Module 29. Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Devices
|
|
|
- Aubrey Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Home Health Aide Training Module 29. Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Devices Goal The goal of this module is to prepare participants to assist clients with a variety of equipment, supplies, and devices that are prescribed to assist the client with ambulation, elimination, or respiration. Time 8 hours [2 hours on the first day; 6 hours on the second day] Trainer s Manual Page 29.1
2 Day 1 Activities Teaching Methods Time 1. Introduction to Prescribed Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Devices 2. Your Role in Assisting with the Use of ACE Bandages, Enemas, and Douches Day 2 3. Overview of Respiratory Conditions Interactive presentation, smallgroup discussion, and largegroup discussion Interactive presentations, demonstration, pairs work and reporting Large-group exercise, smallgroup work and large-group discussion, and interactive presentation Interactive presentation with demonstrations 4. Introduction to the Nebulizer and CPAP Machines 5. Working with Oxygen Small-group work, interactive presentation, and demonstrations 6. The Aide s Role in Assisting with Small-group work, large-group Respiratory Equipment, Supplies, reporting and discussion, and and Devices interactive presentation 7. Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Devices: Practice Lab and Return Demonstrations 8. Identifying Your Feelings about Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, Practice triads and return demonstrations Small-group work and largegroup discussion 30 minutes 1 hour and 30 minutes 45 minutes 40 minutes 50 minutes 45 minutes 2 hours and 30 minutes 30 minutes Supplies Flip chart, markers, and tape Paper and pencils Index cards CPAP machine Nebulizer Trainer s Manual Page 29.2
3 Air compressor Oxygen tank Nasal cannula Oxygen mask Liquid oxygen reservoir and oxygen concentrator (if available) Learner s Book 1. What Are Prescribed Medical Equipment,? 2. Why Are Prescribed Medical Equipment, Important? 3. Basic Information about Skin and the Medical Equipment Prescribed to Prevent Skin Breakdown 4. Basic Information about Elimination and the Medical Equipment Prescribed for It 5. Basic Information about Asthma 6. Basic Information about COPD 7. Basic Information about Sleep Apnea 8. Medication Nebulizer 9. CPAP Machine Illustration 10. Safety Precautions to Follow When Oxygen Is in Use 11. Parts of an Oxygen Tank 12. Oxygen Concentrator 13. Stories from Home Health Aides Skills Checklists Skills Checklist 1. Assisting with an ACE Bandage (DOH Procedure Checklist E-1) Skills Checklist 2. Assisting with the Use of a Commercially Prepared Enema (DOH Procedure Checklist E-5) Skills Checklist 3. Assisting with the Use of a Soap Solution Enema (DOH Procedure Checklist E-6) Skills Checklist 4. Assisting with the Use of a Douche (DOH Procedure Checklist E-7) Skills Checklist 5. Assisting with the Use of a Commercially Prepared Douche (DOH Procedure Checklist E-8) Skills Checklist 6. Assisting with the Use of a Medication Nebulizer and Air Compressor (DOH Procedure Checklist E-11) Skills Checklist 7. Assisting with the Use of a CPAP Machine (DOH Procedure Checklist E-12) Trainer s Manual Page 29.3
4 Skills Checklist 8. Assisting with the Use of an Oxygen Tank and Liquid Oxygen Reservoir (DOH Procedure Checklist E-10) Skills Checklist 9. Assisting with the Use of an Oxygen Concentrator (DOH Procedure Checklist E-9) Handouts Handout 1. Key Terms Handout 2. Summary of Key Information Advance Preparation Review all the training instructions and learner s materials for this module. Note that icons are used to remind the trainer of the following: When you are presenting or covering Key Content in the discussion. (Key Content is also addressed in many of the handouts.) When it is important to ask a particular question to get participants input. When it is time to refer to the Learner s Book. When it is time to distribute a skills checklist. When it is time to distribute a worksheet. When it is time to distribute and discuss a handout. Copy all handouts and worksheets for participants Prepare copies of the skills checklists. You will need one copy for each participant, to be collected and reused for subsequent trainings. Laminating the skills checklists will make them more durable and reusable. Gather all necessary supplies and equipment. Please note that the Key Content is meant to be background information for the trainer. DO NOT READ OUT LOUD TO PARTICIPANTS. Trainer s Manual Page 29.4
5 Activity 1. Introduction to Prescribed Medical Equipment, Supplies and Devices Prepare the flip chart page, Learning Agenda (Step 1). Activity 2. Your Role in Assisting with the Use of ACE Bandages, Enemas, and Douches Prepare the flip chart page, Summary Questions for Skills Checklists (Step 8). Activities 3 to 6 No advance preparation needed. Activity 7. Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, : Practice Lab and Return Demonstrations Set up workstations. Organize the equipment for the number of practice triads that you will have. You should have enough equipment so every triad can be practicing a procedure for assisting with medical equipment, supplies, and devices at all times.. Have the extra set of skills checklists ready for trainers to use in assessing return demonstrations. Additional trainers may be needed for this activity, to assist, monitor, and assess return demonstrations. If possible and if needed, be prepared to observe participants who need to do return demonstrations for skills covered prior to this module. Activity 8. Identifying Your Feelings about Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, No advance preparation needed. Trainer s Manual Page 29.5
6 Activity 1. Introduction to Prescribed Medical Equipment, 30 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Name at least three types of prescribed medical equipment, supplies, or devices. Describe at least one way that prescribed medical equipment, supplies, or devices may benefit for the client. Key Content Prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices play an important role in the well-being of some clients, both in terms of physical health and in terms of quality of life. Medical equipment, supplies, and devices may be prescribed to assist a client with: Mobility Preventing Skin Breakdown Respiration Elimination Activity Steps Interactive Presentation 10 minutes 1. Introduce the activity. Post the prepared flip chart page with the Learning Agenda for this module and review. Ask if there are any questions. Trainer s Manual Page 29.6
7 Flip Chart LEARNING AGENDA: Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, Understand why medical equipment, supplies, and devices are important and how they are used. Understand your role in assisting clients with prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices. Explore your own feelings and attitudes about assisting clients with prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices. 2. Define prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices. Explain that prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices help a client to gain or maintain functions of the body. Explain that this equipment may assist the client with one of four body functions or systems. 3. Refer to 1. What Are Prescribed Medical Equipment,? in the Learner s Book. Ask if there are any questions. Small-Group and Large-Group Discussion 20 minutes 4. Form small groups and give directions. Divide participants into groups of three to four people, and then refer to 2. Why Are Prescribed Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Devices Important? in the Learner s Book. Read the directions in the first paragraph out loud. Let the groups know that they will have ten minutes to read the three stories on 2 and to answer the discussion questions for each of them. Ask the participants if they have any questions. Trainer s Manual Page 29.7
8 5. Debrief with participants. After ten minutes, ask the small groups to return to the large group. Then, read the first story out loud and ask one or two small groups how they answered the discussion questions for this story. Next, read the second story out loud and ask one or two different small groups how they answered the discussion questions. Repeat this process with the third story. 6. Summarize this activity. Point out that the clients in these three stories all were able to improve their bodily functions when medical equipment was prescribed for them. Emphasize that, once these clients had the medical equipment they needed, they all felt better and the quality of their lives improved. Explain that, in the rest of this module, participants will learn about their own role in assisting clients with prescribed medical equipment. Trainer s Manual Page 29.8
9 Activity 2. Your Role in Assisting with the Use of ACE Bandages, Enemas, and Douches 1 hour and 30 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Describe their role in assisting with ACE bandages, enemas, and douches. Describe what to observe, record, and report when assisting with the ACE bandages, enemas, and douches. Key Content The direct-care worker has an important role in assisting with prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices. When assisting with prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices, safety is very important! Always wash your hands before and after each procedure and wear gloves or other protective personal equipment if you may be exposed to body fluids. You will need to carefully record the procedures you assist with. Recording must be done accurately, carefully, and promptly. Trainer s Manual Page 29.9
