EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122
|
|
|
- Patricia Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1
2 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: Hz Mental activity: + alpha: 8-13 Hz theta: 4-8 Hz Sleep spindle delta: Hz - K complex 2
3 The waves of the EEG beta: Hz alpha: 8-13 Hz Mental activity: + theta: 4-8 Hz delta: Hz - Electroencephalography eyes open eyes closed 3
4 Characteristics of EEG activity change in different situations, 1. with the level of vigilance: alertness, rest, sleep and dreaming. 2. mental tasks also alter the pattern of the waves in different parts of the brain. 3. electroencephalograms are also used in neurology and psychiatry, to help diagnose diseases of the brain, such as epilepsy, sleep disorders brain tumors. The origin of EEG waves Slow electrical activity of neurons. Summed postsynaptic potentials of parallelly arranged pyramidal cells, 4
5 The origin of the EEG The origin of the EEG mv + - negativer pole Dipole - Pyramidal cell Afferent fiber EPSP positiver pole mv time 5
6 The origin of the EEG The origin of the EEG 6
7 The origin of alpha activity The origin of alpha activity Relay nuclei - + Nuc. reticularis thalami + Cortex 7
8 EEG synchronization and desynchronization Apical dentrit (DC) Thalamic afferent Efferent Resting state Activation EEG desynchronization and synchronization low amplitude high amplitude synchronized activity desynchronized activity afferent input 16 8
9 Epilepsy 9
10 Epilepsy Epilepsy 10
11 Evoced potential The topographic study of brain electrical activity was born again only when fast desktop computers became available in the 80s. Thus, EEG brain topography was developed. It is also called Color Brain Mapping. 11
12 BRAIN MAPING Brain Mapping 12
13 Magnetoencephalography MEG) Sleep 13
14 14
15 15
16 16
17 Characteristics of sleep: How do we claim that somebody is sleeping? 1. Loss of conscioussness 2. Decrease (or loss ) in muscle tone 3. Change of respiration (rhythmic, slow, superficial) 4. Autonomic signs (blood presure, heart rate) 5. Cortical activity (EEG) 17
18 Non-REM sleep Sleep stages Slow waves in EEG Muscle tone, respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, metabolic rate decreases. stage 1. Flat EEG, theta waves stage 2. Sleep spindles, K complexes stage 3. Theta and delta waves stage 4. (delta sleep) Delta waves REM sleep (paradoxical sleep) Fast EEG, absence of muscle tone, PGO-waves, rapid eye movemenents Respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure fluctuates. erection Non-REM sleep Sleep stages Slow waves in EEG Muscle tone, respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, metabolic rate decreases. stage 1. Flat EEG, theta waves stage 2. Sleep spindles, K complexes stage 3. Theta and delta waves stage 4. (delta sleep) Delta waves REM sleep (paradoxical sleep) REM-sleep deep non-rem sleep Wakefulness Fast EEG, absence of muscle tone, PGO-waves, rapid eye movemenents Respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure fluctuates. erection 18
19 Non-REM sleep Sleep stages Slow waves in EEG Muscle tone, respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, metabolic rate decreases. stage 1. Flat EEG, theta waves stage 2. Sleep spindles, K complexes stage 3. Theta and delta waves stage 4. (delta sleep) Delta waves REM sleep (paradoxical sleep) Fast EEG, absence of muscle tone, PGO-waves, rapid eye movemenents Respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure fluctuates. erection wakefulness sleep spindle REM sleep Sleep stages 19
