Autor(en): Snow, W.F. / Tarimo, S.A. / Staak, C. Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 4. PDF erstellt am:
|
|
|
- Gilbert Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The feeding habits of the tsetse, "Glossina pallidipes" Austen on the south Kenya coast, in the context of its host range and trypanosome infection rates in other parts of East Africa Autor(en): Snow, W.F. / Tarimo, S.A. / Staak, C. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (988) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am: Persistenter Link: Nutzungsbedingungen Die ETH-Bibliothek ist Anbieterin der digitalisierten Zeitschriften. Sie besitzt keine Urheberrechte an den Inhalten der Zeitschriften. Die Rechte liegen in der Regel bei den Herausgebern. Die auf der Plattform e-periodica veröffentlichten Dokumente stehen für nicht-kommerzielle Zwecke in Lehre und Forschung sowie für die private Nutzung frei zur Verfügung. Einzelne Dateien oder Ausdrucke aus diesem Angebot können zusammen mit diesen Nutzungsbedingungen und den korrekten Herkunftsbezeichnungen weitergegeben werden. Das Veröffentlichen von Bildern in Print- und Online-Publikationen ist nur mit vorheriger Genehmigung der Rechteinhaber erlaubt. Die systematische Speicherung von Teilen des elektronischen Angebots auf anderen Servern bedarf ebenfalls des schriftlichen Einverständnisses der Rechteinhaber. Haftungsausschluss Alle Angaben erfolgen ohne Gewähr für Vollständigkeit oder Richtigkeit. Es wird keine Haftung übernommen für Schäden durch die Verwendung von Informationen aus diesem Online-Angebot oder durch das Fehlen von Informationen. Dies gilt auch für Inhalte Dritter, die über dieses Angebot zugänglich sind. Ein Dienst der ETH-Bibliothek ETH Zürich, Rämistrasse 0, 8092 Zürich, Schweiz,
2 Acta Tropica (988) International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology, P.O. Box Nairobi. Kenya The feeding habits of the tsetse, Glossina pallidipes Austen on the south Kenya coast, in the context of its host range and trypanosome infection rates in other parts of East Africa W. F. Snow. S. A. Tarimo. C. Staak, L. Butler Summary The results of blood-meal identifications for 65 Glossina pallidipes from 5 subpopulations near the Kenya coast south of Mombasa, and one, 70 km inland, are presented. Bushpigs and/or warthogs were important hosts for G. pallidipes at all sites. Other major hosts included elephant, buffalo and bushbuck where they were present, and on a dairy ranch nearly 30% of feeds were taken from cattle. There was a general relationship between the numbers and diversity of wild herbivores and the abundance of G. pallidipes. These results are discussed in relation to published data on feeding patterns and trypanosome infection rates for G. pallidipes from other parts of East Africa. Overall, there are significant correlations between the proportions of bovid feeds and 7. vivax infections. Bovid-feeding G. pallidipes populations with high T. vivax infection rates in south-east Uganda and western Kenya contrast with the coastal, suidfecding populations with low T. vivax rates. These characteristics are presented as clines extending across East Africa. Key words: Glossina pallidipes; Kenya; East Africa; feeding patterns; trypano some infection rates. Introduction The feeding patterns of tsetse are a major determinant in the epidemiology of African trypanosomiasis: trypanosome prevalence in tsetse is governed by the number of feeds on infected hosts, and the frequency of infected feeds on man and his livestock determines the severity of the problems of sleeping Correspondence: Dr. W. F The Gambia Snow. International Trypanotolérance Centre. P.M.B. 4. Banjul. 339
3 sickness and nagana. and their impact on human health and prosperity. The identification of the origin of blood in recently engorged tsetse flies is the best basis for assessing tsetse-host interactions, despite the problem of likely sam pling biases. Since the original work of Weitz (963) there has been a tendency to pool the results of blood-meal identifications from throughout the range of a tsetse species and generalise from such totals. For example, the recent training manual by FAO (982) suggests that G. pallidipes takes more than half its meals from bushbuck with warthog, bushpig and buffalo as other important hosts. How ever, G. pallidipes in particular may show markedly different feeding patterns between localities, in part at least, independently of the abundance of different potential hosts. This paper describes bloodmeal identifications for G. pallidipes from a number of localities on or near the south Kenya coast and compares these results with data on feeding patterns and infection rates for this tsetse at these localities and in other parts of East Africa. Materials and Methods. Study sites Collections of blood-fed tsetse were made at six localities to the south and west of Mombasa. These are described below and estimates of the relative abundance of herbivore host species are given in Table. Diani: An 8 ha area of degraded lowland rain forest 25 km south of Mombasa which has been described in greater detail by Snow and Tarimo (983). who also included some blood-meal indentifications for this site which are included in the totals below. This forest relict was situated on a small dairy ranch in a densely settled and cultivated area. Cattle, sheep and goats were grazed around the forest and the cattle were on regular chemoprophylaxis against trypanosomiasis. A medium density population of G. pallidipes was present, with G. austeni and G. brevipalpis. Malaga: A sparsely settled area of bush and forest 20 km south-west of Mombasa. Small numbers of domestic stock were present and some game, including bushpig (Potamochoerus porcus). warthog (Phacochoenis aethiopicus). buffalo (Syncerus caller), bushbuck (Tragelaphus scriptus) and smaller antelopes persisted. A medium density population of G. pallidipes. with G. austeni and G. brevipalpis. was located around a forest relict and throughout bushed grassland in the area. Muhaka: This site was an area of relict lowland rain forest covering some 50 ha in a densely settled area 35 km south of Mombasa and 5 km inland. As at Diani. many trees had been removed and the forest had a broken canopy and dense undcrstorey. Domestic cattle, sheep and goats were grazed around the forest and such wildlife as remained was very secretive. A medium to low density population of G. pallidipes was present, with substantial numbers of G. austeni and G. brevipalpis. Mwalewa: This study area was located on the edge of Gonja Forest Reserve, 80 km south of Mombasa and 4 km from the coast. The forest was considerably degraded and consisted of scattered mature trees with a densely thicketed understory, which graded into bushed grassland with an irregular, thicketed forest/grassland interface. There were no nearby settlements and the area was not visited by domestic animals. Medium to high densities of G. pallidipes were encountered with some G. austeni and G. brevipalpis. Shimba Hills: Shimba Hills National Reserve. 35 km south-west of Mombasa, included areas of moist lowland forest, semi-humid Brachystegia woodland, fire-maintained bushed grassland (where the trap sites were located) and Hyphaene savanna. No domestic animals were present. High densi ties of G. pallidipes were present with G. austeni and G. brevipalpis. 340
4 Table. Summary of the abundance of mammalian herbivore hosts oftsetse at localities on the south Kenya coast Hosts Localitv Shimba Mwalewa Matuga Diani Muhaka Hills Domestic stock Cattle Sheep and goats Wild ungulates Bushbuck Buffalo Sable and roan antelope Duiker and suni Wild suids Bushpig Warthog Others Elephant common, animals or traces of animals regularly seen frequent, occasionally seen or presumptively present in fair numbers rare, occasional examples reported or infrequent presence inferred from blood-meal results =absent Taru Ranch: A medium density population of Glossina pallidipes and a few G. austeni were encountered in an area of dry sub-humid woodland in a zone of semi-arid woodland dominated by Acacia and Commiphora spp.. south-east of Mackinnon Road and some 70 km west of Mombasa. Cattle and goats were kept on the ranch and some plains game also occurred seasonally. Zebra (Equus burchelli). Impala (Aepyceros melampus) and Grimm's duiker (Silvicapra grimmia) were seen during surveys of this area although these undoubtedly represented only a fraction of the species present. 2. Collection of blood-fed tsetse Blood-fed tsetse were taken from biconical trap collections at the six localities described above. In general, very few flies contained blood and this was often little and partly digested. Glossina pallidipes was readily captured in biconical traps (in contrast to G. austeni and G. brevipalpis) and a value for relative density of flies was based on a geometric mean catch per trap per day. For a comparison between localities, a mean from densities observed during all visits to each site was determined. This data gave the basis for the density rankings used above. The guts of tsetse contain ing blood were smeared onto filter paper and stored in a dessicator. 3. Identification of blood-meals The smears were tested against appropriate antisera in the haemagglutination inhibition test (by Imperial College. U.K. in an early series of tests) or the complement fixation test (by The Robert von Ostertag Institut. Berlin) for the later 75% of determinations. Of 776 blood-smears collected from 22 Ada Tropica 34