10 Activity Steps Interactive Presentation 5 minutes 1. Introduce the activity. Explain that this activity will focus on their role in assisting with certain kinds of prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices. Note that participants already learned about their role in assisting with prescribed medical equipment and devices related to mobility in the module on Assisting with Ambulation and Transfers; Making a Bed. In this module, they will learn about their role in assisting with an ACE bandage and with equipment, supplies, and devices related to elimination and respiration. 2. Refer to 3. Basic Information about Skin and Medical Equipment Prescribed to Prevent Skin Breakdown in the Learner s Book. Ask if there are any questions. Teaching Tip Note to participants that they will learn more about special skin care and assisting with a dressing change in other modules. Demonstration 10 minutes 3. Demonstrate the procedure. Show participants an ACE bandage. Then ask for a volunteer to help you demonstrate how to put an ACE bandage on a client. Apply the ACE bandage, following the steps described in Skills Checklist 1. Assisting with an ACE Bandage. Explain that assisting with an ACE bandage is done only under special circumstances, which means that the nurse would teach them how to follow the procedure described on the skills checklist in the client s home. 4. Distribute and review Skills Checklist 1. Assisting with an ACE Bandage. 5. Describe what to observe, record, and report. Explain that it is important for participants to observe the client s skin for any signs of discoloration, irritation, or swelling. If these are observed, they should be reported to the nurse. Ask participants if they have any questions. Trainer s Manual Page 29.10
11 Interactive Presentation 10 minutes 6. Discuss and display equipment, supplies, and devices prescribed for elimination. Refer to 4. Basic Information about Elimination and Medical Equipment Prescribed for It in the Learner s Book. Show a sample of each item as you are discussing its purpose. Explain that participants will learn about assisting with catheters, catheter tubing, and drainage bags in the module on Assisting with Ostomy Care. Pairs Work 20 minutes 7. Form pairs and give instructions. Divide the participants into pairs. Explain that each pair will be given a skills checklist that describes their role in assisting with a procedure related to elimination. Explain that they will read this procedure with their partner. They will then answer some questions about this procedure. These questions will help them remember important safety information about the procedure, and also help them remember what they need to observe, record, and report. 8. Distribute skills checklists and give remaining instructions. Distribute Skills Checklist 2. Assisting with the Use of a Commercially Prepared Enema to one pair. Each of the remaining pairs should get one of the following skills checklists: Skills Checklist 3. Assisting with the Use of a Soap Solution Enema Skills Checklist 4. Assisting with the Use of a Douche Skills Checklist 5. Assisting with the Use of a Commercially Prepared Douche 9. Post and review the flip chart page with summary questions. Make sure participants understand that they should read their skills checklist with their partner and then work together to answer the questions on the flip chart. Note that they will have 15 minutes for this activity. After 15 minutes, they will come back to the large group to share their answers to these questions with everybody. Trainer s Manual Page 29.11
12 Flip Chart SUMMARY QUESTIONS FOR SKILLS CHECKLISTS: 1. What steps will help you prevent the spread of infection? 2. What do you need to observe (look for) during this procedure? 3. What might you need to report to the supervising nurse? 4. What do you need to record after this procedure? Teaching Tips Do not distribute all four skills checklists to all of the participants yet because this might be confusing or overwhelming. Instead, give one copy of each skills checklist to the pair that is assigned to read it and discuss it. After the pairs work, participants will get copies of all skills checklists. You may not have enough participants to distribute one skills checklist to each pair. If this is the case, you can assign more than one skills checklist to each pair. 10. Monitor the pairs work. Be sure to observe the pairs carefully while they are working to make sure they have understood your directions, and to offer help as needed. Ask them to wrap up after 15 minutes. Demonstration with Pairs Reporting 45 minutes 11. Demonstrate how to assist with using a commercially prepared enema. After the pairs have finished their work, distribute Skills Checklist 2. Assisting with the Use of a Commercially Prepared Enema to all the participants (except for the pair that has it already) and read it out loud. Demonstrate how to use the equipment or supplies, as appropriate. Note that they will practice these procedures later in this module. Ask the pair(s) that was assigned to this skills checklist to share their answers to the four discussion questions on the flip chart page. Briefly discuss their answers, clarifying or adding any information as needed. Trainer s Manual Page 29.12
13 Teaching Tip The pairs should stay seated together. This is because they will discuss another skills checklist with the same partner in the next activity. 12. Discuss Skills Checklists 3 through 5. Repeat Step 11 for each of the remaining skills checklists that were distributed to the pairs. 13. Summarize. Briefly review the importance of safety, including infection control, in the procedures discussed in this activity. Trainer s Manual Page 29.13
14 Activity 3. Overview of Respiratory Conditions 45 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Identify equipment, supplies, and devices that may be prescribed to clients to assist enhance respiratory function. Key Content There are many diseases and conditions that can have an impact on respiratory functioning. Some of the most common are: Asthma COPD Sleep apnea The respiratory equipment that the home health aide may assist with includes: The medication nebulizer and air compressor The CPAP machine The oxygen tank The liquid oxygen reservoir The oxygen concentrator There are some tasks that the home health aide is permitted to do, and some tasks that the home health aide is not permitted to do when assisting with respiratory equipment, supplies, and devices. There are also some tasks that the home health aide may assist with under special circumstances only. There are certain things that the aide will observe, record, and report. Trainer s Manual Page 29.14
15 Activity Steps Large-Group Exercise 10 minutes 1. Introduce respiration and conduct an experiment. Begin by explaining that respiration is the term used to describe how the body uses oxygen to sustain its vital functions. We bring oxygen into the body when we breathe. Explain that it is extremely important for the body to get enough oxygen. Demonstrate how important oxygen is for the body by conducting an experiment with participants: tell them that when you say go, you want them all to exhale all of the air in their lungs and see how long they can go without inhaling. Explain that you will count out loud for one minute (counting each second) so that participants can time themselves to see how long they can go without inhaling. Say go, and then count each second out loud for one minute. After one minute, ask participants how many seconds they were able to hold their breath. Then, point out that their experience with this experiment demonstrates that the body needs a constant supply of oxygen. Share the following facts about breathing and respiration: A person can only go without oxygen for only three to four minutes before brain cells start to die. The average person breathes 10 times per minute, 600 times per hour, over 14 thousand times per month and over five million times per year! Small-Group Work and Large-Group Discussion 15 minutes 2. Introduce small-group work. Next, explain that many diseases and conditions make it difficult for the body to get the oxygen it needs in order to function properly. Then explain that you would like participants to share their own experiences with these diseases and conditions. Divide participants into small groups of three to four people. Then explain that they will have ten minutes to discuss the following questions: Do you know anyone who has a respiratory condition or disease? What is the condition or disease? What are their symptoms? Trainer s Manual Page 29.15
16 3. Facilitate discussion. After ten minutes, ask the small groups to share with the large group the diseases and conditions that they discussed. Point out that, fortunately, there are many different types of equipment, supplies, and devices that can help clients who have these diseases and conditions. Explain that, later in the activity, they will be introduced to the equipment, supplies, and devices that may be prescribed to clients, and will also learn about their role in using them. Interactive Presentation 20 minutes 4. Review Learner s Book sections about asthma, COPD, and sleep apnea. Explain that participants will now learn about some of the most common respiratory diseases and conditions. Refer to 5. Basic Information about Asthma, 6. Basic Information about COPD, and 7. Basic Information about Sleep Apnea in the Learner s Book. Review sections with participants. When reviewing section 6, explain that oxygen equipment may be prescribed to clients who have a range of diseases or conditions, but that COPD is the most common condition for which oxygen is prescribed. Ask participants if they have any questions. 5. Review the home health aide s role. Explain that the home health aide plays a very important role in assisting the client with respiratory equipment, supplies, and devices. As always, knowing what to observe, record, and report is vital. However, what they are allowed to do beyond that is different with each piece of equipment or device. Therefore, it is very important to know what they are allowed to do, are not allowed to do, and are allowed to do only under special circumstances (that is, with training from the supervising nurse). The remainder of this module will focus on their specific roles in the use of each type of respiratory equipment or device. Trainer s Manual Page 29.16
