Implementing receptor theory in PK-PD modeling
|
|
|
- Bryan Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
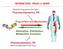
1 Drug in Biophase Drug Receptor Interaction Transduction EFFECT Implementing receptor theory in PK-PD modeling Meindert Danhof & Bart Ploeger PAGE, Marseille, 19 June 2008
2 Mechanism-based PK-PD modeling current status and future directions Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics Pharmacodynamics Disease Clinical outcome Physiologicallybased PK modeling - Biophase..distribution Mechanism-based PD modeling - Receptor theory - PD Interactions - Dynamical..Systems analysis Mechanism-based PD modeling - Receptor theory - PD Interactions - Dynamical Systems analysis Mechanism-based disease modeling - Disease system..analysis Danhof M. et al., (2007) Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 47: Intrinsic and Operational Efficacy/Safety
3 Mechanism-based PK-PD modeling a pharmacologist s view Describe processes on the causal chain between (plasma) concentration and effect 1. Target site distribution 2. Target binding and activation 3. Transduction processes 4. Pharmacodynamic interactions 5. Homeostatic feedback In Vivo Transduction Danhof M. et al., (2007) Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 47:
4 Implementing receptor theory in PK-PD modeling Concentration-effect relationship
5 Concentration-effect relationships can differ between tissues, species and individuals Affinity R 0, k e, E m, n E max DRUG SYSTEM N Intrinsic Efficay EC 50 Tissue Species Gender Age Disease Chronic treatment
6 Receptor theory for prediction of concentration-effect relationships In vivo concentration-effect relationships Tissue selectivity of drug effects Interspecies differences in concentration-effect relationships Tolerance and sensitization Intra- and inter-individual variability Receptor function as a determinant of drug effect
7 Receptor theory for prediction of concentration-effect relationships S = ε R K PD [ D ] + [ D ] tot = e K PD PD + [ D ] [ D ] E = f ([ S ]) [S] Receptor Activation e PD E Transducer Function? K PD [D] [S]
8 Identification of the receptor model application to GABA A receptor agonists Simultaneous analysis of the concentration-effect curves of flunitrazepam, midazolam, oxazepam and clobazam Assumption of a single and unique transducer function (non-parametric; continuously increasing function) Description of the receptor activation process on basis of a hyperbolic function Comparative method for estimation of the drugspecific parameters
9 Midazolam: plasma concentrations and EEG effect in individual rats PK-PD Simultaneous monitoring of plasma concentration and EEG effect results in data sets that can be subjected to PK-PD modelling In this manner concentration effect relationships are obtained in individual rats From: Mandema et al., Br. J. Pharmacol. 102: (1991)
10 EEG effect: benzodiazepines differ in potency and intrinsic activity Amplitudes Hz (μv/s)... PK-PD In vivo concentration- EEG effect relationships of 4 benzodiazepines: Flunitrazepam ( ) Midazolam ( ) Oxazepam ( )and Clobazam ( ) Plasma concentration (mg/l) From: Mandema et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 257: (1991)
11 Non-linear transducer function with no saturation at high stimulus intensities Drug-specific receptor interaction parameters System-specific transducer function Drug KPD epd ng.ml -1 Flunitrazepam 21 ± Midazolam 43 ± ± 0.03 Oxazepam 411 ± ± 0.04 Clobazam 782 ± ± 0.03 Beta amplitude (μv/s) Stimulus From: Tuk et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 289: (1999)
12 Neurosteroids and benzodiazepines share the same transducer function O O CH 3 N O Cl N OH H Alphaxalone Pregnanolone ORG ORG Diazepam Flunitrazepam Midazolam Clobazam Zolpidem Oxazepam Zopiclone Bretazenil
13 EEG effects of alphaxalone and midazolam are quantitatively and qualitatively different In vivo effect-time course Concentration-effect relationship From: Visser et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302: (2002)
14 A parabolic function describes the stimulusresponse relationship of alphaxalone Drug-receptor interaction Stimulus-response relationship From: Visser et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302: (2002)
15 Mechanism-Based PK-PD Model for Neurosteroids and Benzodiazepines Drug-receptor interaction Stimulus-response relationship Stimulus Response Concentration Stimulus Stimulus = S( C ) = e C e C + K PD e PD E = f ( S ) = E top a( S d 2 b )
16 Model predicts monophasic concentration effect relationships for partial agonists Drug-receptor interaction Concentration-effect relationship
17 Benzodiazepines are partial agonists at the GABA A receptor in vivo Drug-receptor interaction Stimulus-response relationship Stimulus EEG effect Hz (μv) Concentration (ng.ml -1 ) Stimulus From: Visser et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 304: (2003)
18 Mechanism-based PK-PD model allows prediction of potency and intrinsic efficacy pk i versus pk PD GABA-shift versus e PD Log (K PD, unbound) (ng.ml -1 ) e PD Log K 1 (ng.ml -1 ) GABA-Shift From: Visser et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 304: (2003)
19 Application of receptor theory in PK-PD modeling is generally feasible A 1 adenosine receptor agonists Synthetic μ opioid receptor agonists 5-HT 1A serotonin receptor agonists GABA A receptor agonists Beta receptor antagonists herg channel ligands..
20 Application of receptor theory in PK-PD modeling challenges Kinetics of receptor association and dissociation Modeling of constitutive activity and inverse agonism Modeling of allosteric modulation Modeling of the role of receptor subunit composition Interspecies extrapolation Intra- and inter-individual variation
21 Implementing receptor theory in PK-PD modeling Kinetics of drug action
22 Kinetics of drug-action: receptor kinetics and transducer function Time-course of drug effect = Receptor kinetics + Transducer Function Effect Time Receptor occupancy Time Effect Receptor occupancy
23 How to distinguish receptor kinetics from the transducer function? Two-stage approach Estimate the receptor kinetics independently In vitro receptor binding experiment Measuring the concentration in the biophase Fix receptor kinetics and estimate transducer function Simultaneous approach Collect detailed data on pharmacology Different doses and/or infusion scheme s Combine data from compounds acting on the same system Full and partial agonist, agonists and antagonists, etc.
