Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy
|
|
|
- Nathan Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
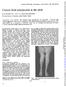
1 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy with vocal cord paralysis I D YOUNG AND P S HARPER From the Section ofmedical Genetics, Department ofmedicine, University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff SUMMARY A large kindred is described in which an unusual form of spinal muscular atrophy is segregating in an autosomal dominant manner. The disease presents most commonly in the teens with small muscle wasting in the hands, particularly involving median nerve musculature. Subsequently distal muscle wasting and weakness occur in the lower limbs. Vocal cord paralysis is a characteristic and potentially hazardous feature. No previous report of this condition has been found. The spinal muscular atrophies comprise a large group of hereditary disorders characterised by degeneration of the anterior horn cells in the spinal cord and to a lesser extent in the motor nuclei of the brain stem, resulting in progressive muscle weakness and wasting. The diversity of clinical findings in these disorders makes classification difficult. This report describes a large family in which an unusual form of chronic distal spinal muscular atrophy is segregating; the upper limb changes precede those in the lower limbs, and are accompanied by laryngeal involvement. Case histories The family pedigree is shown in fig 1. Subject III 24, the father of the proposita, has been intensively investigated and his findings are described in detail below. Relevant clinical data on other affected family members are included and summarised in table 1. Table 2 shows the results of nerve conduction studies. III 24. Born in 1929, this man initially complained of bilateral wasting of thenar eminence musculature at the age of 14 years, associated with stiffness and curling of his fingers. When aged 20 years he noticed distal weakness and wasting in the lower limbs. By this time his voice had become husky and he could neither sing nor shout. By age 30 years walking became painful and difficult. Insidious progression of distal wasting and weakness has severely limited Address for reprint requests: Dr PS Harper, Section of Medical Genetics, University Hospital of Wales, Heath Park, Cardiff CF4 4XW Wales. Accepted 22 January his activity so that he can no longer earn his living. At present he can walk only for short distances, drives with difficulty and can barely hold a pen. His general health has been good. He underwent appendicectomy aged 25 years without incident. However, since age 40 years he has noticed increasing dyspnoea on effort, which has contributed to impaired exercise tolerance. He has no other pulmonary symptoms and has never smoked. At recent examination he showed marked distal wasting and weakness with typical "inverted champagne bottle" legs and bilateral pes cavus (fig 2). Severe wasting of small hand musculature, particularly the thenar eminences, was noted (figs 3 and 4). Despite full passive movements he was unable to extend the medial three digits in both hands. Deep tendon reflexes were absent at wrists and ankles. No thickened nerves were palpated nor myotonia elicited. His outstretched hands showed a pronounced tremor. Sensation was intact. Table 1 Summary of affected family members Sex Age Age at Vocal cord Upper limb Lower limb (yr) onset changes involvement involvement (yr) III 24 M Left cord fixed IV 25 F Hoarse voice III 15 M Right cord fixed IV 23 F Left cord fixed III 17 F Bilateral palsy IV 24 M Bilateral palsy + + ± + III5 F Leftcord fixed + + IV 10 F III 25 F Hoarse voice Severe, + + Moderate, + Mild, - Normal.
2 414 I D Young and P S Harper Table 2 Electrophysiological studies Age at Nerve studied Nerve conduction EMG testing (yr) Motor Sensory Velocity Distal latency Amplitude Latency (m/s) (ms) (Av) (ms) III Right median No response in apb Right ulnar N.D. IV Right median Left median Right ulnar N.D. Right common peroneal Il Lat popliteal 28 Ulnar 41 NR "Normal" IV Right Lat popliteal 38 NR Right median "Normal" N.D. Right ulnar 56 NR III Right Lat popliteal 44 Right ulnar 44 NR "Normal" N.D. IV Right Lat popliteal 26 Right tibialis anterior Right ulnar 31 NR "Normal" Spontaneous fibrillation with 24 Post tibial 28 7 reduced volitional activity III 5 55 Right median No response in apb Right ulnar Left median N.D. Left ulnar IV Right median Right ulnar N.D Right common peroneal III Left median 43 NR Small, dispersed, delayed sensory Spontaneous fibrillation + action potentials. reduced interference pattern in Right ulnar 52 "Normal" a.d.m. Abbreviations N.D.-not done apb-abductor pollicis brevis a.d.m.-abductor digiti minimi NR-not recorded Cranial nerve examination was entirely normal apart from laryngoscopy which showed a fixed left vocal cord. Chest movements were poor; otherwise the respiratory system was normal. Routine blood cytology and biochemistry, including creatine kinase, were normal. Nerve conduction studies showed normal median nerve sensory action potentials: no motor nerve conduction velocity could be obtained from the median nerve as no muscle action potential was discernible from abductor pollicis brevis. Ulnar nerve motor conduction velocity and sensory action potentials were normal. Lung function tests showed a reduced vital capacity with impaired inspiratory and expiratory flow suggestive of reduced muscle effort. The diaphragm moved I II III TV V normally on screening. Electrocardiography showed left axis deviation with no evidence of conduction abnormality. Attempts at biopsy of the sural nerve were unsuccessful. IV 25. This is the daughter of III 24. Born in 1956, her mother states that she has had a husky voice since childhood. She first noticed wasting of small muscles of both hands age 16 years. She now complains of painful cramps when her thumb goes into opposition and she has to pull it back into position. Recent examination confirmed the presence of profound weakness and wasting of thenar musculature with relative powerful preservation of ulnar innervated muscles. There was definite weakness of ankle dorsiflexion with high arched feet. No myotonia Fig 1 The family pedigree. Shaded symbols indicate affected individuals.