17 Activity 4. Introduction to the Nebulizer and CPAP Machines 40 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Describe their role in assisting with nebulizers and CPAP machines. Key Content A nebulizer changes liquid medication into a mist that is inhaled through a mouthpiece. The parts of the nebulizer include the cup, mouthpiece, tubing, and an air compressor. The home health aide can assist the client in using the nebulizer by setting up the equipment, adding saline to the nebulizer cup, cleaning the equipment after use, and putting it away. The home health aide is allowed to add medication to the nebulizer cup under SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES ONLY. While the client is using the nebulizer, the home health aide should observe and record: Client s pulse and respiration (before, during, and after using the nebulizer) Signs that the client is not getting enough oxygen (stop the machine IMMEDIATELY if these signs are observed and CALL THE SUPERVISOR) When the nebulizer was used and for how long The home health aide should report to the supervisor any signs of the client not getting enough oxygen while using the nebulizer, and if the client does not use the nebulizer as directed in the care plan. CPAP stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. A CPAP machine blows air into the client s nose and throat. The air pressure is high enough to keep the client s airway open while he or she is asleep. Trainer s Manual Page 29.17
18 When assisting your client with a CPAP machine, make sure that: The mask is not too tight, because this can irritate the face. The mask is not too loose, because air will blow into their eyes. The air filter on the machine has air flowing around it. Make sure the machine is not against a wall or too close to the bed. The HHA can assist the client in using the CPAP machine by setting up the equipment, cleaning it, and then putting it away. They can also help the client to adjust the mask and head straps and to remove them after sleep, and help them to get comfortable for sleep. While the client is using the CPAP machine, the home health aide should observe the client for snoring or sleep interruptions. In general, they should observe and report if there are any problems with the equipment or if the client has: Runny nose Dry throat Headache Ear pain Daytime sleepiness Loud snoring Complaints of not sleeping well, or needing to sit up to breathe Activity Steps Interactive Presentation with Demonstrations 40 minutes 1. Display and describe the medications and equipment used for asthma treatment. Show participants samples of asthma medications and an oxygen mask. Describe their role in assisting the client with these treatments. 2. Display a medication nebulizer and describe the procedure. Explain that a nebulizer turns medication into a mist that can be inhaled. The medication helps to loosen mucus in the lungs so that the client can cough this up. Explain that the medication is mixed with saline and put into the nebulizer with an eye dropper or syringe. Show participants a nebulizer, and where the medication is placed in the nebulizer. Also, show how the client inhales the medication through the mouthpiece. Refer to 8. Medication Nebulizer in the Learner s Book. Ask participants if they have any questions so far. Trainer s Manual Page 29.18
19 3. Demonstate the HHA s role in assisting with a medication nebulizer. Distribute Skills Checklist 6. Assisting with the Use of a Medication Nebulizer and Air Compressor. Review the skills checklist with participants and answer any questions. Be sure to emphasize that the home health aide is permitted to add saline to the nebulizer, and that it is very important to use saline instead of tap water. This is because saline is sterile, and is specially mixed with salt. Also emphasize that the home health aide is only permitted to add the medication to the nebulizer under special circumstances. Ask the participants to recall what is meant by special circumstances. Teaching Tip If needed, clarify that special circumstances means a situation when they will be allowed to do a task after they have been taught how to do it by a nurse at the client s home. 4. Display a CPAP machine and describe the procedure. Show participants a CPAP machine and describe the various parts of the machine and how they function. Refer to 9. CPAP Machine Illustration in the Learner s Book and ask participants if they have any questions. 5. Demonstrate the HHA s role in assisting with a CPAP Machine. Distribute Skills Checklist 7. Assisting with the Use of a CPAP Machine and briefly demonstrate the steps. Explain that participants will have a chance to practice this procedure in the practice lab later in the module. Trainer s Manual Page 29.19
20 Activity 5. Working with Oxygen 50 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Describe their role in assisting with oxygen equipment. List the safety precautions that must be followed when working with oxygen. Key Content Oxygen is flammable, which means it can easily start a fire and burn quickly. Therefore, it is very important to follow certain safety precautions when oxygen is in use. These safety precautions are: Remove from the area any materials that can burn. Post no smoking or oxygen in use signs. Learn how to turn off the oxygen tank in case of fire. Equipment that may be used by the home health aide include: Oxygen tank Air tube and nasal cannula Liquid oxygen reservoir Oxygen concentrator The home health aide can assist the client in using oxygen equipment by setting up the equipment, adding distilled (sterile) water to the humidifying bottle, checking if there is enough oxygen in the tank, turning the oxygen tank on and off, checking the level of the flow meter, turning the flow meter on and off, checking that air is coming through the mask or nasal cannula, assisting the client to put on the mask or nasal cannula, and putting the equipment away. Trainer s Manual Page 29.20
21 The home health aide is allowed to adjust the flow meter under SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES ONLY. While the client is using the oxygen equipment, the home health aide should observe and record: Client s pulse and respiration (before, during, and after using the equipment) Signs that the client is not getting enough oxygen (stop the machine IMMEDIATELY if these signs are observed and CALL THE SUPERVISOR) When the oxygen equipment was used and for how long Activity Steps Small-Group Work 10 minutes 1. Introduce the importance of safety when assisting with oxygen. Explain that you are about to review procedures for assisting with oxygen equipment, but that before you review these procedures, you want to review important safety information. Ask participants: Why do you think safety is especially important when assisting with oxygen equipment? Listen to participants responses. Then emphasize that one reason safety is especially important when assisting with oxygen equipment is that oxygen is flammable. This means that there is a danger that the oxygen could explode if certain safety precautions are not followed. 2. Set up small-group activity. Explain that you would like participants to return to the same small groups that they were in earlier in the module (for Overview of Respiratory Conditions ). Explain that you would like the small groups to spend five minutes brainstorming what safety precautions need to be in place in the client s home in order to prevent a fire or explosion when oxygen is present. 3. Debrief small-group activity. After five minutes, ask the participants to share their brainstorming ideas with the large group. Trainer s Manual Page 29.21
22 Interactive Presentation and Demonstrations 40 minutes 4. Explain safety precautions. Refer to 10. Safety Precautions to Follow When Oxygen Is in Use in the Learner s Book. Ask participants if they have any questions. 5. Describe the oxygen tank. Show participants an oxygen tank and point out the flow meter, the flow meter valve, the regulator gauge, the tank valve, the air tube, and the humidifying bottle. Explain the function of each part of the oxygen tank. Then explain that oxygen tanks come in many different sizes; some tanks are portable so that the client can get oxygen treatment when they are not at home. Refer to 11. Parts of an Oxygen Tank. Ask participants if they have any questions. 6. Demonstrate how to assist with the use of an oxygen tank and liquid oxygen reservoir. Describe the procedure for assisting with the use of an oxygen tank, and then distribute Skills Checklist 8. Assisting with the Use of an Oxygen Tank and Liquid Oxygen Reservoir. Explain that participants will have a chance to practice this procedure at a later time. Be sure to emphasize that: The only thing they are permitted to adjust on an oxygen tank is the tank valve. They are permitted to turn this valve on at the beginning of a client s treatment, and off at the end of the treatment. They should check the flow meter to make sure that the valve is set for the dosage indicated in the care plan. If it is set for a different dosage, they should call their supervisor, because they are only permitted to adjust the flow valve UNDER SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES. They should check the regulator gauge to make sure there is enough oxygen left in the tank for the treatment. If there is not enough oxygen, they should call the supervisor. If the oxygen tank has a humidifying bottle, it should be filled with sterile water. The home health aide is permitted to add the sterile water to the bottle. Note that using tap water is not permitted. Trainer s Manual Page 29.22
