Neuroscience of Consciousness I
|
|
|
- MargaretMargaret Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness I Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham
2 2 What is consciousness?
3 3 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive Contents of consciousness ( consciousness of... ) particular (reportable) experience at a certain level of consciousness Laureys (2005) Trends in Cogn. Sci. 9:
4 4 Does consciousness matter to you? 1)Yes, very much! Consciousness is central to my life! 2) No, I can t see what difference consciousness makes to my life!
5 5 Great public interest in the brain substrates of consciousness reflected by an abundance of popular-science books on the topic. Etc.
6 6 Problems of consciousness what is to explain? Difference between wakefulness and sleep Difference between being responsive and unresponsive Reportability of our mental states Integration of information Easy problems Ability to access own internal states Focus of attention Deliberate control of behaviour (as opposed to automatic behaviour) The hard problem: Subjective experience ( phenomenal consciousness, qualia ) Chalmers (1995) Facing up to the problem of consciousness Journal of Consciousness Studies 2:
7 7 Today States of consciousness and neural correlates Neurological disorders of (the states of) consciousness Next week Contents of consciousness and neural correlates Neurological disorders affecting contents of consciousness What s left to explain?
8 8 States of consciousness Baars et al. (2003) Trends Neurosci. 26:
9 9 Key brain substrates of consciousness Mormann & Koch (2007) Scholarpedia 2(12):1740
10 Wakefulness 10 and sleep - the cardinal states of consciousness Sleep Hobson & Pace-Schott (2002) Nature Rev Neurosci 3:
11 11 Neurochemistry of wakefulness and sleep Jones (2005) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26:
12 12 Cortico-thalamic mechanisms in wakefulness and sleep Falling asleep: Reticular thalamic nucleus neurons fire rhythmic bursts - reflected by EEG spindles - which inhibits thalamo-cortical neurons, thereby blocking information transfer to cortex. Awake: Cortical and thalamic neurons show tonic singlespike firing and afferent information is transferred to cortex. EEG is largely desynchronised, but fast oscillations occur. Sleep (non- REM/slow-wave): cortical and thalamic neurons show rhythmic slow changes between down and up states - reflected by slow EEG oscillations. Waking up: Cholinergic neurons inhibit neurons in reticular thalamic nucleus and activate thalamocortical neurons reflected by the replacement of slow oscillations by faster EEG oscillations, thereby facilitating information transfer to cortex. Figure from Franks (2008) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 9: ; for detailed explanation see: Steriade (2003) Front. Biosci. 8:d
13 13 Comparison of wakefulness and dreams: 40-Hz oscillations characterise conscious states Spontaneous 40-Hz oscillations during wakefulness and REM sleep, but not slow-wave sleep Re-set of 40-Hz oscillations by sensory stimulus (tone) during wakefulness Similar to the awake state, REM sleep the main dream phase of sleep is characterised by 40 Hz oscillations as measured by surface MEG or EEG. Thus, 40-Hz oscillations are a correlate of conscious processing and have been hypothesised to play a key role in such processing. Depth recordings in animal models suggest 40-Hz oscillations are generated by thalamo-cortical circuits. Only during wakefulness, but not REM sleep, 40-Hz oscillations are re-set by sensory stimulus (tone), in line with fast oscillations being critical for conscious perception of sensory information. Llinas & Ribary (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:
14 Thalamo-cortical circuitry hypothesised to underlie 40-Hz 14 oscillations and consciousness Widespread cortical projections of intra-laminar thalamus Sensory information Llinas & Ribary (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:
15 15 Anaesthesia and consciousness Loss of consciousness is the objective of anaesthesia. Loss of consciousness is not trivial to determine, as unresponsiveness and amnesia are no proof. Neuropharmacological targets of current anaesthetics Inhibitory neuro-transmission is enhanced, excitatory transmission decreased. Note: this can lead to excitation of certain brain regions due to network effects (e.g., ketamine). Brain sites associated with anaesthetic effects Thalamus: Activity is decreased by many, but not all, anaesthetics (e.g., ketamine); may be secondary to cortical deactivation. Neocortical areas: Deactivation of, especially posterior, mesial cortical areas and of a lateral temporo-parieto-occipital complex. Note: Primary sensory cortices can often show unchanged responsiveness under anaesthesia! Anaesthesia may not necessarily involve cortical deactivation, but disruption of cortical integration, i.e. of the interaction of several cortical areas. Alkire et al. (2008) Science 322:
16 Anaesthesia disrupts cortico-cortical interactions organised 16 by fast oscillations Alkire et al. (2008) Science 322: , based on Imas et al. (2005) Neurosci. Letters 387:
17 17 Similarities between sleep and anaesthesia Regional decreases in brain metabolic activity during sleep and anaesthesia Franks (2008) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 9: ;
18 18 (Abnormal) Dissociated states of consciousness There are several abnormal conditions in which wakefulness is relatively preserved whereas consciousness (of anything) appears to be largely absent. Deactivated brain areas (in comparison to conscious wakefulness) Laureys (2005) Trends in Cogn. Sci. 9:
19 19 Loss of consciousness in epilepsy Yu & Blumenfeld (2009) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1157:48-60
20 20 States of reduced consciousness following brain injury Resting brain metabolism in patients following brain injury and in healthy control Normal consciousness! Laureys et al. (2004) Lancet Neurol. 3: Brain injury associated with vegetative state Zeman (1997) Lancet 350:
21 21 In a nut shell states of consciousness and brain substrates Neocortical areas Thalamus Ascending activating systems Global states of consciousness depend on a distributed brain network, comprising ascending activating systems, thalamus and neocortex. Consciousness seems to involve the temporal coordination of distributed activity in thalamic and neocortical areas as reflected by fast oscillations. Neuronal correlates of specific contents of consciousness (e.g., specific percepts, specific plans, specific memories)...??? Next week!
22 22 Neuroscience of consciousness I Selected Reading General overviews: Chalmers D (1995) Facing up to the problem of consciousness. Journal of Consciousness Studies 2: ( Zeman A (2001) Consciousness. Brain 124: Tononi G & Koch C (2008) The neural correlates of consciousness: and update. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1124: Sleep & anaesthesia: Alkire MT, Hudetz AG, Tononi G (2008) Consciousness and anaesthesia. Science 322: Franks NP (2008) General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal pathways of sleep and arousal. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 9: Dissociated states of consciousness: Laureys S (2005) The neural correlates of (un)awareness. Trends Cogn. Sci. 9:
23 Neuroscience of consciousness I Some questions to guide your revision 23 What is consciousness, what are the problems of consciousness? What strategies can neuroscientists pursue to study the brain substrates of consciousness? In terms of brain substrates, what seem conscious states to have in common? What happens in your brain, so you wake up ( regain consciousness ) after a night s sleep? How do anaesthetics act in our brains to (hopefully!) result in loss of consciousness? What goes wrong in the brains of patients that suffer from disorders of consciousness?
Neuroscience of Consciousness II
 1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness II Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive Contents
1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness II Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive Contents
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY
 states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
Circadian rhythm and Sleep. Radwan Banimustafa MD
 Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions. Visual awareness
 Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions Visual awareness Phylosphy of mind Art AI Normal and abnormal states Coma Drugs Hypnosis Religion Cosciousness 2 Unconscious processes Normal and abnormal contents
Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions Visual awareness Phylosphy of mind Art AI Normal and abnormal states Coma Drugs Hypnosis Religion Cosciousness 2 Unconscious processes Normal and abnormal contents
CONSCIOUSNESS. Phil/Psych 256. Chris Eliasmith
 CONSCIOUSNESS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith The C Word One main difficulty with consciousness is defining what we are talking about: Do we mean awareness (e.g., awake vs. asleep)? Qualia (what-it-is-like)?
CONSCIOUSNESS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith The C Word One main difficulty with consciousness is defining what we are talking about: Do we mean awareness (e.g., awake vs. asleep)? Qualia (what-it-is-like)?
Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms
 203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Neuroimaging & Consciousness
 Neuroimaging & Consciousness Georgios ANTONOPOULOS PhD student Coma Science Group GIGA Consciousness University & University Hospital Liège, Belgium Arousal & awareness Conscious Wakefulness Lucid Dreaming
Neuroimaging & Consciousness Georgios ANTONOPOULOS PhD student Coma Science Group GIGA Consciousness University & University Hospital Liège, Belgium Arousal & awareness Conscious Wakefulness Lucid Dreaming
The Role of thethalamus in Human Consciousness
 The Role of thethalamus in Human Consciousness Lawrence M. Ward Department of Psychology, The Brain Research Centre, and Peter Wall Institute for Advanced Studies University of British Columbia Professeur
The Role of thethalamus in Human Consciousness Lawrence M. Ward Department of Psychology, The Brain Research Centre, and Peter Wall Institute for Advanced Studies University of British Columbia Professeur
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122
 EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
Consciousness: Exploring brain activity in coma & related states of consciousness
 Consciousness: Exploring brain activity in coma & related states of consciousness Helena CASSOL PhD student Steven LAUREYS MD University Hospital & University of Liège Belgium coma@ulg.ac.be www.comascience.org
Consciousness: Exploring brain activity in coma & related states of consciousness Helena CASSOL PhD student Steven LAUREYS MD University Hospital & University of Liège Belgium coma@ulg.ac.be www.comascience.org
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep)
 EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
EEG Electrode Placement
 EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
from sleep to attention lecture 4 April 9, 2012 control of sleep/wake state production II
 from sleep to attention lecture 4 April 9, 2012 control of sleep/wake state production II "From the moment of my birth, the angels of anxiety, worry, and death stood at my side, followed me out when I
from sleep to attention lecture 4 April 9, 2012 control of sleep/wake state production II "From the moment of my birth, the angels of anxiety, worry, and death stood at my side, followed me out when I
Using Multi-electrode Array Recordings to detect unrecognized electrical events in epilepsy
 Using Multi-electrode Array Recordings to detect unrecognized electrical events in epilepsy December 1, 2012 Catherine Schevon, MD, PhD Columbia University New York, NY American Epilepsy Society Annual
Using Multi-electrode Array Recordings to detect unrecognized electrical events in epilepsy December 1, 2012 Catherine Schevon, MD, PhD Columbia University New York, NY American Epilepsy Society Annual
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Similarities between deep slow wave sleep and absence epilepsy
 Similarities between deep slow wave sleep and absence epilepsy A.M.L. COENEN NICI, DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF NIJMEGEN P.O. BOX 9104 6500 HE NIJMEGEN THE NETHERLANDS Prologue Deep slow wave
Similarities between deep slow wave sleep and absence epilepsy A.M.L. COENEN NICI, DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF NIJMEGEN P.O. BOX 9104 6500 HE NIJMEGEN THE NETHERLANDS Prologue Deep slow wave
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
The Role of Mitral Cells in State Dependent Olfactory Responses. Trygve Bakken & Gunnar Poplawski
 The Role of Mitral Cells in State Dependent Olfactory Responses Trygve akken & Gunnar Poplawski GGN 260 Neurodynamics Winter 2008 bstract Many behavioral studies have shown a reduced responsiveness to
The Role of Mitral Cells in State Dependent Olfactory Responses Trygve akken & Gunnar Poplawski GGN 260 Neurodynamics Winter 2008 bstract Many behavioral studies have shown a reduced responsiveness to
Synaptic excitation of principal cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus during focal epileptic seizures in the visual cortex
 Synaptic excitation of principal cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus during focal epileptic seizures in the visual cortex Andrzej wr6be11, Anders ~ edstr~m~ and Sivert ~indstrsm~ 'Department
Synaptic excitation of principal cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus during focal epileptic seizures in the visual cortex Andrzej wr6be11, Anders ~ edstr~m~ and Sivert ~indstrsm~ 'Department
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms. Reading: BCP Chapter 19
 Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Rhythms of the Brain 1 of 8
 Rhythms of the Brain 1 of 8 I. EEG A. Measures current flow during synaptic excitation of the dendrites of a large number of pyramidal cells. 1. 80% of the brain made up of these cells 2. thousands of
Rhythms of the Brain 1 of 8 I. EEG A. Measures current flow during synaptic excitation of the dendrites of a large number of pyramidal cells. 1. 80% of the brain made up of these cells 2. thousands of
Index. Behaviour, posthypnotic see Posthypnotic behaviour
 Index Amnesia, posthypnotic see Posthypnotic amnesia Analgesia, hypnotic see Pain Animal hypnosis, 4 duration of, affected by caffeine and X-rays, 71-72 as emotional reaction, 69 emotional stress, role
Index Amnesia, posthypnotic see Posthypnotic amnesia Analgesia, hypnotic see Pain Animal hypnosis, 4 duration of, affected by caffeine and X-rays, 71-72 as emotional reaction, 69 emotional stress, role
Normal brain rhythms and the transition to epileptic activity
 School on Modelling, Automation and Control of Physiological variables at the Faculty of Science, University of Porto 2-3 May, 2007 Topics on Biomedical Systems Modelling: transition to epileptic activity
School on Modelling, Automation and Control of Physiological variables at the Faculty of Science, University of Porto 2-3 May, 2007 Topics on Biomedical Systems Modelling: transition to epileptic activity
Oscillations: From Neuron to MEG
 Oscillations: From Neuron to MEG Educational Symposium, MEG UK 2014, Nottingham, Jan 8th 2014 Krish Singh CUBRIC, School of Psychology Cardiff University What are we trying to achieve? Bridge the gap from
Oscillations: From Neuron to MEG Educational Symposium, MEG UK 2014, Nottingham, Jan 8th 2014 Krish Singh CUBRIC, School of Psychology Cardiff University What are we trying to achieve? Bridge the gap from
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 September 19.
 Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Hallucinations in schizophrenia, sensory impairment, and brain disease: A unifying model
 BEHAVIORAL AND BRAIN SCIENCES (2004) 27, 771 830 Printed in the United States of America Hallucinations in schizophrenia, sensory impairment, and brain disease: A unifying model Ralf-Peter Behrendt Department
BEHAVIORAL AND BRAIN SCIENCES (2004) 27, 771 830 Printed in the United States of America Hallucinations in schizophrenia, sensory impairment, and brain disease: A unifying model Ralf-Peter Behrendt Department
****REVISED 4/27/2015****
 Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
Thalamo-Cortical Relationships Ultrastructure of Thalamic Synaptic Glomerulus
 Central Visual Pathways V1/2 NEUR 3001 dvanced Visual Neuroscience The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus () is more than a relay station LP SC Professor Tom Salt UCL Institute of Ophthalmology Retina t.salt@ucl.ac.uk
Central Visual Pathways V1/2 NEUR 3001 dvanced Visual Neuroscience The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus () is more than a relay station LP SC Professor Tom Salt UCL Institute of Ophthalmology Retina t.salt@ucl.ac.uk
Students will be able to determine what stage of sleep someone is in by analyzing their EEG.
 Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to engage students with the concept of the neural circuit. The lesson and unit as a whole use sleep, a behavior everyone is familiar
Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to engage students with the concept of the neural circuit. The lesson and unit as a whole use sleep, a behavior everyone is familiar
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT.
 CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
Consciousness The final frontier!
 Consciousness The final frontier! How to Define it??? awareness perception - automatic and controlled memory - implicit and explicit ability to tell us about experiencing it attention. And the bottleneck
Consciousness The final frontier! How to Define it??? awareness perception - automatic and controlled memory - implicit and explicit ability to tell us about experiencing it attention. And the bottleneck
Introduction to EEG del Campo. Introduction to EEG. J.C. Martin del Campo, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada
 Introduction to EEG J.C. Martin, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada What is EEG? A graphic representation of the difference in voltage between two different cerebral locations plotted over
Introduction to EEG J.C. Martin, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada What is EEG? A graphic representation of the difference in voltage between two different cerebral locations plotted over
The Study of Brain Activity in Sleep
 The Study of Brain Activity in Sleep The hours of our life other activities (19%) sport (1%) phone/e-mail (1%) Sleep 36% household activities (8%) work and work-related (16%) television (11%) eat/drink
The Study of Brain Activity in Sleep The hours of our life other activities (19%) sport (1%) phone/e-mail (1%) Sleep 36% household activities (8%) work and work-related (16%) television (11%) eat/drink
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Scaling a slow-wave sleep cortical network model using NEOSIM*
 NEUROCOMPUTING ELSEVIER Neurocomputing 44-46 (2002) 453-458 Scaling a slow-wave sleep cortical network model using NEOSIM* adivision of Informatics, Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation, University
NEUROCOMPUTING ELSEVIER Neurocomputing 44-46 (2002) 453-458 Scaling a slow-wave sleep cortical network model using NEOSIM* adivision of Informatics, Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation, University
