OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY SURGERY FOR CONGENITAL NASAL PYRIFORM APERTURE STENOSIS (CNPAS) John Wood, Graeme Van Der Meer Congenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis (CNPAS) is a very rare condition of the newborn, in which the nasal pyriform aperture is narrowed by bony overgrowth of the nasal process of the maxilla (Figure 1). As the narrowest point of the nasal airway, a small change in its diameter may significantly increase nasal airway resistance. As infants are obligate nose breathers for the first three months of life (or longer if premature), such an increased airway resistance causes functional airway obstruction and respiratory distress. While 1 in 5000 births has some form of congenital nasal airway obstruction, the majority is choanal atresia. The differential diagnosis includes nasal cavity masses, dacryocystocoeles, severe septal deviations and CNPAS. Embryology The palate develops from 3 structures: the primary palate that forms the hard palate anterior to the incisive fossa; and 2 lateral plates from outgrowths of the maxillary prominences. CNPAS can be explained by a deficiency of the fused medial nasal prominence, with subsequent faulty development of a small triangular primary palate, often abnormal incisors, and a narrow nasal cavity. During the 8 th week of gestation, maxillary ossification commences from the growth centres above the canine teeth. It has been suggested that over-ossification of the nasal process of the maxilla may be responsible, or it may be due to hypoplastic growth of the primary palate, suggesting that a local dysostosis of the maxilla with bony overgrowth is the abnormality, rather than failed recanalisation of the nasal cavity. Associated midline abnormalities can also occur, and may even be considered a minor form of holoprosencephaly (a spectrum of defects or malformations of the brain and face in which the forebrain fails to develop into 2 hemispheres). Abnormalities such as microcephaly, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum or olfactory bulbs can occur. Facial anomalies may include ocular abnormalities, hypotelorism and dental anomalies. Most serious is the occurrence of pituitary dysfunction, which occurs in 15 to 25% of patients. After initial blood testing, clinical monitoring for at least 12 months is recommended, with poor or slowing growth at one year a positive predictor requiring further investigation. Figure 1: Axial CT demonstrates pyriform aperture stenosis (top) in contrast to bilateral choanal atresia (below)
2 Diagnosis History and Examination CNPAS presents like other causes of nasal airway obstruction with cyclical cyanosis, respiratory distress, feeding difficulties and failure to thrive. Failure to pass a nasogastric tube suggests choanal atresia or CNPAS, the difference being the level of obstruction. Obstruction within the 1 st 1cm is typical of CNPAS, while obstruction beyond 3cm is more likely to signify choanal atresia. Bilateral choanal atresia is typically diagnosed very early, but the diagnosis of CNPAS may be delayed. Some craniofacial syndromes e.g. Crouzon syndrome may present with similar signs and symptoms, but have stenosis affecting the entire length of the nose. They are not amenable to surgical correction and a tracheostomy should be offered instead. Examination of the nasal cavity with a nasendoscope should generate a high degree of suspicion, especially when unable to pass the scope into the nose. Examination of the oral cavity may reveal an absent frenulum of the upper lip and may indicate the presence of a solitary median maxillary central incisor (SMMCI) syndrome. As a manifestation of holoprosencephaly, it should prompt investigation of other midline abnormalities of the brain, cranial bones and maxilla. Consequently, failure to pass a 5Fr catheter or 1.9mm endoscope through the anterior third of the nose should prompt further investigation. diagnostic of CNPAS (Figures 1, 2). This measurement however does not determine the need for surgical intervention, as this would depend on the clinical presentation. Figure 2: Axial CT scan demonstrating 5mm measurement of pyriform aperture stenosis Figure 3: Axial CT scan demonstrating solitary median maxillary central incisor Other radiological features should also be reviewed, including the presence of a midline bony ridge on the underside of the hard palate, and particularly the presence of a solitary median maxillary central incisor (Figures 3, 4). The presence of the latter is an indication for MRI scan and chromosomal analysis if available. Investigations When CNPAS is suspected, a craniofacial CT scan with 2mm slices will confirm the diagnosis. One study reported the average width of the pyriform aperture in CNPAS to be 8.5mm, compared to 16.9mm in a control group 1. A pyriform aperture of >11mm in a term infant is considered Figure 4: Median maxillary central incisor 2
