE: NOVICE & AIRWAY TARGET: NOVICE INITIAL ASSESSMENT OF COMPETENCY ALL ANAESTHETISTS BACKGROUND: Management of the Can t Intubate, Can t Ventilate situation
Section: Universal Benefit Programs. Respiratory Equipment Program
 Section: Universal Benefit Programs Date Reviewed January 2018 Drug Plan & Extended Benefits Respiratory Equipment Program INTENT The Respiratory Equipment Program offers the loan of a selection of respiratory
Section: Universal Benefit Programs Date Reviewed January 2018 Drug Plan & Extended Benefits Respiratory Equipment Program INTENT The Respiratory Equipment Program offers the loan of a selection of respiratory
CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR
 CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR 801-467-0800 Phone 800-800-HFJV (4358) Hotline TABLE OF CONTENTS Respiratory Care Considerations..3 Physician Considerations
CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR 801-467-0800 Phone 800-800-HFJV (4358) Hotline TABLE OF CONTENTS Respiratory Care Considerations..3 Physician Considerations
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. Emergency Procedures in PT
 Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Emergency Procedures in PT BLS Can be learned & practiced by the general public Includes: CPR First Aid (e.g. choking relief) Use of AED ACLS Used by healthcare
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Emergency Procedures in PT BLS Can be learned & practiced by the general public Includes: CPR First Aid (e.g. choking relief) Use of AED ACLS Used by healthcare
INTUBATION/RSI. PURPOSE: A. To facilitate secure, definitive control of the airway by endotracheal intubation in an expeditious and safe manner
 Manual: LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Section: Adult/Pediatrics Protocol #: AP1-009 Approval Date: 03/01/2018 Effective Date: 03/05/2018 Revision Due Date: 12/01/2018 INTUBATION/RSI PURPOSE: A. To facilitate
Manual: LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Section: Adult/Pediatrics Protocol #: AP1-009 Approval Date: 03/01/2018 Effective Date: 03/05/2018 Revision Due Date: 12/01/2018 INTUBATION/RSI PURPOSE: A. To facilitate
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2?
 Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2? American Association of Critical Care Nurses National Teaching Institute Expo Ed 2013 Susan Thibeault MS, CRNA, APRN, CCRN, EMT-P
Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2? American Association of Critical Care Nurses National Teaching Institute Expo Ed 2013 Susan Thibeault MS, CRNA, APRN, CCRN, EMT-P
Airway and Breathing
 Airway and Breathing ETAT Module 2 Adapted from Emergency Triage Assessment and Treatment (ETAT): Manual for Participants, World Health Organization, 2005 Learning Objectives Accurately determine whether
Airway and Breathing ETAT Module 2 Adapted from Emergency Triage Assessment and Treatment (ETAT): Manual for Participants, World Health Organization, 2005 Learning Objectives Accurately determine whether
F: Respiratory Care. College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 59
 F: Respiratory Care College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 59 Competency: F-1 Airway Management F-1-1 F-1-2 F-1-3 F-1-4 F-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability
F: Respiratory Care College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 59 Competency: F-1 Airway Management F-1-1 F-1-2 F-1-3 F-1-4 F-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability
10/17/2016 OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT COURSE OBJECTIVES COMMON CAUSES OF RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT J U L I E Z I M M E R M A N, R N, M S N C L I N I C A L N U R S E S P E C I A L I S T E L O I S A C U T L E R, R R T, B S R C C L I N I C A L / E D U C
OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT J U L I E Z I M M E R M A N, R N, M S N C L I N I C A L N U R S E S P E C I A L I S T E L O I S A C U T L E R, R R T, B S R C C L I N I C A L / E D U C
Scenario title. We re Coming Down Intrahospital Transfer post MET. Designed for (specific group) ICU MET team. Scenario Design team.