5 Table 2. Identification of blood meals from Glossina pallidipes from localities on or near the south Kenya coast Host species Locality Shimba Hills Mwalewa females males females Bushbuck Buffalo Roan/Sable 3 - Cattle (ox) Sheep/goat Unidentified bovid Total % bovid (M + F) 35.6% 0.0% Warthog Bushpig Unidentified sind Total % suid (M + F)* 47.5% 85.3% Mixed feeds (Bovid + suid)* - - " Elephant 7 8 Carnivore Man Mammal - 4 Total identified Relative density of tsetse population (M + F) No. of visits 2 9 * Mixed bovid + suid feeds have been included as both bo\id and suid in calculation of the totals a unid. bovid + unid. suid b 4 unid. bovid + unid. suid. unid. bovid + bushpig. ox + unid. suid. ox + bushpig c unid. bovid + unid suid. 2 ox + unid. suid. sheep/goat + unid. suid d ox + unid. suid Host not present G. pallidipes 84% gave positive host identifications. The range of antisera is indicated in Table summarising results. Mammal, unidentified bovid and unidentified suid reactions were often from poor or well-digested smears. However, specific duiker (Cephalophiis spp.) and suni (Xcsotragus moschatus) antiscra were not available and the "unidentified bovid" category probably included some feeds from these antelopes which were widespread even in the rural areas. Results The results of the blood-meal identifications for G. pallidipes arc presented in Table 2, where the localities are ranked in order of the relative density of the 342
6 ality u Ranch Matuga Diani Muhaka es females males females males females males females % % % % 65.4% 48.% 75.0% 7" fly populations. The importance of wild suids as a blood-source for G. pallidipes at all the sites is noteworthy although the relative importance of bushpig and warthog varied from locality to locality. Other important hosts were elephant (Loxodonta africana), buffalo and bushbuck, when they were present. At Diani nearly 30% of feeds were identified from cattle and more may have been included in the "unidentified bovid" category. Comparing Tables and 2 there appeared to be a general relationship between numbers of wild herbivores and the abundance of G. pallidipes. Highest tsetse population densités were obser ved in Shimba Hills which also harboured the greatest diversity and abundance of host animals. Although this tsetse would feed readily on cattle, as at Diani, even where domestic stock was numerous G. pallidipes population densities were often low. It appeared that at Mwalewa there were few alternative hosts, for G. pallidipes, to warthog and bushpig. The results demonstrated that the primary hosts of G. pallidipes were large herbivores and that other feeds were taken only occasionally from casual hosts. 343
7 The samples from Shimba Hills (SHB), Mwalewa (MWL) and Diani (DNI) were large enough to apply a ft test to compare the numbers of bovid and suid feeds taken at each site. The only other large herbivore represented in the blood-meal identifications, elephant, occurred only in Shimba Hills and is omitted from these comparisons. Mixed bovid/suid feeds are counted in both bovid and suid totals. Firstly, comparing feeds taken by males and females: SHB-ft (ldf) 0.0, p>0.5 MWL-ft (ldf)= >p>0.2 DNI -ft (ldf) 7.5, p<0.0 At the first two localities the feeding patterns of the sexes were similar, but it is difficult to assign a biological significance to the apparent heterogeneity of feeding habits at Diani. Secondly, when these three localities are compared (ââ - ft (2df) p< 0.00: 99 -ft (2df) p<0.00) significant heterogeneity between the sampling sites is apparent. However, if they are compared in pairs (with males and females pooled) there were significant differences between Mwalewa and Shimba Hills or Diani (MWL vs SHB -^2(ld , p < 0.00 ; MWL vs DNI -ft( ldf) p< 0.00) but the feeding patterns in the Shimba Hills and at Diani appear similar (ft (ldf).92, 0.2>p>0.) until it is remembered that the bovid feeds were from wild ungulates and cattle at the two sites, respec tively. Discussion The successful completion of each stage of tsetse behaviour involved in host location, alighting and engorgement, can be considered in probabalistic terms which determine both tsetse survival and the host range indicated by blood-meal identifications. Host abundance, their attractiveness to tsetse and their tolerance of tsetse attack are major factors in their utilisation by tsetse populations. Any factor, including host rarity or anti-feeding responses which reduces feeding frequency or feeding success, could result in increased fly mortality or reduced fecundity. This implies that each host population will have a "carrying capacity" which could act in such a wav as to regulate fly numbers and is one explanation of the apparent relationship between the density of G. pallidipes populations on the Kenya coast and the abundance and diversity of wild herbivore hosts. These observations on the Kenya coast demonstrated the importance of the often very secretive wildlife populations as maintenance hosts for G. pallidipes in rural areas. The presence of low-density fly populations where cattle were numerous, implied that feeding success was poor on the local livestock and that they were not completely satisfactory alternative hosts for this tsetse. The expression of tsetse feeding patterns is the result of both exoge nous and endogenous factors. It seems likely that the heterogeneity in the host 344
8 range of G. pallidipes on the Kenya coast is the result of host availability at different sites - an exogenous factor - rather than any inherent character in a genetically relatively homogenous set of fly sub-populations (van Etten ). Tarimo et al. (984) were unable to demonstrate any clear relationship between trypanosome infection rates and the feeding patterns of sub-popula tions of G. pallidipes on the Kenya coast. However, G. pallidipes occurs in scattered, isolated fly-belts across East Africa and the data from the Kenya coast should be considered in this wider context. In western (Kangwagyé. 97) and south-east Uganda (Southon. 963: Moloo et al.. 980) and western Kenya (England and Baldry. 972: Wilson et al.. 972) G. pallidipes fed predominantly on bovids. even in areas where wild suids were common and fed upon by sympatric tsetse species. In central Kenya (Challier et al., 98; Tarimo et al. 986). on the Kenyan. Somalian (Ryan et al. 983) and Tanzanian (Gates and Williamson. 984) coasts and near the southern shores of Lake Victoria (Glas gow et al. 958) a much higher proportion of feeds were taken from suids. When previously published data, and those reported above, are plotted against longi tude as in Fig. these behavioural characteristics appear as a west-east cline. However, the localities for which data is available lie closer to a north-west (s.e. Uganda) to south-east (Kenya coast) axis. In Fig.. and the attempted correla tions below, bovid and suid feeds are expressed as percentages or proportions of the total taken from herbivores. The third category "other herbivores" includes elephant, rhinocerus and hippopotamus while feeds from other hosts such as man and carnivores are omitted. In East Africa, feeding patterns and trypanosome infection rates in G. pal lidipes correlate fairly well when the percentage of bovid feeds arc compared with T. vivax rates - % bovid % vivax, r p< but there is a less significant relationship between % suid feeds and Nan nomonas spp. (7". congolense group) infections - %suid= % Nannomonas, r <p< (cf. Jordan. 965: Moloo et al.. 980). However, trypanosome infection rates in tsetse are. to a large extent, determined by the rates in the host population and. for Nannomonas parasites in particular, may be affected by the suscepti bility of tsetse to infection (Maudlin and Dukes. 985; Maudlin et al, 986) which may vary between populations. If infection is expressed as the proportion of T. vivax or Nannomonas in T. vivax + Nannomonas infections there is a highly significant correlation between the proportion of bovid feeds and pro portion of T. vivax (Fig. 2 A). Following from this, because of the western, bovid-feeding, vivax predominated populations contrasting with eastern, suidfeeding populations with relatively low vivax infection rates, there is a further striking cline in the relationship between the proportion of T vivax and longi tude of the study site (Fig. A). Infection rate data from localities for which no 345
9 % '> o ='S 0-6 a c 02- A. W E The proportions of bovid or suid feeds and of T. vivax or Nannomonas spp. infections in Fig.. G. pallidipes in East Africa, in relation to longitude. The closed symbols refer to data presented in the present paper and Tarimo et al. 984). Open symbols arc for data from literature (see text) although the more southerly. Tanzanian records of Glasgow et al. (98) and Gates et al. (984) have been omitted. feeding pattern data are available (Moloo et al., 973; Owaga. 98) also fits this pattern. The complementary correlation between proportions of suid feeds and of Nannomonas infections is also highly significant (Fig. 2 B) and an increasing proportion of Nannomonas infections occurs with longitude (Fig. B). How ever, the true nature of these relationships may be obscured by the likely presence of T. simiae among apparant Nannomonas infections. Trypanosoma simiae occurs on the Kenya coast (Wilson et al., 97: Snow et al, in press) where it may be common, and almost certainly comprises a significant, but 346