3 Management Immediate The baby may present with varying degrees of respiratory distress. The patient should be admitted to a neonatal intensive care unit with continuous oxygen saturation monitoring. Significant distress may require an oral airway, as is used for newborns with bilateral choanal atresia (Figure 5). An oral airway is generally adequate to temporarily secure an airway. Other options include high flow oxygen administered via nasal prongs, a McGovern Nipple, a standard feeding bottle teat or dummy with the tip cut off (Figure 6), or a Guedel oropharyngeal airway (Figure 7). Feeding can be established via an orogastric tube until nasal patency is achieved. Neonatologists, geneticists, paediatric ENT and paediatricians should be consulted. Conservative Conservative management is the first line of treatment for CNPAS to allow the baby to grow beyond the 3 months age of obligate nasal breathing and to potentially avoid surgery. Measures may include nasal irrigation with saline, nasal decongestants, short-term xylometazoline drops, or intranasal dexamethasone drops. Children that respond to conservative treatment should be closely monitored following discharge from hospital for apnoeic episodes, cyanosis, sleep disordered breathing, respiratory infections and poor growth. Failed conservative management typically declares itself within the first 3 weeks of treatment. Such children require surgery by the end of the first month. Indications for surgery Figure 5: Oral airway secured with tape Figure 6: Standard dummy with the tip cut off Figure 7: Guedel oropharyngeal airway Surgery is indicated if conservative management fails. Indications for surgical intervention include apnoeic episodes cyanosis poor growth failure to thrive inability to wean from airway assistance Predicting failure of conservative management is difficult. One study found a pyriform aperture measurement of <5.7mm had an 88% sensitivity and specificity for predicting surgical intervention 2. It is important to note that studies have suggested that there may often be no correlation with the circumference of the nasal inlet, em- 3
4 phasising that every baby has a different ability to recover from airway obstruction. Surgical options A sublabial approach is most common used as it permits lateral drilling of the nasal process of the maxilla. This technique is described below. Postoperative nasal stenting is the norm, although the optimal duration for stenting is a matter of debate. Balloon dilatation has also been used 3. A 7mm airway balloon is inflated to a pressure of 10 atmospheres for 5min, with subsequent nasal stenting with a 14Fr nasopharyngeal airway. This provided a satisfactory nasal airway at 1, 2 and 12 months without further procedures being required. Although only a case report, this technique may provide at worst a temporising measure until further equipment and expertise is sought as required. Figure 8: Blanching of alveolar mucosa following infiltration of local anaesthetic Surgical technique A sublabial approach is used The procedure is done under general anaesthesia with the baby intubated transorally Secure the endotracheal tube in a position that allows good access to the oral cavity A head ring and shoulder roll can be used Drape to protect the eyes, leaving the nose, midface and mouth accessible Prepare the nose with neurosurgical pledgets soaked in nasal decongestant Using a dental syringe, infiltrate local anaesthetic (1% lidocaine with 1: adrenaline) into the upper gingival sulcus and pyriform aperture mucosa (Figure 8) Make a 1.5cm sublabial incision with a 15 blade down to bone, taking care not to damage the soft bone overlying the dental buds (Figure 9) Figure 9: Sublabial incision and elevation of periosteum over maxilla with Cottle s elevator Dissect subperiosteally to expose the anterior nasal spine and the floor of each nostril, remaining anterior to the inferior turbinates to avoid injury to the nasolacrimal system (Figures 9, 10) Use a 2mm coarse diamond drill to widen the pyriform aperture laterally (Figure 11) Avoid drilling inferiorly to avoid the tooth buds 4
5 Use the CT scan as a guide and the inferior turbinate as a surgical landmark to obtain an optimal depth of drilling Continue drilling until the nasal cavity can accommodate a 3.5 endotracheal tube bilaterally Liston dilators can be used once the anterior drilling is complete As in choanal atresia repair, while dilating it is important to keep a Liston dilator in the opposite nasal cavity to prevent the nasal septum from being displaced (Figure 12) Figure 12: Endotracheal tube and Liston dilator (16Fr) in opposing nostrils Figure 10: Identification of right pyriform aperture, the anterior nasal spine and the nasal process of the maxilla Figure 11: 2mm coarse diamond drill used to remove bone from nasal process of maxilla Replace the nasal mucosa Some surgeons recommend making a releasing incision in the mucosa along the floor of the nose Create stents by trimming size 3.5 endotracheal tubes Insert each stent into the nose Ensure the tips of the stents are in the oropharynx just below the soft palate To prevent the stents becoming dislodged, a suture is passed between the tips of the tubes as follows: o Pass a small suction catheter down each tube so that the catheters protrude into the oropharynx o Grasp the ends of the catheters and advance them out of the mouth o Tie a single 3.0 silk suture to the end of each catheter o Pull the catheters back along the endotracheal tubes and out of the nose, carrying the sutures with them (Figure 13) o This loops the 3.0 silk suture around posterior end of the nasal 5