 Scenario title We re Coming Down Intrahospital Transfer post MET Designed for (specific group) ICU MET team Scenario Design team Name Maurice Le Guen Cameron Knott Organisation Austin Hospital Date of
Scenario title We re Coming Down Intrahospital Transfer post MET Designed for (specific group) ICU MET team Scenario Design team Name Maurice Le Guen Cameron Knott Organisation Austin Hospital Date of
Difficult Airway. Victor M. Gomez, M.D. Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine Medical City Dallas Hospital
 Difficult Airway Victor M. Gomez, M.D. Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine Medical City Dallas Hospital Difficult Airway Definition Predicting a difficult airway Preparing for a difficult airway Extubation
Difficult Airway Victor M. Gomez, M.D. Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine Medical City Dallas Hospital Difficult Airway Definition Predicting a difficult airway Preparing for a difficult airway Extubation
In-hospital Resuscitation
 In-hospital Resuscitation Introduction This new section in the guidelines describes the sequence of actions for starting in-hospital resuscitation. Hospital staff are often trained in basic life support
In-hospital Resuscitation Introduction This new section in the guidelines describes the sequence of actions for starting in-hospital resuscitation. Hospital staff are often trained in basic life support
CAPNOGRAPHY. 1.1 To set forth the policy and procedure for performing continuous end-tidal waveform capnography.
 OFFICE OF MEDICAL AFFAIRS DIRECTIVE 2009-02 CAPNOGRAPHY 1. PURPOSE 1.1 To set forth the policy and procedure for performing continuous end-tidal waveform capnography. 2. SCOPE 2.1 This procedure applies
OFFICE OF MEDICAL AFFAIRS DIRECTIVE 2009-02 CAPNOGRAPHY 1. PURPOSE 1.1 To set forth the policy and procedure for performing continuous end-tidal waveform capnography. 2. SCOPE 2.1 This procedure applies
AVOIDING THE CRASH: OPTIMIZE YOUR PRE, PERI, AND POST AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AVOIDING THE CRASH 1: DON T INTUBATE, OPTIMIZE PRE-AIRWAY MANAGEMENT
 AVOIDING THE CRASH: OPTIMIZE YOUR PRE, PERI, AND POST AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Robert J. Vissers MD Chief, Emergency Medicine, Quality Chair, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center Adjunct Associate Professor, OHSU Portland,
AVOIDING THE CRASH: OPTIMIZE YOUR PRE, PERI, AND POST AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Robert J. Vissers MD Chief, Emergency Medicine, Quality Chair, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center Adjunct Associate Professor, OHSU Portland,
EXTRA CORPOREAL MEMBRANE OXYGENATION
 EXTRA CORPOREAL MEMBRANE OXYGENATION Basic Overview and Case Study Bob Hayes, Chief Perfusionist Enloe Medical Center Jenny Humphries, RN, BSN, MBA, CFRN Chief Flight Nurse, Enloe FlightCare Normal Cardiopulmonary
EXTRA CORPOREAL MEMBRANE OXYGENATION Basic Overview and Case Study Bob Hayes, Chief Perfusionist Enloe Medical Center Jenny Humphries, RN, BSN, MBA, CFRN Chief Flight Nurse, Enloe FlightCare Normal Cardiopulmonary
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Policy x.xxx. Issued: Artificial Airways and Airway Care. ABC Home Medical Company Policy & Procedure Manual. A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes)
 A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes) A tracheotomy is a surgical procedure whereby an opening is cut into the trachea of the patient for the purpose of inserting a tube (trach tube). The trach tube allows
A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes) A tracheotomy is a surgical procedure whereby an opening is cut into the trachea of the patient for the purpose of inserting a tube (trach tube). The trach tube allows
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TRACHEOSTOMY MANAGEMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : TRACHEOSTOMY MANAGEMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 tracheostomy management tracheostomy management pdf tracheostomy management Tracheostomy is a common procedure in intensive
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TRACHEOSTOMY MANAGEMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 tracheostomy management tracheostomy management pdf tracheostomy management Tracheostomy is a common procedure in intensive
CAE Healthcare Human Patient Simulator (HPS)
 CAE Healthcare Human Patient Simulator (HPS) The Human Patient Simulator, HPS, is a tethered simulator that is capable of patient assessment and treatment including mechanical ventilation and anesthesia.
CAE Healthcare Human Patient Simulator (HPS) The Human Patient Simulator, HPS, is a tethered simulator that is capable of patient assessment and treatment including mechanical ventilation and anesthesia.