10 J U p BOVID FEEDS p SUID FEEDS Fig. 2. Relationships between feeding patterns and trypanosome infections in G. pallidipes in East Africa. Closed symbols refer to data presented in the present paper and Tarimo et al. (984): open symbols to data from literature (see text). A) Proportion of bovid feeds vs proportion of T. vivax Regression line: looy X 2df. r p<0.00 B) Proportion of suid feeds vs Nannomonas spp. infections 00) = X 2df r= 0.92, p<0.00. unknown, proportion of infections wherever G. pallidipes feeds on bushpigs or warthogs. The poor relationship between % suid feeds and Nannomonas infec tion rates may result from true T. congolense infections in western, bovid-feeding tsetse populations being replaced by 7. simiae in the eastern, suid-feeding G. pallidipes communities. The heterogeneity of feeding patterns in coastal subpopulations of G. pal lidipes was attributed above to local host availability - an exogenous effect. If pooled numbers of bovid and suid feeds from the Kenya coast are compared with results from Lugala in south-cast Uganda (Southon. 963; Moloo et al., 980) the G. pallidipes patterns are significantly different (ft (ldf) 49.2, p < while coastal G. pallidipes and Lugala G. brevipalpis are very similar (ft (ldf) >p>0.5) (although at Lugala brevipalpis. takes a large proportion of its feeds from Hippopotamus). Nevertheless, host availability does not adequately explain the difference in feeding habits of the Kenya coast and western G. pallidipes populations. The difference in host range of eastern and western populations appears more likely to be the result of endogenous effects in the responses of G. pallidipes to available hosts. This is the first time that differences in the feeding patterns of different tsetse populations have been so clearly attributable to their inherent perception of and responsiveness to different hosts. 347
11 Acknowledgments The support of the Dutch International Technical Help (DITH) and the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) for W. F. Snow and S. A. Tarimo is acknowledged. Challier A.. Snow W. F., Owaga M. L. A.. Turner D. A., Lambrecht F. L.: A comparison of the ecology of G. pallidipes Austen in selected areas of Kenya. Paper presented at a KETRI-Department of Veterinary Services "Seminar on Epidemiology and Economics of Trypanosomiasis Control in Selected Areas of Kenya" held at ILRAD. 8th and 9th June 98 (unpublished). England E. C. Baldry D. A. T.: The hosts and trypanosome infection rates of G. pallidipes in the Lambwe and Roo Valleys. Bull. Wld Hlth Org. 47, (972). FAO: Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Training manual for Tsetse Control Personnel, by J. Pollock. Vol. : Tsetse biology systematics and distribution; techniques. 280 p. FAO. Rome 982. van Etten..: A comparison of the performance of laboratory colonies of G. pallidipes Austen from two allopatric populations in Kenya. Ins. Sci. Appi (98). van Etten J.: Enzyme polymorphism in populations of the tsetse fly G. pallidipes Austen in Kenya. Ent. exp. Appi (982). Gates D. B.. Williamson D. L.: Tsetse fly feeding preference as determined by vehicular trapping in Tanzania. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 78, (984). Glasgow J. P.. Isherwood F.. Lee-Jones F.. Weitz B.: Factors influencing the staple food of tsetse flies. J. anim. Ecol (958). Harlcy J. M. B.: Studies on age and trypanosome infection rate in females of G. pallidipes Ausf. G. palpalis fuscipes Newst. and G. brevipalpis Newst. in Uganda. Bull. ent. Res (966). Harley J. M. B.: Further studies on age and trypanosome infection rates G. pallidipes Aust.. G. palpalis fuscipes Newst. and G. brevipalpis Newst. in Uganda. Bull. ent. Res. 57, (967). ICIPE: "Tsetse Research Programme", p. 7. The International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology: Tenth Annual Report Nairobi 983. Jordan A. M.: The hosts of Glossina as the main factor affecting trypanosome infection rates of tsetse flies in Nigeria. Trans, roy. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg (965). Kangwagye T. N.: Obervations on Glossina fuscipes Newstead. G. fusciplcuris Austen and G. pallidi pes Austen in Western Uganda. Proc. 3th Meet. ISCTRC, Lagos 97. Maudlin I.. Dukes P.: Extrachromosomal inheritance of susceptibility to trypanosome infection in tsetse flies. I. Selection of susceptible and refractory lines of Glossina morsitans morsitans. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit (985). Maudlin I.. Dukes P.. Luckins A. G.. Hudson K. M.: Extrachromosomal inheritance of susceptibility to trypanosome infection in tsetse flies. II. Susceptibility of selected lines of Glossina morsitans morsitans to different stock and species of trypanosome. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit (986). Moloo S. K.. Steiger R. F.. Brun R.: Trypanosome infection rates in Glossina swynnertoni and G. pallidipes in Ikoma. Musoma District. Tanzania. Parasitology (973). Moloo S. K.. Kutuza S. B.. Borcham P. F. L.: Studies on G. pallidipes. G. fuscipes fuscipes and G. brevipalpis in terms of the epidemiology and epizootiology of trypanosomiases in south-eastern Uganda. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit (980). Owaga M. L. A. Trypanosome infection rate in the tsetse species G. pallidipes. in a rural situation in Kenya. Ins. Sci. Appi. / (98). Ryan L.. Abdillahi M.. Ali M. H. H.: Local population density estimates of G', pallidipes in Somalia. Rev. Elev. Méd vét. Pays trop (983). Snow W. F.. Tarimo S. A.: A quantification of the risk of trypanosomiasis infection to cattle on the south Kenya coast. Acta trop. (Basel) (983). 348
12 Snow W. F., Dukes P., Rawlings P.: High incidence of Trypanosoma simiae obscuring the composi tion of trypanosome infections observed in tsetse: a neglected problem. Proc. 9th Meet. ISCTRC. Lomé 987 (in press). Southon H. A. W.: The hosts of Glossina in South Busoga. Uganda. E. Afr. Tryp. Res. Org. Report for 96, p Govt. Printer, Entebbe 963. Tarimo S. A., Golder T. K., Dransfield R. D., Chaudhury M. F. B.. Brightwell R.: Preliminary observations on trypanosome infection rates in G. pallidipes at Nkruman, Kenya and the factors affecting them. Proc. 8th Meet. ISCTRC, Harare, p (986). Tarimo S. A., Snow W. F., Butler L.: Trypanosome infections in wild tsetse G. pallidipes Austen on the Kenya coast. Ins. Sci. Appi (984). Weitz B.: The feeding habits of Glossina. Bull. Wld Hlth Org (963). Wilson A. J., DarF. K., Paris J.: Isolation and preservation oft. simiae from Coast Province, Kenya. E. Afr. Tryp. Res. Org. Report 970, p. 0-. Govt. Printer. Entebbe 97. Wilson A. J.. Dar F. K., Paris J.: A study of the transmission of salivarian trypanosomes isolated from wild tsetse flies. Trop. Anim. Hlth Prod (972). 349
13
Berenil (diminazene aceturate)-resistant "Trypanosoma congolense" in cattle under natural tsetse challenge at Kibaha, Tanzania
 Berenil (diminazene aceturate)-resistant "Trypanosoma congolense" in cattle under natural tsetse challenge at Kibaha, Tanzania Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mbwambo, H.A. / Mella, P.N.P. / Lekaki, K.A. Article
Berenil (diminazene aceturate)-resistant "Trypanosoma congolense" in cattle under natural tsetse challenge at Kibaha, Tanzania Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mbwambo, H.A. / Mella, P.N.P. / Lekaki, K.A. Article
Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthetic on "Glossina"
 Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthetic on "Glossina" Autor(en): Objekttyp: Moloo, S.K. / Kutuza, S.B. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 02.12.2017 Persistenter
Effects of carbon dioxide anaesthetic on "Glossina" Autor(en): Objekttyp: Moloo, S.K. / Kutuza, S.B. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 02.12.2017 Persistenter
Experimental superimposed infection of the hamster with "Leishmania mexicana" and "L. braziliensis"
 Experimental superimposed infection of the hamster with "Leishmania mexicana" and "L. braziliensis" Autor(en): Zeledón, R. / Soto, R. / González, G. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Experimental superimposed infection of the hamster with "Leishmania mexicana" and "L. braziliensis" Autor(en): Zeledón, R. / Soto, R. / González, G. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Haemolytic activity in the blood clot of "Aedes aegypti"
 Haemolytic activity in the blood clot of "Aedes aegypti" Autor(en): Geering, K. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 27.07.2018 Persistenter Link:
Haemolytic activity in the blood clot of "Aedes aegypti" Autor(en): Geering, K. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 27.07.2018 Persistenter Link:
Effect of cortisone upon the tissue synthesis of acid mucopolysaccharidee
 Effect of cortisone upon the tissue synthesis of acid mucopolysaccharidee Autor(en): Layton, Laurence L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen Wissenschaften
Effect of cortisone upon the tissue synthesis of acid mucopolysaccharidee Autor(en): Layton, Laurence L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen Wissenschaften
The control of reproduction by a blood meal : the mosquito as a model for vector endocrinology
 The control of reproduction by a blood meal : the mosquito as a model for vector endocrinology Autor(en): Lea, Arden O. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt
The control of reproduction by a blood meal : the mosquito as a model for vector endocrinology Autor(en): Lea, Arden O. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 32 (1975) Heft 2 PDF erstellt
Conclusions [for "Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien"]
![Conclusions [for Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien] Conclusions [for Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien]](/thumbs/81/83890744.jpg) Conclusions [for "Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien"] Autor(en): Diczfalusy, E. / Lunenfeld, B. / Ferin, J. Objekttyp: Postface Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie
Conclusions [for "Symposion : Wirkung oraler Progestativa bei Zyklusanomalien"] Autor(en): Diczfalusy, E. / Lunenfeld, B. / Ferin, J. Objekttyp: Postface Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie
Freud and the "School of Helmholtz"