6 septum and secures the stents in each nasal cavity o It also obviates the need for posterior suturing of the tubes and allows for removal of the tubes in outpatients by simply cutting the anterior knot and pulling out the suture o Separate the anterior ends of the stents by using a piece of endotracheal tube as a bridge and passing the suture through small holes made in the sides of the stents (Figure 14) o Trim the stents to facilitate feeding (especially if breastfeeding) o It is important to measure the length of each stent to allow for accurate suctioning to maintain patency of the stents There is no consensus regarding the duration of stenting and varies from a few days to > 4 weeks. If removed too early, tissue dehiscence or restenosis may occur while longer durations are associated with a higher risk of pressure injury to the anterior nose and septum and formation of granulation tissue Postoperative care Figure 13: Stent secured in each nasal cavity by a 3.0 silk suture looped around posterior end of the nasal septum Monitoring in an intensive care unit for hours is recommended to ensure nasal airway patency Care of the stents is critical with regular irrigation with saline and suctioning to maintain patency Suctioning should be done to the ends of the tubes (measured) to ensure no trauma to the posterior pharyngeal wall occurs Use a suction catheter twice the size of the ETT e.g. 7Fr catheter for a 3.5 ETT Once the stents have been removed, use nasal decongestants in conjunction with normal saline drops to minimise oedema and crusting. Intranasal corticosteroids such as fluticasone can be used over the ensuing weeks Complications Figure 14: Middle bridge formed from ETT to keep the stents from migrating and the suture from injuring the columella Take care intraoperatively to prevent injury to the nasal mucosa, tooth buds, nasolacrimal ducts and inferior turbinates Inspect the nostril daily for signs of pressure areas from the stents Feeding difficulties are not uncommon, even with adequate nasal patency 6
7 Restenosis of the pyriform aperture is not uncommon and should be checked for if symptoms recur Long term follow-up Long term care should involve a general paediatrician. Consider airway and feeding difficulties, particularly requiring hospital readmission. If signs of restenosis do occur and are symptomatic, then re-expansion may be required e.g. with a balloon or Liston dilator as it is mostly a soft tissue stenosis. If pituitary deficiency has been noted, then long-term endocrinology follow-up is required. References 1. Belden CJ, Mancuso AA, Schmalfuss I M. CT features of congenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis: initial experience. Radiology 213, 1999; Wormald R, Hinton-Bayre A, Bumbak P et al. Congenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis 5.7mm or less is associated with surgical intervention: A pooled case series. Int J Ped Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;79(11) Gungor AA, Reiersen DA. Balloon dilatation for congenital nasal piriform aperture stenosis (CNPAS): a novel conservative technique. Am J Otolaryngol. 2014; 35(3) Authors Graeme Van Der Meer MBChB MMed(ENT) Paediatric ORL Consultant Starship Children s Health Grafton, Auckland, New Zealand graemevdm@gmail.com Paediatric Section Editor Nico Jonas MBChB, FCORL, MMed Paediatric ENT Consultant Addenbrookes Hospital Cambridge University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Cambridge, United Kingdom nicojonas@gmail.com Editor Johan Fagan MBChB, FCORL, MMed Professor and Chairman Division of Otolaryngology University of Cape Town Cape Town, South Africa johannes.fagan@uct.ac.za THE OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY The Open Access Atlas of Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Operative Surgery by Johan Fagan (Editor) johannes.fagan@uct.ac.za is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution - Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported License John Wood FRACS, MBBS, MSurg, BSocSci (Hons) BA(Hons) Paediatric ORL Fellow Starship Children s Health Grafton, Auckland, New Zealand drjmwood@gmail.com 7
8 8
Congenital Nasal Pyriform Aperture Stenosis Is There a Role for Nasal Dilation?