H: Respiratory Care. Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 79
 H: Respiratory Care Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 79 Competency: H-1 Airway Management H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge
H: Respiratory Care Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 79 Competency: H-1 Airway Management H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge
Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO 2 table Warm
 NRP Skills Stations Performance Skills Station OR Integrated Skills Station STATION: Assisting with and insertion of endotracheal tube (ETT) Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO
NRP Skills Stations Performance Skills Station OR Integrated Skills Station STATION: Assisting with and insertion of endotracheal tube (ETT) Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO
Basic Airway Management
 Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Module 2: Facilitator instructions for Airway & Breathing Skills Station
 Module 2: Facilitator instructions for Airway & Breathing Skills Station 1. Preparation a. Assemble equipment beforehand. b. Make sure that you have what you need and that it is functioning properly. 2.
Module 2: Facilitator instructions for Airway & Breathing Skills Station 1. Preparation a. Assemble equipment beforehand. b. Make sure that you have what you need and that it is functioning properly. 2.
Critical Care Services: Equipment and Procedures Information for Patients, Relatives and Carers
 Critical Care Services: Equipment and Procedures Information for Patients, Relatives and Carers The Critical Care unit can be a frightening place for patients and visitors. Seeing a loved one attached
Critical Care Services: Equipment and Procedures Information for Patients, Relatives and Carers The Critical Care unit can be a frightening place for patients and visitors. Seeing a loved one attached
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline. Advanced Paediatric Life Support. Sequence of actions. 1. Establish basic life support
 Advanced Paediatric Life Support Sequence of actions 1. Establish basic life support 2. Oxygenate, ventilate, and start chest compression: - Provide positive-pressure ventilation with high-concentration
Advanced Paediatric Life Support Sequence of actions 1. Establish basic life support 2. Oxygenate, ventilate, and start chest compression: - Provide positive-pressure ventilation with high-concentration
Managing Risk in Airway Management Procedures
 A1. Airway Management Managing Risk in Airway Management Procedures Ellen S Deutsch, MD, MS, FACS, FAAP SUN Meeting, December, 2014 Disclosures No financial support received for this presentation Employment:
A1. Airway Management Managing Risk in Airway Management Procedures Ellen S Deutsch, MD, MS, FACS, FAAP SUN Meeting, December, 2014 Disclosures No financial support received for this presentation Employment:
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults
 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
NRP Raising the Bar for Providers and Instructors
 NRP 2011 Raising the Bar for Providers and Instructors What is the same? 1. Minimum course requirement is Lessons 1 through 4 and Lesson 9. The NRP Provider Card requires renewal every 2 years. Your facility
NRP 2011 Raising the Bar for Providers and Instructors What is the same? 1. Minimum course requirement is Lessons 1 through 4 and Lesson 9. The NRP Provider Card requires renewal every 2 years. Your facility
ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010
 ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010 Jim Tibballs Officer, RCH Convenor, Paediatric Sub-Committee, (ARC) ARC Paediatric Representative International Liaison Committee on (ILCOR)
ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010 Jim Tibballs Officer, RCH Convenor, Paediatric Sub-Committee, (ARC) ARC Paediatric Representative International Liaison Committee on (ILCOR)
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
Capnography Connections Guide
 Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
Emergency Care Progress Log
 Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
Where Emergency Medicine Meets Critical Care: Next Level Resuscitation
 Where Emergency Medicine Meets Critical Care: Next Level Resuscitation Rob Green, BSc, MD, DABEM, FRCPC, FRCP(Edin) Professor, Dalhousie University Departments of Emergency Medicine,Critical Care Medicine
Where Emergency Medicine Meets Critical Care: Next Level Resuscitation Rob Green, BSc, MD, DABEM, FRCPC, FRCP(Edin) Professor, Dalhousie University Departments of Emergency Medicine,Critical Care Medicine
SEMINOLE COUNTY EMS PROVISIONAL EMT SKILLS VERIFICATION
 The following individual has completed the Seminole County EMS Provisional EMT Skills Verification check in the following areas: Oxygen, Airway and Ventilation Skills ALS Assistance Trauma Management Medical
The following individual has completed the Seminole County EMS Provisional EMT Skills Verification check in the following areas: Oxygen, Airway and Ventilation Skills ALS Assistance Trauma Management Medical