23 The home health aide can help prevent the skin behind the client s ears from becoming irritated by padding the tubing. 7. Describe an oxygen concentrator and demonstrate the procedure for using it. Review 12. Oxygen Concentrator in the Learner s Book.. Next, distribute Skills Checklist 9. Assisting with the Use of an Oxygen Concentrator and demonstrate the procedure. Explain that participants will have a chance to practice this procedure during the practice lab. Trainer s Manual Page 29.23
24 Activity 6. The Aide s Role in Assisting with Respiratory Equipment, 45 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Describe what they are permitted to do when assisting with respiratory equipment, supplies, and devices, as well as what they are not permitted to do or are permitted to do under special circumstances only. Key Content It is very important for the home health aide to be aware of what they are and are not permitted to do to assist their client. Participants can become more familiar with what they are and are not permitted to do by carefully reviewing the procedures in this module. If they ever have a question about what they are permitted to do, they can always call their supervisor for clarification. Activity Steps Small-Group Work 20 minutes 1. Set up small-group work. Explain that you will now review some of the key information about assisting with equipment, supplies, and devices related to respiration. Ask participants to work in the same small groups. Distribute Worksheet 1. Review of the Dos and Don ts. Explain that this worksheet lists some of the tasks related to the procedures that were reviewed. Their task will be to work with their small group to decide which of these tasks they are permitted to assist with, which tasks they are not permitted to assist with, and which ones they can only do under special circumstances. Explain that they can refer back to the skills checklists that describe these procedures (Skills Checklists 6 through 9). Ask if participants have any questions about the task. Explain that they will have 15 minutes to complete this activity. Trainer s Manual Page 29.24
25 Large-Group Reporting and Discussion 15 minutes 2. Facilitate large-group reporting. After 15 minutes (or sooner, if the groups have completed their work), have the small groups take turns sharing their responses on Worksheet 1. Review of the Dos and Don'ts. Review the procedures as necessary and answer any questions. Be sure that participants understand that, if they find any equipment that is broken or any supply that needs to be reordered, they are simply to inform the client or the client s family. It is the responsibility of the client or the client s family to call the supplier. Explain that if the issue is not addressed, the home health aide should follow up by calling their supervisor. Interactive Presentation 10 minutes 3. Review what to report. Explain that it is very important to observe the client during the procedures that they have just reviewed and to report IMMEDIATELY any signs that the client is not getting enough oxygen. Ask participants: What are some of the signs that might tell you that your client is not getting enough oxygen? 4. Listen to participants responses. Make sure the following signs are mentioned: Difficulty breathing Rapid pulse and respiration Cold, clammy skin Blue or darkened lips, fingernails, or eyelids Being unable to sit still Not responding when you call his/her name Having headaches or complaining of no energy Trainer s Manual Page 29.25
26 Activity 7. Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, : Practice Lab and Return Demonstrations 2 hours and 30 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Demonstrate how to assist with the use of a commercially prepared enema and a soap solution enema. Demonstrate how to assist with the use of a douche. Demonstrate how to assist with the use of a medication nebulizer and air compressor. Demonstrate how to assist with the use of a CPAP machine. Demonstrate how to assist with the use of oxygen equipment. Key Content By the end of this activity, every participant should have had the opportunity to demonstrate how to use all of the prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices covered in this module. For each return demonstration, a trainer will observe and assess the participant, using the skills checklist. While some participants are doing their return demonstrations, other participants will continue to practice these skills, working in practice triads as before. Some participants may need to do return demonstrations for skills covered prior to this module. Trainer s Manual Page 29.26
27 Activity Steps Practice Triads and Return Demonstrations 2 hours and 30 minutes 1. Note the workstations for this activity. Point out which skills will be practiced at each location: assisting with an enema, assisting with a douche, assisting with the use of the medication nebulizer and air compressor, assisting with the CPAP machine, and assisting with the oxygen equipment. (See Advance Preparation for tips for setting these up.) 2. Set up triads and explain your role. Participants will work in triads for skills practice, until they are ready to do their return demonstrations. Explain that you (and other trainers, if available) will be observing their practice and answering questions as needed. Participants will use the skills checklists that were distributed during the activities when the skills were introduced. Teaching Tips If this is the first time they are practicing a particular skill, each participant should take a turn in each role: practicing the task as a direct-care worker, experiencing what it feels like as a client, and observing (reviewing the steps for each task on the checklist while observing teammates and encouraging them as they perform the steps). For return demonstrations, participants will probably remain in their triads, depending on time, space, and the number of trainers available to observe return demonstrations (see Advance Preparation). Trainers should have enough copies of all the skills checklists to assess return demonstrations for all participants who did not do their return demonstrations earlier. 3. Conduct practice and return demonstrations. Trainer s Manual Page 29.27
28 Activity 8. Identifying Your Feelings about Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, 30 minutes Learning Outcomes By the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Identify their attitudes and feelings about assisting with the use of prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices, as well as how these attitudes and feelings may impact the client. Key Content Home health aides feel a range of emotions when they assist with medical equipment, supplies, and devices. These feelings are normal. It is helpful for the home health aide to pay attention to his or her own feelings and to get support when they need it. It is important for home health aides to be aware that their feelings can have an impact on their clients. Home health aides should be encouraging and supportive when they are assisting their clients with medical equipment, supplies, and devices. Home health aides should also encourage clients to be as independent as possible. Activity Steps Small-Group Work 15 minutes 1. Review the importance of being aware of their feelings and the possible impact on the client. Discuss the two bullets under Key Content. Trainer s Manual Page 29.28
29 2. Set up small-group work. Ask participants to stay in their triads for this discussion. Refer to 13. Stories from Home Health Aides in the Learner s Book. Read the three stories out loud. Ask participants to spend about 10 minutes discussing the stories in their group and answering the question in section 13. Large-Group Discussion 15 minutes 3. Encourage sharing with the large group. After 10 minutes, ask the triads to end their discussions. Ask if anyone would like to share with the larger group the feelings that they talked about with their partners. Validate the feelings that participants share by explaining that there is no wrong way to feel. Reassure participants that certain difficult feelings (like nervousness) will likely become less strong with time and additional practice. Encourage participants to approach you outside of class to speak further about their feelings if they want to. Teaching Tip If no one mentions having similar feelings to the home health aides in section 15, you may want to ask the participants to raise their hands if they can identify with each one. Most likely, more than one person will raise their hand. People who are feeling the same way will be reassured that they are not alone. 4. Summarize the module. Distribute and review Handout 1. Key Terms and Handout 2. Summary of Key Information. Answer any questions. Trainer s Manual Page 29.29
30 Learner s Book Module 29. Assisting with Prescribed Medical Equipment, Activity 1. Introduction to Prescribed Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Devices 1. What Are Prescribed Medical Equipment,? 2. Why Are Prescribed Medical Equipment, Important? Activity 2. Your Role in Assisting with the Use of ACE Bandages, Enemas, and Douches 3. Basic Information about Skin and Medical Equipment Prescribed to Prevent Skin Breakdown Skills Checklist 1. Assisting with an ACE Bandage 4. Basic Information about Elimination and Medical Equipment Prescribed for It Skills Checklist 2. Assisting with the Use of a Commercially Prepared Enema Skills Checklist 3. Assisting with the Use of a Soap Solution Enema Skills Checklist 4. Assisting with the Use of a Douche Skills Checklist 5. Assisting with the Use of a Commercially Prepared Douche Learner s Book Page 29.1