 Freud and the "School of Helmholtz" Autor(en): Cranefield, Paul F. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal of the history of medicine and sciences Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1-2 PDF erstellt
Freud and the "School of Helmholtz" Autor(en): Cranefield, Paul F. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal of the history of medicine and sciences Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1-2 PDF erstellt
Microfilarial polyarthritis in a massive Loa loa infestation : a case report
 Microfilarial polyarthritis in a massive Loa loa infestation : a case report Autor(en): Bouvet, J.P. / Thérizol, Madeleine / Auquier, L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (977)
Microfilarial polyarthritis in a massive Loa loa infestation : a case report Autor(en): Bouvet, J.P. / Thérizol, Madeleine / Auquier, L. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (977)
The long term effects of repeated diethylcarbamazine administration with special reference to microfilaraemia and elephantiasis
 The long term effects of repeated diethylcarbamazine administration with special reference to microfilaraemia and elephantiasis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Partono, F. / Purnomo / Oemijati, Sri Article Zeitschrift:
The long term effects of repeated diethylcarbamazine administration with special reference to microfilaraemia and elephantiasis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Partono, F. / Purnomo / Oemijati, Sri Article Zeitschrift:
The parasitic diseases of school children in Lagos State, Nigeria
 The parasitic diseases of school children in Lagos State, Nigeria Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ejezie, G.C. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 38 (1981) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am: 19.07.2018 Persistenter
The parasitic diseases of school children in Lagos State, Nigeria Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ejezie, G.C. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 38 (1981) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am: 19.07.2018 Persistenter
Incidence of and beliefs about trypanosomiasis in the Senegal River Basin
 Incidence of and beliefs about trypanosomiasis in the Senegal River Basin Autor(en): Objekttyp: Imperato, Pascal James / Fofana, Benitieni / Sow, Ousmane Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Incidence of and beliefs about trypanosomiasis in the Senegal River Basin Autor(en): Objekttyp: Imperato, Pascal James / Fofana, Benitieni / Sow, Ousmane Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr):
Miscellanea : The neutropenic (pancytopenic?) type of bacillary dysentery
 Miscellanea : The neutropenic (pancytopenic?) type of bacillary dysentery Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vinke, B. / Donker, A.J.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am:
Miscellanea : The neutropenic (pancytopenic?) type of bacillary dysentery Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vinke, B. / Donker, A.J.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 23 (1966) Heft 1 PDF erstellt am:
Reproductive disorders in African trypanosomiasis : a review
 Reproductive disorders in African trypanosomiasis : a review Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ikede, B.O. / Elhassan, Elizabeth / Akpavie, S.O. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 1 PDF
Reproductive disorders in African trypanosomiasis : a review Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ikede, B.O. / Elhassan, Elizabeth / Akpavie, S.O. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 1 PDF
Familial predisposition to filarial infection : not linked to HLA-A or -B locus specificities
 Familial predisposition to filarial infection : not linked to HLA-A or -B locus specificities Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ottesen, E.A. / Mendell, Nancy R. / MacQueen, J. Marilyn Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Familial predisposition to filarial infection : not linked to HLA-A or -B locus specificities Autor(en): Objekttyp: Ottesen, E.A. / Mendell, Nancy R. / MacQueen, J. Marilyn Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Human monkeypox : confusion with chickenpox
 Human monkeypox : confusion with chickenpox Autor(en): Objekttyp: Jezek, Z. / Szczeniowski, M. / Paluku, K.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am: 18.7.218 Persistenter
Human monkeypox : confusion with chickenpox Autor(en): Objekttyp: Jezek, Z. / Szczeniowski, M. / Paluku, K.M. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 45 (1988) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am: 18.7.218 Persistenter
Cryoglobulins in "Schistosoma haematobium" infection
 Cryoglobulins in "Schistosoma haematobium" infection Autor(en): Objekttyp: Adeiga, A.A. / Ade-Serrano, M.A. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 40 (1983) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 26.10.2017 Persistenter
Cryoglobulins in "Schistosoma haematobium" infection Autor(en): Objekttyp: Adeiga, A.A. / Ade-Serrano, M.A. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 40 (1983) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 26.10.2017 Persistenter
Palynology of a bumble-bee nest
 Palynology of a bumble-bee nest Autor(en): Objekttyp: Faegri, Knut Article Zeitschrift: Veröffentlichungen des Geobotanischen Institutes der Eidg. Tech. Hochschule, Stiftung Rübel, in Zürich Band (Jahr):
Palynology of a bumble-bee nest Autor(en): Objekttyp: Faegri, Knut Article Zeitschrift: Veröffentlichungen des Geobotanischen Institutes der Eidg. Tech. Hochschule, Stiftung Rübel, in Zürich Band (Jahr):
Tricarboxylic acid and glyoxylate cycles in the "Leishmaniae"
 Tricarboxylic acid and glyoxylate cycles in the "Leishmaniae" Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mukkada, A.J. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (1977) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 03.10.2018 Persistenter
Tricarboxylic acid and glyoxylate cycles in the "Leishmaniae" Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mukkada, A.J. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 34 (1977) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am: 03.10.2018 Persistenter
Stürchler, D. / Weiss, N. / Dietrich, F.M. Band (Jahr): 38 (1981) Heft 4. PDF erstellt am:
 Immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis outside endemic areas : use of histamine release from basophils by schistosomal antigens and radioallergosorbent test Autor(en): Objekttyp: Stürchler, D. / Weiss, N.
Immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis outside endemic areas : use of histamine release from basophils by schistosomal antigens and radioallergosorbent test Autor(en): Objekttyp: Stürchler, D. / Weiss, N.
Site of resistance to "Necator americanus" in hamsters
 Site of resistance to "Necator americanus" in hamsters Autor(en): Objekttyp: Rajasekariah, G.R. / Deb, B.N. / Dhage, K.R. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 42 (985) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am:
Site of resistance to "Necator americanus" in hamsters Autor(en): Objekttyp: Rajasekariah, G.R. / Deb, B.N. / Dhage, K.R. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 42 (985) Heft 4 PDF erstellt am:
Curriculum Vitae : Mohamed Musa Mohamed-Ahmed Date & Place of Birth : , Sennar Nationality : Sudanese
 Curriculum Vitae Name : Mohamed Musa Mohamed-Ahmed Date & Place of Birth : 1.1.1949, Sennar Nationality : Sudanese Religion : Moslem Marital Status : Married with Five Children Academic Qualification:
Curriculum Vitae Name : Mohamed Musa Mohamed-Ahmed Date & Place of Birth : 1.1.1949, Sennar Nationality : Sudanese Religion : Moslem Marital Status : Married with Five Children Academic Qualification:
Identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild Tsetse flies in Nkhotakota Wild Life Reserve by PCR
 Identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild Tsetse flies in Nkhotakota Wild Life Reserve by PCR 32 nd International Scientific Council for Trypanosomiasis Research and Control (ISCTRC), September
Identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild Tsetse flies in Nkhotakota Wild Life Reserve by PCR 32 nd International Scientific Council for Trypanosomiasis Research and Control (ISCTRC), September
Effect of pheromone trap position in large and small trees and in the open field on the catch of codling moth, Cydia pomonella, males
 Effect of pheromone trap position in large and small trees and in the open field on the catch of codling moth, Cydia pomonella, males Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mani, Erwin / Wildbolz, Theodor / Riggenbach,
Effect of pheromone trap position in large and small trees and in the open field on the catch of codling moth, Cydia pomonella, males Autor(en): Objekttyp: Mani, Erwin / Wildbolz, Theodor / Riggenbach,
Differential pathogenicity of "Brugia malayi", "B. patei" and "B. pahangi" in immunodeficient nude mice
 Differential pathogenicity of "Brugia malayi", "B. patei" and "B. pahangi" in immunodeficient nude mice Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vickery, A.C. / Nayar, J.K. / Albertine, K.H. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Differential pathogenicity of "Brugia malayi", "B. patei" and "B. pahangi" in immunodeficient nude mice Autor(en): Objekttyp: Vickery, A.C. / Nayar, J.K. / Albertine, K.H. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Full length research article
 Full length research article EXPERIMENTAL ESTIMATION OF CHALLENGE OF A NATURAL POPULATION OF GLOSSINA PALPALIS PALPALIS R-D (DIPTERA:GLOSSINIDAE) ON CATTLE IN THE SOUTHERN GUINEA SAVANNA, NIGERIA. *A.B.