3 Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy with vocal cord paralysis Fig 2 Shows distal wasting in lower limbs giving inverted "champagne bottle" appearance. was elicited. All reflexes were present and sensation intact. Electrical studies showed normal sensory nerve action potentials, with normal motor nerve conduction velocities. Her 21 year old brother, IV 26, has recently noted weakness in both thumbs along with a husky voice. III 15. This 57 year old man dates the onset of his illness to age 14 years when he noticed weakness in his hands, followed shortly afterwards by lower limb weakness. Recent examination showed gross distal atrophy in upper and lower limbs, most marked in the hands. Laryngoscopy showed tilting of the right arytenoid with immobility of the right vocal cord. IV 23. The 25 year old daughter of III 15 first noticed weakness in both thumbs when aged 12 years, when her voice also became hoarse. At examination, she had wasting and weakness of both thenar eminences and the first dorsal interossei. Laryngoscopy showed tilting of the left arytenoid with immobility of the left vocal cord. III 17. This severely disabled 57 year old lady dates the onset of her condition to age years, when she began to walk on her toes. This is the only member of the family where lower limb involvement preceded that in the upper limbs, which appeared ten years later. By age 37 years she was noted to have bilateral abductor cord palsies compromising her airway and contributing to recurrent chest infections. These problems were very successfully relieved by a left Woodman's operation. IV 24. The 33 year old son of the above lady first noticed a weak grip when age 13 years with rapid progression to marked distal weakness and atrophy. Dyspnoea on effort was noted. Laryngoscopy revealed a fixed left vocal cord with limited abduction of the right, resulting in an aperture of 7 mm. Electromyography revealed moderately severe partial denervation in tibialis anterior and the plantar flexors of the right foot. III 5. This 56 year old lady first noticed muscle wasting in her right thumb when aged 19 years, followed by onset of a husky voice 10 years later. She has no lower limb involvement. Her left vocal cord is immobile. IV 10. The 35 year old daughter of the above lady has a 20 year history of wasting of both thenar eminences. Clinically her voice and lower limbs are normal. II 4. The father of III 5 is said by all his living relatives, to have been unaffected. His voice was strong and he worked as a miner until his death from peritonitis aged 37 years, caused by untreated appendicitis due to his reluctance to consult a doctor. No photographs or medical records of this man are available. III 25. This 42 year old lady first complained of paraesthesiae in median nerve distribution 11 years ago, when examination showed weakness and wasting of the small muscles of the right hand, with minor wasting of the left hand. Bilateral pes cavus was also noted. Recent examination showed an almost useless right hand with a grossly wasted and paralysed thenar eminence. Milder but similar changes were present in the left arm. This lady was unusual in that she showed sensory loss in a glove distribution up both forearms, although both history and examination were complicated by a large functional overlay. She has also complained of a husky voice and weak cough. Her 18 year old son, IV 29, has started to complain of wasting and weakness in both hands. Discussion 415 NEUROLOGICAL ASPECTS These patients all share the common feature of
4 416 insidious onset of progressive distal muscle wasting and weakness, usually appearing during the teenage years with upper limb changes preceding those in the lower limbs. In all patients the onset has been gradual and the course prolonged. The main differential diagnosis rests between a distal spinal muscular atrophy and Charcot- Marie-Tooth disease. Dyck and Lambert' 2 have shown that Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease may include at least three pathological disorders. The first of these is a "hypertrophic" neuropathy showing segmental demyelination in the peripheral nerve with marked reduction in nerve conduction. In the second "neuronal" type, axonal degeneration is found in association with normal nerve conduction. This subdivision into two main types has been confirmed on the basis of nerve conduction3 and sural nerve biopsy I D Young and P S Harper Figs 3 and 4 Demonstrate severe wasting of small hand musculature. studies.4 The third group consists of a rare progressive "spinal" form of the disease presenting with profound distal weakness and atrophy in the lower limbs with no sensory abnormality. In the four patients described the onset was insidious and the course prolonged with nerve conduction velocities in the normal or low normal range. In this group the primary disease process is believed to consist of degeneration of the anterior horn cell and so this form could equally well be classified as a distal spinal muscular atrophy. In the present family the absence of sensory changes in combination with the electrophysiological findings of normal (or low normal) motor and sensory conduction with chronic partial denervation are most consistent with a diagnosis of chronic distal spinal muscular atrophy. In some affected members with severe longstanding
5 Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy with vocal cord paralysis disease the slight reduction in motor nerve conduction velocity may be attributed to loss of large motor neurones. The absence of pyramidal signs and the slowly progressive course of the disease, make it unlikely that the condition in this family is motor-neurone disease. Only one patient showed sensory changes. In this lady the presence of a large degree of functional overlay and the normal ulnar sensory action potentials indicate that the sensory loss of glove distribution in the upper limbs may have been a spurious observation. The clinical features in this lady are consistent with an associated carpal tunnel syndrome. There have been several reports of distal spinal muscular atrophy occurring in more than one member of a family. Meadows and Marsden5 described three elderly siblings who had suffered from weakness of the hands from childhood with later onset of mild changes in the lower limbs occurring in two of these patients. Pedigree interpretation in this family is complicated by the fact that their father suffered from a