31 Activity 4. Overview of Respiratory Conditions 5. Basic Information about Asthma 6. Basic Information about COPD 7. Basic Information about Sleep Apnea Activity 5. Introduction to the Nebulizer and CPAP Machines 8. Medication Nebulizer Skills Checklist 6. Assisting with the Use of a Medication Nebulizer and Air Compressor 9. CPAP Machine Illustration Skills Checklist 7. Assisting with the Use of a CPAP Machine Activity 6. Working with Oxygen 10. Safety Precautions to Follow When Oxygen Is in Use 11. Parts of an Oxygen Tank Skills Checklist 8. Assisting with the Use of an Oxygen Tank and Liquid Oxygen Reservoir 12. Oxygen Concentrator Skills Checklist 9. Assisting with the Use of an Oxygen Concentrator Learner s Book Page 29.2
32 Activity 9. Identifying Your Feelings about Assisting with Respiratory Equipment, 13. Stories from Home Health Aides Learner s Book Page 29.3
33 1. What Are Prescribed Medical Equipment,? Prescribed medical equipment, supplies, and devices assist the client with basic bodily functioning. Medical equipment may be prescribed to assist a client in: Mobility (movement) This equipment helps the client to ambulate (walk) or to change positions. Examples: o Canes o Walkers o Hoyer Lift Preventing skin breakdown This equipment helps the client to regain or maintain healthy skin that is free of sores, wounds, or swelling. Examples: o Bandages o Sheepskin or lamb s wool o Water mattress or gel padding Elimination This equipment helps the client to eliminate waste from the body (to void urine and stool). Examples: o Enemas o Douches o Catheters Respiration This equipment helps the client to breathe. Examples: o Oxygen tanks o Nebulizers o CPAP machines Learner s Book Page 29.4
34 2. Why Are Prescribed Medical Equipment, Important? Page 1 of 2 Below, three direct-care workers share stories about why prescribed medical equipment, supplies, or devices are important for the clients they assist. After you read each story, work together to answer the discussion questions. Miguel s story: Mr. Ricardo s ankles were swollen after his surgery. It was uncomfortable for him, and it made it difficult for him to walk. Mr. Ricardo was very frustrated by that. The nurse showed me how to apply ACE bandages around his ankles, and this helped the swelling go down after a few weeks. He s so happy to be up on his feet again! Discussion questions: How was Mr. Ricardo feeling at the beginning of the story? What equipment, supply, or device was prescribed to help him? How did Mr. Ricardo feel after using this equipment, supply, or device? Carla s story: Miss Elena was on a medication for a few months that made her constipated. Once, she went two weeks without a bowel movement! She was so uncomfortable. Then her doctor prescribed an enema for her, and I assisted her with it. About ten minutes later, she was able to have a bowel movement. She felt so much better afterward! Discussion questions: How was Miss Elena feeling at the beginning of the story? What equipment, supply, or device was prescribed to help her? How did Miss Elena feel after using this equipment, supply, or device? Learner s Book Page 29.5
35 2. Why Are Prescribed Medical Equipment, Important? Page 2 of 2 Liliana s story: Mrs. Sanchez has a lot of mucus that builds up in her lungs. It used to make her cough a lot, and the coughing made it hard for her to sleep. Her doctor just diagnosed her with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and he prescribed a nebulizer for her. This is a machine that she uses to inhale a medicine that breaks up the mucus. It really seems to help her. She doesn t cough as much now, and that means she s able to rest. Discussion questions: How was Mrs. Sanchez feeling at the beginning of the story? What equipment, supply, or device was prescribed to help her? How did Mrs.Sanchez feel after using this equipment, supply, or device? Learner s Book Page 29.6
36 3. Basic Information about Skin and Medical Equipment Prescribed To Prevent Skin Breakdown What is skin? Skin is the barrier that covers the outside of our bodies. Why is skin important? Skin protects the inside of the body from germs. It also helps the body maintain the right temperature and the right amount of water. What kinds of conditions can cause skin breakdown? Wounds Pressure sores Edema Swelling due to injury What medical equipment might be prescribed to prevent skin breakdown? Dressings (bandages) on wounds or sores Elastic bandages (ACE bandages) What will your role be in assisting the client with this equipment? You may: o Apply an elastic bandage UNDER SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES ONLY You will not: o Apply or change dressings that need to be sterile. o Apply or change dressings on skin that is not stable Learner s Book Page 29.7
37 4. Basic Information about Elimination and Medical Equipment Prescribed for It Page 1 of 2 What is elimination? Elimination is how the body gets rid of waste. The body eliminates liquid wastes in urine and solid wastes in stool. Why is elimination important? When a person eats, the cells of the body absorb the nutrients that they need in order to function. The body needs to get rid of anything that is not absorbed. When the body can t control the elimination of urine, this is called urinary incontinence. This may cause inconvenience and emotional distress. It can also contribute to skin breakdown. When the body can t eliminate solid waste (stool), this is called constipation. This may cause a person pain or discomfort. What kinds of conditions can lead to problems with elimination? Aging Surgery Medications Cancer Lack of exercise Learner s Book Page 29.8
38 4. Basic Information about Elimination and Medical Equipment Prescribed for It Page 2 of 2 What medical equipment might be prescribed? An enema: a procedure that introduces liquids into the rectum and colon through the anus. There are different kinds of enemas. The two you may be asked to assist with are: o A commercially prepared enema o A soap solution enema A douche: a procedure that introduces liquid into the vagina in order to help keep it clean. (Also refers to the equipment used) A catheter: a thin tube inserted into the body that is used to drain urine from the body. A condom catheter: a catheter that has a covering that is placed over the penis. This kind of catheter is also called an external catheter. A urinary drainage bag: a bag at the end of catheter tubing that is used to collect urine. What will your role be in assisting the client with this equipment? You may: o Assist with the use of an enema o Assist with the use of a douche o Assist with cleaning the skin around a catheter o Assist in cleaning catheter tubing o Assist with emptying a urinary drainage bag o Assist with the use of a condom catheter You may NOT: o Insert any tube (a catheter tube, for example) into any opening of the body. Learner s Book Page 29.9
39 5. Basic Information about Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a disease that affects the airways that carry air to and from the lungs. In people with asthma, these airways are swollen or inflamed, and become narrow so that less air can pass through them. People with asthma tend to be very sensitive to irritants in the air (like pollen or pollution). Up to 80 percent of people with asthma have allergies to airborne irritants. What are the symptoms of asthma? Wheezing (a hissing sound when breathing) Tightness in the chest Coughing Difficulty breathing What is an asthma attack? This is when the symptoms of asthma are worse than usual. This is often due to exposure to irritants or allergens, or because of stress or exercise. These attacks can come on suddenly, and may be mild, moderate, or severe. Very severe asthma attacks can be life threatening. How is asthma treated? There is no cure for asthma, but people can take medications to manage their symptoms. They can also learn what triggers their asthma attacks, so that they can avoid these triggers. What kinds of equipment, supplies, or devices may be used by a client with asthma? Inhalers Nebulizers Oxygen tanks with a mask or nasal cannula Sterile (distilled) water Learner s Book Page 29.10
40 6. Basic Information about COPD What is COPD? COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, which is a term used to describe two diseases that tend to coexist: bronchitis and emphysema. These diseases cause the airways to become narrow and the lungs to become inflamed. COPD tends to be progressive, which means that the symptoms become worse over time. What are the symptoms of COPD? Chronic shortness of breath Acute episodes, when shortness of breath becomes worse than usual What is the cause of COPD? One cause of COPD is smoking, but it can be caused by long-term exposure to other irritants besides cigarette smoke. What kinds of equipment, supplies, or devices may be used by a client with COPD? Oxygen concentrators Oxygen tanks with a mask or nasal cannula Mechanical ventilators Learner s Book Page 29.11