20 Non-REM sleep Sleep stages Slow waves in EEG Muscle tone, respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, metabolic rate decreases. stage 1. Flat EEG, theta waves stage 2. Sleep spindles, K complexes stage 3. Theta and delta waves stage 4. (delta sleep) Delta waves REM sleep (paradoxical sleep) Fast EEG, absence of muscle tone, PGO-waves, rapid eye movemenents Respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure fluctuates. erection The sleep during a night Sleep is entered through non-rem sleep. Non-REM sleep and REM sleep alternate with a period near 90 min. Slow wave sleep predominates in the first third of the night and is linked to the initiation of sleep, REM sleep predominates in the last third of the. 20
21 The distribution of sleep stages is dependent upon age Hours Awake Week Month Years % Time spent in sleep h 21
22 Mortality rate and the length of sleep óra Time spent in sleep 22
23 Characteristics of dreams: 1. visually dominated 2. irregular 3. irreal 4. bizarre 5. difficult to retrieve 6. periodic 7. emotional Biological role of dreams Freud model: People are driven by aggressive and sexual instincts that are repressed from conscious awareness. While these thoughts are not consciously expressed, they find their way into our awareness via dreams. Hobson concepts (lack of sensory information, PGO waves) 23
24 The 2 process model of sleep regulation sleep wake sleep wake Basal forebrain 24
25 1: encephale isolé 2: cerveau isolé Consequences of lesions Basal forebrain - insomnia Post. hypothalamus - sleepiness Mesencephalic form. ret. - sleepiness Transection in the pons - insomnia 25
26 Ascending Arousal System (Locus Coeruleus, Formatio Reticularis) NA, Ach The ascending arousal system. Adapted from Saper et al. Hypothalamic Regulation of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms. Nature 2005;437:
27 The posterior hypothalamus (histamin, orexin), the locus coeruleus, the mesencephalic formation reticular system and other brainstem regions contains cholinergic, monoaminergic (mainly noradrenergic) and glutamatergic wake-on neurons. The most important brain structures involved in the regulation of sleep-wake activity 27
28 The basal forebrain (specially the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus) and the anterior hypothalamus contains sleep-on neurons (GABA, galanin). Non-REM-on cells: in the anterior hypothalamus and the basal forebrain REM-waking-on cells: in the brain stem reticular formation REM-off cells: Noradrenergic, adrenergic, and serotonergic cells in the brainstem and histaminergic cells in the forebrain. REM-on cells. 28
29 Promotion of sleep and wakefulness 5-HT??? The activity of serotonergic cells increase in wakefulness. Depletion of 5-HT results in insomnia. 29
30 REM sleep Cholinergic REM-sleep promoting mechanism DR LC HT NE ACh REM-sleep PONS Cholinerg structures: Nucl. Gigantocellularis Nucl. reticularis 30
31 Acetilcholine REM sleep Wakefulness REM sleep Glutamatergic REM-sleep promoting mechanism Model of the network responsible for PS. DPGi dorsal paragigantocellular reticular nucleus, ddpme dorsal deep mesencephalic reticular nucleus, DRN dorsal raphe nucleus, GiV ventral gigantocellular reticular nucleus, Gly glycine, Hcrt hypocretin (orexin)-containing neurons, LC locus coeruleus, vlpag ventrolateral periaqueductal gray, SLD sublaterodorsal nucleus 31
32 Lack of Hyporectin (Orexin) Narcolepsia Melatonin Adenosine VIP,Prolactin Orexin Cytokins NO CCK ACh NA - decreases sleep threshold - increase non-rem sleep (coffeine: receptor blocker) - increases REM sleep - increases wakefulness - increases sleep,mainly non-rem sleep - basal forebrain: non-rem brainstem:rem - increases non-rem sleep - increases wakefulness (basal forebrain) increases REM sleep (brainstem ) -increases wakefulness 32
33 Regulation of melatonin production The circadian rhythm under normal conditions and in isolation Natural lightdark rhythm A zeitgeber is any external or environmental cue that entrains, or synchronizes, an organism's biological rhythms to the Earth's 24- hour light/dark cycle. Minimum of body temperature Time 12 h light 12h dark Isolation from the zeitgeber Alvás ébrenlét Sleep Wakefulness 33