24 Estimating receptor kinetics in vitro using competition with a tracer Parameters of interest Kd D k ond Tracer Drug R + D + T k offd R_D Kd T k offt R_T k ont Kd D (Kd drug)=k offd /k ond Kd T (Kd tracer)= =k offt /k ont R: target D: drug T: tracer RD: target-drug complex RT: target-tracer complex
25 Estimating receptor kinetics in vitro experimental approach K d,t k on,t Equilibrium experiment Association experiment k on,d & k off,d k off,t Dissociation experiment Competitive binding experiment
26 Estimating receptor kinetics in vitro model structure Stuctural model: CL=concentration ligand; CD=concentration drug Assumption: CL and CD in excess DADT(1)= k on L*A(2)*L-A(1)*k off L DADT(2)=-(k on L*CL+k on D*CD)*A(2)+A(1)*k off L+A(3)*k off D DADT(3)= k on D*A(2)*CD-A(3)*k off D ; RL ; free R ; RD Association: Dissociation: Equilibrium: IPRED= A(1) IPRED= A(3) IPRED= B max *CL/(K d L+CL) Stochastic model: Between experiment variability on B max Proportional residual error k on D k on L R+L RL + k off L D k off D RD
27 Estimating receptor kinetics in vitro optimal design k offt k ond & k offd Kd T k ont Equilibrium exp. Association exp. Dissociation exp. Competitive binding exp. All rate constants can be identified using equilibrium and competitive binding experiments Repeat competitive binding experiments for at least 3 drug concentrations For the simulated compounds at least 10 measurements in the first hour are required
28 Estimating receptor kinetics in vitro application to a slow-offset drug RT concentration (pm) Equilibrium experiments Tracer concentration (pm) RT concentration (pm) Parameter estimates Competitive binding experiments Time (min) Parameter equilibrium + competitive binding exp. equilibrium + competitive binding + association exp. kofft (1/min) KdT (pm) koff drug Kd drug (pm)
29 Estimating receptor kinetics in vivo using biophase concentration data intravenous saturating injection of [ 11 C]Flumazenil male Wistar rat arterial blood sampling scanning under anaesthesia Flumazenil in brain with PET-scanner data analysis (NONMEM) Spec. Binding Plasma Conc. HPLC-UV analysis of Flumazenil in blood LC Liefaard et al. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2005;7(6):
30 Estimating receptor kinetics of flumazenil in rat brain in vivo Blood Non linearity Brain LC Liefaard et al. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2005;7(6):
31 Pharmacokinetic model for estimation of flumazenil receptor kinetics in vivo LC Liefaard et al. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2005;7(6):
32 Pharmacokinetic model for estimation of flumazenil receptor kinetics in vivo Conc. FMZ (ng/ml) Blood-PK Conc. FMZ (ng/ml) Brain-PK PRED Time (min) Time (min) LC Liefaard et al. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2005;7(6):
33 Effect of amygdala kindling on blood-brain transport and receptor kinetics Flumazenil bound to GABA Receptor control kindled Amygdala kindling: Decrease in receptor capacity 36% of control rats Increase in blood-brain distribution 178% of control rats Total brain concentration LC Liefaard et al. Epilepsia 2008;accepted
34 Simultaneous estimation of receptor kinetics and transducer function: opioids Natural and (semi-)synthetic opioids are effective analgesics Potentially life-threatening respiratory depression is a major concern Design of novel opioids with optimized efficacysafety Partial agonism as the basis for improved selectivity of action
35 Whole body plethysmography for monitoring of respiratory depression in rats
36 PK-PD correlation of semi-synthetic opioids mechanisms of hysteresis Plasma concentration biophase concentration receptor Yassen et al., (2006) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319:
37 Modeling of hysteresis in the effects of fentanyl and buprenorphine (a) Biophase distribution model dce = ke0 (C p Ce ) dt (b) Receptor association/dissociation model dc p dt R = k on C (c) Combined model (a + b) dcer dt = k on * * C e p * * ( 1 C R) k * C R p off ( 1 C R) k * C R e Yassen et al., (2006) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319: off e p
38 Modeling of the concentration-effect relations of fentanyl and buprenorphine Sigmoid E max model (Hill equation) E = 1 n α C EC + C Receptor model with linear transduction n 50 [ CeR] Ce = [ Rtot ] K D + Ce n E = E 0 1 α [ C ] er [ R ] tot Yassen et al., (2006) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319:
39 Yassen et al., (2006) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319: Time course of respiratory depression in rats following buprenorphine mg/kg 0.05 mg/kg 0.1 mg/kg 0.3 mg/kg Detailed dataset with wide dose range Slow receptor dissociation? Partial agonist?
40 Time course of respiratory depression in rats following fentanyl 0.03 mg/kg 0.06 mg/kg 0.08 mg/kg mg/kg Fast receptor association/dissociation Full agonist? Yassen et al., (2006) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319:
41 Mechanism-based model for respiratory depression parameter estimates Fentanyl Buprenorphine k e0, min -1 T ½,keO, min 0.44 (-) (79%) 19.9 k on, ml.ng -1.min -1 ( > 100) (-) k off, min -1 T ½,koff, min ( > 100) (~ 0) (75%) 7.8 K D, ng.ml -1 EC 50, ng.ml -1 n.a (84%) 0.16 n.a. α ~ (14%) Hill factor 1.15 (-) n.a. Yassen et al., (2006) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319:
42 Animal to human extrapolation of the pharmacodynamics of buprenorphine Simultaneous analysis of the effects in rats and humans Respiratory depression Antinociception No scaling of receptor association-dissociation kinetics (drug-specific properties) Allometric scaling of biophase distribution kinetics k e0 = a WT b Yassen et al., (2007) Clin. Pharmacokin. 46:
43 Animal to human extrapolation of the pharmacodynamics of buprenorphine R 2 = R 2 = Yassen et al., (2007) Clin. Pharmacokin. 46:
44 Animal to human extrapolation of the pharmacodynamics of buprenorphine Drug specific parameters k on, ml.ng -1.min -1 k off, min -1 K D, nm α System specific parameter k e0 = a.wt b a, min -1 b Antinociception (18.3) (23.1) 7.5 n.e (11.3) (9.6) Respiratory depression 0.23 (15.8) (27.7) Yassen et al., (2007) Clin. Pharmacokin. 46:
45 Implementing receptor theory in PK-PD modeling Concluding remarks
46 Implementing receptor theory in PK-PD modeling conclusions Estimation of receptor theory PK-PD models requires detailed information on pharmacology Data should allow to distinguish drug-specific and system-specific parameters Combine in vitro and in vivo data Evaluate different dose levels and/or infusion scheme s Combine data from compounds acting on the same system
Pharmacology. Biomedical Sciences. Dynamics Kinetics Genetics. School of. Dr Lindsey Ferrie
 Pharmacology Dynamics Kinetics Genetics Dr Lindsey Ferrie lindsey.ferrie@ncl.ac.uk MRCPsych Neuroscience and Psychopharmacology School of Biomedical Sciences Dynamics What the drug does to the body What
Pharmacology Dynamics Kinetics Genetics Dr Lindsey Ferrie lindsey.ferrie@ncl.ac.uk MRCPsych Neuroscience and Psychopharmacology School of Biomedical Sciences Dynamics What the drug does to the body What