41 7. Basic Information about Sleep Apnea What is sleep apnea? Sleep apnea is a condition that causes a person to stop breathing when they are asleep. What is the cause of sleep apnea? Sleep apnea occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat become too relaxed while the body is sleeping. This closes the airway, which leads to a shortage of oxygen in the blood. The brain responds to the oxygen shortage by waking up the body just enough to reopen the airway. People with sleep apnea may wake up hundreds of times a night without knowing it. What are the symptoms of sleep apnea? Fatigue Poor concentration Why is sleep apnea dangerous? It increases the risk of accidents (due to fatigue). It puts strain on the heart and lungs. It increases the risk for diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and weight gain. What kinds of equipment, supplies, or devices may be used by a client with sleep apnea? CPAP machine Learner s Book Page 29.12
42 8. Medication Nebulizer [See page 421 of Providing Home Care 1 for a photo of a medication nebulizer.] A medication nebulizer changes liquid medication into a mist that is inhaled through a mouthpiece. The medication is mixed with saline in the nebulizer cup. The cup and mouthpiece are connected by tubing to an air compressor. 1 William Leahy, Jetta Fuzy, and Julie Grafe, Providing Home Care, 4 th ed. (Albuquerque, NM: Hartman Publishing, Inc., 2013). Learner s Book Page 29.13
Module 32. Assisting with Ostomy Care
 Home Health Aide Training Module 32. Assisting with Ostomy Care Goal The goal of this module is to prepare participants to assist a home care client who has an ostomy. Time 7 hours and 30 minutes [1 hour
Home Health Aide Training Module 32. Assisting with Ostomy Care Goal The goal of this module is to prepare participants to assist a home care client who has an ostomy. Time 7 hours and 30 minutes [1 hour
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
In case of an urgent concern or emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency department right away.
 Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather
 Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Breathe Easy. Tips for controlling your Asthma
 Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Ohio Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes swelling
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Ohio Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes swelling
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Washington Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Washington Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Medications. Managing and Administering Medication
 Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Positive Pressure Therapy
 Positive Pressure Therapy Positive Pressure Therapy...2 What is Sleep Apnea?....2 Positive Pressure Machines..................................................... 4 Types..................................................................................
Positive Pressure Therapy Positive Pressure Therapy...2 What is Sleep Apnea?....2 Positive Pressure Machines..................................................... 4 Types..................................................................................
Cough Associated with Bronchitis
 Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
Procedures/Risks: pulmonology, sleep, critical care
 Procedures/Risks: pulmonology, sleep, critical care Bronchoscopy (and bronchoaveolar lavage) Purpose: The purpose of the bronchoscopy is to collect cells and fluid from the lung, so that information can
Procedures/Risks: pulmonology, sleep, critical care Bronchoscopy (and bronchoaveolar lavage) Purpose: The purpose of the bronchoscopy is to collect cells and fluid from the lung, so that information can
Module 9. Body Mechanics
 Home Health Aide Training Module 9. Body Mechanics Goal The goal for this module is to help participants learn the principles of good body mechanics and how to use these principles to prevent injury when
Home Health Aide Training Module 9. Body Mechanics Goal The goal for this module is to help participants learn the principles of good body mechanics and how to use these principles to prevent injury when
Sources. Taking Charge of Your Asthma. Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company
 Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) Green Zone: (80 to 00% of my personal best) Peak Flow between and (00% = personal best) You can do all the things you usually do. Your asthma medicine
Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) Green Zone: (80 to 00% of my personal best) Peak Flow between and (00% = personal best) You can do all the things you usually do. Your asthma medicine
Welcome to our Asthma Program
 Welcome to our Asthma Program We re here to help you be your healthiest through information, education and support for your asthma. We ll work with you by: Partnering with your health care team to make
Welcome to our Asthma Program We re here to help you be your healthiest through information, education and support for your asthma. We ll work with you by: Partnering with your health care team to make
Asthma Basic Facts. Staying safe and well with asthma. For people with asthma and their carers.
 Asthma Basic Facts Staying safe and well with asthma. For people with asthma and their carers. Asthma App Contact your local Asthma Foundation asthmaaustralia.org.au Breathing Breathing is how we get air
Asthma Basic Facts Staying safe and well with asthma. For people with asthma and their carers. Asthma App Contact your local Asthma Foundation asthmaaustralia.org.au Breathing Breathing is how we get air
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A breathtaking condition
 1. Jan Crouch JC 2. Diane Cruikshank DC 3. Jillian Millar Drysdale JMD 4. Medical Editor 5. Robert Clarke Article: COPD & smoking.doc Section: Growing Older Family Health: Fall 2008 Chronic Obstructive
1. Jan Crouch JC 2. Diane Cruikshank DC 3. Jillian Millar Drysdale JMD 4. Medical Editor 5. Robert Clarke Article: COPD & smoking.doc Section: Growing Older Family Health: Fall 2008 Chronic Obstructive
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Helping You to Breathe Better, Sleep Easy & Live Well
 Helping You to Breathe Better, Sleep Easy & Live Well Your Guide to CPAP Therapy info@cansleep.ca Vancouver Island Lower Mainland Fraser Valley Sleep Apnea & Symptoms Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) occurs
Helping You to Breathe Better, Sleep Easy & Live Well Your Guide to CPAP Therapy info@cansleep.ca Vancouver Island Lower Mainland Fraser Valley Sleep Apnea & Symptoms Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) occurs
Understanding and Managing Your Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
 Understanding and Managing Your Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. 2 LIVING WITH COPD You may have been told that you have COPD. It is a lung disease
Understanding and Managing Your Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. 2 LIVING WITH COPD You may have been told that you have COPD. It is a lung disease
Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARE AND USE OF NEBULIZER AND INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE BREATHING DEVICE
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 421 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARE AND USE OF NEBULIZER AND INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 421 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARE AND USE OF NEBULIZER AND INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Patient Information Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Author: Pulmonary physiology, sleep and ventilation Produced and designed by the Communications Team Issue date July 2017 Expiry date July
Patient Information Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Author: Pulmonary physiology, sleep and ventilation Produced and designed by the Communications Team Issue date July 2017 Expiry date July
Copyright, ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved. The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy. Asthma Questionnaire
 Copyright, 1994 - ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy Asthma Questionnaire This survey contains a series of statements, written in the first person, concerning your
Copyright, 1994 - ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy Asthma Questionnaire This survey contains a series of statements, written in the first person, concerning your
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy
 Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Pulmo-Park Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D
 Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should not perform the
Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should not perform the
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION
 Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Recommended Component: Manage Physical Activity for Students with Asthma
 Recommended Component: Manage Physical Activity for Students with Asthma Individuals with exercise-induced asthma do not necessarily have other asthma triggers. For others with asthma, exercise may be
Recommended Component: Manage Physical Activity for Students with Asthma Individuals with exercise-induced asthma do not necessarily have other asthma triggers. For others with asthma, exercise may be
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Michigan Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Michigan Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
Asthma. If an Ambulance is required - call immediately - do not delay. H & A Training PL RTO No:90871
 Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
 Obstructive Sleep Apnea Introduction Obstructive sleep apnea is an interruption in breathing during sleep. It is caused by throat and tongue muscles collapsing and relaxing. This blocks, or obstructs,
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Introduction Obstructive sleep apnea is an interruption in breathing during sleep. It is caused by throat and tongue muscles collapsing and relaxing. This blocks, or obstructs,
Because the more you know, the better you ll feel.
 ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma and the things you can do every day to help control symptoms. As always, talk to your
ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma and the things you can do every day to help control symptoms. As always, talk to your
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING
 UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in Taking Care of Your Child s Asthma. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
Asthma. & Older Adults. A guide to living with asthma for people aged 65 years and over FOR PATIENTS & CARERS
 Asthma & Older Adults A guide to living with asthma for people aged 65 years and over FOR PATIENTS & CARERS what is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the airways, the small tubes which carry air in and out
Asthma & Older Adults A guide to living with asthma for people aged 65 years and over FOR PATIENTS & CARERS what is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the airways, the small tubes which carry air in and out
MANAGING COPD AT HOME. Karla Schlichtmann, RRT
 MANAGING COPD AT HOME Karla Schlichtmann, RRT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease. WHAT IS COPD? The airways in your lungs become inflamed and thickens. This results
MANAGING COPD AT HOME Karla Schlichtmann, RRT Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease. WHAT IS COPD? The airways in your lungs become inflamed and thickens. This results
Living well with COPD
 This factsheet aims to show people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and their friends and family how they can live a full life with this disease. What is COPD? COPD is a condition that
This factsheet aims to show people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and their friends and family how they can live a full life with this disease. What is COPD? COPD is a condition that
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters
 Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Sleep Apnea. What is sleep apnea? How does it occur? What are the symptoms?
 What is sleep apnea? Sleep Apnea Sleep apnea is a serious sleep problem. If you have it, you stop breathing for more than 10 seconds at a time many times while you sleep. Another term for this problem
What is sleep apnea? Sleep Apnea Sleep apnea is a serious sleep problem. If you have it, you stop breathing for more than 10 seconds at a time many times while you sleep. Another term for this problem
Respiratory Emergencies. Chapter 11
 Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
A patient educational resource provided by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
PomPom SHOOTER. Activity Background: Common Obstructive Lung Disorders:
 CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
Patient & Family Guide. Bowel Surgery.
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Bowel Surgery www.nshealth.ca Bowel Surgery This pamphlet will answer some of your questions about your stay in hospital and care at home. We hope this information will help
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Bowel Surgery www.nshealth.ca Bowel Surgery This pamphlet will answer some of your questions about your stay in hospital and care at home. We hope this information will help
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Anaesthetic choices for hip or knee replacement
 Anaesthetic choices for hip or knee replacement Information for patients Fourth Edition 2014 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet explains what to expect when you have an operation to replace a hip
Anaesthetic choices for hip or knee replacement Information for patients Fourth Edition 2014 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet explains what to expect when you have an operation to replace a hip
Because the more you know, the better you ll feel.
 ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. What You ll Find Attitudes and Beliefs Asthma What Is It? Where You ll Find It Page 4-5 This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma
ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. What You ll Find Attitudes and Beliefs Asthma What Is It? Where You ll Find It Page 4-5 This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Texas Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the Provider
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Texas Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the Provider
WELCOME TO... Please read this brochure & the Provent Instructions For Use before starting Provent Sleep Apnea Therapy.
 WELCOME TO... Please read this brochure & the Provent Instructions For Use before starting Provent Sleep Apnea Therapy. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a serious medical condition characterized by pauses
WELCOME TO... Please read this brochure & the Provent Instructions For Use before starting Provent Sleep Apnea Therapy. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a serious medical condition characterized by pauses
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Asthma (Short wind) in Children
 In partnership: Asthma (Short wind) in Children The lungs You have two lungs. They sit inside your chest, above your stomach and surround your heart. The lungs have a very important job inside your body.
In partnership: Asthma (Short wind) in Children The lungs You have two lungs. They sit inside your chest, above your stomach and surround your heart. The lungs have a very important job inside your body.
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Medicare Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Medicare Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
Teacher Training on Asthma
 Teacher Training on Asthma Understanding Asthma and How It Can Be Managed at School This presentation is made possible by a grant from: Training Objectives Describe the effects of asthma on students Discuss
Teacher Training on Asthma Understanding Asthma and How It Can Be Managed at School This presentation is made possible by a grant from: Training Objectives Describe the effects of asthma on students Discuss
Helping You to Breathe Better, Sleep Easy & Live Well
 Helping You to Breathe Better, Sleep Easy & Live Well Your Guide to CPAP Therapy info@cansleep.ca Lower Mainland Vancouver Island Fraser Valley Sleep Apnea & Symptoms Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) occurs
Helping You to Breathe Better, Sleep Easy & Live Well Your Guide to CPAP Therapy info@cansleep.ca Lower Mainland Vancouver Island Fraser Valley Sleep Apnea & Symptoms Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) occurs
Asthma 101. Introduction
 TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Critical Care Services: Equipment and Procedures Information for Patients, Relatives and Carers
 Critical Care Services: Equipment and Procedures Information for Patients, Relatives and Carers The Critical Care unit can be a frightening place for patients and visitors. Seeing a loved one attached
Critical Care Services: Equipment and Procedures Information for Patients, Relatives and Carers The Critical Care unit can be a frightening place for patients and visitors. Seeing a loved one attached
Understanding Lung Problems Make Each Breath Healthy
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Understanding Lung Problems Make Each Breath Healthy Lupe has smoked for over 45 years. This year she started having trouble keeping up with her 3-year-old grandson
National Institute on Aging AgePage Understanding Lung Problems Make Each Breath Healthy Lupe has smoked for over 45 years. This year she started having trouble keeping up with her 3-year-old grandson
Anaesthesia and pain (Daycase Patient) Patient information Leaflet
 Anaesthesia and pain (Daycase Patient) Patient information Leaflet February 2018 INTRODUCTION Welcome to Tameside Hospital, this leaflet gives basic information to help you prepare for your anaesthetic,
Anaesthesia and pain (Daycase Patient) Patient information Leaflet February 2018 INTRODUCTION Welcome to Tameside Hospital, this leaflet gives basic information to help you prepare for your anaesthetic,
This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
My Asthma Log. Tommy Traffic Light. NHS Number: Name:
 My Asthma Log Tommy Traffic Light NHS Number: Name: My Asthma Log Book This book is designed to help you understand and learn about managing your asthma. You should take your book with you to all your
My Asthma Log Tommy Traffic Light NHS Number: Name: My Asthma Log Book This book is designed to help you understand and learn about managing your asthma. You should take your book with you to all your
WELCOME TO THE NORTHSHORE UNIVERSITY HEALTHSYSTEM SLEEP CENTERS
 WELCOME TO THE NORTHSHORE UNIVERSITY HEALTHSYSTEM SLEEP CENTERS Prior to your office visit, we request that you complete this questionnaire. It asks questions not only about your sleeping habits and behavior
WELCOME TO THE NORTHSHORE UNIVERSITY HEALTHSYSTEM SLEEP CENTERS Prior to your office visit, we request that you complete this questionnaire. It asks questions not only about your sleeping habits and behavior
Sleep History Questionnaire
 Sleep History Questionnaire Name: DOB: Phone: Date of Consultation: Consultation is requested by: Primary care provider: _ Preferred pharmacy: Chief complaint: Please tell us why you are here: How long
Sleep History Questionnaire Name: DOB: Phone: Date of Consultation: Consultation is requested by: Primary care provider: _ Preferred pharmacy: Chief complaint: Please tell us why you are here: How long
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide ASTHMA
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
Preventing delirium while in hospital Tips for family, whānau, and friends who are supporting an older person
 Preventing delirium while in hospital Tips for family, whānau, and friends who are supporting an older person This brochure shares some simple ways you can help our care staff to prevent delirium, recognize
Preventing delirium while in hospital Tips for family, whānau, and friends who are supporting an older person This brochure shares some simple ways you can help our care staff to prevent delirium, recognize
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia
 1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
*521634* Sleep History Questionnaire. Name of primary care doctor:
 *521634* Today s Date: Sleep History Questionnaire Appointment Date: Please answer the following questions before coming to your appointment. Please arrive 15 minutes early with this packet filled out.