Full length research article EXPERIMENTAL ESTIMATION OF CHALLENGE OF A NATURAL POPULATION OF GLOSSINA PALPALIS PALPALIS R-D (DIPTERA:GLOSSINIDAE) ON CATTLE IN THE SOUTHERN GUINEA SAVANNA, NIGERIA. *A.B.
Tsetse flies vectors of trypanosomiasis
 Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 3 Tsetse flies vectors of trypanosomiasis Tsetse colonies at ILRAD Some research results Tsetse characteristics
Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 3 Tsetse flies vectors of trypanosomiasis Tsetse colonies at ILRAD Some research results Tsetse characteristics
Frequent occurrence of hepatic lesions in boutonneuse fever
 Frequent occurrence of hepatic lesions in boutonneuse fever Autor(en): Walker, D.H. / Staiti, A. / Mansueto, S. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 43 (1986) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am:
Frequent occurrence of hepatic lesions in boutonneuse fever Autor(en): Walker, D.H. / Staiti, A. / Mansueto, S. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica Band (Jahr): 43 (1986) Heft 2 PDF erstellt am:
"Opisthorchis viverrini" : liver changes in golden hamsters maintained on high and low protein diets
 "Opisthorchis viverrini" : liver changes in golden hamsters maintained on high and low protein diets Autor(en): Objekttyp: Flavell, D.J. / Pattanapanyasat, K. / Lucas, S.B. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
"Opisthorchis viverrini" : liver changes in golden hamsters maintained on high and low protein diets Autor(en): Objekttyp: Flavell, D.J. / Pattanapanyasat, K. / Lucas, S.B. Article Zeitschrift: Acta Tropica
Glossina dynamics in and around the sleeping sickness endemic Serengeti ecosystem of northwestern Tanzania
 Vol. 32, no. 2 Journal of Vector Ecology 263 Glossina dynamics in and around the sleeping sickness endemic Serengeti ecosystem of northwestern Tanzania I. I. Malele 1, S. M. Kinung'hi 2, H. S. Nyingilili
Vol. 32, no. 2 Journal of Vector Ecology 263 Glossina dynamics in and around the sleeping sickness endemic Serengeti ecosystem of northwestern Tanzania I. I. Malele 1, S. M. Kinung'hi 2, H. S. Nyingilili
Control Options for Human Sleeping Sickness in Relation to the Animal Reservoir of Disease 1
 Chapter 8 Control Options for Human Sleeping Sickness in Relation to the Animal Reservoir of Disease 1 S.C. Welburn 2, K. Picozzi 2, M. Kaare 3, E.M. Fèvre 2, P.G. Coleman 4 and T. Mlengeya 5 Sleeping
Chapter 8 Control Options for Human Sleeping Sickness in Relation to the Animal Reservoir of Disease 1 S.C. Welburn 2, K. Picozzi 2, M. Kaare 3, E.M. Fèvre 2, P.G. Coleman 4 and T. Mlengeya 5 Sleeping
Journal Of Agriculture and Social Research (JASR) Vol. 8, No.1, 2008
 PREVALENCE OF TSETSE FLY AND BOVINE TRYPANOSOMOSIS IN THE BIOLOGICAL CONTROL OF TSETSE FLY PROJECT (BICOT) WITHIN LAFIA LOCAL GOVERNMENT AREA OF NASARAWA STATE, NIGERIA OLUWAFEMI, R. A, ILEMOBADE, A. A
PREVALENCE OF TSETSE FLY AND BOVINE TRYPANOSOMOSIS IN THE BIOLOGICAL CONTROL OF TSETSE FLY PROJECT (BICOT) WITHIN LAFIA LOCAL GOVERNMENT AREA OF NASARAWA STATE, NIGERIA OLUWAFEMI, R. A, ILEMOBADE, A. A
Disparlure and its role in gypsy moth population manipulation
 Disparlure and its role in gypsy moth population manipulation Autor(en): Objekttyp: Cameron, E. Alan Article Zeitschrift: Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft = Bulletin de la
Disparlure and its role in gypsy moth population manipulation Autor(en): Objekttyp: Cameron, E. Alan Article Zeitschrift: Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft = Bulletin de la
THE ROLE OF LIVESTOCK IN THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SLEEPING SICKNESS IN TANZANIA
 THE ROLE OF LIVESTOCK IN THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SLEEPING SICKNESS IN TANZANIA Imna Malele, Hamisi Nyingilili, Eugen Lyaruu, Winston Kitwika Tsetse & Trypanosomiasis Research Institute Majani Mapana, Off Korogwe
THE ROLE OF LIVESTOCK IN THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SLEEPING SICKNESS IN TANZANIA Imna Malele, Hamisi Nyingilili, Eugen Lyaruu, Winston Kitwika Tsetse & Trypanosomiasis Research Institute Majani Mapana, Off Korogwe
Abstract. Keywords: Trypanosomosis /Tsetse/ Prevalence/Density/ Sibu Sire/ Guto Gida/ Western Ethiopia. Shimelis Dagnachew 1 * and Sisay Shibeshi
 Prevalence and vector distributions of bovine trypanosomosis in control (Sibu Sire) and noncontrol (Guto Gida) districts bordering upper Anger valley of East Wollega Zone, Western Ethiopia Shimelis Dagnachew
Prevalence and vector distributions of bovine trypanosomosis in control (Sibu Sire) and noncontrol (Guto Gida) districts bordering upper Anger valley of East Wollega Zone, Western Ethiopia Shimelis Dagnachew
Repellent properties of δ-octalactone against the tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans morsitans
 Repellent properties of δ-octalactone against the tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans morsitans Martin T. Mwangi 1,2,a, Nicholas K. Gikonyo 2,3,b and Isaiah O. Ndiege 2,3,c 1 Department of Chemistry, University
Repellent properties of δ-octalactone against the tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans morsitans Martin T. Mwangi 1,2,a, Nicholas K. Gikonyo 2,3,b and Isaiah O. Ndiege 2,3,c 1 Department of Chemistry, University
guidelines COLLECTION OF ENTOMOLOGICAL BASELINE DATA FOR TSETSE AREA-WIDE INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH
 1 ISSN 1810-0708 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines COLLECTION OF ENTOMOLOGICAL BASELINE DATA FOR TSETSE AREA-WIDE INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES 1 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines
1 ISSN 1810-0708 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines COLLECTION OF ENTOMOLOGICAL BASELINE DATA FOR TSETSE AREA-WIDE INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES 1 FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH guidelines
am id <3-ls Qfyeplebrale
 I.U.C.N. Publications new series No. 6 Presented at the First International Congress of Parasitology ROME, 21-26 SEPTEMBER 1964 eview e
I.U.C.N. Publications new series No. 6 Presented at the First International Congress of Parasitology ROME, 21-26 SEPTEMBER 1964 eview e
Bovine Trypanosomosis in three districts of East Gojjam Zone bordering the Blue Nile River in Ethiopia
 Original Article Bovine Trypanosomosis in three districts of East Gojjam Zone bordering the Blue Nile River in Ethiopia Adane Mihret, 1,2 Gezahagne Mamo, 3 1 Addis Ababa University, Faculty of Medicine,
Original Article Bovine Trypanosomosis in three districts of East Gojjam Zone bordering the Blue Nile River in Ethiopia Adane Mihret, 1,2 Gezahagne Mamo, 3 1 Addis Ababa University, Faculty of Medicine,
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Sodalis glossinidius prevalence and trypanosome presence in tsetse from Luambe National Park, Zambia Citation for published version: Dennis, JW, Durkin, SM, Horsley Downie,
Edinburgh Research Explorer Sodalis glossinidius prevalence and trypanosome presence in tsetse from Luambe National Park, Zambia Citation for published version: Dennis, JW, Durkin, SM, Horsley Downie,
Trypanosomiasis. Introduction. Epidemiology. Global Epidemiology. Trypanosomiasis Risk in UK Travellers
 Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
THE PREVALENCE OF ANTIBODY TO INFECTIOUS BOVINE RHINOTRACHEITIS VIRUS IN SOME GAME ANIMALS OF EAST AFRICA
 THE PREVALENCE OF ANTIBODY TO INFECTIOUS BOVINE RHINOTRACHEITIS VIRUS IN SOME GAME ANIMALS OF EAST AFRICA Author(s): C. S. RAMPTON and D. M. JESSETT Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 12(1):2-5. Published
THE PREVALENCE OF ANTIBODY TO INFECTIOUS BOVINE RHINOTRACHEITIS VIRUS IN SOME GAME ANIMALS OF EAST AFRICA Author(s): C. S. RAMPTON and D. M. JESSETT Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 12(1):2-5. Published
Better Training for Safer Food BTSF
 Better Training for Safer Food BTSF Importation of vector-borne infectious diseases Tanguy Marcotty Institute of Tropical Medicine Importation routes Trade Infected live animals (e.g. H5N1 avian influenza)
Better Training for Safer Food BTSF Importation of vector-borne infectious diseases Tanguy Marcotty Institute of Tropical Medicine Importation routes Trade Infected live animals (e.g. H5N1 avian influenza)
Immune complexes and complément in rheumatoïde arthritis
 Immune complexes and complément in rheumatoïde arthritis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Lambert, Paul Henri / Casali, Paolo / Nydegger, Urs Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen
Immune complexes and complément in rheumatoïde arthritis Autor(en): Objekttyp: Lambert, Paul Henri / Casali, Paolo / Nydegger, Urs Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen
P. VAN DEN BOSSCHE INTRODUCTION. Regional Tsetse and Trypanosomosis Control Programme {RTTCP) P.O. BoxA560, Avondale, Harare, Zimbabwe
 Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 64:251-257 (1997) The control of Glossina morsitans morsitans (Diptera: Glossinidae) in a settled area in Petauke District (Eastern Province, Zambia) using
Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 64:251-257 (1997) The control of Glossina morsitans morsitans (Diptera: Glossinidae) in a settled area in Petauke District (Eastern Province, Zambia) using