Fundamentals of Pharmacology
 Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
MR04A3 An isoindoline derivative, New Sedative/Anesthetic Agent
 MR04A3 An isoindoline derivative, ew Sedative/Anesthetic Agent ovember 2009 1 Introduction Sedatives are widely used in: Settings providing stressful and painful procedures Gastroenterology (colonoscopy
MR04A3 An isoindoline derivative, ew Sedative/Anesthetic Agent ovember 2009 1 Introduction Sedatives are widely used in: Settings providing stressful and painful procedures Gastroenterology (colonoscopy
Concentration of drug [A]
![Concentration of drug [A] Concentration of drug [A]](/thumbs/74/70683906.jpg) Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS 1 Receptor occupancy - mass action The interaction of a drug with a receptor is reversible due to interactions via weak bonds (not covalent). [A] +
Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS 1 Receptor occupancy - mass action The interaction of a drug with a receptor is reversible due to interactions via weak bonds (not covalent). [A] +
PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS. Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. Office: 2B 84
 PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Quantitative aspects of drugs By the end of this lecture, you should: Determine quantitative
PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Quantitative aspects of drugs By the end of this lecture, you should: Determine quantitative
Basic pharmacokinetics. Frédérique Servin APHP hôpital Bichat Paris, FRANCE
 Basic pharmacokinetics Frédérique Servin APHP hôpital Bichat Paris, FRANCE DOSE CONCENTRATION EFFECT Pharmacokinetics What the body does to the drug Pharmacodynamics What the drug does to the body Transfer
Basic pharmacokinetics Frédérique Servin APHP hôpital Bichat Paris, FRANCE DOSE CONCENTRATION EFFECT Pharmacokinetics What the body does to the drug Pharmacodynamics What the drug does to the body Transfer
S.A.G. VISSER, 1 F.L.C. WOLTERS, J. M. GUBBENS-STIBBE, E. TUKKER, P. H. VAN DER GRAAF, L. A. PELETIER, and M. DANHOF
 0022-3565/03/3041-88 101$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 304, No. 1 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 42341/1029541
0022-3565/03/3041-88 101$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 304, No. 1 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 42341/1029541
Clinical Pharmacology. Pharmacodynamics the next step. Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand
 1 Pharmacodynamic Principles and the Course of Immediate Drug s Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand The time course of drug action combines the principles
1 Pharmacodynamic Principles and the Course of Immediate Drug s Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand The time course of drug action combines the principles
January 25, Introduction to Pharmacology
 January 25, 2015 Introduction to Pharmacology Edward Fisher, Ph.D., R.Ph. Professor and Associate Dean for Academic Affairs Director MS Clinical Psychopharmacology University of Hawaii at Hilo College
January 25, 2015 Introduction to Pharmacology Edward Fisher, Ph.D., R.Ph. Professor and Associate Dean for Academic Affairs Director MS Clinical Psychopharmacology University of Hawaii at Hilo College
Dose-Dependent EEG Effects of Zolpidem Provide Evidence for GABA A Receptor Subtype Selectivity in Vivo
 0022-3565/03/3043-1251 1257$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 304, No. 3 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 44859/1048182
0022-3565/03/3043-1251 1257$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 304, No. 3 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 44859/1048182
Ideal Sedative Agent. Benzodiazepines 11/12/2013. Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines Used for Conscious Sedation in Dentistry.
 Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines Used for Conscious Sedation in Dentistry Peter Walker Ideal Sedative Agent Anxiolysis Analgesic No effect on CVS No effect on respiratory system Not metabolised Easy and
Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines Used for Conscious Sedation in Dentistry Peter Walker Ideal Sedative Agent Anxiolysis Analgesic No effect on CVS No effect on respiratory system Not metabolised Easy and
Ideal Sedative Agent. Pharmacokinetics. Benzodiazepines. Pharmacodynamics 11/11/2013
 Ideal Sedative Agent Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines Used for Conscious Sedation in Dentistry Peter Walker Anxiolysis Analgesic No effect on CVS No effect on respiratory system Not metabolised Easy and
Ideal Sedative Agent Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines Used for Conscious Sedation in Dentistry Peter Walker Anxiolysis Analgesic No effect on CVS No effect on respiratory system Not metabolised Easy and
Receptor Occupancy Theory
 Pharmacodynamics 1 Receptor Occupancy Theory The Law of Mass Action Activation of membrane receptors and target cell responses is proportional to the degree of receptor occupancy. Assumptions: Association
Pharmacodynamics 1 Receptor Occupancy Theory The Law of Mass Action Activation of membrane receptors and target cell responses is proportional to the degree of receptor occupancy. Assumptions: Association
Biomath M263 Clinical Pharmacology
 Training Program in Translational Science Biomath M263 Clinical Pharmacology Spring 2013 www.ctsi.ucla.edu/education/training/webcasts Wednesdays 3 PM room 17-187 CHS 4/3/2013 Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Training Program in Translational Science Biomath M263 Clinical Pharmacology Spring 2013 www.ctsi.ucla.edu/education/training/webcasts Wednesdays 3 PM room 17-187 CHS 4/3/2013 Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
PEDRO AMORIM, MD PORTUGAL.
 PEDRO AMORIM, MD Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine Hospital Santo António Centro Hospitalar do Porto University of Porto PORTUGAL pamorim@vianw.pt Drug Pharmacology Any
PEDRO AMORIM, MD Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine Hospital Santo António Centro Hospitalar do Porto University of Porto PORTUGAL pamorim@vianw.pt Drug Pharmacology Any
Pharmacodynamics. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Pharmacodynamics Dr. Alia Shatanawi Drug Receptor Interactions Sep-17 Dose response relationships Graduate dose-response relations As the dose administrated to single subject or isolated tissue is increased,
Pharmacodynamics Dr. Alia Shatanawi Drug Receptor Interactions Sep-17 Dose response relationships Graduate dose-response relations As the dose administrated to single subject or isolated tissue is increased,
Pharmacodynamic principles and the time course of immediate drug effects
 TCP 2017;25(4):157-161 http://dx.doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2017.25.4.157 Pharmacodynamic principles and the time course of immediate drug effects TUTORIAL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology,