34 The suprachiasmatic nucleus, or internal pacemaker, is responsible for regulating the body's biological rhythms. Cortex Unspecific thalamus Lateral hypothalamus Pontine reticular formation Locus coeruleus Dorsal raphe Laterodorsal temental nucleus Suprachiasmatic nucleus 34
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
Lecture 8. Arousal & Sleep. Cogs17 * UCSD
 Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Sleep. No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness,
 Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep. No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness,
 Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Introduction to Physiological Psychology
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Psych 260 Kim Sweeney ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html What could possibly go wrong? n Causes of Narcolepsy Uncertain, but appears
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Psych 260 Kim Sweeney ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html What could possibly go wrong? n Causes of Narcolepsy Uncertain, but appears
Physiology of Sleep. Dr Nervana
 Physiology of Sleep Dr Nervana Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between sleep and coma. 2. Define NREM (non-rapid eye movement, SWS) and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 3. Describe how NREM and REM
Physiology of Sleep Dr Nervana Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between sleep and coma. 2. Define NREM (non-rapid eye movement, SWS) and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 3. Describe how NREM and REM
Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology
 1 Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology Giancarlo Vanini, MD, Helen A. Baghdoyan, PhD, and Ralph Lydic, PhD Introduction Although general anesthetics are used for
1 Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology Giancarlo Vanini, MD, Helen A. Baghdoyan, PhD, and Ralph Lydic, PhD Introduction Although general anesthetics are used for
Rhythms of the Brain 1 of 8
 Rhythms of the Brain 1 of 8 I. EEG A. Measures current flow during synaptic excitation of the dendrites of a large number of pyramidal cells. 1. 80% of the brain made up of these cells 2. thousands of
Rhythms of the Brain 1 of 8 I. EEG A. Measures current flow during synaptic excitation of the dendrites of a large number of pyramidal cells. 1. 80% of the brain made up of these cells 2. thousands of
EEG Electrode Placement
 EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep)
 EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms. Reading: BCP Chapter 19
 Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
The Neural Control of Behavioral State
 The Neural Control of Behavioral State Learning objectives: Introduction - Behavioral State; why do we sleep? A Clinical Case - The Sleeping Beauty of Oak Park. EEG - A Neural Signature of Behavioral State.
The Neural Control of Behavioral State Learning objectives: Introduction - Behavioral State; why do we sleep? A Clinical Case - The Sleeping Beauty of Oak Park. EEG - A Neural Signature of Behavioral State.
NEOCORTEX. Laminar pattern 6 layers billion neurons 95 % surface of the hemisphere
 THE CEREBRAL CORTEX NEOCORTEX Laminar pattern 6 layers 10 20 billion neurons 95 % surface of the hemisphere Six Layers of Cortex LGN input Parvo Magno B-Slide 4 NEOCORTEX, types of neurons Pyramidal neurons
THE CEREBRAL CORTEX NEOCORTEX Laminar pattern 6 layers 10 20 billion neurons 95 % surface of the hemisphere Six Layers of Cortex LGN input Parvo Magno B-Slide 4 NEOCORTEX, types of neurons Pyramidal neurons
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
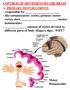 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE. Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D.
 SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to
 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
Basic Science of Representative Normal Human EEG Potentials
 Basic Science of Representative Normal Human EEG Potentials Seyed M Mirsattari, MD, PhD, FRCPC Departments of Clinical Neurological Sciences, Medical Biophysics, Diagnostic Imaging, Psychology University
Basic Science of Representative Normal Human EEG Potentials Seyed M Mirsattari, MD, PhD, FRCPC Departments of Clinical Neurological Sciences, Medical Biophysics, Diagnostic Imaging, Psychology University
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY
 states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms
 Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Circadian rhythm and Sleep. Radwan Banimustafa MD
 Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming. Elaine M. Hull
 Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms
 203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
Special Lecture 6 Effects of Sleep on Seizures ; A Path to sleep neurology (Somno-neurology)
 Special Lecture 6 Effects of Sleep on Seizures ; A Path to sleep neurology (Somno-neurology) Jun Kohyama, MD Tokyo Bay Urayasi/Ichikawa Medical Center Taiwan Pediatric Epilepsy Congress 2010 Dec. 26, 2010,
Special Lecture 6 Effects of Sleep on Seizures ; A Path to sleep neurology (Somno-neurology) Jun Kohyama, MD Tokyo Bay Urayasi/Ichikawa Medical Center Taiwan Pediatric Epilepsy Congress 2010 Dec. 26, 2010,
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
from sleep to attention lecture 4 April 9, 2012 control of sleep/wake state production II
 from sleep to attention lecture 4 April 9, 2012 control of sleep/wake state production II "From the moment of my birth, the angels of anxiety, worry, and death stood at my side, followed me out when I
from sleep to attention lecture 4 April 9, 2012 control of sleep/wake state production II "From the moment of my birth, the angels of anxiety, worry, and death stood at my side, followed me out when I
Normal Sleep: Neurobiological Mechanisms
 Normal Sleep: Neurobiological Mechanisms Objectives Why sleep? What makes us sleep? How is normal sleep achieved? When do we sleep? why do we need sleep? Biologic and Homeostatic Drives eat to satisfy
Normal Sleep: Neurobiological Mechanisms Objectives Why sleep? What makes us sleep? How is normal sleep achieved? When do we sleep? why do we need sleep? Biologic and Homeostatic Drives eat to satisfy
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Reticular Formation George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Reticular Formation George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the anatomical and functional organization of the brainstem reticular formation into three general regions: median (raphe), medial
Reticular Formation George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the anatomical and functional organization of the brainstem reticular formation into three general regions: median (raphe), medial
Page 1 L 58. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems /2013 RETICULAR FORMATION
 Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9
 Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Outline 3/5/2013. Practice Question. Practice question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness
 Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Sleep and Consciousness
 * Sleep and Dreaming The Neural Basis of Consciousness Sleep and Consciousness 1 Sleep and Dreaming readily observable, consists of different levels of consciousness, and can be studied scientifically
* Sleep and Dreaming The Neural Basis of Consciousness Sleep and Consciousness 1 Sleep and Dreaming readily observable, consists of different levels of consciousness, and can be studied scientifically
Chapter Eleven. Sleep and Waking
 Chapter Eleven Sleep and Waking Sleep Are we getting enough. How z it work? Sleep Deprivation contributed to the Exxon Valdez, Challenger Explosion, and 3 Mile Island Deprivation is VERY common, and quite
Chapter Eleven Sleep and Waking Sleep Are we getting enough. How z it work? Sleep Deprivation contributed to the Exxon Valdez, Challenger Explosion, and 3 Mile Island Deprivation is VERY common, and quite
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Brown EN, Lydic R, Schiff ND, et al. General anesthesia, sleep,
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Brown EN, Lydic R, Schiff ND, et al. General anesthesia, sleep,
COGS 107B. Week 7 Section IA: Ryan Szeto OH: Wednesday CSB Kitchen
 COGS 107B Week 7 Section IA: Ryan Szeto OH: Wednesday 1PM @ CSB Kitchen MT2: Tomorrow Question 1 NE: Locus coeruleus HA: Posterior hypothalamus ACh: Two pockets- located in pons and basal forebrain DA:
COGS 107B Week 7 Section IA: Ryan Szeto OH: Wednesday 1PM @ CSB Kitchen MT2: Tomorrow Question 1 NE: Locus coeruleus HA: Posterior hypothalamus ACh: Two pockets- located in pons and basal forebrain DA:
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
2/22/2012. Cerebrum CNS
 Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
Brain Circuitry Controlling Sleep and Wakefulness Richard L. Horner, PhD; John H. Peever, PhD
 Review Article Brain Circuitry Controlling Sleep and Wakefulness Richard L. Horner, PhD; John H. Peever, PhD ABSTRACT Purpose of Review: This article outlines the fundamental brain mechanisms that control