How Insomnia Reduces Declarative and Non- Declarative Memory Sonsolidation
 Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2014 How Insomnia Reduces Declarative and Non- Declarative Memory Sonsolidation Kseniya Chumachenko Parkland College Recommended Citation Chumachenko,
Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2014 How Insomnia Reduces Declarative and Non- Declarative Memory Sonsolidation Kseniya Chumachenko Parkland College Recommended Citation Chumachenko,
Spectral Analysis of EEG Patterns in Normal Adults
 Spectral Analysis of EEG Patterns in Normal Adults Kyoung Gyu Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Ewha Medical Research Center, Ewha Womans University Medical College, Background: Recently, the
Spectral Analysis of EEG Patterns in Normal Adults Kyoung Gyu Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Ewha Medical Research Center, Ewha Womans University Medical College, Background: Recently, the
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming. Elaine M. Hull
 Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Patho-physiology of nervous System Talk 2 Syndromes in neurosciences. Petr Maršálek Dept pathological physiology 1.Med. F. CUNI
 Patho-physiology of nervous System Talk 2 Syndromes in neurosciences Petr Maršálek Dept pathological physiology 1.Med. F. CUNI Talks on NS Talk 1 - Pain and Motor disorders Talk 2 - This - Syndromes in
Patho-physiology of nervous System Talk 2 Syndromes in neurosciences Petr Maršálek Dept pathological physiology 1.Med. F. CUNI Talks on NS Talk 1 - Pain and Motor disorders Talk 2 - This - Syndromes in
A Biophysical Model of Cortical Up and Down States: Excitatory-Inhibitory Balance and H-Current
 A Biophysical Model of Cortical Up and Down States: Excitatory-Inhibitory Balance and H-Current Zaneta Navratilova and Jean-Marc Fellous ARL Division of Neural Systems, Memory and Aging University of Arizona,
A Biophysical Model of Cortical Up and Down States: Excitatory-Inhibitory Balance and H-Current Zaneta Navratilova and Jean-Marc Fellous ARL Division of Neural Systems, Memory and Aging University of Arizona,
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Sleep. No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness,
 Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep. No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness,
 Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
What is Consciousness?
 What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
Nuclear imaging of the human brain
 Nuclear imaging of the human brain Steven Laureys Coma Science Group Cyclotron Research Centre & Neurology Dept. University of Liège, Belgium Neuroimaging structure function Neuroimaging: Modalities Structural
Nuclear imaging of the human brain Steven Laureys Coma Science Group Cyclotron Research Centre & Neurology Dept. University of Liège, Belgium Neuroimaging structure function Neuroimaging: Modalities Structural
States of Consciousness:
 States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
CNS MCQ 2 nd term. Select the best answer:
 Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Experimental Model of Study of Consciousness at the Awakening: FMRI, EEG and Behavioral Methods
 Experimental Model of Study of Consciousness at the Awakening: FMRI, EEG and Behavioral Methods Vladimir B. Dorokhov 1(&), Denis G. Malakhov 2, Vyacheslav A. Orlov 2, and Vadim L. Ushakov 2,3 1 Institute
Experimental Model of Study of Consciousness at the Awakening: FMRI, EEG and Behavioral Methods Vladimir B. Dorokhov 1(&), Denis G. Malakhov 2, Vyacheslav A. Orlov 2, and Vadim L. Ushakov 2,3 1 Institute
C81ADD Psychology of Addiction. Alcohol. Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) School of Psychology. Tobias Bast.