similar but clearly different neurological disorder with marked pyramidal signs, but inheritance of the disease affecting the siblings was probably autosomal recessive. In a subsequent publication" this sibship is again described along with three other unrelated patients showing distal symmetrical chronic spinal muscular atrophy. None of these patients showed laryngeal involvement. Autosomal dominant transmission of distal spinal muscular atrophy has also been described, involving two generations in one family,7 and three generations in two further families.7 8 The initial complaint was of lower limb involvement. Six unrelated patients with a form of distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy affecting the hands have recently been described.9 None of these patients had any relevant family history. In none of these cases also was there evidence of any laryngeal involvement. In the subjects of our report only one affected member (IV 10) had a normal voice at the time of examination. All others showed at least unilateral abductor paralysis causing an immobilised fixed cord. In those with bilateral involvement (III 17 and IV 24), the airway had been severely compromised. Individual families have been reported showing adductor or abductor laryngeal paralysis. Plottlo described three brothers with congenital laryngeal abductor paralysis. These boys were also mentally retarded. A family has been described where three male infants had laryngeal stridor due to abductor paralysis, with severe mental and physical retardation.'1 The authors proposed that an abiotrophy of the middle part of the nucleus ambiguus was the most likely pathology. Autosomal dominantly inherited adductor laryngeal paralysis has been reported with a possible linkage to HLA loci on chromosome 6.12 No other clinical abnormalities were present in affected individuals. GENETIC ASPECTS Genetic heterogeneity in spinal muscular atrophy is well recognised and most forms of conventional Mendelian inheritance have been described.13 Allelomorphic activator genes have also been postulated.14 The pedigree of our family is entirely consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance with several examples of male to male transmission. There is no evidence that the sex of the individual alters disease severity. It is notable that the disease pattern tends to be very similar in affected parent and child. Variable expressivity and complete lack of penetrance of the mutant gene are well recognised features of autosomal dominant conditions. In this family one individual (IV 10) showed only bilateral thenar wasting at age 35 years, whereas her second cousin (IV 24) was seriously incapacitated at age 33 years. It is possible that II 4 represented true lack of penetrance. In favour of this is his alleged normality and the teenage onset in most other family members. However, his reluctance to seek medical advice when he had appendicitis may have been based on a realisation of impending muscle weakness with all the implications that would hold for a miner in a depressed area in An alternative explanation for the findings in this family is that two discrete disorders might be segregating, the one being a spinal muscular atrophy and the other a laryngeal palsy. Mathematically this is extremely unlikely unless the loci are so closely linked that recombination does not occur. It is much more probable that the clinical features of this condition represent the pleiotropic effects of a single mutant gene. Conclusion 417 The clinical features in this family appear to be unique and we are unaware of any other reports describing this condition. Electrophysiological data indicate that the basic pathology lies in the anterior horn cell and thus this condition may be classified as a spinal muscular atrophy.
6 418 This report provides further evidence of the wide degree of heterogeneity present in this group of disorders. We are indebted to all staff of the University Hospital of Wales who have assisted in this study. In particular, we thank Dr CEC Wells for referring the family and Drs JG Graham, INF Mc- Queen and D Scruton for the nerve conduction studies. Our thanks also go to Mr RB Bradshaw, Cardiff, Dr C Crawford of Napier, New Zealand and Dr P Hudgson, Newcastle for providing details of family members under their care, and to Professor PK Thomas for advice on the preparation of the manuscript. This paper was presented at the Clinical Genetic Society in Oxford, April References I Dyck PJ, Lambert EH. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. Part 1. (Neurologic, genetic and electrophysiological findings in hereditary polyneuropathies). Arch Neurol 1968; 18: Dyck PJ, Lambert EH. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. Part 2. (Neurologic, genetic and electrophysiological findings in various neuronal degenerations). Arch Neurol 1968; 18: Thomas PK, Calne DB. Motor nerve conduction velocity in peroneal muscular atrophy: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1974; 37: I D Young and P S Harper 4 Behse F, Buchthal F. Peroneal muscular atrophy (PMA) and related disorders-ii. Brain 1977; 100: Meadows JC, Marsden CD. A distal form of chronic spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology (Minneap) 1969; 19: Meadows JC, Marsden CD, Harriman DGF. Chronic spinal muscular atrophy in adults. Part 2. Other forms. J Neurol Sci 1969; 9: McLeod JG, Prineas JW. Distal type of chronic spinal muscular atrophy. Clinical, electrophysiological and pathological studies. Brain 1971; 94: Nelson JW, Amick LD. Heredofamilial progressive spinal muscular atrophy: a clinical and electromyographic study of a kinship Neurology (Minneap) 1966; 16: O'Sullivan DJ, McLeod JG. Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1978; 41: Plott D. Congenital laryngeal-abductor paralysis due to nucleus ambiguus dysgenesis in three brothers. N Engl J Med 1964; 271: Watters GV, Fitch N. Familial laryngeal abductor paralysis and psychomotor retardation. Clin Genet 1973; 4: Mace M, Williamson E, Worgan D. Autosomal dominantly inherited adductor laryngeal paralysis -a new syndrome with a suggestion of linkage to HLA. Clin Genet 1978; 14: Emery AEH. The nosology of the spinal muscular atrophies. J Med Genet 1971; 8: Zellweger H, Hanhart E, Schneider HJ. A new genetic variant of the spinal muscular atrophies in infancy. J Med Genet 1972; 9: J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 May Downloaded from on 3 November 2018 by guest.