*521634* Today s Date: Sleep History Questionnaire Appointment Date: Please answer the following questions before coming to your appointment. Please arrive 15 minutes early with this packet filled out.
Asthma. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing worldwide, but why this is happening is not known.
 Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA
 Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Asthma Action Plan and Education
 Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies
 Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies Health Promotion for Community Health Workers Cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer Class #9 Heart Failure (date) Course Objectives:
Sinclair Community College, Division of Allied Health Technologies Health Promotion for Community Health Workers Cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer Class #9 Heart Failure (date) Course Objectives:
What Is This Module About? What Will You Learn From This Module?
 What Is This Module About? Breathing is very important and natural to man. Every breath means life. Do you know what system of the human body helps us breathe? What elements in air does man need to live?
What Is This Module About? Breathing is very important and natural to man. Every breath means life. Do you know what system of the human body helps us breathe? What elements in air does man need to live?
Revised 12/10. Copyright 2003 St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Page 1 of 5
 Some treatments, such as starting an IV or putting a needle in a port, are painful. Whenever possible, your child should have the option of reducing this pain as much as possible. One way to not feel the
Some treatments, such as starting an IV or putting a needle in a port, are painful. Whenever possible, your child should have the option of reducing this pain as much as possible. One way to not feel the
Oxfordshire Asthma Guidelines. for use in schools and other child care settings
 Oxfordshire Asthma Guidelines for use in schools and other child care settings This document is underpinned by the principles of the United Nations Convention on the rights of the child, in particular
Oxfordshire Asthma Guidelines for use in schools and other child care settings This document is underpinned by the principles of the United Nations Convention on the rights of the child, in particular
Date of Assessment: Assessed By: Questionnaire: Assessing Student Readiness to Self- Carry
 Student Name: Score: Date of Assessment: Assessed By: naire: Assessing Student Readiness to Self- Carry Having immediate access to quick- relief medicine is critical for people with asthma. The purpose
Student Name: Score: Date of Assessment: Assessed By: naire: Assessing Student Readiness to Self- Carry Having immediate access to quick- relief medicine is critical for people with asthma. The purpose
Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Vaginal repair Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives information about vaginal repair surgery used to treat a vaginal prolapse. The leaflet explains what a
Vaginal repair Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives information about vaginal repair surgery used to treat a vaginal prolapse. The leaflet explains what a
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE. Name: Home Telephone. Address: Work Telephone: Marital Status: Date of Birth: Age: Sex: Height: Weight: Pharmacy & Phone #:
 q JHMCE q JHS q SMEH SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE 1. DEMOGRAPHIC DATA Name: Home Telephone Address: Work Telephone: Marital Status: Date of Birth: Age: Sex: Height: Weight: 2. PHYSICIAN INFORMATION Name of Primary
q JHMCE q JHS q SMEH SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE 1. DEMOGRAPHIC DATA Name: Home Telephone Address: Work Telephone: Marital Status: Date of Birth: Age: Sex: Height: Weight: 2. PHYSICIAN INFORMATION Name of Primary
Breathe Easy. Living with Asthma
 Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
Asthma Management. Photo from
 Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses
 Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
Year 2, 3 or 4 Asthma lesson presentation HARMFUL
 Year 2, 3 or 4 Asthma lesson presentation HARMFUL Asthma is a condition that affects the airways of the lungs. It can lead to the airways getting narrower; this makes it hard for the person to breathe.
Year 2, 3 or 4 Asthma lesson presentation HARMFUL Asthma is a condition that affects the airways of the lungs. It can lead to the airways getting narrower; this makes it hard for the person to breathe.
Complex Care Hub Manual Section: Asthma
 Complex Care Hub Manual Section: Asthma Table of Contents 1 What is Asthma?... 2 2 What causes asthma?... 2 2.1 Triggers... 2 3 Signs and Symptoms... 2 4 Treatment... 2 4.1 Relievers... 2 4.2 Preventers...
Complex Care Hub Manual Section: Asthma Table of Contents 1 What is Asthma?... 2 2 What causes asthma?... 2 2.1 Triggers... 2 3 Signs and Symptoms... 2 4 Treatment... 2 4.1 Relievers... 2 4.2 Preventers...
Flu: What You Can Do. Caring for People at Home
 Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home For more information, please visit: www.mass.gov/dph/flu CONTENTS: What is the flu? 2 table of contents Flu
Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home For more information, please visit: www.mass.gov/dph/flu CONTENTS: What is the flu? 2 table of contents Flu
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions
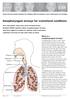 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)
in China Shanghai Office Beijing Office (+86) (+86)
 SLEEP Apnea in China Guide 2018-2019 Shanghai Office (+86) 21 2426 6400 Beijing Office (+86) 010 6464 0611 www.pacificprime.cn Follow us on WeChat t A comprehensive overview of sleep apnea Perhaps you
SLEEP Apnea in China Guide 2018-2019 Shanghai Office (+86) 21 2426 6400 Beijing Office (+86) 010 6464 0611 www.pacificprime.cn Follow us on WeChat t A comprehensive overview of sleep apnea Perhaps you
Your Anaesthetic Explained
 Your Anaesthetic Explained Patient Information Sheet Pre Admission Assessment Clinic Tel: 4920307 What is anaesthesia? The word anaesthesia means loss of sensation. If you have ever had a dental injection
Your Anaesthetic Explained Patient Information Sheet Pre Admission Assessment Clinic Tel: 4920307 What is anaesthesia? The word anaesthesia means loss of sensation. If you have ever had a dental injection