 C81ADD Psychology of Addiction Alcohol Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) Tobias Bast School of Psychology tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk 1 Selected aspects of the psychopharmacology of alcohol (ethanol) Primary neuropharmacological
C81ADD Psychology of Addiction Alcohol Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) Tobias Bast School of Psychology tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk 1 Selected aspects of the psychopharmacology of alcohol (ethanol) Primary neuropharmacological
Functional reorganization in thalamocortical networks: Transition between spindling and delta sleep rhythms
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 15417 15422, December 1996 Neurobiology Functional reorganization in thalamocortical networks: Transition between spindling and delta sleep rhythms D. TERMAN*, A.BOSE*,
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 15417 15422, December 1996 Neurobiology Functional reorganization in thalamocortical networks: Transition between spindling and delta sleep rhythms D. TERMAN*, A.BOSE*,
The Neurobiology of Consciousness Professor Christof Koch
 California Institute of Technology www.klab.caltech.edu 1 Science explains many things very well 2 3 1 4 5 Yet science has no idea how consciousness comes about! Some philosophers say that consciousness
California Institute of Technology www.klab.caltech.edu 1 Science explains many things very well 2 3 1 4 5 Yet science has no idea how consciousness comes about! Some philosophers say that consciousness
Mechanisms of Consciousness with Emphasis on the Cerebral Cortical Component
 Consciousness: Cortical Component 13 Mechanisms of Consciousness with Emphasis on the Cerebral Cortical Component 2 G. Bryan Young INTRODUCTION Concepts of Consciousness Consciousness has been defined
Consciousness: Cortical Component 13 Mechanisms of Consciousness with Emphasis on the Cerebral Cortical Component 2 G. Bryan Young INTRODUCTION Concepts of Consciousness Consciousness has been defined
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
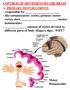 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
BRAIN FUNCTION IN THE VEGETATIVE STATE
 Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 550 (2004) 229-38 BRAIN FUNCTION IN THE VEGETATIVE STATE Steven Laureys, Marie-Elisabeth Faymonville, Xavier De Tiège, Philippe Peigneux, Jacques Berré,,
Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 550 (2004) 229-38 BRAIN FUNCTION IN THE VEGETATIVE STATE Steven Laureys, Marie-Elisabeth Faymonville, Xavier De Tiège, Philippe Peigneux, Jacques Berré,,
pdf NIH Overview Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from:
 1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
Natural Waking and Sleep States: A View From Inside Neocortical Neurons
 Natural Waking and Sleep States: A View From Inside Neocortical Neurons M. STERIADE, I. TIMOFEEV, AND F. GRENIER Laboratoire de Neurophysiologie, Faculté de Médicine, Université Laval, Quebec G1K 7P4,
Natural Waking and Sleep States: A View From Inside Neocortical Neurons M. STERIADE, I. TIMOFEEV, AND F. GRENIER Laboratoire de Neurophysiologie, Faculté de Médicine, Université Laval, Quebec G1K 7P4,
A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to
 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
Leading role of thalamic over cortical neurons during postinhibitory rebound excitation
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 13929 13934, November 1998 Neurobiology Leading role of thalamic over cortical neurons during postinhibitory rebound excitation F. GRENIER, I.TIMOFEEV, AND M. STERIADE*
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 13929 13934, November 1998 Neurobiology Leading role of thalamic over cortical neurons during postinhibitory rebound excitation F. GRENIER, I.TIMOFEEV, AND M. STERIADE*
GROUPING OF BRAIN RHYTHMS IN CORTICOTHALAMIC SYSTEMS
 Neuroscience 137 (2006) 1087 1106 GROUPING OF BRAIN RHYTHMS IN CORTICOTHALAMIC SYSTEMS M. STERIADE* Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Laval University, Faculty of Medicine, Quebec, Canada G1K 7P4 Abstract
Neuroscience 137 (2006) 1087 1106 GROUPING OF BRAIN RHYTHMS IN CORTICOTHALAMIC SYSTEMS M. STERIADE* Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Laval University, Faculty of Medicine, Quebec, Canada G1K 7P4 Abstract
The connection between sleep spindles and epilepsy in a spatially extended neural field model
 The connection between sleep spindles and epilepsy in a spatially extended neural field model 1 2 3 Carolina M. S. Lidstrom Undergraduate in Bioengineering UCSD clidstro@ucsd.edu 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
The connection between sleep spindles and epilepsy in a spatially extended neural field model 1 2 3 Carolina M. S. Lidstrom Undergraduate in Bioengineering UCSD clidstro@ucsd.edu 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Model of Thalamocortical Slow-Wave Sleep Oscillations and Transitions to Activated States
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 2002, 22(19):8691 8704 Model of Thalamocortical Slow-Wave Sleep Oscillations and Transitions to Activated States Maxim Bazhenov, 1 Igor Timofeev, 2 Mircea Steriade,
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 2002, 22(19):8691 8704 Model of Thalamocortical Slow-Wave Sleep Oscillations and Transitions to Activated States Maxim Bazhenov, 1 Igor Timofeev, 2 Mircea Steriade,
Biomedical Research 2013; 24 (3): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2013; 24 (3): 359-364 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info Investigating relative strengths and positions of electrical activity in the left and right hemispheres of the human brain
Biomedical Research 2013; 24 (3): 359-364 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info Investigating relative strengths and positions of electrical activity in the left and right hemispheres of the human brain
NEUROSCIENCE. W1 Divisions of the nervous system PSYC1002 NOTES
 PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
CHAPTER TWO. The Philosophical Approach: Enduring Questions
 CHAPTER TWO The Philosophical Approach: Enduring Questions The Philosophy Perspective Philosophy is the search for knowledge. The branch of metaphysics examines the nature of reality. The branch of epistemology
CHAPTER TWO The Philosophical Approach: Enduring Questions The Philosophy Perspective Philosophy is the search for knowledge. The branch of metaphysics examines the nature of reality. The branch of epistemology
March 14. Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part Dream Journal Assignment
 March 14 Agenda: 1. Graphic Organizer Part 1 for Unit 5 2. Sleep episode Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & 15 92. Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part 1 93. Dream Journal Assignment Homework: 1. Test on Friday!