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
 Joturnal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 88-93 A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease A P BROOKS* AND A E H EMERY From the University Department of Human Genetics, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh
Joturnal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 88-93 A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease A P BROOKS* AND A E H EMERY From the University Department of Human Genetics, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh
Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 982-986 Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome LUDWIG GUTMANN From the Department of Neurology, West Virginia University,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 982-986 Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome LUDWIG GUTMANN From the Department of Neurology, West Virginia University,
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Table 1: Nerve Conduction Studies (summarised)
 Table 1: Nerve Conduction Studies (summarised) Sensory nerve conduction 1 week* 3 months Superficial radial sensory Normal, symmetric SNAP and CV No change Median to digit II Normal, symmetric SNAP and
Table 1: Nerve Conduction Studies (summarised) Sensory nerve conduction 1 week* 3 months Superficial radial sensory Normal, symmetric SNAP and CV No change Median to digit II Normal, symmetric SNAP and
Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT) Sometimes known as Hereditary Motor and Sensory neuropathy (HMSN) or Peroneal Muscular Atrophy (PMA)
 Version: 2 Published: January 2004 Updated: December 2009 Date of review: November 2011 Author: Dr.Hilton-Jones MD, FRCP, FRCPE Clinical Director, Oxford MDC Muscle and Nerve Centre, and revised by Dr.
Version: 2 Published: January 2004 Updated: December 2009 Date of review: November 2011 Author: Dr.Hilton-Jones MD, FRCP, FRCPE Clinical Director, Oxford MDC Muscle and Nerve Centre, and revised by Dr.
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG
 Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital
 A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital Nerve Conduction Studies Test to evaluate the function of motor / sensory nerves Evaluate Paraesthesia (numbness, tingling, burning) Weakness of arms and legs
A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital Nerve Conduction Studies Test to evaluate the function of motor / sensory nerves Evaluate Paraesthesia (numbness, tingling, burning) Weakness of arms and legs
The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48: 999-1003 The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome SHN J OH, HYUN S KM, BASHRUDDN K AHMAD From the Department ofneurology,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48: 999-1003 The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome SHN J OH, HYUN S KM, BASHRUDDN K AHMAD From the Department ofneurology,
For convenience values outside the normal range are bolded. Normal values for the specified patient are stated below the tables.
 Case tudy 8 or convenience values outside the normal range are bolded. Normal values for the specified patient are stated below the tables. History: 60 year-ol man with a history of left hand weakness
Case tudy 8 or convenience values outside the normal range are bolded. Normal values for the specified patient are stated below the tables. History: 60 year-ol man with a history of left hand weakness
Three patients in a Chinese family with hereditary sensory neuropathy mimicking leprosy
 Lepr Rev (2008) 79, 441 446 CASE REPORT Three patients in a Chinese family with hereditary sensory neuropathy mimicking leprosy JIANPING SHEN*, GUOCHENG ZHANG*, RONGDE YANG**, TINGYING HU** & MIN ZHOU*
Lepr Rev (2008) 79, 441 446 CASE REPORT Three patients in a Chinese family with hereditary sensory neuropathy mimicking leprosy JIANPING SHEN*, GUOCHENG ZHANG*, RONGDE YANG**, TINGYING HU** & MIN ZHOU*
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnostic criteria that predict the response to immunoglobulin treatment
 Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnostic criteria that predict the response to immunoglobulin treatment 7 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, H Franssen, JHJ Wokke, HW Van Es, LH Van den Berg Annals of Neurology 2000;
Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnostic criteria that predict the response to immunoglobulin treatment 7 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, H Franssen, JHJ Wokke, HW Van Es, LH Van den Berg Annals of Neurology 2000;
PERIPHERAL NERVE CONDUCTION IN DIABETIC NEUROPATHYI
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1962, 25, 11. PERIPHERAL NERVE CONDUCTION IN DIABETIC NEUROPATHYI R. W. GILLIATT and R. G. WILLISON2 From the Institute of Clinical Research, the Middlesex Hospital Medical
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1962, 25, 11. PERIPHERAL NERVE CONDUCTION IN DIABETIC NEUROPATHYI R. W. GILLIATT and R. G. WILLISON2 From the Institute of Clinical Research, the Middlesex Hospital Medical
Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of
 Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain. Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic
 Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
Timing of tendon-transfer surgery
 Lepr Rev ( 1983) 54, 109-1 14 Timing of tendon-transfer surgery J W BRANDSMA & T LIJFTOGT All Africa Leprosy and Rehabilitation Training Centre (ALER T), PO Box 165, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Received for
Lepr Rev ( 1983) 54, 109-1 14 Timing of tendon-transfer surgery J W BRANDSMA & T LIJFTOGT All Africa Leprosy and Rehabilitation Training Centre (ALER T), PO Box 165, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Received for
Abstract. Introduction
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 1403-1407 Thr(118)Met in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease ISSN 0100-879X 1403 Thr(118)Met amino acid substitution in the peripheral myelin protein
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 1403-1407 Thr(118)Met in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease ISSN 0100-879X 1403 Thr(118)Met amino acid substitution in the peripheral myelin protein
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerve Site Latency ms Amplitude mv Distance mm Conduction Velocity m/s
 Clinical Electrophysiology Instructions and Sample Reports NCS/EMG REPORT Date: August 2007 Reason for Electrophysiologic Referral: Bilateral upper extremity pain and numbness. History: 59 year-old female
Clinical Electrophysiology Instructions and Sample Reports NCS/EMG REPORT Date: August 2007 Reason for Electrophysiologic Referral: Bilateral upper extremity pain and numbness. History: 59 year-old female
Electrodiagnostic Measures
 Electrodiagnostic Measures E lectrodiagnostic assessments are sensitive, specific, and reproducible measures of the presence and severity of peripheral nerve involvement in patients with diabetes (1).