Climate change and vector-borne diseases of livestock in the tropics. Peter Van den Bossche
 Climate change and vector-borne diseases of livestock in the tropics Peter Van den Bossche Climate change & animal health Climate change in Africa: Temperature Rainfall Variability Climate change & animal
Climate change and vector-borne diseases of livestock in the tropics Peter Van den Bossche Climate change & animal health Climate change in Africa: Temperature Rainfall Variability Climate change & animal
The use of specific and generic primers to identify trypanosome infections of wild tsetse flies in Tanzania by PCR
 Infection, Genetics and Evolution 3 (2003) 271 279 The use of specific and generic primers to identify trypanosome infections of wild tsetse flies in Tanzania by PCR Imna Malele a,b, Lisa Craske c, Claire
Infection, Genetics and Evolution 3 (2003) 271 279 The use of specific and generic primers to identify trypanosome infections of wild tsetse flies in Tanzania by PCR Imna Malele a,b, Lisa Craske c, Claire
Temporal and spatial epidemiology of sleeping sickness and use of geographical information system (GIS) in Kenya
 J Vector Borne Dis 46, March 2009, pp. 18 25 Research Articles Temporal and spatial epidemiology of sleeping sickness and use of geographical information system (GIS) in Kenya Jane Jemeli Rutto & Julia
J Vector Borne Dis 46, March 2009, pp. 18 25 Research Articles Temporal and spatial epidemiology of sleeping sickness and use of geographical information system (GIS) in Kenya Jane Jemeli Rutto & Julia
KINETOPLASTIDS. Kinetoplast. Nucleus
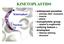 KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8516461728* BIOLOGY 0610/31 Paper 3 Extended May/June 2008 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8516461728* BIOLOGY 0610/31 Paper 3 Extended May/June 2008 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
of endemic and enzootic trypanosomiases
 Bull. Org. mond. Sante 1972, 47, 735-746 Bull. Wid Hlth Org. The role of game animals in the maintenance of endemic and enzootic trypanosomiases in the Lambwe Valley, South Nyanza District, Kenya R. ALLSOPP
Bull. Org. mond. Sante 1972, 47, 735-746 Bull. Wid Hlth Org. The role of game animals in the maintenance of endemic and enzootic trypanosomiases in the Lambwe Valley, South Nyanza District, Kenya R. ALLSOPP
Kinetoplastids Handout
 Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle
 Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 1 no 9 pp 833 839 september 5 Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle P. Van den Bossche, A. Ky-Zerbo, J. Brandt, T. Marcotty,
Tropical Medicine and International Health volume 1 no 9 pp 833 839 september 5 Transmissibility of Trypanosoma brucei during its development in cattle P. Van den Bossche, A. Ky-Zerbo, J. Brandt, T. Marcotty,
GROWING TRYPANOSOMES IN THE LABORATORY
 Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 1 Growing trypanosomes in the laboratory A closer look at the trypanosome lifecycle Cultivating trypanosomes in
Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 1 Growing trypanosomes in the laboratory A closer look at the trypanosome lifecycle Cultivating trypanosomes in
Collagenase and prostaglandin in connective tissue destruction : cell-cell and humoral interactions
 Collagenase and prostaglandin in connective tissue destruction : cell-cell and humoral interactions Autor(en): Dayer, Jean-Michel / Goldring, Steven R. / Robinson, Dwight R. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift:
Collagenase and prostaglandin in connective tissue destruction : cell-cell and humoral interactions Autor(en): Dayer, Jean-Michel / Goldring, Steven R. / Robinson, Dwight R. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift:
Trypanosomiasis. By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy
 Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Factors Affecting the Propensity of Tsetse Flies to Enter Houses and Attack Humans Inside: Increased Risk of Sleeping Sickness in Warmer Climates
 Factors Affecting the Propensity of Tsetse Flies to Enter Houses and Attack Humans Inside: Increased Risk of Sleeping Sickness in Warmer Climates Glyn A. Vale 1,2 *, John W. Hargrove 2, Andrew Chamisa
Factors Affecting the Propensity of Tsetse Flies to Enter Houses and Attack Humans Inside: Increased Risk of Sleeping Sickness in Warmer Climates Glyn A. Vale 1,2 *, John W. Hargrove 2, Andrew Chamisa
Trypanosome infection rate of Glossina morsitans and trypanosomosis prevalence in cattle in upper Didessa valley western Ethiopia
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 3 (2014) pp. 378-388 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Trypanosome infection rate of Glossina morsitans and trypanosomosis prevalence in cattle in upper Didessa
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 3 (2014) pp. 378-388 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Trypanosome infection rate of Glossina morsitans and trypanosomosis prevalence in cattle in upper Didessa
TRYPANASOMA INFECTION RATES IN GLOSSINA SPECIES IN MTITO ANDEI DIVISION, MAKUENI COUNTY, KENYA
 TRYPANASOMA INFECTION RATES IN GLOSSINA SPECIES IN MTITO ANDEI DIVISION, MAKUENI COUNTY, KENYA BY DANIEL MUTISO NTHIWA, B.Sc. I56/65273/2010 A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT
TRYPANASOMA INFECTION RATES IN GLOSSINA SPECIES IN MTITO ANDEI DIVISION, MAKUENI COUNTY, KENYA BY DANIEL MUTISO NTHIWA, B.Sc. I56/65273/2010 A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT
Effect of elephants on vegetation in Pongola Game Reserve. Dr Heather Gilbert, Operation Wallacea
 Effect of elephants on vegetation in Pongola Game Reserve Dr Heather Gilbert, Operation Wallacea Contents Key Findings... 2 Introduction... 2 Research Site... 3 Results and discussion... 4 Changes over
Effect of elephants on vegetation in Pongola Game Reserve Dr Heather Gilbert, Operation Wallacea Contents Key Findings... 2 Introduction... 2 Research Site... 3 Results and discussion... 4 Changes over
Rift Valley Fever. What is Rift Valley Fever?
 Rift Valley Fever What is Rift Valley Fever? Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a peracute or acute insect-borne disease of man and animals, historically restricted to Africa. An outbreak of RVF in animals frequently
Rift Valley Fever What is Rift Valley Fever? Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a peracute or acute insect-borne disease of man and animals, historically restricted to Africa. An outbreak of RVF in animals frequently
Trypanotolerant livestock: Potential and future exploitation
 Page 1 of 15 Trypanotolerant livestock: Potential and future exploitation Max Murray, J. C. M. Trail 1, and J. G. Grootenhuis International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases (ILRAD), P O Box 30709,
Page 1 of 15 Trypanotolerant livestock: Potential and future exploitation Max Murray, J. C. M. Trail 1, and J. G. Grootenhuis International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases (ILRAD), P O Box 30709,
Page1 FULL LENGTH RESEARCH ARTICLE. HIGH TRYPANOSOME INFECTIONS IN Glossina palpalis palpalis ROBINEAU-DESVOIDY 1830 IN SOUTHERN KADUNA STATE, NIGERIA
 SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL 2(NO2) 27 FULL LENGTH RESEARCH ARTICLE HIGH TRYPANOSOME INFECTIONS IN Glossina palpalis palpalis ROBINEAU-DESVOIDY 83 IN SOUTHERN KADUNA STATE, NIGERIA A. B. AHMED Department
SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL 2(NO2) 27 FULL LENGTH RESEARCH ARTICLE HIGH TRYPANOSOME INFECTIONS IN Glossina palpalis palpalis ROBINEAU-DESVOIDY 83 IN SOUTHERN KADUNA STATE, NIGERIA A. B. AHMED Department
Investment in new knowledge and tools for control of Glossina: Current status and future perspectives
 Investment in new knowledge and tools for control of Glossina: Current status and future perspectives Mike Lehane Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine Total Papers Published 44 new papers published with
Investment in new knowledge and tools for control of Glossina: Current status and future perspectives Mike Lehane Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine Total Papers Published 44 new papers published with
The effect of the refusal avoidance training experiment on final disposition codes in the German ESS-2 Schnell, Rainer; Trappmann, Mark
 www.ssoar.info The effect of the refusal avoidance training experiment on final disposition codes in the German ESS-2 Schnell, Rainer; Trappmann, Mark Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Arbeitspapier
www.ssoar.info The effect of the refusal avoidance training experiment on final disposition codes in the German ESS-2 Schnell, Rainer; Trappmann, Mark Veröffentlichungsversion / Published Version Arbeitspapier
Review of tsetse flies and trypanosomosis
 Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 65:195-203 (1998) Review of tsetse flies and trypanosomosis in South Africa KARIN KAPPMEIER 1 *, E.M. NEVILL 1 and R.J. BAGNALL 2 ABSTRACT KAPPMEIER, KARIN,
Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 65:195-203 (1998) Review of tsetse flies and trypanosomosis in South Africa KARIN KAPPMEIER 1 *, E.M. NEVILL 1 and R.J. BAGNALL 2 ABSTRACT KAPPMEIER, KARIN,
CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE TSETSE FREE AREAS IN THE NORTH-WEST AND NORTH-EAST GEOPOLITICAL ZONES OF NIGERIA.
 CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE TSETSE FREE AREAS IN THE NORTH-WEST AND NORTH-EAST GEOPOLITICAL ZONES OF NIGERIA. BY Dede, P.M.; Enwezor, F.N. and Mamman M. PATTEC-Nigeria, Nigerian Institute for Trypanosomiasis
CREATION OF SUSTAINABLE TSETSE FREE AREAS IN THE NORTH-WEST AND NORTH-EAST GEOPOLITICAL ZONES OF NIGERIA. BY Dede, P.M.; Enwezor, F.N. and Mamman M. PATTEC-Nigeria, Nigerian Institute for Trypanosomiasis
BIO Parasitology Spring 2009
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
Socio-Economic and Agricultural Factor In Control of Trypanosomiasis in Nigeria A Review
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 11, Issue 1 Ver. I (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 19-23 www.iosrjournals.org Socio-Economic and Agricultural
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 11, Issue 1 Ver. I (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 19-23 www.iosrjournals.org Socio-Economic and Agricultural
Specific issues related to FMD surveillance in the eastern Africa sub-region. Gideon Brückner
 Specific issues related to FMD surveillance in the eastern Africa sub-region Gideon Brückner 1 Why do we do surveillance for FMD? Demonstrating freedom from FMD, FMDV infection and/or FMDV transmission
Specific issues related to FMD surveillance in the eastern Africa sub-region Gideon Brückner 1 Why do we do surveillance for FMD? Demonstrating freedom from FMD, FMDV infection and/or FMDV transmission
ANIMAL TRYPANOSOMIASIS IN AFRICA: AETIOLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY
 Animal Research International (2008) 5(1): 811 815 811 ANIMAL TRYPANOSOMIASIS IN AFRICA: AETIOLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY UGOCHUKWU, Emma Ikenna Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Nigeria, Nsukka,
Animal Research International (2008) 5(1): 811 815 811 ANIMAL TRYPANOSOMIASIS IN AFRICA: AETIOLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY UGOCHUKWU, Emma Ikenna Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Nigeria, Nsukka,
The content assessed by the examination papers and the type of questions is unchanged.
 Location Entry Codes As part of CIE s continual commitment to maintaining best practice in assessment, CIE uses different variants of some question papers for our most popular assessments with large and
Location Entry Codes As part of CIE s continual commitment to maintaining best practice in assessment, CIE uses different variants of some question papers for our most popular assessments with large and
Tropentag 2007 University of Kassel-Witzenhausen and University of Göttingen, October 9-11, 2007
 Tropentag 2007 University of Kassel-Witzenhausen and University of Göttingen, October 9-11, 2007 Conference on International Agricultural Research for Development Participatory Assessment of Incidence
Tropentag 2007 University of Kassel-Witzenhausen and University of Göttingen, October 9-11, 2007 Conference on International Agricultural Research for Development Participatory Assessment of Incidence
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Characterisation of the wildlife reservoir community for human and animal trypanosomiasis in the Luangwa Valley, Zambia Citation for published version: Anderson, N, Mubanga,
Edinburgh Research Explorer Characterisation of the wildlife reservoir community for human and animal trypanosomiasis in the Luangwa Valley, Zambia Citation for published version: Anderson, N, Mubanga,
Bovine Trypanosomiasis And Tsetse Fly Survey In Some Parts Of Kaduna State, North Western Nigeria.
 IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 10, Issue 11 Ver. I (November 2017), PP 72-76 www.iosrjournals.org Bovine Trypanosomiasis And
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 10, Issue 11 Ver. I (November 2017), PP 72-76 www.iosrjournals.org Bovine Trypanosomiasis And
Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta State, Nigeria
 JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-28-32 Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta
JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 2006 Vol. 5 No.2 pp-28-32 Confirmation of Trypanosome Parasitaemia in Previously Serologically Positive Individuals in the Abraka Area of Delta
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences ISSN Vol. 2(11), , November (2013)
 International Research Journal of Environment Sciences ISSN 2319 1414 Man- Conflict: Case Study from Angul Forest Division, Odisha, India Rudra Narayan Pradhan, Pandab Behera and Sandeep Ranjan Mishra
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences ISSN 2319 1414 Man- Conflict: Case Study from Angul Forest Division, Odisha, India Rudra Narayan Pradhan, Pandab Behera and Sandeep Ranjan Mishra
AIC. Schweiz Suisse Svizzera Switzerland skyguide, swiss air navigation services ltd AIP services ch-8602 wangen bei dübendorf
 AIP services phone: +41 (0) 43 931 61 68 fax: +41 (0) 43 931 61 59 AFTN: LSSAYOYX aip@skyguide.ch AIC Schweiz Suisse Svizzera Switzerland skyguide, swiss air navigation services ltd AIP services ch-8602
AIP services phone: +41 (0) 43 931 61 68 fax: +41 (0) 43 931 61 59 AFTN: LSSAYOYX aip@skyguide.ch AIC Schweiz Suisse Svizzera Switzerland skyguide, swiss air navigation services ltd AIP services ch-8602
Conservation status of chimpanzees Pan troglodytes verus and other large mammals in Liberia: a nationwide survey
 Conservation status of chimpanzees Pan troglodytes verus and other large mammals in Liberia: a nationwide survey CLEMENT G. TWEH, MENLADI M. LORMIE, CÉLESTIN Y. KOUAKOU, ANNIKA HILLERS HJALMAR S. KÜHL
Conservation status of chimpanzees Pan troglodytes verus and other large mammals in Liberia: a nationwide survey CLEMENT G. TWEH, MENLADI M. LORMIE, CÉLESTIN Y. KOUAKOU, ANNIKA HILLERS HJALMAR S. KÜHL
[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY
![[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY [689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY](/thumbs/91/107443416.jpg) [689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY E. BURSELL Department of Zoology, University College of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia {Received 7 March i960) INTRODUCTION
[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY E. BURSELL Department of Zoology, University College of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia {Received 7 March i960) INTRODUCTION
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين
 اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
Assessing CI Trends - the facts behind the stats. Inga Kreiensiek & Adèle Groyer
 1 Assessing CI Trends - the facts behind the stats Inga Kreiensiek & Adèle Groyer 2 Presentation overview Background to the study Challenges Why it s not as simple as fitting a trend line through data
1 Assessing CI Trends - the facts behind the stats Inga Kreiensiek & Adèle Groyer 2 Presentation overview Background to the study Challenges Why it s not as simple as fitting a trend line through data
Case Study Brief Guinea Worm Disease Outbreak in Mazmum, Sudan Background Information
 Case Study Brief You are working as an Epidemic Intelligence Services Officer for the World Health Organization and you have received a report of a suspected outbreak of Guinea Worm Disease in Sudan. Guinea
Case Study Brief You are working as an Epidemic Intelligence Services Officer for the World Health Organization and you have received a report of a suspected outbreak of Guinea Worm Disease in Sudan. Guinea
1974 Bachelor of Science (BSc.), Zoology, Botany and Chemistry (Nairobi)
 1 Dr. Jedida A. Kongoro P.O Box 4742-00100 GPO Nairobi Kenya. 254-733-572863 (Cell-phone) E-mail: jkongoro@hotmail.com ACADEMIC QUALIFICATIONS 1998 Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Biochemistry/Physiology (Kenyatta
1 Dr. Jedida A. Kongoro P.O Box 4742-00100 GPO Nairobi Kenya. 254-733-572863 (Cell-phone) E-mail: jkongoro@hotmail.com ACADEMIC QUALIFICATIONS 1998 Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Biochemistry/Physiology (Kenyatta
Science for Development. Brian Williams, Department of Zoology, University of Oxford OX1 3PS Gavin Williams, St Peter's College, Oxford OX1 2DL