 Research Original Investigation Is There a Role for Nasal Dilation? Todd M. Wine, MD; Kavita Dedhia, MD; David H. Chi, MD IMPORTANCE Congenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis (CNPAS) may require sublabial
Research Original Investigation Is There a Role for Nasal Dilation? Todd M. Wine, MD; Kavita Dedhia, MD; David H. Chi, MD IMPORTANCE Congenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis (CNPAS) may require sublabial
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY LARYNGOMALACIA Laryngomalacia is characterised by collapse of the supraglottic tissues on inspiration, and is the most common cause of
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY LARYNGOMALACIA Laryngomalacia is characterised by collapse of the supraglottic tissues on inspiration, and is the most common cause of
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
Clinical course and implications of congenital nasal pyriform stenosis and solitary median maxillary central incisor in a newborn: a case report
 Günther et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:215 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Clinical course and implications of congenital nasal pyriform stenosis and solitary median
Günther et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:215 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Clinical course and implications of congenital nasal pyriform stenosis and solitary median
Introduction Material & Methods Results Discussion Conclusion
 Dr Maryam Ali AlQaydi,MBBS R5 otolaryngology head & neck surgery In Saudi board From UAE, Ministry of Health 19/3/2015 Outline Introduction Material & Methods Results Discussion Conclusion Choanal Atresia
Dr Maryam Ali AlQaydi,MBBS R5 otolaryngology head & neck surgery In Saudi board From UAE, Ministry of Health 19/3/2015 Outline Introduction Material & Methods Results Discussion Conclusion Choanal Atresia
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Cleft Lip and Palate: The Effects on Speech and Resonance
 Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY ENDOSCOPIC DACRYOCYSTORHINOSTOMY (DCR) SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Hisham Wasl, Darlene Lubbe Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY ENDOSCOPIC DACRYOCYSTORHINOSTOMY (DCR) SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Hisham Wasl, Darlene Lubbe Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical
Advanced Airway Management. University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track
 Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY VERTICAL PARTIAL LARYNGECTOMY Management of small tumours involving the true vocal folds can be contentious. Tumour control is achieved
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY VERTICAL PARTIAL LARYNGECTOMY Management of small tumours involving the true vocal folds can be contentious. Tumour control is achieved
Nasotracheal Intubation for Head and Neck Surgery
 Nasotracheal Intubation for Head and Neck Surgery Dr A J Cartwright Introduction History Anatomy Indications for Technique of Complications Contraindications Conclusions History First described in 1902
Nasotracheal Intubation for Head and Neck Surgery Dr A J Cartwright Introduction History Anatomy Indications for Technique of Complications Contraindications Conclusions History First described in 1902
Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting. dacryocystorhinostomy with and
 Original Research Article Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting Kirti Ambani 1, Niraj Suri 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Assistant Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
Original Research Article Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting Kirti Ambani 1, Niraj Suri 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Assistant Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient. Barts and The London NHS Trust
 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Upper Airway Obstruction
 Upper Airway Obstruction Adriaan Pentz Division of Otorhinolaryngology University of Stellenbosch and Tygerberg Hospital Stridor/Stertor Auditory manifestations of disordered respiratory function ie noisy
Upper Airway Obstruction Adriaan Pentz Division of Otorhinolaryngology University of Stellenbosch and Tygerberg Hospital Stridor/Stertor Auditory manifestations of disordered respiratory function ie noisy
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY THE NASAL SEPTUM IN RHINOPLASTY: BASIC SEPTOPLASTY TECHNIQUES FWA Otten Introduction Septal corrections form an important step in rhinoplastic
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY THE NASAL SEPTUM IN RHINOPLASTY: BASIC SEPTOPLASTY TECHNIQUES FWA Otten Introduction Septal corrections form an important step in rhinoplastic
Rhinology Products. Rhinology Products. Superior solutions for superior patient care.