Electrodiagnostic Measures E lectrodiagnostic assessments are sensitive, specific, and reproducible measures of the presence and severity of peripheral nerve involvement in patients with diabetes (1).
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM. Andrzej Sladkowski
 Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study. Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting
 Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Leprotic Involvement of Multiple Peripheral Nerves in the Absence of Skin Lesions
 LEPROSY REVIEW Leprotic Involvement of Multiple Peripheral Nerves in the Absence of Skin Lesions (A case report) J. C. HARGRAVE, M.B. ; B.S. ; D.T. M. & H. (Medical Officer in Charge, East Arm Leprosarium,
LEPROSY REVIEW Leprotic Involvement of Multiple Peripheral Nerves in the Absence of Skin Lesions (A case report) J. C. HARGRAVE, M.B. ; B.S. ; D.T. M. & H. (Medical Officer in Charge, East Arm Leprosarium,
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG
 Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG Limitations of other methods of investigations of the neuromuscular system - Dr Rob Henderson, Neurologist Assessment of Weakness Thanks Peter Silburn PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG Limitations of other methods of investigations of the neuromuscular system - Dr Rob Henderson, Neurologist Assessment of Weakness Thanks Peter Silburn PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities
 Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL
 A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
Hereditary quadriceps myopathy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 1041-1045 Hereditary quadriceps myopathy MICHAEL L. E. ESPIR AND W. B. MATTHEWS' From the Department of Neurology, Derbyshire Royal Infirmary,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 1041-1045 Hereditary quadriceps myopathy MICHAEL L. E. ESPIR AND W. B. MATTHEWS' From the Department of Neurology, Derbyshire Royal Infirmary,
Jose Santiago Campos, MD and Eric L. Altschuler, MD, PhD
 Numb Toes Jose Santiago Campos, MD and Eric L. Altschuler, MD, PhD No one involved in the planning of this CME activity have anyy relevant financial relationships to disclose. Authors/faculty have nothingg
Numb Toes Jose Santiago Campos, MD and Eric L. Altschuler, MD, PhD No one involved in the planning of this CME activity have anyy relevant financial relationships to disclose. Authors/faculty have nothingg
Ahmed Abbas, Mark Cook, Liong Hiew Fu, Alistair Lewthwaite, Colin Shirley, Yusuf A. Rajabally
 2016, Elsevier. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ Accepted Manuscript A case of POEMS mimicking
2016, Elsevier. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ Accepted Manuscript A case of POEMS mimicking
Neonatal Hypotonia. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy. Neurology Chapter of IAP
 The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy'
 Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
ACUTE SYMMETRICAL MOTOR NEUROPATHY IN DIABETES MELLITUS
 Prize-Winning Paper Summary ACUTE SYMMETRICAL MOTOR NEUROPATHY IN DIABETES MELLITUS A distinct clinical entity M. Gourie Devi* The main clinical features in 12 patients with acute motor neuropathy associated
Prize-Winning Paper Summary ACUTE SYMMETRICAL MOTOR NEUROPATHY IN DIABETES MELLITUS A distinct clinical entity M. Gourie Devi* The main clinical features in 12 patients with acute motor neuropathy associated
Muscle Weakness Or Paralysis With Compromise Of Peripheral Nerve
 Muscle Weakness Or Paralysis With Compromise Of Peripheral Nerve Muscle weakness or complete paralysis may be secondary to an interruption in the communication between the brain and nerve cells in the
Muscle Weakness Or Paralysis With Compromise Of Peripheral Nerve Muscle weakness or complete paralysis may be secondary to an interruption in the communication between the brain and nerve cells in the
419 Church Street East, Penrose, Auckland 1642 P O Box 12063, Penrose, Auckland
 CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH DISEASE What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease? First described in 1886 by three physicians Jean-Marie Charcot, Pierre Marie, and Howard Henry Tooth, CharcotMarie-Tooth (CMT) is a group
CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH DISEASE What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease? First described in 1886 by three physicians Jean-Marie Charcot, Pierre Marie, and Howard Henry Tooth, CharcotMarie-Tooth (CMT) is a group
Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb.
 Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Definitions Radiculopathy Process affecting the nerve root, most commonly by a herniated disc Weakness in muscles supplied by the
Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Definitions Radiculopathy Process affecting the nerve root, most commonly by a herniated disc Weakness in muscles supplied by the
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression. Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre
 Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer
 AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Is Bell s palsy a component of polyneuropathy?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Bell s palsy a component of polyneuropathy? Tu ba Tunç MD, Erkan Tarhan MD,, Haldun O uz MD, Mustafa As m Þafak MD, Gülnihal Kutlu MD, Levent E. nan MD From Ministry of Health, Ankara
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Bell s palsy a component of polyneuropathy? Tu ba Tunç MD, Erkan Tarhan MD,, Haldun O uz MD, Mustafa As m Þafak MD, Gülnihal Kutlu MD, Levent E. nan MD From Ministry of Health, Ankara
Compound Action Potential, CAP
 Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Electrodiagnosis of the carpal tunnel syndrome
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 23-27 FRANK KEMBLE From the Department of Neurology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In the carpal tunnel syndrome median nerve motor conduction may be delayed
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 23-27 FRANK KEMBLE From the Department of Neurology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In the carpal tunnel syndrome median nerve motor conduction may be delayed
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle AOFAS Resident Review Course September 28, 2013
 Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Case Example. Nerve Entrapments in the Lower limb
 Nerve Entrapments in the Lower limb February, 2013 William S. Pease, M.D. Ernest W. Johnson Professor of PM&R Case Example CC: Right ankle dorsiflexion weakness with minimal paresthesias HPI: 87 year-old
Nerve Entrapments in the Lower limb February, 2013 William S. Pease, M.D. Ernest W. Johnson Professor of PM&R Case Example CC: Right ankle dorsiflexion weakness with minimal paresthesias HPI: 87 year-old
Treatment of multifocal motor neuropathy with interferon-β1a
 Treatment of multifocal motor neuropathy with interferon-β1a 12 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, LH Van den Berg, H Franssen, PA Van Doorn, ISJ Martina, JHJ Wokke Adapted from Neurology 2000; 54: 1518-1521. Chapter
Treatment of multifocal motor neuropathy with interferon-β1a 12 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, LH Van den Berg, H Franssen, PA Van Doorn, ISJ Martina, JHJ Wokke Adapted from Neurology 2000; 54: 1518-1521. Chapter
Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature D Reichner, G Evans Citation D Reichner,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature D Reichner, G Evans Citation D Reichner,
Clinical and Electrophysiological Study in Carpel Tunnel Syndrome
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. IV (May - Jun. 2015), PP 32-37 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical and Electrophysiological
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. IV (May - Jun. 2015), PP 32-37 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical and Electrophysiological
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
diphenylhydantoin therapy1
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 1235-1239 Motor nerve conduction study in patients on diphenylhydantoin therapy1 S. CHOKROVERTY2 AND Z. A. SAYEED3 From the Neurology Service
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 1235-1239 Motor nerve conduction study in patients on diphenylhydantoin therapy1 S. CHOKROVERTY2 AND Z. A. SAYEED3 From the Neurology Service
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Wrist, Elbow Hand. Surface Recording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle
 Surface ecording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle Original Settings Sensitivity, duration of pulse, sweep speed, low-frequency filter, high- frequency filter, and the machine used were not
Surface ecording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle Original Settings Sensitivity, duration of pulse, sweep speed, low-frequency filter, high- frequency filter, and the machine used were not
LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES
 Neurology DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-382 LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES ANA MARIA GALAMB, IOAN DAN MINEA Department of Medical and Surgical Specialities, Faculty of Medicine,
Neurology DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-382 LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES ANA MARIA GALAMB, IOAN DAN MINEA Department of Medical and Surgical Specialities, Faculty of Medicine,
Pedigree Construction Notes
 Name Date Pedigree Construction Notes GO TO à Mendelian Inheritance (http://www.uic.edu/classes/bms/bms655/lesson3.html) When human geneticists first began to publish family studies, they used a variety
Name Date Pedigree Construction Notes GO TO à Mendelian Inheritance (http://www.uic.edu/classes/bms/bms655/lesson3.html) When human geneticists first began to publish family studies, they used a variety
Case Report. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(1):109-115 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.109 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Sonographic Evaluation of the Peripheral Nerves
Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(1):109-115 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.109 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Sonographic Evaluation of the Peripheral Nerves
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Audit of CTS screening guidelines. Introduction and background Robin Kennett
 Audit of CTS screening guidelines Introduction and background Robin Kennett NHS requirements Reduced waiting times Delivery of service close to patient s home Choice of provider Standardization of results,
Audit of CTS screening guidelines Introduction and background Robin Kennett NHS requirements Reduced waiting times Delivery of service close to patient s home Choice of provider Standardization of results,
Motor neurone disease
 Motor neurone disease n abnormality of nerve metabolism J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1969, 32, 1-5 HGWN SHHNI* ND W. RITCHIE RUSSELL From the Department of Neurology, Churchill Hospital, Oxford Recent
Motor neurone disease n abnormality of nerve metabolism J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1969, 32, 1-5 HGWN SHHNI* ND W. RITCHIE RUSSELL From the Department of Neurology, Churchill Hospital, Oxford Recent
Multifocal motor neuropathy: long-term clinical and electrophysiological assessment of intravenous immunoglobulin maintenance treatment
 Multifocal motor neuropathy: long-term clinical and electrophysiological assessment of intravenous immunoglobulin maintenance treatment 11 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, H Franssen, JHJ Wokke, LH Van den Berg
Multifocal motor neuropathy: long-term clinical and electrophysiological assessment of intravenous immunoglobulin maintenance treatment 11 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, H Franssen, JHJ Wokke, LH Van den Berg
Conclusions The modified segmental palmar test is a sensitive, robust and easily applicable method in diagnosing CTS.