Review Article Brain Circuitry Controlling Sleep and Wakefulness Richard L. Horner, PhD; John H. Peever, PhD ABSTRACT Purpose of Review: This article outlines the fundamental brain mechanisms that control
SUBCORTICAL MODULATORY SYSTEMS (Honors Class, March 11, 2004)
 SUBCORTICAL MODULATORY SYSTEMS (Honors Class, March 11, 2004) Over the past 50 years, the basic mechanisms of sleep-wake states have been studied with an interdisciplinary approach embracing neurophysiology,
SUBCORTICAL MODULATORY SYSTEMS (Honors Class, March 11, 2004) Over the past 50 years, the basic mechanisms of sleep-wake states have been studied with an interdisciplinary approach embracing neurophysiology,
Understanding the Interplay between Neurobiochemistry of Sleep-wake Systems and Cognition
 Article ID: WMC002361 ISSN 2046-1690 Understanding the Interplay between Neurobiochemistry of Sleep-wake Systems and Cognition Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Torabi Nami, MD, PhD Neuroscience, Institute
Article ID: WMC002361 ISSN 2046-1690 Understanding the Interplay between Neurobiochemistry of Sleep-wake Systems and Cognition Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Torabi Nami, MD, PhD Neuroscience, Institute
SLEEP. -in 1953, first demonstration that brain was active during sleep. 4. Stages 3& 4: Delta Waves, large slow waves; deep sleep
 SLEEP DEF: altered state, between waking and unconsciousness, defined by specific patterns of brain activity. I. How much sleep do I need? 1. Long vs. Short Sleepers -across developmental stages -individual
SLEEP DEF: altered state, between waking and unconsciousness, defined by specific patterns of brain activity. I. How much sleep do I need? 1. Long vs. Short Sleepers -across developmental stages -individual
pdf NIH Overview Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from:
 1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
****REVISED 4/27/2015****
 Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Jerome M. Siegel. Generation of Cortical Electroencephalogram. Ponto-Geniculo-Occipital (PGO) Spikes. Neuronal Activity across the Sleep Cycle
 Generation of Cortical Electroencephalogram Jerome M. Siegel The electroencephalogram (EEG) (brain waves) recorded from the cerebral cortex result from the synchronized occurrence of excitatory and inhibitory
Generation of Cortical Electroencephalogram Jerome M. Siegel The electroencephalogram (EEG) (brain waves) recorded from the cerebral cortex result from the synchronized occurrence of excitatory and inhibitory
Chapter 5. Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition
 Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
6/29/2009. Awareness of everything going on inside and outside of you CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS. Meaning of consciousness
 6/29/2009 ness ness Links to Learning Objectives CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS LO 4.1 Meaning of consciousness LO 4.6 LO 4.2 Why people sleep LO 4.3 of sleep LO 4.4 disorders LO 4.5 Dreaming PSYCHOACTIVE
6/29/2009 ness ness Links to Learning Objectives CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS LO 4.1 Meaning of consciousness LO 4.6 LO 4.2 Why people sleep LO 4.3 of sleep LO 4.4 disorders LO 4.5 Dreaming PSYCHOACTIVE
Neuroscience of Consciousness I
 1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness I Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 What is consciousness? 3 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive
1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness I Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 What is consciousness? 3 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams. Defined:
 Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams I. Consciousness Conscious is: Waking Consciousness Defined: Altered State of Consciousness Defined: Most of waking life Fuzzy, organized, bizarre thoughts Examples:
Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams I. Consciousness Conscious is: Waking Consciousness Defined: Altered State of Consciousness Defined: Most of waking life Fuzzy, organized, bizarre thoughts Examples:
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
Normal sleep and circadian rhythms: Neurobiologic mechanisms underlying sleep and wakefulness
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Psychiatry and Human Behavior Faculty Papers Department of Psychiatry and Human Behavior December 2006 Normal sleep and circadian rhythms:
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Psychiatry and Human Behavior Faculty Papers Department of Psychiatry and Human Behavior December 2006 Normal sleep and circadian rhythms:
Sleep and Dreaming Notes December 14, 2015
 an altered state of consciousness Sleep serves as a restorative process of the body Scientists know the neurochemical melatonin plays a role in sleep and body restoration and repair. A definite cause effect
an altered state of consciousness Sleep serves as a restorative process of the body Scientists know the neurochemical melatonin plays a role in sleep and body restoration and repair. A definite cause effect
Hypothalamus is related to most area of the brain especially the subcortical and limbic system.