Training. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Training The training module will follow the national standard curriculum as it relates to the application and use of CPAP. The proposed curriculum will closely resemble the following algorithm utilizing
Training The training module will follow the national standard curriculum as it relates to the application and use of CPAP. The proposed curriculum will closely resemble the following algorithm utilizing
Airway and Ventilation. Emergency Medical Response
 Airway and Ventilation Lesson 14: Airway and Ventilation You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your medical emergency response team has been called to the fitness center by building security on a report
Airway and Ventilation Lesson 14: Airway and Ventilation You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your medical emergency response team has been called to the fitness center by building security on a report
The essential principles of tracheostomy care
 The essential principles of tracheostomy care Deborah Dawson Consultant Nurse Critical Care Excellence in specialist and community healthcare Key publications https://www.stgeorges.nhs.uk/gps-andclinicians/clinical-resources/tracheostomyguidelines/
The essential principles of tracheostomy care Deborah Dawson Consultant Nurse Critical Care Excellence in specialist and community healthcare Key publications https://www.stgeorges.nhs.uk/gps-andclinicians/clinical-resources/tracheostomyguidelines/
Pediatric Shock. Hypovolemia. Sepsis. Most common cause of pediatric shock Small blood volumes (80cc/kg)
 Critical Concepts: Shock Inadequate peripheral perfusion where oxygen delivery does not meet metabolic demand Adult vs Pediatric Shock - Same causes/different frequencies Pediatric Shock Hypovolemia Most
Critical Concepts: Shock Inadequate peripheral perfusion where oxygen delivery does not meet metabolic demand Adult vs Pediatric Shock - Same causes/different frequencies Pediatric Shock Hypovolemia Most
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During. Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Appendix D An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires:
 Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD)
 P03 Procedures 2017-05-12 All ages Office of the Medical Director Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD) Primary Intermediate Advanced Critical From AIRWAY & BREATHING MANAGEMENT or AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION Yes
P03 Procedures 2017-05-12 All ages Office of the Medical Director Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD) Primary Intermediate Advanced Critical From AIRWAY & BREATHING MANAGEMENT or AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION Yes
Safer Tracheostomy Care Course
 Patients Name: Samira Patel Patients Age / DOB: 65 year old female on a general ward Major Medical Problem Blocked tracheostomy tube Learning Goal Medical Early recognition of respiratory distress Understanding
Patients Name: Samira Patel Patients Age / DOB: 65 year old female on a general ward Major Medical Problem Blocked tracheostomy tube Learning Goal Medical Early recognition of respiratory distress Understanding
CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS
 CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS PRACTICAL STATIONS CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS 1. CARDIAC ARREST MANAGEMENT 2. AIRWAY & RESPIRATORY MANAGEMENT 3. SPINAL IMMOBILIZATION
CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS PRACTICAL STATIONS CHANHASSEN FIRE DEPARTMENT MEDICAL / RESCUE SKILLS 1. CARDIAC ARREST MANAGEMENT 2. AIRWAY & RESPIRATORY MANAGEMENT 3. SPINAL IMMOBILIZATION
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Tracheostomy. Hope Building Neurosurgery
 Tracheostomy Hope Building Neurosurgery 0161 206 5055 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Unique Identifier: CS36(17). Review date: November 2019 What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy
Tracheostomy Hope Building Neurosurgery 0161 206 5055 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Unique Identifier: CS36(17). Review date: November 2019 What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy
Emergency Room Resuscitation of the Unstable Trauma Patient
 Emergency Room Resuscitation of the Unstable Trauma Patient Goals of trauma resuscitation Maintain: Systemic oxygenation Systemic perfusion Neurologic function Approach to unstable trauma patient Primary
Emergency Room Resuscitation of the Unstable Trauma Patient Goals of trauma resuscitation Maintain: Systemic oxygenation Systemic perfusion Neurologic function Approach to unstable trauma patient Primary
ASPIRATION DURING ANAESTHESIA
 ASPIRATION DURING ANAESTHESIA MODULE: CRITICAL INCIDENTS TARGET: ALL ANAESTHETISTS BACKGROUND: Passive regurgitation or vomiting can occur during the pre-, peri- or post- operative period risking aspiration
ASPIRATION DURING ANAESTHESIA MODULE: CRITICAL INCIDENTS TARGET: ALL ANAESTHETISTS BACKGROUND: Passive regurgitation or vomiting can occur during the pre-, peri- or post- operative period risking aspiration
Welcome to the Specialized Medical Services respiratory training webinar series!