 Abstract Objective To test our hypothesis that comparing the sensory nerve conduction velocity of the median nerve across the wrist with that of the forearm is more sensitive than comparing it with that
Abstract Objective To test our hypothesis that comparing the sensory nerve conduction velocity of the median nerve across the wrist with that of the forearm is more sensitive than comparing it with that
Hands on Nerve Conduction Studies
 Hands on Nerve Conduction Studies N. CUTANEUS ANTEBRACHII LATERALIS Type of measurement: Antidromic. Position of limb: Subject supine, elbow extended, and forearm supinated. Type of recording electrodes:
Hands on Nerve Conduction Studies N. CUTANEUS ANTEBRACHII LATERALIS Type of measurement: Antidromic. Position of limb: Subject supine, elbow extended, and forearm supinated. Type of recording electrodes:
Left peroneal neuropathy icd 10 code
 Cari untuk: Cari Cari Left peroneal neuropathy icd 10 code 2018 ICD-10 code for Injury of deep peroneal nerve at ankle and foot level, left leg is S94.22. Lookup the complete ICD 10 Code details for S94.22.
Cari untuk: Cari Cari Left peroneal neuropathy icd 10 code 2018 ICD-10 code for Injury of deep peroneal nerve at ankle and foot level, left leg is S94.22. Lookup the complete ICD 10 Code details for S94.22.
A CLINICAL AND ELECTRICAL STUDY OF ULNAR
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1960, 23, 1. A CLINICAL AND ELECTRICAL STUDY OF ULNAR NERVE LESIONS IN THE HAND BY PETER EBELING,* R. W. GILLIATT, and P. K. THOMAS From the Department of Applied Electrophysiology,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1960, 23, 1. A CLINICAL AND ELECTRICAL STUDY OF ULNAR NERVE LESIONS IN THE HAND BY PETER EBELING,* R. W. GILLIATT, and P. K. THOMAS From the Department of Applied Electrophysiology,
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat. Dr Hadi Manji
 CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries. First Global Conflict Medicine Congress
 Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Pediatric Aspects of EDX
 Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
electrophysiological and nerve biopsy study
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:543-548 Delayed neuropathy after organophosphorus insecticide (Dipterex) poisoning: a clinical, electrophysiological and nerve biopsy study C
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:543-548 Delayed neuropathy after organophosphorus insecticide (Dipterex) poisoning: a clinical, electrophysiological and nerve biopsy study C
Foot. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
MARTIN- GRUBER ANASTOMOSIS AND CARPAL TUNNEL PHYSIOLOGIC IMPLICATIONS AND PITFALLS. Daniel Dumitru, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION
 MARTIN- GRUBER ANASTOMOSIS AND CARPAL TUNNEL PHYSIOLOGIC IMPLICATIONS AND PITFALLS Daniel Dumitru, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION Focal compressive median nerve sensory and motor neuropathies about the wrist
MARTIN- GRUBER ANASTOMOSIS AND CARPAL TUNNEL PHYSIOLOGIC IMPLICATIONS AND PITFALLS Daniel Dumitru, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION Focal compressive median nerve sensory and motor neuropathies about the wrist
MSA. Sleep disorders MULTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY AND NOCTURNAL STRIDOR 1/26/2015. Alex Iranzo Neurology Service Hospital Clinic de Barcelona Spain
 MULTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY AND NOCTURNAL STRIDOR Alex Iranzo Neurology Service Hospital Clinic de Barcelona Spain MSA Neurodegenerative disease Parkinsonism, cerebellar, dysautonomia Mean survival is less
MULTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY AND NOCTURNAL STRIDOR Alex Iranzo Neurology Service Hospital Clinic de Barcelona Spain MSA Neurodegenerative disease Parkinsonism, cerebellar, dysautonomia Mean survival is less
Peripheral Nerve Problems
 Patient Education Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout provides general information about how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral
Patient Education Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout provides general information about how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral
Prognosis of alcoholic peripheral neuropathy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:699-703 Prognosis of alcoholic peripheral neuropathy MATTI HILLBOM,* ARNE WENNBERGt From the Department of Clinical Alcohol and Drug Research,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:699-703 Prognosis of alcoholic peripheral neuropathy MATTI HILLBOM,* ARNE WENNBERGt From the Department of Clinical Alcohol and Drug Research,
Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report.
 Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report. Brogren, Elisabeth; Dahlin, Lars Published in: Journal of Hand Surgery DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.09.014
Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report. Brogren, Elisabeth; Dahlin, Lars Published in: Journal of Hand Surgery DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.09.014
Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve Action Potential in Common Peroneal Neuropathy
 J Korean Med Sci 2008; 23: 117-21 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.117 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve
J Korean Med Sci 2008; 23: 117-21 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.117 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve
A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies
 Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
PERIPHERAL NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITIES AND HANDEDNESS IS THERE ANY CORELATION? (govt. Medical College surat.)(anirudha Apte-consultant Neurologist)
 6 PERIPHERAL NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITIES AND HANDEDNESS IS THERE ANY CORELATION? ABSTRACT: SWAPNA APTE 1, ANIRUDHA APTE 2, HETAL THAKER 1 RAVI SAXENA 1 RINI TEKRIWAL 2, DHARITRI PARMAR 2. (govt. Medical
6 PERIPHERAL NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITIES AND HANDEDNESS IS THERE ANY CORELATION? ABSTRACT: SWAPNA APTE 1, ANIRUDHA APTE 2, HETAL THAKER 1 RAVI SAXENA 1 RINI TEKRIWAL 2, DHARITRI PARMAR 2. (govt. Medical
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017
 A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
How To Approach Clinical Examinations In Medicine
 How To Approach Clinical Examinations In Medicine This document is based on the handout from the Medicine for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are relevant
How To Approach Clinical Examinations In Medicine This document is based on the handout from the Medicine for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are relevant
EVALUATION OF HYPERPOLARIZATION POTENTIALS AND NERVE CONDUCTION PARAMETERS IN AXONAL NEUROPATHIC PATIENTS
 EVALUATION OF HYPERPOLARIZATION POTENTIALS AND NERVE CONDUCTION PARAMETERS IN AXONAL NEUROPATHIC PATIENTS Muhammad Abdul Azeem, Nabeeh Ibrahim Ali Rakkah, Muhammad Amir Mustufa, Anwar Ali *, Najamuddin
EVALUATION OF HYPERPOLARIZATION POTENTIALS AND NERVE CONDUCTION PARAMETERS IN AXONAL NEUROPATHIC PATIENTS Muhammad Abdul Azeem, Nabeeh Ibrahim Ali Rakkah, Muhammad Amir Mustufa, Anwar Ali *, Najamuddin
SENSORY NERVE ACTION POTENTIALS IN PATIENTS WITH PERIPHERAL NERVE LESIONS
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1958, 21, 19. SENSORY NERVE ACTION POTENTIALS IN PATIENTS WITH PERIPHERAL NERVE LESIONS BY R. W. GILLIATT and T. A. SEARS From the Department of Applied Electrophysiology,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1958, 21, 19. SENSORY NERVE ACTION POTENTIALS IN PATIENTS WITH PERIPHERAL NERVE LESIONS BY R. W. GILLIATT and T. A. SEARS From the Department of Applied Electrophysiology,
Deformity and Pain in Foot of Neuromuscular Disease
 Deformity and Pain in Foot of Neuromuscular Disease CHA 의과학대학재활의학과김민영 (2012.11.10 제 4 회대한발의학회 ) Neuromuscular Diseases & Foot Deformity : almost Pain : infrequent Non-ambulatory, Ambulatory Neuromuscular
Deformity and Pain in Foot of Neuromuscular Disease CHA 의과학대학재활의학과김민영 (2012.11.10 제 4 회대한발의학회 ) Neuromuscular Diseases & Foot Deformity : almost Pain : infrequent Non-ambulatory, Ambulatory Neuromuscular
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
Case Report. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2018;42(3):483-487 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.3.483 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Diagnosis of Pure Ulnar Sensory Neuropathy Around
Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2018;42(3):483-487 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.3.483 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Diagnosis of Pure Ulnar Sensory Neuropathy Around
ND Lesson 2.5 Jigsaw Case Study #1
 ND Lesson 2.5 Jigsaw Case Study #1 Gabby Gabby is 5 years old. Her parents have consulted with many specialists throughout their daughter s life in hopes of finding an explanation for why their daughter
ND Lesson 2.5 Jigsaw Case Study #1 Gabby Gabby is 5 years old. Her parents have consulted with many specialists throughout their daughter s life in hopes of finding an explanation for why their daughter
ACUTE AND CHRONIC NEUROPATHIES
 ACUTE AND CHRONIC NEUROPATHIES American College of Osteopathic Internists Internal Medicine Board Review Course 2018 April 25-29, 2018 Marriott Chicago Downtown Chicago, Illinois Scott Spradlin D.O.,FACP,FACOI
ACUTE AND CHRONIC NEUROPATHIES American College of Osteopathic Internists Internal Medicine Board Review Course 2018 April 25-29, 2018 Marriott Chicago Downtown Chicago, Illinois Scott Spradlin D.O.,FACP,FACOI
Update: Plasmapheresis in Neurologic Disorders
 Update: Plasmapheresis in Neurologic Disorders Case Presentation A 62-year-old, right-hand-dominant male presented to the emergency department with a 3-day history of progressive weakness. Initially he
Update: Plasmapheresis in Neurologic Disorders Case Presentation A 62-year-old, right-hand-dominant male presented to the emergency department with a 3-day history of progressive weakness. Initially he