March 14 Agenda: 1. Graphic Organizer Part 1 for Unit 5 2. Sleep episode Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & 15 92. Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part 1 93. Dream Journal Assignment Homework: 1. Test on Friday!
CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS
 Neuroscience 147 (2007) 272 276 RAPID REPORT CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS Y. CISSÉ, 1,2 D. A. NITA, 2 M. STERIADE AND I. TIMOFEEV* Department of
Neuroscience 147 (2007) 272 276 RAPID REPORT CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS Y. CISSÉ, 1,2 D. A. NITA, 2 M. STERIADE AND I. TIMOFEEV* Department of
Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old
 Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old V. Mohan Kumar Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram 1 What is sleep? As per behavioral criteria: Reduced motor
Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old V. Mohan Kumar Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram 1 What is sleep? As per behavioral criteria: Reduced motor
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety
 C82NAB Neuroscience and Behaviour Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 1 Outline Emotion I (first part) Studying brain substrates of
C82NAB Neuroscience and Behaviour Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 1 Outline Emotion I (first part) Studying brain substrates of
Bursting dynamics in the brain. Jaeseung Jeong, Department of Biosystems, KAIST
 Bursting dynamics in the brain Jaeseung Jeong, Department of Biosystems, KAIST Tonic and phasic activity A neuron is said to exhibit a tonic activity when it fires a series of single action potentials
Bursting dynamics in the brain Jaeseung Jeong, Department of Biosystems, KAIST Tonic and phasic activity A neuron is said to exhibit a tonic activity when it fires a series of single action potentials
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
Consciousness (Response to the Hard Problem)
 Indiana Undergraduate Journal of Cognitive Science 3 (2008) 21-27 Copyright 2008 IUJCS. All rights reserved Consciousness (Response to the Hard Problem) Artem Tsvetkov Cognitive Science and Biological
Indiana Undergraduate Journal of Cognitive Science 3 (2008) 21-27 Copyright 2008 IUJCS. All rights reserved Consciousness (Response to the Hard Problem) Artem Tsvetkov Cognitive Science and Biological
Page 1 L 58. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems /2013 RETICULAR FORMATION
 Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
Oscillations and effective connectivity in human corticothalamic networks
 Oscillations and effective connectivity in human corticothalamic networks Mario Rosanova, MD, PhD Department of clinical sciences «Luigi Sacco» University of Milan, Milan, Italy -Characterize EEG oscillations
Oscillations and effective connectivity in human corticothalamic networks Mario Rosanova, MD, PhD Department of clinical sciences «Luigi Sacco» University of Milan, Milan, Italy -Characterize EEG oscillations
Consciousness as representation formation from a neural Darwinian perspective *
 Consciousness as representation formation from a neural Darwinian perspective * Anna Kocsis, mag.phil. Institute of Philosophy Zagreb, Croatia Vjeran Kerić, mag.phil. Department of Psychology and Cognitive
Consciousness as representation formation from a neural Darwinian perspective * Anna Kocsis, mag.phil. Institute of Philosophy Zagreb, Croatia Vjeran Kerić, mag.phil. Department of Psychology and Cognitive
Basic Science of Representative Normal Human EEG Potentials
 Basic Science of Representative Normal Human EEG Potentials Seyed M Mirsattari, MD, PhD, FRCPC Departments of Clinical Neurological Sciences, Medical Biophysics, Diagnostic Imaging, Psychology University
Basic Science of Representative Normal Human EEG Potentials Seyed M Mirsattari, MD, PhD, FRCPC Departments of Clinical Neurological Sciences, Medical Biophysics, Diagnostic Imaging, Psychology University
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
Chapter 5. Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition
 Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Brown EN, Lydic R, Schiff ND, et al. General anesthesia, sleep,
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Brown EN, Lydic R, Schiff ND, et al. General anesthesia, sleep,
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis
 Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
SLEEP AND AROUSAL: Thalamocortical Mechanisms
 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1997. 20:185 215 Copyright c 1997 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved SLEEP AND AROUSAL: Thalamocortical Mechanisms David A. McCormick and Thierry Bal 1 Section of Neurobiology,
Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1997. 20:185 215 Copyright c 1997 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved SLEEP AND AROUSAL: Thalamocortical Mechanisms David A. McCormick and Thierry Bal 1 Section of Neurobiology,
States of Consciousness
 1 Unit 5 Review of Key Concepts and Terms States of Consciousness (2-4% of the AP exam/curriculum) Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our environment. Preconscious: something that is not in
1 Unit 5 Review of Key Concepts and Terms States of Consciousness (2-4% of the AP exam/curriculum) Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our environment. Preconscious: something that is not in
Metaphysics and consciousness. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Metaphysics and consciousness Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Why neurophilosophy? Nature of the mind Classically part of philosophy Thought about without insight from neuroscience.