 بسم هللا الرحمن الر حيم Hypothalamus &Sleep: Homeostasis: keeping the internal environment within the normal range and this is the main function of the hypothalamus. Two regulatory systems that work on
بسم هللا الرحمن الر حيم Hypothalamus &Sleep: Homeostasis: keeping the internal environment within the normal range and this is the main function of the hypothalamus. Two regulatory systems that work on
Functions of hypothalamus
 The Hypothalamus Functions of hypothalamus Endocrine function Caloric balance Osmolarity balance Thermal regulation Autonomic balance Sleep Affective behavior Memory Somatic movements Anatomy of
The Hypothalamus Functions of hypothalamus Endocrine function Caloric balance Osmolarity balance Thermal regulation Autonomic balance Sleep Affective behavior Memory Somatic movements Anatomy of
COMA BIOLOGY. Assist. Prof. Mehmet Akif KARAMERCAN Gazi University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine
 COMA BIOLOGY Assist. Prof. Mehmet Akif KARAMERCAN Gazi University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Outlines Definitions Classification and Major Causes Arousal Systems (Reticular Activating
COMA BIOLOGY Assist. Prof. Mehmet Akif KARAMERCAN Gazi University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Outlines Definitions Classification and Major Causes Arousal Systems (Reticular Activating
Sleep Neurobiology from a Clinical Perspective
 REVIEW OF SLEEP NEUROBIOLOGY FROM A CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE Sleep Neurobiology from a Clinical Perspective Rodrigo A. España, PhD 1 ; Thomas E. Scammell, MD 2 DOI: 10.5665/SLEEP.1112 1 Department of Physiology
REVIEW OF SLEEP NEUROBIOLOGY FROM A CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE Sleep Neurobiology from a Clinical Perspective Rodrigo A. España, PhD 1 ; Thomas E. Scammell, MD 2 DOI: 10.5665/SLEEP.1112 1 Department of Physiology
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS. Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
CURRICULUM VITAE. Danielle M. Cusmano. Degree and date to be conferred: Doctor of Philosophy, Drew University
 CURRICULUM VITAE Name: Email: Danielle M. Cusmano dcusmano225@gmail.com Degree and date to be conferred: Doctor of Philosophy, 2014 Collegiate Institutions Attended: 2004-2008 Drew University Bachelor
CURRICULUM VITAE Name: Email: Danielle M. Cusmano dcusmano225@gmail.com Degree and date to be conferred: Doctor of Philosophy, 2014 Collegiate Institutions Attended: 2004-2008 Drew University Bachelor
Central Neurocircuitry Functioning during the Wake-Sleep Cycle
 Chapter 1 OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Central Neurocircuitry Functioning during the Wake-Sleep Cycle The
Chapter 1 OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Central Neurocircuitry Functioning during the Wake-Sleep Cycle The
Functions and Mechanisms of Sleep
 Functions and Mechanisms of Sleep The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable
Functions and Mechanisms of Sleep The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Neuron. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 December 22.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neuron. 2010 December 22; 68(6): 1023 1042. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.032. Sleep State Switching Clifford B. Saper, Patrick M.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neuron. 2010 December 22; 68(6): 1023 1042. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.032. Sleep State Switching Clifford B. Saper, Patrick M.
Normal sleep mechanisms & why do we sleep?