 Welcome to the Specialized Medical Services respiratory training webinar series! SMS is your LTC facility single source for oxygen, medical equipment, respiratory care services and supplies nationwide.
Welcome to the Specialized Medical Services respiratory training webinar series! SMS is your LTC facility single source for oxygen, medical equipment, respiratory care services and supplies nationwide.
Waitin In The Wings. Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider
 Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
This interdisciplinary clinical support document provides guidelines for the safe establishment of an artificial airway.
 PURPOSE This interdisciplinary clinical support document provides guidelines for the safe establishment of an artificial airway. POLICY STATEMENTS Endotracheal intubation will be performed by the Most
PURPOSE This interdisciplinary clinical support document provides guidelines for the safe establishment of an artificial airway. POLICY STATEMENTS Endotracheal intubation will be performed by the Most
Date: I hereby consent to and authorize Chest Medicine Associates and other individuals involved in my care to perform a thoracentesis procedure.
 Consent for Surgical and Medical Treatment Patient Name: ----------- Date: --------------- Patient Number: _ Treatment Location: Chest Medicine Associates Date of Birth: ~~ I hereby consent to and authorize
Consent for Surgical and Medical Treatment Patient Name: ----------- Date: --------------- Patient Number: _ Treatment Location: Chest Medicine Associates Date of Birth: ~~ I hereby consent to and authorize
Emergency Department/Trauma Adult Airway Management Protocol
 Emergency Department/Trauma Adult Airway Management Protocol Purpose: A standardized protocol for management of the airway in the setting of trauma in an academic center, with the goal of maximizing successful
Emergency Department/Trauma Adult Airway Management Protocol Purpose: A standardized protocol for management of the airway in the setting of trauma in an academic center, with the goal of maximizing successful
I. Subject: Therapeutic Bronchoscopy and Bronchoscope Assisted Intubation
 I. Subject: Therapeutic Bronchoscopy and Bronchoscope Assisted Intubation II. Policy: Therapeutic flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedures and bronchoscope assisted intubations will be performed by
I. Subject: Therapeutic Bronchoscopy and Bronchoscope Assisted Intubation II. Policy: Therapeutic flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedures and bronchoscope assisted intubations will be performed by
Tracheostomy management Kate Regan MRCP FRCA Katharine Hunt FRCA
 Kate Regan MRCP FRCA Katharine Hunt FRCA The use of tracheostomy has increased over recent years. Traditionally, it was confined to the emergency management of upper airway obstruction; more recently,
Kate Regan MRCP FRCA Katharine Hunt FRCA The use of tracheostomy has increased over recent years. Traditionally, it was confined to the emergency management of upper airway obstruction; more recently,
The Pediatric Airway. Andrew Wackett, MD
 The Pediatric Airway Andrew Wackett, MD Objectives 1) Demonstrate understanding of the indications for intubation 2) Perform rapid sequence intubation 3) Learn the pharmacology behind emergency airway
The Pediatric Airway Andrew Wackett, MD Objectives 1) Demonstrate understanding of the indications for intubation 2) Perform rapid sequence intubation 3) Learn the pharmacology behind emergency airway
CASE PRIMERS. Pediatric Anesthesia Fellowship Program. Laryngotracheal Reconstruction (LTR) Tufts Medical Center
 CASE PRIMERS Pediatric Anesthesia Fellowship Program Tufts Medical Center Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine Division of Pediatric Anesthesia 800 Washington Street, Box 298 Boston,
CASE PRIMERS Pediatric Anesthesia Fellowship Program Tufts Medical Center Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine Division of Pediatric Anesthesia 800 Washington Street, Box 298 Boston,
Pediatric Resuscitation
 Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Capnography: The Most Vital Sign
 Capnography: The Most Vital Sign Mike McEvoy, PhD, NRP, RN, CCRN Cardiac Surgical ICU RN & Chair Resuscitation Committee Albany Medical Center EMS Coordinator Saratoga County, NY www.mikemcevoy.com CO
Capnography: The Most Vital Sign Mike McEvoy, PhD, NRP, RN, CCRN Cardiac Surgical ICU RN & Chair Resuscitation Committee Albany Medical Center EMS Coordinator Saratoga County, NY www.mikemcevoy.com CO
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Snapshots from the development process