TCP 2017;25(4):157-161 http://dx.doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2017.25.4.157 Pharmacodynamic principles and the time course of immediate drug effects TUTORIAL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology,
Dr. Nele Plock. Dr. N. Plock, March 11, 2008, American Conference on Pharmacometrics
 Parallel PKPD modeling of an endogenous agonist (A) and exogenous antagonist (B) based on research PKPD data to predict an effective first-in-man dose of B A combination of physiologically based PK and
Parallel PKPD modeling of an endogenous agonist (A) and exogenous antagonist (B) based on research PKPD data to predict an effective first-in-man dose of B A combination of physiologically based PK and
DRUG EVALUATION IN PEDIATRICS USING K-PD MODELS: PERSPECTIVES
 DRUG EVALUATION IN PEDIATRICS USING K-PD MODELS: PERSPECTIVES Michel TOD, PhD Pascal Girard, PhD EA3738, Faculté Médecine Lyon Sud Lyon I University, France Tod / Girard 1 EMEA 14 April 008 USES OF MODELS
DRUG EVALUATION IN PEDIATRICS USING K-PD MODELS: PERSPECTIVES Michel TOD, PhD Pascal Girard, PhD EA3738, Faculté Médecine Lyon Sud Lyon I University, France Tod / Girard 1 EMEA 14 April 008 USES OF MODELS
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of the Antinociceptive Effect of Buprenorphine and Fentanyl in Rats: Role of Receptor Equilibration Kinetics
 0022-3565/05/3133-1136 1149$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 313, No. 3 Copyright 2005 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 82560/1199533
0022-3565/05/3133-1136 1149$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 313, No. 3 Copyright 2005 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 82560/1199533
General Pharmacology MCQs
 General Pharmacology MCQs GP01 [Mar96] A drug is given at a dose of 50 mg/kg to a 70 kg man. The plasma concentration after giving it is 10 mg/ml. The elimination half-life is 8 hours. Clearance would
General Pharmacology MCQs GP01 [Mar96] A drug is given at a dose of 50 mg/kg to a 70 kg man. The plasma concentration after giving it is 10 mg/ml. The elimination half-life is 8 hours. Clearance would
Drug-Disease Modeling Applied to Drug Development and Regulatory Decision Making in the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Arena
 Drug-Disease Modeling Applied to Drug Development and Regulatory Decision Making in the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Arena Tokyo, Japan, December 8, 2015 Stephan Schmidt, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Center for
Drug-Disease Modeling Applied to Drug Development and Regulatory Decision Making in the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Arena Tokyo, Japan, December 8, 2015 Stephan Schmidt, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Center for
Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of the D 2 and 5-HT 2A Receptor Occupancy of Risperidone and Paliperidone in Rats
 Pharm Res (2012) 29:1932 1948 DOI 10.1007/s11095-012-0722-8 RESEARCH PAPER Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of the D 2 and 5-HT 2A Receptor Occupancy of Risperidone and Paliperidone in Rats Magdalena
Pharm Res (2012) 29:1932 1948 DOI 10.1007/s11095-012-0722-8 RESEARCH PAPER Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of the D 2 and 5-HT 2A Receptor Occupancy of Risperidone and Paliperidone in Rats Magdalena
Recording and Analysing Concentration- Response Curves. should be slightly higher, or at least within the range of the dissociation constant K D
 6.4 784 Recording and Analysing Concentration- Response Curves Stefan Dhein Introduction In many cases it is the goal of a study to evaluate the effect of a physiological mediator or a drug on a given
6.4 784 Recording and Analysing Concentration- Response Curves Stefan Dhein Introduction In many cases it is the goal of a study to evaluate the effect of a physiological mediator or a drug on a given
Lecture 1 and 2 ONE. Definitions. Pharmacology: the study of the interaction of drugs within living systems
 Lecture 1 and 2 ONE 1. Explain what pharmacology encompasses and how it relates to other disciplines 2. Discuss the types of drug target and the factors that influence the binding of drugs to these targets
Lecture 1 and 2 ONE 1. Explain what pharmacology encompasses and how it relates to other disciplines 2. Discuss the types of drug target and the factors that influence the binding of drugs to these targets
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology
 General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology Parisa Gazerani, Pharm D, PhD Assistant Professor Center for Sensory-Motor Interaction (SMI) Department of Health Science and Technology Aalborg University
General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology Parisa Gazerani, Pharm D, PhD Assistant Professor Center for Sensory-Motor Interaction (SMI) Department of Health Science and Technology Aalborg University
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY- BASED PHARMACOLOGY MOLECULAR-BASED APPROACHES: RECEPTOR AGONISTS, ANTAGONISTS, ENZYME INHIBITORS
 PharmaTrain Cooperative European Medicines Development Course (CEMDC) Budapest, October, 2017 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY- BASED PHARMACOLOGY MOLECULAR-BASED APPROACHES: RECEPTOR AGONISTS, ANTAGONISTS,
PharmaTrain Cooperative European Medicines Development Course (CEMDC) Budapest, October, 2017 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY- BASED PHARMACOLOGY MOLECULAR-BASED APPROACHES: RECEPTOR AGONISTS, ANTAGONISTS,
Time to Lowest BIS after an Intravenous Bolus and an Adaptation of the Time-topeak-effect
 Adjustment of k e0 to Reflect True Time Course of Drug Effect by Using Observed Time to Lowest BIS after an Intravenous Bolus and an Adaptation of the Time-topeak-effect Algorithm Reported by Shafer and
Adjustment of k e0 to Reflect True Time Course of Drug Effect by Using Observed Time to Lowest BIS after an Intravenous Bolus and an Adaptation of the Time-topeak-effect Algorithm Reported by Shafer and
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology
 Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Principles of Pharmacology: A Foundation for Discussion on Low-Dose Effects & Non-Monotonic Dose Responses
 Principles of Pharmacology: A Foundation for Discussion on Low-Dose Effects & Non-Monotonic Dose Responses Scott M. Belcher, PhD University of Cincinnati Department of Pharmacology and Cell Biophysics
Principles of Pharmacology: A Foundation for Discussion on Low-Dose Effects & Non-Monotonic Dose Responses Scott M. Belcher, PhD University of Cincinnati Department of Pharmacology and Cell Biophysics
Life History of A Drug
 DRUG ACTION & PHARMACODYNAMIC M. Imad Damaj, Ph.D. Associate Professor Pharmacology and Toxicology Smith 652B, 828-1676, mdamaj@hsc.vcu.edu Life History of A Drug Non-Specific Mechanims Drug-Receptor Interaction
DRUG ACTION & PHARMACODYNAMIC M. Imad Damaj, Ph.D. Associate Professor Pharmacology and Toxicology Smith 652B, 828-1676, mdamaj@hsc.vcu.edu Life History of A Drug Non-Specific Mechanims Drug-Receptor Interaction