 4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 18 Basics of sleep medicine - Level 1 Normal sleep mechanisms & why do we sleep? Rolf Fronczek Leiden,
4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 18 Basics of sleep medicine - Level 1 Normal sleep mechanisms & why do we sleep? Rolf Fronczek Leiden,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
PSYCH 260 Exam 2. March 2, Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name:
 PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
NEUROSCIENCE. W1 Divisions of the nervous system PSYC1002 NOTES
 PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
THE ACTIVITY RECORDED IN THE EEG
 Version 4. A Monthly Publication presented by Professor Yasser Metwally April 2008 THE ACTIVITY RECORDED IN THE EEG here is now considerable evidence from studies in experimental animals to suggest that
Version 4. A Monthly Publication presented by Professor Yasser Metwally April 2008 THE ACTIVITY RECORDED IN THE EEG here is now considerable evidence from studies in experimental animals to suggest that
Introduction to EEG del Campo. Introduction to EEG. J.C. Martin del Campo, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada
 Introduction to EEG J.C. Martin, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada What is EEG? A graphic representation of the difference in voltage between two different cerebral locations plotted over
Introduction to EEG J.C. Martin, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada What is EEG? A graphic representation of the difference in voltage between two different cerebral locations plotted over
392 Index. HPG axis, see Hypothalamic-pituitarygonadal
 Index 389 INDEX A Acetylcholine, acetylcholinergic inputs to orexin neurons, 66, 67 brainstem cholinergic nuclei arousal circuits activated by orexins, 144 vigilance control by cholinergic neurons, 182
Index 389 INDEX A Acetylcholine, acetylcholinergic inputs to orexin neurons, 66, 67 brainstem cholinergic nuclei arousal circuits activated by orexins, 144 vigilance control by cholinergic neurons, 182
Indication. Ingredients
 GABAdone Product Information Indication GABAdone is intended for use in sleep disorders involving difficulty in falling asleep, maintaining sleep, falling back to sleep after awakening at night, feeling
GABAdone Product Information Indication GABAdone is intended for use in sleep disorders involving difficulty in falling asleep, maintaining sleep, falling back to sleep after awakening at night, feeling
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Practical 3 Nervous System Physiology 2 nd year English Module. Dept. of Physiology, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy
 Electroencephalography l h (EEG) Practical 3 Nervous System Physiology 2 nd year English Module Dept. of Physiology, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy What is EEG EEG noninvasively records
Electroencephalography l h (EEG) Practical 3 Nervous System Physiology 2 nd year English Module Dept. of Physiology, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy What is EEG EEG noninvasively records
How Your Body Clock Affects Sleep And
 1 of 6 11/26/2012 1:23 PM How do you feel when you wake up in the morning? Are you refreshed and ready to go, or groggy and grumpy? For many people, the second scenario is all too common. Sleep-related
1 of 6 11/26/2012 1:23 PM How do you feel when you wake up in the morning? Are you refreshed and ready to go, or groggy and grumpy? For many people, the second scenario is all too common. Sleep-related
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Functional Overview of the Nervous System. Dr. Ersin Koylu EÜ Tıp Fakültesi Fizyoloji AD
 Functional Overview of the Nervous System Dr. Ersin Koylu EÜ Tıp Fakültesi Fizyoloji AD Autonomic System Sympathetic System Motor System Cental Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM?
Functional Overview of the Nervous System Dr. Ersin Koylu EÜ Tıp Fakültesi Fizyoloji AD Autonomic System Sympathetic System Motor System Cental Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM?