 Rhinology Products Superior solutions for superior patient care. The Doyle Open-Lumen Splint addresses the problem of potential closure of the airway lumen by a hypertrophied turbinate. We also offer the
Rhinology Products Superior solutions for superior patient care. The Doyle Open-Lumen Splint addresses the problem of potential closure of the airway lumen by a hypertrophied turbinate. We also offer the
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
Choanal Atresia - Corrective Surgery Using Hegar's Dilators
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Choanal Atresia - Corrective Surgery Using Hegar's Dilators Authors: Vikas Sinha*, Niral Modi**, Viral A. Chhaya***, Vishal Parmar****,
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Choanal Atresia - Corrective Surgery Using Hegar's Dilators Authors: Vikas Sinha*, Niral Modi**, Viral A. Chhaya***, Vishal Parmar****,
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PAEDIATRIC TRACHEOSTOMY The open tracheostomy technique in the paediatric patient differs from that undertaken in the adult. In the paediatric
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PAEDIATRIC TRACHEOSTOMY The open tracheostomy technique in the paediatric patient differs from that undertaken in the adult. In the paediatric
MAXILLARY SWING APPROACH TO THE NASOPHARYNX
 CC-BY-NC 3.0 MAXILLARY SWING APPROACH TO THE NASOPHARYNX Pathology in the nasopharynx can be addressed endoscopically, or as an open procedure. The advantage of an open procedure is that it affords better
CC-BY-NC 3.0 MAXILLARY SWING APPROACH TO THE NASOPHARYNX Pathology in the nasopharynx can be addressed endoscopically, or as an open procedure. The advantage of an open procedure is that it affords better
PUMANI bcpap GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS. An Overview of the Pumani bcpap, Indications for bcpap, and Instructions for Use
 An Overview of the Pumani bcpap, Indications for bcpap, and Instructions for Use What is bcpap? bcpap stands for bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Sometimes called Continuous Distending Pressure,
An Overview of the Pumani bcpap, Indications for bcpap, and Instructions for Use What is bcpap? bcpap stands for bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Sometimes called Continuous Distending Pressure,
Management of Upper Airway Obstruction in Pierre Robin Sequence
 Management of Upper Airway Obstruction in Pierre Robin Sequence South Wales Cleft Team Pierre Robin Sequence Triad of cleft palate, micrognathia and airway obstruction was described by St Hilaire in 1822,
Management of Upper Airway Obstruction in Pierre Robin Sequence South Wales Cleft Team Pierre Robin Sequence Triad of cleft palate, micrognathia and airway obstruction was described by St Hilaire in 1822,
Practical Application of CPAP
 CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
Dr.Bharghavi.M 2 nd year post graduate Dept of Anaesthesia
 DIFFICULT AIRWAY CANNOT VENTILATE, CANNOT INTUBATE. Dr.Bharghavi.M 2 nd year post graduate Dept of Anaesthesia Difficult airway According to AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ANAESTHESIOLOGISTS Difficult Airway is defined
DIFFICULT AIRWAY CANNOT VENTILATE, CANNOT INTUBATE. Dr.Bharghavi.M 2 nd year post graduate Dept of Anaesthesia Difficult airway According to AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ANAESTHESIOLOGISTS Difficult Airway is defined
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE. Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic
 MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions
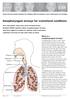 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
NASAL OBSTRUCTION. Andy Whyte PERTH RADIOLOGICAL CLINIC UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE UNIVERSITY OF WA
 NASAL OBSTRUCTION Andy Whyte PERTH RADIOLOGICAL CLINIC UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE UNIVERSITY OF WA INTRODUCTION sinonasal imaging focuses on structural abnormalities of the POSTERIOR (BONY 3/4 ) of the nose
NASAL OBSTRUCTION Andy Whyte PERTH RADIOLOGICAL CLINIC UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE UNIVERSITY OF WA INTRODUCTION sinonasal imaging focuses on structural abnormalities of the POSTERIOR (BONY 3/4 ) of the nose
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
CLEFT LIP and PALATE. Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden. Information about Cleft Lip and Palate. English version
 CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes. Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center
 Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Mammals. Dr. Olaf Oftedal - National Zoological Park. Dr. Peter Emily - Father of Veterinarian Dentistry.
 Mammals There are 4640 species of mammals. Most are ideal. Humans are but one species. Mammals are unique in that they have an epiglottis. All species breastfeed their young. Dr. Olaf Oftedal - National
Mammals There are 4640 species of mammals. Most are ideal. Humans are but one species. Mammals are unique in that they have an epiglottis. All species breastfeed their young. Dr. Olaf Oftedal - National
Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction
 Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative.
Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative.
DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE. J Harewood DDS MA MS
 DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE J Harewood DDS MA MS CLEFT LIP/PALATE: INCIDENCE Cleft lip and/or palate 1:1000 Varies with race Japan: 20: 10 000 Western Europe: 12: 10 000 USA: 10.2:10 000
DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE J Harewood DDS MA MS CLEFT LIP/PALATE: INCIDENCE Cleft lip and/or palate 1:1000 Varies with race Japan: 20: 10 000 Western Europe: 12: 10 000 USA: 10.2:10 000
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Figure 1. Basic anatomy of the palate
 CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY TOTAL GLOSSECTOMY FOR TONGUE CANCER Johan Fagan Total glossectomy has significant morbidity in terms of intelligible speech, mastication,
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY TOTAL GLOSSECTOMY FOR TONGUE CANCER Johan Fagan Total glossectomy has significant morbidity in terms of intelligible speech, mastication,
Bilateral Complete Congenital Choanal Atresia in an Adult Managed Endoscopically with Mucosal Flaps without Stenting
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Case Report Volume 6 Issue 3: 122 2016 Bilateral Complete Congenital Choanal Atresia in an Adult Managed ally with Mucosal Flaps without Stenting Sujata Apurva Gawai 1 * and Nishit J Shah
ISSN: 2250-0359 Case Report Volume 6 Issue 3: 122 2016 Bilateral Complete Congenital Choanal Atresia in an Adult Managed ally with Mucosal Flaps without Stenting Sujata Apurva Gawai 1 * and Nishit J Shah
October Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE
 October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 Original Article Full text online at http://www.jiaps.com Trans-nasal puncture for bilateral congenital choanal atresia Alireza Alam Sahebpor, Vajihe Ghaffari, Ali Reza Elisay Department of Pediatric Surgery,
Original Article Full text online at http://www.jiaps.com Trans-nasal puncture for bilateral congenital choanal atresia Alireza Alam Sahebpor, Vajihe Ghaffari, Ali Reza Elisay Department of Pediatric Surgery,
Impact of tongue size on occlusion.
 Impact of tongue size on occlusion. D1 D2 Macroglossia (large tongue) in patient with severe OSA D3 Massive tongue can impact position of teeth. D4 This massive tongue has contributed to Class III occlusion.
Impact of tongue size on occlusion. D1 D2 Macroglossia (large tongue) in patient with severe OSA D3 Massive tongue can impact position of teeth. D4 This massive tongue has contributed to Class III occlusion.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE The XprESS Multi-Sinus Dilation System for the treatment of 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The XprESS
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE The XprESS Multi-Sinus Dilation System for the treatment of 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The XprESS
What is Craniosynostosis?
 What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology. Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity
 Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies
 Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY
 OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Treatments Chapter 2
 Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Treatments Chapter 2 CAUSES OF SNORING AND SLEEP APNEA We inhale air through our nose and mouth. From the nostrils, air flows
Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Treatments Chapter 2 CAUSES OF SNORING AND SLEEP APNEA We inhale air through our nose and mouth. From the nostrils, air flows
ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with
 REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES
 PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
General Medical Procedure. Emergency Airway Techniques (General Airway Protocol)
 General Medical Procedure Appropriate airway management is often the most important intervention a prehospital care provider makes, as ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation is crucial to the survival
General Medical Procedure Appropriate airway management is often the most important intervention a prehospital care provider makes, as ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation is crucial to the survival
Alexander C Vlantis. Midline Step Mandibulotomy and Mandibulectomy 85
 10 Maxillary Swing Approach to the Nasopharynx Alexander C Vlantis Midline Step Mandibulotomy and Mandibulectomy 85 INTRODUCTION The nasopharynx may contain pathology that requires surgical intervention.
10 Maxillary Swing Approach to the Nasopharynx Alexander C Vlantis Midline Step Mandibulotomy and Mandibulectomy 85 INTRODUCTION The nasopharynx may contain pathology that requires surgical intervention.
Airway/Breathing. Chapter 5
 Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Trust Guideline for the Management of: A Neonate with Difficult Airway
 For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job titles of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by: Neonatal unit, Delivery Suite,
For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job titles of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by: Neonatal unit, Delivery Suite,
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line.
 Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line. After reading the article, the staff will be able to: Define facial trauma
Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line. After reading the article, the staff will be able to: Define facial trauma
TREATMENT OF CLEFT PALATE ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA. By RANDELL CHAMPION, F.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Duchess of York Hospital for Babies, Manchester
 TREATMENT OF CLEFT PALATE ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA By RANDELL CHAMPION, F.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Duchess of York Hospital for Babies, Manchester IN spite of the present-day technique and medical research
TREATMENT OF CLEFT PALATE ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA By RANDELL CHAMPION, F.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Duchess of York Hospital for Babies, Manchester IN spite of the present-day technique and medical research
BONE GRAFTING IN TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 337
 PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
Lawrence A. Kotlow, DDS
 The Influence of the Maxillary Frenum on the Development and Pattern of Dental Caries on Anterior Teeth in Breastfeeding Infants: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment Lawrence A. Kotlow, DDS [AQ: 1] Keywords:
The Influence of the Maxillary Frenum on the Development and Pattern of Dental Caries on Anterior Teeth in Breastfeeding Infants: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment Lawrence A. Kotlow, DDS [AQ: 1] Keywords:
Minimally Invasive Technique of Dacryocystorhinostomy
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Research Protocol Mohammad Idrees* Consultant Ophthalmology, REDO Eye Hospital, Rawalpindi, Pakistan *Corresponding Author: Mohammad Idrees, Consultant Ophthalmology,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Research Protocol Mohammad Idrees* Consultant Ophthalmology, REDO Eye Hospital, Rawalpindi, Pakistan *Corresponding Author: Mohammad Idrees, Consultant Ophthalmology,
Dundee Focused FRCS ENT Viva Course
 Dundee Focused FRCS ENT Viva Course Choanal atresia Nasal masses Craniofacial Micrognathia Glossomegaly IM Retropharyngeal abscess Caustics Vascular compression FB Bacterial tracheitis TOF Bronchiolitis
Dundee Focused FRCS ENT Viva Course Choanal atresia Nasal masses Craniofacial Micrognathia Glossomegaly IM Retropharyngeal abscess Caustics Vascular compression FB Bacterial tracheitis TOF Bronchiolitis
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE DEFINING TERMS PRIMARY PALATE- Structures anterior to the incisive foramen Includes the nose, lip alveolus, and hard palate back to the incisive
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE DEFINING TERMS PRIMARY PALATE- Structures anterior to the incisive foramen Includes the nose, lip alveolus, and hard palate back to the incisive
MedStar Health considers Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty medically necessary for the following indications:
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.038.MH Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar CareFirst
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.038.MH Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar CareFirst
Basic Science Review Wound Healing
 Subglottic Stenosis Deborah P. Wilson, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Norman Friedman, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 14, 1999 Basic Science
Subglottic Stenosis Deborah P. Wilson, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Norman Friedman, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 14, 1999 Basic Science
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide
 Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Embryo#1. Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد. 0 P a g e
 Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
Procedure No: Procedure Approved for Use By: WCCSS Divisional Quality Meeting. Date: May 2017
 Standard Operating Procedure (SOP): Standard operating procedure for Neonatal Difficult Airway Kit and Intubation Pathway Procedure No: 1 Document replaced: Version 1 Version: 2.0 Procedure Written By:
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP): Standard operating procedure for Neonatal Difficult Airway Kit and Intubation Pathway Procedure No: 1 Document replaced: Version 1 Version: 2.0 Procedure Written By:
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Department of Neurosurgery. Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly
 Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Other methods for maintaining the airway (not definitive airway as still unprotected):
 Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in
 The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in Congenital Lip and Palate Cases CHARLES E. HUGH H. JEROME E. HORTON, M.D. CRAWFORD, M.D. ADAMSON, M.D. SAMUEL BUXTON, D.D.S. REUBEN COOPER, M.S. JACK KANTER, D.D.S.
The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in Congenital Lip and Palate Cases CHARLES E. HUGH H. JEROME E. HORTON, M.D. CRAWFORD, M.D. ADAMSON, M.D. SAMUEL BUXTON, D.D.S. REUBEN COOPER, M.S. JACK KANTER, D.D.S.