8 Respiratory depression by tramadol in the cat: involvement of opioid receptors?
 8 Respiratory depression by tramadol in the cat: involvement of opioid receptors? A MAJOR ADVERSE effect of opioid analgesics is respiratory depression which is probably mediated by an effect on µ-opioid
8 Respiratory depression by tramadol in the cat: involvement of opioid receptors? A MAJOR ADVERSE effect of opioid analgesics is respiratory depression which is probably mediated by an effect on µ-opioid
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics
 Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
PKPD. Workshop. Warfarin Data. What does this mean? Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand
 1 PKPD Workshop Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand 2 Holford NHG, Sheiner LB. Kinetics of pharmacologic response. Pharmacol. Ther. 1982;16:143-166
1 PKPD Workshop Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand 2 Holford NHG, Sheiner LB. Kinetics of pharmacologic response. Pharmacol. Ther. 1982;16:143-166
Use of Target Tissue Concentrations in PK-PD Modeling of Inhaled Drugs Ramon Hendrickx, AstraZeneca, RIA IMed Gothenburg, Sweden
 Use of Target Tissue Concentrations in PK-PD Modeling of Inhaled Drugs Ramon Hendrickx, AstraZeneca, RIA IMed Gothenburg, Sweden IQ DMPK Leadership Group 31 May 2017 What s On? Lung as target organ Benefit
Use of Target Tissue Concentrations in PK-PD Modeling of Inhaled Drugs Ramon Hendrickx, AstraZeneca, RIA IMed Gothenburg, Sweden IQ DMPK Leadership Group 31 May 2017 What s On? Lung as target organ Benefit
PK-PD modelling to support go/no go decisions for a novel gp120 inhibitor
 PK-PD modelling to support go/no go decisions for a novel gp120 inhibitor Phylinda LS Chan Pharmacometrics, Pfizer, UK EMA-EFPIA Modelling and Simulation Workshop BOS1 Pharmacometrics Global Clinical Pharmacology
PK-PD modelling to support go/no go decisions for a novel gp120 inhibitor Phylinda LS Chan Pharmacometrics, Pfizer, UK EMA-EFPIA Modelling and Simulation Workshop BOS1 Pharmacometrics Global Clinical Pharmacology
Allosteric Modulation
 Allosteric Modulation David Hall, GlaxoSmithKline Topics What is an allosteric modulator? How do allosteric modulators behave? Build up theory from known properties Use theory to predict & qualify behaviours
Allosteric Modulation David Hall, GlaxoSmithKline Topics What is an allosteric modulator? How do allosteric modulators behave? Build up theory from known properties Use theory to predict & qualify behaviours
DEFINITIONS. Pharmacokinetics. Pharmacodynamics. The process by which a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and eliminated by the body
 PHARMACOLOGY BASICS DEFINITIONS Pharmacokinetics The process by which a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and eliminated by the body Pharmacodynamics The interactions of a drug and the receptors
PHARMACOLOGY BASICS DEFINITIONS Pharmacokinetics The process by which a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and eliminated by the body Pharmacodynamics The interactions of a drug and the receptors
PKPD. Workshop. Warfarin Data. What does this mean? Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand
 1 PKPD Workshop Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand Holford NHG, Sheiner LB. Kinetics of pharmacologic response. Pharmacol. Ther. 198;16:143-166 Pharmacokinetics
1 PKPD Workshop Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand Holford NHG, Sheiner LB. Kinetics of pharmacologic response. Pharmacol. Ther. 198;16:143-166 Pharmacokinetics
Receptors. Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel
 Receptors Types and Theories Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel Some terms in receptor-drug interactions Agonists: drugs that mimic the natural messengers and activate receptors. Antagonist: drugs that block receptors.
Receptors Types and Theories Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel Some terms in receptor-drug interactions Agonists: drugs that mimic the natural messengers and activate receptors. Antagonist: drugs that block receptors.
Pharmacology of intravenous induction agents
 Pharmacology of intravenous induction agents Ákos Csomós MD, PhD Professor, Head of Department Medical Centre, Hungarian Defence Force, Budapest What do we have in the market? Thiopental Metohexital Etomidate
Pharmacology of intravenous induction agents Ákos Csomós MD, PhD Professor, Head of Department Medical Centre, Hungarian Defence Force, Budapest What do we have in the market? Thiopental Metohexital Etomidate
Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook with Computer Simulations
 Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook with Computer Simulations Rosenbaum, Sara E. ISBN-13: 9780470569061 Table of Contents 1 Introduction to Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics.
Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook with Computer Simulations Rosenbaum, Sara E. ISBN-13: 9780470569061 Table of Contents 1 Introduction to Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics.
Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of
 Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of Sedative Agents Dr Simon Chan Consultant Anaesthesiologist Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Prince of Wales Hospital Hong Kong 21 February 2009 Aims
Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of Sedative Agents Dr Simon Chan Consultant Anaesthesiologist Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Prince of Wales Hospital Hong Kong 21 February 2009 Aims
The MOLECULES of LIFE
 The MOLECULES of LIFE Physical and Chemical Principles Solutions Manual Prepared by James Fraser and Samuel Leachman Chapter 16 Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Problems True/False and Multiple Choice 1.
The MOLECULES of LIFE Physical and Chemical Principles Solutions Manual Prepared by James Fraser and Samuel Leachman Chapter 16 Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Problems True/False and Multiple Choice 1.
Lecture 6: Allosteric regulation of enzymes
 Chem*3560 Lecture 6: Allosteric regulation of enzymes Metabolic pathways do not run on a continuous basis, but are regulated according to need Catabolic pathways run if there is demand for ATP; for example
Chem*3560 Lecture 6: Allosteric regulation of enzymes Metabolic pathways do not run on a continuous basis, but are regulated according to need Catabolic pathways run if there is demand for ATP; for example
Pharmacodynamics. Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology
 Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
PHARMACODYNAMICS II. The total number of receptors, [R T ] = [R] + [AR] + [BR] (A = agonist, B = antagonist, R = receptors) = T. Antagonist present
![PHARMACODYNAMICS II. The total number of receptors, [R T ] = [R] + [AR] + [BR] (A = agonist, B = antagonist, R = receptors) = T. Antagonist present PHARMACODYNAMICS II. The total number of receptors, [R T ] = [R] + [AR] + [BR] (A = agonist, B = antagonist, R = receptors) = T. Antagonist present](/thumbs/73/69197936.jpg) Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS II Antagonists Are structurally similar to the binding site of a receptor and thus show affinity towards the receptor. However, they have zero intrinsic
Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS II Antagonists Are structurally similar to the binding site of a receptor and thus show affinity towards the receptor. However, they have zero intrinsic
Pharmacokinetic pharmacodynamic modeling in acute and chronic pain: an overview of the recent literature
 Expert of Clinical Pharmacology ISSN: 1751-2433 (Print) 1751-2441 (Online) Journal homepage: https://tandfonline.com/loi/ierj2 Pharmacokinetic pharmacodynamic modeling in acute and chronic pain: an overview
Expert of Clinical Pharmacology ISSN: 1751-2433 (Print) 1751-2441 (Online) Journal homepage: https://tandfonline.com/loi/ierj2 Pharmacokinetic pharmacodynamic modeling in acute and chronic pain: an overview
Delayed Drug Effects. Distribution to Effect Site. Physiological Intermediate
 1 Pharmacodynamics Delayed Drug Effects In reality all drug effects are delayed in relation to plasma drug concentrations. Some drug actions e.g. anti-thrombin III binding and inhibition of Factor Xa by
1 Pharmacodynamics Delayed Drug Effects In reality all drug effects are delayed in relation to plasma drug concentrations. Some drug actions e.g. anti-thrombin III binding and inhibition of Factor Xa by
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability derived from various body fluids. Saliva samples instead of plasma samples
 Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability derived from various body fluids Saliva samples instead of plasma samples Willi Cawello, Schwarz BioSciences, Monheim am Rhein 1 Overview Introduction Sampling tissues/fluids
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability derived from various body fluids Saliva samples instead of plasma samples Willi Cawello, Schwarz BioSciences, Monheim am Rhein 1 Overview Introduction Sampling tissues/fluids
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi
 number 11 Done by Lojayn Salah Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi The last thing we talked about in the previous lecture was the effect of a drug at a particular dose, and we took this equation: E= Emax
number 11 Done by Lojayn Salah Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi The last thing we talked about in the previous lecture was the effect of a drug at a particular dose, and we took this equation: E= Emax
Benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines
 : History 1950s - Invented by Swiss chemists who identified its sedative effects 1950s 60s - Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) marketed as a safer alternative to barbiturates; along with newer benzodiazepines
: History 1950s - Invented by Swiss chemists who identified its sedative effects 1950s 60s - Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) marketed as a safer alternative to barbiturates; along with newer benzodiazepines
The Time Course of Placebo Response in Clinical Trials
 The Time Course of Placebo Response in Clinical Trials Do Antidepressants Really Take 2 s To Work? Nick Holford Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, University of Auckland, New Zealand
The Time Course of Placebo Response in Clinical Trials Do Antidepressants Really Take 2 s To Work? Nick Holford Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, University of Auckland, New Zealand
Neuropharmacodynamic Profile of NKTR-181: Correlation to Low Abuse Potential
 Neuropharmacodynamic Profile of NKTR-181: Correlation to Low Abuse Potential Laurie VanderVeen, Takahiro Miyazaki, Irene Choi, Michael A. Eldon, Xue Snow Ge, Hema Gursahani, Faye Hsieh, Aleksandrs Odinecs,
Neuropharmacodynamic Profile of NKTR-181: Correlation to Low Abuse Potential Laurie VanderVeen, Takahiro Miyazaki, Irene Choi, Michael A. Eldon, Xue Snow Ge, Hema Gursahani, Faye Hsieh, Aleksandrs Odinecs,
Children are small adults and babies are young children
 1 Children are small adults and babies are young children Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology Brian Anderson Dept Anaesthesia & Starship Hospital University of Auckland, New Zealand
1 Children are small adults and babies are young children Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology Brian Anderson Dept Anaesthesia & Starship Hospital University of Auckland, New Zealand
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi
 number 10 Done by Mohammad Shatnawi Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi Agonist: a drug or a molecule that binds to a receptor and causes the activation of the receptor, exp: adrenaline is an agonist for
number 10 Done by Mohammad Shatnawi Corrected by Doctor Alia Shatnawi Agonist: a drug or a molecule that binds to a receptor and causes the activation of the receptor, exp: adrenaline is an agonist for
Basic Pharmacokinetic Principles Stephen P. Roush, Pharm.D. Clinical Coordinator, Department of Pharmacy
 Basic Pharmacokinetic Principles Stephen P. Roush, Pharm.D. Clinical Coordinator, Department of Pharmacy I. General principles Applied pharmacokinetics - the process of using drug concentrations, pharmaco-kinetic
Basic Pharmacokinetic Principles Stephen P. Roush, Pharm.D. Clinical Coordinator, Department of Pharmacy I. General principles Applied pharmacokinetics - the process of using drug concentrations, pharmaco-kinetic
Nelleke Snelder, Bart A Ploeger, Olivier Luttringer, Dean F Rigel, Randy L Webb, David
 Title page Title: Characterization and prediction of cardiovascular effects of fingolimod and siponimod using a systems pharmacology modelling approach Authors: Nelleke Snelder, Bart A Ploeger, Olivier
Title page Title: Characterization and prediction of cardiovascular effects of fingolimod and siponimod using a systems pharmacology modelling approach Authors: Nelleke Snelder, Bart A Ploeger, Olivier
Validation Report for the Neogen Fentanyl Kit for ELISA Screening of Whole Blood and Urine Specimens
 Validation Report for the Neogen Fentanyl Kit for ELISA Screening of Whole Blood and Urine Specimens This document describes the validation of a Neogen Fentanyl kit for the semi-quantitative analysis of
Validation Report for the Neogen Fentanyl Kit for ELISA Screening of Whole Blood and Urine Specimens This document describes the validation of a Neogen Fentanyl kit for the semi-quantitative analysis of
Pharmacodynamics. OUTLINE Definition. Mechanisms of drug action. Receptors. Agonists. Types. Types Locations Effects. Definition
 Pharmacodynamics OUTLINE Definition. Mechanisms of drug action. Receptors Types Locations Effects Agonists Definition Types Outlines of Pharmacodynamics Antagonists Definition Types Therapeutic Index Definition
Pharmacodynamics OUTLINE Definition. Mechanisms of drug action. Receptors Types Locations Effects Agonists Definition Types Outlines of Pharmacodynamics Antagonists Definition Types Therapeutic Index Definition
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Receptor pharmacology in neuroscience prac3ce Lecture 1: basic terms, experimental approaches and caveats
 Receptor pharmacology in neuroscience prac3ce Lecture 1: basic terms, experimental approaches and caveats Neuroscience 201A, October 22nd, 2015 Ionotropic vs. metabotropic neurotransmider receptors What
Receptor pharmacology in neuroscience prac3ce Lecture 1: basic terms, experimental approaches and caveats Neuroscience 201A, October 22nd, 2015 Ionotropic vs. metabotropic neurotransmider receptors What
Overview of Pharmacodynamics. Psyc 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs. Pharmacodynamics. Effects on Target Binding Site.