Metaphysics and consciousness Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Why neurophilosophy? Nature of the mind Classically part of philosophy Thought about without insight from neuroscience.
Modelling corticothalamic feedback and the gating of the thalamus by the cerebral cortex
 J. Physiol. (Paris) 94 (2000) 391 410 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. Published by Éditions scientifiques et médicales Elsevier SAS. All rights reserved PII: S0928-4257(00)01093-7/FLA Modelling corticothalamic
J. Physiol. (Paris) 94 (2000) 391 410 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. Published by Éditions scientifiques et médicales Elsevier SAS. All rights reserved PII: S0928-4257(00)01093-7/FLA Modelling corticothalamic
The role of amplitude, phase, and rhythmicity of neural oscillations in top-down control of cognition
 The role of amplitude, phase, and rhythmicity of neural oscillations in top-down control of cognition Chair: Jason Samaha, University of Wisconsin-Madison Co-Chair: Ali Mazaheri, University of Birmingham
The role of amplitude, phase, and rhythmicity of neural oscillations in top-down control of cognition Chair: Jason Samaha, University of Wisconsin-Madison Co-Chair: Ali Mazaheri, University of Birmingham
Photoreceptors Rods. Cones
 Photoreceptors Rods Cones 120 000 000 Dim light Prefer wavelength of 505 nm Monochromatic Mainly in periphery of the eye 6 000 000 More light Different spectral sensitivities!long-wave receptors (558 nm)
Photoreceptors Rods Cones 120 000 000 Dim light Prefer wavelength of 505 nm Monochromatic Mainly in periphery of the eye 6 000 000 More light Different spectral sensitivities!long-wave receptors (558 nm)
Outline 3/5/2013. Practice Question. Practice question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness
 Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Theories and models of consciousness in neuroscience.
 Theories and models of consciousness in neuroscience. Abstract: Over the past decade, neuroscientific studies of consciousness have produced a rapidly growing body of experimental data. Theories and models
Theories and models of consciousness in neuroscience. Abstract: Over the past decade, neuroscientific studies of consciousness have produced a rapidly growing body of experimental data. Theories and models
The Neural Control of Behavioral State
 The Neural Control of Behavioral State Learning objectives: Introduction - Behavioral State; why do we sleep? A Clinical Case - The Sleeping Beauty of Oak Park. EEG - A Neural Signature of Behavioral State.
The Neural Control of Behavioral State Learning objectives: Introduction - Behavioral State; why do we sleep? A Clinical Case - The Sleeping Beauty of Oak Park. EEG - A Neural Signature of Behavioral State.
Sleep and Wakefulness in the Cuneate Nucleus: A Computational Study
 Sleep and wakefulness in the cuneate nucleus: a computational study Eduardo Sánchez 1, Senén Barro 1, Jorge Mari~no 3, and Antonio Canedo 2 1 Grupo de Sistemas Intelixentes (GSI) Departamento de Electrónica
Sleep and wakefulness in the cuneate nucleus: a computational study Eduardo Sánchez 1, Senén Barro 1, Jorge Mari~no 3, and Antonio Canedo 2 1 Grupo de Sistemas Intelixentes (GSI) Departamento de Electrónica
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention
 Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