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY CRICOTHYROIDOTOMY & NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Johan Fagan Cricothyroidotomy, also known as cricothyrotomy refers to the creation of a communication
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY CRICOTHYROIDOTOMY & NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Johan Fagan Cricothyroidotomy, also known as cricothyrotomy refers to the creation of a communication
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
Airway Anatomy. Soft palate. Hard palate. Nasopharynx. Tongue. Oropharynx. Hypopharynx. Thyroid cartilage
 Airway Anatomy Hard palate Soft palate Tongue Nasopharynx Oropharynx Hypopharynx Thyroid cartilage Airway Anatomy Hyoid bone Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Trachea Cricothyroid membrane Airway Anatomy
Airway Anatomy Hard palate Soft palate Tongue Nasopharynx Oropharynx Hypopharynx Thyroid cartilage Airway Anatomy Hyoid bone Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Trachea Cricothyroid membrane Airway Anatomy
Basic Airway Management
 Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Normal fetal face and neck
 Normal fetal face and neck Maria A. Calvo-Garcia, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Cincinnati, Ohio Disclosure I have no disclosures Goals & objectives
Normal fetal face and neck Maria A. Calvo-Garcia, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Cincinnati, Ohio Disclosure I have no disclosures Goals & objectives
Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies
 Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Royalties: Financial Disclosures Book: Kummer, AW. Cleft Palate
Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Royalties: Financial Disclosures Book: Kummer, AW. Cleft Palate
Case Report Mid Facial Degloving Procedure: Managing A Case of Multiple Mid Face Fractures with Significant External Deformity
 55 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(1): 51-56 Case Report Mid Facial Degloving Procedure: Managing A Case of Multiple Mid Face Fractures with Significant External Deformity Akhil Chndra Biswas 1,
55 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(1): 51-56 Case Report Mid Facial Degloving Procedure: Managing A Case of Multiple Mid Face Fractures with Significant External Deformity Akhil Chndra Biswas 1,
Discussing feline tracheal disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
Sohit Paul Kanotra M.D. Director, Pediatric Aerodigestive Center
 Sohit Paul Kanotra M.D. Director, Pediatric Aerodigestive Center Children s Hospital of New Orleans Assistant Professor, Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Louisiana State University. I do not have any
Sohit Paul Kanotra M.D. Director, Pediatric Aerodigestive Center Children s Hospital of New Orleans Assistant Professor, Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Louisiana State University. I do not have any
The Crooked Nose and its Functional Surgical Correction
 The Crooked Nose and its Functional Surgical Correction Armando González Romero Introduction The nose is a highly specialized organ of the respiratory system and is essential for homeostasis. The pathological
The Crooked Nose and its Functional Surgical Correction Armando González Romero Introduction The nose is a highly specialized organ of the respiratory system and is essential for homeostasis. The pathological
Overview. The ENT Manifestations of Tongue and Lip Tie. Bone formation and stress. Facial Skeleton (adult)
 The ENT Manifestations of Tongue and Lip Tie Bobby Ghaheri, MD The Oregon Clinic Portland, Oregon www.drghaheri.com Physics The Palate Sleep Apnea Dental Problems Speech Overview Facial Skeleton (child)
The ENT Manifestations of Tongue and Lip Tie Bobby Ghaheri, MD The Oregon Clinic Portland, Oregon www.drghaheri.com Physics The Palate Sleep Apnea Dental Problems Speech Overview Facial Skeleton (child)
Total Maxillectomy. A review. Dr T Balasubramanian
 Total Maxillectomy A review Dr T Balasubramanian Maxillectomy a review Introduction: The concept of maxillectomy was first described by Lazars in 1826. After this description it took nearly three years
Total Maxillectomy A review Dr T Balasubramanian Maxillectomy a review Introduction: The concept of maxillectomy was first described by Lazars in 1826. After this description it took nearly three years
A METHOD OF INTERNAL SPLINTING FOR UNSTABLE NASAL FRACTURES. A. J. SEAR, M.B.,Ch.B., B.D.S., F.D.S.
 British Journal of Oral Surgery 14 (I 977) 203-209 A METHOD OF INTERNAL SPLINTING FOR UNSTABLE NASAL FRACTURES A. J. SEAR, M.B.,Ch.B., B.D.S., F.D.S. Worcester Royal Injirmary Summary. A method of intra-nasal
British Journal of Oral Surgery 14 (I 977) 203-209 A METHOD OF INTERNAL SPLINTING FOR UNSTABLE NASAL FRACTURES A. J. SEAR, M.B.,Ch.B., B.D.S., F.D.S. Worcester Royal Injirmary Summary. A method of intra-nasal
Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal and Anterior Mediastinal Abscess
 Hindawi Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 1848945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1848945 Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal
Hindawi Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 1848945, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1848945 Case Report Complete Obstruction of Endotracheal Tube in an Infant with a Retropharyngeal
Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures Alice Z.
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures Alice Z.
An important indication for imaging the anterior skull base
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.C. Hughes M.J. Kaduthodil D.J.A. Connolly P.D. Griffiths Dimensions and Ossification of the Normal Anterior Cranial Fossa in Children BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interpretation of CT of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.C. Hughes M.J. Kaduthodil D.J.A. Connolly P.D. Griffiths Dimensions and Ossification of the Normal Anterior Cranial Fossa in Children BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interpretation of CT of
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