 Pharmacodynamics Overview of Pharmacodynamics Psychology 472: Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs Generally is defined as effects of drugs on a systems Can be associated with any system Neural, Heart, Liver,
Pharmacodynamics Overview of Pharmacodynamics Psychology 472: Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs Generally is defined as effects of drugs on a systems Can be associated with any system Neural, Heart, Liver,
JNJ : selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor. Central and Peripheral PK/PD
 JNJ-42165279: selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor Central and Peripheral PK/PD The Endocannabinoid System Research initiated by efforts to elucidate the active substance of Cannabis (THC in
JNJ-42165279: selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor Central and Peripheral PK/PD The Endocannabinoid System Research initiated by efforts to elucidate the active substance of Cannabis (THC in
Respiratory toxicity of maintenance therapy in drug addicts: contribution of animal models
 Prescription opioids : first cause of toxic death in the US toxicity of maintenance therapy in drug addicts: contribution of animal models National Center for Health Statistics, 1 Bruno Mégarbane, MD,
Prescription opioids : first cause of toxic death in the US toxicity of maintenance therapy in drug addicts: contribution of animal models National Center for Health Statistics, 1 Bruno Mégarbane, MD,
Model-based quantification of the relationship between age and anti-migraine therapy
 6 Model-based quantification of the relationship between age and anti-migraine therapy HJ Maas, M Danhof, OE Della Pasqua Submitted to BMC. Clin. Pharmacol. Migraine is a neurological disease that affects
6 Model-based quantification of the relationship between age and anti-migraine therapy HJ Maas, M Danhof, OE Della Pasqua Submitted to BMC. Clin. Pharmacol. Migraine is a neurological disease that affects
USES OF PHARMACOKINETICS
 CLINICAL PHARMACOKINETICS Juan J.L. Lertora, M.D., Ph.D. Director Clinical Pharmacology Program Office of Clinical Research Training and Medical Education National Institutes of Health Clinical Center
CLINICAL PHARMACOKINETICS Juan J.L. Lertora, M.D., Ph.D. Director Clinical Pharmacology Program Office of Clinical Research Training and Medical Education National Institutes of Health Clinical Center
Principles of Toxicokinetics/Toxicodynanics
 Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology ENVR 442; TOXC 442; BIOC 442 Principles of Toxicokinetics/Toxicodynanics Kim L.R. Brouwer, PharmD, PhD kbrouwer@unc.edu; 919-962-7030 Pharmacokinetics/ Toxicokinetics:
Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology ENVR 442; TOXC 442; BIOC 442 Principles of Toxicokinetics/Toxicodynanics Kim L.R. Brouwer, PharmD, PhD kbrouwer@unc.edu; 919-962-7030 Pharmacokinetics/ Toxicokinetics:
EMA EFPIA workshop Breakout Session 2 Assessing the Probability of Drug-Induced QTc-Interval Prolongation During Early Clinical Drug Development
 EMA EFPIA workshop Breakout Session 2 Assessing the Probability of Drug-Induced QTc-Interval Prolongation During Early Clinical Drug Development Oscar Della Pasqua GSK Background Drugs that prolong QT
EMA EFPIA workshop Breakout Session 2 Assessing the Probability of Drug-Induced QTc-Interval Prolongation During Early Clinical Drug Development Oscar Della Pasqua GSK Background Drugs that prolong QT
OST. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. Leo O. Lanoie, MD, MPH, FCFP, CCSAM, ABAM, MRO
 OST Pharmacology & Therapeutics Leo O. Lanoie, MD, MPH, FCFP, CCSAM, ABAM, MRO Disclaimer In the past two years I have received no payment for services from any agency other than government or academic.
OST Pharmacology & Therapeutics Leo O. Lanoie, MD, MPH, FCFP, CCSAM, ABAM, MRO Disclaimer In the past two years I have received no payment for services from any agency other than government or academic.
Understanding the Hysteresis Loop Conundrum in Pharmacokinetic / Pharmacodynamic Relationships
 Understanding the Hysteresis Loop Conundrum in Pharmacokinetic / Pharmacodynamic Relationships Christopher Louizos 1, Jaime A. Yáñez 2, M. Laird Forrest 3, Neal M. Davies 1 1 Faculty of Pharmacy, University
Understanding the Hysteresis Loop Conundrum in Pharmacokinetic / Pharmacodynamic Relationships Christopher Louizos 1, Jaime A. Yáñez 2, M. Laird Forrest 3, Neal M. Davies 1 1 Faculty of Pharmacy, University
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics
 Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Assem Al Refaei. Sameer Emeish. Sameer Emeish. Alia Shatnawi
 5 Assem Al Refaei Sameer Emeish Sameer Emeish Alia Shatnawi Sheet Checklist: - Lock And Key Model Explanation. - Specificity, Selectivity And Sensitivity Explanation. - Spare And Orphan Receptors. - Features
5 Assem Al Refaei Sameer Emeish Sameer Emeish Alia Shatnawi Sheet Checklist: - Lock And Key Model Explanation. - Specificity, Selectivity And Sensitivity Explanation. - Spare And Orphan Receptors. - Features
BASIC PHARMACOKINETICS
 BASIC PHARMACOKINETICS MOHSEN A. HEDAYA CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business Table of Contents Chapter
BASIC PHARMACOKINETICS MOHSEN A. HEDAYA CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business Table of Contents Chapter
CLINICAL TRIAL SIMULATION & ANALYSIS
 1 CLINICAL TRIAL SIMULATION & ANALYSIS Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand NHG Holford, 217, all rights reserved. 2 SIMULATION Visualise the expected
1 CLINICAL TRIAL SIMULATION & ANALYSIS Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand NHG Holford, 217, all rights reserved. 2 SIMULATION Visualise the expected
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam administered as a concentrated intranasal spray. A study in healthy volunteers
 Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam administered as a concentrated intranasal spray. A study in healthy volunteers P. D. Knoester, 1 D. M. Jonker, 2 R. T. M. van der Hoeven, 1 T. A. C. Vermeij,
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam administered as a concentrated intranasal spray. A study in healthy volunteers P. D. Knoester, 1 D. M. Jonker, 2 R. T. M. van der Hoeven, 1 T. A. C. Vermeij,
The mastermind approach to CNS drug therapy: translational prediction of human brain distribution, target site kinetics, and therapeutic effects
 de Lange Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 2013, 10:12 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS REVIEW Open Access The mastermind approach to CNS drug therapy: translational prediction of human brain distribution,
de Lange Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 2013, 10:12 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS REVIEW Open Access The mastermind approach to CNS drug therapy: translational prediction of human brain distribution,
Pharmacokinetics of drug infusions
 SA Hill MA PhD FRCA Key points The i.v. route provides the most predictable plasma concentrations. Pharmacodynamic effects of a drug are related to plasma concentration. Both plasma and effect compartments
SA Hill MA PhD FRCA Key points The i.v. route provides the most predictable plasma concentrations. Pharmacodynamic effects of a drug are related to plasma concentration. Both plasma and effect compartments
General and Local Anesthetics TURNING POINT PHARM THURSDAY IMC606 Neuroscience Module
 General and Local Anesthetics TURNING POINT PHARM THURSDAY IMC606 Neuroscience Module Peter Bradford, PhD pgb@buffalo.edu, JSMBS 3204 13-December-2018 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR
General and Local Anesthetics TURNING POINT PHARM THURSDAY IMC606 Neuroscience Module Peter Bradford, PhD pgb@buffalo.edu, JSMBS 3204 13-December-2018 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR
Define the term pharmacodynamics and identify which drug characteristics are pharmacodynamic characteristics.