 Snapshots from the development process The SimBaby Softwares SimBaby SimBaby Pocket Debrief Viewer Scenario Editor Handler Editors Trend Editor Manikin Update SimBaby Application Based on MicroSim software
Snapshots from the development process The SimBaby Softwares SimBaby SimBaby Pocket Debrief Viewer Scenario Editor Handler Editors Trend Editor Manikin Update SimBaby Application Based on MicroSim software
Capnography: The Most Vital of Vital Signs. Tom Ahrens, PhD, RN, FAAN Research Scientist, Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis, MO May, 2017
 Capnography: The Most Vital of Vital Signs Tom Ahrens, PhD, RN, FAAN Research Scientist, Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis, MO May, 2017 Assessing Ventilation and Blood Flow with Capnography Capnography
Capnography: The Most Vital of Vital Signs Tom Ahrens, PhD, RN, FAAN Research Scientist, Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis, MO May, 2017 Assessing Ventilation and Blood Flow with Capnography Capnography
Information resource for the safer management of patients with tracheostomies and laryngectomies
 Information resource for the safer management of patients with tracheostomies and laryngectomies Draft guidance for review November 2010 2 Introduction This guide is a resource to help promote and facilitate
Information resource for the safer management of patients with tracheostomies and laryngectomies Draft guidance for review November 2010 2 Introduction This guide is a resource to help promote and facilitate
Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care
 Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care Date Revised: January 2015 Course Description Student Learning Objectives:
Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care Date Revised: January 2015 Course Description Student Learning Objectives:
true training true anatomy true to life
 true training true anatomy true to life Why TruCorp? Since 2002, TruCorp have been committed to improving medical best practice through the design and production of the highest quality airway management
true training true anatomy true to life Why TruCorp? Since 2002, TruCorp have been committed to improving medical best practice through the design and production of the highest quality airway management
WELCOME. Welcome to the Children s Hospital PICU (Pediatric Intensive Care Unit). We consider it a privilege to care for your child and your family.
 ECMO FAMILY GUIDE WELCOME Welcome to the Children s Hospital PICU (Pediatric Intensive Care Unit). We consider it a privilege to care for your child and your family. This book was created to give you the
ECMO FAMILY GUIDE WELCOME Welcome to the Children s Hospital PICU (Pediatric Intensive Care Unit). We consider it a privilege to care for your child and your family. This book was created to give you the
The student guide to simulation
 CETL 2008 1 The following guide will introduce you to what the simulators can do But firstly a few words on communication Please verbally and non-verbally communicate with the simulator as if it were a
CETL 2008 1 The following guide will introduce you to what the simulators can do But firstly a few words on communication Please verbally and non-verbally communicate with the simulator as if it were a
Code Blue III PLUS. Emergency Care Simulators
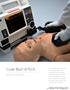 Code Blue III PLUS Emergency Care Simulators Our Code Blue III system teaches ALS skills using realistic code scenarios. Each step you take is monitored by software providing important feedback, not only
Code Blue III PLUS Emergency Care Simulators Our Code Blue III system teaches ALS skills using realistic code scenarios. Each step you take is monitored by software providing important feedback, not only
Nihon Kohden America. Capnography Monitoring with the CapONE CO2 Sensor For use with the BSM 2300/4100/5100 and the BSM 6000 Series Bedside Monitors
 Nihon Kohden America Capnography Monitoring with the CapONE CO2 Sensor For use with the BSM 2300/4100/5100 and the BSM 6000 Series Bedside Monitors Self Study Training Packet August 2011 Table of Contents
Nihon Kohden America Capnography Monitoring with the CapONE CO2 Sensor For use with the BSM 2300/4100/5100 and the BSM 6000 Series Bedside Monitors Self Study Training Packet August 2011 Table of Contents
Cardiovascular Institute
 Allegheny Health Network Cardiovascular Institute Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Program Our patient survival rate is higher than the national average. ECMO experts. Multidisciplinary team.
Allegheny Health Network Cardiovascular Institute Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Program Our patient survival rate is higher than the national average. ECMO experts. Multidisciplinary team.