Brain Neurotransmitters
 Brain Neurotransmitters * Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane * Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane * Binds to and
Brain Neurotransmitters * Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane * Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane * Binds to and
Alpha-Stim 6/19/2018. Objectives. Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation 3, 6 History
 Alpha-Stim Tamra Standage, DPT, COMT Objectives Participants should be able to state underlining principles behind the usage of microcurrent therapy, both with probe application and with cranial electrotherapy
Alpha-Stim Tamra Standage, DPT, COMT Objectives Participants should be able to state underlining principles behind the usage of microcurrent therapy, both with probe application and with cranial electrotherapy
The Science of Wellness: Why Your Doctor Continues to Insist You Sleep and Exercise to be Well. Nicole Rausch, DO
 The Science of Wellness: Why Your Doctor Continues to Insist You Sleep and Exercise to be Well Nicole Rausch, DO Sleep Cycle O Spend 1/3 of our time in sleep O Two types of Sleep O Non-rapid eye movement
The Science of Wellness: Why Your Doctor Continues to Insist You Sleep and Exercise to be Well Nicole Rausch, DO Sleep Cycle O Spend 1/3 of our time in sleep O Two types of Sleep O Non-rapid eye movement
 This article was originally published in the Encyclopedia of Sleep published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author's benefit and for the benefit of the author's institution,
This article was originally published in the Encyclopedia of Sleep published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author's benefit and for the benefit of the author's institution,
States of Consciousness:
 States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Neurophysiology & EEG
 Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
Marieb, E.N. (2004), Human Anatomy & Physiology, Pearson Education, Inc, San Francisco, CA, USA, p459
 Neuroscience Tutorial: Sleep and Dreams Discuss the following diagram with the students: Marieb, E.N. (2004), Human Anatomy & Physiology, Pearson Education, Inc, San Francisco, CA, USA, p459 1 Purves,
Neuroscience Tutorial: Sleep and Dreams Discuss the following diagram with the students: Marieb, E.N. (2004), Human Anatomy & Physiology, Pearson Education, Inc, San Francisco, CA, USA, p459 1 Purves,
Chapter 6. Consciousness
 Consciousness Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? The Value of Consciousness Setting Priorities for Mental Functioning Sleeping and Dreaming Altering Awareness: Psychoactive Drugs
Consciousness Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? The Value of Consciousness Setting Priorities for Mental Functioning Sleeping and Dreaming Altering Awareness: Psychoactive Drugs
CHARACTERIZING A ROLE FOR DOPAMINE ON SLEEP AND CATAPLEXY IN NARCOLEPTIC MICE
 CHARACTERIZING A ROLE FOR DOPAMINE ON SLEEP AND CATAPLEXY IN NARCOLEPTIC MICE by GAVIN TSE A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements For the degree of Master of Science Graduate Department
CHARACTERIZING A ROLE FOR DOPAMINE ON SLEEP AND CATAPLEXY IN NARCOLEPTIC MICE by GAVIN TSE A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements For the degree of Master of Science Graduate Department
ADHD Medications & How They Work. Gail C. Rodin, Ph.D. January 21, 2008
 ADHD Medications & How They Work Gail C. Rodin, Ph.D. January 21, 2008 Agenda How the (ADHD) Brain Works (or doesn t) Neurons and neurotransmitters NE & DA: the major players in ADHD Channel vs. state
ADHD Medications & How They Work Gail C. Rodin, Ph.D. January 21, 2008 Agenda How the (ADHD) Brain Works (or doesn t) Neurons and neurotransmitters NE & DA: the major players in ADHD Channel vs. state
CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems
 CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems Brain Function Important Concepts Functional areas of the cerebral cortex Sensory, Motor, Association Cerebral lateralization each hemisphere has functions not shared
CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems Brain Function Important Concepts Functional areas of the cerebral cortex Sensory, Motor, Association Cerebral lateralization each hemisphere has functions not shared
Name: BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012 sec 002) MIDTERM EXAM 3 (Practice exam)
 Name: BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012 sec 002) MIDTERM EXAM 3 (Practice exam) Mark the ONE BEST letter choice (either A, B, C, D, or E) on the computer-graded sheet in NUMBER TWO PENCIL. If you need to erase,
Name: BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012 sec 002) MIDTERM EXAM 3 (Practice exam) Mark the ONE BEST letter choice (either A, B, C, D, or E) on the computer-graded sheet in NUMBER TWO PENCIL. If you need to erase,
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology LECTURE NO (-) Hypothalamus. Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology
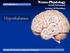 LECTURE NO (-) Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology Hypothalamus Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology Hypothalamus Less than 1% of the brain mass Many connect the hypothalamus to the
LECTURE NO (-) Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology Hypothalamus Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology Hypothalamus Less than 1% of the brain mass Many connect the hypothalamus to the
Week 4 Psychology. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding that they and others think, feel, perceive, and have private experiences.
 Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