 Week 1: Introduction Learning Objectives What is Pharmacology? The study of drugs Drug = anything that is administered to a person in order to bring about a therapeutic or diagnostic effect or control
Week 1: Introduction Learning Objectives What is Pharmacology? The study of drugs Drug = anything that is administered to a person in order to bring about a therapeutic or diagnostic effect or control
1. Immediate 2. Delayed 3. Cumulative
 1 Pharmacodynamic Principles and the Time Course of Delayed Drug Effects Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand The time course of drug action combines
1 Pharmacodynamic Principles and the Time Course of Delayed Drug Effects Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland, New Zealand The time course of drug action combines
PubH 7405: REGRESSION ANALYSIS
 PubH 7405: REGRESSION ANALYSIS APLLICATIONS B: MORE BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS #. SMOKING & CANCERS There is strong association between lung cancer and smoking; this has been thoroughly investigated. A study
PubH 7405: REGRESSION ANALYSIS APLLICATIONS B: MORE BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS #. SMOKING & CANCERS There is strong association between lung cancer and smoking; this has been thoroughly investigated. A study
Introduction to Receptor Pharmacology
 Introduction to Receptor Pharmacology Dr Taufiq Rahman 2 nd August 2016 Part I: A general overview of receptors what is sustaining life? how a cell biologist will look at this? sustaining life means that
Introduction to Receptor Pharmacology Dr Taufiq Rahman 2 nd August 2016 Part I: A general overview of receptors what is sustaining life? how a cell biologist will look at this? sustaining life means that
Identification of influential proteins in the classical retinoic acid signaling pathway
 Ghaffari and Petzold Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling (2018) 15:16 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12976-018-0088-7 RESEARCH Open Access Identification of influential proteins in the classical retinoic
Ghaffari and Petzold Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling (2018) 15:16 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12976-018-0088-7 RESEARCH Open Access Identification of influential proteins in the classical retinoic
Prediction of THC Plasma and Brain Concentrations following. Marijuana Administration: Approach and Challenges
 Prediction of THC Plasma and Brain Concentrations following Marijuana Administration: Approach and Challenges Contents: 1. Background and Significance 1.1. Introduction 1.2. THC - the primary chemical
Prediction of THC Plasma and Brain Concentrations following Marijuana Administration: Approach and Challenges Contents: 1. Background and Significance 1.1. Introduction 1.2. THC - the primary chemical
Application Note LCMS-108 Quantitation of benzodiazepines and Z-drugs in serum with the EVOQ TM LC triple quadrupole mass spectrometer
 Application Note LCMS-108 Quantitation of benzodiazepines and Z-drugs in serum with the EVOQ TM LC triple quadrupole mass spectrometer Abstract This study demonstrates a sensitive, rapid and reliable research
Application Note LCMS-108 Quantitation of benzodiazepines and Z-drugs in serum with the EVOQ TM LC triple quadrupole mass spectrometer Abstract This study demonstrates a sensitive, rapid and reliable research
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters. Paul Glue
 Amino Acid Neurotransmitters Paul Glue Objectives Review: Relative abundance of AAs vs monoamines Pharmacology of glutamate, GABA Postulated role of glutamate, GABA dysfunction in neuropsych disorders
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters Paul Glue Objectives Review: Relative abundance of AAs vs monoamines Pharmacology of glutamate, GABA Postulated role of glutamate, GABA dysfunction in neuropsych disorders
 No! No! No! No! With the possible exception of humans Public Health Question Does the compound have the potential to be abused? Public Health Question Does the compound have the potential to be abused?
No! No! No! No! With the possible exception of humans Public Health Question Does the compound have the potential to be abused? Public Health Question Does the compound have the potential to be abused?
Anxiety Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE -NURSING PROGRAM
 Anxiety Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE NURSING PROGRAM NURS 203 GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY DANITA NARCISO PHARM D Learning Objectives Understand the normal processing of fear vs fear processing
Anxiety Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE NURSING PROGRAM NURS 203 GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY DANITA NARCISO PHARM D Learning Objectives Understand the normal processing of fear vs fear processing
DEVELOPMENTAL PK/PD: WHAT HAVE WE LEARNT? Geoff Tucker
 DEVELOPMENTAL PK/PD: WHAT HAVE WE LEARNT? Geoff Tucker UNDERSTANDING AND PREDICTING PK/PD IN JUVENILES PHARMACOKINETICS Can we scale from juvenile animals? Can we scale from allometry? Can we scale from
DEVELOPMENTAL PK/PD: WHAT HAVE WE LEARNT? Geoff Tucker UNDERSTANDING AND PREDICTING PK/PD IN JUVENILES PHARMACOKINETICS Can we scale from juvenile animals? Can we scale from allometry? Can we scale from
Substitution Therapy for Opioid Use Disorder The Role of Suboxone
 Substitution Therapy for Opioid Use Disorder The Role of Suboxone Methadone/Buprenorphine 101 Workshop, December 10, 2016 Leslie Lappalainen, MD, CCFP, dip ABAM Prepared by Mandy Manak, MD, ABAM, CCSAM
Substitution Therapy for Opioid Use Disorder The Role of Suboxone Methadone/Buprenorphine 101 Workshop, December 10, 2016 Leslie Lappalainen, MD, CCFP, dip ABAM Prepared by Mandy Manak, MD, ABAM, CCSAM
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics
 Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Neuroactive steroids have multiple actions to potentiate GABA A receptors
 J Physiol 558.1 (2004) pp 59 74 59 Neuroactive steroids have multiple actions to potentiate GABA A receptors Gustav Akk 1, John R. Bracamontes 1, Douglas F. Covey 2,AlexEvers 1, Tim Dao 3 and Joe Henry
J Physiol 558.1 (2004) pp 59 74 59 Neuroactive steroids have multiple actions to potentiate GABA A receptors Gustav Akk 1, John R. Bracamontes 1, Douglas F. Covey 2,AlexEvers 1, Tim Dao 3 and Joe Henry
Modeling of prolactin response following dopamine D 2 receptor antagonists in rats: can it be translated to clinical dosing?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Modeling of prolactin response following dopamine D 2 receptor antagonists in rats: can it be translated to clinical dosing? Amit Taneja 1, An Vermeulen 2, Dymphy R. H. Huntjens 2, Meindert
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Modeling of prolactin response following dopamine D 2 receptor antagonists in rats: can it be translated to clinical dosing? Amit Taneja 1, An Vermeulen 2, Dymphy R. H. Huntjens 2, Meindert
General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology
 General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology Parisa Gazerani, Pharm D, PhD Assistant Professor Center for Sensory-Motor Interaction (SMI) Department of Health Science and Technology Aalborg University
General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology Parisa Gazerani, Pharm D, PhD Assistant Professor Center for Sensory-Motor Interaction (SMI) Department of Health Science and Technology Aalborg University
OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4
![OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4 OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4](/thumbs/90/104143670.jpg) Opioid MCQ OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4 OP02 [Mar96] Which factor does NOT predispose to bradycardia with
Opioid MCQ OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4 OP02 [Mar96] Which factor does NOT predispose to bradycardia with
Mathematical Framework for Health Risk Assessment
 Mathematical Framework for Health Risk Assessment Health Risk Assessment Does a substance pose a health hazard and, if so how is it characterized? A multi-step process Risk Characterization MSOffice1 Hazard
Mathematical Framework for Health Risk Assessment Health Risk Assessment Does a substance pose a health hazard and, if so how is it characterized? A multi-step process Risk Characterization MSOffice1 Hazard