 Science for Development Brian Williams, Department of Zoology, University of Oxford OX1 3PS Gavin Williams, St Peter's College, Oxford OX1 2DL Williams B, Williams G. Science for development. Perspect
Science for Development Brian Williams, Department of Zoology, University of Oxford OX1 3PS Gavin Williams, St Peter's College, Oxford OX1 2DL Williams B, Williams G. Science for development. Perspect
Estimated Lyme borreliosis incidence in the canton of Neuchâtel (Switzerland)
 Estimated Lyme borreliosis incidence in the canton of Neuchâtel (Switzerland) Autor(en): Objekttyp: Moosmann, Yves / Brossard, Michel / Raeber, Pierre-Alain Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin de la Société
Estimated Lyme borreliosis incidence in the canton of Neuchâtel (Switzerland) Autor(en): Objekttyp: Moosmann, Yves / Brossard, Michel / Raeber, Pierre-Alain Article Zeitschrift: Bulletin de la Société
Rift Valley Fever in Africa. Kariuki Njenga, DVM, PhD Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, Nairobi, Kenya
 Rift Valley Fever in Africa Kariuki Njenga, DVM, PhD Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, Nairobi, Kenya Density map of human and animal cases on solonchak soil Legend: Livestock confirmed cases
Rift Valley Fever in Africa Kariuki Njenga, DVM, PhD Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, Nairobi, Kenya Density map of human and animal cases on solonchak soil Legend: Livestock confirmed cases
Control and surveillance of human African trypanosomiasis
 In the 1960s, it appeared that human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) could be effectively controlled, but by the beginning of the twenty-first century several decades of neglect had led to alarming numbers
In the 1960s, it appeared that human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) could be effectively controlled, but by the beginning of the twenty-first century several decades of neglect had led to alarming numbers
Basic Biology and Anatomy of the Tsetse Fly
 1 Section 1 Basic Biology and Anatomy of the Tsetse Fly 1.1. Introduction The objective of this section is to provide essential information for the subsequent two sections, which give guidelines for conducting
1 Section 1 Basic Biology and Anatomy of the Tsetse Fly 1.1. Introduction The objective of this section is to provide essential information for the subsequent two sections, which give guidelines for conducting
A RECENT OUTBREAK OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE IN THE EQUID POPULATION OF THE CENTRAL RIVER DISTRICT OF THE GAMBIA
 A RECENT OUTBREAK OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE IN THE EQUID POPULATION OF THE CENTRAL RIVER DISTRICT OF THE GAMBIA Laura Peachey BVSc BSc MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College Clinical problem Cases of neurological
A RECENT OUTBREAK OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE IN THE EQUID POPULATION OF THE CENTRAL RIVER DISTRICT OF THE GAMBIA Laura Peachey BVSc BSc MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College Clinical problem Cases of neurological
Africa East G. m. morsitans in, 8349 G. pallidipes in, 8349 trypanosomiasis in humans, control, 8182 East and West T. b. brucei stocks from, 8350
 Africa East G. m. morsitans in, 8349 G. pallidipes in, 8349 trypanosomiasis in humans, control, 8182 East and West T. b. brucei stocks from, 8350 South T. brucei in Zululand, historic, 8181 sub-saharan
Africa East G. m. morsitans in, 8349 G. pallidipes in, 8349 trypanosomiasis in humans, control, 8182 East and West T. b. brucei stocks from, 8350 South T. brucei in Zululand, historic, 8181 sub-saharan
Betrayal! The 1806 English Translation of Pinel's "Traité médico-philosophique sur l'aliénation mentale ou la manie"
 Betrayal! The 1806 English Translation of Pinel's "Traité médico-philosophique sur l'aliénation mentale ou la manie" Autor(en): Weiner, Dora B. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal
Betrayal! The 1806 English Translation of Pinel's "Traité médico-philosophique sur l'aliénation mentale ou la manie" Autor(en): Weiner, Dora B. Objekttyp: Article Zeitschrift: Gesnerus : Swiss Journal
Bethel s Global Reach GOING DOING. Kenya, Africa Missions Trip June 1-11, 2019
 Bethel s Global Reach GOING DOING www.bethelsglobalreach.org Kenya, Africa Missions Trip June 1-11, 2019 Marcus D. Holman mholman@bethelsglobalreach.org Katherine Carey kcarey@bethelsglobalreach.org Darrellon
Bethel s Global Reach GOING DOING www.bethelsglobalreach.org Kenya, Africa Missions Trip June 1-11, 2019 Marcus D. Holman mholman@bethelsglobalreach.org Katherine Carey kcarey@bethelsglobalreach.org Darrellon
Malawi Medical Journal 29 (1): March 2017
 Molecular identification of T. b. rhodesiense in tsetse flies 11 Original Research Polymerase chain reaction identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild tsetse flies from Nkhotakota Wildlife
Molecular identification of T. b. rhodesiense in tsetse flies 11 Original Research Polymerase chain reaction identification of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense in wild tsetse flies from Nkhotakota Wildlife
Patterns in Age-Seroprevalence Consistent with Acquired Immunity against Trypanosoma brucei in Serengeti Lions
 Patterns in Age-Seroprevalence Consistent with Acquired Immunity against Trypanosoma brucei in Serengeti Lions Sue Welburn 1 *, Kim Picozzi 1, Paul G. Coleman 2, Craig Packer 3 1 Centre for Infectious
Patterns in Age-Seroprevalence Consistent with Acquired Immunity against Trypanosoma brucei in Serengeti Lions Sue Welburn 1 *, Kim Picozzi 1, Paul G. Coleman 2, Craig Packer 3 1 Centre for Infectious
Baba SALL 1, Momar Talla SECK2, Jérémy BOUYER3, Marc J.B. VREYSEN4
 Baba SALL 1, Momar Talla SECK2, Jérémy BOUYER3, Marc J.B. VREYSEN4 1 Direction des Services vétérinares/ Ministère de l Elevage et des Productions animales 2Laboratoire national de l Elevage et de Recherches
Baba SALL 1, Momar Talla SECK2, Jérémy BOUYER3, Marc J.B. VREYSEN4 1 Direction des Services vétérinares/ Ministère de l Elevage et des Productions animales 2Laboratoire national de l Elevage et de Recherches
Elements of the FMD control problem in Southern Africa: 2
 Elements of the FMD control problem in Southern Africa: 2 Gavin Thomson Commodity-based trade of beef and enhanced market access: The vital role of the Department of Veterinary Services Gaborone; 6-7 January
Elements of the FMD control problem in Southern Africa: 2 Gavin Thomson Commodity-based trade of beef and enhanced market access: The vital role of the Department of Veterinary Services Gaborone; 6-7 January
Epidemiology of tsetse flies and trypanosomes with a case study in Ethiopia 1
 Reports - Rapports afrika focus Volume 29, Nr. 2, 2016 pp. 109-116 Epidemiology of tsetse flies and trypanosomes with a case study in Ethiopia 1 Reta Duguma Abdi Department of Animal Science, Institute
Reports - Rapports afrika focus Volume 29, Nr. 2, 2016 pp. 109-116 Epidemiology of tsetse flies and trypanosomes with a case study in Ethiopia 1 Reta Duguma Abdi Department of Animal Science, Institute
In 1841 G. Valentin in Berne, Switzerland, saw a protozoan in the blood of a trout that moved by means of its undulating membrane; it was a
 In 1841 G. Valentin in Berne, Switzerland, saw a protozoan in the blood of a trout that moved by means of its undulating membrane; it was a trypanosome. Two years later David Gruby in Paris discovered
In 1841 G. Valentin in Berne, Switzerland, saw a protozoan in the blood of a trout that moved by means of its undulating membrane; it was a trypanosome. Two years later David Gruby in Paris discovered
Adenota kob trypanosome infection, prevalence, Benin, 7662 Africa Central T. brucei population genetics, 8014 East and West T. b. brucei stocks from,
 Adenota kob trypanosome infection, prevalence, Benin, 7662 Africa Central T. brucei population genetics, 8014 East and West T. b. brucei stocks from, 8108 trypanosomiasis in small ruminants, 7817 Equatorial
Adenota kob trypanosome infection, prevalence, Benin, 7662 Africa Central T. brucei population genetics, 8014 East and West T. b. brucei stocks from, 8108 trypanosomiasis in small ruminants, 7817 Equatorial
